|
1810 In Canada
Events from the year 1810 in Canada. Incumbents *Monarch: George III Federal government *Parliament of Lower Canada: 6th (January 29 – March 1) then 7th (starting December 12) *Parliament of Upper Canada: 5th Governors * Governor of the Canadas: Robert Milnes * Governor of New Brunswick: Thomas Carleton *Governor of Nova Scotia: John Wentworth * Commodore-Governor of Newfoundland: Sir John Duckworth, 1st Baronet * Governor of Prince Edward Island: Joseph Frederick Wallet DesBarres Events * January – A Governor declares that, in case of hostilities, a force of regulars, adequate for the defence of Canada, will cooperate with the Militia. * March – ''Le Canadien'' of Quebec is suppressed, for " seditious utterances." Soldiers, led by a magistrate, seize the plant and apprehend the printer. Warrants to arrest Bedard, Taschereau, Papineau, Viger and others are issued. The Governor asks: "During the fifty years you have been under British rule, has one act of oppression, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Canadian Monarchs
Listed here are the monarchs who reigned over Canada, starting with the Canada (New France), French colony of Canada which subsequently became a The Canadas, British colony, followed by the British Dominion of Canada, and finally the present-day sovereign state of Canada. The date of the first claim by a monarch over Canada varies, with most sources giving the year as 1497, when John Cabot made landfall somewhere on the North American coast (likely either modern-day Newfoundland or Nova Scotia), and claimed the land for England on behalf of Henry VII of England, King Henry VII. However, some sources instead put this date at 1535 when the word "Canada" was first used to refer to the French Canada (New France), colony of Canada, which was founded in the name of Francis I of France, King Francis I. Monarchical governance subsequently evolved under a continuous succession of French, British, and eventually uniquely Canadian sovereigns. Since the first claim by Henry VII, there have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sex Scandal
Public scandals involving allegations or information about possibly immoral sexual activities are often associated with the sexual affairs of film stars, politicians, famous athletes, or others in the public eye. Sex scandals receive attention if a prominent figure is involved, if there is a perception of hypocrisy, if a public figure's sexuality is non-normative, or if it involves non-consensual acts. A scandal may be based on reality, the product of false allegations, or a mixture of both. Whether the scandal is based in fact or not, it may lead to the celebrity disappearing from the public eye or to the resignation of prominent political figures. Sex scandals involving politicians often become political scandals, particularly when there is an attempt at a cover-up or suspicions of illegality. Attempts at coverups include payoffs, threats, or, in extreme cases, murder. While some commentators see sex scandals as irrelevant to politics, particularly where "professional perfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Wood (merchant)
Alexander Wood (January 1772 – 11 September 1844) was a Scottish merchant and magistrate in Upper Canada who was the centre of a sex scandal in 1810.Alexander Wood at the . Early life and career Wood was born at Fetteresso near , , and he moved to Upper Canada in 17 ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
York, Upper Canada
York was a town and second capital of the colony of Upper Canada. It is the predecessor to the Old Toronto, old city of Toronto (1834–1998). It was established in 1793 by Lieutenant-Governor John Graves Simcoe as a "temporary" location for the capital of Upper Canada, while he made plans to build a capital near today's London, Ontario. Simcoe renamed the location York after Prince Frederick, Duke of York and Albany, George III of the United Kingdom, George III's second son. Simcoe gave up his plan to build a capital at London, and York became the permanent capital of Upper Canada on February 1, 1796. That year Simcoe returned to Britain and was temporarily replaced by Peter Russell (politician), Peter Russell. The original townsite was a compact ten blocks near the mouth of the Don River (Ontario), Don River and a Fort York, garrison was built at the channel to Toronto Harbour. Government buildings and a law court were established. Yonge Street was built, connecting York to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flathead River
The Flathead River ( fla, label=Salish, člq̓etkʷ ntx̣ʷetkʷ, , kut, kananmituk), in the northwestern part of the U.S. state of Montana, originates in the Canadian Rockies to the north of Glacier National Park and flows southwest into Flathead Lake, then after a journey of , empties into the Clark Fork. The river is part of the Columbia River drainage basin, as the Clark Fork is a tributary of the Pend Oreille River, a Columbia River tributary. With a drainage basin extending over and an average discharge of , the Flathead is the largest tributary of the Clark Fork and constitutes over half of its flow. Course The Flathead River rises in forks in the Rocky Mountains of northwestern Montana. The largest tributary is the North Fork, which runs from the Canadian province of British Columbia southwards. The North Fork is sometimes considered the main stem of the Flathead River. Near West Glacier the North Fork combines with the Middle Fork to form the main Flathead River. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
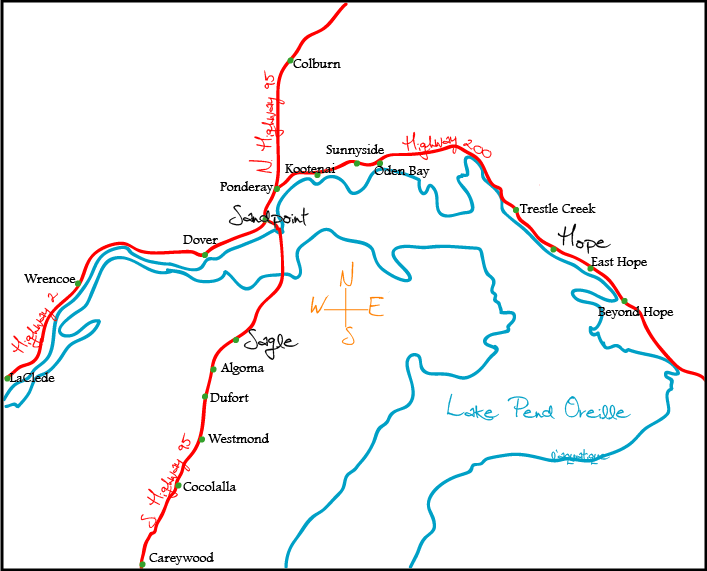
Pend Oreille Lake
Lake Pend Oreille ( ) in the northern Idaho Panhandle is the largest lake in the U.S. state of Idaho and the 38th-largest lake by area in the United States, with a surface area of . It is long, and deep in some regions, making it the fifth-deepest in the nation and having a volume of 43,939,940 acre feet = 54 km3. The lake is fed by the Clark Fork River and the Pack River, and drains into the Pend Oreille River, as well as subsurfacely into the Spokane Valley–Rathdrum Prairie Aquifer. It is surrounded by national forests and a few small towns, with the largest population on the lake at Sandpoint. The majority of the shoreline is non-populated and all but the southern tip of the lake is in Bonner County. The southern tip is in Kootenai County and is home to Farragut State Park, formerly the Farragut Naval Training Station during World War II, of which a small part is still active and conducts U.S. Navy acoustic underwater submarine research. The surrounding forests consis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Thompson (explorer)
David Thompson (30 April 1770 – 10 February 1857) was a English Canadian, British-Canadian fur trader, surveying, surveyor, and Cartography, cartographer, known to some native people as "Koo-Koo-Sint" or "the Stargazer". Over Thompson's career, he travelled across North America, mapping of North America along the way. For this historic feat, Thompson has been described as the "greatest practical land geographer that the world has produced". Early life David Thompson was born in Westminster, Middlesex, to recent Welsh migrants David and Ann Thompson. When Thompson was two, his father died. Due to the financial hardship with his mother without resources, Thompson, 29 April 1777, the day before his seventh birthday, and his older brother were placed in the Grey Coat Hospital, a school for the disadvantaged of Westminster. Thompson graduated to the Grey Coat mathematical school, well known for teaching navigation and surveying. He received an education for the Royal Navy: inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connecting the American Great Lakes to the North Atlantic Ocean, and forming the primary drainage outflow of the Great Lakes Basin. The river traverses the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec, as well as the U.S. state of New York, and demarcates part of the international boundary between Canada and the United States. It also provides the foundation for the commercial St. Lawrence Seaway. Names Originally known by a variety of names by local First Nations, the St. Lawrence became known in French as ''le fleuve Saint-Laurent'' (also spelled ''St-Laurent'') in 1604 by Samuel de Champlain. Opting for the ''grande riviere de sainct Laurens'' and ''fleuve sainct Laurens'' in his writings and on his maps, de Champlain supplanted previous Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Molson
John Molson (December 28, 1763 – January 11, 1836) was an English-born brewer and entrepreneur in colonial Quebec, which during his lifetime became Lower Canada. In addition to founding Molson Brewery, he built the first steamship and the first public railway in Canada, was a president of the Bank of Montreal, and established a hospital, a hotel, and a theatre in Montreal. The dynasty he founded, the Molson family, is still a wealthy and powerful force in Canada. Early life John Molson was born in 1763, in the parish of Moulton near Spalding, Lincolnshire, England. His father John Molson senior (1730–1770) had, in 1760, married Mary Elsdale (1739–1772), the eldest daughter of Samuel Elsdale (1704–1788), of Surfleet. Her brother, Robinson Elsdale (1744–1783), was a privateer, whose unpublished exploits formed the basis of the novel by Frederick Marryat, ''The Privateersman'' (1846). Before the marriage, John Molson senior inherited a property known as Snake Hall, in Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemin Craig
Craig Road was a road created in the early 19th century on the order of James Henry Craig, Governor of British North America. It was intended to connect Quebec City with the United States and to promote settlement of the Eastern Townships. History At the turn of the 19th century, in Lower Canada, nearly all of the population lived in communities along the St. Lawrence River. The land between the river and the US border had been surveyed and was ready for settlement. In 1810, Governor James Henry Craig authorized construction of a road to link Quebec and the US city of Boston. He also wanted to promote colonization of the Eastern Townships by anglophones. His ultimate goal was to assimilate the French-Canadian population. The planned route went from Saint-Gilles to Richmond, where an existing road (modern-day Quebec Route 143) continued to the Canadian–American border. Construction of the road began in August 1810 and took three months. The workforce of 180 soldiers cut trees ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magistrate
The term magistrate is used in a variety of systems of governments and laws to refer to a civilian officer who administers the law. In ancient Rome, a '' magistratus'' was one of the highest ranking government officers, and possessed both judicial and executive powers. In other parts of the world, such as China, a magistrate was responsible for administration over a particular geographic area. Today, in some jurisdictions, a magistrate is a judicial officer who hears cases in a lower court, and typically deals with more minor or preliminary matters. In other jurisdictions (e.g., England and Wales), magistrates are typically trained volunteers appointed to deal with criminal and civil matters in their local areas. Original meaning In ancient Rome, the word '' magistratus'' referred to one of the highest offices of state. Analogous offices in the local authorities, such as ''municipium'', were subordinate only to the legislature of which they generally were members, '' ex officio'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

