|
Åsaka
is a designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the third-most populous city in Japan, following the special wards of Tokyo and Yokohama. With a population of 2.7 million in the 2020 census, it is also the largest component of the Keihanshin Metropolitan Area, which is the second-largest metropolitan area in Japan and the 10th- largest urban area in the world with more than 19 million inhabitants. Åsaka was traditionally considered Japan's economic hub. By the Kofun period (300â538) it had developed into an important regional port, and in the 7th and 8th centuries, it served briefly as the imperial capital. Osaka continued to flourish during the Edo period (1603â1867) and became known as a center of Japanese culture. Following the Meiji Restoration, Osaka greatly expanded in size and underwent rapid industrialization. In 1889, Osaka was officially established as a municipality. The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osaka Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located in the Kansai region of Honshu. Osaka Prefecture has a population of 8,778,035 () and has a geographic area of . Osaka Prefecture borders HyÅgo Prefecture to the northwest, Kyoto Prefecture to the north, Nara Prefecture to the southeast, and Wakayama Prefecture to the south. Osaka is the capital and largest city of Osaka Prefecture, and the third-largest city in Japan, with other major cities including Sakai, HigashiÅsaka, and Hirakata. Osaka Prefecture is located on the western coast of the Kii Peninsula, forming the western is open to Osaka Bay. Osaka Prefecture is the third-most-populous prefecture, but by geographic area the second-smallest; at it is the second-most densely populated, below only Tokyo. Osaka Prefecture is one of Japan's two " urban prefectures" using the designation ''fu'' (åº) rather than the standard '' ken'' for prefectures, along with Kyoto Prefecture. Osaka Prefecture forms the center of the Keihanshin metro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keihanshin
is a metropolitan region in the Kansai region of Japan encompassing the metropolitan areas of the cities of Kyoto in Kyoto Prefecture, Osaka in Osaka Prefecture and Kobe in HyÅgo Prefecture. The entire region has a population () of 19,302,746 over an area of .Japan Statistics Bureau - "2015 Census", retrieved June 27, 2021 It is the second-most-populated largest Japanese metropolitan areas, urban region in Japan (after the Greater Tokyo Area), containing approximately 15% of Japan's population. The Gross domestic product, GDP in OsakaâKobe is $681 billion as measured by PPP , making it one of the world's most productive regions, a match with Paris and London. MasterCard, MasterCard Worldwide reported that Osaka is the 19th ranking city of the world's leading global cities and has an instru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities In Japan
This is a list of Cities of Japan, cities in Japan sorted by Prefectures of Japan, prefecture and within prefecture by founding date. The list is also sortable by population, area, density and foundation date. Most large Cities of Japan, cities in Japan are Cities designated by government ordinance of Japan, cities designated by government ordinance. Some regionally important cities are designated as core cities of Japan, core cities. Tokyo is ''not'' included on this list, as the Tokyo City, City of Tokyo ceased to exist on July 1, 1943. Tokyo now exists as a special metropolis prefecture (é½ ''to''), with Special wards of Tokyo, 23 special wards (with the same status of city) making up the former boundaries of the former city in the eastern half of the prefecture. Cities Dissolved cities Source data * The area figures are according tGeographical Survey Institute of Japanas of 2007-10-01. * The source websites of each prefectures' populations are according to :ja:Temp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prefectures Of Japan
Japan is divided into 47 prefectures (, , ), which rank immediately below the national government and form the country's first level of jurisdiction and Administrative divisions of Japan, administrative division. They include 43 prefectures proper (, ''Prefectures of Japan#Ken, ken''), two Fu (administrative division), urban prefectures (, ''Prefectures of Japan#Fu, fu'': Osaka Prefecture, Osaka and Kyoto Prefecture, Kyoto), one regional prefecture (, ''Prefectures of Japan#DÅ, dÅ'': Hokkaido, HokkaidÅ) and one metropolis (, ''Prefectures of Japan#To, to'': Tokyo). In 1868, the Meiji Restoration, Meiji ''Fuhanken sanchisei'' administration created the first prefectures (urban ''fu'' and rural ''ken'') to replace the urban and rural administrators (''bugyÅ'', ''daikan'', etc.) in the TenryÅ, parts of the country previously controlled directly by the shogunate and a few territories of rebels/shogunate loyalists who had not submitted to the new government such as Aizu domain, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
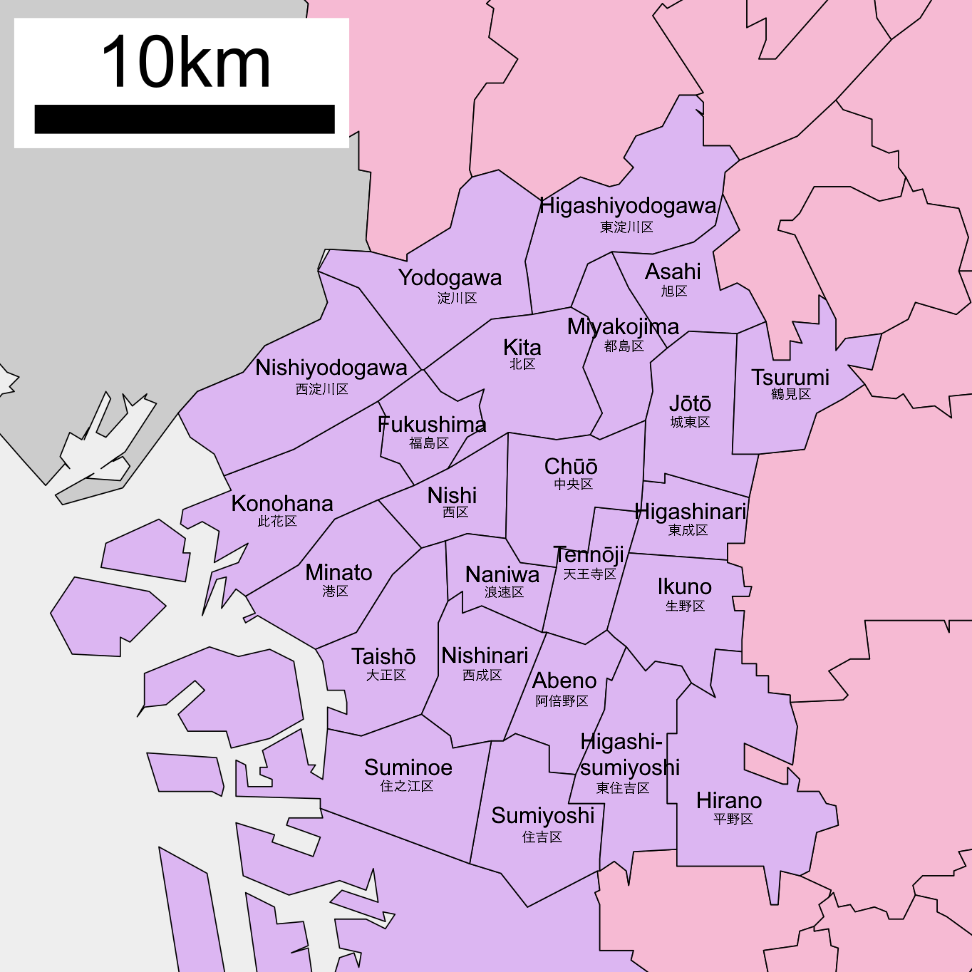
Politics Of Osaka City
Politics of Osaka City, as in all municipalities of Japan, takes place in the framework of local autonomy that is guaranteed by chapter 8 of the Constitution and laid out in the Local Autonomy Law. As one of Japan's 20 major cities designated by government ordinance (''seirei shitei toshi''), Osaka City has some administrative responsibilities that are handled by the prefectures in ordinary municipalities and is subdivided into wards. The administration is headed by a mayor directly elected by the people every four years in first-past-the-post elections. Enacting and amending city ordinances, passing the budget and approving important administrative appointments, including the vice-mayors and the treasurer, are handled by the city assembly that is directly elected by the people every four years by single-non transferable vote. As in all prefectures and municipalities, citizens may initiate ''chokusetsu seikyū'' ("direct demands"), i.e. mayor and assembly are subject to recall ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osaka City Council
The is the legislature of Osaka City. It is responsible for the "enactment, amendment and repeal of ordinances, budgetary decisions, approval of account settlements, matters of financial importances including acquisition and disposal of city assets, and others." The assembly has a regular membership 81 members, with 41 needed to form a majority. Overview *Members: 81 *Term: 4 years *Voting System: Mediumâsize constituency system (Single non-transferable vote) *President: Kazutaka Ohashiï¼Osaka Restoration Associationï¼ *Vice-President: Teruaki Nishizaki ï¼Komeitoï¼ The municipal government consists of 24 electoral districts, representing the 24 administrative wards of the city. The number of members elected from each district is proportional to the ward's population. Members are elected to four-year terms with no term limits. Japanese citizens of voting age who have been living in Osaka city continuously for three months have the right to vote in municipal governme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
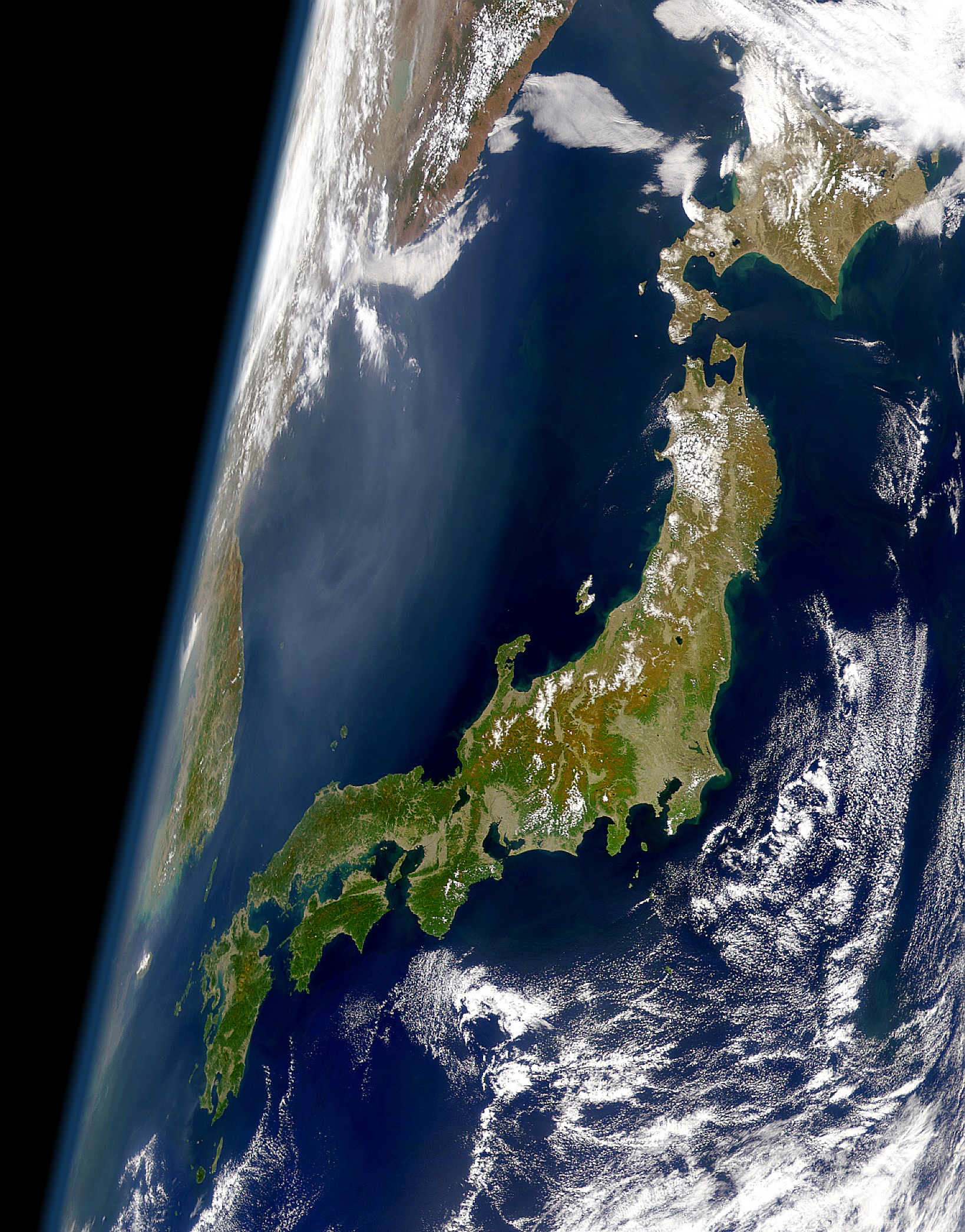
Honshu
, historically known as , is the largest of the four main islands of Japan. It lies between the Pacific Ocean (east) and the Sea of Japan (west). It is the list of islands by area, seventh-largest island in the world, and the list of islands by population, second-most populous after the list of islands of Indonesia, Indonesian island of Java. Honshu had a population of 104 million , constituting 81.3% of the entire population of Japan, and mostly concentrated in the coastal areas and plains. Approximately 30% of the total population resides in the Greater Tokyo Area on the KantÅ Plain. As the historical center of Japanese cultural and political power, the island includes several past Japanese capitals, including Kyoto, KyÅto, Nara (city), Nara, and Kamakura. Much of the island's southern shore forms part of the TaiheiyÅ Belt, a megalopolis that spans several of the Japanese islands. Honshu also contains Japan's highest mountain, Mount Fuji, and its largest lake, Lake Biwa. Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ShitennÅ-ji
ShitennÅ-ji (, ''Temple of the Four Heavenly Kings'') is a Buddhist temple in Åsaka, Japan. It is also known as Arahaka-ji, Nanba-ji, or Mitsu-ji. The temple is sometimes regarded as the first Buddhist and oldest officially administered temple in Japan, although the temple complex and buildings have been rebuilt over the centuries, with the last reconstruction taking place in 1963. Shortly after World War II, ShitennÅ-ji became independent of the parent Tendai sect and formed the Wa sect (''wa-shÅ«'', ) of Buddhism. History Prince ShÅtoku was known for his profound Buddhist faith when Buddhism was not widespread in Japan during the 6th century. In order to popularize Buddhism, Prince ShÅtoku led a massive national project to promote Buddhism and he commissioned the construction of ShitennÅ-ji. Prince ShÅtoku invited three Korean carpenters from Baekje. They brought knowledge and led the construction of ShitennÅ-ji. The commission of ShitennÅ-ji was part of a massive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osaka Castle
is a Japanese castle in ChÅ«Å-ku, Osaka, ChÅ«Å-ku, Osaka, Japan. The castle is one of Japan's most famous landmarks and played a major role in the unification of Japan during the sixteenth century of the AzuchiâMomoyama period. Layout The inner keep of Osaka Castle is situated on a plot of land roughly one square kilometre. It is built on two raised platforms of landfill supported by sheer walls of cut rock, using a technique called burdock piling, each overlooking a moat. The keep is five stories on the outside and eight stories on the inside and built atop a tall stone foundation to protect its occupants from attackers. The main keep is surrounded by a series of moats and defensive fortifications. The castle has two moats (an inner and an outer one). The inner castle moat lies within the castle grounds and consists of two types: wet (northern-easterly) and dry (south-westerly). The outer moat meanwhile surrounds the entire castle premise, denotes the castle's outer limi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Regions Of Japan
Japan is often divided into regions, each containing one or more of the country's 47 prefectures at large. Sometimes, they are referred to as "blocs" (ãããã¯, ''burokku''), or "regional blocs" (å°åãããã¯, ''chiiki burokku'') as opposed to more granular regional divisions. They are not official administrative units, though they have been used by government officials for statistical and other purposes since 1905. They are widely used in, for example, maps, geography textbooks, and weather reports, and many businesses and institutions use their home regions in their names as well, for example Kyushu National Museum, Kinki Nippon Railway, ChÅ«goku Bank, and TÅhoku University. One common division, preferred by the English Wikipedia, groups the prefectures into eight regions. In that division, of the four main islands of Japan, HokkaidÅ, Shikoku, and KyÅ«shÅ« make up one region each, the latter also containing the Satsunan Islands, while the largest island H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kansai Region
The or the lies in the southern-central region of Japan's main island HonshÅ«. The region includes the prefectures of Nara, Wakayama, Kyoto, Osaka, HyÅgo and Shiga, often also Mie, sometimes Fukui, Tokushima and Tottori. The metropolitan region of Osaka, Kobe and Kyoto ( Keihanshin region) is the second-most populated in Japan after the Greater Tokyo Area. Name The terms , , and have their roots during the Asuka period. When the old provinces of Japan were established, several provinces in the area around the then-capital Yamato Province were collectively named Kinai and Kinki, both roughly meaning "the neighbourhood of the capital". Kansai (literally ''west of the tollgate'') in its original usage refers to the land west of the Osaka Tollgate (), the border between Yamashiro Province and Åmi Province (present-day Kyoto and Shiga prefectures).Entry for . KÅjien, fifth edition, 1998, During the Kamakura period, this border was redefined to include Åmi a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osaka Restoration Association
The , also referred to as One Osaka, is a regional political party in Osaka Prefecture, Japan. Founded in 2010 by then-Governor (Japan), Governor TÅru Hashimoto, its main platform is pursuing the Osaka Metropolis plan of merging the prefecture and some of its cities into "One Osaka", reducing overlapping bureaucratic organizations of Osaka Prefecture, the prefecture and the city of Osaka, towards DÅshÅ«sei. The party is a major force in the politics within Osaka Prefecture, with the party holding the most seats in the Osaka Prefectural Assembly, Osaka City Assembly and Sakai, Osaka, Sakai City Assembly, as well as the positions of Governor of Osaka and mayor of three cities within the prefecture (Osaka, Moriguchi, Osaka, Moriguchi and Hirakata, Osaka, Hirakata). History Hashimoto, a lawyer and popular TV personality, was elected Governor of Osaka in 2008 Osaka gubernatorial election, January 2008 with the support of the local branches of the Liberal Democratic Party (Japan), L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |