|
1867 In Science
The year 1867 in science and technology involved many significant events, listed below. Events * April – First clear recorded use of the word ''science'' in English with today's usage as restricted to the natural and physical sciences (by Catholic theologian and mathematician W. G. Ward writing in the London-published '' Dublin Review''). Botany * Gorse naturalises in New Zealand and soon becomes the worst invasive weed. * Swiss botanist Simon Schwendener proposes his dual theory of lichens. * Rosa 'La France', the first hybrid tea rose, is cultivated by Jean-Baptiste Guillot. * The Big Trees Ranch at Felton, California, is bought by San Francisco businessman Joseph Warren Welch to preserve the giant redwoods (''Sequoia sempervirens'') from logging. Chemistry * Alfred Nobel patents dynamite (in the United Kingdom on May 7, and in Sweden on October 19). * Henry Enfield Roscoe isolates vanadium. * Charles-Adolphe Wurtz synthesizes neurine. Economics * Publication of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science
Science is a systematic endeavor that Scientific method, builds and organizes knowledge in the form of Testability, testable explanations and predictions about the universe. Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for scientific reasoning is tens of thousands of years old. The earliest written records in the history of science come from Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia in around 3000 to 1200 Common Era, BCE. Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, whereby formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the Universe, physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of History of science in classical antiquity, Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but was preserved in the Muslim world during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hybrid Tea Rose
Hybrid tea is an informal horticultural classification for a group of garden roses. The first hybrid tea roses were created in France in the mid-1800s, by cross-breeding the large, floriferous Hybrid Perpetuals with the tall, elegant Tea roses. The Hybrid tea is the oldest class of Modern garden roses. Hybrid teas exhibit traits midway between their parents, being hardier than the often delicate Tea roses, and with a better ability for repeat-flowering than the more robust Hybrid Perpetuals. Hybrid tea flowers are well-formed with large, high-centred buds, supported by long, straight and upright stems. Each flower can grow to 8–12.5 cm wide. Hybrid teas are the largest and most popular group of rose, due to their elegant form and large variety of colours. Their flowers are usually borne singly at the end of long stems which also makes them very popular as cut flowers. Description Hybrid tea is an informal horticultural classification for a group of garden roses. Hybri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proceedings Of The Royal Society Of London
''Proceedings of the Royal Society'' is the main research journal of the Royal Society. The journal began in 1831 and was split into two series in 1905: * Series A: for papers in physical sciences and mathematics. * Series B: for papers in life sciences. Many landmark scientific discoveries are published in the Proceedings, making it one of the most historically significant science journals. The journal contains several articles written by the most celebrated names in science, such as Paul Dirac, Werner Heisenberg, Ernest Rutherford, Erwin Schrödinger, William Lawrence Bragg, Lord Kelvin, J.J. Thomson, James Clerk Maxwell, Dorothy Hodgkin and Stephen Hawking. In 2004, the Royal Society began ''The Journal of the Royal Society Interface'' for papers at the interface of physical sciences and life sciences. History The journal began in 1831 as a compilation of abstracts of papers in the ''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society'', the older Royal Society publication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanadium
Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery-grey, malleable transition metal. The elemental metal is rarely found in nature, but once isolated artificially, the formation of an oxide layer ( passivation) somewhat stabilizes the free metal against further oxidation. Spanish scientist Andrés Manuel del Río discovered compounds of vanadium in 1801 in Mexico by analyzing a new lead-bearing mineral he called "brown lead". Though he initially presumed its qualities were due to the presence of a new element, he was later erroneously convinced by French chemist Hippolyte Victor Collet-Descotils that the element was just chromium. Then in 1830, Nils Gabriel Sefström generated chlorides of vanadium, thus proving there was a new element, and named it "vanadium" after the Scandinavian goddess of beauty and fertility, Vanadís (Freyja). The name was based on the wide range of colors found in vanadium compounds. Del Rio's lead mineral w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Enfield Roscoe
Sir Henry Enfield Roscoe (7 January 1833 – 18 December 1915) was a British chemist. He is particularly noted for early work on vanadium, photochemical studies, and his assistance in creating Oxo (food), in its earlier liquid form. Life and work Henry Enfield Roscoe was born in London, the son of Henry Roscoe (1800–1836) and Maria Roscoe, née Fletcher (1798–1885), and grandson of William Roscoe (1753–1831). Stanley Jevons the Australian economist was a cousin. Roscoe studied at the Liverpool Institute for Boys and University College London. He then went to Heidelberg to work under Robert Bunsen, who became a lifelong friend. He also befriended William Dittmar. In 1857, Roscoe returned to England with Dittmar and was appointed to the chair of chemistry at Owens College, Manchester, with Dittmar as his assistant. In 1858 the state of the college was such that the ''Manchester Guardian'' called it "a mortifying failure". In the same year Roscoe was accoste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopædia Britannica
The ( Latin for "British Encyclopædia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various times through the centuries. The encyclopaedia is maintained by about 100 full-time editors and more than 4,000 contributors. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, which spans 32 volumes and 32,640 pages, was the last printed edition. Since 2016, it has been published exclusively as an online encyclopaedia. Printed for 244 years, the ''Britannica'' was the longest running in-print encyclopaedia in the English language. It was first published between 1768 and 1771 in the Scottish capital of Edinburgh, as three volumes. The encyclopaedia grew in size: the second edition was 10 volumes, and by its fourth edition (1801–1810) it had expanded to 20 volumes. Its rising stature as a scholarly work helped recruit eminent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweden
Sweden, ; fi, Ruotsi; fit, Ruotti; se, Ruoŧŧa; smj, Svierik; sje, Sverji; sju, Sverje; sma, Sveerje or ; yi, שוועדן, Shvedn; rmu, Svedikko; rmf, Sveittiko. formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic country and the List of European countries by area, fifth-largest country in Europe. The Capital city, capital and largest city is Stockholm. Sweden has a population of 10.5 million, and a low population density of ; around 87% of Swedes reside in urban areas in the central and southern half of the country. Sweden’s urban areas together cover 1.5% of its land area. Because the country is so long, ranging from 55th parallel north, 55°N to 69th parallel north, 69°N, the climate of Sweden is diverse. Sweden has been inhabited since Prehistoric Sweden, prehistoric times, . T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many List of islands of the United Kingdom, smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares Republic of Ireland–United Kingdom border, a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamite
Dynamite is an explosive made of nitroglycerin, sorbents (such as powdered shells or clay), and stabilizers. It was invented by the Swedish chemist and engineer Alfred Nobel in Geesthacht, Northern Germany, and patented in 1867. It rapidly gained wide-scale use as a more robust alternative to black powder. History Dynamite was invented by Swedish chemist Alfred Nobel in the 1860s and was the first safely manageable explosive stronger than black powder. Alfred Nobel's father, Immanuel Nobel, was an industrialist, engineer, and inventor. He built bridges and buildings in Stockholm and founded Sweden's first rubber factory. His construction work inspired him to research new methods of blasting rock that were more effective than black powder. After some bad business deals in Sweden, in 1838 Immanuel moved his family to Saint Petersburg, where Alfred and his brothers were educated privately under Swedish and Russian tutors. At age 17, Alfred was sent abroad for two year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an sufficiency of disclosure, enabling disclosure of the invention."A patent is not the grant of a right to make or use or sell. It does not, directly or indirectly, imply any such right. It grants only the right to exclude others. The supposition that a right to make is created by the patent grant is obviously inconsistent with the established distinctions between generic and specific patents, and with the well-known fact that a very considerable portion of the patents granted are in a field covered by a former relatively generic or basic patent, are tributary to such earlier patent, and cannot be practiced unless by license thereunder." – ''Herman v. Youngstown Car Mfg. Co.'', 191 F. 579, 584–85, 112 CCA 185 (6th Cir. 1911) In most countries, patent rights fall under private law ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Nobel
Alfred Bernhard Nobel ( , ; 21 October 1833 – 10 December 1896) was a Swedish chemist, engineer, inventor, businessman, and philanthropist. He is best known for having bequeathed his fortune to establish the Nobel Prize, though he also made several important contributions to science, holding 355 patents in his lifetime. Nobel's most famous invention was dynamite, a safer and easier means of harnessing the explosive power of nitroglycerin; it was patented in 1867. Nobel displayed an early aptitude for science and learning, particularly in chemistry and languages; he became fluent in six languages and filed his first patent at age 24. He embarked on many business ventures with his family, most notably owning Bofors, an iron and steel producer that he developed into a major manufacturer of cannons and other armaments. Nobel was later inspired to donate his fortune to the Nobel Prize institution, which would annually recognize those who "conferred the greatest benefit to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
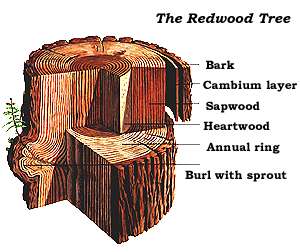
Sequoia Sempervirens
''Sequoia sempervirens'' ()''Sunset Western Garden Book,'' 1995:606–607 is the sole living species of the genus '' Sequoia'' in the cypress family Cupressaceae (formerly treated in Taxodiaceae). Common names include coast redwood, coastal redwood, and California redwood. It is an evergreen, long-lived, monoecious tree living 1,200–2,200 years or more. This species includes the tallest living trees on Earth, reaching up to in height (without the roots) and up to in diameter at breast height. These trees are also among the oldest living things on Earth. Before commercial logging and clearing began by the 1850s, this massive tree occurred naturally in an estimated along much of coastal California (excluding southern California where rainfall is not sufficient) and the southwestern corner of coastal Oregon within the United States. The name sequoia sometimes refers to the subfamily Sequoioideae, which includes ''S. sempervirens'' along with '' Sequoiadendron' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)