|
1,5-Diazabicyclo(4.3.0)non-5-ene
1,5-Diazabicyclo .3.0on-5-ene (DBN) is a chemical compound with the formula CHN. It is an amidine base used in organic synthesis. A related compound with related functions is 1,8-diazabicyclo .4.0ndec-7-ene (DBU). The relatively complex nature of the formal names for DBU and DBN (hence the common use of acronyms) reflects the fact that these compounds are bicyclic and contain several functional groups. Synthesis DBN could be synthesized in the following manner, similarly to DBU:Möller, F.; Oediger, H. "1,5-Diazabicyclo .4.0ndec-5-ene, a New Hydrogen Halide Acceptor" ''Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. '', 1967, ''5'', 76. : The synthetic procedure starts with a Michael addition of 2-pyrrolidone to acrylonitrile, followed by hydrogenation, and finally dehydration. Uses As a base in organic synthesis Similar to many other organic bases, DBN could be employed for dehydrohalogenation reactions, base-catalyzed rearrangement reactions, as well as Aldol condensation. Several examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-nucleophilic Bases
As the name suggests, a non-nucleophilic base is a Steric effects#Steric hindrance, sterically hindered organic compound, organic base (chemistry), base that is a poor nucleophile. Normal bases are also nucleophiles, but often chemists seek the proton-removing ability of a base without any other functions. Typical non-nucleophilic bases are bulky, such that protons can attach to the basic center but alkylation and complexation is inhibited. Non-nucleophilic bases A variety of amines and nitrogen heterocycles are useful bases of moderate strength (pKa of conjugate acid *N,N-Diisopropylethylamine, ''N'',''N''-Diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA, also called Hünig's Base), p *1,8-Diazabicycloundec-7-ene (DBU) - useful for E2 elimination reactions, pKa = 13.5 *1,5-Diazabicyclo(4.3.0)non-5-ene (DBN) - comparable to DBU *2,6-Di-tert-butylpyridine, a weak non-nucleophilic base pKa = 3.58 *Phosphazene, Phosphazene bases, such as t-Bu-P4''Activation in anionic polymerization: Why phosphazene base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DBU (chemistry)
1,8-Diazabicyclo .4.0ndec-7-ene, or more commonly DBU, is a chemical compound and belongs to the class of amidine compounds. It is used in organic synthesis as a catalyst, a complexing ligand, and a non-nucleophilic base. Occurrence Although all commercially available DBU is produced synthetically, it may also be isolated from the sea sponge '' Niphates digitalis''. The biosynthesis of DBU has been proposed to begin with 1,6-hexanedial and 1,3-diaminopropane. Uses As a reagent in organic chemistry, DBU is used as a catalyst, a complexing ligand, and a non-nucleophilic base. It is also used as a curing agent for epoxy resins. It is used in the separation of fullerenes in conjunction with trimethylbenzene. It reacts with C70 and higher fullerenes, but not with to C60 It is also used as a catalyst in the production of polyurethanes. It also exhibited its dual character (base and nucleophile) in the synthesis of aryl- and styryl-terminal acetylenes. See also * 1,5-Diazabic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amidines
Amidines are organic compounds with the functional group RC(NR)NR2, where the R groups can be the same or different. They are the imine derivatives of amides (RC(O)NR2). The simplest amidine is formamidine, HC(=NH)NH2. Examples of amidines include: * DBU * diminazene * benzamidine * Pentamidine * Paranyline Preparation A common route to primary amidines is the Pinner reaction. Reaction of the nitrile with alcohol in the presence of acid gives an iminoether. Treatment of the resulting compound with ammonia then completes the conversion to the amidine. Instead of using a Bronsted acid, Lewis acids such as aluminium trichloride promote the direct amination of nitriles. They are also generated by amination of an imidoyl chloride. They are also prepared by the addition of organolithium reagents to diimines, followed by protonation or alkylation. Dimethylformamide acetal reacts with primary amines to give amidines: :Me2NC(H)(OMe)2 + RNH2 → Me2NC=NHR + 2 MeOH Properties and applica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyocell
Lyocell, originally trademarked in 1982 as Tencel, is a form of regenerated cellulose. It consists of cellulose fibers, made by dissolving pulp and then reconstituting it by dry jet-wet spinning. The fiber is used to make textiles for clothing and other purposes. Unlike rayon made by some of the more common viscose processes, Lyocell production does not use carbon disulfide, which is toxic to workers and the environment. "Lyocell" has become a genericized trademark, used to refer to the Lyocell process for making cellulose fibers. The U.S. Federal Trade Commission defines Lyocell as "a fiber composed of cellulose precipitated from an organic solution in which no substitution of the hydroxy groups takes place, and no chemical intermediates are formed". It classifies the fiber as a sub-category of rayon. Names Other trademarked names for Lyocell fibers are Lenzing Lyocell (Lenzing), Newcell (Akzo Nobel), and Seacell (Zimmer AG).B. Ozipek, H. Karakas, in Advances in Filament Yar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-Methylmorpholine N-oxide
''N''-Methylmorpholine ''N''-oxide (more correctly 4-methylmorpholine 4-oxide), NMO or NMMO is an organic compound. This heterocyclic amine oxide and morpholine derivative is used in organic chemistry as a co-oxidant and sacrificial catalyst in oxidation reactions for instance in osmium tetroxide oxidations and the Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation or oxidations with TPAP. NMO is commercially supplied both as a monohydrate C5H11NO2·H2O and as the anhydrous compound. The monohydrate is used as a solvent for cellulose in the lyocell process to produce cellulose fibers. Uses Solvent of cellulose NMMO monohydrate is used as a solvent in the lyocell process to produce lyocell fiber. It dissolves cellulose to form a solution called dope, and the cellulose is reprecipitated in a water bath to produce a fiber. The process is similar but not analogous to the viscose process. In the viscose process, cellulose is made soluble by conversion to its xanthate derivatives. With NMMO, cellul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rayon
Rayon is a semi-synthetic fiber, made from natural sources of regenerated cellulose, such as wood and related agricultural products. It has the same molecular structure as cellulose. It is also called viscose. Many types and grades of viscose fibers and films exist. Some imitate the feel and texture of natural fibers such as silk, wool, cotton, and linen. The types that resemble silk are often called artificial silk. The fibre is used to make textiles for clothing and other purposes. Rayon production involves solubilizing cellulose to allow turning the fibers into required form. Three common ways to solubilize are the cuprammonium process, not in use today, using ammoniacal solutions of copper salts; the viscose process, the most common today, using alkali and carbon sulfide; and the Lyocell process, using amine oxide. The last avoids the neurotoxic carbon sulfide of the viscose process but is also more expensive. Rayon and its variants Rayon is produced by dissolving cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
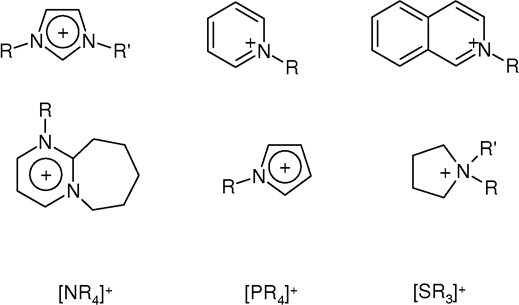
Ionic Liquid
An ionic liquid (IL) is a salt in the liquid state. In some contexts, the term has been restricted to salts whose melting point is below a specific temperature, such as . While ordinary liquids such as water and gasoline are predominantly made of electrically neutral molecules, ionic liquids are largely made of ions. These substances are variously called liquid electrolytes, ionic melts, ionic fluids, fused salts, liquid salts, or ionic glasses. Ionic liquids have many potential applications. They are powerful solvents and can be used as electrolytes. Salts that are liquid at near-ambient temperature are important for electric battery applications, and have been considered as sealants due to their very low vapor pressure. Any salt that melts without decomposing or vaporizing usually yields an ionic liquid. Sodium chloride (NaCl), for example, melts at into a liquid that consists largely of sodium cations () and chloride anions (). Conversely, when an ionic liquid is cooled, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetate
An acetate is a salt (chemistry), salt formed by the combination of acetic acid with a base (e.g. Alkali metal, alkaline, Alkaline earth metal, earthy, Transition metal, metallic, nonmetallic or radical Radical (chemistry), base). "Acetate" also describes the conjugate acid, conjugate base or ion (specifically, the negatively charged ion called an anion) typically found in aqueous solution and written with the chemical formula . The neutral molecules formed by the combination of the acetate ion and a ''positive'' ion (called a cation) are also commonly called "acetates" (hence, ''acetate of lead'', ''acetate of aluminum'', etc.). The simplest of these is hydrogen acetate (called acetic acid) with corresponding salts, esters, and the polyatomic ion, polyatomic anion , or . Most of the approximately 5 billion kilograms of acetic acid produced annually in industry are used in the production of acetates, which usually take the form of polymers. In nature, acetate is the most common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using deep tank fermentation and then purified. A number of natural penicillins have been discovered, but only two purified compounds are in clinical use: penicillin G (intramuscular or intravenous use) and penicillin V (given by mouth). Penicillins were among the first medications to be effective against many bacterial infections caused by staphylococci and streptococci. They are still widely used today for different bacterial infections, though many types of bacteria have developed resistance following extensive use. 10% of the population claims penicillin allergies but because the frequency of positive skin test results decreases by 10% with each year of avoidance, 90% of these patients can tolerate penicillin. Additionally, those with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_in_2002.png)