|
1745 Establishment
The 1745 Establishment was the third and final formal establishment of dimensions for ships to be built for the Royal Navy. It completely superseded the previous 1719 Establishment, which had subsequently been modified in 1733 and again in 1741 (but not formally replaced on either occasion). Although partially intended to correct the problems of the ships built to the earlier Establishments, the ships of the 1745 Establishment proved just as unsatisfactory, and important changes in the make-up of the Board of Admiralty, Admiralty and Navy Boards finally led to the end of the establishment era by around 1751.Lavery, The Ship of the Line - Volume 1, p 86–97. Origins When the 1706 Establishment had come into effect, British naval architecture had been set on a path of conservatism that caused stagnation in the advance of shipbuilding in Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain. Over the course of the existence of the 1706 and 1719 Establishments, the sizes of ships had remaine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1719 Establishment
The 1719 Establishment was a set of mandatory requirements governing the construction of all Royal Navy warships capable of carrying more than 20 naval long guns. It was designed to bring economies of scale through uniform vessel design, and ensure a degree of certainty about vessel capability once at sea, and was applied to all vessels from the first-rate to the fifth-rate. Once in effect, it superseded the 1706 Establishment, which had specified major dimensions for ships of the second-rate, third-rate and fourth-rate only.Lavery 2003, p. 75 The new Establishment in 1719 was not simply limited to specifying the overall dimensions of each type of warship, but now set out in great detail other factors used in constructing the ship, down to the thickness of timbers ("scantlings") used in construction and planking. The Establishment adopted in 1719 was subject to substantial revisions in both 1733 and 1741, although on neither occasion was the 1719 Establishment replaced. A new Es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Toulon (1744)
The Battle of Toulon, also known as the Battle of Cape Sicié, took place between 21 to 22 February 1744 NS near the French Mediterranean port of Toulon. Although France was not yet at war with Great Britain, ships from their Levant Fleet sailed out with a Spanish force, which had been trapped in Toulon for two years, to break the blockade imposed by the British Mediterranean Fleet. The initial engagement on 21 February was largely indecisive and the British continued their pursuit until midday on 22nd before their commander, Admiral Thomas Mathews, called off the chase. With several of his ships in need of repair, he withdrew to Menorca, which meant the Royal Navy temporarily lost control of the waters around Italy and allowed the Spanish to take the offensive against Savoy. In his report, Mathews blamed his subordinate Richard Lestock for the failure and the issue was hotly debated in Parliament. At the subsequent court-martial, Mathews was held responsible and dismissed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Slade
Sir Thomas Slade (1703/4–1771) was an English naval architect, most famous for designing HMS ''Victory'', Lord Nelson's flagship at the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805. Early life He was the son of Arthur Slade (1682–1746) and his wife Hannah Moore. His paternal uncle was Benjamin Slade, Master Shipwright at Deptford Dockyard. Career outline Like many who rose to the pinnacle of the design of British sailing warships, Thomas Slade began as a shipwright in the Royal Dockyards. His uncle Benjamin Slade was Master Shipwright at Plymouth Dockyard (a master shipwright was responsible for all ship construction and repair at the dockyard in which he served). In 1744 Thomas became Deputy Master Shipwright at Woolwich Dockyard. On 22 November 1750 he replaced his uncle, who had died that year, as Master Shipwright at Plymouth. On 27 May 1752 he was transferred temporarily back to Woolwich Dockyard as Master Shipwright, and from there to Chatham Dockyard on 17 June 1752 and subsequently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Allin
Joseph Allin was an 18th century shipbuilder to the Royal Navy. His works merge with those of his namesake son who was also a Master Shipwright at Portsmouth Dockyard and later Surveyor to the Navy at which point he became Sir Joseph Allin. Joseph Allin the elder, first appears as "Assistant Master Shipwright" in Portsmouth in December 1700 as assistant to Elias Waffe. Typically this position followed at least seven years on a ship training and a further period serving as a ship's carpenter, bringing his probable age to around 30. As his son was born around 1690 it may be assumed that Joseph Allin the elder was born around 1670. From 1701 to 1705 he served as Master Shipwright at Sheerness Dockyard and also dis some work overseeing Woolwich before settling as Master Shipwright of Deptford Dockyard in November 1705. Joseph Allin the elder died in 1716. His son had a parallel career but as Master Shipwright of different yards: Portsmouth 1726 to 1742 (in place of John Naish (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth-rate
In 1603 all English warships with a compliment of fewer than 160 men were known as 'small ships'. In 1625/26 to establish pay rates for officers a six tier naval ship rating system was introduced.Winfield 2009 These small ships were divided into three tiers, Fourth, Fifth and Sixth rates. Up to the end of the 17th century the number of guns and the compliment size was adjusted until the rating system was actually clarified. A 'Fourth Rate' was nominally a ship of over thirty guns with a complement of 140 men. In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorize sailing warships in the 18th century, a fourth-rate was a ship of the line with 46 to 60 guns mounted. They were phased out of ship of the line service during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, as their usefulness was declining; though they were still in service, especially on distant stations such as the East Indies. ''Fourth-rates'' took many forms, initially as small two decked warships, later as larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third-rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy, a third rate was a ship of the line which from the 1720s mounted between 64 and 80 guns, typically built with two gun decks (thus the related term two-decker). Years of experience proved that the third rate ships embodied the best compromise between sailing ability (speed, handling), firepower, and cost. So, while first-rates and second-rates were both larger and more powerful, third-rate ships were the optimal configuration. Rating When the rating system was first established in the 1620s, the third rate was defined as those ships having at least 200 but not more than 300 men; previous to this, the type had been classified as "middling ships". By the 1660s, the means of classification had shifted from the number of men to the number of carriage-mounted guns, and third rates at that time mounted between 48 and 60 guns. By the turn of the century, the criterion boundaries had increased and third rate carried more than 60 guns, with seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
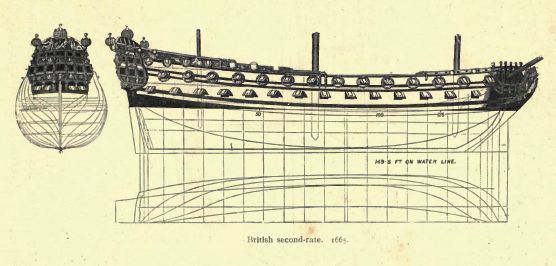
Second-rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a second-rate was a ship of the line which by the start of the 18th century mounted 90 to 98 guns on three gun decks; earlier 17th-century second rates had fewer guns and were originally two-deckers or had only partially armed third gun decks. A "second rate" was the second largest class of warships in a hierarchical system of six "ratings" based on size and firepower. They were essentially smaller and hence cheaper versions of the three-decker first rates. Like the first rates, they fought in the line of battle, but unlike the first rates, which were considered too valuable to risk in distant stations, the second rates often served also in major overseas stations as flagships. They had a reputation for poor handling and slow sailing. They were popular as flagships of admirals commanding the Windward and/or Leeward Islands station, which was usually a Rear-admiral of the red. Rating Typically measuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Builder's Old Measurement
Builder's Old Measurement (BOM, bm, OM, and o.m.) is the method used in England from approximately 1650 to 1849 for calculating the cargo capacity of a ship. It is a volumetric measurement of cubic capacity. It estimated the tonnage of a ship based on length and maximum beam (nautical), beam. It is expressed in "tons burden" ( en-em , burthen , enm , byrthen ), and abbreviated "tons bm". The formula is: : \text = \frac where: * ''Length'' is the length, in foot (length), feet, from the stem (ship), stem to the sternpost; * ''Beam (nautical), Beam'' is the maximum beam, in feet. The Builder's Old Measurement formula remained in effect until the advent of steam propulsion. Steamships required a different method of estimating tonnage, because the ratio of length to beam was larger and a significant volume of internal space was used for boilers and machinery. In 1849, the Moorsom System was created in the United Kingdom. The Moorsom system calculates the cargo-carrying capaci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Of The Line
A ship of the line was a type of naval warship constructed during the Age of Sail from the 17th century to the mid-19th century. The ship of the line was designed for the naval tactic known as the line of battle, which depended on the two columns of opposing warships maneuvering to volley fire with the cannons along their broadsides. In conflicts where opposing ships were both able to fire from their broadsides, the opponent with more cannons firingand therefore more firepowertypically had an advantage. Since these engagements were almost invariably won by the heaviest ships carrying more of the most powerful guns, the natural progression was to build sailing vessels that were the largest and most powerful of their time. From the end of the 1840s, the introduction of steam power brought less dependence on the wind in battle and led to the construction of screw-driven wooden-hulled ships of the line; a number of purely sail-powered ships were converted to this propulsion mech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privy Council Of The United Kingdom
The Privy Council (PC), officially His Majesty's Most Honourable Privy Council, is a formal body of advisers to the sovereign of the United Kingdom. Its membership mainly comprises senior politicians who are current or former members of either the House of Commons or the House of Lords. The Privy Council formally advises the sovereign on the exercise of the Royal Prerogative, and as a body corporate (as King-in-Council) it issues executive instruments known as Orders in Council which, among other powers, enact Acts of Parliament. The Council also holds the delegated authority to issue Orders of Council, mostly used to regulate certain public institutions. The Council advises the sovereign on the issuing of Royal Charters, which are used to grant special status to incorporated bodies, and city or borough status to local authorities. Otherwise, the Privy Council's powers have now been largely replaced by its executive committee, the Cabinet of the United Kingdom. Certai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sixth Rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a sixth-rate was the designation for small warships mounting between 20 and 28 carriage-mounted guns on a single deck, sometimes with smaller guns on the upper works and sometimes without. It thus encompassed ships with up to 30 guns in all. In the first half of the 18th century the main battery guns were 6-pounders, but by mid-century these were supplanted by 9-pounders. 28-gun sixth rates were classed as frigates, those smaller as 'post ships', indicating that they were still commanded by a full ('post') captain, as opposed to sloops of 18 guns and less under commanders. Rating Sixth-rate ships typically had a crew of about 150–240 men, and measured between 450 and 550 tons. A 28-gun ship would have about 19 officers; commissioned officers would include the captain, and two lieutenants; warrant officers would include the master, ship's surgeon, and purser. The other quarterdeck officers were the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Bilson Legge
Henry Bilson-Legge (29 May 1708 – 23 August 1764) was an English statesman. He notably served three times as Chancellor of the Exchequer in the 1750s and 1760s. Background and education Bilson-Legge was the fourth son of William Legge, 1st Earl of Dartmouth, by his wife Lady Anne, daughter of Heneage Finch, 1st Earl of Aylesford. He was educated at Christ Church, Oxford. Political career He became private secretary to Sir Robert Walpole. In 1739 was appointed Chief Secretary for Ireland by the Lord Lieutenant, William Cavendish, 3rd Duke of Devonshire; being chosen Member of Parliament for the borough of East Looe in 1740, and for Orford, Suffolk, at the general election in the succeeding year. Legge only shared temporarily in the downfall of Walpole, and became in quick succession Surveyor-General of Woods and Forests, a Lord of the Admiralty, and a Lord of the Treasury. In 1748 he was sent as envoy extraordinary to Frederick the Great, and although his conduct in Berl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_-_02.jpg)