Wrought Iron on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Wrought iron is an
 Wrought iron has been used for many centuries, and is the "iron" that is referred to throughout Western history. The other form of iron,
Wrought iron has been used for many centuries, and is the "iron" that is referred to throughout Western history. The other form of iron,
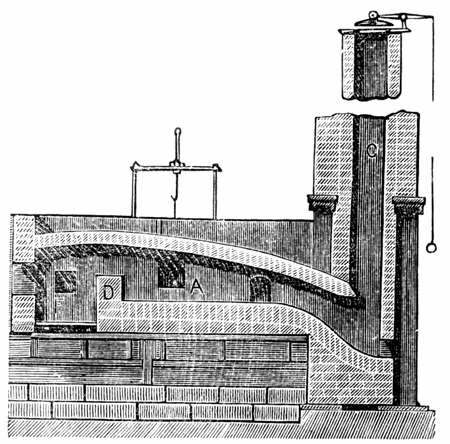 A number of processes for making wrought iron without charcoal were devised as the
A number of processes for making wrought iron without charcoal were devised as the
 Wrought iron contains approximately 250,000 slag inclusions, or stringers, per square inch, giving it properties not found in other forms of ferrous metal. A fresh fracture shows a clear bluish color with a high silky luster and fibrous appearance.
Wrought iron lacks the carbon content necessary for hardening through heat treatment, but in areas where steel was uncommon or unknown, tools were sometimes cold-worked (hence cold iron) to harden them. An advantage of its low carbon content is its excellent weldability. Furthermore, sheet wrought iron cannot bend as much as steel sheet metal when cold worked. Wrought iron can be melted and cast; however, the product is no longer wrought iron, since the slag stringers characteristic of wrought iron disappear on melting, so the product resembles impure, cast, Bessemer steel. There is no engineering advantage to melting and casting wrought iron, as compared to using cast iron or steel, both of which are cheaper.
Due to the variations in iron ore origin and iron manufacture, wrought iron can be inferior or superior in corrosion resistance, compared to other iron alloys. There are many mechanisms behind its corrosion resistance. Chilton and Evans found that nickel enrichment bands reduce corrosion. They also found that in puddled, forged, and piled iron, the working-over of the metal spread out copper, nickel, and tin impurities that produce electrochemical conditions that slow down corrosion. The slag inclusions have been shown to disperse corrosion to an even film, enabling the iron to resist pitting. Another study has shown that slag inclusions are pathways to corrosion. Other studies show that sulfur in the wrought iron decreases corrosion resistance, while phosphorus increases corrosion resistance. Chloride ions also decrease wrought iron's corrosion resistance.
Wrought iron may be welded in the same manner as mild steel, but the presence of oxide or inclusions will give defective results.
The material has a rough surface, so it can hold platings and coatings better than smooth steel. For instance, a galvanic zinc finish applied to wrought iron is approximately 25–40% thicker than the same finish on steel. In Table 1, the chemical composition of wrought iron is compared to that of pig iron and carbon steel. Although it appears that wrought iron and plain carbon steel have similar chemical compositions, that is deceptive. Most of the manganese, sulfur, phosphorus, and silicon in the wrought iron are incorporated into the slag fibers, making wrought iron purer than plain carbon steel.
Amongst its other properties, wrought iron becomes soft at
Wrought iron contains approximately 250,000 slag inclusions, or stringers, per square inch, giving it properties not found in other forms of ferrous metal. A fresh fracture shows a clear bluish color with a high silky luster and fibrous appearance.
Wrought iron lacks the carbon content necessary for hardening through heat treatment, but in areas where steel was uncommon or unknown, tools were sometimes cold-worked (hence cold iron) to harden them. An advantage of its low carbon content is its excellent weldability. Furthermore, sheet wrought iron cannot bend as much as steel sheet metal when cold worked. Wrought iron can be melted and cast; however, the product is no longer wrought iron, since the slag stringers characteristic of wrought iron disappear on melting, so the product resembles impure, cast, Bessemer steel. There is no engineering advantage to melting and casting wrought iron, as compared to using cast iron or steel, both of which are cheaper.
Due to the variations in iron ore origin and iron manufacture, wrought iron can be inferior or superior in corrosion resistance, compared to other iron alloys. There are many mechanisms behind its corrosion resistance. Chilton and Evans found that nickel enrichment bands reduce corrosion. They also found that in puddled, forged, and piled iron, the working-over of the metal spread out copper, nickel, and tin impurities that produce electrochemical conditions that slow down corrosion. The slag inclusions have been shown to disperse corrosion to an even film, enabling the iron to resist pitting. Another study has shown that slag inclusions are pathways to corrosion. Other studies show that sulfur in the wrought iron decreases corrosion resistance, while phosphorus increases corrosion resistance. Chloride ions also decrease wrought iron's corrosion resistance.
Wrought iron may be welded in the same manner as mild steel, but the presence of oxide or inclusions will give defective results.
The material has a rough surface, so it can hold platings and coatings better than smooth steel. For instance, a galvanic zinc finish applied to wrought iron is approximately 25–40% thicker than the same finish on steel. In Table 1, the chemical composition of wrought iron is compared to that of pig iron and carbon steel. Although it appears that wrought iron and plain carbon steel have similar chemical compositions, that is deceptive. Most of the manganese, sulfur, phosphorus, and silicon in the wrought iron are incorporated into the slag fibers, making wrought iron purer than plain carbon steel.
Amongst its other properties, wrought iron becomes soft at
iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have prop ...
with a very low carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
content (less than 0.05%) in contrast to that of cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content of more than 2% and silicon content around 1–3%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloying elements determine the form in which its car ...
(2.1% to 4.5%), or 0.25 for low carbon "mild" steel. Wrought iron is manufactured by heating and melting high carbon cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content of more than 2% and silicon content around 1–3%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloying elements determine the form in which its car ...
in an open charcoal or coke hearth or furnace in a process known as puddling. The high temperatures cause the excess carbon to oxidise, the iron being stirred or puddled during the process in order to achieve this. As the carbon content reduces, the melting point of the iron increases, ultimately to a level which is higher than can be achieved by the hearth, hence the wrought iron is never fully molten and many impurities remain.
The primary advantage of wrought iron over cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content of more than 2% and silicon content around 1–3%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloying elements determine the form in which its car ...
is its malleability - where cast iron is too brittle to bend or shape without breaking, wrought iron is highly malleable, and much easier to bend.
Wrought iron is a semi-fused mass of iron with fibrous slag inclusions (up to 2% by weight), which give it a wood-like "grain" that is visible when it is etched, rusted, or bent to failure
Failure is the social concept of not meeting a desirable or intended objective, and is usually viewed as the opposite of success. The criteria for failure depends on context, and may be relative to a particular observer or belief system. On ...
. Wrought iron is tough, malleable, ductile, corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engine ...
resistant, and easily forge welded, but is more difficult to weld electrically.
Before the development of effective methods of steelmaking and the availability of large quantities of steel, wrought iron was the most common form of malleable iron. It was given the name ''wrought'' because it was hammered, rolled, or otherwise worked while hot enough to expel molten slag. The modern functional equivalent of wrought iron is mild steel, also called low-carbon steel. Neither wrought iron nor mild steel contain enough carbon to be hardened by heating and quenching.
The properties of wrought iron vary, depending upon the type of iron used and the variability inherent in the relatively crude and labour intensive manufacturing process. It is generally relatively pure iron with a very low carbon content plus a small amount of mostly silicate slag, which forms fibreous or laminar inclusions, caused by the hot rolling process used to form it into long bars or rods. Because these silicate inclusions separate layers of iron and form planes of weakness, wrought iron is anisotropic, its strength varying depending on its orientation. Wrought iron may typically be composed of around 99.4% iron by mass. The presence of slag can be beneficial for blacksmithing operations, such as forge welding, since the silicate inclusions act as a flux and give the material its unique, fibrous structure. The silicate filaments in the slag also protect the iron from corrosion and may diminish the effect of fatigue caused by shock and vibration.
Historically, a modest amount of wrought iron was refined into steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
, which was used mainly to produce sword
A sword is an edged and bladed weapons, edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter ...
s, cutlery, chisels, axes, and other edged tools, as well as springs and files. The demand for wrought iron reached its peak in the 1860s, being in high demand for ironclad warships and railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in railway track, tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel railway track, rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of ...
use. However, as advances in ferrous metallurgy improved the quality of mild steel, and as the Bessemer process and the Siemens–Martin process made steel much cheaper to produce, the use of wrought iron declined.
Many items, before they came to be made of mild steel, were produced from wrought iron, including rivets, nails, wire
file:Sample cross-section of high tension power (pylon) line.jpg, Overhead power cabling. The conductor consists of seven strands of steel (centre, high tensile strength), surrounded by four outer layers of aluminium (high conductivity). Sample d ...
, chains, rails, railway couplings, water and steam pipes, nuts, bolts, horseshoes, handrails, wagon tires, straps for timber roof trusses, and ornamental ironwork, among many other things.
Wrought iron is no longer produced on a commercial scale. Many products described as wrought iron, such as guard rail
Guard rails, guardrails, railings or protective guarding, in general, are a boundary feature and may be a means to prevent or deter access to dangerous or off-limits areas while allowing light and visibility in a greater way than a fence. Commo ...
s, garden furniture, and gate
A gate or gateway is a point of entry to or from a space enclosed by walls. The word is derived from Proto-Germanic language, Proto-Germanic ''*gatan'', meaning an opening or passageway. Synonyms include yett (which comes from the same root w ...
s are made of mild steel. They are described as "wrought iron" only because they have been made to resemble objects which in the past were wrought (worked) by hand by a blacksmith
A blacksmith is a metalsmith who creates objects primarily from wrought iron or steel, but sometimes from #Other metals, other metals, by forging the metal, using tools to hammer, bend, and cut (cf. tinsmith). Blacksmiths produce objects such ...
(although many decorative iron objects, including fences and gates, were often cast rather than wrought).
Terminology
The word "wrought" is an archaic past participle of the verb "to work", and so "wrought iron" literally means "worked iron". Wrought iron is a general term for the commodity, but is also used more specifically for finished iron goods, as manufactured by ablacksmith
A blacksmith is a metalsmith who creates objects primarily from wrought iron or steel, but sometimes from #Other metals, other metals, by forging the metal, using tools to hammer, bend, and cut (cf. tinsmith). Blacksmiths produce objects such ...
. It was used in that narrower sense in British Customs
Customs is an authority or Government agency, agency in a country responsible for collecting tariffs and for controlling International trade, the flow of goods, including animals, transports, personal effects, and hazardous items, into and out ...
records, such manufactured iron was subject to a higher rate of duty than what might be called "unwrought" iron. Cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content of more than 2% and silicon content around 1–3%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloying elements determine the form in which its car ...
, unlike wrought iron, is brittle and cannot be worked either hot or cold.
In the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries, wrought iron went by a wide variety of terms according to its form, origin, or quality.
While the bloomery
A bloomery is a type of metallurgical furnace once used widely for smelting iron from its iron oxides, oxides. The bloomery was the earliest form of smelter capable of smelting iron. Bloomeries produce a porous mass of iron and slag called ...
process produced wrought iron directly from ore, cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content of more than 2% and silicon content around 1–3%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloying elements determine the form in which its car ...
or pig iron
Pig iron, also known as crude iron, is an intermediate good used by the iron industry in the production of steel. It is developed by smelting iron ore in a blast furnace. Pig iron has a high carbon content, typically 3.8–4.7%, along with si ...
were the starting materials used in the finery forge and puddling furnace
Puddling is the process of converting pig iron to bar (wrought) iron in a coal fired reverberatory furnace. It was developed in England during the 1780s. The molten pig iron was stirred in a reverberatory furnace, in an Redox, oxidizing enviro ...
. Pig iron and cast iron have higher carbon content than wrought iron, but have a lower melting point than iron or steel. Cast and especially pig iron have excess slag which must be at least partially removed to produce quality wrought iron. At foundries it was common to blend scrap wrought iron with cast iron to improve the physical properties of castings.
For several years after the introduction of Bessemer and open hearth steel, there were different opinions as to what differentiated iron from steel; some believed it was the chemical composition and others that it was whether the iron heated sufficiently to melt and "fuse". Fusion eventually became generally accepted as relatively more important than composition below a given low carbon concentration. Another difference is that steel can be hardened by heat treating.
Historically, wrought iron was known as "commercially pure iron"; however, it no longer qualifies because current standards for commercially pure iron require a carbon content of less than 0.008 wt%.
Types and shapes
Bar iron is a generic term sometimes used to distinguish it from cast iron. It is the equivalent of an ingot of cast metal, in a convenient form for handling, storage, shipping and further working into a finished product. The bars were the usual product of the finery forge, but not necessarily made by that process: * Rod iron—cut from flat bar iron in a slitting mill provided the raw material for spikes and nails. * Hoop iron—suitable for the hoops of barrels, made by passing rod iron through rolling dies. * Plate iron—sheets suitable for use asboiler
A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid (generally water) is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, centra ...
plate.
* Blackplate—sheets, perhaps thinner than plate iron, from the black rolling stage of tinplate production.
* Voyage iron—narrow flat bar iron, made or cut into bars of a particular weight, a commodity for sale in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
for the Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade or transatlantic slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of Slavery in Africa, enslaved African people to the Americas. European slave ships regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Pass ...
. The number of bars per ton gradually increased from 70 per ton in the 1660s to 75–80 per ton in 1685 and "near 92 to the ton" in 1731.
Origin
* Charcoal iron—until the end of the 18th century, wrought iron was smelted from ore using charcoal, by thebloomery
A bloomery is a type of metallurgical furnace once used widely for smelting iron from its iron oxides, oxides. The bloomery was the earliest form of smelter capable of smelting iron. Bloomeries produce a porous mass of iron and slag called ...
process. Wrought iron was also produced from pig iron
Pig iron, also known as crude iron, is an intermediate good used by the iron industry in the production of steel. It is developed by smelting iron ore in a blast furnace. Pig iron has a high carbon content, typically 3.8–4.7%, along with si ...
using a finery forge or in a Lancashire hearth. The resulting metal was highly variable, both in chemistry and slag content.
* Puddled iron—the puddling process was the first large-scale process to produce wrought iron. In the puddling process, pig iron is refined in a reverberatory furnace to prevent contamination of the iron from the sulfur in the coal or coke. The molten pig iron is manually stirred, exposing the iron to atmospheric oxygen, which decarburizes the iron. As the iron is stirred, globs of wrought iron are collected into balls by the stirring rod (rabble arm or rod) and those are periodically removed by the puddler. Puddling was patented in 1784 and became widely used after 1800. By 1876, annual production of puddled iron in the UK alone was over 4 million tons. Around that time, the open hearth furnace was able to produce steel of suitable quality for structural purposes, and wrought iron production went into decline.
* Oregrounds iron—a particularly pure grade of bar iron made ultimately from iron ore from the Dannemora mine in Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
. Its most important use was as the raw material for the cementation process of steelmaking.
* Danks iron—originally iron imported to Great Britain from Gdańsk
Gdańsk is a city on the Baltic Sea, Baltic coast of northern Poland, and the capital of the Pomeranian Voivodeship. With a population of 486,492, Data for territorial unit 2261000. it is Poland's sixth-largest city and principal seaport. Gdań ...
, but in the 18th century more probably the kind of iron (from eastern Sweden) that once came from Gdańsk.
* Forest iron—iron from the English Forest of Dean, where haematite ore enabled tough iron to be produced.
* Lukes iron—iron imported from Liège
Liège ( ; ; ; ; ) is a City status in Belgium, city and Municipalities in Belgium, municipality of Wallonia, and the capital of the Liège Province, province of Liège, Belgium. The city is situated in the valley of the Meuse, in the east o ...
, whose Dutch name is "Luik".
* Ames iron or amys iron—another variety of iron imported to England from northern Europe. Its origin has been suggested to be Amiens
Amiens (English: or ; ; , or ) is a city and Communes of France, commune in northern France, located north of Paris and south-west of Lille. It is the capital of the Somme (department), Somme Departments of France, department in the region ...
, but it seems to have been imported from Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ...
in the 15th century and Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former provinces of the Netherlands, province on the western coast of the Netherland ...
later, suggesting an origin in the Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
valley. Its origins remain controversial.
* Botolf iron or Boutall iron—from Bytów
Bytów (; ; ) is a town in the Gdańsk Pomerania region of northern Poland with 16,730 inhabitants as of December 2021. It is the capital of Bytów County in the Pomeranian Voivodeship.
In the early Middle Ages a fortified stronghold stood nea ...
(Polish Pomerania
Pomerania ( ; ; ; ) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The central and eastern part belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship, West Pomeranian, Pomeranian Voivod ...
) or Bytom (Polish Silesia).
* Sable iron (or Old Sable)—iron bearing the mark (a sable) of the Demidov
The Demidov family (Russian: Деми́довы), also known as Demidoff or Dimidov, is a prominent Russian nobility, Russian noble family that rose to immense wealth and influence during the 18th and 19th centuries. The Demidovs became a wealth ...
family of Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
n ironmaster
An ironmaster is the manager, and usually owner, of a forge or blast furnace for the processing of iron. It is a term mainly associated with the period of the Industrial Revolution, especially in Great Britain.
The ironmaster was usually a larg ...
s, one of the better brands of Russian iron.
Quality
;Tough iron: Also spelled "tuf", is not brittle and is strong enough to be used for tools. ;Blend iron: Made using a mixture of different types ofpig iron
Pig iron, also known as crude iron, is an intermediate good used by the iron industry in the production of steel. It is developed by smelting iron ore in a blast furnace. Pig iron has a high carbon content, typically 3.8–4.7%, along with si ...
.
;Best iron: Iron put through several stages of piling and rolling to reach the stage regarded (in the 19th century) as the best quality.
;Marked bar iron: Made by members of the Marked Bar Association and marked with the maker's brand mark as a sign of its quality.
Defects
Wrought iron is a form of commercial iron containing less than 0.10% of carbon, less than 0.25% of impurities total of sulfur, phosphorus, silicon and manganese, and less than 2% slag by weight. Wrought iron is '' redshort'' or ''hot short'' if it contains sulfur in excess quantity. It has sufficient tenacity when cold, but cracks when bent or finished at a red heat. Hot short iron was considered unmarketable. ''Cold short'' iron, also known as ''coldshear'', ''colshire'', contains excessive phosphorus. It is very brittle when cold and cracks if bent. It may, however, be worked at high temperature. Historically, coldshort iron was considered sufficient for nails. Phosphorus is not necessarily detrimental to iron. Ancient Near Eastern smiths did not add lime to their furnaces. The absence of calcium oxide in the slag, and the deliberate use of wood with high phosphorus content during the smelting, induces a higher phosphorus content (typically <0.3%) than in modern iron (<0.02–0.03%). Analysis of the Iron Pillar of Delhi gives 0.11% in the iron. The included slag in wrought iron also imparts corrosion resistance. Antique music wire, manufactured at a time when mass-produced carbon-steels were available, was found to have low carbon and high phosphorus; iron with high phosphorus content, normally causing brittleness when worked cold, was easily drawn into music wires. Although at the time phosphorus was not an easily identified component of iron, it was hypothesized that the type of iron had been rejected for conversion to steel but excelled when tested for drawing ability.History
China
During the Han dynasty (202 BC – 220 AD), new iron smelting processes led to the manufacture of new wrought iron implements for use in agriculture, such as the multi-tube seed drill and iron plough. In addition to accidental lumps of low-carbon wrought iron produced by excessive injected air in ancient Chinese cupola furnaces. The ancient Chinese created wrought iron by using the finery forge at least by the 2nd century BC, the earliest specimens of cast andpig iron
Pig iron, also known as crude iron, is an intermediate good used by the iron industry in the production of steel. It is developed by smelting iron ore in a blast furnace. Pig iron has a high carbon content, typically 3.8–4.7%, along with si ...
fined into wrought iron and steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
found at the early Han dynasty site at Tieshengguo. Pigott speculates that the finery forge existed in the previous Warring States period
The Warring States period in history of China, Chinese history (221 BC) comprises the final two and a half centuries of the Zhou dynasty (256 BC), which were characterized by frequent warfare, bureaucratic and military reforms, and ...
(403–221 BC), due to the fact that there are wrought iron items from China dating to that period and there is no documented evidence of the bloomery
A bloomery is a type of metallurgical furnace once used widely for smelting iron from its iron oxides, oxides. The bloomery was the earliest form of smelter capable of smelting iron. Bloomeries produce a porous mass of iron and slag called ...
ever being used in China. The fining process involved liquifying cast iron in a fining hearth and removing carbon from the molten cast iron through oxidation
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
. Wagner writes that in addition to the Han dynasty hearths believed to be fining hearths, there is also pictorial evidence of the fining hearth from a Shandong
Shandong is a coastal Provinces of China, province in East China. Shandong has played a major role in Chinese history since the beginning of Chinese civilization along the lower reaches of the Yellow River. It has served as a pivotal cultural ...
tomb mural dated 1st to 2nd century AD, as well as a hint of written evidence in the 4th century AD Daoist text '' Taiping Jing''.
Western world
 Wrought iron has been used for many centuries, and is the "iron" that is referred to throughout Western history. The other form of iron,
Wrought iron has been used for many centuries, and is the "iron" that is referred to throughout Western history. The other form of iron, cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content of more than 2% and silicon content around 1–3%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloying elements determine the form in which its car ...
, was in use in China since ancient times but was not introduced into Western Europe until the 15th century; even then, due to its brittleness, it could be used for only a limited number of purposes. Throughout much of the Middle Ages, iron was produced by the direct reduction of ore in manually operated bloomeries, although water power had begun to be employed by 1104.
The raw material produced by all indirect processes is pig iron. It has a high carbon content and as a consequence, it is brittle and cannot be used to make hardware. The osmond process was the first of the indirect processes, developed by 1203, but bloomery production continued in many places. The process depended on the development of the blast furnace, of which medieval examples have been discovered at Lapphyttan, Sweden and in Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
.
The bloomery and osmond processes were gradually replaced from the 15th century by finery processes, of which there were two versions, the German and Walloon. They were in turn replaced from the late 18th century by puddling, with certain variants such as the Swedish Lancashire process. Those, too, are now obsolete, and wrought iron is no longer manufactured commercially.
Bloomery process
Wrought iron was originally produced by a variety of smelting processes, all described today as "bloomeries". Different forms of bloomery were used at different places and times. The bloomery was charged with charcoal and iron ore and then lit. Air was blown in through a tuyere to heat the bloomery to a temperature somewhat below the melting point of iron. In the course of the smelt, slag would melt and run out, andcarbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
from the charcoal would reduce the ore to iron, which formed a spongy mass (called a "bloom") containing iron and also molten silicate minerals (slag) from the ore. The iron remained in the solid state. If the bloomery were allowed to become hot enough to melt the iron, carbon would dissolve into it and form pig or cast iron, but that was not the intention. However, the design of a bloomery made it difficult to reach the melting point of iron and also prevented the concentration of carbon monoxide from becoming high.
After smelting was complete, the bloom was removed, and the process could then be started again. It was thus a batch process, rather than a continuous one such as a blast furnace. The bloom had to be forged mechanically to consolidate it and shape it into a bar, expelling slag in the process.
During the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, water-power was applied to the process, probably initially for powering bellows, and only later to hammers for forging the blooms. However, while it is certain that water-power was used, the details remain uncertain. That was the culmination of the direct process of ironmaking. It survived in Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
and southern France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
as Catalan Forges to the mid 19th century, in Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
as the ''stuckofen'' to 1775, and near Garstang in England until about 1770; it was still in use with hot blast in New York in the 1880s. In Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
the last of the old '' tatara'' bloomeries used in production of traditional tamahagane steel, mainly used in swordmaking, was extinguished only in 1925, though in the late 20th century the production resumed on a low scale to supply the steel to the artisan swordmakers.
Osmond process
Osmond iron consisted of balls of wrought iron, produced by melting pig iron and catching the droplets on a staff, which was spun in front of a blast of air so as to expose as much of it as possible to the air and oxidise its carbon content. The resultant ball was often forged into bar iron in a hammer mill.Finery process
In the 15th century, the blast furnace spread into what is nowBelgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
where it was improved. From there, it spread via the Pays de Bray on the boundary of Normandy
Normandy (; or ) is a geographical and cultural region in northwestern Europe, roughly coextensive with the historical Duchy of Normandy.
Normandy comprises Normandy (administrative region), mainland Normandy (a part of France) and insular N ...
and then to the Weald in England. With it, the finery forge spread. Those remelted the pig iron and (in effect) burnt out the carbon, producing a bloom, which was then forged into bar iron. If rod iron was required, a slitting mill was used.
The finery process existed in two slightly different forms. In Great Britain, France, and parts of Sweden, only the Walloon process was used. That employed two different hearths, a finery hearth for finishing the iron and a chafery hearth for reheating it in the course of drawing the bloom out into a bar. The finery always burnt charcoal, but the chafery could be fired with mineral coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal i ...
, since its impurities would not harm the iron when it was in the solid state. On the other hand, the German process, used in Germany, Russia, and most of Sweden used a single hearth for all stages.
The introduction of coke for use in the blast furnace by Abraham Darby in 1709 (or perhaps others a little earlier) initially had little effect on wrought iron production. Only in the 1750s was coke pig iron used on any significant scale as the feedstock of finery forges. However, charcoal continued to be the fuel for the finery.
Potting and stamping
From the late 1750s, ironmasters began to develop processes for making bar iron without charcoal. There were a number of patented processes for that, which are referred to today as potting and stamping. The earliest were developed by John Wood of Wednesbury and his brother Charles Wood of Low Mill at Egremont, patented in 1763. Another was developed for the Coalbrookdale Company by the Cranage brothers. Another important one was that of John Wright and Joseph Jesson ofWest Bromwich
West Bromwich ( ), commonly known as West Brom, is a market town in the borough of Sandwell, in the county of the West Midlands (county), West Midlands, England. Historic counties of England, Historically part of Staffordshire, it is northwes ...
.
Puddling process
 A number of processes for making wrought iron without charcoal were devised as the
A number of processes for making wrought iron without charcoal were devised as the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
began during the latter half of the 18th century. The most successful of those was puddling, using a puddling furnace (a variety of the reverberatory furnace), which was invented by Henry Cort in 1784. It was later improved by others including Joseph Hall, who was the first to add iron oxide to the charge. In that type of furnace, the metal does not come into contact with the fuel, and so is not contaminated by its impurities. The heat of the combustion products passes over the surface of the puddle and the roof of the furnace reverberates (reflects) the heat onto the metal puddle on the fire bridge of the furnace.
Unless the raw material used is white cast iron, the pig iron or other raw product of the puddling first had to be refined into refined iron, or finers metal. That would be done in a refinery where raw coal was used to remove silicon and convert carbon within the raw material, found in the form of graphite, to a combination with iron called cementite.
In the fully developed process (of Hall), this metal was placed into the hearth of the puddling furnace where it was melted. The hearth was lined with oxidizing agents such as haematite and iron oxide. The mixture was subjected to a strong current of air and stirred with long bars, called puddling bars or rabbles, through working doors. The air, the stirring, and the "boiling" action of the metal helped the oxidizing agents to oxidize the impurities and carbon out of the pig iron. As the impurities oxidize, they formed a molten slag or drifted off as gas, while the remaining iron solidified into spongy wrought iron that floated to the top of the puddle and was fished out of the melt as puddle balls, using puddle bars.
Shingling
There was still some slag left in the puddle balls, so while they were still hot they would be shingled to remove the remaining slag and cinder. That was achieved by forging the balls under a hammer, or by squeezing the bloom in a machine. The material obtained at the end of shingling is known as bloom. The blooms are not useful in that form, so they were rolled into a final product. Sometimes European ironworks would skip the shingling process completely and roll the puddle balls. The only drawback to that is that the edges of the rough bars were not as well compressed. When the rough bar was reheated, the edges might separate and be lost into the furnace.Rolling
The bloom was passed through rollers and to produce bars. The bars of wrought iron were of poor quality, called muck bars or puddle bars. To improve their quality, the bars were cut up, piled and tied together by wires, a process known as faggoting or piling. They were then reheated to a welding state, forge welded, and rolled again into bars. The process could be repeated several times to produce wrought iron of desired quality. Wrought iron that has been rolled multiple times is called merchant bar or merchant iron.Lancashire process
The advantage of puddling was that it used coal, not charcoal as fuel. However, that was of little advantage in Sweden, which lacked coal. Gustaf Ekman observed charcoal fineries at Ulverston, which were quite different from any in Sweden. After his return to Sweden in the 1830s, he experimented and developed a process similar to puddling but used firewood and charcoal, which was widely adopted in the Bergslagen in the following decades.Aston process
In 1925, James Aston of theUnited States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
developed a process for manufacturing wrought iron quickly and economically. It involved taking molten steel from a Bessemer converter and pouring it into cooler liquid slag. The temperature of the steel is about 1500 °C and the liquid slag is maintained at approximately 1200 °C. The molten steel contains a large amount of dissolved gases so when the liquid steel hit the cooler surfaces of the liquid slag the gases were liberated. The molten steel then froze to yield a spongy mass having a temperature of about 1370 °C. The spongy mass would then be finished by being shingled and rolled as described under puddling (above). Three to four tons could be converted per batch with the method.
Decline
Steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
began to replace iron for railroad rails as soon as the Bessemer process for its manufacture was adopted (1865 on). Iron remained dominant for structural applications until the 1880s, because of problems with brittle steel, caused by introduced nitrogen, high carbon, excess phosphorus, or excessive temperature during or too-rapid rolling. By 1890 steel had largely replaced iron for structural applications.
Sheet iron (Armco 99.97% pure iron) had good properties for use in appliances, being well-suited for enamelling and welding, and being rust-resistant.
In the 1960s, the price of steel production was dropping due to recycling, and even using the Aston process, wrought iron production was labor-intensive. It has been estimated that the production of wrought iron is approximately twice as expensive as that of low-carbon steel. In the United States, the last plant closed in 1969. The last in the world was the Atlas Forge of Thomas Walmsley and Sons in Bolton
Bolton ( , locally ) is a town in Greater Manchester in England. In the foothills of the West Pennine Moors, Bolton is between Manchester, Blackburn, Wigan, Bury, Greater Manchester, Bury and Salford. It is surrounded by several towns and vill ...
, Great Britain, which closed in 1973. Its 1860s-era equipment was moved to the Blists Hill site of Ironbridge Gorge Museum for preservation. Some wrought iron is still being produced for heritage restoration purposes, but only by recycling scrap.
Properties
 Wrought iron contains approximately 250,000 slag inclusions, or stringers, per square inch, giving it properties not found in other forms of ferrous metal. A fresh fracture shows a clear bluish color with a high silky luster and fibrous appearance.
Wrought iron lacks the carbon content necessary for hardening through heat treatment, but in areas where steel was uncommon or unknown, tools were sometimes cold-worked (hence cold iron) to harden them. An advantage of its low carbon content is its excellent weldability. Furthermore, sheet wrought iron cannot bend as much as steel sheet metal when cold worked. Wrought iron can be melted and cast; however, the product is no longer wrought iron, since the slag stringers characteristic of wrought iron disappear on melting, so the product resembles impure, cast, Bessemer steel. There is no engineering advantage to melting and casting wrought iron, as compared to using cast iron or steel, both of which are cheaper.
Due to the variations in iron ore origin and iron manufacture, wrought iron can be inferior or superior in corrosion resistance, compared to other iron alloys. There are many mechanisms behind its corrosion resistance. Chilton and Evans found that nickel enrichment bands reduce corrosion. They also found that in puddled, forged, and piled iron, the working-over of the metal spread out copper, nickel, and tin impurities that produce electrochemical conditions that slow down corrosion. The slag inclusions have been shown to disperse corrosion to an even film, enabling the iron to resist pitting. Another study has shown that slag inclusions are pathways to corrosion. Other studies show that sulfur in the wrought iron decreases corrosion resistance, while phosphorus increases corrosion resistance. Chloride ions also decrease wrought iron's corrosion resistance.
Wrought iron may be welded in the same manner as mild steel, but the presence of oxide or inclusions will give defective results.
The material has a rough surface, so it can hold platings and coatings better than smooth steel. For instance, a galvanic zinc finish applied to wrought iron is approximately 25–40% thicker than the same finish on steel. In Table 1, the chemical composition of wrought iron is compared to that of pig iron and carbon steel. Although it appears that wrought iron and plain carbon steel have similar chemical compositions, that is deceptive. Most of the manganese, sulfur, phosphorus, and silicon in the wrought iron are incorporated into the slag fibers, making wrought iron purer than plain carbon steel.
Amongst its other properties, wrought iron becomes soft at
Wrought iron contains approximately 250,000 slag inclusions, or stringers, per square inch, giving it properties not found in other forms of ferrous metal. A fresh fracture shows a clear bluish color with a high silky luster and fibrous appearance.
Wrought iron lacks the carbon content necessary for hardening through heat treatment, but in areas where steel was uncommon or unknown, tools were sometimes cold-worked (hence cold iron) to harden them. An advantage of its low carbon content is its excellent weldability. Furthermore, sheet wrought iron cannot bend as much as steel sheet metal when cold worked. Wrought iron can be melted and cast; however, the product is no longer wrought iron, since the slag stringers characteristic of wrought iron disappear on melting, so the product resembles impure, cast, Bessemer steel. There is no engineering advantage to melting and casting wrought iron, as compared to using cast iron or steel, both of which are cheaper.
Due to the variations in iron ore origin and iron manufacture, wrought iron can be inferior or superior in corrosion resistance, compared to other iron alloys. There are many mechanisms behind its corrosion resistance. Chilton and Evans found that nickel enrichment bands reduce corrosion. They also found that in puddled, forged, and piled iron, the working-over of the metal spread out copper, nickel, and tin impurities that produce electrochemical conditions that slow down corrosion. The slag inclusions have been shown to disperse corrosion to an even film, enabling the iron to resist pitting. Another study has shown that slag inclusions are pathways to corrosion. Other studies show that sulfur in the wrought iron decreases corrosion resistance, while phosphorus increases corrosion resistance. Chloride ions also decrease wrought iron's corrosion resistance.
Wrought iron may be welded in the same manner as mild steel, but the presence of oxide or inclusions will give defective results.
The material has a rough surface, so it can hold platings and coatings better than smooth steel. For instance, a galvanic zinc finish applied to wrought iron is approximately 25–40% thicker than the same finish on steel. In Table 1, the chemical composition of wrought iron is compared to that of pig iron and carbon steel. Although it appears that wrought iron and plain carbon steel have similar chemical compositions, that is deceptive. Most of the manganese, sulfur, phosphorus, and silicon in the wrought iron are incorporated into the slag fibers, making wrought iron purer than plain carbon steel.
Amongst its other properties, wrought iron becomes soft at red heat '' Red heat'' is a practice of using colours to determine the temperature of metal
Red Heat may also refer to:
* ''Red Heat'' (1985 film), a 1985 film starring Linda Blair
* ''Red Heat'' (1988 film), a 1988 film starring Arnold Schwarzenegger a ...
and can be easily forged and forge welded. It can be used to form temporary magnets, but it cannot be magnetized permanently, and is ductile, malleable, and tough.
Ductility
For most purposes, ductility rather than tensile strength is a more important measure of the quality of wrought iron. In tensile testing, the best irons are able to undergo considerable elongation before failure. Higher tensile wrought iron is brittle. Because of the large number of boiler explosions on steamboats in the early 1800s, the U.S. Congress passed legislation in 1830 which approved funds for correcting the problem. The treasury awarded a $1500 contract to the Franklin Institute to conduct a study. As part of the study, Walter R. Johnson and Benjamin Reeves conducted strength tests on boiler iron using a tester they had built in 1832 based on a design by Lagerhjelm in Sweden. Because of misunderstandings about tensile strength and ductility, their work did little to reduce failures. The importance of ductility was recognized by some very early in the development of tube boilers, evidenced by Thurston's comment: Various 19th century investigations of boiler explosions, especially those by insurance companies, found causes to be most commonly the result of operating boilers above the safe pressure range, either to get more power, or due to defective boiler pressure relief valves and difficulties of obtaining reliable indications of pressure and water levels. Poor fabrication was also a common problem. Also, the thickness of the iron in steam drums was low, by modern standards. By the late 19th century, when metallurgists were able to better understand what properties and processes made good iron, iron in steam engines was being displaced by steel, whilst the old cylindrical boilers with fire tubes were displaced by inherently safer water tube boilers.Purity
In 2010, Gerry McDonnell demonstrated in England by analysis that a wrought iron bloom, from a traditional smelt, could be worked into 99.7% pure iron with no evidence of carbon. It was found that the stringers common to other wrought irons were not present, thus making it very malleable for the smith to work hot and cold. A commercial source of pure iron is available and is used by smiths as an alternative to traditional wrought iron and other new generation ferrous metals.Applications
Wrought iron furniture has a long history, dating back to Roman times. There are 13th century wrought iron gates in Westminster Abbey in London, and wrought iron furniture seemed to reach its peak popularity in Britain in the 17th century, during the reign of William III and Mary II. However, cast iron and cheaper steel caused a gradual decline in wrought iron manufacture; the last wrought ironworks in Britain closed in 1974. It is also used to make home decor items such as baker's racks, wine racks, pot racks, etageres, table bases, desks, gates, beds, candle holders, curtain rods, bars, and bar stools. The vast majority of wrought iron available today is from reclaimed materials. Old bridges and anchor chains dredged from harbors are major sources. The greater corrosion resistance of wrought iron is due to the siliceous impurities (naturally occurring in iron ore), namely ferroussilicate
A silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used ...
.
Wrought iron has been used for decades as a generic term across the gate and fencing
Fencing is a combat sport that features sword fighting. It consists of three primary disciplines: Foil (fencing), foil, épée, and Sabre (fencing), sabre (also spelled ''saber''), each with its own blade and set of rules. Most competitive fe ...
industry, even though mild steel is used for manufacturing these "wrought iron" gates. This is mainly because of the limited availability of true wrought iron. Steel can also be hot-dip galvanised to prevent corrosion, which cannot be done with wrought iron.
See also
* Bronze and brass ornamental work *Cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content of more than 2% and silicon content around 1–3%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloying elements determine the form in which its car ...
* Semi-steel casting
Notes
References
Further reading
* *External links
* {{Authority control Architectural elements Building materials Chinese inventions Ferrous alloys Han dynasty Iron Ironmongery Metalworking