|
įø
įø (minuscule: įø) is a Latin script letter formed from '' C'' with added acute accent and cedilla. Usage It is used in the Estonian KNAB transliteration standard when representing Cyrillic letters of several Northwest Caucasian languages The Northwest Caucasian languages, also called West Caucasian, Abkhazo-Adyghean, Abkhazo-Circassian, Circassic, or sometimes Pontic languages (from Ancient Greek, ''pontos'', referring to the Black Sea, in contrast to the Northeast Caucasian .... In transliteration of Abaza, it represents the letter Š§Ó. In transliteration of Abkhaz, it represents the letter Ņ¶. In transliteration of Adyghe, it represents the digraph ŠÓ. Unicode The Unicode codepoints are for the upper-case letter, and for the lower-case one. References {{Latin script , show diacritic = cedilla , show diacritic 2 = acute Letters with cedilla Letters with acute Latin letters with diacritics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cedilla
A cedilla ( ; from Spanish language, Spanish ', "small ''ceda''", i.e. small "z"), or cedille (from French , ), is a hook or tail () added under certain letters (as a diacritic, diacritical mark) to indicate that their pronunciation is modified. In Catalan language, Catalan (where it is called ), French language, French, and Portuguese language, Portuguese (where it is called a ) it is used only under the letter (to form ), and the entire letter is called, respectively, (i.e. "broken C"), , and (or , colloquially). It is used to mark vowel nasalization in many languages of Sub-Saharan Africa, including Vute language, Vute from Cameroon. This diacritic is not to be confused with the ''ogonek'' (āĢØ), which resembles the cedilla but mirrored. It looks also very similar to the Comma#Diacritical_usage, diacritical comma, which is used in the Romanian and Latvian alphabet, and which is misnamed "cedilla" in the Unicode standard. There is substantial overlap between the cedil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Accent
The acute accent (), , is a diacritic used in many modern written languages with alphabets based on the Latin alphabet, Latin, Cyrillic script, Cyrillic, and Greek alphabet, Greek scripts. For the most commonly encountered uses of the accent in the Latin and Greek alphabets, precomposed characters are available. Uses History An early precursor of the acute accent was the Apex (diacritic), apex, used in Latin language, Latin inscriptions to mark vowel length, long vowels. The acute accent was first used in French in 1530 by Geoffroy Tory, the royal printer. Pitch Ancient Greek The acute accent was first used in the Greek diacritics, polytonic orthography of Ancient Greek, where it indicated a syllable with a high pitch accent, pitch. In Modern Greek, a stress (linguistics), stress accent has replaced the pitch accent, and the acute marks the stressed syllable of a word. The Greek name of the accented syllable was and is (''oxeĆ®a'', Modern Greek ''oxĆa'') "sharp" or "h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Script
The Latin script, also known as the Roman script, is a writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae in Magna Graecia. The Greek alphabet was altered by the Etruscan civilization, Etruscans, and subsequently their alphabet was altered by the Ancient Romans. Several Latin-script alphabets exist, which differ in graphemes, collation and phonetic values from the classical Latin alphabet. The Latin script is the basis of the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), and the 26 most widespread letters are the letters contained in the ISO basic Latin alphabet, which are the same letters as the English alphabet. Latin script is the basis for the largest number of alphabets of any writing system and is the List of writing systems by adoption, most widely adopted writing system in the world. Latin script is used as the standard method of writing the languages of Western and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeta
Zeta (, ; uppercase Ī, lowercase Ī¶; , , classical or ''zÄĢta''; ''zĆta'') is the sixth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 7. It was derived from the Phoenician alphabet, Phoenician letter zayin . Letters that arose from zeta include the Roman Z and Cyrillic Ze (Cyrillic), Š. Name Unlike the other Greek alphabet, Greek letters, this letter did not take its name from the Phoenician alphabet, Phoenician letter from which it was derived; it was given a new name on the pattern of Beta (letter), beta, eta and theta. The word ''zeta'' is the ancestor of ''zed'', the name of the Latin letter Z in Commonwealth English. Swedish language, Swedish and many Romance languages (such as Italian language, Italian and Spanish language, Spanish) do not distinguish between the Greek and Roman forms of the letter; "''zeta''" is used to refer to the Roman letter Z as well as the Greek letter. Uses Letter The letter Ī¶ represents the voiced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Letters With Cedilla
Letter, letters, or literature may refer to: Characters typeface * Letter (alphabet), a character representing one or more of the sounds used in speech or none in the case of a silent letter; any of the symbols of an alphabet * Letterform, the graphic form of a letter of the alphabet, either as written or in a particular type font * Rehearsal letter in an orchestral score Communication * Letter (message), a form of written communication ** Mail * Letters, the collected correspondence of a writer or historically significant person **Pauline epistles, addressed by St. Paul to various communities or congregations, such as "Letters to the Galatians" or "Letters to the Corinthians", and part of the canonical books of the Bible ** Maktubat (other), the Arabic word for collected letters * The letter as a form of second-person literature; see Epistle ** Epistulae (Pliny) ** Epistolary novel, a long-form fiction composed of letters (epistles) * Open letter, a public letter as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicode Codepoint
Unicode or ''The Unicode Standard'' or TUS is a character encoding standard maintained by the Unicode Consortium designed to support the use of text in all of the world's writing systems that can be digitized. Version 16.0 defines 154,998 characters and 168 scripts used in various ordinary, literary, academic, and technical contexts. Unicode has largely supplanted the previous environment of a myriad of incompatible character sets used within different locales and on different computer architectures. The entire repertoire of these sets, plus many additional characters, were merged into the single Unicode set. Unicode is used to encode the vast majority of text on the Internet, including most web pages, and relevant Unicode support has become a common consideration in contemporary software development. Unicode is ultimately capable of encoding more than 1.1 million characters. The Unicode character repertoire is synchronized with ISO/IEC 10646, each being code-for-code identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
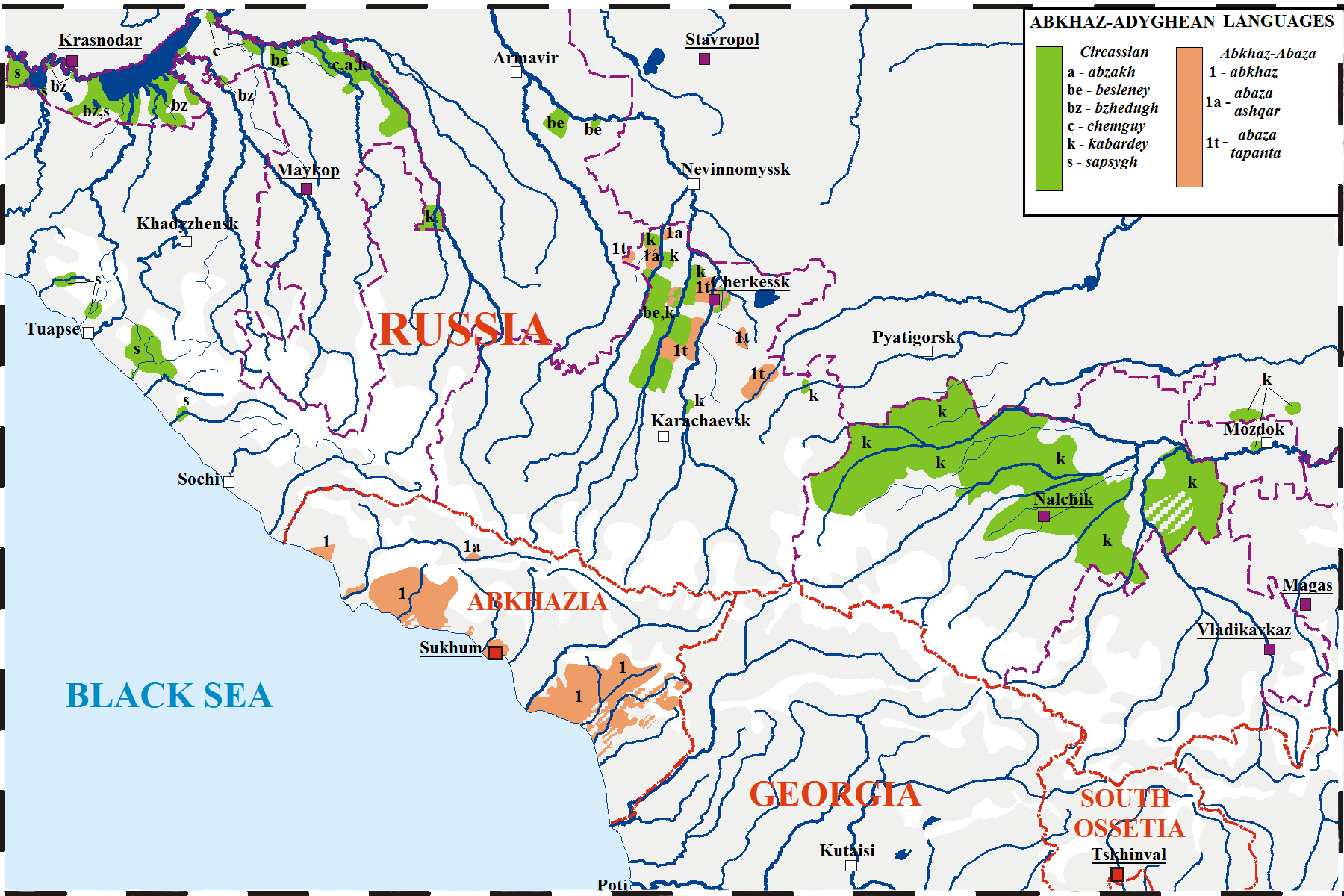
Northwest Caucasian Languages
The Northwest Caucasian languages, also called West Caucasian, Abkhazo-Adyghean, Abkhazo-Circassian, Circassic, or sometimes Pontic languages (from Ancient Greek, ''pontos'', referring to the Black Sea, in contrast to the Northeast Caucasian languages as the ''Caspian languages''), is a family of languages spoken in the northwestern Caucasus region,Hoiberg, Dale H. (2010) chiefly in three Russian republics ( Adygea, Kabardino-Balkaria, KarachayāCherkessia), the disputed territory of Abkhazia, Georgia, and Turkey, with smaller communities scattered throughout the Middle East. The group's relationship to any other language family is uncertain and unproven. One language, Ubykh, became extinct in 1992, while all of the other languages are in some form of endangerment, with UNESCO classifying all as either "vulnerable", "endangered", or "severely endangered". The Northwest Caucasian languages possess highly complex sets of consonant distinctions paired with a lack of vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visigothic Script
Visigothic script was a type of medieval script that originated in the Visigothic Kingdom in Hispania (the Iberian Peninsula). Its more limiting alternative designations and associate it with scriptoria specifically in Toledo and with Mozarabic culture more generally, respectively. The script, which exists in book-hand and cursive versions, was used from approximately the late seventh century until the thirteenth century, mostly in Visigothic Iberia but also somewhat in the Catalan kingdom in current southern France. It was perfected in the 9thā11th centuries and declined afterwards. It developed from uncial script, and shares many features of uncial, especially an uncial form of the letter . Other features of the script include an open-top (very similar to the letter ), similar shapes for the letters and , and a long letter resembling the modern letter . There are two forms of the letter , one with a straight vertical ascender and another with an ascender sla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
š
The Old Italic scripts are a family of ancient writing systems used in the Italian Peninsula between about 700 and 100 BC, for various languages spoken in that time and place. The most notable member is the Etruscan alphabet, which was the immediate ancestor of the Latin alphabet used by more than 100 languages today, including English. The runic alphabets used in Northern Europe are believed to have been separately derived from one of these alphabets by the 2nd century AD. Origins The Old Italic alphabets ultimately derive from the Phoenician alphabet, but the general consensus is that the Etruscan alphabet was imported from the Euboean Greek colonies of Cumae and Ischia (PithekoÅ«sai) situated in the Gulf of Naples in the 8th century BC; this Euboean alphabet is also called 'Cumaean' (after Cumae), or 'Chalcidian' (after its metropolis Chalcis). The Cumaean hypothesis is supported by the 1957ā58 excavations of Veii by the British School at Rome, which found pieces of Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abkhaz Language
Abkhaz, also known as Abkhazian, is a Northwest Caucasian languages, Northwest Caucasian language most closely related to Abaza language, Abaza. It is spoken mostly by the Abkhazians, Abkhaz people. It is one of the official languages of Abkhazia, where around 190,000 people speak it. Furthermore, it is spoken by thousands of members of the Abkhazian diaspora in Turkey, Georgia (country), Georgia's autonomous republic of Adjara, Syria, Jordan, and several Western countries. 27 October is the day of the Abkhazian language in Georgia (country), Georgia. Classification Abkhaz is a Northwest Caucasian languages, Northwest Caucasian language and is thus related to Adyghe language, Adyghe. The language of Abkhaz is especially close to Abaza language, Abaza, and they are sometimes considered dialects of the same language,''B. G. Hewitt Abkhaz 1979;'' page 1. Abazgi, of which the literary dialects of Abkhaz and Abaza are simply two ends of a dialect continuum. Grammatically, the two ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |