|
1775
Events Summary The American Revolutionary War began this year, with the first military engagement being the April 19 Battles of Lexington and Concord on the day after Paul Revere's now-legendary ride. The Second Continental Congress takes various steps toward organizing an American government, appointing George Washington commander-in-chief (June 14), Benjamin Franklin postmaster general (July 26) and creating a Continental Navy (October 13) and a Marine force (November 10) as landing troops for it, but as yet the 13 colonies have not declared independence, and both the British (June 12) and American (July 15) governments make laws. On July 6, Congress issues the Declaration of the Causes and Necessity of Taking Up Arms and on August 23, King George III of Great Britain declares the American colonies in rebellion, announcing it to Parliament on November 10. On June 17, two months into the colonial siege of Boston, at the Battle of Bunker Hill, just north of Boston, Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of the United States, fighting began on April 19, 1775, followed by the Lee Resolution on July 2, 1776, and the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776. The American Patriots were supported by the Kingdom of France and, to a lesser extent, the Dutch Republic and the Spanish Empire, in a conflict taking place in North America, the Caribbean, and the Atlantic Ocean. Established by royal charter in the 17th and 18th centuries, the American colonies were largely autonomous in domestic affairs and commercially prosperous, trading with Britain and its Caribbean colonies, as well as other European powers via their Caribbean entrepôts. After British victory over the French in the Seven Years' War in 1763, tensions between the motherla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
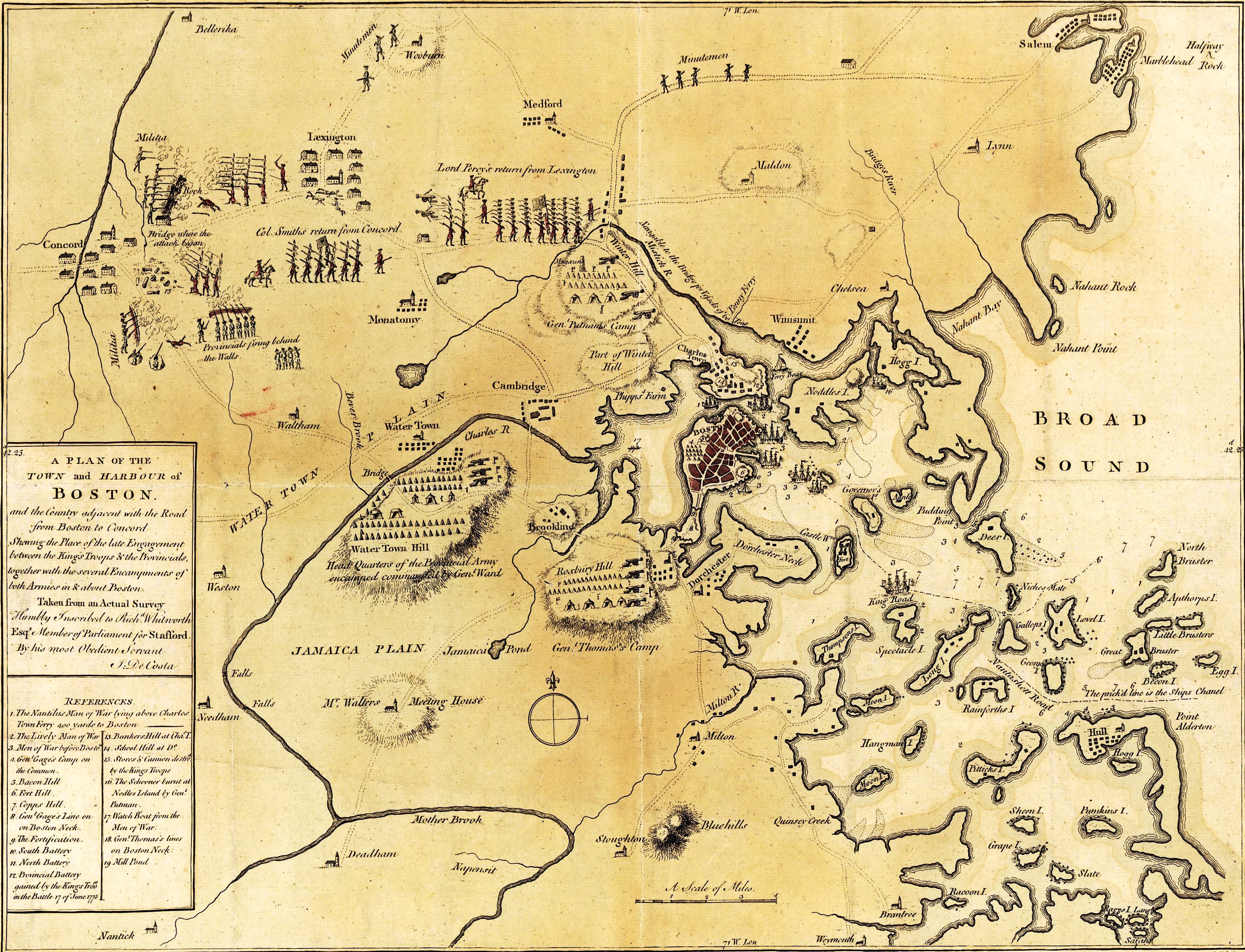
Battles Of Lexington And Concord
The Battles of Lexington and Concord were the first military engagements of the American Revolutionary War. The battles were fought on April 19, 1775, in Middlesex County, Province of Massachusetts Bay, within the towns of Lexington, Concord, Lincoln, Menotomy (present-day Arlington), and Cambridge. They marked the outbreak of armed conflict between the Kingdom of Great Britain and its thirteen colonies in America. In late 1774, Colonial leaders adopted the Suffolk Resolves in resistance to the alterations made to the Massachusetts colonial government by the British parliament following the Boston Tea Party. The colonial assembly responded by forming a Patriot provisional government known as the Massachusetts Provincial Congress and calling for local militias to train for possible hostilities. The Colonial government effectively controlled the colony outside of British-controlled Boston. In response, the British government in February 1775 declared Massachusetts to be i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of the Continental Army, Washington led the Patriot (American Revolution), Patriot forces to victory in the American Revolutionary War and served as the president of the Constitutional Convention (United States), Constitutional Convention of 1787, which created the Constitution of the United States and the American federal government. Washington has been called the "Father of the Nation, Father of his Country" for his manifold leadership in the formative days of the country. Washington's first public office was serving as the official Surveying, surveyor of Culpeper County, Virginia, from 1749 to 1750. Subsequently, he received his first military training (as well as a command with the Virginia Regiment) d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasion Of Canada (1775)
The Invasion of Quebec (June 1775 – October 1776, french: Invasion du Québec) was the first major military initiative by the newly formed Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War. The objective of the campaign was to seize the Province of Quebec (part of modern-day Canada) from Great Britain, and persuade French-speaking to join the revolution on the side of the Thirteen Colonies. One expedition left Fort Ticonderoga under Richard Montgomery, besieged and captured Fort St. Johns, and very nearly captured British General Guy Carleton when taking Montreal. The other expedition, under Benedict Arnold, left Cambridge, Massachusetts and traveled with great difficulty through the wilderness of Maine to Quebec City. The two forces joined there, but they were defeated at the Battle of Quebec in December 1775. Montgomery's expedition set out from Fort Ticonderoga in late August, and in mid-September began besieging Fort St. Johns, the main defensive point south of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Boston
The siege of Boston (April 19, 1775 – March 17, 1776) was the opening phase of the American Revolutionary War. New England militiamen prevented the movement by land of the British Army, which was garrisoned in what was then the peninsular town of Boston, Massachusetts Bay. Both sides had to deal with resource, supply, and personnel issues over the course of the siege. British resupply and reinforcement was limited to sea access, which was impeded by American vessels. The British abandoned Boston after eleven months and transferred their troops and equipment to Nova Scotia. The siege began on April 19 after the Battles of Lexington and Concord, when Massachusetts militias blocked land access to Boston. The Continental Congress formed the Continental Army from the militias involved in the fighting and appointed George Washington as Commander in Chief. In June 1775, the British seized Bunker and Breed's Hills, from which the Continentals were preparing to bombard the city, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Navy
The Continental Navy was the navy of the United States during the American Revolutionary War and was founded October 13, 1775. The fleet cumulatively became relatively substantial through the efforts of the Continental Navy's patron John Adams and vigorous Congressional support in the face of stiff opposition, when considering the limitations imposed upon the Patriot supply pool. The main goal of the navy was to intercept shipments of British matériel and generally disrupt British maritime commercial operations. The initial fleet consisted of converted merchantmen because of the lack of funding, manpower, and resources, with exclusively designed warships being built later in the conflict. The vessels that successfully made it to sea met with success only rarely, and the effort contributed little to the overall outcome of the war. The fleet did serve to highlight a few examples of Continental resolve, notably launching Captain John Barry into the limelight. It provided need ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Independence Hurricane
The 1775 Newfoundland hurricane, also known as the Independence Hurricane, was a hurricane that struck the Thirteen Colonies and the Colony of Newfoundland in August and September, 1775, at the outset of the American War of Independence. It is believed to have killed at least 4,000 people, making it one of the deadliest Atlantic hurricanes of all time. There is disagreement among historians and meteorologists whether the events were one storm or two distinct storms. Impact North Carolina and Virginia On August 27, 1775, a hurricane hit the Outer Banks of North Carolina. It turned northeastward and left the state on September 2, bringing heavy wind and rain to southeastern Virginia. A letter from New Bern, North Carolina, recounted, ''"We had a violent hurricane...which has done a vast deal of damage here, at the Bar, and at Matamuskeet, near 150 lives being lost at the Bar, and 15 in one neighborhood at Matamuskeet."'' The September 9, 1775, edition of The Virginia Gazette repor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capture Of Fort Ticonderoga
The capture of Fort Ticonderoga occurred during the American Revolutionary War on May 10, 1775, when a small force of Green Mountain Boys led by Ethan Allen and Colonel Benedict Arnold surprised and captured the fort's small British garrison. The cannons and other armaments at Fort Ticonderoga were later transported to Boston by Colonel Henry Knox in the noble train of artillery and used to fortify Dorchester Heights and break the standoff at the siege of Boston. Capture of the fort marked the beginning of offensive action taken by the Americans against the British. After seizing Ticonderoga, a small detachment captured the nearby Fort Crown Point on May 11. Seven days later, Arnold and 50 men raided Fort Saint-Jean on the Richelieu River in southern Quebec, seizing military supplies, cannons, and the largest military vessel on Lake Champlain. Although the scope of this military action was relatively minor, it had significant strategic importance. It impeded communication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
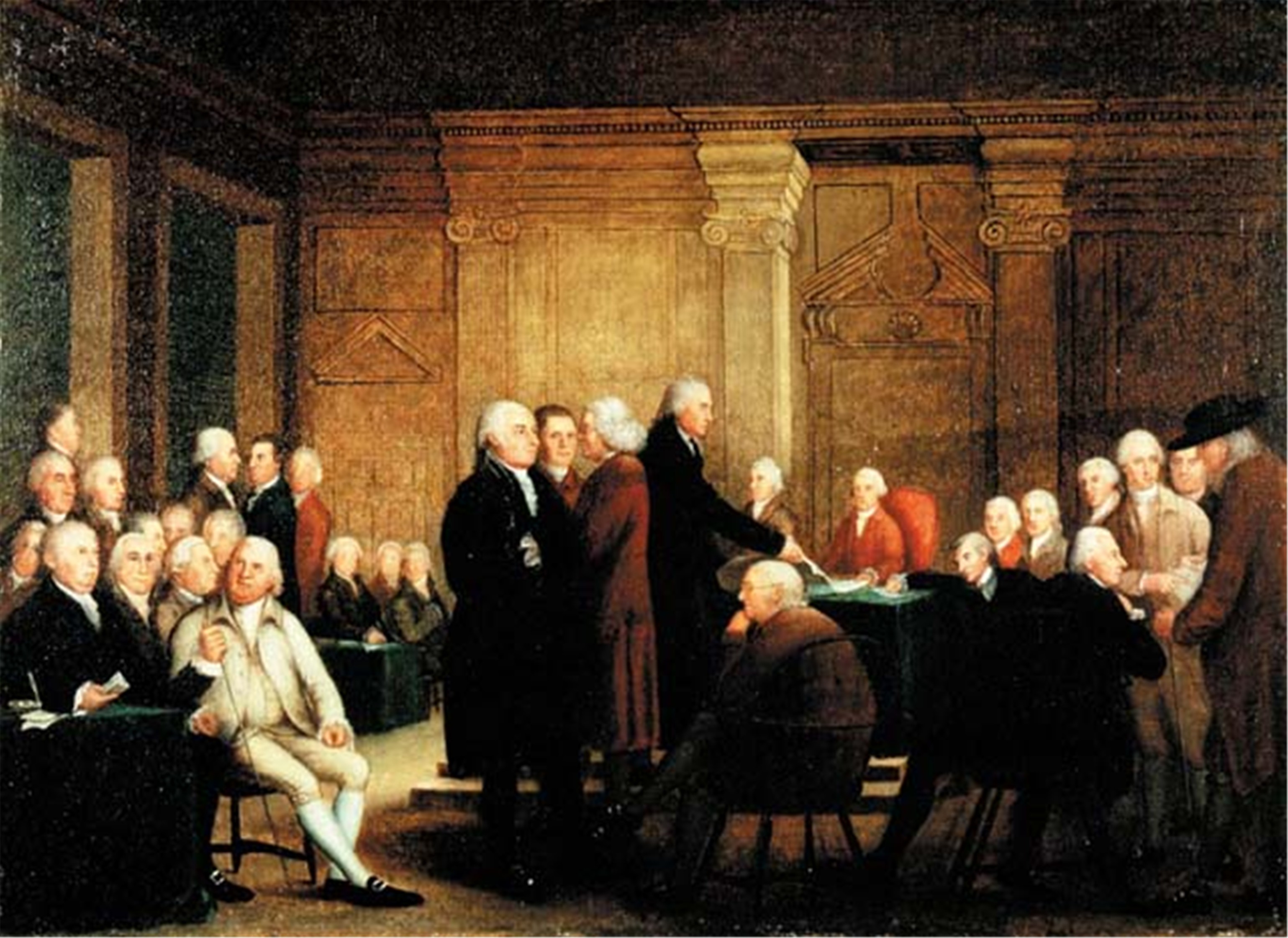
Second Continental Congress
The Second Continental Congress was a late-18th-century meeting of delegates from the Thirteen Colonies that united in support of the American Revolutionary War. The Congress was creating a new country it first named " United Colonies" and in 1776 renamed "United States of America." It convened in Philadelphia on May 10, 1775, with representatives from 12 of the colonies. This came shortly after the Battles of Lexington and Concord and was in succession to the First Continental Congress which met from September 5 to October 26, 1774. The Second Congress functioned as a ''de facto'' national government at the outset of the Revolutionary War by raising armies, directing strategy, appointing diplomats, and writing petitions such as the Declaration of the Causes and Necessity of Taking Up Arms and the Olive Branch Petition. All thirteen colonies were represented by the time the Congress adopted the Lee Resolution which declared independence from Britain on July 2, 1776, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
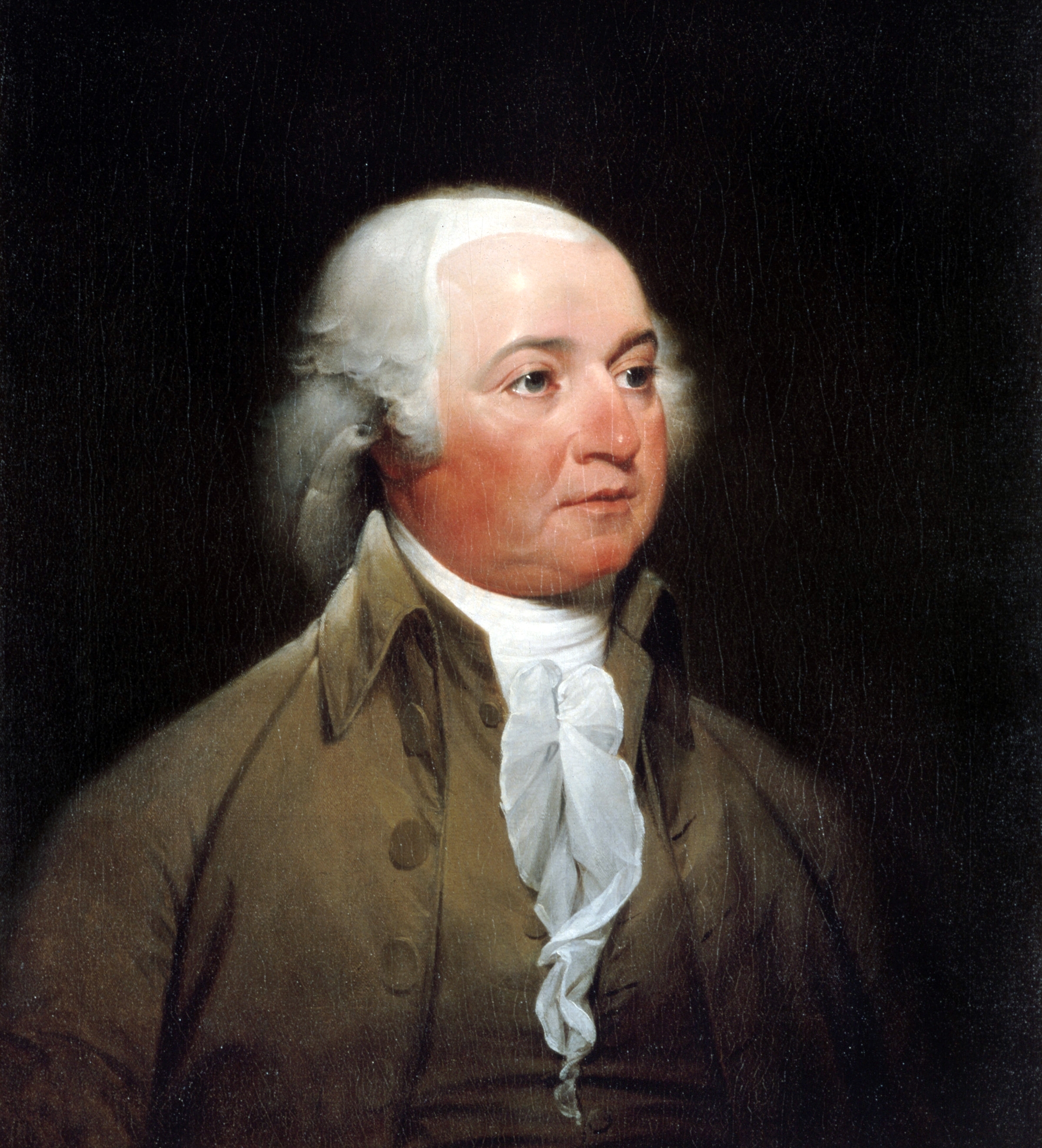
Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin ( April 17, 1790) was an American polymath who was active as a writer, scientist, inventor An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition, idea or process. An invention may be an improvement upon a machine, product, or process for increasing efficiency or lowering cost. It may also be an entirely new concept. If an ..., Statesman (politician), statesman, diplomat, printer (publishing), printer, publisher, and Political philosophy, political philosopher.#britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the leading intellectuals of his time, Franklin was one of the Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Fathers of the United States, a Committee of Five, drafter and signer of the United States Declaration of Independence, and the first United States Postmaster General. As a scientist, he was a major figure in the American Enlightenment and the history of physics for his studies of electricity, and for charting and naming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Bunker Hill
The Battle of Bunker Hill was fought on June 17, 1775, during the Siege of Boston in the first stage of the American Revolutionary War. The battle is named after Bunker Hill in Charlestown, Massachusetts, which was peripherally involved in the battle. It was the original objective of both the colonial and British troops, though the majority of combat took place on the adjacent hill which later became known as Breed's Hill. On June 13, 1775, the leaders of the colonial forces besieging Boston learned that the British were planning to send troops out from the city to fortify the unoccupied hills surrounding the city, which would give them control of Boston Harbor. In response, 1,200 colonial troops under the command of William Prescott stealthily occupied Bunker Hill and Breed's Hill. During the night, the colonists constructed a strong redoubt on Breed's Hill, as well as smaller fortified lines across the Charlestown Peninsula. By daybreak of June 17, the British became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Voyage Of James Cook
The second voyage of James Cook, from 1772 to 1775, commissioned by the British government with advice from the Royal Society, was designed to circumnavigate the globe as far south as possible to finally determine whether there was any great southern landmass, or Terra Australis. On his first voyage, Cook had demonstrated by circumnavigating New Zealand that it was not attached to a larger landmass to the south, and he charted almost the entire eastern coastline of Australia, yet Terra Australis was believed to lie further south. Alexander Dalrymple and others of the Royal Society still believed that this massive southern continent should exist. After a delay brought about by the botanist Joseph Banks' unreasonable demands, the ships '' Resolution'' and ''Adventure'' were fitted for the voyage and set sail for the Antarctic in July 1772. On 17 January 1773, ''Resolution'' was the first ship to venture south of the Antarctic Circle, which she did twice more on this voyage. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |