Von Hippel–Lindau Tumor Suppressor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor also known as pVHL is a
 The resultant protein is produced in two forms, an 18 kDa and a 30 kDa protein that functions as a
The resultant protein is produced in two forms, an 18 kDa and a 30 kDa protein that functions as a
VHL Alliance
GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Von Hippel–Lindau Syndrome or Angiomatosis Retinae, VHL Syndrome, von Hippel–Lindau Disease
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Von Hippel-Lindau Tumor Suppressor Tumor suppressor genes EC 6.3
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
that, in humans, is encoded by the ''VHL'' gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
. Mutations of the VHL gene are associated with Von Hippel–Lindau disease, which is characterized by hemangioblastomas of the brain, spinal cord and retina. It is also associated with kidney and pancreatic lesions.
Function
The protein encoded by the VHL gene is the substrate recognition component of a protein complex that includes elongin B, elongin C, and cullin-2, and possesses E3ubiquitin ligase
A ubiquitin ligase (also called an E3 ubiquitin ligase) is a protein that recruits an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme that has been loaded with ubiquitin, recognizes a protein substrate, and assists or directly catalyzes the transfer of ubiquitin ...
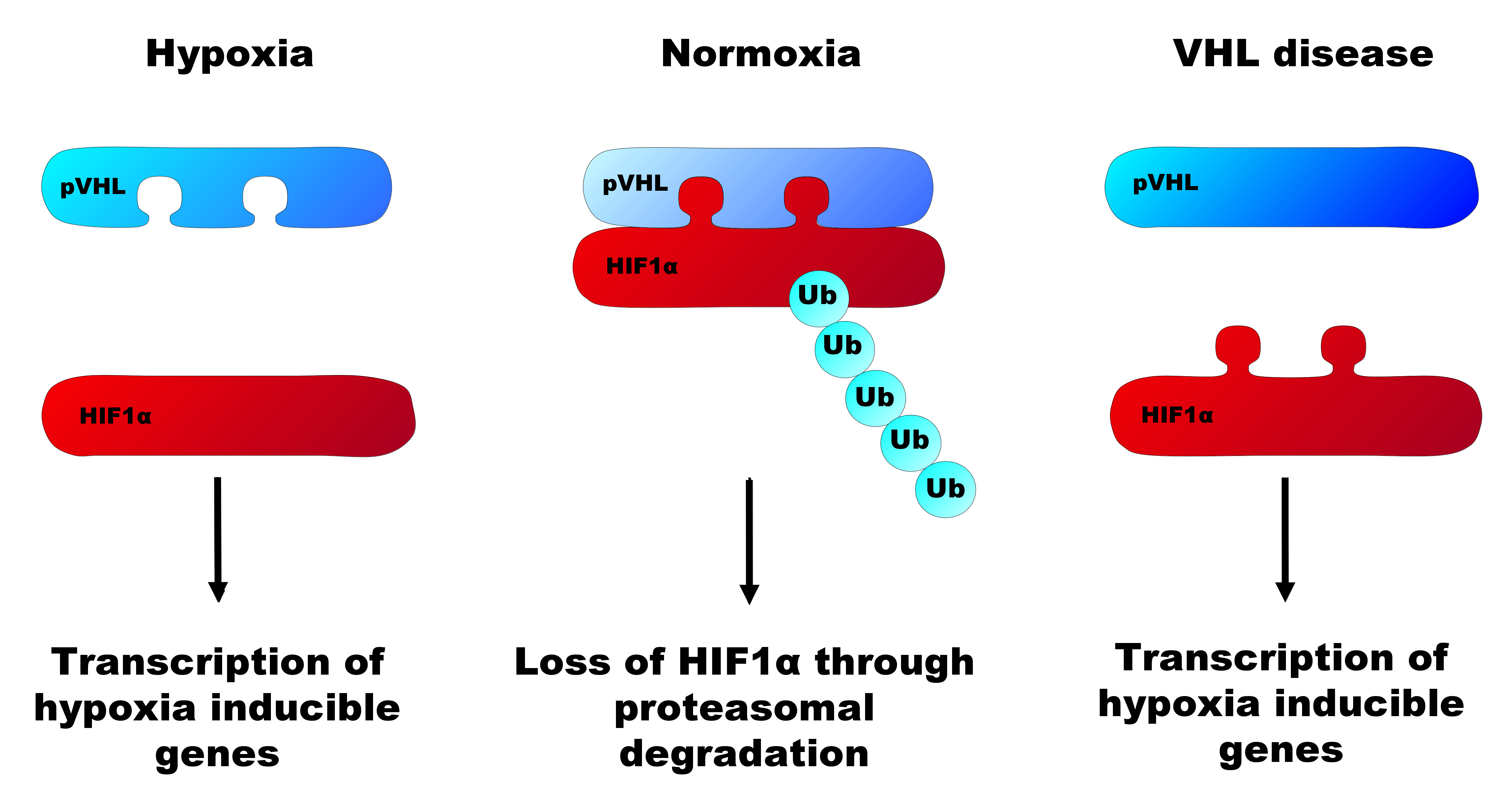
activity. This complex is involved in the ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs), which are transcription factors that play a central role regulating gene expression in response to changing oxygen levels. RNA polymerase II subunit POLR2G/RPB7 is also reported to be a target of this protein. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been observed.
 The resultant protein is produced in two forms, an 18 kDa and a 30 kDa protein that functions as a
The resultant protein is produced in two forms, an 18 kDa and a 30 kDa protein that functions as a tumor suppressor
A tumor suppressor gene (TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell (biology), cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer. When a tumor suppressor gene is mutated, it results ...
. The main action of the VHL protein is thought to be its E3 ubiquitin ligase activity that results in specific target proteins being 'marked' for degradation.
The most researched of these targets is hypoxia inducible factor 1a (HIF1a), a transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding t ...
that induces the expression of a number of angiogenesis
Angiogenesis is the physiological process through which new blood vessels form from pre-existing vessels, formed in the earlier stage of vasculogenesis. Angiogenesis continues the growth of the vasculature mainly by processes of sprouting and ...
related factors.
HIFs are necessary for tumor growth because most cancers demand high metabolic activity and are only supplied by structurally or functionally inadequate vasculature. Activation of HIFs allow for enhanced angiogenesis
Angiogenesis is the physiological process through which new blood vessels form from pre-existing vessels, formed in the earlier stage of vasculogenesis. Angiogenesis continues the growth of the vasculature mainly by processes of sprouting and ...
, which in turn allow for increased glucose uptake. While HIFs are mostly active in hypoxic conditions, VHL-defective renal carcinoma cells show constitutive activation of HIF even in oxygenated environments.
It is clear that VHL and HIFs interact closely. Firstly, all renal cell carcinoma mutations in VHL that have been tested affect the protein's ability to modify HIF. Additionally, HIF activation can be detected in the earliest events in tumorigenesis in patients with VHL syndrome. In normal cells in hypoxic conditions, HIF1A is activated with little activation of HIF2A. However, in tumors the balance of HIF1A and HIF2A is tipped towards HIF2A. While HIF1A serves as a pro-apoptotic factor, HIF2A interacts with cyclin D1. This leads to increased survival due to lower rates of apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biol ...
and increased proliferation due to the activation of cyclin D1.Maxwell, 2005 Recent genome-wide analysis (GWAS) of HIF binding in kidney cancer showed that HIF1A binds upstream of majorly good prognosis genes, while HIF2A binds upstream to majorly poor prognosis genes. This indicates that the HIF transcription factor distribution in kidney cancer is of major importance in determining the outcome of the patients.
In the normal cell with active VHL protein, HIF alpha is regulated by hydroxylation in the presence of oxygen. When iron, 2-oxoglutarate and oxygen are present, HIF is inactivated by HIF hydroxylases. Hydroxylation of HIF creates a binding site for pVHL (the protein product of the VHL gene). pVHL directs the polyubiquitylation of HIF1A, ensuring that this protein will be degraded by the proteasome. In hypoxic conditions, HIF1A subunits accumulate and bind to HIFB. This heterodimer of HIF is a transcription factor that activates genes that encode for proteins such as vascular endothelial growth factor ( VEGF) and erythropoietin, proteins that are both involved in angiogenesis. Cells with abnormal pVHL are unable to disrupt the formation of these dimers, and therefore behave like they are hypoxic even in oxygenated environments.
HIF has also been linked to mTOR, a central controller of growth decisions. It has recently been shown that HIF activation can inactivate mTOR.
HIF can help explain the organ-specific nature of VHL syndrome. It has been theorized that constitutively activating HIF in any cell could lead to cancer, but that there are redundant regulators of HIF in organs not affected by VHL syndrome. This theory has been disproved multiple times since in all cell types loss of VHL function leads to constitutive activation of HIF and its downstream effects. Another theory holds that although in all cells loss of VHL leads to activation of HIF, in ''most'' cells this leads to no advantage in proliferation or survival. Additionally, the nature of the mutation in the VHL protein leads to phenotypic manifestations in the pattern of cancer that develops. Nonsense or deletion mutations of VHL protein have been linked to type 1 VHL with a low risk of pheochromocytoma
Pheochromocytoma is a rare tumor of the adrenal medulla composed of chromaffin cells and is part of the paraganglioma (PGL) family of tumors, being defined as an intra-adrenal PGL. These neuroendocrine tumors can be sympathetic, where they relea ...
(adrenal gland tumors). Type 2 VHL has been linked to missense mutations and is linked to a high risk of pheochromocytoma. Type 2 has also been further subdivided based on risks of renal cell carcinoma. In types 1, 2A and 2B the mutant pVHL is defective in HIF regulation, while type 2C mutant are defective in protein kinase C
In cell biology, protein kinase C, commonly abbreviated to PKC (EC 2.7.11.13), is a family of protein kinase enzymes that are involved in controlling the function of other proteins through the phosphorylation of hydroxyl groups of serine and t ...
regulation. These genotype–phenotype correlations suggest that missense mutations of pVHL lead to a ' gain of function' protein.
The involvement in VHL in renal cell cancer can be rationalized via multiple characteristics of renal cells. First, they are more sensitive to the effects of growth factors created downstream of HIF activation than other cells. Secondly, the link to Cyclin D1 (as mentioned above) is only seen in renal cells. Finally, many cells in the kidney normally operate under hypoxic conditions. This may give them a proliferative advantage over other cells while in hypoxic environments.
In addition to its interaction with HIF the VHL protein can also associate with tubulin
Tubulin in molecular biology can refer either to the tubulin protein superfamily of globular proteins, or one of the member proteins of that superfamily. α- and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules, a major component of the eukaryotic cytosk ...
. It is then capable to stabilize and thus elongate microtubules. This function plays a key role in the stabilisation of the spindle during mitosis. Deletion or downregulation of VHL causes a drastic increase of misorientated and rotating spindles during mitosis. Through a not-yet-known mechanism, VHL also increases the concentration of MAD2, an important protein of the spindle checkpoint. Also, VHL colocalizes with the microtubule. Thus VHL loss leads to a weakened checkpoint and subsequently chromosome missegregation and aneuploidy
Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell (biology), cell, for example a human somatic (biology), somatic cell having 45 or 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. It does not include a difference of one or more plo ...
.
Pathology
Von Hippel–Lindau syndrome (VHL) is a dominantly inherited hereditary cancer syndrome predisposing to a variety of malignant and benign tumors of the eye, brain, spinal cord, kidney, pancreas, and adrenal glands. Agermline mutation
A germline mutation, or germinal mutation, is any detectable variation within germ cells (cells that, when fully developed, become sperm and Egg cell, ova). Mutations in these cells are the only mutations that can be passed on to offspring, when e ...
of this gene is the basis of familial inheritance of VHL syndrome. Individuals with VHL syndrome inherit one mutation in the VHL protein that causes the protein's normal function to be lost or altered. Over time, sporadic mutation in the second copy of the VHL protein can lead to carcinomas, in particular hemangioblastomas affecting the liver and kidneys, renal (and vaginal) clear cell adenocarcinomas.
The loss of VHL protein activity results in an increased amount of HIF1a, and thus increased levels of angiogenic factors, including VEGF and PDGF. In turn, this leads to unregulated blood vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (bi ...
growth, one of the prerequisites of a tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
. Additionally, VHL has been implicated in maintaining the differentiated phenotype in renal cells. Furthermore, cell culture experiments with VHL -/- cells have shown that the addition of pVHL can induce a mesenchymal
Mesenchyme () is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood, or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly ever ...
to epithelial
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
transition. This evidence suggests that VHL has a central role in maintaining a differentiated phenotype in the cell.
Additionally, pVHL is important for extracellular matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix (ICM), is a network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and bio ...
formation. This protein may also be important in inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases. These ideas are extremely important in the metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, ...
of VHL-deficient cells. In classical VHL disease a single wild-type allele in VHL appears to be sufficient to maintain normal cardiopulmonary function.
Diseases associated with mutation in the VHL gene such as subtype 1, 2A, and 2B has shown an upregulation of HIF. Which is some worth expected. However, there is normal expression of HIF in subtype 2C VHL disease which has a clinical phenotype as Phaeochromocytoma.
There are different mutations such as BRAF,TP53
p53, also known as tumor protein p53, cellular tumor antigen p53 (UniProt name), or transformation-related protein 53 (TRP53) is a regulatory transcription factor protein that is often mutated in human cancers. The p53 proteins (originally thou ...
, PTEN, RB1, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and ERBB2
Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 is a protein that normally resides in the membranes of cells and is encoded by the ''ERBB2'' gene. ERBB is abbreviated from erythroblastic oncogene B, a gene originally isolated from the avian genome. The ...
observed in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma ( ccRCC).However, more than 97% of those with ccRcc have a VHL mutation.
Treatment
Suggested targets for VHL-related cancers include targets of the HIF pathway, such as VEGF. Inhibitors of VEGF receptor sorafenib, sunitinib, pazopanib, and recently axitinib have been approved by the FDA. The mTOR inhibitorrapamycin
Sirolimus, also known as rapamycin and sold under the brand name Rapamune among others, is a macrolide compound that is used to coat coronary stents, prevent organ rejection, organ transplant rejection, treat a rare lung disease called lymphang ...
analogs everolimus and temsirolimus
Temsirolimus, sold under the brand name Torisel, is an intravenous drug for the treatment of renal cell carcinoma (RCC), developed by Wyeth Pharmaceuticals and approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in May 2007, and was also app ...
or VEGF monoclonal antibody bevacizumab may also be an option.
Since iron, 2-oxoglutarate and oxygen are necessary for the inactivation of HIF, it has been theorized that a lack of these cofactors could reduce the ability of hydroxylases in inactivating HIF. A recent study has shown that in cells with a high activation of HIF even in oxygenated environments was reversed by supplying the cells with ascorbate. Thus, Vitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits, berries and vegetables. It is also a generic prescription medication and in some countries is sold as a non-prescription di ...
may be a potential treatment for HIF induced tumors.
Applications
VHL has been frequently utilized for its E3 ubiquitin ligase activity in targeted protein degradation applications such as with PROTACs. Derivatized VHL ligands that act as molecular glue degraders have also been discovered through high-throughput screening.Interactions
Von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor has been shown to interact with: * CCDC82, * CUL2, *Filamin Filamins are a class of proteins that hold two actin filaments at large angles. Filamin protein in mammals is made up of an actin-binding domain at its N-terminus that is followed by 24 immunoglobulin-like repeat modules of roughly 95 amino acids
...
,
* HIF1AN,
* HIF1A,
* Nerve Growth factor IB
The nuclear receptor 4A1 (NR4A1 for "nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 1") also known as Nur77, TR3, and NGFI-B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NR4A1'' gene.
Nuclear receptor 4A1 (NR4A1) is a member of the ''NR4A'' nucle ...
,
* PHF17,
* PSMC3,
* SAP130,
* TCEB1,
* TCEB2, and
* USP33.
See also
*References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
VHL Alliance
GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Von Hippel–Lindau Syndrome or Angiomatosis Retinae, VHL Syndrome, von Hippel–Lindau Disease
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Von Hippel-Lindau Tumor Suppressor Tumor suppressor genes EC 6.3