|
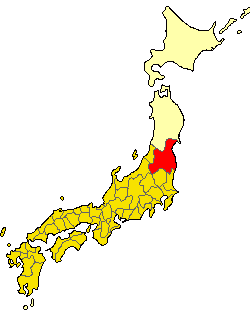
┼īsato, Miyagi
is a town located in Miyagi Prefecture, Japan. , the town had an estimated population of 7,972, and a population density of 97 persons per km┬▓ in 2813 households. The total area of the town is . Geography ┼īsato is located in central Miyagi Prefecture. The Yoshida River runs east to west through the center of the town, and the fields spread along the river. Hills extend from north to south. Neighboring municipalities Miyagi Prefecture * ┼īsaki *Taiwa * ┼īhira * Matsushima *Rifu Climate The town has a climate characterized by cool summers and long cold winters (K├Čppen climate classification ''Cfa''). The average annual temperature in ┼īsato is 11.9 ┬░C. The average annual rainfall is 1225 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 24.6 ┬░C, and lowest in January, at around 0.4 ┬░C. Demographics Per Japanese census data, the population of ┼īsato has declined rapidly over the past 30 years. Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Towns Of Japan
A town (ńö║; ''ch┼Ź'' or ''machi'') is a local administrative unit in Japan. It is a local public body along with prefecture (''ken'' or other equivalents), city (''shi''), and village (''mura''). Geographically, a town is contained within a district. Note that the same word (ńö║; ''machi'' or ''ch┼Ź'') is also used in names of smaller regions, usually a part of a ward in a city. This is a legacy of when smaller towns were formed on the outskirts of a city, only to eventually merge into it. Towns See also * Municipalities of Japan * Japanese addressing system The Japanese addressing system is used to identify a specific location in Japan. When written in Japanese characters, addresses start with the largest geographical entity and proceed to the most specific one. When written in Latin characters, ad ... References {{reflist External links "Large_City_System_of_Japan";_graphic_shows_towns_compared_with_other_Japanese_city_types_at_p._1_[PDF_7_of_40/nowiki>">DF_7_of_4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
┼īsaki, Miyagi
┼īsaki City Hall is a city located in Miyagi Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 128,763 in 51,567 households, and a population density of 160 persons per km┬▓. The total area of the city is . ┼īsaki is a member of the World Health OrganizationŌĆÖs Alliance for Healthy Cities (AFHC). Geography ┼īsaki is in north-central Miyagi Prefecture in the northern Sendai Plain. The Furukawa area in the center of the city is a base for commercial and service industries in the northern portion of Miyagi Prefecture, and the Naruko area in the northwestern of the city is noted for hot spring tourism . The Kashimadai and Matsuyama districts in the southeastern part of the city are within the commuting zone of Sendai. Climate ┼īsaki has a humid subtropical climate (K├Čppen climate classification ''Cfa'') characterized by hot summers and mild winters. The average annual temperature in ┼īsaki is 11.5 ┬░C. The average annual rainfall is 1249 mm with September ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Fujiwara
The Northern Fujiwara (ÕźźÕĘ×ĶŚżÕĤµ░Å ''┼īsh┼½ Fujiwara-shi'') were a Japanese noble family that ruled the T┼Źhoku region (the northeast of Honsh┼½) of Japan during the 12th century as their own realm.Esashi Fujiwara no Sato (in English) The ┼īsh┼½ Fujiwara were one of the four great clans during the ŌĆö the other three were the , the , and the |
Heian Period
The is the last division of classical Japanese history, running from 794 to 1185. It followed the Nara period, beginning when the 50th emperor, Emperor Kanmu, moved the capital of Japan to Heian-ky┼Ź (modern Kyoto). means "peace" in Japanese. It is a period in Japanese history when the Chinese influences were in decline and the national culture matured. The Heian period is also considered the peak of the Japanese imperial court and noted for its art, especially poetry and literature. Two types of Japanese script emerged, including katakana, a phonetic script which was abbreviated into hiragana, a cursive alphabet with a unique writing method distinctive to Japan. This gave rise to Japan's famous vernacular literature, with many of its texts written by court women who were not as educated in Chinese compared to their male counterparts. Although the Imperial House of Japan had power on the surface, the real power was in the hands of the Fujiwara clan, a powerful aristocratic f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kofun Period
The is an era in the history of Japan from about 300 to 538 AD (the date of the introduction of Buddhism), following the Yayoi period. The Kofun and the subsequent Asuka periods are sometimes collectively called the Yamato period. This period is the earliest era of recorded history in Japan, but studies depend heavily on archaeology since the chronology of historical sources tends to be distorted. The word '' kofun'' is Japanese for the type of burial mound dating from this era. It was a period of cultural import. Continuing from the Yayoi period, the Kofun period is characterized by influence from China and the Korean Peninsula; archaeologists consider it a shared culture across the southern Korean Peninsula, Kyūshū and Honshū. On the other hand, the most prosperous keyhole-shaped burial mounds in Japan during this period were approximately 5,000 in Japan from the middle of the 3rd century in the Yayoi period to the 7th century in the Asuka period, and many of them had huge t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kofun
are megalithic tombs or tumuli in Northeast Asia. ''Kofun'' were mainly constructed in the Japanese archipelago between the middle of the 3rd century to the early 7th century CE.Õ▓Īńö░ĶŻĢõ╣ŗŃĆīÕēŹµ¢╣ÕŠīÕååÕó│ŃĆŹŃĆĵŚźµ£¼ÕÅżõ╗ŻÕÅ▓Õż¦ĶŠ×ÕģĖŃĆÅÕż¦ÕÆīµøĖµł┐ŃĆü2006Õ╣┤ŃĆé The term is the origin of the name of the Kofun period, which indicates the middle 3rd century to earlyŌĆōmiddle 6th century. Many ''kofun'' have distinctive keyhole-shaped mounds (). The Mozu- Furuichi kofungun or tumulus clusters were inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 2019, while Ishibutai Kofun is one of a number in Asuka-Fujiwara residing on the Tentative List. Overview The ''kofun tumuli'' have assumed various shapes throughout history. The most common type of ''kofun'' is known as a , which is shaped like a keyhole, having one square end and one circular end, when viewed from above. There are also circular-type (), "two conjoined rectangles" typed (), and square-type () kofun. Orientation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
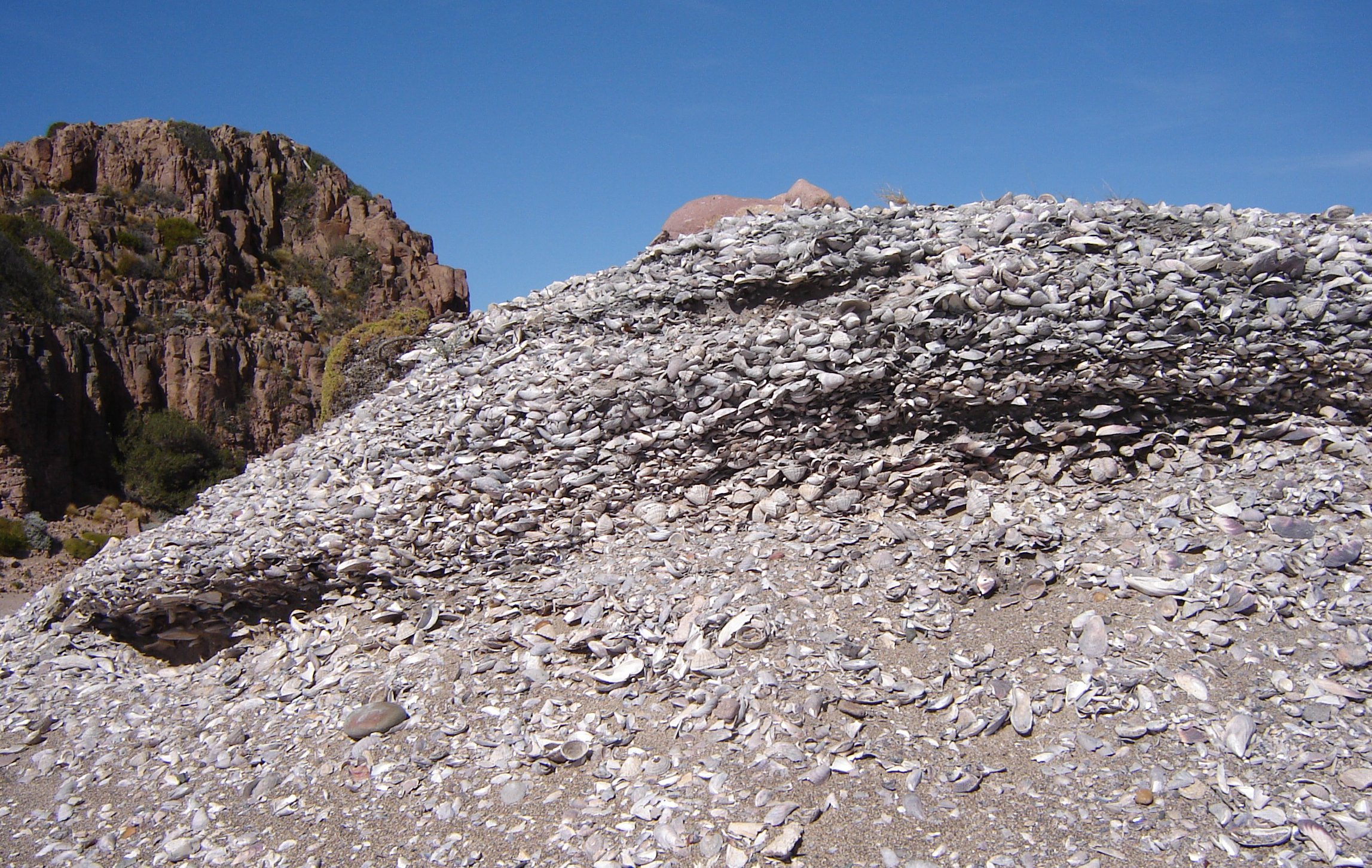
Midden
A midden (also kitchen midden or shell heap) is an old dump for domestic waste which may consist of animal bone, human excrement, botanical material, mollusc shells, potsherds, lithics (especially debitage), and other artifacts and ecofacts associated with past human occupation. These features provide a useful resource for archaeologists who wish to study the diets and habits of past societies. Middens with damp, anaerobic conditions can even preserve organic remains in deposits as the debris of daily life are tossed on the pile. Each individual toss will contribute a different mix of materials depending upon the activity associated with that particular toss. During the course of deposition sedimentary material is deposited as well. Different mechanisms, from wind and water to animal digs, create a matrix which can also be analysed to provide seasonal and climatic information. In some middens individual dumps of material can be discerned and analysed. Shells A shell mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emishi
The (also called Ebisu and Ezo), written with Chinese characters that literally mean "shrimp barbarians," constituted an ancient ethnic group of people who lived in parts of Honsh┼½, especially in the T┼Źhoku region, referred to as in contemporary sources. The first mention of the Emishi in literature that can be corroborated with outside sources dates to the 5th century AD, in which they are referred to as (µ»øõ║║ - "hairy people") in Chinese records. Some Emishi tribes resisted the rule of various Japanese Emperors during the Asuka, Nara and early Heian periods (7thŌĆō10th centuries AD). The origin of the Emishi is disputed. They are often thought to have descended from some tribes of the J┼Źmon people. Some historians believe that they were related to the Ainu people, but others disagree with this theory and see them as a completely distinct ethnicity.Aston, W.G., trans. Nihongi: Chronicles of Japan from the Earliest Times to AD 697. Tokyo: Charles E.Tuttle Co., 1972 (r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J┼Źmon Period
The is the time in Japanese history, traditionally dated between 6,000ŌĆō300 BCE, during which Japan was inhabited by a diverse hunter-gatherer and early agriculturalist population united through a common J┼Źmon culture, which reached a considerable degree of sedentism and cultural complexity. The name "cord-marked" was first applied by the American zoologist and orientalist Edward S. Morse, who discovered sherds of pottery in 1877 and subsequently translated it into Japanese as ''J┼Źmon''.Mason, 14 The pottery style characteristic of the first phases of J┼Źmon culture was decorated by impressing cords into the surface of wet clay and is generally accepted to be among the oldest in the world. The J┼Źmon period was rich in tools and jewelry made from bone, stone, shell and antler; pottery figurines and vessels; and lacquerware.Imamura, K. (1996) ''Prehistoric Japan: New Perspectives on Insular East Asia''. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press It is often compared to pre-C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutsu Province
was an old province of Japan in the area of Fukushima, Miyagi, Iwate and Aomori Prefectures and the municipalities of Kazuno and Kosaka in Akita Prefecture. Mutsu Province is also known as or . The term is often used to refer to the combined area of Mutsu and the neighboring province Dewa, which together make up the entire T┼Źhoku region. History Invasion by the Kinai government Mutsu, on northern Honsh┼½, was one of the last provinces to be formed as land was taken from the indigenous Emishi, and became the largest as it expanded northward. The ancient regional capital of the Kinai government was Tagaj┼Ź in present-day Miyagi Prefecture. * 709 ('' Wad┼Ź 2, 3rd month''), an uprising against governmental authority took place in Mutsu and in nearby Echigo Province. Troops were dispatched to subdue the revolt. * 712 (''Wad┼Ź 5''), Mutsu was separated from Dewa Province. Empress Genmei's ''Daij┼Ź-kan'' made cadastral changes in the provincial map of the Nara period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
K├Čppen Climate Classification
The K├Čppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir K├Čppen (1846ŌĆō1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by K├Čppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894ŌĆō1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the K├ČppenŌĆōGeiger climate classification system. The K├Čppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rifu, Miyagi
is a town located in Miyagi Prefecture, Japan. , the town had an estimated population of 36,014, and a population density of 800 persons per km2 in 13,568 households. The total area of the town is . Rifu is known for its nashi pears. Recently, wine and candy made from nashi pears have been developed in the town. Geography Rifu is located in east-central Miyagi Prefecture, bordered by Sendai metropolis to the south and by Matsushima Bay to the east. Neighboring municipalities Miyagi Prefecture *Sendai *Tagaj┼Ź *Shiogama * Tomiya * ┼īsato *Taiwa * Matsushima Climate Rifu has a humid climate (K├Čppen climate classification ''Cfa'') characterized by mild summers and cold winters. The average annual temperature in Rifu is 11.9 ┬░C. The average annual rainfall is 1237 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 24.4 ┬░C, and lowest in January, at around 0.6 ┬░C. Demographics Per Japanese census data, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |