|
1468
Year 1468 ( MCDLXVIII) was a leap year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events January–December *June 30 – Catherine Cornaro is married by proxy to James II of Cyprus, beginning the Venetian conquest of Cyprus. * August 26 – Baeda Maryam succeeds his father Zara Yaqob, as Emperor of Ethiopia. * October 14 – The Treaty of Péronne is signed by Charles the Bold, Duke of Burgundy, and Louis XI of France. Date unknown * The Lancastrians surrender Harlech Castle to King Edward IV of England after a seven-year siege. * The Great Council of the Republic of Venice attempts to curb the power of the Council of Ten through legislation restricting them to acting on emergency matters. * Orkney is pledged by Christian I, in his capacity as King of Norway, as security against the payment of the dowry of his daughter Margaret, betrothed to James III of Scotland. As the money is never paid, the connection w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
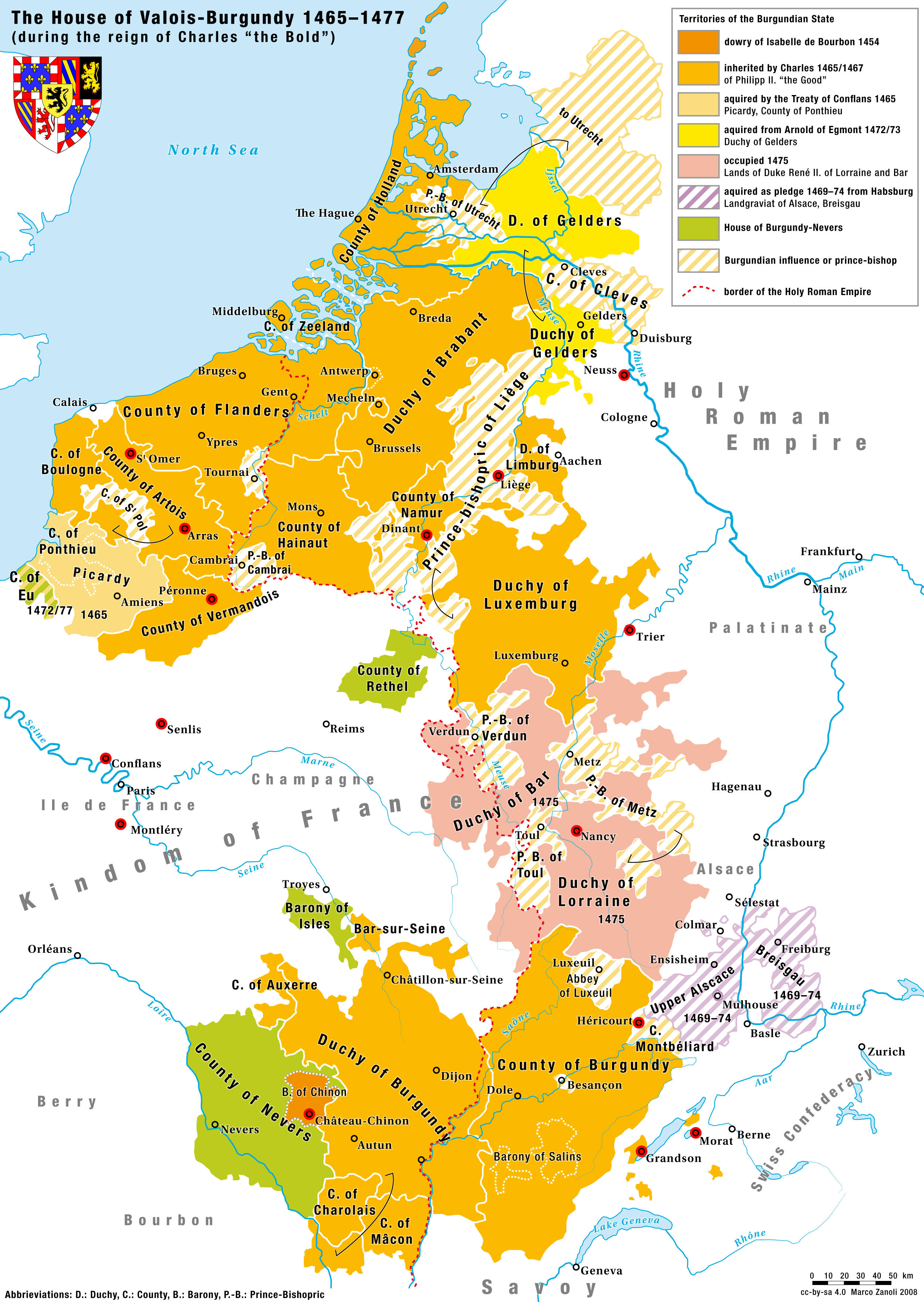
Charles I, Duke Of Burgundy
Charles I (Charles Martin; german: Karl Martin; nl, Karel Maarten; 10 November 1433 – 5 January 1477), nicknamed the Bold (German: ''der Kühne''; Dutch: ''de Stoute''; french: le Téméraire), was Duke of Burgundy from 1467 to 1477. Charles's main objective was to be crowned king by turning the growing Burgundian State into a territorially continuous kingdom. He declared himself and his lands independent, bought Alsace, Upper Alsace and conquered County of Zutphen, Zutphen, Duchy of Guelders, Guelders and Duchy of Lorraine, Lorraine, uniting at last Burgundian northern and southern possessions. This caused the enmity of several European powers and triggered the Burgundian Wars. Charles's early death at the Battle of Nancy at the hands of Swiss mercenaries fighting for René II, Duke of Lorraine, was of great consequence in European history. The Burgundian domains, long wedged between the Kingdom of France and the Habsburg Empire, were divided, but the precise disposi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Paul III
Pope Paul III ( la, Paulus III; it, Paolo III; 29 February 1468 – 10 November 1549), born Alessandro Farnese, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 13 October 1534 to his death in November 1549. He came to the papal throne in an era following the sack of Rome in 1527 and rife with uncertainties in the Catholic Church following the Protestant Reformation. His pontificate initiated the Counter-Reformation with the Council of Trent in 1545, as well as the wars of religion with Emperor Charles V's military campaigns against the Protestants in Germany. He recognized new Catholic religious orders and societies such as the Jesuits, the Barnabites, and the Congregation of the Oratory. His efforts were distracted by nepotism to advance the power and fortunes of his family, including his illegitimate son Pier Luigi Farnese. Paul III was a significant patron of artists including Michelangelo, and it is to him that Nicolaus Copernicus dedicated his h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Péronne (1468)
The Treaty of Péronne was signed in Péronne (in the county of Vermandois, a then Burgundian territory) on October 14, 1468 between Charles the Bold, Duke of Burgundy and Louis XI of France. Based on the terms of the treaty, Charles especially acquired the English claimed county of Ponthieu. On the Burgundian side the accord was discussed by Charles, mainly assisted by his long-time favorite Guillaume de Bische and his councillor Ferry de Clugny ; on the French side it was negotiated by the king Louis himself and the cardinal de La Balue. See also *List of treaties This list of treaties contains known agreements, pacts, peaces, and major contracts between states, armies, governments, and tribal groups. Before 1200 CE 1200–1299 1300–1399 1400–1499 1500–1599 1600–1699 1700–1799 ... External linksRichard III Society - The Cely Papers [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harlech Castle
Harlech Castle ( cy, Castell Harlech; ) in Harlech, Gwynedd, Wales, is a Grade I listed medieval fortification built onto a rocky knoll close to the Irish Sea. It was built by Edward I during his invasion of Wales between 1282 and 1289 at the relatively modest cost of £8,190. Over the next few centuries, the castle played an important part in several wars, withstanding the siege of Madog ap Llywelyn between 1294 and 1295, but falling to Prince Owain Glyndŵr in 1404. It then became Glyndŵr's residence and military headquarters for the remainder of the uprising until being recaptured by English forces in 1409. During the 15th century Wars of the Roses, Harlech was held by the Lancastrians for seven years, before Yorkist troops forced its surrender in 1468, a siege memorialised in the song "Men of Harlech". Following the outbreak of the English Civil War in 1642, the castle was held by forces loyal to Charles I, holding out until 1647 when it became the last fortification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baeda Maryam Of Ethiopia
Baeda Maryam I ( gez, በእደ ማርያም; Bäˀəda Maryam, meaning "He who is in the hand of Mary"; 1448 – 8 November 1478), otherwise known as Cyriacus was Emperor of Ethiopia from 1468 to 1478, and a member of the Solomonic dynasty. His reign was characterized by a number of military campaigns, most notably against the Dobe'a who lived along the western escarpment of the Ethiopian Highlands. Early years Born at Debre Berhan, he was the son of Zara Yaqob by Seyon Mogesa. Towards the end of Zara Yaqob's life, the Emperor became increasingly convinced that members of his family were plotting against him, and had several of them beaten. Baeda Maryam I's mother died from this mistreatment in 1462, and Baeda Maryam I buried her in secret in the church of Maqdesa Maryam, near Debre Berhan, and donated incense and other gifts to support the church. Zara Yaqob then directed his anger at Baeda Maryam I, until members of the Ethiopian Orthodox Church repaired the rift between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catherine Cornaro
Catherine Cornaro ( el, Αικατερίνη Κορνάρο, vec, Catarina Corner) (25 November 1454 – 10 July 1510) was the last monarch of the Kingdom of Cyprus, also holding the titles of the Queen of Jerusalem and Armenia. She was queen consort of Cyprus by marriage to James II of Cyprus, regent of Cyprus during the minority of her son James III of Cyprus in 1473–1474, and finally queen regnant of Cyprus. She reigned from 26 August 1474 to 26 February 1489 and was declared a "Daughter of Saint Mark" in order that the Republic of Venice could claim control of Cyprus after the death of her husband, James II. Life Catherine was a daughter of Venetian Marco Cornaro, Cavaliere del Sacro Romano Impero (Knight of the Holy Roman Empire) and Fiorenza Crispo. She was the younger sister of the ''Nobil Huomo'' Giorgio Cornaro (1452 – 31 July 1527), "Padre della Patria" and Knight of the Holy Roman Empire. The Cornaro family had produced four Doges. Her family had long associ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James II Of Cyprus
James II (french: Jacques; c. 1438/1439 or c. 1440 – 10 July 1473) was the penultimate King of Cyprus (usurper), reigning from 1463 until his death. Archbishop of Nicosia James was born in Nicosia as the illegitimate son of John II of Cyprus and Marietta de Patras. He was a great favourite of his father, and in 1456, at the age of 16, he was appointed to the archbishopric of Nicosia. After murdering Iacopo Urri, the royal chamberlain, on 1 April 1457, he was deprived of the archbishopric and fled to Rhodes on a ship of the Catalan Juan Tafures. He was pardoned by his father, and the archbishopric was returned to him. King of Cyprus In 1458, his father died, and his half-sister Charlotte became Queen of Cyprus. In 1460, with support from the Egyptian Mamluk sultan Sayf ad-Din Inal, James challenged her right to the throne, blockading her and her husband, Louis of Savoy, in the castle of Kyrenia for three years. When Charlotte fled to Rome in 1463, James was crowned king. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venetian Cyprus
The island of Cyprus was an overseas possession of the Republic of Venice from 1489, when the independent Kingdom of Cyprus ended, until 1570–71, when the island was conquered by the Ottoman Empire. History Acquisition Venice for centuries wanted to control Cyprus and Venetian merchants worked on the island beginning in 1000 AD, when the Venetian (commercial and military) expansion in the eastern Mediterranean had started. In 1468, James II of Cyprus of the house of Lusignan became King of Cyprus. In 1468, he chose Catherine Cornaro (born in Venice from the noble family of the "Corner") as his wife and Queen consort of Cyprus. The King's choice was extremely pleasing to the Republic of Venice, as it could henceforth secure the commercial rights and other privileges of Venice in Cyprus. They married in Venice on 30 July 1468 by proxy when she was 14 years old. James died soon after the wedding due to a sudden illness and, according to his will, Caterina, who at the time w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Songhai Empire
The Songhai Empire (also transliterated as Songhay) was a state that dominated the western Sahel/Sudan in the 15th and 16th century. At its peak, it was one of the largest states in African history. The state is known by its historiographical name, derived from its leading ethnic group and ruling elite, the Songhai. Sonni Ali established Gao as the capital of the empire although a Songhai state had existed in and around Gao since the 11th century. Other important cities in the empire were Timbuktu and Djenné, conquered in 1468 and 1475 respectively, where urban-centered trade flourished and to the south is the north Akan state of Bonoman. Initially, the empire was ruled by the Sonni dynasty (–1493), but it was later replaced by the Askia dynasty (1493–1901). During the second half of the 13th century, Gao and the surrounding region had grown into an important trading center and attracted the interest of the expanding Mali Empire. Mali conquered Gao towards the end of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethiopian Empire
The Ethiopian Empire (), also formerly known by the exonym Abyssinia, or just simply known as Ethiopia (; Amharic and Tigrinya: ኢትዮጵያ , , Oromo: Itoophiyaa, Somali: Itoobiya, Afar: ''Itiyoophiyaa''), was an empire that historically spanned the geographical area of present-day Ethiopia and Eritrea from the establishment of the Solomonic dynasty by Yekuno Amlak approximately in 1270 until the 1974 coup d'etat of Emperor Haile Selassie by the Derg. By 1896, the Empire incorporated other regions such as Hararghe, Gurage and Wolayita, and saw its largest expansion with the federation of Eritrea in 1952. Throughout much of its existence, it was surrounded by hostile forces in the African Horn; however, it managed to develop and preserve a kingdom based on its ancient form of Christianity. Founded in 1270 by the Solomonic Dynasty nobleman Yekuno Amlak, who claimed to descend from the last Aksumite king and ultimately the Biblical Menelik I and the Queen of Sheba, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timbuktu
Timbuktu ( ; french: Tombouctou; Koyra Chiini: ); tmh, label=Tuareg, script=Tfng, ⵜⵏⴱⴾⵜ, Tin Buqt a city in Mali, situated north of the Niger River. The town is the capital of the Tombouctou Region, one of the eight administrative regions of Mali and one town of Songhai people. It had a population of 54,453 in the 2009 census. Timbuktu began as a seasonal settlement and became a permanent settlement early in the 12th century. After a shift in trading routes, particularly after the visit by Mansa Musa around 1325, Timbuktu flourished from the trade in salt, gold, ivory and slaves. It gradually expanded as an important Islamic city on the Saharan trade route and attracted many scholars and traders. It became part of the Mali Empire early in the 14th century. In the first half of the 15th century, the Tuareg people took control of the city for a short period until the expanding Songhai Empire absorbed the city in 1468. A Moroccan army defeated the Songhai in 159 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metz Cathedral
Metz Cathedral, otherwise the Cathedral of Saint Stephen, Metz (french: Cathédrale Saint Étienne de Metz), is a Roman Catholic cathedral in Metz, capital of Lorraine, France. It is dedicated to Saint Stephen. First begun in the early 14th century, it was joined with the collegiate church of Notre-Dame in the mid-14th century, and given a new transept and late Gothic chevet, finished between 1486 and 1520. It is the cathedral of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Metz as the seat of the bishops of Metz. The cathedral treasury displays the collection, assembled over 1,000 years, of the bishopric of Metz, including paraments and items used for the Eucharist. Metz Cathedral has the third-highest nave of cathedrals in France (41.41 meters (135.9 ft)), behind Amiens Cathedral and Beauvais Cathedral. It is nicknamed ("the Good Lord's lantern"), displaying the largest expanse of stained glass in the world with .Jolin J.L. (2001) La lanterne du Bon Dieu. Eds. Serpnoise. . The stained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)
