|
é tiavnickûˋ Bane
é tiavnickûˋ Bane is a village in the BanskûÀ é tiavnica District, in the BanskûÀ Bystrica Region of Slovakia. Name First, in 1352 it was recorded as ''Sygluspergh'', then in 1388 as ''Pergh'', in 1457 as ''Sigelsperg'', in 1559 as ''Pergh'', later as ''Szûˋlakna'', ''Windschacht'' and then until 1891 as ''Pjerg'', after ''HegybûÀnya''. Slovaks used ''Piarg'' until 1948, after ''é tiavnickûˋ Bane''. Recently, Germans use the form ''Siegelsberg'', while Hungarians use ''HegybûÀnya''. Famous people é tiavnickûˋ Bane was the birthplace of the 18th century astronomer Maximilian Hell and the controversial World War II politician Vojtech Tuka Vojtech LûÀzar "Bûˋla" Tuka (4 July 1880 ã 20 August 1946) was a Slovak politician who served as prime minister and minister of Foreign Affairs of the First Slovak Republic between 1939 and 1945. Tuka was one of the main forces behind the depor .... References External links *http://www.obecstiavnickebane.sk Villages and municipali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 UN member states, 2 UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a special political status (2 states, both in free association with New Zealand). Compiling a list such as this can be a complicated and controversial process, as there is no definition that is binding on all the members of the community of nations concerni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church In Slovakia
The Catholic Church in Slovakia is part of the worldwide Catholic Church, under the spiritual leadership of the Pope in Rome. Around 55.8% of the total population is Latin (Roman) Catholic and another 3.8% is Greek Catholic. The country is divided into 8 Latin dioceses including 3 archdioceses, and there is also a separate Metropolitan jurisdiction for those of the Byzantine Rite, see Slovak Greek Catholic Church. Taking the percentage of membership in the Catholic Church as an indicator, Slovakia is the third most Catholic Slavic country, after Poland and Croatia. Structure Roman Catholic *Archdiocese of Bratislava with the following suffragans: **Archdiocese of Trnava **Diocese of Nitra **Diocese of é§ilina **Diocese of BanskûÀ Bystrica *Archdiocese of KoéÀice with the following suffragans: **Diocese of SpiéÀ **Diocese of Roéƒéava *Military Ordinariate of Slovakia Greek Catholic * Archeparchy of PreéÀov with the following suffragans: **Eparchy of Bratislava **Eparchy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countriesãincluding all of the great powersãforming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximilian Hell
Maximilian Hell ( hu, Hell Miksa) (born Rudolf Maximilian HûÑll; May 15, 1720 ã April 14, 1792) was an astronomer and an ordained Jesuit priest from the Kingdom of Hungary. Biography Born as Rudolf Maximilian HûÑll in SelmecbûÀnya, Hont County, Kingdom of Hungary (present-day BanskûÀ é tiavnica, Slovakia), but later changed his surname to ''Hell''. He was the third son from the second marriage of his father Matthias Cornelius Hell (MatthûÊus Kornelius Hell) and his mother Julianna Staindl. The couple had a total of 22 children. Registry entries indicate that the family was of German descent, while Maximilian Hell later in life (ca. 1750) is known to declare himself as Hungarian. The place of birth of Maximilian's father is unknown; the settlements KûÑrmûÑcbûÀnya (today Kremnica), Schlagenwald, (today HornûÙ Slavkov) or Schlackenwerth (today Ostrov nad OhéûÙ) are most frequently given. Born in a mixed German, Hungarian and Slovak town, he presumably knew Slovak to a cert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, SlovenskûÀ republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the southwest, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's mostly mountainous territory spans about , with a population of over 5.4 million. The capital and largest city is Bratislava, while the second largest city is KoéÀice. The Slavs arrived in the territory of present-day Slovakia in the fifth and sixth centuries. In the seventh century, they played a significant role in the creation of Samo's Empire. In the ninth century, they established the Principality of Nitra, which was later conquered by the Principality of Moravia to establish Great Moravia. In the 10th century, after the dissolution of Great Moravia, the territory was integrated into the Principality of Hungary, which then became the Kingdom of Hungary in 1000. In 1241 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Village
A village is a clustered human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town (although the word is often used to describe both hamlets and smaller towns), with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Though villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban village is also applied to certain urban neighborhoods. Villages are normally permanent, with fixed dwellings; however, transient villages can occur. Further, the dwellings of a village are fairly close to one another, not scattered broadly over the landscape, as a dispersed settlement. In the past, villages were a usual form of community for societies that practice subsistence agriculture, and also for some non-agricultural societies. In Great Britain, a hamlet earned the right to be called a village when it built a church. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-religious
Irreligion or nonreligion is the absence or rejection of religion, or indifference to it. Irreligion takes many forms, ranging from the casual and unaware to full-fledged philosophies such as atheism and agnosticism, secular humanism and antitheism. Social scientists tend to define irreligion as a purely naturalist worldview that excludes a belief in anything supernatural. The broadest and loosest definition, serving as an upper limit, is the lack of religious identification, though many non-identifiers express metaphysical and even religious beliefs. The narrowest and strictest is subscribing to positive atheism. According to the Pew Research Center's 2012 global study of 230 countries and territories, 16% of the world's population does not identify with any religion. The population of the religiously unaffiliated, sometimes referred to as "nones", has grown significantly in recent years. Measurement of irreligiosity requires great cultural sensitivity, especially outside th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jehovah's Witnesses
Jehovah's Witnesses is a millenarian restorationist Christian denomination with nontrinitarian beliefs distinct from mainstream Christianity. The group reports a worldwide membership of approximately 8.7 million adherents involved in evangelism and an annual Memorial attendance of over 21 million. Jehovah's Witnesses are directed by the Governing Body of Jehovah's Witnesses, a group of elders in Warwick, New York, United States, which establishes all doctrines based on its interpretations of the Bible. They believe that the destruction of the present world system at Armageddon is imminent, and that the establishment of God's kingdom over the earth is the only solution for all problems faced by humanity. The group emerged from the Bible Student movement founded in the late 1870s by Charles Taze Russell, who also co-founded Zion's Watch Tower Tract Society in 1881 to organize and print the movement's publications. A leadership dispute after Russell's death resul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evangelical Church Of The Augsburg Confession In Slovakia
The Evangelical Church of the Augsburg Confession in Slovakia (in Slovak ''EvanjelickûÀ cirkev augsburskûˋho vyznania na Slovensku'', ECAV) is the only Lutheran church in Slovakia. The Church is a member of the Ecumenical Council of Churches in Slovakia, and the Lutheran World Federation (Central Eastern Europe Region). History of the church The church was established in 1922 following the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian empire. The church opposed the Nazis in World War II. After the Communist coup d'ûˋtat of 1948, the Lutheran Church lost control over its schools and social services, and many church periodicals ceased to be published. More than one hundred clergy were persecuted; many were imprisoned and restrained from exercising their ministry. Until 1989 the Church lived under the strict control of the regime and in 1993 the Synod adopted a new constitution. Number of adherents and beliefs The ECAV is the second largest church in Slovakia (c. 7% of population). It cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
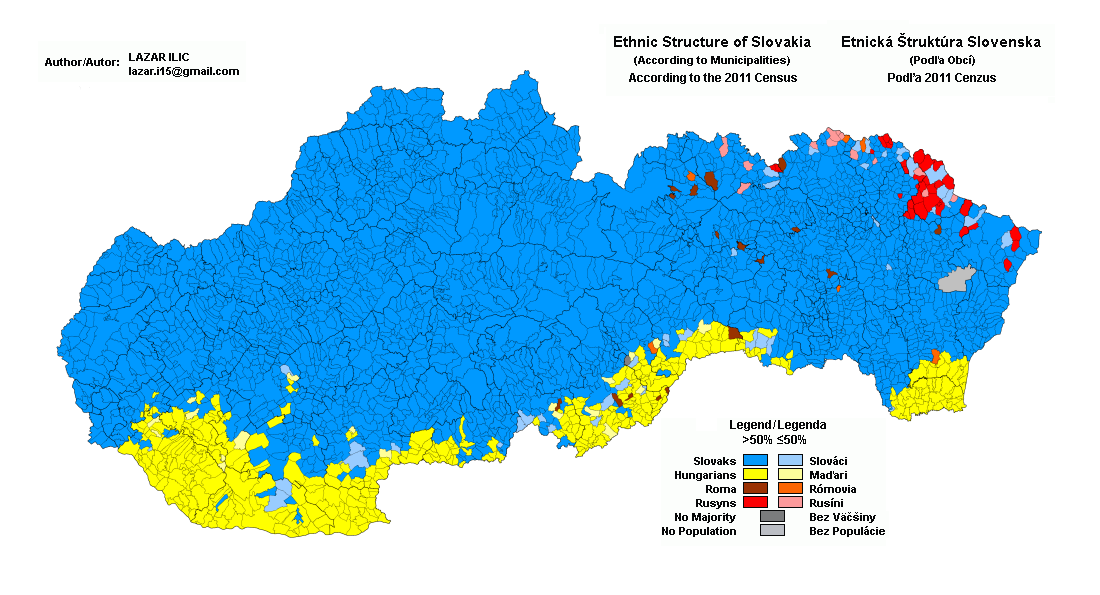
Hungarians In Slovakia
Hungarians are the largest ethnic minority in Slovakia. According to th2021 Slovak census 422,065 people (or 7.75% of the population) declared themselves Hungarians, while 462,175 (8.48% of the population) stated that Hungarian was their mother tongue. Hungarians in Slovakia are concentrated mostly in the southern part of the country, near the border with Hungary. They form the majority in two districts, KomûÀrno and DunajskûÀ Streda. History The First Czechoslovak Republic (1918ã1938) Origins of the Hungarian minority After the defeat of the Central Powers on the Western Front in 1918, the Treaty of Trianon was signed between the winning Entente powers and Hungary in 1920 at the Paris Peace Conference. The treaty greatly reduced the Kingdom of Hungary's borders, including ceding all of Upper Hungary to Czechoslovakia, in which Slovaks made up the dominant ethnicity. In consideration of the strategic and economic interests of their new ally, Czechoslovakia, the victor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Slovakia
Since 1949 (except 1990ã1996), Slovakia has been divided into a number of ''kraje'' (singular ''kraj''; usually translated as "Regions" with capital R). Their number, borders and functions have been changed several times. There are eight regions of Slovakia and they correspond to the EU's NUTS 3 level of local administrative units. Each kraj consists of '' okresy'' (counties or districts). There are 79 districts. List After a period without kraje and without any equivalent (1990ã1996), the kraje were reintroduced in 1996. As for administrative division, Slovakia has been subdivided into 8 ''kraje'' since 24 July 1996: Since 2002, Slovakia is divided into 8 ''samosprûÀvne kraje'' (self-governing regions), which are called by the Constitution ''vyéÀéÀie û¤zemnûˋ celky'' (Higher Territorial Units), abbr. VûC. The territory and borders of the self-governing regions are identical with the territory and borders of the ''kraje''. Therefore, the word "kraj" can be replaced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czech Diaspora
The Czech diaspora refers to both historical and present emigration from the Czech Republic, as well as from the former Czechoslovakia and the Czech lands (including Bohemia, Moravia and Silesia). The country with the largest number of Czechs living abroad is the United States. Communities * Austria (Vienna) * Czechs and Slovaks in Bulgaria * Czechs of Croatia * Czechs in Poland * Czechs in Romania * Czechs in Serbia * Czech New Zealanders * Czech South Africans * Czechs in Ukraine * Czech migration to France * Czech migration to the United Kingdom * Czech diaspora in Israel * Czech Americans (Baltimore, Omaha, Texas) * Czech Canadians * Czech immigration to Mexico * Czechs in Argentina * Czech Brazilian * Czech Australians Distrubution by country Here is the top 10 countries with most Czech immigrants. : 503,000 : 89,000 : 82,000 : 65,000 : 36,000 : 21,000 : 16,000 : 14,000 : 11,000 : 11,000 Famous people of Czech descent * Madeleine Albright, the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)