|
1-Chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene
1-Chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene (HFO-1233zd) is the unsaturated chlorofluorocarbon with the formula HClC=C(H)CF3. This colorless gas is of interest as a more environmentally friendly (lower GWP; global warming potential) refrigerant A refrigerant is a working fluid used in the heat pump and refrigeration cycle, refrigeration cycle of air conditioning systems and heat pumps where in most cases they undergo a repeated phase transition from a liquid to a gas and back again. Ref ... in air conditioners. The compound exists as E- and Z-isomers. It is prepared by fluorination and dehydrohalogenation reactions starting with 1,1,1,3,3-pentachloropropane.Tung, Hseuh Sung; Ulrich, Kevin D.; Merkel, Daniel C. "Low-temperature catalytic fluorination process for the manufacture of 1-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene from 1,1,1,3,3-pentachloropropane and hydrogen fluoride" U.S. (2005), US 6844475 B2 20050118 to Honeywell International Business Machines. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Chloro-3,3,3- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturated And Unsaturated Compounds
In chemistry, a saturated compound is a chemical compound (or ion) that resists the addition reactions, such as hydrogenation, oxidative addition, and binding of a Lewis acids and bases, Lewis base. The term is used in many contexts and for many classes of chemical compounds. Overall, saturated compounds are less reactive than unsaturated compounds. Saturation is derived from the Latin word ''saturare'', meaning 'to fill'. Organic chemistry Unsaturated compounds generally carry out typical addition reactions that are not possible with saturated compounds such as alkanes. A saturated organic compound has only single bonds between carbon atoms. An important class of saturated compounds are the alkanes. Many saturated compounds have functional groups, e.g., alcohols. Unsaturated organic compounds The concept of saturation can be described using various naming systems, formulas, and Analytical chemistry, analytical tests. For instance, IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry, IU ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorofluorocarbon
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) are fully or partly halogenated hydrocarbons that contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), chlorine (Cl), and fluorine (F), produced as volatile derivatives of methane, ethane, and propane. They are also commonly known by the DuPont brand name Freon. The most common representative is dichlorodifluoromethane (R-12 or Freon-12). Many CFCs have been widely used as refrigerants, propellants (in aerosol applications), and solvents. Because CFCs contribute to ozone depletion in the upper atmosphere, the manufacture of such compounds has been phased out under the Montreal Protocol, and they are being replaced with other products such as hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) including R-410A and R-134a. Structure, properties and production As in simpler alkanes, carbon in the CFCs bond with tetrahedral symmetry. Because the fluorine and chlorine atoms differ greatly in size and effective charge from hydrogen and from each other, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refrigerant
A refrigerant is a working fluid used in the heat pump and refrigeration cycle, refrigeration cycle of air conditioning systems and heat pumps where in most cases they undergo a repeated phase transition from a liquid to a gas and back again. Refrigerants are heavily regulated due to their toxicity, flammability and the contribution of CFC and HCFC refrigerants to ozone depletion and that of HFC refrigerants to climate change. Refrigerants are used in a Direct Expansion (DX) system to transfer energy from one environment to another, typically from inside a building to outside (or vice versa) commonly known as an "air conditioner" or "heat pump". Refrigerants can carry per kg 10 times more energy than water and 50 times more than air. Refrigerants are controlled substances due to 1) High Pressures (100-145 psi), 2) Extreme temperatures (-50°C to 145°C), 3) Flammability A1 class non-flammable, A2/A2L class flammable & A3 class extremely flammable/explosive and 4) Toxicity B1-low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical & Engineering News
''Chemical & Engineering News'' (''C&EN'') is a weekly news magazine published by the American Chemical Society, providing professional and technical news and analysis in the fields of chemistry and chemical engineering.C&EN Magazine Website Chemical and Engineering News, October 12, 2009, accessed October 12, 2009 It includes information on recent news and research in these fields, career and employment information, business and industry news, government and policy news, funding in these fields, and special reports. The magazine is available to all members of the American Chemical Society. History The magazine was established in 1923,C&EN- Happy Birthday to Us, accessed O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
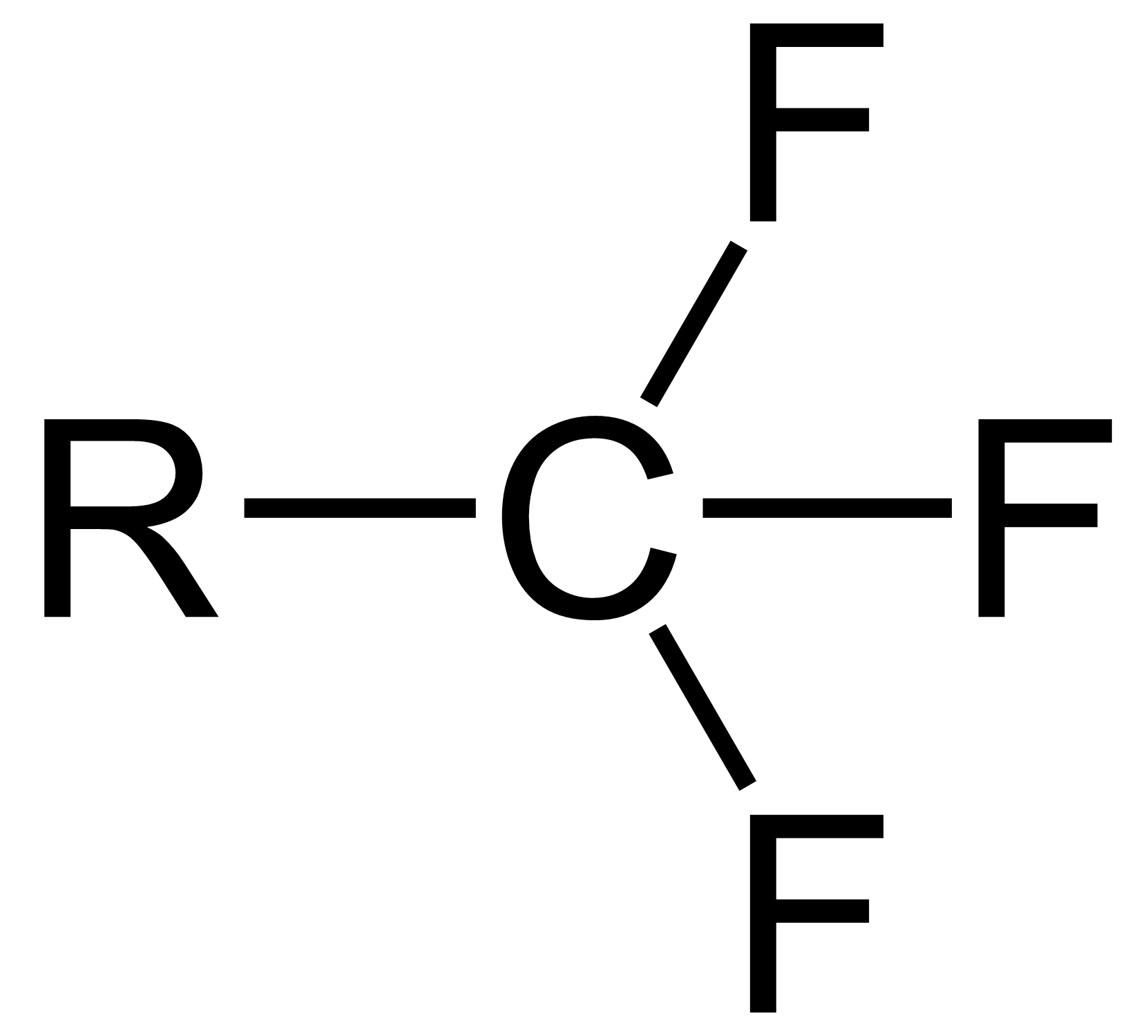
Trifluoromethyl Compounds
The trifluoromethyl group is a functional group that has the formula -CF3. The naming of is group is derived from the methyl group (which has the formula -CH3), by replacing each hydrogen atom by a fluorine atom. Some common examples are trifluoromethane H–, 1,1,1-trifluoroethane –, and hexafluoroacetone –CO–. Compounds with this group are a subclass of the organofluorines. Properties The trifluoromethyl group has a significant electronegativity that is often described as being intermediate between the electronegativities of fluorine and chlorine. For this reason, trifluoromethyl-substituted compounds are often strong acids, such as trifluoromethanesulfonic acid and trifluoroacetic acid. Conversely, the trifluoromethyl group lowers the basicity of compounds like trifluoroethanol. Uses The trifluoromethyl group occurs in certain pharmaceuticals, drugs, and abiotically synthesized natural fluorocarbon based compounds. The medicinal use of the trifloromethyl group dates from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refrigerants
A refrigerant is a working fluid used in the refrigeration cycle of air conditioning systems and heat pumps where in most cases they undergo a repeated phase transition from a liquid to a gas and back again. Refrigerants are heavily regulated due to their toxicity, flammability and the contribution of CFC and HCFC refrigerants to ozone depletion and that of HFC refrigerants to climate change. Refrigerants are used in a Direct Expansion (DX) system to transfer energy from one environment to another, typically from inside a building to outside (or vice versa) commonly known as an "air conditioner" or "heat pump". Refrigerants can carry per kg 10 times more energy than water and 50 times more than air. Refrigerants are controlled substances due to 1) High Pressures (100-145 psi), 2) Extreme temperatures (-50°C to 145°C), 3) Flammability A1 class non-flammable, A2/A2L class flammable & A3 class extremely flammable/explosive and 4) Toxicity B1-low, B2-medium & B3-high, as classifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |