Ohio on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ohio ( ) is a
 Archeological evidence of spear points of both the Folsom and Clovis types indicate that the Ohio Valley was inhabited by
Archeological evidence of spear points of both the Folsom and Clovis types indicate that the Ohio Valley was inhabited by 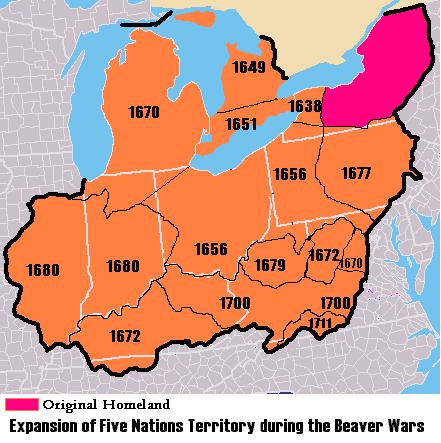 Indians in the Ohio Valley were greatly affected by the aggressive tactics of the Iroquois Confederation, based in central and western New York.Knepper (1989), p. 14. After the
Indians in the Ohio Valley were greatly affected by the aggressive tactics of the Iroquois Confederation, based in central and western New York.Knepper (1989), p. 14. After the

 Although many Native Americans migrated west to evade American encroachment, others remained in the state, sometimes assimilating in part. Starting around 1809, the
Although many Native Americans migrated west to evade American encroachment, others remained in the state, sometimes assimilating in part. Starting around 1809, the
 Ohio's central position and its population gave it an important place in the
Ohio's central position and its population gave it an important place in the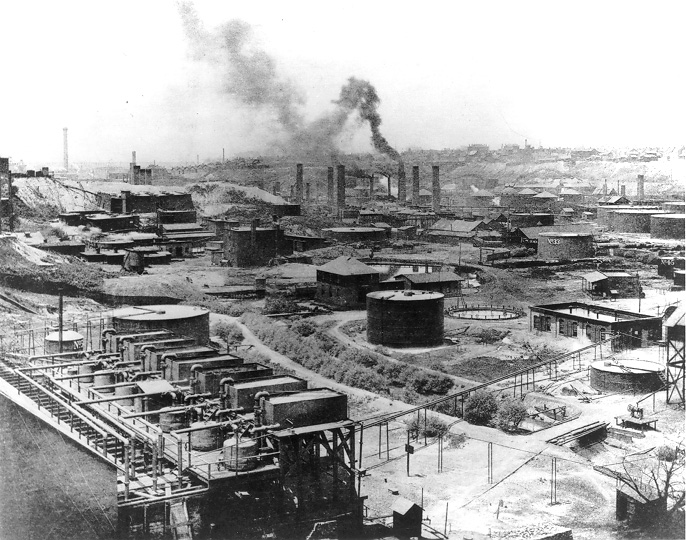  During much of the 19th century, industry was rapidly introduced to complement an existing agricultural economy. One of the first iron manufacturing plants, Hopewell Furnace, opened near
During much of the 19th century, industry was rapidly introduced to complement an existing agricultural economy. One of the first iron manufacturing plants, Hopewell Furnace, opened near
, Ohio Legislative Service Commission. In 2015, Ohio's total GDP accounted for 3.4% of U.S. GDP and 0.8% of world GDP. Politically, Ohio has been long regarded as a
 Ohio's location has proven to be an asset for economic growth and expansion. Because it links the Northeast to the Midwest, much cargo and business traffic passes through its borders along its well-developed highways. Ohio has the nation's 10th-largest highway network and is within a one-day drive of 50% of North America's population and 70% of North America's manufacturing capacity. To the north, Ohio has of coastline with Lake Erie, which allows for numerous cargo ports such as Cleveland and Toledo. Ohio's southern border is defined by the
Ohio's location has proven to be an asset for economic growth and expansion. Because it links the Northeast to the Midwest, much cargo and business traffic passes through its borders along its well-developed highways. Ohio has the nation's 10th-largest highway network and is within a one-day drive of 50% of North America's population and 70% of North America's manufacturing capacity. To the north, Ohio has of coastline with Lake Erie, which allows for numerous cargo ports such as Cleveland and Toledo. Ohio's southern border is defined by the
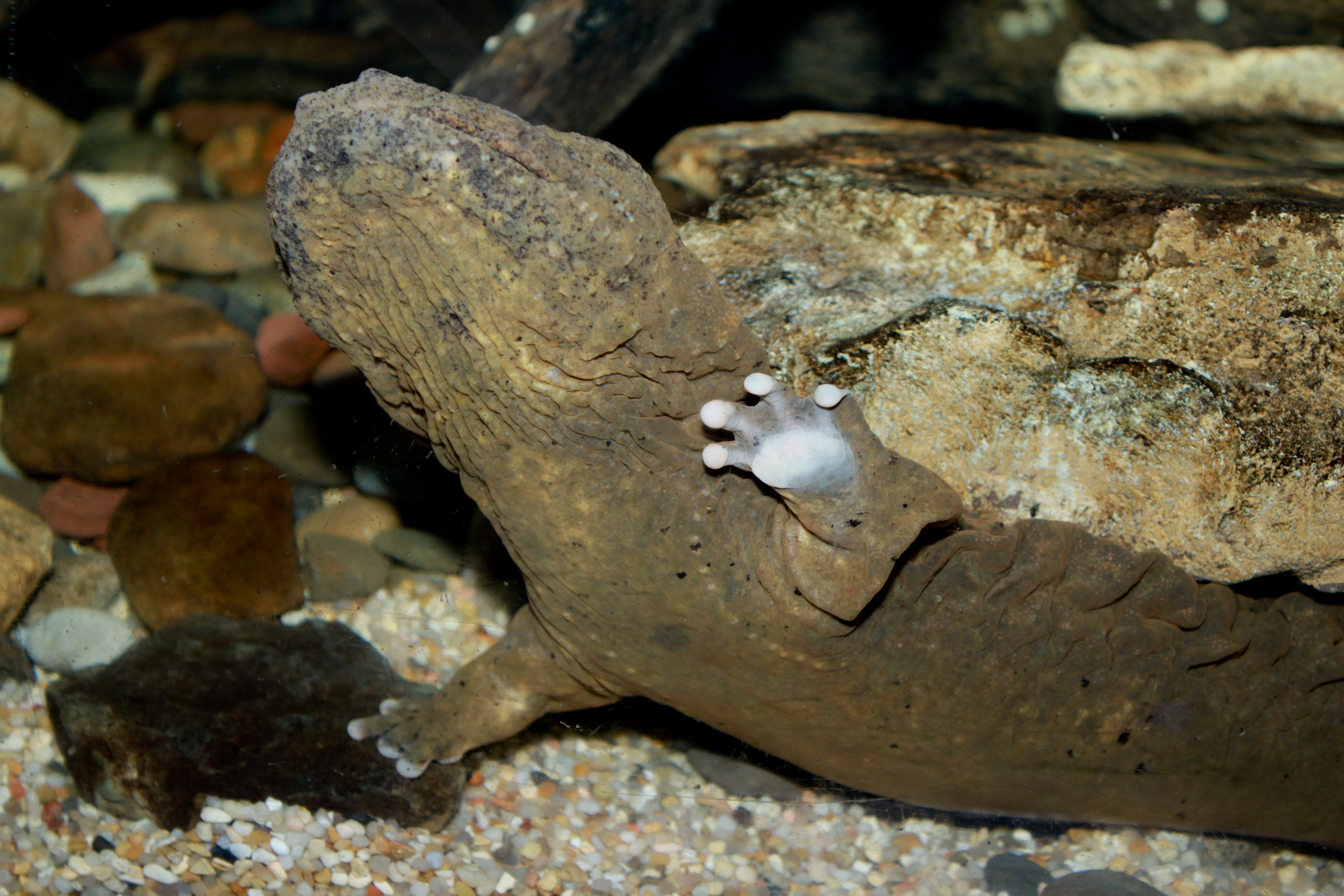 Ohio has wide variety of unique animal species. Rare and endangered species include the Eastern Hellbender, which is found in the Southeastern Appalachian region of Ohio and is classified as state endangered. The Eastern Hellbender is the 3rd largest
Ohio has wide variety of unique animal species. Rare and endangered species include the Eastern Hellbender, which is found in the Southeastern Appalachian region of Ohio and is classified as state endangered. The Eastern Hellbender is the 3rd largest
 In 2010, there were 469,700 foreign-born residents in Ohio, corresponding to 4.1% of the total population. Of these, 229,049 (2.0%) were naturalized U.S. citizens and 240,699 (2.1%) were not. The largest groups were: Mexico (54,166), India (50,256), China (34,901), Germany (19,219), Philippines (16,410), United Kingdom (15,917), Canada (14,223), Russia (11,763), South Korea (11,307), and Ukraine (10,681). Though predominantly white, Ohio has large black populations in all major metropolitan areas throughout the state, Ohio has a significant Hispanic population made up of Mexicans in Toledo and Columbus, and Puerto Ricans in Cleveland and Columbus, and also has a significant and diverse Asian population in Columbus.
Ancestry groups (which the census defines as not including racial terms) in the state were: 26.5%
In 2010, there were 469,700 foreign-born residents in Ohio, corresponding to 4.1% of the total population. Of these, 229,049 (2.0%) were naturalized U.S. citizens and 240,699 (2.1%) were not. The largest groups were: Mexico (54,166), India (50,256), China (34,901), Germany (19,219), Philippines (16,410), United Kingdom (15,917), Canada (14,223), Russia (11,763), South Korea (11,307), and Ukraine (10,681). Though predominantly white, Ohio has large black populations in all major metropolitan areas throughout the state, Ohio has a significant Hispanic population made up of Mexicans in Toledo and Columbus, and Puerto Ricans in Cleveland and Columbus, and also has a significant and diverse Asian population in Columbus.
Ancestry groups (which the census defines as not including racial terms) in the state were: 26.5%
 About 6.7% of the population age 5 years and older reported speaking a language other than English, with 2.2% of the population speaking Spanish, 2.6% speaking other Indo-European languages, 1.1% speaking Asian and Austronesian languages, and 0.8% speaking other languages. Numerically: 10,100,586 spoke English, 239,229
About 6.7% of the population age 5 years and older reported speaking a language other than English, with 2.2% of the population speaking Spanish, 2.6% speaking other Indo-European languages, 1.1% speaking Asian and Austronesian languages, and 0.8% speaking other languages. Numerically: 10,100,586 spoke English, 239,229
 According to the
According to the
Ohio's unemployment rate up to 5.2 percent: 5 things you need to know
Cleveland.com. The labor force participation as of April 2015 is 63%, slightly above the national average. , Ohio's per capita income was $60,402, ranking 38th in the U.S., and the state's
 Ohio is home to 30 art institutions, including the Columbus Museum of Art, Cincinnati Art Museum, Cleveland Museum of Art, and other entities. The full list includes:
*
Ohio is home to 30 art institutions, including the Columbus Museum of Art, Cincinnati Art Museum, Cleveland Museum of Art, and other entities. The full list includes:
*
 Buckeyes are a variation of standard peanut butter cups popular in Ohio. Coated in chocolate with a partially exposed center of peanut butter fudge, the candy resembles the appearance of the nut that grows on the state tree, commonly known as the buckeye. The Klondike bar originated in Mansfield in 1922. Dum Dums lollipops were originally produced in
Buckeyes are a variation of standard peanut butter cups popular in Ohio. Coated in chocolate with a partially exposed center of peanut butter fudge, the candy resembles the appearance of the nut that grows on the state tree, commonly known as the buckeye. The Klondike bar originated in Mansfield in 1922. Dum Dums lollipops were originally produced in
 The
The
 The state government of Ohio consists of the executive, legislative, and judicial branches.
The executive branch is headed by the
The state government of Ohio consists of the executive, legislative, and judicial branches.
The executive branch is headed by the  There are three levels of the Ohio state
There are three levels of the Ohio state
 Historian R. Douglas Hurt asserts that not since Politics of Virginia, Virginia "had a state made such a mark on national political affairs" as Ohio.Holli (1999), p. 162. ''The Economist'' notes that "This slice of the mid-west contains a bit of everything American—part north-eastern and part southern, part urban and part rural, part hardscrabble poverty and part booming suburb".
Ohio is considered a moderately Republican-leaning state politically. It had been a
Historian R. Douglas Hurt asserts that not since Politics of Virginia, Virginia "had a state made such a mark on national political affairs" as Ohio.Holli (1999), p. 162. ''The Economist'' notes that "This slice of the mid-west contains a bit of everything American—part north-eastern and part southern, part urban and part rural, part hardscrabble poverty and part booming suburb".
Ohio is considered a moderately Republican-leaning state politically. It had been a

 Mass transit exists in many forms in Ohio cities, primarily through bus systems. The Greater Cleveland Regional Transit Authority (GCRTA) operates the RTA Rapid Transit system, which consists of one heavy rail line, three Light rail in the United States, light rail lines, and three bus rapid transit lines. Cincinnati is served by the Southwest Ohio Regional Transit Authority (SORTA) bus network as well as a streetcar line, the Cincinnati Bell Connector. Other major transit agencies in Ohio include the Central Ohio Transit Authority (COTA) serving Columbus and the Greater Dayton Regional Transit Authority (GDRTA) serving Dayton.
Mass transit exists in many forms in Ohio cities, primarily through bus systems. The Greater Cleveland Regional Transit Authority (GCRTA) operates the RTA Rapid Transit system, which consists of one heavy rail line, three Light rail in the United States, light rail lines, and three bus rapid transit lines. Cincinnati is served by the Southwest Ohio Regional Transit Authority (SORTA) bus network as well as a streetcar line, the Cincinnati Bell Connector. Other major transit agencies in Ohio include the Central Ohio Transit Authority (COTA) serving Columbus and the Greater Dayton Regional Transit Authority (GDRTA) serving Dayton.
''Thunder in the Heartland: A Chronicle of Outstanding Weather Events in Ohio''
. The Kent State university Press. Kent, Ohio. .
State of Ohio official website
Ohio State Facts from USDA
USGS real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of Ohio
* {{coord, 40, -83, dim:300000_region:US-OH_type:adm1st, name=State of Ohio, display=title Ohio, States of the United States Midwestern United States States and territories established in 1803 Former British colonies and protectorates in the Americas Former French colonies 1803 establishments in the United States Contiguous United States
state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
in the Midwestern
The Midwestern United States (also referred to as the Midwest, the Heartland or the American Midwest) is one of the four census regions defined by the United States Census Bureau. It occupies the northern central part of the United States. It ...
region of the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
. It borders Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( ) is the fourth-largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and also has the shortest avera ...
to the north, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
to the east, West Virginia
West Virginia is a mountainous U.S. state, state in the Southern United States, Southern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States.The United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau and the Association of American ...
to the southeast, Kentucky
Kentucky (, ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north, West Virginia to the ...
to the southwest, Indiana
Indiana ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Michigan to the northwest, Michigan to the north and northeast, Ohio to the east, the Ohio River and Kentucky to the s ...
to the west, and Michigan
Michigan ( ) is a peninsular U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, Upper Midwestern United States. It shares water and land boundaries with Minnesota to the northwest, Wisconsin to the west, ...
to the northwest. Of the 50 U.S. states
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its so ...
, it is the 34th-largest by area. With a population of nearly 11.9 million, Ohio is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated state. Its capital
Capital and its variations may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** Capital region, a metropolitan region containing the capital
** List of national capitals
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter
Econom ...
and most populous city is Columbus, with the two other major metropolitan centers being Cleveland
Cleveland is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County. Located along the southern shore of Lake Erie, it is situated across the Canada–U.S. maritime border and approximately west of the Ohio-Pennsylvania st ...
and Cincinnati
Cincinnati ( ; colloquially nicknamed Cincy) is a city in Hamilton County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. Settled in 1788, the city is located on the northern side of the confluence of the Licking River (Kentucky), Licking and Ohio Ri ...
, alongside Dayton
Dayton () is a city in Montgomery County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of cities in Ohio, sixth-most populous city in Ohio, with a population of 137,644 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The Dayton metro ...
, Akron
Akron () is a city in Summit County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. It is the fifth-most populous city in Ohio, with a population of 190,469 at the 2020 census. The Akron metropolitan area, covering Summit and Portage counties, had ...
, and Toledo. Ohio is nicknamed the "Buckeye State" after its Ohio buckeye trees, and Ohioans are also known as "Buckeyes".
Ohio derives its name from the Ohio River
The Ohio River () is a river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing in a southwesterly direction from Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, to its river mouth, mouth on the Mississippi Riv ...
that forms its southern border, which, in turn, originated from the Seneca word ', meaning "good river", "great river", or "large creek". The state was home to several ancient indigenous civilizations, with humans present as early as 10,000 BCE. It arose from the lands west of the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a mountain range in eastern to northeastern North America. The term "Appalachian" refers to several different regions associated with the mountain range, and its surrounding terrain ...
that were contested by various native tribes and European colonists from the 17th century through the Northwest Indian War
The Northwest Indian War (1785–1795), also known by other names, was an armed conflict for control of the Northwest Territory fought between the United States and a united group of Native Americans in the United States, Native American na ...
s of the late 18th century. Ohio was partitioned from the Northwest Territory
The Northwest Territory, also known as the Old Northwest and formally known as the Territory Northwest of the River Ohio, was formed from part of the unorganized western territory of the United States after the American Revolution. Established ...
, the first frontier of the new United States, becoming the 17th state admitted to the Union on March 1, 1803, and the first under the Northwest Ordinance
The Northwest Ordinance (formally An Ordinance for the Government of the Territory of the United States, North-West of the River Ohio and also known as the Ordinance of 1787), enacted July 13, 1787, was an organic act of the Congress of the Co ...
. It was the first post-colonial free state admitted to the union and became one of the earliest and most influential industrial powerhouses during the 20th century.
Although Ohio has shifted to a more information
Information is an Abstraction, abstract concept that refers to something which has the power Communication, to inform. At the most fundamental level, it pertains to the Interpretation (philosophy), interpretation (perhaps Interpretation (log ...
and service-based economy in the 21st century, it remains an industrial state, ranking seventh in GDP , with the third-largest manufacturing sector and second-largest automobile production. Seven presidents of the United States
The president of the United States is the head of state and head of government of the United States, indirectly elected to a four-year term via the Electoral College. Under the U.S. Constitution, the officeholder leads the executive bra ...
have come from the state, earning it the moniker "the Mother of Presidents".
History
Indigenous settlement
 Archeological evidence of spear points of both the Folsom and Clovis types indicate that the Ohio Valley was inhabited by
Archeological evidence of spear points of both the Folsom and Clovis types indicate that the Ohio Valley was inhabited by nomadic people
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pas ...
as early as 13,000 BC.Knepper (1989), p. 9. These early nomads disappeared from Ohio by 1,000 BC. Between 1,000 and 800 BC, the sedentary Adena culture
The Adena culture was a pre-Columbian Native American culture that existed from 500 BCE to 100 CE, in a time known as the Early Woodland period. The Adena culture refers to what were probably a number of related Native American societies sharin ...
emerged. The Adena established "semi-permanent" villages because they domesticated plants, including sunflowers, and "grew squash and possibly corn"; with hunting and gathering, this cultivation supported more settled, complex villages.Knepper (1989), p. 10. The most notable remnant of the Adena culture is the Great Serpent Mound, located in Adams County, Ohio
Adams County is a county in the U.S. state of Ohio. As of the 2020 census, the population was 27,477. Its county seat and largest village is West Union. The county is named after John Adams, the second President of the United States.
Geogr ...
.
Around 100 BC, the Adena evolved into the Hopewell people, who were also mound builders. Their complex, large and technologically sophisticated earthworks can be found in modern-day Marietta, Newark, and Circleville.Knepper (1989), p. 11. They were also a prolific trading society, their trading network spanning a third of the continent. The Hopewell disappeared from the Ohio Valley about 600 AD. The Mississippian culture
The Mississippian culture was a collection of Native American societies that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 to 1600 CE, varying regionally. It was known for building la ...
rose as the Hopewell culture declined. Many Siouan-speaking peoples from the plains and east coast claim them as ancestors and say they lived throughout the Ohio region until approximately the 13th century.Knepper (1989), p. 13.
There were three other cultures contemporaneous with the Mississippians: the Fort Ancient
The Fort Ancient culture is a Native American archaeological culture that dates back to . Members of the culture lived along the Ohio River valley, in an area running from modern-day Ohio and western West Virginia through to northern Kentucky ...
people, the Whittlesey Culture Whittlesey culture is an archaeological designation for a Native American people, who lived in northeastern Ohio during the Late Precontact and Early Contact period between A.D. 1000 to 1640. By 1500, they flourished as an agrarian society that g ...
and the Monongahela Culture
The Monongahela culture were an Iroquoian Native American cultural manifestation of Late Woodland peoples from AD 1050 to 1635 in present-day Western Pennsylvania, western Maryland, eastern Ohio, and West Virginia. The culture was named by Mary ...
. All three disappeared in the 17th century. Their origins are unknown. The Shawnees may have absorbed the Fort Ancient people. It is also possible that the Monongahela held no land in Ohio during the Colonial Era. The Mississippian culture was close to and traded extensively with the Fort Ancient people.
 Indians in the Ohio Valley were greatly affected by the aggressive tactics of the Iroquois Confederation, based in central and western New York.Knepper (1989), p. 14. After the
Indians in the Ohio Valley were greatly affected by the aggressive tactics of the Iroquois Confederation, based in central and western New York.Knepper (1989), p. 14. After the Beaver Wars
The Beaver Wars (), also known as the Iroquois Wars or the French and Iroquois Wars (), were a series of conflicts fought intermittently during the 17th century in North America throughout the Saint Lawrence River valley in Canada and the Great L ...
in the mid-17th century, the Iroquois claimed much of the Ohio country as hunting and, more importantly, beaver-trapping ground. After the devastation of epidemics and war in the mid-17th century, which largely emptied the Ohio country of Indigenous people by the mid-to-late 17th century, the land gradually became repopulated by the mostly Algonquian. Many of these Ohio-country nations were multiethnic (sometimes multi-linguistic) societies born out of the earlier devastation brought about by disease, war, and subsequent social instability. They subsisted on agriculture (corn, sunflowers, beans, etc.) supplemented by seasonal hunts. By the 18th century, they were part of a larger global economy brought about by European entry into the fur trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal ecosystem, boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals h ...
.Roseboom (1967), p. 20.
Some of the Indigenous nations that historically inhabited Ohio include the Iroquoian, the Algonquian, and the Siouan.Knepper (1989), pp. 14–17. Ohio country
The Ohio Country (Ohio Territory, Ohio Valley) was a name used for a loosely defined region of colonial North America west of the Appalachian Mountains and south of Lake Erie.
Control of the territory and the region's fur trade was disputed i ...
was also the site of Indian massacres, such as the Yellow Creek massacre and the Gnadenhutten massacre
The Gnadenhutten massacre, also known as the Moravian massacre, was the killing of 96 pacifist Moravian Christian Indians (primarily Lenape and Mohican) by U.S. militiamen from Pennsylvania, under the command of David Williamson, on March 8, ...
.Knepper (1989), pp. 43–44. After the War of 1812
The War of 1812 was fought by the United States and its allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and its allies in North America. It began when the United States United States declaration of war on the Uni ...
, when Natives suffered serious losses such as at Tippecanoe, most Native tribes either left Ohio or had to live on only limited reservations. By 1842, all remaining Natives were forced out of the state.
Colonial and Revolutionary eras
During the 18th century, the French set up a system oftrading post
A trading post, trading station, or trading house, also known as a factory in European and colonial contexts, is an establishment or settlement where goods and services could be traded.
Typically a trading post allows people from one geogr ...
s to control the fur trade in the region. Beginning in 1754, the Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the Middle Ages, medieval and Early modern France, early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe from th ...
and Kingdom of Great Britain
Great Britain, also known as the Kingdom of Great Britain, was a sovereign state in Western Europe from 1707 to the end of 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the Kingd ...
fought in the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War, 1754 to 1763, was a colonial conflict in North America between Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of France, France, along with their respective Native Americans in the United States, Native American ...
, with various Native American tribes on each side. As a result of the Treaty of Paris, the French ceded control of Ohio and the remainder of the Old Northwest
The Northwest Territory, also known as the Old Northwest and formally known as the Territory Northwest of the River Ohio, was formed from part of the unorganized western territory of the United States after the American Revolution. Established ...
to Great Britain in 1763.
Before the American Revolution, Britain thinly exercised sovereignty over Ohio Country by lackadaisical garrisoning of the French forts. Just beyond Ohio Country was the great Miami
Miami is a East Coast of the United States, coastal city in the U.S. state of Florida and the county seat of Miami-Dade County, Florida, Miami-Dade County in South Florida. It is the core of the Miami metropolitan area, which, with a populat ...
capital of Kekionga
Kekionga (, meaning "blackberry bush"), also known as KiskakonCharles R. Poinsatte, ''Fort Wayne During the Canal Era 1828-1855,'' Indianapolis: Indiana Historical Bureau, 1969, p. 1 or Pacan's Village, was the capital of the Miami tribe. It wa ...
, which became the center of British trade and influence in Ohio Country and throughout the future Northwest Territory
The Northwest Territory, also known as the Old Northwest and formally known as the Territory Northwest of the River Ohio, was formed from part of the unorganized western territory of the United States after the American Revolution. Established ...
. By the Royal Proclamation of 1763
The Royal Proclamation of 1763 was issued by British King George III on 7 October 1763. It followed the Treaty of Paris (1763), which formally ended the Seven Years' War and transferred French territory in North America to Great Britain. The ...
, British lands west of Appalachia
Appalachia ( ) is a geographic region located in the Appalachian Mountains#Regions, central and southern sections of the Appalachian Mountains in the east of North America. In the north, its boundaries stretch from the western Catskill Mountai ...
were forbidden to settlement by colonists. The Treaty of Fort Stanwix
The Treaty of Fort Stanwix was a treaty signed between representatives from the Iroquois and Great Britain (accompanied by negotiators from New Jersey, Virginia and Province of Pennsylvania, Pennsylvania) in 1768 at Fort Stanwix. It was negotia ...
in 1768 explicitly reserved lands north and west of the Ohio as Native lands. British military occupation in the region contributed to the outbreak of Pontiac's War
Pontiac's War (also known as Pontiac's Conspiracy or Pontiac's Rebellion) was launched in 1763 by a confederation of Native Americans who were dissatisfied with British rule in the Great Lakes region following the French and Indian War (1754– ...
in 1763. Ohio tribes participated in the war until an armed expedition in Ohio led by Brigadier General Henry Bouquet brought about a truce. Another colonial military expedition into the Ohio Country in 1774 brought Lord Dunmore's War
Lord Dunmore's War, also known as Dunmore's War, was a brief conflict in the fall of 1774 between the British Colony of Virginia and the Shawnee and Mingo in the trans-Appalachia region of the colony south of the Ohio River. Broadly, the war incl ...
, kicked off by the Yellow Creek massacre in Ohio, to a conclusion. In 1774, Britain passed the Quebec Act
The Quebec Act 1774 ( 14 Geo. 3. c. 83) () was an act of the Parliament of Great Britain which set procedures of governance in the Province of Quebec. One of the principal components of the act was the expansion of the province's territory t ...
, which formally annexed Ohio and other western lands to the Province of Quebec
Quebec is Canada's largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, New Brunswick to the southeast and a coastal border ...
in order to provide a civil government and to centralize British administration of the Montreal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cit ...
-based fur trade. The prohibition of settlement west of the Appalachians remained, contributing to the American Revolution.
By the start of the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which Am ...
, the movement of Natives and Americans between the Ohio Country and Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were the British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America which broke away from the British Crown in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), and joined to form the United States of America.
The Thirteen C ...
had resulted in tension. Fort Pitt in Pennsylvania had become the main fort where expeditions into Ohio started. Intrusions into the area included General Edward Hand's 1778 movement of 500 Pennsylvania militiamen from Fort Pitt towards Mingo towns on the Cuyahoga River
The Cuyahoga River (see ) is a river located in Northeast Ohio that bisects the City of Cleveland and feeds into Lake Erie.
As Cleveland emerged as a major manufacturing center, the river became heavily affected by industrial pollution, so mu ...
, where the British stored military supplies which they distributed to Indian raiding parties; Colonel Daniel Brodhead
Brigadier General Daniel Brodhead (October 17, 1736 – November 15, 1809) was an Continental Army officer and politician who served in the American Revolutionary War.
Early life
Brodhead was born in Marbletown, Province of New York, the so ...
's invasion in 1780 and destruction of the Lenape Indian capital of Coshocton; a detachment of one hundred of George Rogers Clark
George Rogers Clark (November 19, 1752 – February 13, 1818) was an American military officer and surveyor from Virginia who became the highest-ranking Patriot (American Revolution), Patriot military officer on the American frontier, nort ...
's troops that were ambushed near the Ohio River by Indians led by Joseph Brant
Thayendanegea or Joseph Brant (March 1743 – November 24, 1807) was a Mohawk military and political leader, based in present-day New York and, later, Brantford, in what is today Ontario, who was closely associated with Great Britain du ...
in the same year; a British and Native American attack on the U.S.' Fort Laurens
Fort Laurens was an American Revolutionary War fort on a northern tributary of the Muskingum River in what would become Northeast Ohio, United States. The fort's location is in the present-day town of Bolivar, Ohio, along the Ohio and Erie ...
; and the 1782 detainment and murder of 96 Moravian Lenape pacifists by Pennsylvania militiamen in the Gnadenhutten massacre
The Gnadenhutten massacre, also known as the Moravian massacre, was the killing of 96 pacifist Moravian Christian Indians (primarily Lenape and Mohican) by U.S. militiamen from Pennsylvania, under the command of David Williamson, on March 8, ...
.
The western theatre never had a decisive victor. In the Treaty of Paris in 1783, Britain ceded all claims to Ohio Country to the new United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
after its victory in the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which Am ...
.
Northwest Territory
The United States created theNorthwest Territory
The Northwest Territory, also known as the Old Northwest and formally known as the Territory Northwest of the River Ohio, was formed from part of the unorganized western territory of the United States after the American Revolution. Established ...
under the Northwest Ordinance
The Northwest Ordinance (formally An Ordinance for the Government of the Territory of the United States, North-West of the River Ohio and also known as the Ordinance of 1787), enacted July 13, 1787, was an organic act of the Congress of the Co ...
of 1787.Cayton (2002), p. 3. Slavery was not permitted in the new territory. Settlement began with the founding of Marietta by the Ohio Company of Associates
The Ohio Company of Associates, also known as the Ohio Company, was a land company whose members are today credited with becoming the first non-Native Americans in the United States, Native American group to permanently settle west of the Alle ...
, which had been formed by a group of American Revolutionary War veterans. Following the Ohio Company, the Miami Company (also referred to as the "Symmes Purchase
The Symmes Purchase, also known as the Miami Purchase, was an area of land totaling roughly in what is now Hamilton, Butler, and Warren counties of southwestern Ohio, purchased by Judge John Cleves Symmes of New Jersey in 1788 from the Contine ...
") claimed the southwestern section, and the Connecticut Land Company
The Connecticut Company or Connecticut Land Company (est. 1795) was a post-colonial land speculation company formed in the late eighteenth century to survey and encourage settlement in the eastern parts of the newly chartered Connecticut Western ...
surveyed and settled the Connecticut Western Reserve
The Connecticut Western Reserve was a portion of land claimed by the Colony of Connecticut and later by the state of Connecticut in what is now mostly the northeastern region of Ohio. Warren, Ohio was the Historic Capital in Trumbull County. T ...
in present-day Northeast Ohio
Northeast Ohio is a geographic and Cultural area, cultural region that comprises the northeastern counties of the U.S. state of Ohio. Definitions of the region consist of 16 to 23 counties between the southern shore of Lake Erie and the foothills ...
. Territorial surveyors from Fort Steuben began surveying an area of eastern Ohio called the Seven Ranges
The Seven Ranges (also known as the Old Seven Ranges) was a land tract in eastern Ohio that was the first tract to be surveyed in what became the Public Land Survey System. The tract is across the northern edge, on the western edge, with the so ...
at about the same time.
The old Northwest Territory originally included areas previously known as Ohio Country
The Ohio Country (Ohio Territory, Ohio Valley) was a name used for a loosely defined region of colonial North America west of the Appalachian Mountains and south of Lake Erie.
Control of the territory and the region's fur trade was disputed i ...
and Illinois Country
The Illinois Country ( ; ; ), also referred to as Upper Louisiana ( ; ), was a vast region of New France claimed in the 1600s that later fell under Spanish and British control before becoming what is now part of the Midwestern United States. Whi ...
. As Ohio prepared for statehood, the Indiana Territory
The Indiana Territory, officially the Territory of Indiana, was created by an organic act that President of the United States, President John Adams signed into law on May 7, 1800, to form an Historic regions of the United States, organized incor ...
was created, reducing the Northwest Territory to approximately the size of present-day Ohio plus the eastern half of the Lower Peninsula of Michigan
The Lower Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Lower Michigan – is the larger, southern and less elevated of the Geography of Michigan, two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; the other being the Upper Peninsula of Mic ...
and the eastern tip of the Upper Peninsula
The Upper Peninsula of Michigan—also known as Upper Michigan or colloquially the U.P. or Yoop—is the northern and more elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; it is separated from the Lower Peninsula b ...
and a sliver of southeastern Indiana called "The Gore".
The coalition of Native American tribes, known as the Western Confederacy
The Northwestern Confederacy, or Northwestern Indian Confederacy, was a loose confederacy of Native Americans in the Great Lakes region of the United States created after the American Revolutionary War. Formally, the confederacy referred to it ...
, was forced to cede extensive territory, including much of present-day Ohio, in the Treaty of Greenville
The Treaty of Greenville, also known to Americans as the Treaty with the Wyandots, etc., but formally titled ''A treaty of peace between the United States of America, and the tribes of Indians called the Wyandots, Delawares, Shawanees, Ottawas ...
in 1795.
Under the Northwest Ordinance
The Northwest Ordinance (formally An Ordinance for the Government of the Territory of the United States, North-West of the River Ohio and also known as the Ordinance of 1787), enacted July 13, 1787, was an organic act of the Congress of the Co ...
, areas could be defined and admitted as states once their population reached 60,000. Although Ohio's population was only 45,000 in December 1801, Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
determined that it was growing rapidly enough and accelerated the process via the Enabling Act of 1802
The Enabling Act of 1802 was passed on April 30, 1802 by the Seventh Congress of the United States. This act authorized the residents of the eastern portion of the Northwest Territory to form the state of Ohio and join the U.S. on an equal footi ...
. In regard to the Leni Lenape natives, Congress decided that 10,000 acres on the Muskingum River
The Muskingum River ( ; ) is a tributary of the Ohio River, approximately long, in southeastern Ohio in the United States. An important commercial route in the 19th century, it flows generally southward through the eastern hill country of Ohio ...
in the present state of Ohio would "be set apart and the property thereof be vested in the Moravian Brethren
The Moravian Church, or the Moravian Brethren ( or ), formally the (Latin: "Unity of the Brethren"), is one of the oldest Protestant denominations in Christianity, dating back to the Bohemian Reformation of the 15th century and the original U ...
... or a society of the said Brethren for civilizing the Indians and promoting Christianity".
Rufus Putnam, the "Father of Ohio"

Rufus Putnam
Rufus Putnam (April 9, 1738 – May 4, 1824) was an American military officer who fought during the French and Indian War and the American Revolutionary War. As an organizer of the Ohio Company of Associates, he was instrumental in the initial co ...
served in important military capacities in both the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War, 1754 to 1763, was a colonial conflict in North America between Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of France, France, along with their respective Native Americans in the United States, Native American ...
and the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which Am ...
. He was one of the most highly respected men in the early years of the United States.
In 1776, Putnam created a method of building portable fortifications, which enabled the Continental Army
The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies representing the Thirteen Colonies and later the United States during the American Revolutionary War. It was formed on June 14, 1775, by a resolution passed by the Second Continental Co ...
to drive the British from Boston. George Washington
George Washington (, 1799) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the first president of the United States, serving from 1789 to 1797. As commander of the Continental Army, Washington led Patriot (American Revoluti ...
was so impressed that he made Putnam his chief engineer. After the war, Putnam and Manasseh Cutler
Manasseh Cutler (May 13, 1742 – July 28, 1823) was an American Congregational clergyman involved in the American Revolutionary War. He was influential in the passage of the Northwest Ordinance of 1787 and wrote the section prohibiting sla ...
were instrumental in creating the Northwest Ordinance
The Northwest Ordinance (formally An Ordinance for the Government of the Territory of the United States, North-West of the River Ohio and also known as the Ordinance of 1787), enacted July 13, 1787, was an organic act of the Congress of the Co ...
, which opened up the Northwest Territory
The Northwest Territory, also known as the Old Northwest and formally known as the Territory Northwest of the River Ohio, was formed from part of the unorganized western territory of the United States after the American Revolution. Established ...
for settlement. This land was used to serve as compensation for what was owed to Revolutionary War veterans. Putnam organized and led the Ohio Company of Associates
The Ohio Company of Associates, also known as the Ohio Company, was a land company whose members are today credited with becoming the first non-Native Americans in the United States, Native American group to permanently settle west of the Alle ...
, who settled at Marietta, Ohio
Marietta is a city in Washington County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. It is located in Appalachian Ohio, southeastern Ohio at the confluence of the Muskingum River, Muskingum and Ohio Rivers, northeast of Parkersburg, West Virginia ...
, where they built a large fort, Campus Martius
The Campus Martius (Latin for 'Field of Mars'; Italian: ''Campo Marzio'') was a publicly owned area of ancient Rome about in extent. In the Middle Ages, it was the most populous area of Rome. The IV rione of Rome, Campo Marzio, which covers ...
. He set substantial amounts of land aside for schools. In 1798, he created the plan for the construction of the Muskingum Academy (now Marietta College
Marietta College (MC) is a private liberal arts college in Marietta, Ohio, United States. Its campus encompasses approximately six city blocks next to downtown Marietta and enrolls 1,200 students.
History
Marietta College began as the Muskin ...
). In 1780, the directors of the Ohio Company appointed him superintendent of all its affairs relating to the settlement north of the Ohio River. In 1796, President George Washington commissioned him as Surveyor-General of United States Lands. In 1788, he served as a judge in the Northwest Territory's first court. In 1802, he served in the convention to form a constitution for the State of Ohio.
Statehood and early years
On February 19, 1803, U.S. presidentThomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (, 1743July 4, 1826) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary author of the United States Declaration of Indepe ...
signed an act of Congress that approved Ohio's boundaries and constitution. But Congress had not passed a formal resolution admitting Ohio as the 17th state. Although no formal resolution of admission was required, when the oversight was discovered in 1953, as Ohio began preparations for celebrating its sesquicentennial, Ohio congressman George H. Bender introduced a bill in Congress to admit Ohio to the Union retroactive to March 1, 1803, the date on which the Ohio General Assembly
The Ohio General Assembly is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Ohio. It consists of the 99-member Ohio House of Representatives and the 33-member Ohio Senate. Both houses of the General Assembly meet at the Ohio Statehouse in Colu ...
first convened. At a special session at the old state capital in Chillicothe, the Ohio state legislature approved a new petition for statehood, which was delivered to Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
, on horseback, and approved that August.
Ohio has had three capital cities: Chillicothe, Zanesville
Zanesville is a city in Muskingum County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. Located at the confluence of the Licking and Muskingum rivers, the city is approximately east of Columbus and had a population of 24,765 as of the 2020 cen ...
, and Columbus. Chillicothe was the capital from 1803 to 1810. The capital was then moved to Zanesville for two years as part of a state legislative compromise to get a bill passed. The capital was then moved back to Chillicothe from 1812 to 1816. Finally, the capital was moved to Columbus, to be near the state's geographic center.
 Although many Native Americans migrated west to evade American encroachment, others remained in the state, sometimes assimilating in part. Starting around 1809, the
Although many Native Americans migrated west to evade American encroachment, others remained in the state, sometimes assimilating in part. Starting around 1809, the Shawnee
The Shawnee ( ) are a Native American people of the Northeastern Woodlands. Their language, Shawnee, is an Algonquian language.
Their precontact homeland was likely centered in southern Ohio. In the 17th century, they dispersed through Ohi ...
pressed resistance to encroachment again. Under Chief Tecumseh
Tecumseh ( ; (March 9, 1768October 5, 1813) was a Shawnee chief and warrior who promoted resistance to the Territorial evolution of the United States, expansion of the United States onto Native Americans in the United States, Native American ...
, Tecumseh's War
Tecumseh's War or Tecumseh's Rebellion was a conflict between the United States and Tecumseh's confederacy, led by the Shawnee leader Tecumseh in the Indiana Territory. Although the war is often considered to have climaxed with William Henry Ha ...
officially began in Ohio in 1811. When the War of 1812
The War of 1812 was fought by the United States and its allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and its allies in North America. It began when the United States United States declaration of war on the Uni ...
began, the British decided to attack from Upper Canada
The Province of Upper Canada () was a Province, part of The Canadas, British Canada established in 1791 by the Kingdom of Great Britain, to govern the central third of the lands in British North America, formerly part of the Province of Queb ...
into Ohio and merge their forces with the Shawnee. This continued until Tecumseh was killed at the Battle of the Thames
The Battle of the Thames , also known as the Battle of Moraviantown, was an American victory in the War of 1812 against Tecumseh's Confederacy and their United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, British allies. It took place on October 5, 1813, ...
in 1813. Most of the Shawnee, excluding the Pekowi
Pekowi was the name of one of the five divisions (or bands) of the Shawnee, a Native American people, during the 18th century. The other four divisions were the Chalahgawtha, Mekoche, Kispoko, and Hathawekela. Together these divisions formed th ...
in Southwest Ohio, were forcibly moved west. Ohio played a key role in the War of 1812, as it was on the front line in the Western theater and the scene of several notable battles both on land and in Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( ) is the fourth-largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and also has the shortest avera ...
. On September 10, 1813, the Battle of Lake Erie
The Battle of Lake Erie, also known as the Battle of Put-in-Bay, was fought on 10 September 1813, on Lake Erie off the shores of Ohio during the War of 1812. Nine vessels of the United States Navy defeated and captured six vessels of the British ...
, one of the major battles, took place near Put-in-Bay, Ohio
Put-in-Bay is a Resort town, resort village located on South Bass Island in Put-in-Bay Township, Ohio, Put-in-Bay Township, Ottawa County, Ohio, United States, west of Cleveland and east of Toledo, Ohio, Toledo. The population was 154 at the ...
. The British eventually surrendered to Oliver Hazard Perry
Oliver Hazard Perry (August 23, 1785 – August 23, 1819) was a United States Navy officer from South Kingstown, Rhode Island. A prominent member of the Perry family naval dynasty, he was the son of Sarah Wallace Alexander and Captain Christo ...
.
Ultimately, after the U.S. government used the Indian Removal Act of 1830 to force countless Native American tribes on the Trail of Tears
The Trail of Tears was the forced displacement of about 60,000 people of the " Five Civilized Tribes" between 1830 and 1850, and the additional thousands of Native Americans and their black slaves within that were ethnically cleansed by the U ...
, where all the southern states except for Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
were emptied of Native peoples, the government panicked because most tribes did not want to be forced out of their own lands. Fearing further wars between Native tribes and American settlers, they pushed all remaining Native tribes in the East to migrate west against their will, including all remaining tribes in Ohio.
In 1835, Ohio fought with the Michigan Territory
The Territory of Michigan was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from June 30, 1805, until January 26, 1837, when the final extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Michigan. Detroit ...
in the Toledo War
The Toledo War (1835–1836), also known as the Michigan–Ohio War or Ohio–Michigan War, was a boundary dispute between the U.S. state of Ohio and the adjoining territory of Michigan over what is now known as the Toledo Strip. Control of th ...
, a mostly bloodless boundary war over the Toledo Strip. Only one person was injured in the conflict. Congress intervened, making Michigan
Michigan ( ) is a peninsular U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, Upper Midwestern United States. It shares water and land boundaries with Minnesota to the northwest, Wisconsin to the west, ...
's admittance as a state conditional on ending the conflict. In exchange for giving up its claim to the Toledo Strip, Michigan was given the western two-thirds of the Upper Peninsula
The Upper Peninsula of Michigan—also known as Upper Michigan or colloquially the U.P. or Yoop—is the northern and more elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; it is separated from the Lower Peninsula b ...
, in addition to the eastern third, which was already considered part of the territory.
Civil War and industrialization
 Ohio's central position and its population gave it an important place in the
Ohio's central position and its population gave it an important place in the Civil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
. The Ohio River was a vital artery for troop and supply movements, as were Ohio's railroads. Ohio's industry made it one of the most important states in the Union during the war. It contributed more soldiers per capita than any other state in the Union. In 1862, the state's morale was badly shaken in the aftermath of the Battle of Shiloh
The Battle of Shiloh, also known as the Battle of Pittsburg Landing, was a major battle in the American Civil War fought on April 6–7, 1862. The fighting took place in southwestern Tennessee, which was part of the war's Western Theater of the ...
, a costly victory in which Ohio forces suffered 2,000 casualties.Knepper (1989), pp. 233–234. Later that year, when Confederate
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a political union of sovereign states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
troops under the leadership of Stonewall Jackson
Thomas Jonathan "Stonewall" Jackson (January 21, 1824 – May 10, 1863) was a Confederate general and military officer who served during the American Civil War. He played a prominent role in nearly all military engagements in the eastern the ...
threatened Washington, D.C., Ohio governor David Tod
David Tod (February 21, 1805 – November 13, 1868) was an American politician and industrialist from the U.S. state of Ohio. As the 25th governor of Ohio, Tod gained recognition for his forceful and energetic leadership during the American Civil ...
recruited 5,000 volunteers to provide three months of service.Roseboom and Weisenburger (1967), p. 188. From July 13 to 26, 1863, towns along the Ohio River were attacked and ransacked in Morgan's Raid
Morgan's Raid (also the Calico Raid or Great Raid of 1863) was a diversionary incursion by Confederate States Army, Confederate cavalry into the Union (American Civil War), Union states of Indiana, Kentucky, Ohio, and West Virginia during the A ...
, starting in Harrison in the west and culminating in the Battle of Salineville
The Battle of Salineville occurred July 26, 1863, near Salineville, Ohio, during the American Civil War. U.S. Brig. Gen. James M. Shackelford destroyed Confederate Brig. Gen. John Hunt Morgan's remaining Confederate cavalry and captured Morga ...
near West Point
The United States Military Academy (USMA), commonly known as West Point, is a United States service academies, United States service academy in West Point, New York that educates cadets for service as Officer_(armed_forces)#United_States, comm ...
in the far east. While this raid was overall insignificant to the Confederacy, it aroused fear among people in Ohio and Indiana
Indiana ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Michigan to the northwest, Michigan to the north and northeast, Ohio to the east, the Ohio River and Kentucky to the s ...
as it was the furthest advancement of troops from the South in the war. Almost 35,000 Ohioans died in the conflict, and 30,000 were physically wounded.Cayton (2002), p. 129. By the end of the Civil War, the Union's top three generals—Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was the 18th president of the United States, serving from 1869 to 1877. In 1865, as Commanding General of the United States Army, commanding general, Grant led the Uni ...
, William Tecumseh Sherman
William Tecumseh Sherman ( ; February 8, 1820February 14, 1891) was an American soldier, businessman, educator, and author. He served as a General officer, general in the Union Army during the American Civil War (1861–1865), earning recognit ...
, and Philip Sheridan
Philip Henry Sheridan (March 6, 1831 – August 5, 1888) was a career United States Army officer and a Union general in the American Civil War. His career was noted for his rapid rise to major general and his close association with General-i ...
—were all from Ohio.Cayton (2002), pp. 128–129.
 During much of the 19th century, industry was rapidly introduced to complement an existing agricultural economy. One of the first iron manufacturing plants, Hopewell Furnace, opened near
During much of the 19th century, industry was rapidly introduced to complement an existing agricultural economy. One of the first iron manufacturing plants, Hopewell Furnace, opened near Youngstown
Youngstown is a city in Mahoning County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of municipalities in Ohio, 11th-most populous city in Ohio with a population of 60,068 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The Mahoning ...
in 1804. By the mid-19th century, 48 blast furnaces were operating in Ohio, most in the southern part of the state. Discovery of coal deposits aided the further development of Ohio's steel industry, and by 1853 Cleveland was the nation's third-largest iron and steel producer. The first Bessemer converter
The Bessemer process was the first inexpensive industrial process for the mass production of steel from molten pig iron before the development of the open hearth furnace. The key principle is removal of impurities and undesired elements, primar ...
was purchased by the Cleveland Rolling Mill Company, which became part of the U.S. Steel Corporation after the merger of Federal Steel Company and Carnegie Steel, the first billion-dollar American corporation. The first open-hearth furnace used for steel production was constructed by the Otis Steel Company in Cleveland, and by 1892, Ohio was the second-largest steel-producing state, behind Pennsylvania. Republic Steel
Republic Steel is a Mexican steel manufacturer that was once America’s third largest steel producer. It was founded as the Republic Iron and Steel Company in Youngstown, Ohio in 1899. After rising to prominence during the early 20th Century, ...
was founded in Youngstown in 1899 and was at one point the nation's third-largest producer. Armco
AK Steel Holdings Corporation was an American steelmaking company headquartered in West Chester Township, Ohio. The company, whose name was derived from the initials of Armco, its predecessor company, and Kawasaki Steel Corporation, was acqui ...
, now AK Steel, was founded in Middletown in 1899.
20th century
The state legislature officially adopted theflag of Ohio
The Ohio Burgee is the official flag of the U.S. state of Ohio. It is a distinctive triangular Swallowtail (flag), swallowtail flag. Its red, white, and blue elements symbolize the state's natural features and order of admission into the Union. ...
on May 9, 1902. Dayton natives Orville and Wilbur Wright made four brief flights at Kitty Hawk, North Carolina
Kitty Hawk is a town in Dare County, North Carolina, United States, located on Bodie Island within the state's Outer Banks. The population was 3,708 at the 2020 United States census. It was established in the early 18th century as Chickahawk.
Hi ...
, on December 17, 1903, inventing the first successful airplane. Ohio was hit by its greatest natural disaster in the Great Flood of 1913
The Great Flood of 1913 occurred between March 23 and March 26, after major rivers in the central and eastern United States flooded from runoff and several days of heavy rain. Related deaths and damage in the United States were widespread and ...
, resulting in at least 428 fatalities and hundreds of millions of dollars in property damage, particularly around the Great Miami River
The Great Miami River (also called the Miami River) (Shawnee language, Shawnee: ''Msimiyamithiipi'') is a tributary of the Ohio River, approximately long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe Nat ...
basin.
The National Football League
The National Football League (NFL) is a Professional gridiron football, professional American football league in the United States. Composed of 32 teams, it is divided equally between the American Football Conference (AFC) and the National ...
was originally founded in Canton, Ohio
Canton () is a city in Stark County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of cities in Ohio, eighth-most populous city in Ohio, with a population of 70,872 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The Canton–Massillo ...
in 1920 as the American Professional Football Conference. It included Ohio League
The Ohio League was an informal and loose association of American football clubs active between 1902 and 1919 that competed for the Ohio Independent Championship (OIC). As the name implied, its teams were mostly based in Ohio. It is the direct p ...
teams in five Ohio cities (Akron, Canton, Cleveland, Columbus, and Dayton), none of which still exist. The first official game occurred on October 3, 1920, when the Dayton Triangles beat the Columbus Panhandles
The Columbus Panhandles were a professional American football team based in Columbus, Ohio. The club was founded in 1901 by workers at the Panhandle shops of the Pennsylvania Railroad. They were a part of the Ohio League from 1904 before foldi ...
14–0 in Dayton. Canton was enshrined as the home of the Pro Football Hall of Fame
The Pro Football Hall of Fame is the hall of fame for professional football (gridiron), professional American football, located in Canton, Ohio. Opened on September 7, 1963, the Hall of Fame enshrines exceptional figures in the sport of profes ...
in 1963.
During the 1930s, the Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
struck the state hard. By 1933, more than 40% of factory workers and 67% of construction workers were unemployed in Ohio. Approximately 50% of industrial workers in Cleveland and 80% in Toledo became unemployed, with the state unemployment rate reaching a high of 37.3%. American Jews watched the rise of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
with apprehension. Cleveland residents Jerry Siegel
Jerome "Jerry" Siegel ( ; October 17, 1914 – January 28, 1996) Roger Stern. ''Superman: Sunday Classics: 1939–1943'' DC Comics/ Kitchen Sink Press, Inc./ Sterling Publishing; 2006 was an American comic book writer. He was the co-creator of ...
and Joe Shuster
Joseph Shuster ( ; July 10, 1914 – July 30, 1992) was a Canadian-American comic book artist best known for co-creating the DC Comics character Superman, with Jerry Siegel, in ''Action Comics'' #1 ( cover-dated June 1938).
Shuster was involv ...
created the Superman
Superman is a superhero created by writer Jerry Siegel and artist Joe Shuster, which first appeared in the comic book ''Action Comics'' Action Comics 1, #1, published in the United States on April 18, 1938.The copyright date of ''Action Comics ...
comic character in the spirit of the Jewish golem
A golem ( ; ) is an animated Anthropomorphism, anthropomorphic being in Jewish folklore, which is created entirely from inanimate matter, usually clay or mud. The most famous golem narrative involves Judah Loew ben Bezalel, the late 16th-century ...
. Many of their comics portrayed Superman fighting and defeating the Nazis
Nazism (), formally named National Socialism (NS; , ), is the far-right politics, far-right Totalitarianism, totalitarian socio-political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Germany. During H ...
. Approximately 839,000 Ohioans served in the U.S. armed forces during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, of whom over 23,000 died or were missing in action.
Artists, writers, musicians and actors developed in the state throughout the 20th century and often moved to other cities that were larger centers for their work. They included Zane Grey
Pearl Zane Grey (January 31, 1872 – October 23, 1939) was an American author and dentist. He is known for his popular adventure novels and stories associated with the Western genre in literature and the arts; he idealized the American frontier ...
, Milton Caniff
Milton Arthur Paul Caniff (; February 28, 1907 – April 3, 1988) was an American cartoonist known for the ''Terry and the Pirates'' and ''Steve Canyon'' comic strips.
Biography
Caniff was born in Hillsboro, Ohio. He was an Eagle Scout and a re ...
, George Bellows
George Wesley Bellows (August 12 or August 19, 1882 – January 8, 1925) was an American realism, American realist painting, painter, known for his bold depictions of urban life in New York City. He became, according to the Columbus Museum of Art ...
, Art Tatum
Arthur Tatum Jr. (, October 13, 1909 – November 5, 1956) was an American jazz pianist who is widely regarded as one of the greatest ever. From early in his career, fellow musicians acclaimed Tatum's technical ability as extraordinary. Tatum a ...
, Roy Lichtenstein
Roy Fox Lichtenstein ( ; October27, 1923September29, 1997) was an American pop artist. He rose to prominence in the 1960s through pieces which were inspired by popular advertising and the comic book style. Much of his work explores the relations ...
, and Roy Rogers
Roy Rogers (born Leonard Franklin Slye; November 5, 1911 – July 6, 1998), nicknamed the King of the Cowboys, was an American singer, actor, television host, and Rodeo, rodeo performer.
Following early work under his given name, first as a c ...
. Alan Freed
Albert James "Alan" Freed (December 15, 1921 – January 20, 1965) was an American disc jockey. He also produced and promoted large traveling concerts with various acts, helping to spread the importance of rock and roll music throughout Nor ...
, who emerged from the swing dance culture in Cleveland, hosted the first live rock 'n roll concert in Cleveland in 1952. Famous filmmakers include Steven Spielberg
Steven Allan Spielberg ( ; born December 18, 1946) is an American filmmaker. A major figure of the New Hollywood era and pioneer of the modern blockbuster, Spielberg is widely regarded as one of the greatest film directors of all time and is ...
, Chris Columbus and the original Warner Brothers
Warner Bros. Entertainment Inc. (WBEI), commonly known as Warner Bros. (WB), is an American filmed entertainment studio headquartered at the Warner Bros. Studios complex in Burbank, California and the main namesake subsidiary of Warner Bro ...
, who set up their first movie theatre in Youngstown before the company relocated to California. The state produced many popular musicians, including Dean Martin
Dean Martin (born Dino Paul Crocetti; June 7, 1917 – December 25, 1995) was an American singer, actor, and comedian. Nicknamed the "Honorific nicknames in popular music, King of Cool", he is regarded as one of the most popular entertainers of ...
, Doris Day
Doris Day (born Doris Mary Kappelhoff; April 3, 1922 – May 13, 2019) was an American actress and singer. She began her career as a big band singer in 1937, achieving commercial success in 1945 with two No. 1 recordings, "Sentimental Journey ...
, The O'Jays
The O'Jays are an American Rhythm and blues, R&B group from Canton, Ohio, formed in summer 1958 and originally consisting of Eddie Levert, Walter Lee Williams, William Powell, Bobby Massey, and Bill Isles. The O'Jays made their first chart appea ...
, Marilyn Manson
Brian Hugh Warner (born January 5, 1969), known professionally as Marilyn Manson, is an American rock musician. He is the lead singer and the only original member remaining of the Marilyn Manson (band), same-titled band he founded in 1989. Th ...
, Dave Grohl
David Eric Grohl (; born January 14, 1969) is an American musician. He founded the rock band Foo Fighters, of which he is the lead singer, guitarist, principal songwriter, and only consistent member. From 1990 to 1994, he was the drummer of th ...
, Devo
Devo is an American new wave band from Akron, Ohio, formed in 1973. Their classic line-up consisted of two sets of brothers, the Mothersbaughs ( Mark and Bob) and the Casales (Gerald and Bob), along with Alan Myers. The band had a No. 14 ...
, Macy Gray
Natalie Renée McIntyre (born September 6, 1967), known professionally as Macy Gray, is an American contemporary R&B, R&B and soul music, soul singer and actress. She is known for her distinctive raspy voice and a singing style heavily influence ...
and The Isley Brothers
The Isley Brothers ( ) are an American soul group originally from Cincinnati, Ohio, that began as a vocal trio consisting of the brothers O'Kelly Isley Jr., Rudolph Isley and Ronald Isley in the 1950s. With a career spanning over seven decades, ...
.
Two Ohio astronauts
An astronaut (from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'star', and (), meaning 'sailor') is a person trained, equipped, and deployed by a List of human spaceflight programs, human spaceflight program to serve as a commander or crew member of a spa ...
completed significant milestones in the space race
The Space Race (, ) was a 20th-century competition between the Cold War rivals, the United States and the Soviet Union, to achieve superior spaceflight capability. It had its origins in the ballistic missile-based nuclear arms race between t ...
in the 1960s: John Glenn
John Herschel Glenn Jr. (July 18, 1921 – December 8, 2016) was an American Marine Corps aviator, astronaut, businessman, and politician. He was the third American in space and the first to orbit the Earth, circling it three times in 1 ...
becoming the first American to orbit the Earth, and Neil Armstrong
Neil Alden Armstrong (August 5, 1930 – August 25, 2012) was an American astronaut and aerospace engineering, aeronautical engineer who, in 1969, became the Apollo 11#Lunar surface operations, first person to walk on the Moon. He was al ...
becoming the first human to walk on the Moon. In 1967, Carl Stokes was elected mayor of Cleveland and became the first African American mayor of one of the nation's 10 most populous cities.
In 1970, an Ohio Army National Guard unit fired at students during an antiwar protest at Kent State University
Kent State University (KSU) is a Public university, public research university in Kent, Ohio, United States. The university includes seven regional campuses in Northeast Ohio located in Kent State University at Ashtabula, Ashtabula, Kent State ...
, killing four and wounding nine. The Guard had been called onto campus after several protests in and around campus became violent, including a riot in downtown Kent and the burning of an ROTC
The Reserve Officers' Training Corps (ROTC; or ) is a group of college- and university-based officer-training programs for training commissioned officers of the United States Armed Forces.
While ROTC graduate officers serve in all branches o ...
building. The main cause of the protests was the United States' invasion of Cambodia during the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (1 November 1955 – 30 April 1975) was an armed conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia fought between North Vietnam (Democratic Republic of Vietnam) and South Vietnam (Republic of Vietnam) and their allies. North Vietnam w ...
.
Ohio was an important state in the developing ties between the United States and the People's Republic of China in the late 1970s and early 1980s. Relations between the two countries normalized in 1979, during the second term of Ohio governor Jim Rhodes
James Allen Rhodes (September 13, 1909 – March 4, 2001) was an American attorney and Republican politician who served as the 61st and 63rd Governor of Ohio from 1963 to 1971 and from 1975 to 1983. Rhodes was one of only seven U.S. governors ...
. Rhodes sought to encourage economic ties, viewing China as a potential market for Ohio machinery exports. In July 1979, Rhodes led a State of Ohio Trade Mission to China. The trip resulted in developing economic ties, a sister state-province relationship with Hubei province
Hubei is a province in Central China. It has the seventh-largest economy among Chinese provinces, the second-largest within Central China, and the third-largest among inland provinces. Its provincial capital at Wuhan serves as a major politi ...
, long-running Chinese exhibitions at the Ohio State Fair
The Ohio State Fair is one of the largest state fairs in the United States, held in Columbus, Ohio during late July through early August. As estimated in a 2011 economic impact study conducted by Saperstein & Associates; the State Fair contribut ...
, and major academic exchanges between Ohio State University and Wuhan University
Wuhan University (WHU; 武汉大学) is a key comprehensive public university in Wuhan, Hubei, China. It is directly affiliated with and funded by the Ministry of Education of the People's Republic of China, Ministry of Education of China. The un ...
. Beginning in the 1980s, the state entered into international economic and resource cooperation treaties and organizations with other Midwestern
The Midwestern United States (also referred to as the Midwest, the Heartland or the American Midwest) is one of the four census regions defined by the United States Census Bureau. It occupies the northern central part of the United States. It ...
states, as well as New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
, Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
, and Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
, including the Great Lakes Charter
The Great Lakes Charter is a good-faith agreement among the governors of the U.S. states of Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania and Wisconsin, and the premiers of the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec. The c ...
, Great Lakes Compact
The Great Lakes–St. Lawrence River Basin Water Resources Compact is a legally binding interstate compact among the U.S. states of Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania and Wisconsin. The compact details how the ...
, and the Council of Great Lakes Governors.
21st century
Ohio's economy has undergone significant change in the 21st century, as the trend ofdeindustrialization
Deindustrialization is a process of social and economic change caused by the removal or reduction of industrial capacity or activity in a country or region, especially of heavy industry or manufacturing industry.
There are different interpr ...
has greatly impacted the American Midwest
The Midwestern United States (also referred to as the Midwest, the Heartland or the American Midwest) is one of the four List of regions of the United States, census regions defined by the United States Census Bureau. It occupies the northern c ...
and the Rust Belt
The Rust Belt, formerly the Steel Belt or Factory Belt, is an area of the United States that underwent substantial Deindustrialization, industrial decline in the late 20th century. The region is centered in the Great Lakes and Mid-Atlantic (Uni ...
. Manufacturing in the Midwest experienced a stark decline during the early 21st century, a trend that greatly impacted Ohio. From 1990 to 2019, it lost over 300,000 manufacturing jobs, but added over 1,000,000 non-manufacturing jobs. Coinciding with this decline, Ohio has seen a large decline in union membership: 17.4% of Ohioan workers were union members in 2000, while 12.8% were union members in 2022.
In the wake of these economic changes, Ohio's state government has looked to promoting new industries to offset manufacturing losses, such as the production of solar energy
Solar energy is the radiant energy from the Sun's sunlight, light and heat, which can be harnessed using a range of technologies such as solar electricity, solar thermal energy (including solar water heating) and solar architecture. It is a ...
and electric vehicle
An electric vehicle (EV) is a motor vehicle whose propulsion is powered fully or mostly by electricity. EVs encompass a wide range of transportation modes, including road vehicle, road and rail vehicles, electric boats and Submersible, submer ...
s. One major program the state government launched was the "Third Frontier" program, created during the governorship of Bob Taft
Robert Alphonso Taft III (born January 8, 1942) is an American politician and attorney who served as the 67th governor of Ohio from 1999 to 2007. A member of the Taft family, Taft political dynasty and Republican Party (United States), Republic ...
, which aimed to increase investment in Ohio and boost its technology sector. As of 2010, the Ohio Department of Development attributes the creation of 9,500 jobs to this program, with an average salary of $65,000, while having a $6.6 billion economic impact with a return on investment
Return on investment (ROI) or return on costs (ROC) is the ratio between net income (over a period) and investment (costs resulting from an investment of some resources at a point in time). A high ROI means the investment's gains compare favorab ...
of 9:1. In 2010 the state won the International Economic Development Council's Excellence in Economic Development Award, celebrated as a national model of success.
Ohio's economy was also heavily afflicted by the Great Recession
The Great Recession was a period of market decline in economies around the world that occurred from late 2007 to mid-2009.
, as the state's unemployment rate
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is the proportion of people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work d ...
rose from 5.6% in the first two months of 2008 up to a peak of 11.1% in December 2009 and January 2010. It took until August 2014 for the unemployment rate to return to 5.6%. From December 2007 to September 2010, Ohio lost 376,500 jobs. In 2009, Ohio had 89,053 foreclosures filings, a then-record for the state. The median household income dropped 7% from 2006–07 to 2008–09, and the poverty rate ballooned to 13.5% by 2009. By 2015, Ohio gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the total market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is often used to measure the economic performanc ...
was $608.1 billion, the seventh-largest economy among the 50 states.Ohio Facts 2016: Ohio's Economy Ranks 7th Largest Among States, Ohio Legislative Service Commission. In 2015, Ohio's total GDP accounted for 3.4% of U.S. GDP and 0.8% of world GDP. Politically, Ohio has been long regarded as a
swing state
In United States politics, a swing state (also known as battleground state, toss-up state, or purple state) is any state that could reasonably be won by either the Democratic or Republican candidate in a statewide election, most often refe ...
, but the success of many Republican candidates in Ohio since the late 2000s has led many to question whether Ohio remains an electoral battleground.
On March 9, 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
reached Ohio, with three cases reported. As of February 2023, over 41,600 Ohioans have died from COVID-19. Ohio's economy was also heavily impacted by the pandemic, as the state saw large job losses in 2020, as well as large amounts of subsequent stimulus spending.
Geography
Ohio River
The Ohio River () is a river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing in a southwesterly direction from Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, to its river mouth, mouth on the Mississippi Riv ...
. Ohio's neighbors are Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
to the east, Michigan
Michigan ( ) is a peninsular U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, Upper Midwestern United States. It shares water and land boundaries with Minnesota to the northwest, Wisconsin to the west, ...
to the northwest, Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( ) is the fourth-largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and also has the shortest avera ...
to the north, Indiana
Indiana ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Michigan to the northwest, Michigan to the north and northeast, Ohio to the east, the Ohio River and Kentucky to the s ...
to the west, Kentucky
Kentucky (, ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north, West Virginia to the ...
on the south, and West Virginia
West Virginia is a mountainous U.S. state, state in the Southern United States, Southern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States.The United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau and the Association of American ...
on the southeast. Ohio's borders were defined by metes and bounds
Metes and bounds is a system or method of describing land, real property (in contrast to personal property) or real estate. The system has been used in England for many centuries and is still used there in the definition of general boundaries. ...
in the Enabling Act of 1802
The Enabling Act of 1802 was passed on April 30, 1802 by the Seventh Congress of the United States. This act authorized the residents of the eastern portion of the Northwest Territory to form the state of Ohio and join the U.S. on an equal footi ...
as follows:
Ohio is bounded by the Ohio River, but nearly all of the river belongs to Kentucky and West Virginia. In 1980, the U.S. Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that turn on question ...
held that, based on the wording of the cessation of territory by Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
(which at the time included what is now Kentucky and West Virginia), the boundary between Ohio and Kentucky (and, by implication, West Virginia) is the northern low-water mark of the river as it existed in 1792. Ohio has only that portion of the river between the river's 1792 low-water mark and the present high-water mark. The border with Michigan has also changed, as a result of the Toledo War
The Toledo War (1835–1836), also known as the Michigan–Ohio War or Ohio–Michigan War, was a boundary dispute between the U.S. state of Ohio and the adjoining territory of Michigan over what is now known as the Toledo Strip. Control of th ...
, to angle slightly northeast to the north shore of the mouth of the Maumee River.
Much of Ohio features glaciated till plains, with an exceptionally flat area in the northwest being known as the Great Black Swamp
The Great Black Swamp (also known simply as the Black Swamp) was a glacier, glacially fed wetland in northwest Ohio and Northern Indiana, northeast Indiana, United States, that existed from the end of the Wisconsin glaciation until the late 19 ...
. This glaciated region in the northwest and central state is bordered to the east and southeast first by a belt known as the glaciated Allegheny Plateau
The Glaciated Allegheny Plateau is that portion of the Allegheny Plateau that lies within the area covered by the last glaciation. As a result, this area of the Allegheny Plateau has lower relief and gentler slopes than the relatively rugged Un ...
, and then by another belt known as the unglaciated Allegheny Plateau
The Unglaciated Allegheny Plateau is located in an arc around southeastern Ohio, West Virginia, into western Pennsylvania and a small portion of southwestern New York State.
This area is a dissected plateau, characterized by sandstone, shale, and ...
. Most of Ohio is of low relief, but the unglaciated Allegheny Plateau features rugged hills and forests.
Ohio's rugged southeastern quadrant, stretching in an outward bow-like arc along the Ohio River from the West Virginia Panhandle to the outskirts of Cincinnati, forms a distinct socioeconomic
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interac ...
unit. Geologically similar to parts of West Virginia and southwestern Pennsylvania, this area's coal mining legacy, dependence on small pockets of old manufacturing establishments, and distinctive regional dialect set this section off from the rest of the state. In 1965, Congress passed the Appalachian Regional Development Act The Appalachian Regional Development Act of 1965 established the Appalachian Regional Commission (ARC), which was tasked with overseeing economic development programs in the Appalachia region, as well as the construction of the Appalachian Developme ...
, an attempt to "address the persistent poverty and growing economic despair of the Appalachian Region". It defines 29 Ohio counties as part of Appalachia. While 1/3 of Ohio's land mass is part of the federally defined Appalachian region, only 12.8% of Ohioans live there (1.476 million people.)
Significant Ohio rivers include the Cuyahoga River
The Cuyahoga River (see ) is a river located in Northeast Ohio that bisects the City of Cleveland and feeds into Lake Erie.
As Cleveland emerged as a major manufacturing center, the river became heavily affected by industrial pollution, so mu ...
, Great Miami River
The Great Miami River (also called the Miami River) (Shawnee language, Shawnee: ''Msimiyamithiipi'') is a tributary of the Ohio River, approximately long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe Nat ...
, Maumee River
The Maumee River (pronounced ) (; ) is a river running in the Midwestern United States from northeastern Indiana into northwestern Ohio and Lake Erie. It is formed at the confluence of the St. Joseph River (Maumee River), St. Joseph and St. Mar ...
, Muskingum River
The Muskingum River ( ; ) is a tributary of the Ohio River, approximately long, in southeastern Ohio in the United States. An important commercial route in the 19th century, it flows generally southward through the eastern hill country of Ohio ...
, and Scioto River
The Scioto River ( ) is a river in central and southern Ohio more than in length. It rises in Hardin County, Ohio, Hardin County just north of Roundhead, Ohio, flows through Columbus, Ohio, where it collects its largest tributary, the Olent ...
. The rivers in northern Ohio drain into the northern Atlantic Ocean via Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( ) is the fourth-largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and also has the shortest avera ...
and the St. Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (, ) is a large international river in the middle latitudes of North America connecting the Great Lakes to the North Atlantic Ocean. Its waters flow in a northeasterly direction from Lake Ontario to the Gulf of St. Lawren ...
, and those in southern Ohio drain into the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico () is an oceanic basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, mostly surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north, and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southw ...
via the Ohio River
The Ohio River () is a river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing in a southwesterly direction from Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, to its river mouth, mouth on the Mississippi Riv ...
and the Mississippi
Mississippi ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Alabama to the east, the Gulf of Mexico to the south, Louisiana to the s ...
. Ohio also includes Bass Islands and Kelleys Island
Kelleys Island is both a village (United States)#Ohio, village in Erie County, Ohio, and the island which it fully occupies in Lake Erie. The island has a total area of and was formed by Glacier, glacial action on limestone and Dolomite (rock) ...
. Grand Lake St. Marys in the west-central part of the state was constructed as a supply of water for canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface ...
s in the canal-building era of 1820–1850. This body of water, over , was the largest artificial lake in the world when completed in 1845. Ohio's canal-building projects were not the economic fiasco that similar efforts were in other states. Some cities, such as Dayton, owe their industrial emergence to their location on canals, and as late as 1910 interior canals carried much of the bulk freight of the state.
Areas under the protection of the National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an List of federal agencies in the United States, agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government, within the US Department of the Interior. The service manages all List ...
include Cuyahoga Valley National Park
Cuyahoga Valley National Park is a List of national parks of the United States, national park of the United States in Ohio that reclaims and preserves the industrial, commercial, and rural landscape along the Cuyahoga River between Akron, Ohio, ...
, Hopewell Culture National Historical Park
Hopewell Culture National Historical Park is a United States national historical park with earthworks and burial mounds from the Hopewell culture, indigenous peoples who flourished from about 200 BC to 500 AD. The park is composed of four s ...
, Dayton Aviation Heritage National Historical Park
Dayton Aviation Heritage National Historical Park is a United States National Historical Park in Dayton, Ohio that commemorates three important historical figures— Wilbur Wright, Orville Wright, and poet Paul Laurence Dunbar—and ...
, First Ladies National Historic Site
First Ladies National Historic Site is a United States National Historic Site located in Canton, Ohio. During her residency in Washington, D.C. Mary Regula, wife of Ohio representative Ralph Regula, spoke regularly about the nation's first l ...
, James A. Garfield National Historic Site
James A. Garfield National Historic Site is a United States National Historic Site located in Mentor, Ohio. The site preserves the Lawnfield estate and surrounding property of James A. Garfield, the 20th president of the United States, and in ...
, William Howard Taft National Historic Site, and the Charles Young Buffalo Soldiers National Monument and Perry's Victory and International Peace Memorial.
Fauna
 Ohio has wide variety of unique animal species. Rare and endangered species include the Eastern Hellbender, which is found in the Southeastern Appalachian region of Ohio and is classified as state endangered. The Eastern Hellbender is the 3rd largest
Ohio has wide variety of unique animal species. Rare and endangered species include the Eastern Hellbender, which is found in the Southeastern Appalachian region of Ohio and is classified as state endangered. The Eastern Hellbender is the 3rd largest amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
in the world, and can grow up to 27 inches in length. It is fully aquatic and breathes almost entirely through its skin. Due to this, it is only found in pristine, cool, clear, fast flowing streams and rivers. It is highly threatened by habitat loss
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss or habitat reduction) occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved elsewhere, or are dead, leading to a decrease ...
, water pollution
Water pollution (or aquatic pollution) is the contamination of Body of water, water bodies, with a negative impact on their uses. It is usually a result of human activities. Water bodies include lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirs and ...
, and sedimentation
Sedimentation is the deposition of sediments. It takes place when particles in suspension settle out of the fluid in which they are entrained and come to rest against a barrier. This is due to their motion through the fluid in response to th ...
due to logging and other human activities.
Climate
The climate of Ohio is ahumid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers, and cold ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (te ...
''Dfa/Dfb'') throughout most of the state, except in the extreme southern counties of Ohio's Bluegrass region
The Bluegrass region is a geographic region in the U.S. state of Kentucky. It makes up the central and northern part of the state, roughly bounded by the cities of Frankfort, Kentucky, Frankfort, Paris, Kentucky, Paris, Richmond, Kentucky, Ric ...
section, which are located on the northern periphery of the humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a subtropical -temperate climate type, characterized by long and hot summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between ...
(''Cfa'') and Upland South
The Upland South and Upper South are two overlapping cultural and geographic subregions in the inland part of the Southern United States. They differ from the Deep South and Atlantic coastal plain by terrain, history, economics, demographics, a ...
region of the United States. Summers are typically hot and humid throughout the state, while winters generally range from cool to cold. Precipitation in Ohio is moderate year-round. Severe weather is not uncommon in the state, although there are typically fewer tornado
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with the surface of Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, although the ...
reports in Ohio than in states located in what is known as the Tornado Alley
Tornado Alley, also known as Tornado Valley, is a loosely defined location of the central United States and, in the 21st century, Canada where tornadoes are most frequent. The term was first used in 1952 as the title of a research project to st ...
. Severe lake effect snowstorms are also not uncommon on the southeast shore of Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( ) is the fourth-largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and also has the shortest avera ...
, which is located in an area designated as the Snowbelt
The Snowbelt, Snow Belt, Frostbelt, or Frost Belt is the region near the Great Lakes in North America where heavy snowfall in the form of lake-effect snow is particularly common. Snowbelts are typically found downwind of the lakes, principally off ...
.
Although predominantly not in a subtropical climate, some warmer-climate flora and fauna do reach well into Ohio. For instance, some trees with more southern ranges, such as the blackjack oak
''Quercus marilandica'', the blackjack oak, is a small oak, one of the red oak group ''Quercus'' sect. ''Lobatae''. It is native to the eastern and central United States.
Description
''Quercus marilandica'' is a small deciduous tree growing to ...
, ''Quercus marilandica'', are found at their northernmost in Ohio just north of the Ohio River. Also evidencing this climatic transition from a subtropical to a continental climate, several plants such as the Southern magnolia ''(Magnolia grandiflora
''Magnolia grandiflora'', commonly known as the southern magnolia or bull bay, is a tree of the family Magnoliaceae native to the Southeastern United States, from Virginia to central Florida, and west to East Texas. Reaching in height, it is a ...
)'', Albizia julibrissin
''Albizia julibrissin'', the Persian silk tree, pink silk tree, or mimosa tree, is a species of tree in the Fabaceae family, native to Western Asia, southwestern and East Asia, eastern Asia.
Taxonomy
It was introduced to Europe in the mid-18th ...
(mimosa), Crape Myrtle
''Lagerstroemia'' (), commonly known as crape myrtle (also spelled crepe myrtle or crêpe myrtle), is a genus of around 50 species of deciduous and evergreen trees and shrubs native to the Indian subcontinent, southeast Asia, northern Australia ...
, and even the occasional Needle Palm
''Rhapidophyllum hystrix'', the needle palm, is a palm native to coastal margins of the subtropical eastern Gulf and south Atlantic states of the United States. Populations can be found from coastal southeast South Carolina, southward to Florida ...
are hardy landscape materials regularly used as street, yard, and garden plantings in the Bluegrass region
The Bluegrass region is a geographic region in the U.S. state of Kentucky. It makes up the central and northern part of the state, roughly bounded by the cities of Frankfort, Kentucky, Frankfort, Paris, Kentucky, Paris, Richmond, Kentucky, Ric ...
of Ohio; but these same plants will simply not thrive in much of the rest of the state. This interesting change may be observed while traveling through Ohio on Interstate 75
Interstate 75 (I-75) is a major north–south Interstate Highway in the Great Lakes and Southeastern regions of the United States. As with most Interstates that end in 5, it is a major cross-country, north–south route, traveling from S ...
from Cincinnati
Cincinnati ( ; colloquially nicknamed Cincy) is a city in Hamilton County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. Settled in 1788, the city is located on the northern side of the confluence of the Licking River (Kentucky), Licking and Ohio Ri ...
to Toledo; the observant traveler of this diverse state may even catch a glimpse of Cincinnati's common wall lizard, one of the few examples of permanent "subtropical" fauna in Ohio.
The highest recorded temperature was , near Gallipolis
Gallipolis ( ) is a village in Gallia County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. It is located in Southeast Ohio along the Ohio River about southeast of Chillicothe and northwest of Charleston, West Virginia. The population was 3,313 ...
on July 21, 1934. The lowest recorded temperature was , at Milligan on February 10, 1899, during the Great Blizzard of 1899
The Great Blizzard of 1899, also known as the Great Arctic Outbreak of 1899 and the St. Valentine's Day Blizzard, was an exceptionally severe winter weather event that affected most of the United States, particularly east of the Rocky Mountain ...
.
The worst weather disaster in Ohio history occurred along the Great Miami River in 1913. Known as the Great Dayton Flood
The Great Dayton Flood of 1913, part of the Great Flood of 1913, resulted from flooding by the Great Miami River reaching Dayton, Ohio, and the surrounding area, causing the greatest natural disaster in Ohio history. In response, the Ohio Gener ...
, the entire Miami River watershed flooded, including the downtown business district of Dayton
Dayton () is a city in Montgomery County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of cities in Ohio, sixth-most populous city in Ohio, with a population of 137,644 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The Dayton metro ...
. As a result, the Miami Conservancy District
The Miami Conservancy District is a river management agency operating in Southwest Ohio to control flooding of the Great Miami River and its tributaries. It was organized in 1915 following the catastrophic Great Dayton Flood of the Great Miami R ...
was created as the first major floodplain engineering project in Ohio and the United States.
Although few have registered as noticeable to the average resident, more than 200 earthquakes with a magnitude
Magnitude may refer to:
Mathematics
*Euclidean vector, a quantity defined by both its magnitude and its direction
*Magnitude (mathematics), the relative size of an object
*Norm (mathematics), a term for the size or length of a vector
*Order of ...
of 2.0 or higher have occurred in Ohio since 1776. The Western Ohio Seismic Zone and a portion of the Southern Great Lakes Seismic Zone are located in the state, and numerous faults lie under the surface.
The most substantial known earthquake in Ohio history was the Anna (Shelby County) earthquake, which occurred on March 9, 1937. It was centered in western Ohio, with a magnitude of 5.4, and was of intensity
Intensity may refer to:
In colloquial use
* Strength (disambiguation)
*Amplitude
* Level (disambiguation)
* Magnitude (disambiguation)
In physical sciences
Physics
*Intensity (physics), power per unit area (W/m2)
*Field strength of electric, m ...
VIII. Other significant earthquakes in Ohio include: one of magnitude 4.8 near Lima
Lima ( ; ), founded in 1535 as the Ciudad de los Reyes (, Spanish for "City of Biblical Magi, Kings"), is the capital and largest city of Peru. It is located in the valleys of the Chillón River, Chillón, Rímac River, Rímac and Lurín Rive ...
on September 19, 1884; one of magnitude 4.2 near Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port city status in the United Kingdom, city and unitary authority in Hampshire, England. Most of Portsmouth is located on Portsea Island, off the south coast of England in the Solent, making Portsmouth the only city in En ...
on May 17, 1901; and one of 5.0 in LeRoy Township in Lake County on January 31, 1986, which continued to trigger 13 aftershocks of magnitude 0.5 to 2.4 for two months.
Notable Ohio earthquakes in the 21st century include one occurring on December 31, 2011, approximately northwest of Youngstown
Youngstown is a city in Mahoning County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of municipalities in Ohio, 11th-most populous city in Ohio with a population of 60,068 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The Mahoning ...
, and one occurring on June 10, 2019, approximately north-northwest of Eastlake under Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( ) is the fourth-largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and also has the shortest avera ...
; both registered a 4.0 magnitude.
Cities
There are 13 metropolitan statistical areas in Ohio, anchored by 16 cities, as defined by the U.S.Office of Management and Budget
The Office of Management and Budget (OMB) is the largest office within the Executive Office of the President of the United States (EOP). The office's most prominent function is to produce the president's budget, while it also examines agency pro ...
. Additionally, 30 Ohio cities function as centers of micropolitan statistical areas, urban clusters smaller than that of metropolitan areas. Ohio's three largest cities are Columbus, Cleveland
Cleveland is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County. Located along the southern shore of Lake Erie, it is situated across the Canada–U.S. maritime border and approximately west of the Ohio-Pennsylvania st ...
, and Cincinnati
Cincinnati ( ; colloquially nicknamed Cincy) is a city in Hamilton County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. Settled in 1788, the city is located on the northern side of the confluence of the Licking River (Kentucky), Licking and Ohio Ri ...
.
Columbus is the capital of the state, near its geographic center, and is well known for Ohio State University
The Ohio State University (Ohio State or OSU) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Columbus, Ohio, United States. A member of the University System of Ohio, it was founded in 1870. It is one ...
. In 2019, the city had six corporations named to the U.S. Fortune 500 list: Alliance Data, Nationwide Mutual Insurance Company
Nationwide Mutual Insurance Company and affiliated companies, commonly shortened to Nationwide, is a group of large U.S. insurance and financial services companies based in Columbus, Ohio. The company also operates regional headquarters in ...
, American Electric Power
American Electric Power Company, Inc. (AEP), (railcar reporting mark: AEPX) is an American domestic electric utility company in the United States. It is one of the largest electric utility companies in the country, with more than five mi ...
, L Brands
Bath & Body Works, Inc. (formerly known as L Brands, Inc., Limited Brands, Inc. and The Limited, Inc.) is an American specialty retail company based in Columbus, Ohio. It owns Bath & Body Works, posted $7.4 billion in revenue in 2023, and was ...
, Huntington Bancshares
Huntington Bancshares Incorporated is an American bank holding company headquartered in Columbus, Ohio. Its banking subsidiary, The Huntington National Bank, operates 1047 banking offices, primarily in the Midwest: 459 in Ohio, 290 in Michigan, ...
, and Cardinal Health
Cardinal Health, Inc. is an American multinational health care services company, and the 14th highest revenue generating company in the United States. Headquartered in Dublin, Ohio, the company specializes in the distribution of pharmaceuticals ...
in suburban Dublin
Dublin is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. Situated on Dublin Bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, and is bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, pa ...
. Other major employers include hospitals (among others, Wexner Medical Center and Nationwide Children's Hospital
Nationwide Children's Hospital (formerly Columbus Children's Hospital) is a nationally ranked pediatric acute care teaching hospital located in the Southern Orchards neighborhood of Columbus, Ohio. The hospital has 673 pediatric beds and is aff ...
), high tech research and development including the Battelle Memorial Institute
Battelle Memorial Institute (or simply Battelle) is an American private nonprofit applied science and technology development company headquartered in Columbus, Ohio.
History
The institute was founded in 1929 by Gordon Battelle. Originall ...
, information-based companies such as OCLC
OCLC, Inc. See also: is an American nonprofit cooperative organization "that provides shared technology services, original research, and community programs for its membership and the library community at large". It was founded in 1967 as the ...
and Chemical Abstracts Service
Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS) is a division of the American Chemical Society. It is a source of chemical information and is located in Columbus, Ohio, United States.
Print periodicals
''Chemical Abstracts'' is a periodical index that provid ...
, manufacturer Worthington Industries
Worthington Enterprises, Inc. (formerly Worthington Industries) is an industrial manufacturing company headquartered in Columbus, Ohio. The company is composed of two business segments, Consumer Products and Building Products. Within these segm ...
, and financial institutions such as JPMorgan Chase
JPMorgan Chase & Co. (stylized as JPMorganChase) is an American multinational financial services, finance corporation headquartered in New York City and incorporated in Delaware. It is List of largest banks in the United States, the largest ba ...
and Huntington Bancshares
Huntington Bancshares Incorporated is an American bank holding company headquartered in Columbus, Ohio. Its banking subsidiary, The Huntington National Bank, operates 1047 banking offices, primarily in the Midwest: 459 in Ohio, 290 in Michigan, ...
. Fast food chains Wendy's
Wendy's International, LLC, is an American international fast food restaurant chain founded by Dave Thomas (businessman), Dave Thomas on November 15, 1969, in Columbus, Ohio. Its headquarters moved to Dublin, Ohio, on January 29, 2006. As of D ...
and White Castle are also headquartered in Columbus.
Located in Northeast Ohio
Northeast Ohio is a geographic and Cultural area, cultural region that comprises the northeastern counties of the U.S. state of Ohio. Definitions of the region consist of 16 to 23 counties between the southern shore of Lake Erie and the foothills ...
along the Lake Erie shore, Cleveland is characterized by its New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
heritage, ethnic immigrant cultures, and history as a major American manufacturing and healthcare center. It anchors the Cleveland–Akron–Canton Combined Statistical Area, of which the industrial cities of Akron
Akron () is a city in Summit County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. It is the fifth-most populous city in Ohio, with a population of 190,469 at the 2020 census. The Akron metropolitan area, covering Summit and Portage counties, had ...
and Canton are constituent parts. Mansfield
Mansfield is a market town and the administrative centre of the Mansfield District in Nottinghamshire, England. It is the largest town in the wider Mansfield Urban Area and the second largest settlement in Nottinghamshire (following the city ...
, Sandusky and Youngstown
Youngstown is a city in Mahoning County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of municipalities in Ohio, 11th-most populous city in Ohio with a population of 60,068 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The Mahoning ...
are also major cities in the region. Northeast Ohio is known for major industrial companies Goodyear Tire and Rubber and Timken, top-ranked colleges Case Western Reserve University
Case Western Reserve University (CWRU) is a Private university, private research university in Cleveland, Ohio, United States. It was established in 1967 by a merger between Western Reserve University and the Case Institute of Technology. Case ...
, Oberlin College
Oberlin College is a Private university, private Liberal arts colleges in the United States, liberal arts college and conservatory of music in Oberlin, Ohio, United States. Founded in 1833, it is the oldest Mixed-sex education, coeducational lib ...
, and Kent State University
Kent State University (KSU) is a Public university, public research university in Kent, Ohio, United States. The university includes seven regional campuses in Northeast Ohio located in Kent State University at Ashtabula, Ashtabula, Kent State ...
, the Cleveland Clinic
Cleveland Clinic is an American Nonprofit organization, nonprofit Academic health science center, academic Medical centers in the United States, medical center based in Cleveland, Ohio. Owned and operated by the Cleveland Clinic Foundation, an O ...
, and cultural attractions including the Cleveland Museum of Art
The Cleveland Museum of Art (CMA) is an art museum in Cleveland, Ohio, United States. Located in the Wade Park District of University Circle, the museum is internationally renowned for its substantial holdings of Asian art, Asian and Art of anc ...
, Big Five member Cleveland Orchestra
The Cleveland Orchestra is an American orchestra based in Cleveland, Ohio. Founded in 1918 by the pianist and impresario Adella Prentiss Hughes, the orchestra is one of the five American orchestras informally referred to as the " Big Five". T ...
, Cuyahoga Valley National Park
Cuyahoga Valley National Park is a List of national parks of the United States, national park of the United States in Ohio that reclaims and preserves the industrial, commercial, and rural landscape along the Cuyahoga River between Akron, Ohio, ...
, Playhouse Square
Playhouse Square is a theater district in downtown Cleveland, Ohio, United States. It is the largest performing arts center in the US outside of New York City (only Lincoln Center is larger). Constructed in a span of 19 months in the early 1920s ...
, the Pro Football Hall of Fame
The Pro Football Hall of Fame is the hall of fame for professional football (gridiron), professional American football, located in Canton, Ohio. Opened on September 7, 1963, the Hall of Fame enshrines exceptional figures in the sport of profes ...
, and the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame
The Rock and Roll Hall of Fame (RRHOF), also simply referred to as the Rock Hall, is a museum and hall of fame located in downtown Cleveland, Ohio, United States, on the shore of Lake Erie. The museum documents the history of rock music and the ...
.
Cincinnati
Cincinnati ( ; colloquially nicknamed Cincy) is a city in Hamilton County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. Settled in 1788, the city is located on the northern side of the confluence of the Licking River (Kentucky), Licking and Ohio Ri ...
anchors Southwest Ohio and the Cincinnati metropolitan area
The Cincinnati metropolitan area (also known as the Cincinnati Tri-State area or Greater Cincinnati) is a metropolitan area with its Urban area, core in Ohio and Kentucky. Its largest city is Cincinnati and includes surrounding counties in the U. ...
, which also encompasses counties in Kentucky and Indiana. The metropolitan area is home to Miami University
Miami University (informally Miami of Ohio or simply Miami) is a public university, public research university in Oxford, Ohio, United States. Founded in 1809, it is the second-oldest List of colleges and universities in Ohio, university in Ohi ...
and the University of Cincinnati
The University of Cincinnati (UC or Cincinnati, informally Cincy) is a public university, public research university in Cincinnati, Ohio, United States. It was founded in 1819 and had an enrollment of over 53,000 students in 2024, making it the ...
, Cincinnati Union Terminal
Cincinnati Union Terminal is an intercity train station and museum center in the Queensgate, Cincinnati, Queensgate neighborhood of Cincinnati, Ohio. Commonly abbreviated as CUT, or by its Amtrak station code, CIN, the Railroad terminal, termin ...
, Cincinnati Symphony Orchestra
The Cincinnati Symphony Orchestra is an American orchestra based in Cincinnati, Ohio. Its primary concert venue is Music Hall. In addition to its symphony concerts, the orchestra gives pops concerts as the Cincinnati Pops Orchestra. The Cinc ...
, and various Fortune 500 companies, including Procter & Gamble
The Procter & Gamble Company (P&G) is an American multinational consumer goods corporation headquartered in Cincinnati, Ohio. It was founded in 1837 by William Procter and James Gamble. It specializes in a wide range of personal health/con ...
, Kroger
The Kroger Company, or simply Kroger, is an American retail company that operates (either directly or through its subsidiaries) supermarkets and multi-department stores throughout the United States.
Founded by Bernard Kroger in 1883 in Cinc ...
, Macy's, Inc., and Fifth Third Bank
Fifth Third Bancorp is a bank holding company headquartered in Cincinnati, Ohio. It is the parent company of Fifth Third Bank (5/3 Bank), which operates 1,100 branches and 2,400 automated teller machines, which are located in 11 states: Oh ...
. Dayton
Dayton () is a city in Montgomery County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of cities in Ohio, sixth-most populous city in Ohio, with a population of 137,644 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The Dayton metro ...
and Springfield are in the Miami Valley, which is home to the University of Dayton
The University of Dayton (UD) is a Private university, private, Catholic research university in Dayton, Ohio, United States. Founded in 1850 by the Society of Mary (Marianists), Society of Mary, it is one of three Marianist universities in the U ...
, the Dayton Ballet, and the extensive Wright-Patterson Air Force Base
Wright-Patterson Air Force Base (WPAFB) is a United States Air Force base and census-designated place just east of Dayton, Ohio, in Greene County, Ohio, Greene and Montgomery County, Ohio, Montgomery counties. It includes both Wright and Patte ...
.
Toledo and Lima
Lima ( ; ), founded in 1535 as the Ciudad de los Reyes (, Spanish for "City of Biblical Magi, Kings"), is the capital and largest city of Peru. It is located in the valleys of the Chillón River, Chillón, Rímac River, Rímac and Lurín Rive ...
are the major cities in Northwest Ohio, an area known for its glass-making industry. It is home to Owens Corning
Owens Corning is an American company that develops and produces insulation, roofing, and fiberglass composites and related products. It is the world's largest manufacturer of fiberglass composites. It was formed in 1935 as a partnership between ...
and Owens-Illinois
O-I Glass, Inc. is an American company that specializes in container glass products. It is the largest manufacturer of glass containers in North America, South America, Asia-Pacific and Europe (after acquiring BSN Glasspack in 2004).
Company ...
, two Fortune 500
The ''Fortune'' 500 is an annual list compiled and published by ''Fortune (magazine), Fortune'' magazine that ranks 500 of the largest United States Joint-stock company#Closely held corporations and publicly traded corporations, corporations by ...
corporations.
Steubenville
Steubenville ( ) is a city in Jefferson County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. Located along the Ohio River west of Pittsburgh, it had a population of 18,161 at the 2020 census. The Weirton–Steubenville metropolitan area has an es ...
is the only metropolitan city in Appalachian Ohio
Appalachian Ohio is a bioregion and political unit in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of Ohio, characterized by the western foothills of the Appalachian Mountains and the Appalachian Plateau. The Appalachian Regional Commission defines th ...
, a region known for its mixed mesophytic forests. Other metropolitan areas that contain cities in Ohio but are primarily in other states include the Huntington, West Virginia
Huntington is a city in Cabell County, West Virginia, Cabell and Wayne County, West Virginia, Wayne counties in the U.S. state of West Virginia. The County seat, seat of Cabell County, the city is located at the confluence of the Ohio River, O ...
and Wheeling, West Virginia
Wheeling is a city in Ohio County, West Virginia, Ohio and Marshall County, West Virginia, Marshall counties in the U.S. state of West Virginia. The county seat of Ohio County, it lies along the Ohio River in the foothills of the Appalachian Mo ...
areas. Ohio is the US state with the highest number of cities with the same name as UK cities.
Demographics
Population
From just over 45,000 residents in 1800, Ohio's population grew faster than 10% per decade (except for the 1940 census) until the 1970 census, which recorded just over 10.65 million Ohioans. Growth then slowed for the next four decades. TheUnited States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the Federal statistical system, U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and American economy, econ ...
counted 11,808,848 in the 2020 census, a 2.4% increase since the 2010 United States census. Ohio's population growth lags that of the entire United States, and whites
White is a racial classification of people generally used for those of predominantly European ancestry. It is also a skin color specifier, although the definition can vary depending on context, nationality, ethnicity and point of view.
De ...
are found in a greater density than the U.S. average. , Ohio's center of population
In Demography, demographics, the center of population (or population center) of a region is a geographical point that describes a centerpoint of the region's population. There are several ways of defining such a "center point", leading to dif ...
is located in Morrow County, in the county seat
A county seat is an administrative center, seat of government, or capital city of a county or parish (administrative division), civil parish. The term is in use in five countries: Canada, China, Hungary, Romania, and the United States. An equiva ...
of Mount Gilead. This is approximately south and west of Ohio's population center in 1990.
Population growth by county in Ohio between the 2010 and 2020 censuses.
As of 2011, 27.6% of Ohio's children under the age of 1 belonged to minority groups. Approximately 6.2% of Ohio's population was under five years of age, 23.7% under 18 years of age, and 14.1% were 65 or older; females made up an estimated 51.2% of the population.
According to HUD's 2022 Annual Homeless Assessment Report, there were an estimated 10,654 homeless
Homelessness, also known as houselessness or being unhoused or unsheltered, is the condition of lacking stable, safe, and functional housing. It includes living on the streets, moving between temporary accommodation with family or friends, liv ...
people in Ohio.
Birth data
''Note: Births in table do not add up because Hispanics are counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.'' * Since 2016, data for births ofWhite Hispanic
White Hispanic and Latin Americans, also called Euro-Hispanics, Euro-Latinos, White Hispanics, or White Latinos, are Americans who self-identify as white of European (diaspora) or West Asian descent with origins from Hispanic countries or Lat ...
origin are not collected, but included in one ''Hispanic'' group; persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race.
Ancestry
 In 2010, there were 469,700 foreign-born residents in Ohio, corresponding to 4.1% of the total population. Of these, 229,049 (2.0%) were naturalized U.S. citizens and 240,699 (2.1%) were not. The largest groups were: Mexico (54,166), India (50,256), China (34,901), Germany (19,219), Philippines (16,410), United Kingdom (15,917), Canada (14,223), Russia (11,763), South Korea (11,307), and Ukraine (10,681). Though predominantly white, Ohio has large black populations in all major metropolitan areas throughout the state, Ohio has a significant Hispanic population made up of Mexicans in Toledo and Columbus, and Puerto Ricans in Cleveland and Columbus, and also has a significant and diverse Asian population in Columbus.
Ancestry groups (which the census defines as not including racial terms) in the state were: 26.5%
In 2010, there were 469,700 foreign-born residents in Ohio, corresponding to 4.1% of the total population. Of these, 229,049 (2.0%) were naturalized U.S. citizens and 240,699 (2.1%) were not. The largest groups were: Mexico (54,166), India (50,256), China (34,901), Germany (19,219), Philippines (16,410), United Kingdom (15,917), Canada (14,223), Russia (11,763), South Korea (11,307), and Ukraine (10,681). Though predominantly white, Ohio has large black populations in all major metropolitan areas throughout the state, Ohio has a significant Hispanic population made up of Mexicans in Toledo and Columbus, and Puerto Ricans in Cleveland and Columbus, and also has a significant and diverse Asian population in Columbus.
Ancestry groups (which the census defines as not including racial terms) in the state were: 26.5% German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
, 14.1% Irish, 9.0% English, 6.4% Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
, 3.8% Polish, 2.5% French, 1.9% Scottish
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including:
*Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland
*Scottish English
*Scottish national identity, the Scottish ide ...
, 1.7% Hungarian, 1.6% Dutch, 1.5% Mexican, 1.2% Slovak, 1.1% Welsh, and 1.1% Scotch-Irish. Ancestries claimed by less than 1% of the population include Sub-Saharan African
Sub-Saharan Africa is the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lie south of the Sahara. These include Central Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa, and West Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the list of sovereign states and ...
, Puerto Rican, Swiss
Swiss most commonly refers to:
* the adjectival form of Switzerland
* Swiss people
Swiss may also refer to: Places
* Swiss, Missouri
* Swiss, North Carolina
* Swiss, West Virginia
* Swiss, Wisconsin
Other uses
* Swiss Café, an old café located ...
, Swedish, Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
, Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
, Norwegian, Romanian
Romanian may refer to:
*anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Romania
**Romanians, an ethnic group
**Romanian language, a Romance language
***Romanian dialects, variants of the Romanian language
**Romanian cuisine, traditional ...
, Austrian, Lithuanian, Finnish, West Indian
A West Indian is a native or inhabitant of the West Indies (the Antilles and the Lucayan Archipelago). According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED''), the term ''West Indian'' in 1597 described the indigenous inhabitants of the West In ...
, Portuguese and Slovene.
Languages
 About 6.7% of the population age 5 years and older reported speaking a language other than English, with 2.2% of the population speaking Spanish, 2.6% speaking other Indo-European languages, 1.1% speaking Asian and Austronesian languages, and 0.8% speaking other languages. Numerically: 10,100,586 spoke English, 239,229
About 6.7% of the population age 5 years and older reported speaking a language other than English, with 2.2% of the population speaking Spanish, 2.6% speaking other Indo-European languages, 1.1% speaking Asian and Austronesian languages, and 0.8% speaking other languages. Numerically: 10,100,586 spoke English, 239,229 Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
**Spanish history
**Spanish culture
...
, 55,970 German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
, 38,990 Chinese, 33,125 Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
, and 32,019 French. In addition, 59,881 spoke a Slavic language
The Slavic languages, also known as the Slavonic languages, are Indo-European languages spoken primarily by the Slavic peoples and their descendants. They are thought to descend from a proto-language called Proto-Slavic, spoken during the Ear ...
and 42,673 spoke another West Germanic language
The West Germanic languages constitute the largest of the three branches of the Germanic family of languages (the others being the North Germanic and the extinct East Germanic languages). The West Germanic branch is classically subdivided ...
according to the 2010 census. Ohio also had the nation's largest population of Slovene speakers, second largest of Slovak speakers, second largest of Pennsylvania Dutch (German) speakers, and the third largest of Serbian speakers.
Religion
According toPublic Religion Research Institute
The Public Religion Research Institute (PRRI) is an American nonprofit, nonpartisan research and education organization that conducts public opinion polls on a variety of topics, specializing in the quantitative and qualitative study of politic ...
's 2021 ''American Values Survey'', 64% of Ohioans identified as Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
. Specifically, 19% of Ohio's population identified as Mainline Protestant
The mainline Protestants (sometimes also known as oldline Protestants) are a group of Protestantism in the United States, Protestant denominations in the United States and Protestantism in Canada, Canada largely of the Liberal Christianity, theolo ...
, 17% as Evangelical Protestant
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide, interdenominational movement within Protestant Christianity that emphasizes evangelism, or the preaching and spreading of the Christian ...
, 7% as Historically Black Protestant, and 18% as Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
. Roughly 30% of the population were unaffiliated with any religious body. Small minorities of Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
(2%), Hindus
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
(1%), Jehovah's Witnesses
Jehovah's Witnesses is a Christian denomination that is an outgrowth of the Bible Student movement founded by Charles Taze Russell in the nineteenth century. The denomination is nontrinitarian, millenarian, and restorationist. Russell co-fou ...
(<1%), Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
(<1%), Buddhists
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or 5th century BCE. It is the world's fourth ...
(<1%), Mormons
Mormons are a Religious denomination, religious and ethnocultural group, cultural group related to Mormonism, the principal branch of the Latter Day Saint movement started by Joseph Smith in upstate New York during the 1820s. After Smith's d ...
(<1%), and other faiths exist according to this study. Altogether, those identifying with a religion or spiritual tradition were 70% of the state's population.
Per the Association of Religion Data Archives
The Association of Religion Data Archives (ARDA) is a free source of online information related to American and international religion. One of the primary goals of the archive is to democratize access to academic information on religion by making t ...
's (ARDA) 2020 study, Christianity remained the predominant religion. Non-denominational Christianity
Non-denominational Christianity (or nondenominational Christianity) consists of churches, and individual Christians, which typically distance themselves from the confessionalism or creedalism of other Christian communities by not formally align ...
, numbering 1,411,863, were the largest Protestant cohort, although Catholicism remained the single-largest denomination with 1,820,233 adherents. According to the ARDA, in 2010 the largest Christian denominations by adherents were the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
with 1,992,567; the United Methodist Church
The United Methodist Church (UMC) is a worldwide mainline Protestant Christian denomination, denomination based in the United States, and a major part of Methodism. In the 19th century, its main predecessor, the Methodist Episcopal Church, was ...
with 496,232; the Evangelical Lutheran Church in America
The Evangelical Lutheran Church in America (ELCA) is a mainline Protestant church headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. The ELCA was officially formed on January 1, 1988, by the merging of three Lutheran church bodies. As of December 31, 2023, it ...
with 223,253, the Southern Baptist Convention
The Southern Baptist Convention (SBC), alternatively the Great Commission Baptists (GCB), is a Christian denomination based in the United States. It is the world's largest Baptist organization, the largest Protestant, and the second-largest Chr ...
with 171,000, the Christian Churches and Churches of Christ with 141,311, the United Church of Christ
The United Church of Christ (UCC) is a socially liberal mainline Protestant Christian denomination based in the United States, with historical and confessional roots in the Congregational, Restorationist, Continental Reformed, and Lutheran t ...
with 118,000, and the Presbyterian Church (USA)
The Presbyterian Church (USA), abbreviated PCUSA, is a mainline Protestant Christian denomination, denomination in the Religion in the United States, United States. It is the largest Presbyterian denomination in the United States too. Its th ...
with 110,000. With about 80,000 adherents in 2020, Ohio had the second largest Amish population of all U.S. states, only behind neighboring Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
.
According to a Pew Forum
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It als ...
poll in 2014, a majority of Ohioans, 56%, felt religion was "very important", 25% that it was "somewhat important", and 19% that religion was "not too important/not important at all". Among them, 38% of Ohioans indicate that they attend religious services at least once weekly, 32% occasionally, and 30% seldom or never.
Economy
 According to the
According to the U.S. Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The U.S. Census Bureau is part of the U ...
, the total number of people employed in 2016 was 4,790,178. The total number of unique employer establishments was 252,201, while the total number of non-employer establishments was 785,833. In 2010, Ohio was ranked second in the country for best business climate by Site Selection magazine, based on a business-activity database. The state has also won three consecutive Governor's Cup awards from the magazine, based on business growth and developments. Ohio's gross domestic product (GDP) was $626 billion in 2016. This ranks Ohio's economy as the seventh-largest among all 50 states and Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
Ohio's unemployment rate
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is the proportion of people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work d ...
stands at 4.5% as of February 2018, down from 10.7% in May 2010. The state still lacks 45,000 jobs compared to the pre-recession
In economics, a recession is a business cycle contraction that occurs when there is a period of broad decline in economic activity. Recessions generally occur when there is a widespread drop in spending (an adverse demand shock). This may be tr ...
numbers of 2007.Olivera Perkins (May 22, 2015Ohio's unemployment rate up to 5.2 percent: 5 things you need to know
Cleveland.com. The labor force participation as of April 2015 is 63%, slightly above the national average. , Ohio's per capita income was $60,402, ranking 38th in the U.S., and the state's
median household income
The median income is the income amount that divides a population into two groups, half having an income above that amount, and half having an income below that amount. It may differ from the mean (or average) income. Both of these are ways of und ...
was $65,720. Also in 2023, 13.4% of the population was living below the poverty line.
The manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of the
secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer ...
and financial activities sectors each compose 18.3% of Ohio's GDP, making them Ohio's largest industries by percentage of GDP. Ohio has the third largest manufacturing workforce behind California and Texas. Ohio has the largest bioscience sector in the Midwest, and is a national leader in the "green" economy. Ohio is the largest producer in the country of plastics, rubber, fabricated metals, electrical equipment, and appliances. 5,212,000 Ohioans are currently employed by wage or salary.
By employment, Ohio's largest sector is trade/transportation/utilities, which employs 1,010,000 Ohioans, or 19.4% of Ohio's workforce, while the health care
Health care, or healthcare, is the improvement or maintenance of health via the preventive healthcare, prevention, diagnosis, therapy, treatment, wikt:amelioration, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other disability, physic ...
and education sector employs 825,000 Ohioans (15.8%). Government employs 787,000 Ohioans (15.1%), manufacturing employs 669,000 Ohioans (12.9%), and professional and technical services employs 638,000 Ohioans (12.2%). Ohio's manufacturing sector is the third-largest of all fifty United States states in terms of gross domestic product. Fifty-nine of the United States' top 1,000 publicly traded companies (by revenue in 2008) are headquartered in Ohio, including Procter & Gamble
The Procter & Gamble Company (P&G) is an American multinational consumer goods corporation headquartered in Cincinnati, Ohio. It was founded in 1837 by William Procter and James Gamble. It specializes in a wide range of personal health/con ...
, Goodyear Tire & Rubber, AK Steel, Timken, Abercrombie & Fitch
Abercrombie & Fitch Co. (A&F) is an American lifestyle store, lifestyle retailer, founded in 1892 which focuses on contemporary clothing targeting customers in their early 20's to mid 40's. Headquartered in New Albany, Ohio, the company operate ...
, and Wendy's
Wendy's International, LLC, is an American international fast food restaurant chain founded by Dave Thomas (businessman), Dave Thomas on November 15, 1969, in Columbus, Ohio. Its headquarters moved to Dublin, Ohio, on January 29, 2006. As of D ...
.
Ohio is also one of 41 states with its own lottery, the Ohio Lottery
The Ohio Lottery is a state lottery run by the Ohio Lottery Commission. Its games consist of scratch tickets; Pick 3, Pick 4, Pick 5 ("numbers games"); Rolling Cash 5, Classic Lotto, Keno, Lucky for Life, Mega Millions, and Powerball.
The Lotter ...
. , the Ohio Lottery has contributed more than $26 billion to education beginning in 1974.
Income inequality
In economics, income distribution covers how a country's total GDP is distributed amongst its population. Economic theory and economic policy have long seen income and its distribution as a central concern. Unequal distribution of income causes ...
in Ohio, both before and after taxes, has risen significantly since the 1970s. Ohio's overall income grew in Ohio from 2009 to 2012, with an overall 7.1% increase in income growth. The top 1% had a 37.0% in income growth, while the bottom 99% grew their income by only 2.3%. The top 1% accounted for 71.9% of the overall shared income during this period. The burden of income tax
An income tax is a tax imposed on individuals or entities (taxpayers) in respect of the income or profits earned by them (commonly called taxable income). Income tax generally is computed as the product of a tax rate times the taxable income. Tax ...
falls disproportionately on lower-income tax bracket
Tax brackets are the divisions at which tax rates change in a progressive tax system (or an explicitly regressive tax system, though that is rarer). Essentially, tax brackets are the cutoff values for taxable income—income past a certain poin ...
s. In 2018, the bottom 20% of earners contributed 12.3% of their income towards various taxes, while the top 1% only paid 6.5%.
Culture
Art
 Ohio is home to 30 art institutions, including the Columbus Museum of Art, Cincinnati Art Museum, Cleveland Museum of Art, and other entities. The full list includes:
*
Ohio is home to 30 art institutions, including the Columbus Museum of Art, Cincinnati Art Museum, Cleveland Museum of Art, and other entities. The full list includes:
* Akron Art Museum
The Akron Art Museum is an art museum in Akron, Ohio, United States.
The museum first opened on February 1, 1922, as the Akron Art Institute. It was located in two borrowed rooms in the basement of the public library. The Institute offered clas ...
, Akron
* Allen Memorial Art Museum
The Allen Memorial Art Museum (AMAM) is an art museum located in Oberlin, Ohio, and it is run by Oberlin College. Founded in 1917, the collection contains over 15,000 works of art.
Overview
The AMAM is primarily a teaching museum and is aimed at ...
, Oberlin College
* Billy Ireland Cartoon Library & Museum
The Billy Ireland Cartoon Library & Museum is a research library of American cartoons and comic art affiliated with the Ohio State University library system in Columbus, Ohio. Formerly known as the Cartoon Research Library and the Cartoon Libra ...
, Ohio State University
* Burchfield Homestead, Salem
* Butler Institute of American Art, Youngstown
* Canton Museum of Art, Canton
* Cincinnati Art Museum
The Cincinnati Art Museum is an art museum in the Eden Park neighborhood of Cincinnati, Ohio. Founded in 1881, it was the first purpose-built art museum west of the Alleghenies, and is one of the oldest in the United States. Its collection of ...
, Cincinnati
* Cleveland Museum of Art
The Cleveland Museum of Art (CMA) is an art museum in Cleveland, Ohio, United States. Located in the Wade Park District of University Circle, the museum is internationally renowned for its substantial holdings of Asian art, Asian and Art of anc ...
, Cleveland
* Columbus Museum of Art
The Columbus Museum of Art (CMA) is an art museum in downtown Columbus, Ohio. Formed in 1878 as the Columbus Gallery of Fine Arts (its name until 1978), it was the first art museum to register its charter with the state of Ohio. The museum collec ...
, Columbus
* Contemporary Arts Center, Cincinnati
* Dayton Art Institute
The Dayton Art Institute (DAI) is a museum of fine arts in Dayton, Ohio, Dayton, Ohio, United States. The Dayton Art Institute has been rated one of the top 10 best art museums in the United States for children. The museum also ranks in the top 3% ...
, Dayton
* Frank Museum of Art, Otterbein University
* National Imperial Glass Museum, Bellaire
* Kennedy Museum of Art, Ohio University
* Temple Museum of Religious Art, Case Western Reserve University
* Mansfield Art Center, Mansfield
* McDonough Museum of Art, Youngstown State University
* Richard and Carole Cocks Art Museum, Miami University
* Museum of Ceramics, East Liverpool
* Museum of Contemporary Art Cleveland, Cleveland
* Ohio Glass Museum, Lancaster
* Richard Ross Museum of Art, Ohio Wesleyan University
* Springfield Center for the Arts at Wittenberg University, Wittenberg University
* Taft Museum of Art, Cincinnati
* Toledo Museum of Art
The Toledo Museum of Art is an internationally known art museum located in the Old West End neighborhood of Toledo, Ohio. It houses a collection of more than 30,000 objects. With 45 galleries, it covers 280,000 square feet and is currently in th ...
, Toledo
* Toy and Plastic Brick Museum, Bellaire
* University of Findlay's Mazza Museum, University of Findlay
* Wexner Center for the Arts
The Wexner Center for the Arts is the Ohio State University's "multidisciplinary, international laboratory for the exploration and advancement of contemporary art."
The Wexner Center is a lab and public gallery, but not an art museum, as it doe ...
, Ohio State University
* Whitby Mansion, Sidney
The Cincinnati Art Museum
The Cincinnati Art Museum is an art museum in the Eden Park neighborhood of Cincinnati, Ohio. Founded in 1881, it was the first purpose-built art museum west of the Alleghenies, and is one of the oldest in the United States. Its collection of ...
holds over 100,000 works spanning 6,000 years of human history, being among the most comprehensive collections in the Midwest. Among its notable collections are works by Master of San Baudelio, Jorge Ingles, Sandro Botticelli
Alessandro di Mariano di Vanni Filipepi ( – May 17, 1510), better known as Sandro Botticelli ( ; ) or simply known as Botticelli, was an Italian painter of the Early Renaissance. Botticelli's posthumous reputation suffered until the late 1 ...
(''Judith with Head of Holofernes''), Matteo di Giovanni
Matteo di Giovanni (c. 1430 – 1495) was an Italian Renaissance artist from the Sienese School.
Biography
Matteo di Giovanni di Bartolo was born in Borgo Sansepolcro around 1430. His family relocated to Siena and he is firmly associated with ...
, Domenico Tintoretto (''Portrait of Venetian dux Marino Grimani''), Mattia Preti
Mattia Preti (24 February 1613 – 3 January 1699) was an Italian Baroque artist who worked in Italy and Malta. He was appointed a Member of the Order of Saint John.
Life
Born in the small town of Taverna in Calabria, Preti was called ''Il Ca ...
, Bernardo Strozzi
Bernardo Strozzi, named il Cappuccino and il Prete Genovese (c. 1581 – 2 August 1644), was an Italian Baroque painter and engraver. A canvas and fresco artist, his wide subject range included History painting, history, Allegory, allegorica ...
, Frans Hals
Frans Hals the Elder (, ; ; – 26 August 1666) was a Dutch Golden Age painter. He lived and worked in Haarlem, a city in which the local authority of the day frowned on religious painting in places of worship but citizens liked to decorate thei ...
, Bartolomé Esteban Murillo
Bartolomé Esteban Murillo ( , ; late December 1617, baptized January 1, 1618April 3, 1682) was a Spanish Baroque painter. Although he is best known for his religious works, Murillo also produced a considerable number of paintings of contempor ...
(''St. Thomas of Villanueva''), Peter Paul Rubens
Sir Peter Paul Rubens ( ; ; 28 June 1577 – 30 May 1640) was a Flemish painting, Flemish artist and diplomat. He is considered the most influential artist of the Flemish Baroque painting, Flemish Baroque tradition. Rubens' highly charged comp ...
('' Samson and Delilah'') and Aert van der Neer. The collection also includes works by Jean-Baptiste-Camille Corot
Jean-Baptiste-Camille Corot ( , , ; 16 July 1796 – 22 February 1875), or simply Camille Corot, was a French Landscape art, landscape and Portraitist, portrait painter as well as a printmaking, printmaker in etching. A pivotal figure in ...
, Pierre-Auguste Renoir
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (; ; 25 February 1841 – 3 December 1919) was a French people, French artist who was a leading painter in the development of the Impressionism, Impressionist style. As a celebrator of beauty and especially femininity, fe ...
, Camille Pissarro
Jacob Abraham Camille Pissarro ( ; ; 10 July 1830 – 13 November 1903) was a Danish-French Impressionist and Neo-Impressionist painter born on the island of St Thomas (now in the US Virgin Islands, but then in the Danish West Indies). ...
, Claude Monet
Oscar-Claude Monet (, ; ; 14 November 1840 – 5 December 1926) was a French painter and founder of Impressionism painting who is seen as a key precursor to modernism, especially in his attempts to paint nature as he perceived it. During his ...
(''Rocks At Belle Isle''), and Pablo Picasso
Pablo Diego José Francisco de Paula Juan Nepomuceno María de los Remedios Cipriano de la Santísima Trinidad Ruiz y Picasso (25 October 1881 – 8 April 1973) was a Spanish painter, sculptor, printmaker, Ceramic art, ceramicist, and Scenic ...
. The museum also has a large collection of paintings by American painter Frank Duveneck
Frank Duveneck (né Decker; October 9, 1848 – January 3, 1919) was an American figure and portrait painter.
Early life
Duveneck was born in Covington, Kentucky, the son of German immigrant Bernhard Decker. Decker died in a cholera epidemic whe ...
(''Elizabeth B. Duveneck'').
The Cleveland Museum of Art
The Cleveland Museum of Art (CMA) is an art museum in Cleveland, Ohio, United States. Located in the Wade Park District of University Circle, the museum is internationally renowned for its substantial holdings of Asian art, Asian and Art of anc ...
is internationally renowned for its substantial holdings of Asian and Egyptian art, and has a permanent collection of more than 61,000 works from around the world. It is the fourth-wealthiest art museum in the United States.
The Columbus Museum of Art
The Columbus Museum of Art (CMA) is an art museum in downtown Columbus, Ohio. Formed in 1878 as the Columbus Gallery of Fine Arts (its name until 1978), it was the first art museum to register its charter with the state of Ohio. The museum collec ...
holds nineteenth and early twentieth-century American and European art, including early Cubist
Cubism is an early-20th-century avant-garde art movement which began in Paris. It revolutionized painting and the visual arts, and sparked artistic innovations in music, ballet, literature, and architecture.
Cubist subjects are analyzed, broke ...
paintings by Pablo Picasso
Pablo Diego José Francisco de Paula Juan Nepomuceno María de los Remedios Cipriano de la Santísima Trinidad Ruiz y Picasso (25 October 1881 – 8 April 1973) was a Spanish painter, sculptor, printmaker, Ceramic art, ceramicist, and Scenic ...
and Juan Gris
José Victoriano González-Pérez (23 March 1887 – 11 May 1927), better known as Juan Gris (; ), was a Spanish painter born in Madrid who lived and worked in France for most of his active period. Closely connected to the innovative artistic g ...
, works by François Boucher
François Boucher ( , ; ; 29 September 1703 – 30 May 1770) was a French painter, draughtsman and etcher, who worked in the Rococo style. Boucher is known for his idyllic and voluptuous paintings on classical themes, decorative allegories ...
, Paul Cézanne
Paul Cézanne ( , , ; ; ; 19 January 1839 – 22 October 1906) was a French Post-Impressionism, Post-Impressionist painter whose work introduced new modes of representation, influenced avant-garde artistic movements of the early 20th century a ...
, Mary Cassatt
Mary Stevenson Cassatt (; May 22, 1844June 14, 1926) was an American painter and printmaker. She was born in Allegheny, Pennsylvania (now part of Pittsburgh's North Side (Pittsburgh), North Side), but lived much of her adult life in France, whe ...
, Jean Auguste Dominique Ingres
Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres ( ; ; 29 August 1780 – 14 January 1867) was a French Neoclassicism, Neoclassical Painting, painter. Ingres was profoundly influenced by past artistic traditions and aspired to become the guardian of academic ...
, Edgar Degas
Edgar Degas (, ; born Hilaire-Germain-Edgar De Gas, ; 19 July 183427 September 1917) was a French Impressionist artist famous for his pastel drawings and oil paintings.
Degas also produced bronze sculptures, prints, and drawings. Degas is e ...
, Henri Matisse
Henri Émile Benoît Matisse (; 31 December 1869 – 3 November 1954) was a French visual arts, visual artist, known for both his use of colour and his fluid and original draughtsmanship. He was a drawing, draughtsman, printmaking, printmaker, ...
, Claude Monet
Oscar-Claude Monet (, ; ; 14 November 1840 – 5 December 1926) was a French painter and founder of Impressionism painting who is seen as a key precursor to modernism, especially in his attempts to paint nature as he perceived it. During his ...
, Edward Hopper
Edward Hopper (July 22, 1882 – May 15, 1967) was an American realism painter and printmaker. He is one of America's most renowned artists and known for his skill in depicting modern American life and landscapes.
Born in Nyack, New York, to a ...
, and Norman Rockwell
Norman Percevel Rockwell (February 3, 1894 – November 8, 1978) was an American painter and illustrator. His works have a broad popular appeal in the United States for their reflection of Culture of the United States, the country's culture. Roc ...
, and installations by Mel Chin
Mel Chin (born 1951 in Houston, Texas, USA) is a conceptual art, conceptual visual artist. Motivated largely by political, cultural, and social circumstances, Chin works in a variety of art media to calculate meaning in modern life. Chin places a ...
, Josiah McElheny, Susan Philipsz
Susan Mary Philipsz Order of the British Empire, OBE (born 1965) is a Scottish artist who won the 2010 Turner Prize. Originally a sculpture, sculptor, she is best known for her Sound art, sound installations. She records herself singing a cappe ...
, and Allan Sekula. Also in Columbus, the Billy Ireland Cartoon Library & Museum
The Billy Ireland Cartoon Library & Museum is a research library of American cartoons and comic art affiliated with the Ohio State University library system in Columbus, Ohio. Formerly known as the Cartoon Research Library and the Cartoon Libra ...
collection includes 450,000 original cartoons, 36,000 books, 51,000 serial titles, and of manuscript materials, plus 2.5 million comic strip clippings and tear sheets, making it the largest research library for cartoon art.
Youngstown's Butler Institute of American Art was the first museum dedicated exclusively to American art
Visual art of the United States or American art is visual art made in the United States or by U.S. artists. Before colonization, there were many flourishing traditions of Native American art, and where the Spanish colonized Spanish Colonial arc ...
.
Playhouse Square
Playhouse Square is a theater district in downtown Cleveland, Ohio, United States. It is the largest performing arts center in the US outside of New York City (only Lincoln Center is larger). Constructed in a span of 19 months in the early 1920s ...
in downtown Cleveland is the nation's second-largest performing arts center, home to ten theaters. The Columbus Association for the Performing Arts manages seven historic Columbus area theaters.
Cuisine
 Buckeyes are a variation of standard peanut butter cups popular in Ohio. Coated in chocolate with a partially exposed center of peanut butter fudge, the candy resembles the appearance of the nut that grows on the state tree, commonly known as the buckeye. The Klondike bar originated in Mansfield in 1922. Dum Dums lollipops were originally produced in
Buckeyes are a variation of standard peanut butter cups popular in Ohio. Coated in chocolate with a partially exposed center of peanut butter fudge, the candy resembles the appearance of the nut that grows on the state tree, commonly known as the buckeye. The Klondike bar originated in Mansfield in 1922. Dum Dums lollipops were originally produced in Bellevue, Ohio
Bellevue ( ) is a city in Erie County, Ohio, Erie, Huron County, Ohio, Huron, Seneca County, Ohio, Seneca, and Sandusky County, Ohio, Sandusky counties in the U.S. state of Ohio, located 61 miles southwest of Cleveland and 45 miles southeast of T ...
in 1924, and have been made by Spangler Candy Company
The Spangler Candy Company is a privately owned confectioner that has been manufacturing and marketing candy for more than a century. Headquartered in Bryan, Ohio, Spangler's products include lollipops, candy canes, and marshmallow circus peanut ...
in Bryan, Ohio
Bryan is a city in, and the county seat of, Williams County, Ohio, United States. It is located in the state's northwestern corner, southwest of Toledo, Ohio, Toledo. The population was 8,729 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census.
Histo ...
since 1953.
Cincinnati-style chili is a Greek-inspired meat sauce used as a topping for spaghetti or hot dogs. Additionally, red beans, chopped onions, and shredded cheese are offered as extra toppings referred to as "ways." German immigrants in Cincinnati invented goetta
Goetta ( ) is a meat-and-grain sausage or mush of German inspiration that is popular in Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky metropolitan area, Metro Cincinnati. It is primarily composed of ground meat (pork, or sausage and beef), steel-cut oats and spic ...
, a breakfast sausage made of meat scraps, spices, and oats. It is typically eaten fried.
The Polish Boy
The Polish Boy is a sausage sandwich native to Cleveland, Ohio. It consists of a link of kielbasa sausage placed in a bun, and covered with a layer of french fries, a layer of barbecue sauce and a layer of coleslaw. While the sausage is typ ...
, “the signature sandwich of Cleveland”, is a kielbasa
Kielbasa (, ; from Polish ) is any type of meat sausage from Poland and a staple of Polish cuisine. In American English, it is typically a coarse, U-shaped smoked sausage of any kind of meat, which closely resembles the ''Wiejska'' ''sausage'' ...
sausage topped with coleslaw, French fries, and barbecue sauce and served on a bun.
Johnny Marzetti is a casserole
A casserole (French language, French: diminutive of , from Provençal dialect, Provençal , meaning 'saucepan') is a kind of large, deep cookware and bakeware, pan or bowl used for cooking a variety of dishes in the oven; it is also a categor ...
dish thought to have originated from Columbus and consisting of some variation of noodles, ground beef, tomatoes, and cheese.
Ohio has hosted nationwide fast food
Fast food is a type of Mass production, mass-produced food designed for commercial resale, with a strong priority placed on speed of service. ''Fast food'' is a commercial term, limited to food sold in a restaurant or store with frozen, preheat ...
companies, including the first Arby's
Arby's is an American fast-food restaurant, fast food sandwich restaurant chain with more than 3,300 restaurants. The flagship property of Inspire Brands, it ranked third in systemwide sales in the United States in the quick-service and fast-ca ...
, Buffalo Wild Wings
Buffalo Wild Wings (originally Buffalo Wild Wings & Weck, and nicknamed BW3, or BDubs or BWW) is an American casual dining restaurant and sports bar franchise specializing in chicken wings.
As of March 2025, there are over 1,300 locations a ...
, Stewart's, and Wendy's
Wendy's International, LLC, is an American international fast food restaurant chain founded by Dave Thomas (businessman), Dave Thomas on November 15, 1969, in Columbus, Ohio. Its headquarters moved to Dublin, Ohio, on January 29, 2006. As of D ...
; the latter is headquartered in Dublin, Ohio
Dublin is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio. A suburb of Columbus, Ohio, Columbus, it falls within the jurisdictions of Franklin County, Ohio, Franklin, Delaware County, Ohio, Delaware, Union County, Ohio, Union, and Madison County, Ohio, Madison ...
. The hamburger chain White Castle is also based in Columbus.
Music
 The
The Rock and Roll Hall of Fame
The Rock and Roll Hall of Fame (RRHOF), also simply referred to as the Rock Hall, is a museum and hall of fame located in downtown Cleveland, Ohio, United States, on the shore of Lake Erie. The museum documents the history of rock music and the ...
and the Rhythm and Blues Music Hall of Fame
The National Rhythm & Blues Hall of Fame is an independent organization whose mission is to educate and to celebrate, preserve, promote, and present rhythm and blues music globally.
History
The National Rhythm & Blues Hall of Fame was founde ...
are both located in Cleveland. Cleveland disc jockey
A disc jockey, more commonly abbreviated as DJ, is a person who plays recorded music for an audience. Types of DJs include Radio personality, radio DJs (who host programs on music radio stations), club DJs (who work at nightclubs or music fes ...
Alan Freed
Albert James "Alan" Freed (December 15, 1921 – January 20, 1965) was an American disc jockey. He also produced and promoted large traveling concerts with various acts, helping to spread the importance of rock and roll music throughout Nor ...
is credited with coining the term and promoting rock and roll
Rock and roll (often written as rock & roll, rock-n-roll, and rock 'n' roll) is a Genre (music), genre of popular music that evolved in the United States during the late 1940s and early 1950s. It Origins of rock and roll, originated from African ...
in the early 1950s. Cincinnati is home to the American Classical Music Hall of Fame and Museum. Six Ohio musicians are Rock and Roll Hall of Fame members, Dave Grohl
David Eric Grohl (; born January 14, 1969) is an American musician. He founded the rock band Foo Fighters, of which he is the lead singer, guitarist, principal songwriter, and only consistent member. From 1990 to 1994, he was the drummer of th ...
(Nirvana
Nirvana, in the Indian religions (Jainism, Hinduism, Buddhism, and Sikhism), is the concept of an individual's passions being extinguished as the ultimate state of salvation, release, or liberation from suffering ('' duḥkha'') and from the ...
and Foo Fighters
The Foo Fighters are an American Rock music, rock band formed in Seattle in 1994. Initially founded as a one-man project by former Nirvana (band), Nirvana drummer Dave Grohl, the band comprises vocalist/guitarist Grohl, bassist Nate Mendel, gu ...
), the Isley Brothers
The Isley Brothers ( ) are an American soul group originally from Cincinnati, Ohio, that began as a vocal trio consisting of the brothers O'Kelly Isley Jr., Rudolph Isley and Ronald Isley in the 1950s. With a career spanning over seven decades, ...
, Nine Inch Nails
Nine Inch Nails, commonly abbreviated as NIN (stylized as NIИ), is an American industrial rock band formed in Cleveland, Ohio in 1988. Its members are the singer-songwriter, multi-instrumentalist and producer Trent Reznor and his frequent col ...
, Bobby Womack
Robert Dwayne Womack ( ; March 4, 1944 – June 27, 2014) was an American singer-songwriter and guitarist. Starting in the early 1950s as the lead singer of his family musical group the Valentinos and as Sam Cooke's backing guitarist, Womack's ...
, Benjamin Orr
Benjamin Orr (, September 8, 1947 – October 3, 2000) was an American musician. He was best known as the bassist, co-lead vocalist, and co-founder of the band the Cars. He sang lead vocals on several of their hits, including "Just What I Nee ...
(The Cars
The Cars were an American Rock music, rock band formed in Boston in 1976. Emerging from the New wave music, new wave Subculture, scene in the late 1970s, they consisted of Ric Ocasek (rhythm guitar), Benjamin Orr (bass guitar), Elliot Easton (l ...
), and Chrissie Hynde
Christine Ellen Hynde (born September 7, 1951) is an American-British musician. She is a founding member of the rock band the Pretenders and is the band's lead vocalist, guitarist, and primary songwriter; she and drummer Martin Chambers are the ...
(The Pretenders
The Pretenders are a British rock band formed in March 1978. The original band consisted of founder and main songwriter Chrissie Hynde (lead vocals, rhythm guitar), James Honeyman-Scott (lead guitar, backing vocals, keyboards), Pete Farndon (ba ...
), in addition to Alan Freed.
Other popular musicians from Ohio include Mamie Smith
Mamie Smith ( Robinson; May 26, 1891 – August or September 16, 1946) was an American singer. As a vaudeville singer, she performed in multiple styles, including jazz and blues. In 1920, she entered blues history as the first African-American a ...
, Dean Martin
Dean Martin (born Dino Paul Crocetti; June 7, 1917 – December 25, 1995) was an American singer, actor, and comedian. Nicknamed the "Honorific nicknames in popular music, King of Cool", he is regarded as one of the most popular entertainers of ...
, Tyler Joseph
Tyler Robert Joseph (born December 1, 1988) is an American singer, rapper, songwriter, musician, and record producer. He is best known as the frontman for the musical duo Twenty One Pilots, alongside bandmate Josh Dun. Across his career he has r ...
and Josh Dun
Joshua William Dun (born June 18, 1988) is an American musician. He is best known as the drummer of the musical duo Twenty One Pilots, alongside Tyler Joseph, but he has collaborated with other artists as well. His band has been nominated for ...
of Twenty One Pilots
Twenty One Pilots is an American musical duo from Columbus, Ohio. Initially a band, the group was formed in 2009 by lead vocalist Tyler Joseph along with Nick Thomas and Chris Salih, who both left in 2011. Since their departure, the line-up h ...
, Frankie Yankovic, Doris Day
Doris Day (born Doris Mary Kappelhoff; April 3, 1922 – May 13, 2019) was an American actress and singer. She began her career as a big band singer in 1937, achieving commercial success in 1945 with two No. 1 recordings, "Sentimental Journey ...
, the McGuire Sisters
The McGuire Sisters were a singing trio in American popular music. The group was composed of three sisters:
* Ruby Christine McGuire (July 30, 1926 – December 28, 2018)
* Dorothy "Dottie" McGuire (February 13, 1928 – September 7, 2012)
* P ...
, Howard Hewett
Howard Hewett Jr. (born October 1, 1955) is an American singer–songwriter. Hewett rose to fame as the lead vocalist of the group Shalamar. In 1985, he left the group to pursue his solo career, but he later returned to the group in 2001. He si ...
, Shirley Murdock
Shirley Murdock (born May 22, 1957) is an American R&B singer-songwriter. She is best known for her guest appearance alongside Charlie Wilson on Zapp and Roger's 1986 single " Computer Love", as well as her 1986 single, "As We Lay". The latt ...
, Boz Scaggs
William Royce "Boz" Scaggs (born June 8, 1944) is an American singer, songwriter, and guitarist. He was a bandmate of Steve Miller (musician), Steve Miller in the Ardells in the early 1960s and a member of the Steve Miller Band from 1967 to 196 ...
, John Legend
John Roger Stephens (born December 28, 1978), known professionally as John Legend, is an American singer, songwriter, and pianist. He began his musical career working behind the scenes for other artists, playing piano on Lauryn Hill's " Every ...
, Marilyn Manson
Brian Hugh Warner (born January 5, 1969), known professionally as Marilyn Manson, is an American rock musician. He is the lead singer and the only original member remaining of the Marilyn Manson (band), same-titled band he founded in 1989. Th ...
, Starset
Starset is an American Rock music, rock band from Columbus, Ohio, formed by Dustin Bates in 2013. They released their debut album, ''Transmissions (Starset album), Transmissions'', in 2014 and their second album, ''Vessels (Starset album), Vesse ...
, Dan Auerbach
Daniel Quine Auerbach (; born May 14, 1979) is an American musician, singer-songwriter, and record producer, best known as the guitarist and vocalist of The Black Keys, a blues rock band from Akron, Ohio. As a member of the group, Auerbach has ...
and Patrick Carney
Patrick James Carney (born April 15, 1980) is an American musician and producer best known as the drummer of the Black Keys, a blues rock band from Akron, Ohio.
Early life
Carney stated in an interview with '' Modern Drummer'' that he never t ...
of the Black Keys
The Black Keys are an American Rock music, rock duo formed in Akron, Ohio in 2001. The group consists of Dan Auerbach (guitar, Singing, vocals) and Patrick Carney (Drum kit, drums). The duo began as an Independent music, independent act, record ...
, Griffin Layne
Griffin Layne is an American country music singer and songwriter.
Layne's debut single,"Nothin like a Southern Girl", has been added to the Most Popular Urban Cowboy Music Tracks Chart, by 93.5 FM. Layne co-wrote and produced his debut single, ...
, Joe Dolce
Joseph Dolce (, originally ; born October 13, 1947) is an American-Australian singer, songwriter, poet and essayist.
Dolce achieved international recognition with his multi-million-selling novelty song, " Shaddap You Face", released worldwide un ...
, Kid Cudi
Scott Ramon Seguro Mescudi (born January 30, 1984), also known by his stage name Kid Cudi ( ; formerly stylized as KiD CuDi), is an American rapper, singer, songwriter, record producer, actor, and fashion designer. Born and raised in Clevelan ...
, William "Bootsy" Collins
William Earl "Bootsy" Collins (born October 26, 1951) is an American bass guitarist, singer, and songwriter. Rising to prominence with James Brown in the early 1970s before joining the Parliament-Funkadelic collective, Collins established himse ...
, Stephanie Eulinberg of Kid Rock
Robert James Ritchie (born January 17, 1971), known professionally as Kid Rock, is an American musician, singer, rapper, and songwriter. After establishing himself in the Music of Detroit#Hip-hop, Detroit hip-hop scene, he broke through into m ...
's Twisted Brown Trucker
Twisted Brown Trucker is the Backup band, backing band for American musician Kid Rock. Formed in 1994, the band has contributed to nine of his twelve studio albums, as well as Uncle Kracker's ''Double Wide (album), Double Wide'' album.
Histor ...
Band, and Devo
Devo is an American new wave band from Akron, Ohio, formed in 1973. Their classic line-up consisted of two sets of brothers, the Mothersbaughs ( Mark and Bob) and the Casales (Gerald and Bob), along with Alan Myers. The band had a No. 14 ...
.
The Cleveland Orchestra
The Cleveland Orchestra is an American orchestra based in Cleveland, Ohio. Founded in 1918 by the pianist and impresario Adella Prentiss Hughes, the orchestra is one of the five American orchestras informally referred to as the " Big Five". T ...
is one of the historic Big Five orchestras in the U.S. and considered among the best worldwide. Many other Ohio cities are home to their own orchestras, including Akron
Akron () is a city in Summit County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. It is the fifth-most populous city in Ohio, with a population of 190,469 at the 2020 census. The Akron metropolitan area, covering Summit and Portage counties, had ...
, Blue Ash, Canton, Cincinnati
Cincinnati ( ; colloquially nicknamed Cincy) is a city in Hamilton County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. Settled in 1788, the city is located on the northern side of the confluence of the Licking River (Kentucky), Licking and Ohio Ri ...
, Columbus, Dayton
Dayton () is a city in Montgomery County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of cities in Ohio, sixth-most populous city in Ohio, with a population of 137,644 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The Dayton metro ...
, Toledo, and Youngstown
Youngstown is a city in Mahoning County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of municipalities in Ohio, 11th-most populous city in Ohio with a population of 60,068 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The Mahoning ...
. Cincinnati is home to its own ballet
Ballet () is a type of performance dance that originated during the Italian Renaissance in the fifteenth century and later developed into a concert dance form in France and Russia. It has since become a widespread and highly technical form of ...
, symphony orchestra
An orchestra (; ) is a large instrumental ensemble typical of classical music, which combines instruments from different families. There are typically four main sections of instruments:
* String instruments, such as the violin, viola, cello, ...
, pops orchestra, and opera
Opera is a form of History of theatre#European theatre, Western theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by Singing, singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically ...
, all housed at the Cincinnati Music Hall
Music Hall, commonly known as Cincinnati Music Hall, is a classical music performance hall in Cincinnati, Ohio, completed in 1878. It serves as the home for the Cincinnati Ballet, Cincinnati Symphony Orchestra, Cincinnati Opera, May Festiva ...
. Dayton is also home to a ballet, orchestra, and opera, collectively known as the Dayton Performing Arts Alliance.
Within the marching arts, Winter Guard International
Winter Guard International (WGI) is an American governing body that sanctions championship events for three competitive performing arts activities: winter guard, percussion ensembles, and indoor wind ensembles. WGI was founded in 1977 in respon ...
has hosted national championships in performing arts at the University of Dayton
The University of Dayton (UD) is a Private university, private, Catholic research university in Dayton, Ohio, United States. Founded in 1850 by the Society of Mary (Marianists), Society of Mary, it is one of three Marianist universities in the U ...
18 times between 1983 and 2003, and has permanently since 2005. The Bluecoats Drum and Bugle Corps are Ohio's highest fielding drum corps, competing in the Drum Corps International
Drum Corps International (DCI) is a governing body for drum and bugle corps. Founded in 1971 and known as "marching music's major league," DCI develops and enforces rules of competition and judges at sanctioned drum and bugle corps competitions t ...
World Class circuit out of Canton.
Sports
Professional sports
Ohio is home to eight professional sports teams across the five different major leagues in the United States. Current teams include theCincinnati Reds
The Cincinnati Reds are an American professional baseball team based in Cincinnati. The Reds compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the National League (baseball), National League (NL) National League Central, Central Divisi ...
and Cleveland Guardians
The Cleveland Guardians are an American professional baseball team based in Cleveland. The Guardians compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) Central Division. Since , the team has played its home gam ...
of Major League Baseball
Major League Baseball (MLB) is a professional baseball league composed of 30 teams, divided equally between the National League (baseball), National League (NL) and the American League (AL), with 29 in the United States and 1 in Canada. MLB i ...
, the Columbus Crew
The Columbus Crew are an American professional soccer club based in Columbus, Ohio. The club competes in Major League Soccer (MLS) as a member of the Eastern Conference (MLS), Eastern Conference. The team began play in 1996 as one of the 10 cha ...
and FC Cincinnati
Football Club Cincinnati is an American professional soccer club based in Cincinnati. The club competes in Major League Soccer (MLS) as a member of the Eastern Conference. The team was first announced on August 12, 2015 as a United Soccer Leag ...
of Major League Soccer
Major League Soccer (MLS) is a professional Association football, soccer league in North America and the highest level of the United States soccer league system. It comprises 30 teams, with 27 in the United States and 3 in Canada, and is sanc ...
, the Cleveland Cavaliers
The Cleveland Cavaliers, often referred to as the Cavs, are an American professional basketball team based in Cleveland. The Cavaliers compete in the National Basketball Association (NBA) as a member of the Central Division (NBA), Central Divis ...
of the National Basketball Association
The National Basketball Association (NBA) is a professional basketball league in North America composed of 30 teams (29 in the United States and 1 in Canada). The NBA is one of the major professional sports leagues in the United States and Ca ...
, the Cincinnati Bengals
The Cincinnati Bengals are a professional American football team based in Cincinnati. The Bengals compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member of the American Football Conference (AFC) AFC North, North division. The team plays its h ...
and Cleveland Browns
The Cleveland Browns are a professional American football team based in Cleveland. The Browns compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member of the American Football Conference (AFC) AFC North, North division. The team is named after ...
of the National Football League
The National Football League (NFL) is a Professional gridiron football, professional American football league in the United States. Composed of 32 teams, it is divided equally between the American Football Conference (AFC) and the National ...
, and the Columbus Blue Jackets
The Columbus Blue Jackets (often simply referred to as the Jackets) are a professional ice hockey team based in Columbus, Ohio. The Blue Jackets compete in the National Hockey League (NHL) as a member of the Metropolitan Division in the Eastern C ...
of the National Hockey League
The National Hockey League (NHL; , ''LNH'') is a professional ice hockey league in North America composed of 32 teams25 in the United States and 7 in Canada. The NHL is one of the major professional sports leagues in the United States and Cana ...
.
Ohio has brought home seven World Series
The World Series is the annual championship series of Major League Baseball (MLB). It has been contested since between the champion teams of the American League (AL) and the National League (NL). The winning team, determined through a best- ...
titles (Reds 1919, 1940, 1975, 1976, 1990; Indians 1920, 1948), three MLS Cup
MLS Cup is the annual championship game of Major League Soccer (MLS) and the culmination of the MLS Playoffs. The game is held in November or December and pits the winner of the Eastern Conference Final against the winner of the Western Confere ...
s (Crew 2008
2008 was designated as:
*International Year of Languages
*International Year of Planet Earth
*International Year of the Potato
*International Year of Sanitation
The Great Recession, a worldwide recession which began in 2007, continued throu ...
, 2020
The year 2020 was heavily defined by the COVID-19 pandemic, which led to global Social impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, social and Economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, economic disruption, mass cancellations and postponements of even ...
, 2023
Catastrophic natural disasters in 2023 included the Lists of 21st-century earthquakes, 5th-deadliest earthquake of the 21st century 2023 Turkey–Syria earthquakes, striking Turkey and Syria, leaving up to 62,000 people dead; Cyclone Freddy ...
), one NBA Championship
The NBA Finals is the annual championship series of the National Basketball Association (NBA). The Eastern Conference (NBA), Eastern and Western Conference (NBA), Western Conference champions play a best-of-seven series to determine the league ...
(Cavaliers 2016), and nine NFL Championships
Throughout its history, the National Football league (NFL) and other rival American football leagues have used several different formats to determine their league champions, including a period of inter-league matchups to determine a true national ...
( Pros 1920; Bulldogs 1922, 1923
In Greece, this year contained only 352 days as 13 days was skipped to achieve the calendrical switch from Julian to Gregorian Calendar. It happened there that Wednesday, 15 February ''(Julian Calendar)'' was followed by Thursday, 1 March ' ...
, 1924
Events
January
* January 12 – Gopinath Saha shoots Ernest Day, whom he has mistaken for Sir Charles Tegart, the police commissioner of Calcutta, and is arrested soon after.
* January 20–January 30, 30 – Kuomintang in Ch ...
; Rams 1945; Browns 1950
Events January
* January 1 – The International Police Association (IPA) – the largest police organization in the world – is formed.
* January 5 – 1950 Sverdlovsk plane crash, Sverdlovsk plane crash: ''Aeroflot'' Lisunov Li-2 ...
, 1954
Events
January
* January 3 – The Italian broadcaster RAI officially begins transmitting.
* January 7 – Georgetown–IBM experiment: The first public demonstration of a machine translation system is held in New York, at the head ...
, 1955
Events January
* January 3 – José Ramón Guizado becomes president of Panama.
* January 17 – , the first nuclear-powered submarine, puts to sea for the first time, from Groton, Connecticut.
* January 18– 20 – Battle of Yijian ...
, 1964
Events January
* January 1 – The Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland is dissolved.
* January 5 – In the first meeting between leaders of the Roman Catholic and Orthodox churches since the fifteenth century, Pope Paul VI and Patria ...
). Despite this success in the NFL
The National Football League (NFL) is a professional American football league in the United States. Composed of 32 teams, it is divided equally between the American Football Conference (AFC) and the National Football Conference (NFC). The N ...
in the first half of the 20th century, no Ohio team has won the Super Bowl
The Super Bowl is the annual History of the NFL championship, league championship game of the National Football League (NFL) of the United States. It has served as the final game of every NFL season since 1966 NFL season, 1966 (with the excep ...
since its inception in 1967
Events January
* January 1 – Canada begins a year-long celebration of the 100th anniversary of Canadian Confederation, Confederation, featuring the Expo 67 World's Fair.
* January 6 – Vietnam War: United States Marine Corps and Army of ...
. No Ohio team has made an appearance in the Stanley Cup Finals
The Stanley Cup Finals in ice hockey (also known as the Stanley Cup Final among various media, ) is the annual championship series of the National Hockey League (NHL). The winner is awarded the Stanley Cup, North America's oldest professional spo ...
.
Ohio played a central role in the development of both Major League Baseball and the National Football League. Baseball's first fully professional team, the Cincinnati Red Stockings
The Cincinnati Red Stockings of were baseball's first all-professional team, with ten salaried players. The Cincinnati Base Ball Club formed in 1866 and fielded competitive teams in the National Association of Base Ball Players (NABBP) 1867� ...
of 1869, were organized in Ohio. An informal early-20th-century American football association, the Ohio League
The Ohio League was an informal and loose association of American football clubs active between 1902 and 1919 that competed for the Ohio Independent Championship (OIC). As the name implied, its teams were mostly based in Ohio. It is the direct p ...
, was the direct predecessor of the modern NFL, although neither of Ohio's modern NFL franchises trace their roots to an Ohio League club. The NFL itself was founded in Canton in 1920 as the American Professional Football Conference. The first official game occurred on October 3, 1920, when the Dayton Triangles beat the Columbus Panhandles
The Columbus Panhandles were a professional American football team based in Columbus, Ohio. The club was founded in 1901 by workers at the Panhandle shops of the Pennsylvania Railroad. They were a part of the Ohio League from 1904 before foldi ...
14–0 in Dayton. Canton was enshrined as the home of the Pro Football Hall of Fame
The Pro Football Hall of Fame is the hall of fame for professional football (gridiron), professional American football, located in Canton, Ohio. Opened on September 7, 1963, the Hall of Fame enshrines exceptional figures in the sport of profes ...
in 1963.
On a smaller scale, Ohio hosts minor league baseball
Minor League Baseball (MiLB) is a professional baseball organization below Major League Baseball (MLB), constituted of teams affiliated with MLB clubs. It was founded on September 5, 1901, in response to the growing dominance of the National Le ...
, arena football
Arena football is a variety of gridiron football designed to be played indoors. The game is played on a smaller field than American or Canadian football, designed to fit in the same surface area as a standard North American ice hockey rink, an ...
, indoor football, mid-level hockey, and lower division soccer.
Individual sports
TheMid-Ohio Sports Car Course
Mid-Ohio Sports Car Course is a road course auto racing facility located in Troy Township, Morrow County, Ohio, United States, just outside the village of Lexington. It hosts a number of racing series such as IndyCar, IMSA WeatherTech Sportsc ...
has hosted several auto racing championships, including CART World Series, IndyCar Series
The IndyCar Series, officially known as the NTT IndyCar Series for sponsorship reasons, is the highest class of American open-wheel car racing in the United States, which has been conducted under the auspices of various sanctioning bodies sinc ...
, NASCAR Nationwide Series
The NASCAR Xfinity Series (NXS) is a stock car racing series organized by NASCAR. It is promoted as NASCAR's second-tier circuit to the organization's top level Cup Series. NXS events are frequently held as a support race on the day prior to a ...
, Can-Am
The Canadian-American Challenge Cup, or Can-Am, was an SCCA/ CASC sports car racing series from 1966 to 1974, and again from 1977 to 1987.
The Can-Am rules were deliberately simple and placed few limits on the entries. This led to a wide variet ...
, Formula 5000
Formula 5000 (or F5000) was an Open-wheel car, open wheel, single seater auto-racing formula that ran in different series in various regions around the world from 1968 to 1982. It was originally intended as a low-cost series aimed at open-wheel ...
, IMSA GT Championship
IMSA GT was a sports car racing series organized by International Motor Sports Association. Races took place primarily in the United States and occasionally in Canada.
History
The series was founded in 1969 by John and Peggy Bishop, and Bill ...
, American Le Mans Series
The American Le Mans Series (ALMS) was a sports car racing series based in the United States and Canada. It consisted of a series of Endurance racing (motorsport), endurance and sprint races, and was created in the spirit of the 24 Hours of Le M ...
and Rolex Sports Car Series
The Rolex Sports Car Series was the premier series run by the Grand American Road Racing Association. It was a North American-based sports car series founded in 2000 under the name Grand American Road Racing Championship to replace the failed ...
. The Grand Prix of Cleveland also hosted CART races from 1982 to 2007. The Eldora Speedway
Eldora Speedway (nicknamed "the Big E", "Auto Racing's Showcase Since 1954," and "the World's Greatest Dirt Track") is a high-banked Dirt track racing, clay dirt oval. Located north of Rossburg, Ohio in the village of New Weston, Ohio, its websit ...
is a major dirt oval that hosts NASCAR Camping World Truck Series
The NASCAR Craftsman Truck Series is a pickup truck racing series owned and operated by the National Association for Stock Car Auto Racing (NASCAR), and is the only series in NASCAR to race production pickup truck-based stock cars. The series i ...
, World of Outlaws
World of Outlaws Sprint Car Series, originally known as the World of Outlaws (often abbreviated WoO) is an American national touring dirt track racing series. It is owned and operated by World Racing Group, and was rebranded when the World of O ...
Sprint Cars and USAC Silver Crown Series races.
Ohio hosts two PGA Tour
The PGA Tour (stylized as PGA TOUR by its officials) is the organizer of professional golf tours in North America. It organizes most of the events on the flagship annual series of tournaments also known as the PGA Tour, the PGA Tour Champion ...
events, the WGC-Bridgestone Invitational
The WGC Invitational was a professional golf tournament that was held in the United States. Established in 1999 as a successor to the World Series of Golf, it was one of three or four annual World Golf Championships (WGC) until 2021, when the nu ...
and Memorial Tournament
The Memorial Tournament (branded as the Memorial Tournament presented by Workday, Inc., Workday for sponsorship reasons, and also referred to as simply the Memorial) is a PGA Tour golf tournament founded in 1976 by Jack Nicklaus. It is played on ...
. The Cincinnati Open
The Cincinnati Open (also known as the Cincinnati Masters) is an annual professional tennis event held in Cincinnati, United States. Due to previous sponsorship, it has also been known as: the Thriftway ATP Championships, the Great American I ...
is an ATP World Tour Masters 1000
The ATP 1000 events, also known as ATP Masters 1000 tournaments, are an annual series of nine tennis tournaments featuring the top-ranked players on the ATP Tour since its inception in 1990. The ATP 1000 tournaments, sitting below the Gran ...
and WTA 1000 tennis tournament.
College sports
Ohio has eightNCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision
The NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS), formerly known as Division I-A, is the highest level of college football in the United States. The FBS consists of the largest schools in the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA). As ...
college football teams, divided among three different conferences
A conference is a meeting, often lasting a few days, which is organized on a particular subject, or to bring together people who have a common interest. Conferences can be used as a form of group decision-making, although discussion, not always d ...
. It has also experienced considerable success in the secondary and tertiary tiers of college football divisions.
There are two programs in the Power Five conferences
The power conferences are the most prominent athletic conferences in college football in the United States. They are part of the Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS) of the National Collegiate Athletic Association's Division I, the highest level o ...
; the Ohio State Buckeyes
The Ohio State Buckeyes are the intercollegiate athletic teams that represent Ohio State University, located in Columbus, Ohio. The athletic programs are named after the colloquial term for people from the state of Ohio and after the state tree, ...
of the Big Ten Conference
The Big Ten Conference (stylized B1G, formerly the Western Conference and the Big Nine Conference, among others) is a collegiate List of NCAA conferences, athletic conference in the United States. Founded as the Intercollegiate Conference of Fa ...
and the Cincinnati Bearcats
The Cincinnati Bearcats are the college sports, athletic teams that represent the University of Cincinnati. The teams compete in the NCAA's Division I and the Football Bowl Subdivision as members of the Big 12 Conference. The Bearcats were pr ...
of the Big 12 Conference
The Big 12 Conference is a collegiate List of NCAA conferences, athletic conference in the United States. It consists of 16 full-member universities (3 private universities and 13 public universities) in the states of Arizona, Colorado, Florida ...
. The Ohio State Buckeyes football
The Ohio State Buckeyes football team competes as part of the NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision, representing Ohio State University in the Big Ten Conference. Ohio State has played its home games at Ohio Stadium in Columbus, Ohio, since 1 ...
team is second in all-time winning percentage, with a 977–335–53 overall record and a 30–29 bowl record as of 2024
The year saw the list of ongoing armed conflicts, continuation of major armed conflicts, including the Russian invasion of Ukraine, the Myanmar civil war (2021–present), Myanmar civil war, the Sudanese civil war (2023–present), Sudane ...
. The program has produced seven Heisman Trophy
The Heisman Memorial Trophy ( ; also known simply as the Heisman) is awarded annually since 1935 to the top player in college football. It is considered the most prestigious award in the sport and is presented by the Heisman Trophy Trust followin ...
winners, forty-one conference titles, and nine undisputed national championships. The men's basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular Basketball court, court, compete with the primary objective of #Shooting, shooting a basketball (ball), basketball (appro ...
program has appeared in the NCAA Division I men's basketball tournament
The NCAA Division I men's basketball tournament, branded as March Madness, or The Big Dance, is a single-elimination tournament played in the United States to determine the men's college basketball national champion of the NCAA Division I, Di ...
27 times.
The Cincinnati Bearcats men's basketball
The Cincinnati Bearcats men's basketball program represents the University of Cincinnati in Cincinnati, Ohio. The school's team competes in NCAA Division I as part of the Big 12 Conference. The Bearcats are currently coached by Wes Miller.
Wit ...
team has over 1,800 wins and 33 March Madness
The NCAA Division I men's basketball tournament, branded as March Madness, or The Big Dance, is a single-elimination tournament played in the United States to determine the men's college basketball national champion of the NCAA Division I, Di ...
appearances, whilst the Bearcats football team became the first so-called "Group of Five" team to qualify to the College Football Playoff
The College Football Playoff (CFP) is an annual single-elimination tournament, knockout invitational tournament to determine a national champion for the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision, D ...
in 2022.
In the Group of Five conferences, six teams are represented in the Mid-American Conference
The Mid-American Conference (MAC) is a collegiate List of NCAA conferences, athletic conference with a membership base in the Great Lakes region (North America), Great Lakes region that stretches from Western New York to Illinois. Its members co ...
: the Akron Zips
The Akron Zips are the intercollegiate athletic teams that represent the University of Akron in Akron, Ohio, United States. The Zips compete in the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) at the NCAA Division I, Division I level as a memb ...
, Bowling Green Falcons
The Bowling Green Falcons are the intercollegiate athletic teams that represent Bowling Green State University (BGSU), in Bowling Green, Ohio, United States. The Falcons compete in the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) at the Divi ...
, Kent State Golden Flashes
The Kent State Golden Flashes are the athletic teams that represent Kent State University. The university fields 19 varsity athletic teams in the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) at the NCAA Division I, Division I level with footba ...
, Miami RedHawks
The Miami RedHawks are the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) NCAA Division I, Division I intercollegiate athletic teams that represent Miami University in Oxford, Ohio, United States. Miami is a member of the Mid-American Conference ...
, Ohio Bobcats
The Ohio Bobcats are the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) NCAA Division I, Division I Intercollegiate athletic teams that represent Ohio University, located in Athens, Ohio, United States. Ohio University is a charter member (1946 ...
and the Toledo Rockets. The MAC headquarters are in Cleveland. The Cincinnati–Miami rivalry game has been played in southwest Ohio every year since 1888 and is the oldest current non-conference NCAA football
College football is gridiron football that is played by teams of amateur Student athlete, student-athletes at universities and colleges. It was through collegiate competition that gridiron football American football in the United States, firs ...
rivalry. Other Division I schools, either part of the NCAA Division I Football Championship Subdivision
The NCAA Division I Football Championship Subdivision (FCS), formerly known as Division I-AA, is the second-highest level of college football in the United States, after the Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS). Sponsored by the National Collegiate ...
or not fielding in football include the Cleveland State Vikings
The Cleveland State Vikings, or Vikes, are the athletic teams of Cleveland State University. Before as Fenn College they were known as the Fenn College Foxes or Fenn Foxes. Cleveland State competes in NCAA Division I. The Vikings have competed ...
, Xavier Musketeers
The Xavier Musketeers are the 19 teams representing Xavier University in intercollegiate athletics, including men's and women's basketball, cross country, golf, soccer, swimming, tennis, indoor track and field, and outdoor track and field. The Mus ...
, Wright State Raiders, and Youngstown State Penguins
The Youngstown State Penguins are the athletic teams of Youngstown State University in Youngstown, Ohio. The university is a member of the National Collegiate Athletic Association's (NCAA) Division I, and the Penguins compete in football as memb ...
. Xavier's men's basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular Basketball court, court, compete with the primary objective of #Shooting, shooting a basketball (ball), basketball (appro ...
has performed particularly well, with 27 March Madness
The NCAA Division I men's basketball tournament, branded as March Madness, or The Big Dance, is a single-elimination tournament played in the United States to determine the men's college basketball national champion of the NCAA Division I, Di ...
appearances. Youngstown State's football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kick (football), kicking a football (ball), ball to score a goal (sports), goal. Unqualified, football (word), the word ''football'' generally means the form of football t ...
has the third most NCAA Division I Football Championship
The NCAA Division I Football Championship is an annual post-season college football game, played since 2006, used to determine a national champion of the NCAA Division I Football Championship Subdivision (FCS). From 1978 to 2005, the game was ca ...
wins, with 3.
There are 12 NCAA Division II
NCAA Division II (D-II) is the intermediate-level division of competition in the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA). It offers an alternative to both the larger and better-funded Division I and to the scholarship-free environment ...
universities and 22 NCAA Division III
NCAA Division III (D-III) is the lowest division of the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) in the United States. D-III consists of athletic programs at colleges and universities that do not offer athletic scholarships to student- ...
universities in Ohio.
Government and politics
State government
 The state government of Ohio consists of the executive, legislative, and judicial branches.
The executive branch is headed by the
The state government of Ohio consists of the executive, legislative, and judicial branches.
The executive branch is headed by the governor of Ohio
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of a state's official representative. Depending on the type of political region or polity, a ''governor'' ma ...
. The current governor is Mike DeWine
Richard Michael DeWine ( ; born January 5, 1947) is an American politician and attorney serving as the 70th List of governors of Ohio, governor of Ohio since 2019. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he served a ...
since 2019, a member of the Republican Party. A lieutenant governor
A lieutenant governor, lieutenant-governor, or vice governor is a high officer of state, whose precise role and rank vary by jurisdiction. Often a lieutenant governor is the deputy, or lieutenant, to or ranked under a governor — a "second-in-comm ...
succeeds the governor in the event of any removal from office, and performs any duties assigned by the governor. The current lieutenant governor is Jim Tressel
James Patrick Tressel (born December 5, 1952) is an American politician and retired college football coach who has served as the 67th lieutenant governor of Ohio since 2025. A member of the Republican Party, Tressel previously was the president ...
. The other elected constitutional offices in the executive branch are the secretary of state (Frank LaRose
Frank LaRose (born April 18, 1979) is an American politician who has served as the 51st Ohio Secretary of State, secretary of state of Ohio since January 2019. A Republican Party (United States), Republican, he was member of the Ohio State Senate ...
), auditor
An auditor is a person or a firm appointed by a company to execute an audit.Practical Auditing, Kul Narsingh Shrestha, 2012, Nabin Prakashan, Nepal To act as an auditor, a person should be certified by the regulatory authority of accounting an ...
( Keith Faber), treasurer
A treasurer is a person responsible for the financial operations of a government, business, or other organization.
Government
The treasury of a country is the department responsible for the country's economy, finance and revenue. The treasure ...
( Robert Sprague), and attorney general
In most common law jurisdictions, the attorney general (: attorneys general) or attorney-general (AG or Atty.-Gen) is the main legal advisor to the government. In some jurisdictions, attorneys general also have executive responsibility for law enf ...
( Dave Yost). There are 21 state administrative departments in the executive branch.
The Ohio General Assembly
The Ohio General Assembly is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Ohio. It consists of the 99-member Ohio House of Representatives and the 33-member Ohio Senate. Both houses of the General Assembly meet at the Ohio Statehouse in Colu ...
is a bicameral
Bicameralism is a type of legislature that is divided into two separate Deliberative assembly, assemblies, chambers, or houses, known as a bicameral legislature. Bicameralism is distinguished from unicameralism, in which all members deliberate ...
legislature consisting of the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
and House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entities. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often ...
. The Senate is composed of 33 districts, each of which is represented by one senator. Each senator represents approximately 330,000 constituents. The House of Representatives has 99 members. The Republican Party is the majority party in both houses as of the 2022 election cycle.
In order to be enacted into law, a bill must be adopted by both houses of the General Assembly and signed by the governor. If the governor vetoes a bill, the General Assembly can override the veto with a three-fifths supermajority of both houses. A bill will also become a law if the governor fails to sign or veto it within 10 days of its being presented. The session laws
Session laws are the collection of statutes enacted by a legislature during a single session of that legislature, often published following the end of the session as a bound volume. The United States Statutes at Large is an example of session la ...
are published in the official ''Law of Ohio
The law of Ohio consists of several levels, including constitutional, statutory, and regulatory, local and common law. The ''Ohio Revised Code'' forms the general statutory law.
Sources
The Constitution of Ohio is the foremost source of state ...
''. These in turn have been codified in the ''Ohio Revised Code
The ''Ohio Revised Code'' (ORC) contains all current statutes of the Ohio General Assembly of a permanent and general nature, consolidated into provisions, titles, chapters and sections. However, the only official publication of the enactments o ...
''. The General Assembly, with the approval of the governor, draws the U.S. congressional district lines for Ohio's 16 seats in the United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives is a chamber of the Bicameralism, bicameral United States Congress; it is the lower house, with the U.S. Senate being the upper house. Together, the House and Senate have the authority under Artic ...
. The Ohio Apportionment Board draws state legislative district lines in Ohio.
 There are three levels of the Ohio state
There are three levels of the Ohio state judiciary
The judiciary (also known as the judicial system, judicature, judicial branch, judiciative branch, and court or judiciary system) is the system of courts that adjudicates legal disputes/disagreements and interprets, defends, and applies the law ...
. The lowest is the court of common pleas: each county maintains its own constitutionally mandated court of common pleas, which maintain jurisdiction over "all justiciable matters". The intermediate-level court system is the district court system. Twelve courts of appeals exist, each retaining jurisdiction over appeals from common pleas, municipal, and county courts in a set geographical area. A case heard in this system is decided by a three-judge panel, and each judge is elected.
The state's highest-ranking court is the Ohio Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the State of Ohio is the highest court in the U.S. state of Ohio, with final authority over interpretations of Ohio law and the Ohio Constitution. The court has seven members, a chief justice and six associate justices, ...
. A seven-justice panel composes the court, which, by its own discretion
Discretion has the meaning of acting on one's own authority and judgment. In law, discretion as to legal rulings, such as whether evidence is excluded at a trial, may be exercised by a judge.
The ability to make decisions which represent a res ...
, hears appeals from the courts of appeals, and retains original jurisdiction over limited matters.
Local government
There are also several levels of local government in Ohio:counties
A county () is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesL. Brookes (ed.) '' Chambers Dictionary''. Edinburgh: Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, 2005. in some nations. The term is derived from the Old French denoti ...
, municipalities (List of cities in Ohio, cities and List of villages in Ohio, villages), List of townships in Ohio, townships, special districts, and school districts.
Ohio is divided into 88 counties. Ohio law defines a structure for county government, although they may adopt charters for home rule. Summit County, Ohio, Summit County and Cuyahoga County, Ohio, Cuyahoga County have chosen an alternate form of government. The other counties have a government with a three-member board of county commissioners, a sheriff, coroner, auditor, treasurer, clerk of the court of common pleas prosecutor, engineer, and recorder.
There are two kinds of incorporated municipalities, 251 cities and 681 villages. If a municipality has five thousand or more residents as of the last United States Census it is a city, otherwise it is a village. Municipalities have full home rule powers, may adopt a charter, ordinances and resolutions for self-government. Each municipality chooses its own form of government, but most have elected mayors and city councils or city commissions. City governments provide much more extensive services than county governments, such as police forces and paid (as opposed to volunteer) fire departments.
The entire area of the state is encompassed by townships. When the boundaries of a township are coterminous with the boundaries of a city or village, the township ceases to exist as a separate government (called a paper township). Townships are governed by a three-member board of township trustees. Townships may have limited home rule powers.
There are more than 600 city, local, and exempted village school districts providing K-12 education in Ohio, as well as about four dozen joint vocation school districts, which are separate from the K-12 districts. Each city school district, local school district, or exempted village school district is governed by an elected board of education. A school district previously under state supervision (municipal school district) may be governed by a board whose members either are elected or appointed by the mayor of the municipality containing the greatest portion of the district's area.
Politics
swing state
In United States politics, a swing state (also known as battleground state, toss-up state, or purple state) is any state that could reasonably be won by either the Democratic or Republican candidate in a statewide election, most often refe ...
in the late 20th and early 21st centuries; this status was called into question after the state voted for Republican Donald Trump at larger margins than the nation as a whole in the 2016 United States presidential election in Ohio, 2016, 2020 United States presidential election in Ohio, 2020 and 2024 United States presidential election in Ohio, 2024 presidential elections. It is also considered a bellwether state. Since 1896 United States presidential election, 1896, Ohio has had only three misses in the general election (1944 United States presidential election in Ohio, 1944, 1960 United States presidential election in Ohio, 1960, 2020 United States presidential election in Ohio, 2020) and had the longest perfect streak of any state, voting for the winning presidential candidate in each election from 1964 United States presidential election, 1964 to 2016 United States presidential election, 2016 and in 34 of the 39 held since the American Civil War. No Republican has ever won the presidency without winning Ohio.
As of 2024, there are more than 8 million registered Ohioan voters, of which over 70% are not affiliated with any political party. They are disproportionate in age, with a million more over 65 than there are 18- to 24-year-olds. Since the 2010 United States elections, 2010 midterm elections, Ohio's voter demographic has leaned towards the Republican Party.
The governor, Mike DeWine
Richard Michael DeWine ( ; born January 5, 1947) is an American politician and attorney serving as the 70th List of governors of Ohio, governor of Ohio since 2019. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he served a ...
, is Republican, as are all other non-judicial statewide elected officials. In the Ohio State Senate the Republicans are the majority, 25–8, and in the Ohio House of Representatives the Republicans control the delegation 64–35.
Following the 2020 census, Ohio has 15 seats in the U.S. House of Representatives. As of the 2024 Ohio elections, 2024 election cycle, ten federal representatives are Republicans while five are Democrats. Marcy Kaptur (D-Ohio's 9th congressional district, 09) is the most senior member of the Ohio delegation to the U.S. House of Representatives. The Seniority in the United States Senate, senior U.S. senator is Bernie Moreno and the junior is Jon Husted. Both are Republicans.
In 2023, Ohioans approved a November 2023 Ohio Issue 1, constitutional amendment strengthening abortion rights.
"Mother of presidents"
Six U.S. presidents hailed from Ohio at the time of their elections, giving rise to its nickname "mother of presidents", a sobriquet it shares withVirginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
. It is also termed "modern mother of presidents", in contrast to Virginia's status as the origin of presidents earlier in American history. Virginia-born William Henry Harrison lived much of his life in North Bend, Ohio, was elected from the state and is also buried there. The other five presidents are Rutherford B. Hayes, James A. Garfield, William McKinley, William Howard Taft and Warren G. Harding. Seven presidents were born in Ohio, making it second to Virginia's eight; in addition to the aforementioned five, Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was the 18th president of the United States, serving from 1869 to 1877. In 1865, as Commanding General of the United States Army, commanding general, Grant led the Uni ...
was elected from Illinois and Benjamin Harrison was elected from Indiana
Indiana ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Michigan to the northwest, Michigan to the north and northeast, Ohio to the east, the Ohio River and Kentucky to the s ...
.
Allegations of voter suppression
In a 2020 study, Ohio was ranked as the 17th hardest state for citizens to vote in. Since 1994, the state has had a policy of purging infrequent voters from its rolls. In April 2016, a lawsuit was filed, challenging this policy on the grounds that it violated the National Voter Registration Act of 1993, National Voter Registration Act (NVRA) of 1993 and the Help America Vote Act of 2002. In June, the federal district court ruled for the plaintiffs and entered a preliminary injunction applicable only to the November 2016 election. The preliminary injunction was upheld in September by the United States Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit, Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit. Had it not been upheld, thousands of voters would have been purged from the rolls just a few weeks before the election.Education
Ohio's system of public education is outlined in Article VI of the Ohio Constitution, state constitution, and in Title XXXIII of theOhio Revised Code
The ''Ohio Revised Code'' (ORC) contains all current statutes of the Ohio General Assembly of a permanent and general nature, consolidated into provisions, titles, chapters and sections. However, the only official publication of the enactments o ...
. Substantively, Ohio's system is similar to those found in Education in the United States, other states. At the State level, the Ohio Department of Education governs primary and secondary educational institutions. At the municipal level, there are approximately 700 school districts statewide. The Ohio Board of Regents coordinates and assists with Ohio's institutions of higher education.
Ohio is home to several public and private institutions of higher learning. Prior to statehood, the Northwest Ordinance
The Northwest Ordinance (formally An Ordinance for the Government of the Territory of the United States, North-West of the River Ohio and also known as the Ordinance of 1787), enacted July 13, 1787, was an organic act of the Congress of the Co ...
of 1787 included a provision to establish an institution of higher education in the region, resulting in the establishment of Ohio University in 1804 as Ohio's first college. The University System of Ohio includes all of Ohio's public institutions of higher education. It includes 14 four-year research university, research universities, 24 branch and regional campuses, and 23 community colleges and Institute of technology, technical colleges. Ohio State University
The Ohio State University (Ohio State or OSU) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Columbus, Ohio, United States. A member of the University System of Ohio, it was founded in 1870. It is one ...
is the largest of the system, with over 60,000 students at its main campus in Columbus.As of fall 2021.
Kenyon College is the state's oldest private liberal arts college, established in 1824 by an Episcopal Church (United States), Episcopal bishop to train clergy on the Ohio frontier. Oberlin College
Oberlin College is a Private university, private Liberal arts colleges in the United States, liberal arts college and conservatory of music in Oberlin, Ohio, United States. Founded in 1833, it is the oldest Mixed-sex education, coeducational lib ...
, established in 1833, was among the earliest colleges in the US to admit African Americans in 1835, and became the first to admit women in 1837.
The Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching, Carnegie Foundation classifies seven of the state's institutions as tier 1 research universities: Case Western Reserve University
Case Western Reserve University (CWRU) is a Private university, private research university in Cleveland, Ohio, United States. It was established in 1967 by a merger between Western Reserve University and the Case Institute of Technology. Case ...
, University of Cincinnati
The University of Cincinnati (UC or Cincinnati, informally Cincy) is a public university, public research university in Cincinnati, Ohio, United States. It was founded in 1819 and had an enrollment of over 53,000 students in 2024, making it the ...
, University of Dayton
The University of Dayton (UD) is a Private university, private, Catholic research university in Dayton, Ohio, United States. Founded in 1850 by the Society of Mary (Marianists), Society of Mary, it is one of three Marianist universities in the U ...
, Kent State University
Kent State University (KSU) is a Public university, public research university in Kent, Ohio, United States. The university includes seven regional campuses in Northeast Ohio located in Kent State University at Ashtabula, Ashtabula, Kent State ...
, Ohio State University, Ohio University, and University of Toledo.
Libraries
Ohio is home to some of the nation's highest-ranked public libraries. Major metropolitan public library systems include the Cleveland Public Library, the Cuyahoga County Public Library, the Cincinnati and Hamilton County Public Library, and the Columbus Metropolitan Library. The Ohio Public Library Information Network provides Ohio residents with internet access to their 251 public libraries. It also provides Ohioans with free home access to high-quality, subscription research databases. The OhioLINK library consortium provides Ohio's college and university libraries with mutual access to their collections. The program allows researchers access to books and other media that might not be otherwise available. CLEVNET, another major library consortium, is based at the Cleveland Public Library and includes 47 public library systems in Northeast Ohio.Transportation

Roads
Many major east–west transportation corridors go through Ohio. One of those pioneer routes, known in the early 20th century as "Main Market Route 3", was chosen in 1913 to become part of the historic Lincoln Highway which was the first road across America, connecting New York City to San Francisco. In Ohio, the Lincoln Highway linked many towns and cities together, including Canton,Mansfield
Mansfield is a market town and the administrative centre of the Mansfield District in Nottinghamshire, England. It is the largest town in the wider Mansfield Urban Area and the second largest settlement in Nottinghamshire (following the city ...
, Wooster, Ohio, Wooster, Lima
Lima ( ; ), founded in 1535 as the Ciudad de los Reyes (, Spanish for "City of Biblical Magi, Kings"), is the capital and largest city of Peru. It is located in the valleys of the Chillón River, Chillón, Rímac River, Rímac and Lurín Rive ...
, and Van Wert, Ohio, Van Wert. The Lincoln Highway's arrival in Ohio was a major influence on the state's development. Upon the advent of the federal numbered highway system in 1926, the Lincoln Highway through Ohio became U.S. Route 30 in Ohio, U.S. Route 30.
Ohio is home to of the National Road, now U.S. Route 40 in Ohio, U.S. Route 40.
Ohio has a highly developed network of roads and interstate highways. Major east-west through routes include the Ohio Turnpike (Interstate 80 in Ohio, I-80/Interstate 90 in Ohio, I-90) in the north, Interstate 76 in Ohio, I-76 through Akron
Akron () is a city in Summit County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. It is the fifth-most populous city in Ohio, with a population of 190,469 at the 2020 census. The Akron metropolitan area, covering Summit and Portage counties, had ...
to Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
, Interstate 70 in Ohio, I-70 through Columbus and Dayton
Dayton () is a city in Montgomery County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of cities in Ohio, sixth-most populous city in Ohio, with a population of 137,644 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The Dayton metro ...
, and the Appalachian Highway (Ohio), Appalachian Highway (Ohio State Route 32, State Route 32) running from West Virginia
West Virginia is a mountainous U.S. state, state in the Southern United States, Southern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States.The United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau and the Association of American ...
to Cincinnati
Cincinnati ( ; colloquially nicknamed Cincy) is a city in Hamilton County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. Settled in 1788, the city is located on the northern side of the confluence of the Licking River (Kentucky), Licking and Ohio Ri ...
. Major north–south routes include Interstate 75 in Ohio, I-75 in the west through Toledo, Dayton, and Cincinnati, Interstate 71, I-71 through the middle of the state from Cleveland
Cleveland is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County. Located along the southern shore of Lake Erie, it is situated across the Canada–U.S. maritime border and approximately west of the Ohio-Pennsylvania st ...
through Columbus and Cincinnati into Kentucky
Kentucky (, ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north, West Virginia to the ...
, and Interstate 77 in Ohio, I-77 in the eastern part of the state from Cleveland through Akron, Canton, New Philadelphia, Ohio, New Philadelphia and Marietta south into West Virginia. Interstate 75 between Cincinnati and Dayton is one of Ohio's most heavily traveled sections of interstate.
Trails
Ohio has a highly developed network of signed state bicycle routes. Many of them follow rail trails, with conversion ongoing. The Ohio to Erie Trail (route 1) connects Cincinnati, Columbus, and Cleveland. U.S. Bicycle Route 50 traverses Ohio fromSteubenville
Steubenville ( ) is a city in Jefferson County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. Located along the Ohio River west of Pittsburgh, it had a population of 18,161 at the 2020 census. The Weirton–Steubenville metropolitan area has an es ...
to the Indiana state line outside Richmond, Indiana, Richmond.
Ohio has several long-distance hiking trails, the most prominent of which is the Buckeye Trail, which extends in a loop around the state. Part of it is on roads and part on wooded trail. Additionally, the North Country Trail (the longest of the 11 National Scenic Trails authorized by Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
) and the American Discovery Trail (a system of recreational trails and roads that collectively form a coast-to-coast route across the mid-tier of the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
) pass through Ohio. Much of these two trails coincide with the Buckeye Trail.
Rail
Ohio has an extensive rail network, though today most lines carry only freight traffic. Three Class I railroads, Class I freight railroads operate in Ohio: CSX Transportation, Norfolk Southern Railway, and Canadian National Railway. Many local freight carriers also exist in the state. Amtrak, the national passenger railroad, operates three long-distance rail routes through Ohio. The ''Lake Shore Limited'' serves , , , , and . The ''Capitol Limited'' stops in those cities as well as in . The ''Cardinal (train), Cardinal'' servesCincinnati Union Terminal
Cincinnati Union Terminal is an intercity train station and museum center in the Queensgate, Cincinnati, Queensgate neighborhood of Cincinnati, Ohio. Commonly abbreviated as CUT, or by its Amtrak station code, CIN, the Railroad terminal, termin ...
. From Ohio, passengers can ride directly to , , South Station, Boston, , , , , and dozens of destinations in-between.
Columbus is the largest city in the U.S. with no passenger rail. Its Union Station (Columbus, Ohio), Union Station was last served in 1979 by the ''National Limited (Amtrak train), National Limited.''
Ohio is home to several Heritage railway, scenic railways and museums, including the Cuyahoga Valley Scenic Railroad through Cuyahoga Valley National Park
Cuyahoga Valley National Park is a List of national parks of the United States, national park of the United States in Ohio that reclaims and preserves the industrial, commercial, and rural landscape along the Cuyahoga River between Akron, Ohio, ...
, the Age of Steam Roundhouse museum, and the Hocking Valley Scenic Railway near Hocking Hills State Park.
Transit
 Mass transit exists in many forms in Ohio cities, primarily through bus systems. The Greater Cleveland Regional Transit Authority (GCRTA) operates the RTA Rapid Transit system, which consists of one heavy rail line, three Light rail in the United States, light rail lines, and three bus rapid transit lines. Cincinnati is served by the Southwest Ohio Regional Transit Authority (SORTA) bus network as well as a streetcar line, the Cincinnati Bell Connector. Other major transit agencies in Ohio include the Central Ohio Transit Authority (COTA) serving Columbus and the Greater Dayton Regional Transit Authority (GDRTA) serving Dayton.
Mass transit exists in many forms in Ohio cities, primarily through bus systems. The Greater Cleveland Regional Transit Authority (GCRTA) operates the RTA Rapid Transit system, which consists of one heavy rail line, three Light rail in the United States, light rail lines, and three bus rapid transit lines. Cincinnati is served by the Southwest Ohio Regional Transit Authority (SORTA) bus network as well as a streetcar line, the Cincinnati Bell Connector. Other major transit agencies in Ohio include the Central Ohio Transit Authority (COTA) serving Columbus and the Greater Dayton Regional Transit Authority (GDRTA) serving Dayton.
Air travel
Ohio has four international airports, four commercial, and two military. The four international include Cleveland Hopkins International Airport, John Glenn Columbus International Airport, Dayton International Airport, and Rickenbacker International Airport (one of two military airfields). The other military airfield is Wright Patterson Air Force Base which is one of the largest Air Force bases in the United States. Other major airports are in Toledo Express Airport, Toledo and Akron-Canton Airport, Akron. Cincinnati's main airport, Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky International Airport, is in Hebron, Kentucky, and therefore is not included in Ohio airport lists.Waterways
See also
* Index of Ohio-related articles * Outline of OhioNotes
References
Bibliography
* ''Profiles of Ohio: history, statistics, demographics for all 1,339 populated places in Ohio, with detailed state and government histories, plus comparative statistics & rankings.'' (6th ed. Grey House Publishing, 2021). 828pp ; covers 88 counties, 248 cities and 689 villages. * Cayton, Andrew R. L. (2002). ''Ohio: The History of a People''. Columbus, OH: The Ohio State University Press. * Kern, Kevin F., and Gregory S. Wilson. (2013) ''Ohio: A History of the Buckeye State'' (Wiley-Blackwell, 2013), 544pp * Knepper, George W. (1989). ''Ohio and Its People''. Kent, OH: Kent State University Press. * Holli, Melvin G. (1999). ''The American Mayor''. State College, PA: Pennsylvania State University Press. * Roseboom, Eugene H.; Weisenburger, Francis P. (1967). ''A History of Ohio''. Columbus: The Ohio Historical Society. * * Schmidlin, Thomas; Schmidlin, Jeanne Appelhans (1996)''Thunder in the Heartland: A Chronicle of Outstanding Weather Events in Ohio''
. The Kent State university Press. Kent, Ohio. .
External links
State of Ohio official website
Ohio State Facts from USDA
USGS real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of Ohio
* {{coord, 40, -83, dim:300000_region:US-OH_type:adm1st, name=State of Ohio, display=title Ohio, States of the United States Midwestern United States States and territories established in 1803 Former British colonies and protectorates in the Americas Former French colonies 1803 establishments in the United States Contiguous United States