|
.rpm
RPM Package Manager (RPM) (originally Red Hat Package Manager, now a recursive acronym) is a free and open-source package management system. The name RPM refers to the file format and the package manager program itself. RPM was intended primarily for Linux distributions; the file format is the baseline package format of the Linux Standard Base. Although it was created for use in Red Hat Linux, RPM is now used in many Linux distributions such as PCLinuxOS, Fedora, AlmaLinux, CentOS, openSUSE, OpenMandriva and Oracle Linux. It has also been ported to some other operating systems, such as Novell NetWare (as of version 6.5 SP3), IBM's AIX (as of version 4), IBM i, and ArcaOS. An RPM package can contain an arbitrary set of files. Most RPM files are “binary RPMs” (or BRPMs) containing the compiled version of some software. There are also “source RPMs” (or SRPMs) containing the source code used to build a binary package. These have an appropriate tag in the file header that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
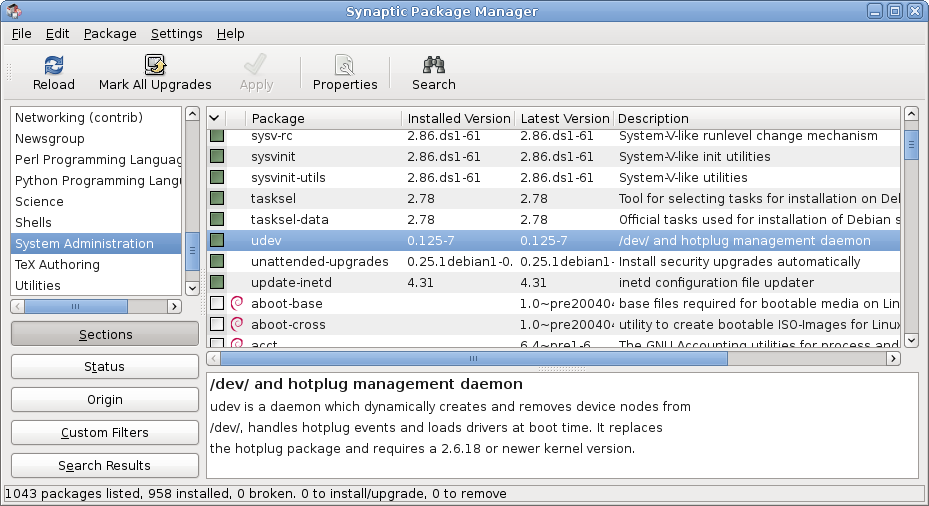
Package Management System
A package manager or package-management system is a collection of software tools that automates the process of installing, upgrading, configuring, and removing computer programs for a computer in a consistent manner. A package manager deals with ''packages'', distributions of software and data in archive files. Packages contain metadata, such as the software's name, description of its purpose, version number, vendor, checksum (preferably a cryptographic hash function), and a list of dependencies necessary for the software to run properly. Upon installation, metadata is stored in a local package database. Package managers typically maintain a database of software dependencies and version information to prevent software mismatches and missing prerequisites. They work closely with software repositories, binary repository managers, and app stores. Package managers are designed to eliminate the need for manual installs and updates. This can be particularly useful for large enter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pristine Sources
Pristine Sources is a software management concept coined by the developers of the short-lived Bogus Linux distribution and popularized by Marc Ewing, co-founder of Red Hat Inc, after he adopted it and RPM Package Manager as a development philosophy for Red Hat Linux. It was the concept that enabled Red Hat to build Linux distributions faster and more reliably than had been possible previously. Briefly, the problem with building an operating system out of the myriad pieces of open source (or free software) components available from teams across the Internet was that there were many of these components and they all upgraded on different schedules at different times. Ewing's insight was to recognize that he could not take responsibility for these components. He and Erik Troan, wanted to build a software package management system, RPM Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Package Management System
A package manager or package-management system is a collection of software tools that automates the process of installing, upgrading, configuring, and removing computer programs for a computer in a consistent manner. A package manager deals with ''packages'', distributions of software and data in archive files. Packages contain metadata, such as the software's name, description of its purpose, version number, vendor, checksum (preferably a cryptographic hash function), and a list of dependencies necessary for the software to run properly. Upon installation, metadata is stored in a local package database. Package managers typically maintain a database of software dependencies and version information to prevent software mismatches and missing prerequisites. They work closely with software repositories, binary repository managers, and app stores. Package managers are designed to eliminate the need for manual installs and updates. This can be particularly useful for large enter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CentOS
CentOS (, from Community Enterprise Operating System; also known as CentOS Linux) is a Linux distribution that provides a free and open-source community-supported computing platform, functionally compatible with its upstream source, Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). In January 2014, CentOS announced the official joining with Red Hat while staying independent from RHEL, under a new CentOS governing board. The first CentOS release in May 2004, numbered as CentOS version 2, was forked from RHEL version 2.1AS. Since version 8, CentOS officially supports the x86-64, ARM64, and POWER8 architectures, and releases up to version 6 also supported the IA-32 architecture. , AltArch releases of CentOS 7 are available for the IA-32 architecture, Power ISA, and for the ARMv7hl and AArch64 variants of the ARM architecture. CentOS 8 was released on 24 September 2019. In December 2020, Red Hat unilaterally terminated CentOS development. In response, CentOS founder Gregory Kurtzer created t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux Standard Base
The Linux Standard Base (LSB) was a joint project by several Linux distributions under the organizational structure of the Linux Foundation to standardize the software system structure, including the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard used in the Linux kernel. LSB was based on the POSIX specification, the Single UNIX Specification (SUS), and several other open standards, but extended them in certain areas. According to LSB: The goal of the LSB is to develop and promote a set of open standards that will increase compatibility among Linux distributions and enable software applications to run on any compliant system even in binary form. In addition, the LSB will help coordinate efforts to recruit software vendors to port and write products for Linux Operating Systems. LSB compliance might be certified for a product by a certification procedure. LSB specified standard libraries (centered around the ), a number of commands and utilities that extend the POSIX standard, the layout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenSUSE
openSUSE () is a free and open source RPM-based Linux distribution developed by the openSUSE project. The initial release of the community project was a beta version of SUSE Linux 10.0. Additionally the project creates a variety of tools, such as YaST, Open Build Service, openQA, Snapper, Machinery, Portus, KIWI and OSEM. Product history In the past, the SUSE Linux company had focused on releasing the SUSE Linux Personal and SUSE Linux Professional box sets which included extensive printed documentation that was available for sale in retail stores. The company's ability to sell an open source product was largely due to the closed-source development process used. Although SUSE Linux had always been free software product licensed with the GNU General Public License (GNU GPL), it was only freely possible to retrieve the source code of the next release 2 months after it was ready for purchase. SUSE Linux' strategy was to create a technically superior Linux distribution with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenMandriva
OpenMandriva Lx is a Linux distribution forked from Mandriva Linux. It is maintained by the OpenMandriva Association. History Origin of the distribution OpenMandriva Lx is a community Linux distribution. Originally an offering of Mandriva Linux, the OpenMandriva product was created in May, 2012, when Mandriva S.A. avoided bankruptcy by abandoning the development of its consumer product to the Mandriva community. The first stable version (OpenMandriva Lx 2013 "Oxygen") was released in late 2013. OpenMandriva Association The OpenMandriva Association was established on December 12, 2012 under 1901 French law, to represent the OpenMandriva Community. It manages free software projects including OpenMandriva Lx. OpenMandriva Lx development environment OpenMandriva Lx's development environment is an ABF (Automated Build Farm) which can manage the source codes, compile it to binaries. Also ABF creates the package repository and ISO images. Versions In late 2013, the first versio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oracle Linux
Oracle Linux (abbreviated OL, formerly known as Oracle Enterprise Linux or OEL) is a Linux distribution packaged and freely distributed by Oracle, available partially under the GNU General Public License since late 2006. It is compiled from Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) source code, replacing Red Hat branding with Oracle's. It is also used by Oracle Cloud and Oracle Engineered Systems such as Oracle Exadata and others. Potential users can freely download Oracle Linux through Oracle's E-delivery service (Oracle Software Delivery Cloud) or from a variety of mirror sites, and can deploy and distribute it without cost. The company's ''Oracle Linux Support program'' aims to provide commercial technical support, covering Oracle Linux and existing RHEL or CentOS installations but without any certification from the former (i.e. without re-installation or re-boot). Oracle Linux had over 15,000 customers subscribed to the support program. RHEL compatibility Oracle Corporation distri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operating Systems
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common services for computer programs. Time-sharing operating systems schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also include accounting software for cost allocation of processor time, mass storage, printing, and other resources. For hardware functions such as input and output and memory allocation, the operating system acts as an intermediary between programs and the computer hardware, although the application code is usually executed directly by the hardware and frequently makes system calls to an OS function or is interrupted by it. Operating systems are found on many devices that contain a computer from cellular phones and video game consoles to web servers and supercomputers. The dominant general-purpose personal computer operating system is Microsoft Windows with a market share of around 74.99%. macOS by Apple Inc. is in second place (14.84%), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marc Ewing
Marc Ewing is an American computer engineer and entrepreneur. He is the creator and originator of the Red Hat brand of software, most notably the Red Hat range of Linux operating system distributions. He was involved in the 86open project in the mid-1990s. Early life The son of an IBM programmer, Marc Ewing attended computer camps as a child, and spent time learning to write programs for Apollo and Commodore computers. He graduated from Carnegie Mellon University in 1992. While at CMU, he was known to wear a red hat. Because of his computer expertise, people would ask for help from the "man in the red hat". Career Following his college education, Ewing began work as engineer at IBM. While at IBM, he spent substantial time customizing Linux workstation installations. From this work, he began the Red Hat Linux Project. Ewing and co-founder Bob Young named their software Red Hat after Ewing's red hat. At the height of the dot com bubble in 1999, Ewing briefly had a net worth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NetWare
NetWare is a discontinued computer network operating system developed by Novell, Inc. It initially used cooperative multitasking to run various services on a personal computer, using the IPX network protocol. The original NetWare product in 1983 supported clients running both CP/M and MS-DOS, ran over a proprietary star network topology and was based on a Novell-built file server using the Motorola 68000 processor. The company soon moved away from building its own hardware, and NetWare became hardware-independent, running on any suitable Intel-based IBM PC compatible system, and able to utilize a wide range of network cards. From the beginning NetWare implemented a number of features inspired by mainframe and minicomputer systems that were not available in its competitors' products. In 1991, Novell introduced cheaper peer-to-peer networking products for DOS and Windows, unrelated to their server-centric NetWare. These are NetWare Lite 1.0 (NWL), and later Perso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AlmaLinux
AlmaLinux is a free and open source Linux distribution, created originally by CloudLinux to provide a community-supported, production-grade enterprise operating system that is binary-compatible with Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). The first stable release of AlmaLinux was published on March 30, 2021, and will be supported through March 1, 2029. Etymology The name of the distribution comes from the word "alma", meaning "soul" in Spanish and other Latin languages. It was chosen to be an homage to the Linux community. History On December 8, 2020, Red Hat announced that development of CentOS Linux, a free-of-cost downstream fork of the commercial Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), would be discontinued and its official support would be cut short to focus on CentOS Stream, a stable LTS release without minor releases officially used by Red Hat to preview what is intended for inclusion in updates to RHEL. In response, CloudLinux – which maintains its own commercial Linux distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |