|
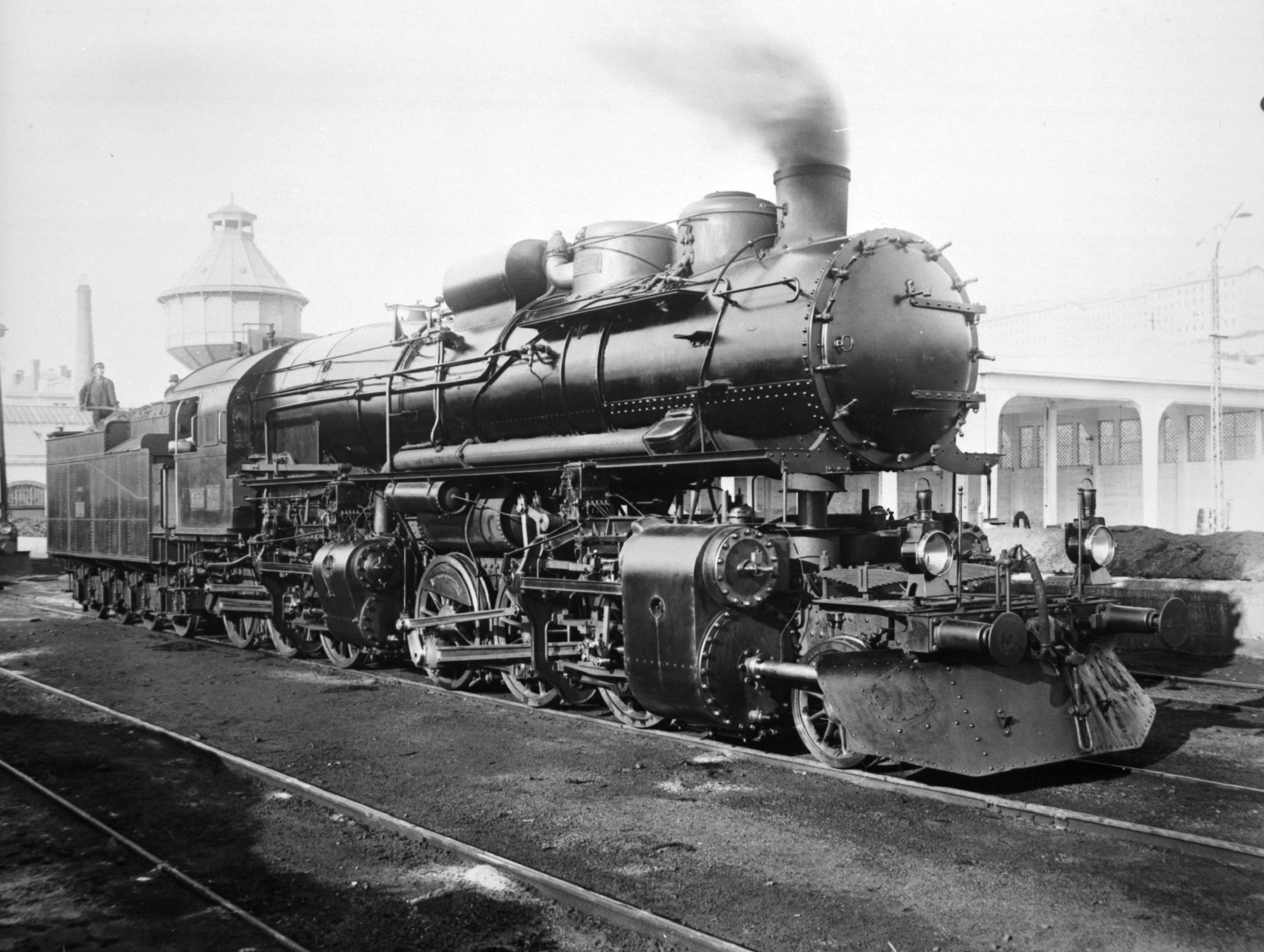
0-4-4-0
In the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotive wheel arrangement, a 0-4-4-0 is a locomotive with no leading truck, two sets of four driving wheels, and no trailing truck. Examples of this type were constructed as Shay, Heisler, Climax, Mallet, Meyer, BMAG and Double Fairlie locomotives. A similar configuration was used on some Garratts, but it is referred to as 0-4-0+0-4-0. Equivalent classifications Other equivalent classifications are: *UIC classification: BB (also known as German classification and Italian classification) *French classification: 020+020 *Turkish classification: 22+22 *Swiss classification: 2/2+2/2 The UIC classification is refined to B'B for a Mallet locomotive or B'B' for a Meyer locomotive. Fairlie examples The first Fairlie 0-4-4-0 was built for the Neath and Brecon Railway in 1866, but the design came to prominence in 1869 with ''Little Wonder'' for the Festiniog Railway in North Wales followed by five others. One locomotiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ffestiniog Railway Rolling Stock
The Ffestiniog Railway owns and operates a number of heritage and modern-day steam and diesel locomotives. A full list of these locomotives with details of their operational status is provided below. Locomotives The list includes past locomotives and present locomotives that are owned by, or permanently housed at, the Ffestiniog Railway: Steam locomotives Diesel locomotives Other rolling stock For more detailed information on current and past rolling stock, visit the Railways owHeritage Group Wikipedia These are the existing vehicles that are owned by or are permanently housed on the Ffestiniog Railway:- Four-wheel passenger coaches and vans The principal source of information for this table is the: "Rheilffordd Ffestiniog Railway Traveller's Guide" by the FR Company circa 2002, supplemented by later information as it becomes available. Bogie passenger coaches and vans The principal source of information for this table is the: "Rheilffordd Ffestiniog Railway Traveller' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mallet Locomotive
The Mallet locomotive is a type of articulated steam railway locomotive, invented by the Swiss engineer Anatole Mallet (1837–1919). The front of the locomotive articulated on a bogie. The compound steam system fed steam at boiler pressure to high-pressure cylinders driving the rear set of driving wheels (rigidly connected to the boiler). The exhaust steam from these cylinders was fed into a low-pressure receiver and was then sent to low-pressure cylinders that powered the driving wheels on the swiveling bogie towards the front of locomotive. Compounding Steam under pressure is converted into mechanical energy more efficiently if it is used in a compound engine; in such an engine steam from a boiler is used in high-pressure (HP) cylinders and then under reduced pressure in a second set of cylinders. The lower-pressure steam occupies a larger volume and the low-pressure (LP) cylinders are larger than the high-pressure cylinders. A third stage (triple expansion) may be emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairlie Locomotive
A Fairlie is a type of articulated steam locomotive that has the driving wheels on bogies. The locomotive may be double-ended (a double Fairlie) or single ended (a single Fairlie). Fairlies are most famously associated with the Ffestiniog Railway in North Wales. While the Fairlie locomotives are now used only on heritage railways, the vast majority of diesel and electric locomotives in the world today follow a form not very different from the Fairlie — two power trucks with all axles driven, and many also follow the Fairlie's double-ended concept, capable of being driven equally well in both directions. Development of the design The Scottish engineer Robert Francis Fairlie patented his design in 1864. He had become convinced that the conventional pattern of locomotive was seriously deficient; they wasted weight on unpowered wheels (the maximum tractive effort a locomotive can exert is a function of the weight on its driving wheels) and on a tender that did nothing b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whyte Notation
Whyte notation is a classification method for steam locomotives, and some internal combustion locomotives and electric locomotives, by wheel arrangement. It was devised by Frederick Methvan Whyte, and came into use in the early twentieth century following a December 1900 editorial in ''American Engineer and Railroad Journal''. The notation was adopted and remains in use in North America and the United Kingdom to describe the wheel arrangements of steam locomotives (in the latter case also for diesel and electric locomotives), but for modern locomotives, multiple units and trams it has been supplanted by the UIC system in Europe and by the AAR system (essentially a simplification of the UIC system) in North America. Structure of the system Basic form The notation in its basic form counts the number of leading wheels, then the number of driving wheels, and finally the number of trailing wheels, numbers being separated by dashes. For example, a locomotive with two lead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Fairlie
A Fairlie is a type of articulated steam locomotive that has the driving wheels on bogies. The locomotive may be double-ended (a double Fairlie) or single ended (a single Fairlie). Fairlies are most famously associated with the Ffestiniog Railway in North Wales. While the Fairlie locomotives are now used only on heritage railways, the vast majority of diesel and electric locomotives in the world today follow a form not very different from the Fairlie — two power trucks with all axles driven, and many also follow the Fairlie's double-ended concept, capable of being driven equally well in both directions. Development of the design The Scottish engineer Robert Francis Fairlie patented his design in 1864. He had become convinced that the conventional pattern of locomotive was seriously deficient; they wasted weight on unpowered wheels (the maximum tractive effort a locomotive can exert is a function of the weight on its driving wheels) and on a tender that did noth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Classification
The UIC classification of locomotive axle arrangements, sometimes known as the German classification''The Railway Data File''. Leicester: Silverdale, 2000. p. 52. . or German system,Kalla-Bishop P.M. & Greggio, Luciano, ''Steam Locomotives'', Crescent, 1985, p. 226. describes the wheel arrangement of locomotives, multiple units and trams. It is used in much of the world, notable exceptions being the United Kingdom, which uses a slightly simplified form of UIC (except for steam locomotives and small diesel shunters, where Whyte notation is used), and in North America, where the AAR wheel arrangement system (essentially another simplification of the UIC system) is used to describe diesel and electric locomotives; Whyte notation is used in North America only for steam locomotives. The classification system is managed by the International Union of Railways (UIC). Structure The UIC uses the following structure: ; Upper-case letters : Indicate driving axles, starting at A for a singl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
0-4-0+0-4-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, the is an articulated locomotive of the Garratt type. The wheel arrangement is effectively two locomotives operating back-to-back or face-to-face, with the boiler and cab suspended between the two power units. Each power unit has no leading wheels, four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles and no trailing wheels. A similar arrangement exists for Mallet and Meyer locomotives, but is referred to as . Overview The first Garratt locomotive, K1, one of two gauge Tasmanian Government Railways K class locomotives built in 1909, has this wheel arrangement and has been restored to operating condition at the Welsh Highland Railway. This arrangement proved one of the less popular Garratt types, since most Garratt locomotives were larger and more powerful, requiring more pairs of driving wheels to operate within the normal axle load limits, and because leading wheels gave more stabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meyer Locomotive
A Meyer locomotive is a type of articulated locomotive. The design was never as popular as the Garratt or Mallet locomotives. It can be best regarded as 19th Century competition for the early compound Mallet and also the Fairlie articulated designs. Most single cab modern trains are of a similar design such as power cars, freight diesel locomotives, and some passenger locomotives. Development and design The Meyer was in fact invented by Austrian engineer Wenzel Günther of the Wiener Neustädter Lokomotivfabrik for the Semmering Trials of 1851. However, the technology wasn't yet developed for the steam to be reliably transported to the bogies with reasonable amount of leaks, and despite generally good performance of the design on the trials the company abandoned the idea. It was reinvigorated by Frenchman Jean-Jacques Meyer (1804-1877), who took out a patent on the design in 1861. The first locomotive, an named ''L'Avenir'' (Future), was built by in 1868 with the support of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UIC Classification
The UIC classification of locomotive axle arrangements, sometimes known as the German classification''The Railway Data File''. Leicester: Silverdale, 2000. p. 52. . or German system,Kalla-Bishop P.M. & Greggio, Luciano, ''Steam Locomotives'', Crescent, 1985, p. 226. describes the wheel arrangement of locomotives, multiple units and trams. It is used in much of the world, notable exceptions being the United Kingdom, which uses a slightly simplified form of UIC (except for steam locomotives and small diesel shunters, where Whyte notation is used), and in North America, where the AAR wheel arrangement system (essentially another simplification of the UIC system) is used to describe diesel and electric locomotives; Whyte notation is used in North America only for steam locomotives. The classification system is managed by the International Union of Railways (UIC). Structure The UIC uses the following structure: ; Upper-case letters : Indicate driving axles, starting at A for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheel Arrangement
In rail transport, a wheel arrangement or wheel configuration is a system of classifying the way in which wheels are distributed under a locomotive. Several notations exist to describe the wheel assemblies of a locomotive by type, position, and connections, with the adopted notations varying by country. Within a given country, different notations may also be employed for different kinds of locomotives, such as steam, electric, and diesel powered. Especially in steam days, wheel arrangement was an important attribute of a locomotive because there were many different types of layout adopted, each wheel being optimised for a different use (often with only some being actually "driven"). Modern diesel and electric locomotives are much more uniform, usually with all axles driven. Major notation schemes The main notations are the Whyte notation (based on counting the wheels), the AAR wheel arrangement notation (based on counting either the axles or the bogies), and the UIC classific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climax Locomotive
A Climax locomotive is a type of geared steam locomotive built by the ''Climax Manufacturing Company'' (later renamed to the ''Climax Locomotive Works''), of Corry, Pennsylvania. These had two steam cylinders attached to a transmission located under the center of the boiler, which sent power to driveshafts running to the front and rear trucks. Some 1000-1100 were built in three classes - A, B, and C - between 1888 and 1928. Invention and production The invention of the Climax locomotive is attributed to Charles D. Scott, who ran a forest railway near Spartansburg, Pennsylvania between 1875 and 1878. A lumberjack of considerable mechanical ingenuity, Scott sought to bring an improved logging locomotive of his own design to market and brought the drawings to the nearby Climax Manufacturing Company in Corry, Pennsylvania. The first four Climax locomotives were built and delivered in 1888. The design patentGeorge D.Gilbert, Proppeling gear for tram carsU.S. Patent 393,89 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomotive's boiler to the point where it becomes gaseous and its volume increases 1,700 times. Functionally, it is a steam engine on wheels. In most locomotives, the steam is admitted alternately to each end of its cylinders, in which pistons are mechanically connected to the locomotive's main wheels. Fuel and water supplies are usually carried with the locomotive, either on the locomotive itself or in a tender coupled to it. Variations in this general design include electrically-powered boilers, turbines in place of pistons, and using steam generated externally. Steam locomotives were first developed in the United Kingdom during the early 19th century and used for railway transport until the middle of the 20th century. Richard Trevith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |