|
1772 In Science
The year 1772 in science and technology involved some significant events. Astronomy * Lagrange finds the special-case solution to the three-body problem that becomes known as the Lagrangian points. Cartography * Johann Heinrich Lambert publishes seven new map projections, including the Lambert conformal conic, transverse Mercator and Lambert azimuthal equal area. Chemistry * Daniel Rutherford isolates nitrogen. * Joseph Priestley synthesizes nitrous oxide as ''phlogisticated nitrous air''. Antoine Lavoisier privately presents his own views on phlogiston theory to the French Academy of Sciences. * Louis-Bernard Guyton de Morveau demonstrates that metals gain weight on calcination. Earth sciences * The Central England temperature (CET) record begins daily measurements of mean surface air temperatures in the Midlands region of England. * William Hamilton publishes ''Observations on Mount Vesuvius, Mount Etna, and Other Volcano's: in a series of letters addressed to the Royal So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe. Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for scientific reasoning is tens of thousands of years old. The earliest written records in the history of science come from Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia in around 3000 to 1200 BCE. Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, whereby formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but was preserved in the Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age and later by the efforts of Byzantine Greek scholars who brought Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Academy Of Sciences
The French Academy of Sciences (French: ''Académie des sciences'') is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV of France, Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French Scientific method, scientific research. It was at the forefront of scientific developments in Europe in the 17th and 18th centuries, and is one of the earliest Academy of Sciences, Academies of Sciences. Currently headed by Patrick Flandrin (President of the Academy), it is one of the five Academies of the Institut de France. History The Academy of Sciences traces its origin to Colbert's plan to create a general academy. He chose a small group of scholars who met on 22 December 1666 in the King's library, near the present-day Bibliothèque nationale de France, Bibliothèque Nationals, and thereafter held twice-weekly working meetings there in the two rooms assigned to the group. The first 30 years of the Academy's existence were relatively informal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
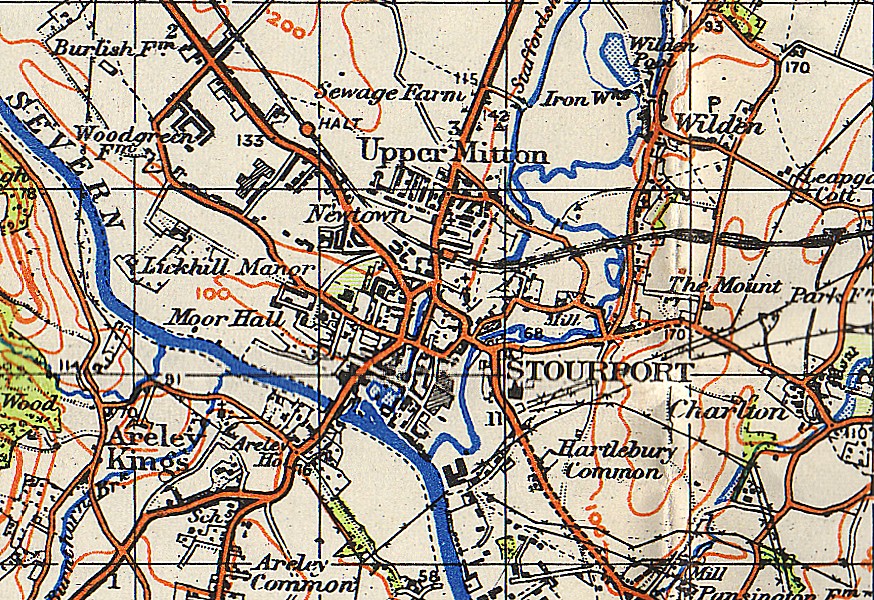
Stourport
Stourport-on-Severn, often shortened to Stourport, is a town and civil parish in the Wyre Forest District of North Worcestershire, England, a few miles to the south of Kidderminster and downstream on the River Severn from Bewdley. At the 2011 census, it had a population of 20,292. History and early growth Stourport came into being around the canal basins at the Severn terminus of the Staffordshire and Worcestershire Canal, which was completed in 1768. In 1772 the junction between the Staffordshire and Worcestershire and the Birmingham Canal was completed and Stourport became one of the principal distributing centres for goods to and from the rest of the West Midlands. The canal terminus was built on meadowland to the south west of the hamlet of Lower Mitton. The terminus was first called Stourmouth and then Newport, with the final name of Stourport settled on by 1771. The population of Stourport rose from about 12 in the 1760s to 1300 in 1795. In 1771 John Wesley had called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Severn
, name_etymology = , image = SevernFromCastleCB.JPG , image_size = 288 , image_caption = The river seen from Shrewsbury Castle , map = RiverSevernMap.jpg , map_size = 288 , map_caption = Tributaries (light blue) and major settlements on and near the Severn (bold blue) , pushpin_map = , pushpin_map_size = 288 , pushpin_map_caption= , subdivision_type1 = Country , subdivision_name1 = England and Wales , subdivision_type2 = , subdivision_name2 = , subdivision_type3 = Region , subdivision_name3 = Mid Wales, West Midlands, South West , subdivision_type4 = Counties , subdivision_name4 = Powys, Shropshire, Worcestershire, Gloucestershire , subdivision_type5 = Cities , subdivision_name5 = Shrewsbury, Worcester, Gloucester, Bristol , length = , width_min = , width_avg = , width_max = , depth_min = , depth_avg = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trent And Mersey Canal
The Trent and Mersey Canal is a canal in Derbyshire, Staffordshire and Cheshire in north-central England. It is a "narrow canal" for the vast majority of its length, but at the extremities to the east of Burton upon Trent and north of Middlewich, it is a wide canal. The narrow locks and bridges are big enough for a single narrowboat wide by long, while the wide locks can accommodate boats wide, or two narrowboats next to each other. History The Trent and Mersey Canal (T&M) was built to link the River Trent at Derwent Mouth in Derbyshire to the River Mersey, and thereby provide an inland route between the major ports of Hull and Liverpool. The Mersey connection is made via the Bridgewater Canal, which it joins at Preston Brook in Cheshire. Although mileposts measure the distance to Preston Brook and Shardlow, Derwent Mouth is about beyond Shardlow. The plan of a canal connection from the Mersey to the Trent ("The Grand Trunk") came from canal engineer James Brindley ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe by the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south. The country covers five-eighths of the island of Great Britain, which lies in the North Atlantic, and includes over 100 smaller islands, such as the Isles of Scilly and the Isle of Wight. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic period, but takes its name from the Angles, a Germanic tribe deriving its name from the Anglia peninsula, who settled during the 5th and 6th centuries. England became a unified state in the 10th century and has had a significant cultural and legal impact on the wider world since the Age of Discovery, which began during the 15th century. The English language, the Anglican Church, and Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staffordshire And Worcestershire Canal
The Staffordshire and Worcestershire Canal is a navigable narrow canal in Staffordshire and Worcestershire in the English Midlands. It is long, linking the River Severn at Stourport in Worcestershire with the Trent and Mersey Canal at Haywood Junction by Great Haywood. History Creation James Brindley was the chief engineer of the canal, which was part of his "Grand Cross" plan for waterways connecting the major ports at Hull (via the Trent), Liverpool (via the Mersey), Bristol (via the Severn) and London (via the Thames). The Act of Parliament authorising the canal was passed on 14 May 1766. This created "The Company of Proprietors of the Staffordshire and Worcestershire Canal Navigation", which was empowered to raise an initial £70,000 (equivalent to £ in ),, with a further £30,000 (equivalent to £ in ), if needed, to fund the canal's construction. The canal was completed in 1771 for a cost that exceeded the authorised capital, and opened to trade in 1772. It was a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integral Calculus
In mathematics, an integral assigns numbers to Function (mathematics), functions in a way that describes Displacement (geometry), displacement, area, volume, and other concepts that arise by combining infinitesimal data. The process of finding integrals is called integration. Along with Derivative, differentiation, integration is a fundamental, essential operation of calculus,Integral calculus is a very well established mathematical discipline for which there are many sources. See and , for example. and serves as a tool to solve problems in mathematics and physics involving the area of an arbitrary shape, the length of a curve, and the volume of a solid, among others. The integrals enumerated here are those termed definite integrals, which can be interpreted as the signed area of the region in the plane that is bounded by the Graph of a function, graph of a given function between two points in the real line. Conventionally, areas above the horizontal axis of the plane are posi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marquis De Condorcet
Marie Jean Antoine Nicolas de Caritat, Marquis of Condorcet (; 17 September 1743 – 29 March 1794), known as Nicolas de Condorcet, was a French philosopher and mathematician. His ideas, including support for a liberal economy, free and equal public instruction, constitutional government, and equal rights for women and people of all races, have been said to embody the ideals of the Age of Enlightenment, of which he has been called the "last witness," and Enlightenment rationalism. He died in prison after a period of hiding from the French Revolutionary authorities. Early years Condorcet was born in Ribemont (in present-day Aisne), descended from the ancient family of Caritat, who took their title from the town of Condorcet in Dauphiné, of which they were long-time residents. Fatherless at a young age, he was taken care of by his devoutly religious mother who dressed him as a girl till age eight. He was educated at the Jesuit College in Reims and at the ''Collège de Navarre'' i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mersenne Prime
In mathematics, a Mersenne prime is a prime number that is one less than a power of two. That is, it is a prime number of the form for some integer . They are named after Marin Mersenne, a French Minim friar, who studied them in the early 17th century. If is a composite number then so is . Therefore, an equivalent definition of the Mersenne primes is that they are the prime numbers of the form for some prime . The exponents which give Mersenne primes are 2, 3, 5, 7, 13, 17, 19, 31, ... and the resulting Mersenne primes are 3, 7, 31, 127, 8191, 131071, 524287, 2147483647, ... . Numbers of the form without the primality requirement may be called Mersenne numbers. Sometimes, however, Mersenne numbers are defined to have the additional requirement that be prime. The smallest composite Mersenne number with prime exponent ''n'' is . Mersenne primes were studied in antiquity because of their close connection to perfect numbers: the Euclid–Euler theorem as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euler
Leonhard Euler ( , ; 15 April 170718 September 1783) was a Swiss mathematician, physicist, astronomer, geographer, logician and engineer who founded the studies of graph theory and topology and made pioneering and influential discoveries in many other branches of mathematics such as analytic number theory, complex analysis, and infinitesimal calculus. He introduced much of modern mathematical terminology and notation, including the notion of a mathematical function. He is also known for his work in mechanics, fluid dynamics, optics, astronomy and music theory. Euler is held to be one of the greatest mathematicians in history and the greatest of the 18th century. A statement attributed to Pierre-Simon Laplace expresses Euler's influence on mathematics: "Read Euler, read Euler, he is the master of us all." Carl Friedrich Gauss remarked: "The study of Euler's works will remain the best school for the different fields of mathematics, and nothing else can replace it." Euler is also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Hamilton (diplomat)
Sir William Hamilton, (13 December 1730 – 6 April 1803), was a British diplomat, antiquarian, archaeologist and vulcanologist. After a short period as a Member of Parliament, he served as British Ambassador to the Kingdom of Naples from 1764 to 1800. He studied the volcanoes Vesuvius and Etna, becoming a Fellow of the Royal Society and recipient of the Copley Medal. His second wife was Emma Hamilton, famed as Horatio Nelson's mistress. Early life and career Hamilton was born on 13 December 1730 (or 12 January 1731) in either London or at Park Place, Berkshire, the fourth son of Lord Archibald Hamilton, governor of Jamaica, seventh son of William Douglas-Hamilton, Earl of Selkirk, by the 3rd Duchess of Hamilton, and Lady Jane Hamilton, daughter of James Hamilton, 6th Earl of Abercorn.Constantine 2001: 1–2. His mother was a favourite, and possibly a mistress, of the Prince of Wales and William grew up with his son George III, who would call him his "foster brother". At age n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |