Uyghurs on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Uyghurs; ; ; ; zh, s=, t=, p=Wéiwú'ěr, IPA: ( ), alternatively spelled Uighurs, Uygurs or Uigurs, are a
 Throughout its history, the term ''Uyghur'' has had an increasingly expansive definition. Initially signifying only a small coalition of Tiele tribes in northern China, Mongolia and the Altai Mountains, it later denoted citizenship in the Uyghur Khaganate. Finally, it was expanded into an ethnicity whose ancestry originates with the fall of the Uyghur Khaganate in the year 842, causing Uyghur migration from
Throughout its history, the term ''Uyghur'' has had an increasingly expansive definition. Initially signifying only a small coalition of Tiele tribes in northern China, Mongolia and the Altai Mountains, it later denoted citizenship in the Uyghur Khaganate. Finally, it was expanded into an ethnicity whose ancestry originates with the fall of the Uyghur Khaganate in the year 842, causing Uyghur migration from
 Rian Thum explored the concepts of identity among the ancestors of the modern Uyghurs in Altishahr (the native Uyghur name for Eastern Turkestan or Southern Xinjiang) before the adoption of the name "Uyghur" in the 1930s, referring to them by the name "Altishahri" in his article ''Modular History: Identity Maintenance before Uyghur Nationalism''. Thum indicated that Altishahri Turkis did have a sense that they were a distinctive group separate from the Turkic Andijanis to their west, the nomadic Turkic Kirghiz, the nomadic Mongol Qalmaq and the Han Chinese Khitay before they became known as Uyghurs. There was no single name used for their identity; various native names Altishahris used for identify were Altishahrlik (Altishahr person), yerlik (local), Turki and Musulmān (Muslim); the term Musulmān in this situation did not signify religious connotations, because the Altishahris exclude other Muslim peoples like the Kirghiz while identifying themselves as Musulmān. Dr. Laura J Newby says the sedentary Altishahri Turkic people considered themselves separate from other Turkic Muslims since at least the 19th century.
The name "Uyghur" reappeared after the
Rian Thum explored the concepts of identity among the ancestors of the modern Uyghurs in Altishahr (the native Uyghur name for Eastern Turkestan or Southern Xinjiang) before the adoption of the name "Uyghur" in the 1930s, referring to them by the name "Altishahri" in his article ''Modular History: Identity Maintenance before Uyghur Nationalism''. Thum indicated that Altishahri Turkis did have a sense that they were a distinctive group separate from the Turkic Andijanis to their west, the nomadic Turkic Kirghiz, the nomadic Mongol Qalmaq and the Han Chinese Khitay before they became known as Uyghurs. There was no single name used for their identity; various native names Altishahris used for identify were Altishahrlik (Altishahr person), yerlik (local), Turki and Musulmān (Muslim); the term Musulmān in this situation did not signify religious connotations, because the Altishahris exclude other Muslim peoples like the Kirghiz while identifying themselves as Musulmān. Dr. Laura J Newby says the sedentary Altishahri Turkic people considered themselves separate from other Turkic Muslims since at least the 19th century.
The name "Uyghur" reappeared after the
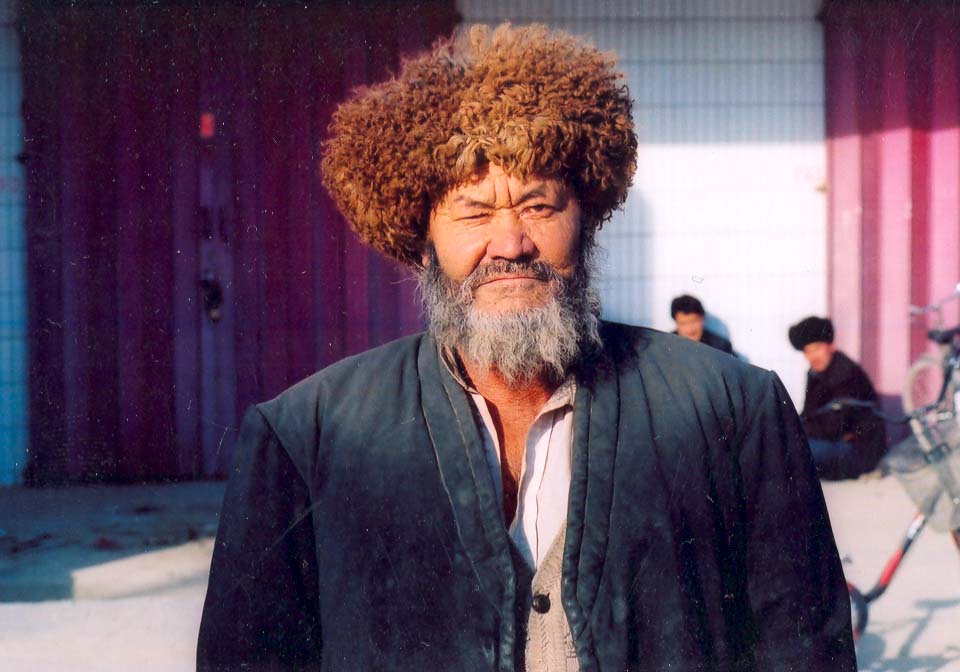 The Uyghur population within China generally remains centered in Xinjiang region with some smaller subpopulations elsewhere in the country, such as in Taoyuan County where an estimated 5,000–10,000 live.
The size of the Uyghur population, particularly in China, has been the subject of dispute. Chinese authorities place the Uyghur population within the Xinjiang region to be just over 12 million, comprising approximately half of the total regional population. As early as 2003, however, some Uyghur groups wrote that their population was being vastly undercounted by Chinese authorities, claiming that their population actually exceeded 20 million. Population disputes have continued into the present, with some activists and groups such as the World Uyghur Congress and Uyghur American Association claiming that the Uyghur population ranges between 20 and 30 million. Some have even claimed that the real number of Uyghurs is actually 35 million. Scholars, however, have generally rejected these claims, with Professor Dru C. Gladney writing in the 2004 book '' Xinjiang: China's Muslim Borderland'' that there is "scant evidence" to support Uyghur claims that their population within China exceeds 20 million.
The Uyghur population within China generally remains centered in Xinjiang region with some smaller subpopulations elsewhere in the country, such as in Taoyuan County where an estimated 5,000–10,000 live.
The size of the Uyghur population, particularly in China, has been the subject of dispute. Chinese authorities place the Uyghur population within the Xinjiang region to be just over 12 million, comprising approximately half of the total regional population. As early as 2003, however, some Uyghur groups wrote that their population was being vastly undercounted by Chinese authorities, claiming that their population actually exceeded 20 million. Population disputes have continued into the present, with some activists and groups such as the World Uyghur Congress and Uyghur American Association claiming that the Uyghur population ranges between 20 and 30 million. Some have even claimed that the real number of Uyghurs is actually 35 million. Scholars, however, have generally rejected these claims, with Professor Dru C. Gladney writing in the 2004 book '' Xinjiang: China's Muslim Borderland'' that there is "scant evidence" to support Uyghur claims that their population within China exceeds 20 million.
 One study by Xu et al. (2008), using samples from Hetian ( Hotan) only, found Uyghurs have about an average of 60% European or West Asian (Western Eurasian) ancestry and about 40%
One study by Xu et al. (2008), using samples from Hetian ( Hotan) only, found Uyghurs have about an average of 60% European or West Asian (Western Eurasian) ancestry and about 40%  A study (2013) based on
A study (2013) based on
 The Uyghurs of the Uyghur Khaganate were part of a Turkic confederation called the Tiele, who lived in the valleys south of
The Uyghurs of the Uyghur Khaganate were part of a Turkic confederation called the Tiele, who lived in the valleys south of
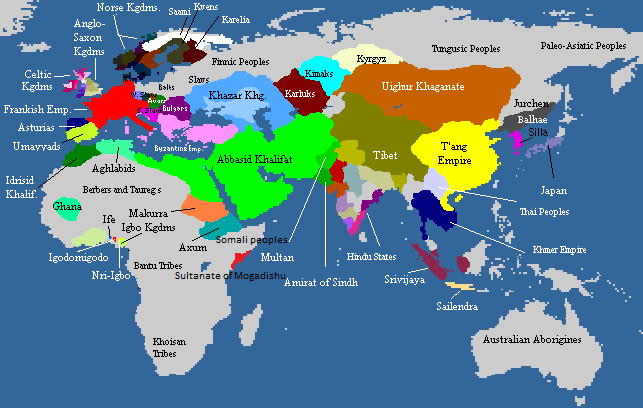 The Uyghurs who founded the Uyghur Khaganate dispersed after the fall of the Khaganate, to live among the Karluks and to places such as
The Uyghurs who founded the Uyghur Khaganate dispersed after the fall of the Khaganate, to live among the Karluks and to places such as
 The 12th and 13th century saw the domination by non-Muslim powers: first the Kara-Khitans in the 12th century, followed by the
The 12th and 13th century saw the domination by non-Muslim powers: first the Kara-Khitans in the 12th century, followed by the
, p. 285. In northern Xinjiang, the Qing brought in Han, Hui, Uyghur, Xibe, Daurs, Solons, Turkic Muslim Taranchis and Kazakh colonists, with one third of Xinjiang's total population consisting of Hui and Han in the northern area, while around two thirds were Uyghurs in southern Xinjiang's Tarim Basin.ed. Starr 2004
, p. 243. In Dzungaria, the Qing established new cities like Ürümqi and Yining. The Dzungarian basin itself is now inhabited by many Kazakhs. The Qing therefore unified Xinjiang and changed its demographic composition as well. The crushing of the Buddhist Dzungars by the Qing led to the empowerment of the Muslim Begs in southern Xinjiang, migration of Muslim Taranchis to northern Xinjiang, and increasing Turkic Muslim power, with Turkic Muslim culture and identity was tolerated or even promoted by the Qing. It was therefore argued by Henry Schwarz that "the Qing victory was, in a certain sense, a victory for Islam". In
Turkic
Turkic may refer to:
* anything related to the country of Turkey
* Turkic languages, a language family of at least thirty-five documented languages
** Turkic alphabets (disambiguation)
** Turkish language, the most widely spoken Turkic language
* ...
ethnic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the general region of Central and East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea ...
. The Uyghurs are recognized as native to the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in Northwest China
Northwest China () is a statistical region of China which includes the autonomous regions of Xinjiang and Ningxia and the provinces of Shaanxi, Gansu and Qinghai. It has an area of 3,107,900 km2.
The region is characterized by a (semi-)ari ...
. They are one of China's 55 officially recognized ethnic minorities. The Uyghurs are recognized by the Chinese government as a regional minority and the titular people of Xinjiang.
The Uyghurs have traditionally inhabited a series of oases scattered across the Taklamakan Desert within the Tarim Basin. These oases have historically existed as independent states or were controlled by many civilization
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system).
C ...
s including China, the Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
, the Tibetans and various Turkic polities. The Uyghurs gradually started to become Islamized in the 10th century and most Uyghurs identified as Muslims by the 16th century. Islam has since played an important role in Uyghur culture and identity.
An estimated 80% of Xinjiang's Uyghurs still live in the Tarim Basin. The rest of Xinjiang's Uyghurs mostly live in Ürümqi, the capital city of Xinjiang, which is located in the historical region of Dzungaria. The largest community of Uyghurs living outside of Xinjiang are the Taoyuan Uyghurs of north-central Hunan's Taoyuan County. Significant diasporic
A diaspora ( ) is a population that is scattered across regions which are separate from its geographic place of origin. Historically, the word was used first in reference to the dispersion of Greeks in the Hellenic world, and later Jews af ...
communities of Uyghurs exist in other Turkic countries such as Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental coun ...
, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked co ...
and Turkey. Smaller communities live in Saudi Arabia, Jordan, Australia, Russia and Sweden.
Since 2014, the Chinese government has subjected Uyghurs living in Xinjiang to widespread human rights abuses including forced sterilization and forced labor. Scholars estimate that at least one million Uyghurs have been arbitrarily detained in the Xinjiang internment camps since 2017; Chinese government officials claim that these camps, created under CCP general secretary Xi Jinping's administration
Administration may refer to:
Management of organizations
* Management, the act of directing people towards accomplishing a goal
** Administrative Assistant, traditionally known as a Secretary, or also known as an administrative officer, administ ...
, serve the goals of ensuring adherence to Chinese Communist Party
The Chinese Communist Party (CCP), officially the Communist Party of China (CPC), is the founding and sole ruling party of the People's Republic of China (PRC). Under the leadership of Mao Zedong, the CCP emerged victorious in the Chinese Ci ...
(CCP) ideology, preventing separatism, fighting terrorism
Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of criminal violence to provoke a state of terror or fear, mostly with the intention to achieve political or religious aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violen ...
, and providing vocational training to Uyghurs. Various scholars, human rights organizations and governments consider abuses perpetrated against the Uyghurs to amount to crimes against humanity or genocide
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the L ...
.
In August 2022, the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizi ...
released a report alleging that the Chinese government was committing crimes against humanity against the Uyghurs, which included physical and mental torture, slave labor, massive displacement, enforced sterilization and separation of children from their parents. The report was criticized by some activists for not calling the crimes a genocide
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the L ...
. Many Uyghurs outside China saw it as a formal acknowledgement of the sufferings of Uyghurs in China, hoping it will add fuel to their campaign at the international level.
Etymology
In theUyghur language
The Uyghur or Uighur language (; , , , or , , , , CTA: Uyğurçä; formerly known as Eastern Turki), is a Turkic language written in a Uyghur Perso-Arabic script with 8-11 million speakers, spoken primarily by the Uyghur people in the Xin ...
, the ethnonym is written in Arabic script, Уйғур in Uyghur Cyrillic and ''Uyghur'' or ''Uygur'' (as the standard Chinese romanization
Romanization or romanisation, in linguistics, is the conversion of text from a different writing system to the Roman (Latin) script, or a system for doing so. Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written text, an ...
, GB 3304–1991) in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
; they are all pronounced as . In Chinese, this is transcribed into characters as / , which is romanized in pinyin
Hanyu Pinyin (), often shortened to just pinyin, is the official romanization system for Standard Mandarin Chinese in China, and to some extent, in Singapore and Malaysia. It is often used to teach Mandarin, normally written in Chinese fo ...
as ''Wéiwú'ěr''.
In English, the name is officially spelled ''Uyghur'' by the Xinjiang government
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
but also appears as ''Uighur'', ''Uigur'' and ''Uygur''. (These reflect the various Cyrillic spellings Уиғур, Уигур and Уйгур.) The name is usually pronounced in English as , although some Uyghurs and Uyghur scholars advocate for using the closer pronunciation instead, with the vowels in the beginning of the word pronounced like the vowels in the English word "ruin".
The term's original meaning is unclear. Old Turkic inscriptions record a word ''uyɣur'' ( otk, 𐰆𐰖𐰍𐰆𐰺, ujǧur); an example is found on the Sudzi inscription, "I am khan ata of Yaglaqar, came from the Uigur land." ( otk, Uyγur jerinte Yaγlaqar qan ata keltim). It is transcribed into Tang annals as / (Mandarin: ''Huíhé'', but probably * �uɒiɣətin Middle Chinese). It was used as the name of one of the Turkic polities formed in the interim between the First and Second Göktürk Khaganates (AD630–684). The '' Old History of the Five Dynasties'' records that in 788 or 809, the Chinese acceded to a Uyghur request and emended their transcription to / (Mandarin: ''Huíhú'', but �uɒiɣuətin Middle Chinese).
Modern etymological explanations for the name ''Uyghur'' range from derivation from the verb "follow, accommodate oneself" and adjective "non-rebellious" (i.e., from Turkic ''uy/uð-'') to the verb meaning "wake, rouse or stir" (i.e., from Turkic ''oðğur-''). None of these is thought to be satisfactory because the sound shift of /ð/ and /ḏ/ to /j/ does not appear to be in place by this time. The etymology therefore cannot be conclusively determined and its referent is also difficult to fix. The "Huihe" and "Huihu" seem to be a political rather than a tribal designation or it may be one group among several others collectively known as the Toquz Oghuz. The name fell out of use in the 15th century, but was reintroduced in the early 20th century by the Soviet Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
to replace the previous terms ''Turk
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic o ...
'' and ''Turki''. The name is currently used to refer to the settled Turkic urban dwellers and farmers of the Tarim Basin who follow traditional Central Asian sedentary practices, distinguishable from the nomadic Turkic populations in Central Asia.
The earliest record of a Uyghur tribe appears in accounts from the Northern Wei (4th–6th century A.D.), wherein they were named ''Yuanhe'' (< MC ZS *''ɦʉɐn-ɦət'') and derived from a confederation named / (lit. "High Carts"), read as ''Gāochē'' in Mandarin Chinese
Mandarin (; ) is a group of Chinese (Sinitic) dialects that are natively spoken across most of northern and southwestern China. The group includes the Beijing dialect, the basis of the phonology of Standard Chinese, the official language ...
but originally with the reconstructed Middle Chinese pronunciation * ɑutɕʰĭa later known as the '' Tiele'' ( / , ''Tiělè''). ''Gāochē'' in turn has been connected to the Uyghur ''Qangqil'' ( or Қаңқил).
Identity
 Throughout its history, the term ''Uyghur'' has had an increasingly expansive definition. Initially signifying only a small coalition of Tiele tribes in northern China, Mongolia and the Altai Mountains, it later denoted citizenship in the Uyghur Khaganate. Finally, it was expanded into an ethnicity whose ancestry originates with the fall of the Uyghur Khaganate in the year 842, causing Uyghur migration from
Throughout its history, the term ''Uyghur'' has had an increasingly expansive definition. Initially signifying only a small coalition of Tiele tribes in northern China, Mongolia and the Altai Mountains, it later denoted citizenship in the Uyghur Khaganate. Finally, it was expanded into an ethnicity whose ancestry originates with the fall of the Uyghur Khaganate in the year 842, causing Uyghur migration from Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 millio ...
into the Tarim Basin. The Uyghurs who moved to the Tarim Basin mixed with the local Tocharians, and converted to the Tocharian religion, and adopted their culture of oasis agriculture. The fluid definition of ''Uyghur'' and the diverse ancestry of modern Uyghurs create confusion as to what constitutes true Uyghur ethnography and ethnogenesis. Contemporary scholars consider modern Uyghurs to be the descendants of a number of peoples, including the ancient Uyghurs of Mongolia migrating into the Tarim Basin after the fall of the Uyghur Khaganate, Iranic Saka tribes and other Indo-European peoples inhabiting the Tarim Basin before the arrival of the Turkic Uyghurs.
Uyghur activists identify with the Tarim mummies, remains of an ancient people inhabiting the region, but research into the genetics of ancient Tarim mummies and their links with modern Uyghurs remains problematic, both to Chinese government officials concerned with ethnic separatism and to Uyghur activists concerned the research could affect their indigenous claim.
Origin of modern nomenclature
The term "Uyghur" was not used to refer to a specific existing ethnicity in the 19th century: it referred to an 'ancient people'. A late-19th-century encyclopedia entitled ''The Cyclopædia of India and of Eastern and Southern Asia'' said "the Uigur are the most ancient of Turkish tribes and formerly inhabited a part of Chinese Tartary (Xinjiang), now occupied by a mixed population of Turk, Mongol andKalmuck
The Kalmyks ( Kalmyk: Хальмгуд, ''Xaľmgud'', Mongolian: Халимагууд, ''Halimaguud''; russian: Калмыки, translit=Kalmyki, archaically anglicised as ''Calmucks'') are a Mongolic ethnic group living mainly in Russia, ...
". Before 1921/1934, Western writers called the Turkic-speaking Muslims of the oases "Turki" and the Turkic Muslims who had migrated from the Tarim Basin to Ili, Ürümqi and Dzungaria in the northern portion of Xinjiang during the Qing dynasty were known as " Taranchi", meaning "farmer". The Russians and other foreigners referred to them as "Sart", "Turk" or "Turki". In the early 20th century they identified themselves by different names to different peoples and in response to different inquiries: they called themselves Sarts in front of Kazakhs and Kyrgyz while they called themselves "Chantou" if asked about their identity after first identifying as a Muslim. The term "Chantou" (, meaning "Rag head" or "Turban Head") was used to refer to the Turkic Muslims of Xinjiang, including by Hui (Tungan) people. These groups of peoples often identify themselves by their originating oasis instead of an ethnicity; for example those from Kashgar may refer to themselves as Kashgarliq or Kashgari, while those from Hotan identity themselves as "Hotani". Other Central Asians once called all the inhabitants of Xinjiang's Southern oases Kashgari, a term still used in some regions of Pakistan. The Turkic people also used "Musulman", which means "Muslim", to describe themselves.
 Rian Thum explored the concepts of identity among the ancestors of the modern Uyghurs in Altishahr (the native Uyghur name for Eastern Turkestan or Southern Xinjiang) before the adoption of the name "Uyghur" in the 1930s, referring to them by the name "Altishahri" in his article ''Modular History: Identity Maintenance before Uyghur Nationalism''. Thum indicated that Altishahri Turkis did have a sense that they were a distinctive group separate from the Turkic Andijanis to their west, the nomadic Turkic Kirghiz, the nomadic Mongol Qalmaq and the Han Chinese Khitay before they became known as Uyghurs. There was no single name used for their identity; various native names Altishahris used for identify were Altishahrlik (Altishahr person), yerlik (local), Turki and Musulmān (Muslim); the term Musulmān in this situation did not signify religious connotations, because the Altishahris exclude other Muslim peoples like the Kirghiz while identifying themselves as Musulmān. Dr. Laura J Newby says the sedentary Altishahri Turkic people considered themselves separate from other Turkic Muslims since at least the 19th century.
The name "Uyghur" reappeared after the
Rian Thum explored the concepts of identity among the ancestors of the modern Uyghurs in Altishahr (the native Uyghur name for Eastern Turkestan or Southern Xinjiang) before the adoption of the name "Uyghur" in the 1930s, referring to them by the name "Altishahri" in his article ''Modular History: Identity Maintenance before Uyghur Nationalism''. Thum indicated that Altishahri Turkis did have a sense that they were a distinctive group separate from the Turkic Andijanis to their west, the nomadic Turkic Kirghiz, the nomadic Mongol Qalmaq and the Han Chinese Khitay before they became known as Uyghurs. There was no single name used for their identity; various native names Altishahris used for identify were Altishahrlik (Altishahr person), yerlik (local), Turki and Musulmān (Muslim); the term Musulmān in this situation did not signify religious connotations, because the Altishahris exclude other Muslim peoples like the Kirghiz while identifying themselves as Musulmān. Dr. Laura J Newby says the sedentary Altishahri Turkic people considered themselves separate from other Turkic Muslims since at least the 19th century.
The name "Uyghur" reappeared after the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
took the 9th-century ethnonym from the Uyghur Khaganate, then reapplied it to all non-nomadic Turkic Muslims of Xinjiang. It followed western European orientalists like Julius Klaproth in the 19th century who revived the name and spread the use of the term to local Turkic intellectuals and a 19th-century proposal from Russian historians that modern-day Uyghurs were descended from the Kingdom of Qocho and Kara-Khanid Khanate formed after the dissolution of the Uyghur Khaganate. Historians generally agree that the adoption of the term "Uyghur" is based on a decision from a 1921 conference in Tashkent, attended by Turkic Muslims from the Tarim Basin (Xinjiang). There, "Uyghur" was chosen by them as the name of their ethnicity, although delegates noted the modern groups referred to as "Uyghur" are distinct from the old Uyghur Khaganate. According to Linda Benson, the Soviets and their client Sheng Shicai intended to foster a Uyghur nationality to divide the Muslim population of Xinjiang, whereas the various Turkic Muslim peoples preferred to identify themselves as "Turki", "East Turkestani" or "Muslim".
On the other hand, the ruling regime of China at that time, the Kuomintang
The Kuomintang (KMT), also referred to as the Guomindang (GMD), the Nationalist Party of China (NPC) or the Chinese Nationalist Party (CNP), is a major political party in the Republic of China, initially on the Chinese mainland and in Tai ...
, grouped all Muslims, including the Turkic-speaking people of Xinjiang, into the " Hui nationality". The Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
and the Kuomintang generally referred to the sedentary oasis-dwelling Turkic Muslims of Xinjiang as "turban-headed Hui" to differentiate them from other predominantly Muslim ethnicities in China. In the 1930s, foreigners travelers in Xinjiang such as George W. Hunter, Peter Fleming, Ella Maillart and Sven Hedin, referred to the Turkic Muslims of the region as "Turki" in their books. Use of the term Uyghur was unknown in Xinjiang until 1934. The area governor, Sheng Shicai, came to power, adopting the Soviet ethnographic classification instead of the Kuomintang's and became the first to promulgate the official use of the term "Uyghur" to describe the Turkic Muslims of Xinjiang. "Uyghur" replaced "rag-head".
Sheng Shicai's introduction of the "Uighur" name for the Turkic people of Xinjiang was criticized and rejected by Turki intellectuals such as Pan-Turkist Jadid
The Jadids were Muslim modernist reformers within the Russian Empire in the late 19th and early 20th century. They normally referred to themselves by the Turkic terms ''Taraqqiparvarlar'' ('progressives'), ''Ziyalilar'' ('intellectuals') or simp ...
s and East Turkestan independence activists Muhammad Amin Bughra (Mehmet Emin) and Masud Sabri. They demanded the names "Türk" or "Türki" be used instead as the ethnonyms for their people. Masud Sabri viewed the Hui people as Muslim Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive v ...
and separate from his people, while Bughrain criticized Sheng for his designation of Turkic Muslims into different ethnicities which could sow disunion among Turkic Muslims. After the Communist victory, the Chinese Communist Party
The Chinese Communist Party (CCP), officially the Communist Party of China (CPC), is the founding and sole ruling party of the People's Republic of China (PRC). Under the leadership of Mao Zedong, the CCP emerged victorious in the Chinese Ci ...
under Chairman Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; also Romanization of Chinese, romanised traditionally as Mao Tse-tung. (26 December 1893 – 9 September 1976), also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the List of national founde ...
continued the Soviet classification, using the term "Uyghur" to describe the modern ethnicity.
In current usage, ''Uyghur'' refers to settled Turkic-speaking urban dwellers and farmers of the Tarim Basin and Ili who follow traditional Central Asian sedentary practices, as distinguished from nomadic Turkic populations in Central Asia. However, Chinese government agents designate as "Uyghur" certain peoples with significantly divergent histories and ancestries from the main group. These include the Lopliks of Ruoqiang County and the Dolan people, thought to be closer to the Oirat Mongols and the Kyrgyz. The use of the term Uyghur led to anachronisms when describing the history of the people. In one of his books, the term Uyghur was deliberately not used by James Millward.
Another ethnicity, the Western Yugur
Western Yugur (Western Yugur: (Yugur speech) or (Yugur word)) also known as Neo-Uygur is the Turkic language spoken by the Yugur people. It is contrasted with Eastern Yugur, a Mongolic language spoken within the same community. Traditionally, b ...
of Gansu, identify themselves as the "Yellow Uyghur" (''Sarïq Uyghur''). Some scholars say the Yugurs' culture, language and religion are closer to the original culture of the original Uyghur Karakorum state than is the culture of the modern Uyghur people of Xinjiang. Linguist and ethnographer S. Robert Ramsey argues for inclusion of both the Eastern and Western Yugur and the Salar as sub-groups of the Uyghur based on similar historical roots for the Yugur and on perceived linguistic similarities for the Salar.
"''Turkistani'' is used as an alternate ethnonym by some Uyghurs. For example, the Uyghur diaspora in Arabia, adopted the identity "''Turkistani''". Some Uyghurs in Saudi Arabia adopted the Arabic nisba of their home city, such as "''Al- Kashgari''" from Kashgar. Saudi-born Uyghur Hamza Kashgari's family originated from Kashgar.
Population
 The Uyghur population within China generally remains centered in Xinjiang region with some smaller subpopulations elsewhere in the country, such as in Taoyuan County where an estimated 5,000–10,000 live.
The size of the Uyghur population, particularly in China, has been the subject of dispute. Chinese authorities place the Uyghur population within the Xinjiang region to be just over 12 million, comprising approximately half of the total regional population. As early as 2003, however, some Uyghur groups wrote that their population was being vastly undercounted by Chinese authorities, claiming that their population actually exceeded 20 million. Population disputes have continued into the present, with some activists and groups such as the World Uyghur Congress and Uyghur American Association claiming that the Uyghur population ranges between 20 and 30 million. Some have even claimed that the real number of Uyghurs is actually 35 million. Scholars, however, have generally rejected these claims, with Professor Dru C. Gladney writing in the 2004 book '' Xinjiang: China's Muslim Borderland'' that there is "scant evidence" to support Uyghur claims that their population within China exceeds 20 million.
The Uyghur population within China generally remains centered in Xinjiang region with some smaller subpopulations elsewhere in the country, such as in Taoyuan County where an estimated 5,000–10,000 live.
The size of the Uyghur population, particularly in China, has been the subject of dispute. Chinese authorities place the Uyghur population within the Xinjiang region to be just over 12 million, comprising approximately half of the total regional population. As early as 2003, however, some Uyghur groups wrote that their population was being vastly undercounted by Chinese authorities, claiming that their population actually exceeded 20 million. Population disputes have continued into the present, with some activists and groups such as the World Uyghur Congress and Uyghur American Association claiming that the Uyghur population ranges between 20 and 30 million. Some have even claimed that the real number of Uyghurs is actually 35 million. Scholars, however, have generally rejected these claims, with Professor Dru C. Gladney writing in the 2004 book '' Xinjiang: China's Muslim Borderland'' that there is "scant evidence" to support Uyghur claims that their population within China exceeds 20 million.
Population in Xinjiang
Genetics
A study of mitochondrial DNA (2004) (therefore the matrilineal genetic contribution) found the frequency of Western Eurasian-specific haplogroup in Uyghurs to be 42.6% and East Asian haplogroup to be 57.4%. Uyghurs in Kazakhstan on the other hand were shown to have 55% European/Western Eurasian maternal mtDNA. A study based on paternal DNA (2005) shows West Eurasian haplogroups (J and R) in Uyghurs make up 65% to 70% and East Asian haplogroups (C, N, D and O) 30% to 35%. One study by Xu et al. (2008), using samples from Hetian ( Hotan) only, found Uyghurs have about an average of 60% European or West Asian (Western Eurasian) ancestry and about 40%
One study by Xu et al. (2008), using samples from Hetian ( Hotan) only, found Uyghurs have about an average of 60% European or West Asian (Western Eurasian) ancestry and about 40% East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea ...
n or Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part o ...
n ancestry (Eastern Eurasian). From the same area, it is found that the proportion of Uyghur individuals with European/West Asian ancestry ranges individually from 40.3% to 84.3% while their East Asian/Siberian ancestry ranges individually from 15.7% to 59.7%. Further study by the same team showed an average of slightly greater European/West Asian component at 52% (ranging individually from 44.9% to 63.1%) in the Uyghur population in southern Xinjiang but only 47% (ranging individually from 30% to 55%) in the northern Uyghur population.
A different study by Li et al. (2009) used a larger sample of individuals from a wider area and found a higher East Asian component of about 70% on average, while the European/West Asian component was about 30%. Overall, Uyghur show relative more similarity to "Western East Asians" than to "Eastern East Asians". The authors also cite anthropologic studies which also estimate about 30% "Western proportions", which are in agreement with their genetic results. A study (2013) based on
A study (2013) based on autosomal DNA
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosomes ...
shows that average Uyghurs are closest to other Turkic people in Central Asia and China as well as various Chinese populations. The analysis of the diversity of cytochrome B further suggests Uyghurs are closer to Chinese and Siberian populations than to various Caucasoid groups in West Asia or Europe. However, there is significant genetic distance between the Xinjiang's southern Uyghurs and Chinese population, but not between the northern Uyghurs and Chinese.
A Study (2016) of Uyghur males living in southern Xinjiang used high-resolution 26 Y-STR loci system high-resolution to infer the genetic relationships between the Uyghur population and European and Asian populations. The results showed the Uyghur population of southern Xinjiang exhibited a genetic admixture of Eastern Asian and European populations but with slightly closer relationship with European populations than to Eastern Asian populations.
An extensive genome study in 2017 analyzed 951 samples of Uyghurs from 14 geographical subpopulations in Xinjiang and observed a southwest and northeast differentiation in the population, partially caused by the Tianshan Mountains which form a natural barrier, with gene flows from the east and west. The study identifies four major ancestral components that may have arisen from two earlier admixed groups: one West-Eurasian component, associated with European ancestry (25–37%), one South Asian ancestry component (12–20%), and two East-Eurasian components with Siberian (15–17%) and East Asian ancestries (29–47%). In total, Uyghurs on average range from 44 to 64% Siberian/East Asian, 33.2% European, and 17.9% South Asian. Western Xinjiang shows more West Eurasian components than East Asian. It suggests at least two major waves of admixture, one ~3,750 years ago coinciding with the age range of the mummies with European feature found in Xinjiang, and another occurring around 750 years ago.
A 2018 study of 206 Uyghur samples from Xinjiang, using the ancestry-informative SNP (AISNP) analysis, found that the average genetic ancestry of Uyghurs is 63.7% East Asian-related and 36.3% European-related.
History
The history of the Uyghur people, as with the ethnic origin of the people, is a matter of contention. Uyghur historians viewed the Uyghurs as the original inhabitants of Xinjiang with a long history. Uyghur politician and historian Muhammad Amin Bughra wrote in his book ''A History of East Turkestan'', stressing the Turkic aspects of his people, that the Turks have a continuous 9000-year-old history, while historianTurghun Almas
Turghun Almas ( Uyghur: تۇرغۇن ئالماس; Simplified Chinese: 吐尔贡·阿力玛斯; 30 October 1924 – 11 September 2001) was a Uyghur historian and poet born in Kashgar. He was criticized for his "support for ethnic nationalist se ...
incorporated discoveries of Tarim mummies to conclude that Uyghurs have over 6400 years of continuous history, and the World Uyghur Congress claimed a 4,000-year history in East Turkestan. However, the official Chinese view, as documented in the white paper ''History and Development of Xinjiang'', asserts that the Uyghur ethnic group formed after the collapse of the Uyghur Khaganate in 840, when the local residents of the Tarim Basin and its surrounding areas were merged with migrants from the khaganate. The name "Uyghur" reappeared after the Soviet Union took the 9th-century ethnonym from the Uyghur Khaganate, then reapplied it to all non-nomadic Turkic Muslims of Xinjiang. Many contemporary Western scholars, however, do not consider the modern Uyghurs to be of direct linear descent from the old Uyghur Khaganate of Mongolia. Rather, they consider them to be descendants of a number of peoples, one of them the ancient Uyghurs.
Early history
Discovery of well-preserved Tarim mummies of a people European in appearance indicates the migration of a European-looking people into the Tarim area at the beginning of theBronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
around 1800 BC. These people may have been of Tocharian origin, and some have suggested them to be the Yuezhi mentioned in ancient Chinese texts. The Tocharians are thought to have developed from the Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, ...
speaking Afanasevo culture of Southern Siberia (c. 3500–2500 BC). A study published in 2021 suggests that the earliest Tarim Basin cultures appear to have high levels of Ancient North Eurasian ancestry, with smaller admixture from Northeast Asians. Uyghur activist Turgun Almas claimed that Tarim mummies were Uyghurs because the earliest Uyghurs practiced shamanism and the buried mummies' orientation suggests that they had been shamanists; meanwhile, Qurban Wäli claimed words written in Kharosthi and Sogdian scripts as "Uyghur" rather than Sogdian words absorbed into Uyghur according to other linguists.
Later migrations brought peoples from the west and northwest to the Xinjiang region, probably speakers of various Iranian languages such as the Saka tribes, who were closely related to the European Scythians and descended from the earlier Andronovo culture, and who may have been present in the Khotan and Kashgar area in the first millennium BC, as well as the Sogdians who formed networks of trading communities across the Tarim Basin from the 4th century AD. There may also be an Indian component as the founding legend of Khotan suggests that the city was founded by Indians from ancient Taxila during the reign of Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, ...
. Other people in the region mentioned in ancient Chinese texts include the Dingling as well as the Xiongnu who fought for supremacy in the region against the Chinese for several hundred years. Some Uyghur nationalists also claimed descent from the Xiongnu (according to the Chinese historical text the ''Book of Wei
The ''Book of Wei'', also known by its Chinese name as the ''Wei Shu'', is a classic Chinese historical text compiled by Wei Shou from 551 to 554, and is an important text describing the history of the Northern Wei and Eastern Wei from 386 to ...
'', the founder of the Uyghurs was descended from a Xiongnu ruler), but the view is contested by modern Chinese scholars.
The Yuezhi were driven away by the Xiongnu but founded the Kushan Empire, which exerted some influence in the Tarim Basin, where Kharosthi texts have been found in Loulan, Niya and Khotan. Loulan and Khotan were some of the many city-states that existed in the Xinjiang region during the Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
; others include Kucha, Turfan, Karasahr and Kashgar. These kingdoms in the Tarim Basin came under the control of China during the Han and Tang dynasties. During the Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdo ...
they were conquered and placed under the control of the Protectorate General to Pacify the West, and the Indo-European cultures of these kingdoms never recovered from Tang rule after thousands of their inhabitants were killed during the conquest. The settled population of these cities later merged with the incoming Turkic people, including the Uyghurs of Uyghur Khaganate, to form the modern Uyghurs. The Indo-European Tocharian language later disappeared as the urban population switched to a Turkic language such as the Old Uyghur language.
The early Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West Asia, West, Central Asia, Central, East Asia, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose memb ...
descended from agricultural communities in Northeast Asia who moved westwards into Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 millio ...
in the late 3rd millennium BC, where they adopted a pastoral lifestyle. By the early 1st millennium BC, these peoples had become equestrian nomads. In subsequent centuries, the steppe populations of Central Asia appear to have been progressively Turkified
Turkification, Turkization, or Turkicization ( tr, Türkleştirme) describes a shift whereby populations or places received or adopted Turkic attributes such as culture, language, history, or ethnicity. However, often this term is more narrowly ...
by East Asian nomadic Turks, moving out of Mongolia.. "These results suggest that Turkic cultural customs were imposed by an East Asian minority elite onto central steppe nomad populations... The wide distribution of the Turkic languages from Northwest China, Mongolia and Siberia in the east to Turkey and Bulgaria in the west implies large-scale migrations out of the homeland in Mongolia.. "Both Chinese histories and modern dna studies indicate that the early and medieval Turkic peoples were made up of heterogeneous populations. The Turkicisation of central and western Eurasia was not the product of migrations involving a homogeneous entity, but that of language diffusion."
Uyghur Khaganate (8th–9th centuries)
 The Uyghurs of the Uyghur Khaganate were part of a Turkic confederation called the Tiele, who lived in the valleys south of
The Uyghurs of the Uyghur Khaganate were part of a Turkic confederation called the Tiele, who lived in the valleys south of Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal (, russian: Oзеро Байкал, Ozero Baykal ); mn, Байгал нуур, Baigal nuur) is a rift lake in Russia. It is situated in southern Siberia, between the Federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast, I ...
and around the Yenisei River. They overthrew the First Turkic Khaganate and established the Uyghur Khaganate.
The Uyghur Khaganate lasted from 744 to 840. It was administered from the imperial capital Ordu-Baliq, one of the biggest ancient cities built in Mongolia. In 840, following a famine and civil war, the Uyghur Khaganate was overrun by the Yenisei Kirghiz, another Turkic people. As a result, the majority of tribal groups formerly under Uyghur control dispersed and moved out of Mongolia.
Uyghur kingdoms (9th–11th centuries)
 The Uyghurs who founded the Uyghur Khaganate dispersed after the fall of the Khaganate, to live among the Karluks and to places such as
The Uyghurs who founded the Uyghur Khaganate dispersed after the fall of the Khaganate, to live among the Karluks and to places such as Jimsar
Jimsar County is a county in Changji Hui Autonomous Prefecture, Xinjiang, China. It contains an area of . According to the 2002 census, it has a population of 130,000.
Near the town of Jimsar are the ruins of the ancient city of Beiting () or Tin ...
, Turpan and Gansu. These Uyghurs soon founded two kingdoms and the easternmost state was the Ganzhou Kingdom (870–1036) which ruled parts of Xinjiang, with its capital near present-day Zhangye, Gansu, China. The modern Yugurs are believed to be descendants of these Uyghurs. Ganzhou was absorbed by the Western Xia in 1036.
The second Uyghur kingdom, the Kingdom of Qocho ruled a larger section of Xinjiang, also known as ''Uyghuristan'' in its later period, was founded in the Turpan area with its capital in Qocho (modern Gaochang) and Beshbalik. The Kingdom of Qocho lasted from the ninth to the fourteenth century and proved to be longer-lasting than any power in the region, before or since. The Uyghurs were originally Tengrists, shamanists, and Manichaean, but converted to Buddhism during this period. Qocho accepted the Qara Khitai as its overlord in the 1130s, and in 1209 submitted voluntarily to the rising Mongol Empire. The Uyghurs of Kingdom of Qocho were allowed significant autonomy and played an important role as civil servants to the Mongol Empire, but was finally destroyed by the Chagatai Khanate by the end of the 14th century.
Islamization
In the tenth century, the Karluks, Yagmas, Chigils and other Turkic tribes founded the Kara-Khanid Khanate in Semirechye, Western Tian Shan, and Kashgaria and later conquered Transoxiana. The Karakhanid rulers were likely to be Yaghmas who were associated with the Toquz Oghuz and some historians therefore see this as a link between the Karakhanid and the Uyghurs of the Uyghur Khaganate, although this connection is disputed by others. The Karakhanids converted to Islam in the tenth century beginning with Sultan Satuq Bughra Khan, the first Turkic dynasty to do so. Modern Uyghurs see the Muslim Karakhanids as an important part of their history; however, Islamization of the people of the Tarim Basin was a gradual process. The Indo-Iranian Saka Buddhist Kingdom of Khotan was conquered by the Turkic Muslim Karakhanids from Kashgar in the early 11th century, but Uyghur Qocho remained mainly Buddhist until the 15th century, and the conversion of the Uyghur people to Islam was not completed until the 17th century. The 12th and 13th century saw the domination by non-Muslim powers: first the Kara-Khitans in the 12th century, followed by the
The 12th and 13th century saw the domination by non-Muslim powers: first the Kara-Khitans in the 12th century, followed by the Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
in the 13th century. After the death of Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' ͡ʃʰiŋɡɪs xaːŋbr /> Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Temüjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent) Ögedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin ...
in 1227, Transoxiana and Kashgar became the domain of his second son, Chagatai Khan. The Chagatai Khanate split into two in the 1340s, and the area of the Chagatai Khanate where the modern Uyghurs live became part of Moghulistan, which meant "land of the Mongols". In the 14th century, a Chagatayid khan Tughluq Temür converted to Islam, Genghisid Mongol nobilities also followed him to convert to Islam. His son Khizr Khoja conquered Qocho and Turfan (the core of Uyghuristan) in the 1390s, and the Uyghurs there became largely Muslim by the beginning of the 16th century. After being converted to Islam, the descendants of the previously Buddhist Uyghurs in Turfan failed to retain memory of their ancestral legacy and falsely believed that the "infidel Kalmuks" ( Dzungars) were the ones who built Buddhist structures in their area.
From the late 14th through 17th centuries, the Xinjiang region became further subdivided into Moghulistan in the north, Altishahr (Kashgar and the Tarim Basin), and the Turfan area, each often ruled separately by competing Chagatayid descendants, the Dughlats, and later the Khojas
The Khojas ( sd}; gu, ખોજા, hi, ख़ोजा) are a mainly Nizari Isma'ili Shia community of people originating in Gujarat, India.
Derived from the Persian Khwaja, a term of honor, the word Khoja is used to refer to Lohana Rajpu ...
.
Islam was also spread by the Sufis, and branches of its Naqshbandi order were the Khojas
The Khojas ( sd}; gu, ખોજા, hi, ख़ोजा) are a mainly Nizari Isma'ili Shia community of people originating in Gujarat, India.
Derived from the Persian Khwaja, a term of honor, the word Khoja is used to refer to Lohana Rajpu ...
who seized control of political and military affairs in the Tarim Basin and Turfan in the 17th century. The Khojas however split into two rival factions, the Aqtaghlik Khojas (also called the Afaqiyya) and the Qarataghlik Khojas (the Ishaqiyya). The legacy of the Khojas lasted until the 19th century. The Qarataghlik Khojas seized power in Yarkand where the Chagatai Khans ruled in the Yarkent Khanate, forcing the Aqtaghlik Afaqi Khoja into exile.
Qing rule
In the 17th century, the Buddhist Dzungar Khanate grew in power in Dzungaria. The Dzungar conquest of Altishahr ended the last independent Chagatai Khanate, the Yarkent Khanate, after the Aqtaghlik Afaq Khoja sought aid from the 5th Dalai Lama and his Dzungar Buddhist followers to help him in his struggle against the Qarataghlik Khojas. The Aqtaghlik Khojas in the Tarim Basin then became vassals to the Dzungars. The expansion of the Dzungars intoKhalkha Mongol
The Khalkha ( Mongolian: mn, Халх, Halh, , zh, 喀爾喀) have been the largest subgroup of Mongol people in modern Mongolia since the 15th century. The Khalkha, together with Chahars, Ordos and Tumed, were directly ruled by Borjigin khans ...
territory in Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 millio ...
brought them into direct conflict with Qing China in the late 17th century, and in the process also brought Chinese presence back into the region a thousand years after Tang China lost control of the Western Regions.
The Dzungar–Qing War lasted a decade. During the Dzungar conflict, two Aqtaghlik brothers, the so-called "Younger Khoja" (), also known as Khwāja-i Jahān, and his sibling, the Elder Khoja (), also known as Burhān al-Dīn, after being appointed as vassals in the Tarim Basin by the Dzungars, first joined the Qing and rebelled against Dzungar rule until the final Qing victory over the Dzungars, then they rebelled against the Qing, an action which prompted the invasion and conquest of the Tarim Basin by the Qing in 1759. The Uyghurs of Turfan and Hami such as Emin Khoja were allies of the Qing in this conflict, and these Uyghurs also helped the Qing rule the Altishahr Uyghurs in the Tarim Basin.
The final campaign against the Dzungars in the 1750s ended with the Dzungar genocide. The Qing "final solution" of genocide to solve the problem of the Dzungar Mongols created a land devoid of Dzungars, which was followed by the Qing sponsored settlement of millions of other people in Dzungaria.Perdue 2009, p. 285. In northern Xinjiang, the Qing brought in Han, Hui, Uyghur, Xibe, Daurs, Solons, Turkic Muslim Taranchis and Kazakh colonists, with one third of Xinjiang's total population consisting of Hui and Han in the northern area, while around two thirds were Uyghurs in southern Xinjiang's Tarim Basin.ed. Starr 2004
, p. 243. In Dzungaria, the Qing established new cities like Ürümqi and Yining. The Dzungarian basin itself is now inhabited by many Kazakhs. The Qing therefore unified Xinjiang and changed its demographic composition as well. The crushing of the Buddhist Dzungars by the Qing led to the empowerment of the Muslim Begs in southern Xinjiang, migration of Muslim Taranchis to northern Xinjiang, and increasing Turkic Muslim power, with Turkic Muslim culture and identity was tolerated or even promoted by the Qing. It was therefore argued by Henry Schwarz that "the Qing victory was, in a certain sense, a victory for Islam". In
Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
, a community of Uyghurs was clustered around the mosque near the Forbidden City
The Forbidden City () is a palace complex in Dongcheng District, Beijing, China, at the center of the Imperial City of Beijing. It is surrounded by numerous opulent imperial gardens and temples including the Zhongshan Park, the sacrific ...
, having moved to Beijing in the 18th century.
The Ush rebellion in 1765 by Uyghurs against the Manchus occurred after several incidents of misrule and abuse that had caused considerable anger and resentment. The Manchu Emperor ordered that the Uyghur rebel town be massacred, and the men were executed and the women and children enslaved.
Yettishar
During the Dungan Revolt (1862–1877), Andijani Uzbeks from the Khanate of Kokand under Buzurg Khan and Yaqub Beg expelled Qing officials from parts of southern Xinjiang and founded an independent Kashgarian kingdom called Yettishar ("Country of Seven Cities"). Under the leadership of Yaqub Beg, it included Kashgar,Yarkand
Yarkant County,, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also Shache County,, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also transliterated from Uyghur as Yakan County, is a county in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomou ...
, Khotan, Aksu, Kucha, Korla
Korla,The official spelling according to also known as Kurla, National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency or from Mandarin Chinese as Ku'erle or Kuerle, is the second largest city in Xinjiang. I ...
, and Turpan. Large Qing dynasty forces under Chinese General Zuo Zongtang attacked Yettishar in 1876.
Qing reconquest
After this invasion, the two regions of Dzungaria, which had been known as the Dzungar region or the Northern marches of the Tian Shan, and the Tarim Basin, which had been known as "Muslim land" or southern marches of the Tian Shan, were reorganized into a province named ''Xinjiang'', meaning "New Territory".First East Turkestan Republic
In 1912, the Qing Dynasty was replaced by the Republic of China. By 1920, Pan-Turkic Jadidists had become a challenge to Chinese warlord Yang Zengxin, who controlled Xinjiang. Uyghurs staged several uprisings against Chinese rule. In 1931, the Kumul Rebellion erupted, leading to the establishment of an independent government in Khotan in 1932, which later led to the creation of the First East Turkestan Republic, officially known as the Turkish Islamic Republic of East Turkestan. Uyghurs joined with Uzbeks, Kazakhs, and Kyrgyz and successfully declared their independence on 12 November 1933. The First East Turkestan Republic was a short-lived attempt at independence around the areas encompassing Kashgar, Yarkent, and Khotan, and it was attacked during the Qumul Rebellion by a Chinese Muslim army under General Ma Zhancang and Ma Fuyuan and fell following the Battle of Kashgar (1934). The Soviets backed Chinese warlord Sheng Shicai's rule over East Turkestan/Xinjiang from 1934 to 1943. In April 1937, remnants of the First East Turkestan Republic launched an uprising known as theIslamic Rebellion in Xinjiang
In 1937 an Islamic rebellion broke out in southern Xinjiang. The rebels were 1,500 Uighur Muslims led by Kichik Akhund, who was tacitly aided by the new 36th Division, against the pro-Soviet provincial forces of the puppet Sheng Shicai.
St ...
and briefly established an independent government, controlling areas from Atush, Kashgar, Yarkent, and even parts of Khotan, before it was crushed in October 1937, following Soviet intervention. Sheng Shicai purged 50,000 to 100,000 people, mostly Uyghurs, following this uprising.
Second East Turkestan Republic
The oppressive reign of Sheng Shicai fueled discontent by Uyghur and other Turkic peoples of the region, and Sheng expelled Soviet advisors following U.S. support for theKuomintang
The Kuomintang (KMT), also referred to as the Guomindang (GMD), the Nationalist Party of China (NPC) or the Chinese Nationalist Party (CNP), is a major political party in the Republic of China, initially on the Chinese mainland and in Tai ...
of the Republic of China. This led the Soviets to capitalize on the Uyghur and other Turkic people's discontent in the region, culminating in their support of the Ili Rebellion in October 1944. The Ili Rebellion resulted in the establishment of the Second East Turkestan Republic on 12 November 1944, in the three districts of what is now the Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture. Several pro-KMT Uyghurs like Isa Yusuf Alptekin, Memet Emin Bugra, and Mesut Sabri opposed the Second East Turkestan Republic and supported the Republic of China. In the summer of 1949, the Soviets purged the thirty top leaders of the Second East Turkestan Republic and its five top officials died in a mysterious plane crash on 27 August 1949. On 13 October 1949, the People's Liberation Army entered the region and the East Turkestan National Army was merged into the PLA's 5th Army Corps, leading to the official end of the Second East Turkestan Republic on 22 December 1949.
Contemporary era
Mao declared the founding of thePeople's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, sli ...
on 1 October 1949. He turned the Second East Turkistan Republic into the Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture, and appointed Saifuddin Azizi as the region's first Communist Party governor. Many Republican loyalists fled into exile in Turkey and Western countries. The name Xinjiang was changed to Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, where Uyghurs are the largest ethnicity, mostly concentrated in the south-western Xinjiang.
The Xinjiang conflict is an ongoing separatist conflict in China's far-west province of Xinjiang, whose northern region is known as Dzungaria and whose southern region (the Tarim Basin) is known as East Turkestan. Uyghur separatists and independence movements claim that the Second East Turkestan Republic was illegally incorporated by China in 1949 and has since been under Chinese occupation.
Uyghur identity remains fragmented, as some support a Pan-Islamic vision, exemplified by the East Turkestan Islamic Movement, while others support a Pan-Turkic
Pan-Turkism is a political movement that emerged during the 1880s among Turkic intellectuals who lived in the Russian region of Kazan (Tatarstan), Caucasus (modern-day Azerbaijan) and the Ottoman Empire (modern-day Turkey), with its aim bei ...
vision, such as the East Turkestan Liberation Organization
The East Turkestan Liberation Organization (ETLO) was a secessionist Uyghur organization that advocated for an independent Uyghur state named East Turkestan in the Western Chinese province known as Xinjiang. The organization was established in T ...
. A third group would like an East Turkestan state, such as the East Turkestan independence movement. While the East Turkistan Government in Exile strives for the restoration of East Turkistan's independence as a secular pluralistic Republic that guarantees freedom and civil liberties for all people. As a result, " Uyghur or East Turkestan group speaks for all Uyghurs, although it might claim to", and Uyghurs in each of these camps have committed violence against other Uyghurs who they think are too assimilated to Chinese or Russian society or are not religious enough. Mindful not to take sides, Uyghur "leaders" such as Rebiya Kadeer
Rebiya Kadeer ( ug, رابىيە قادىر, translit=Rabiye Qadir; born 15 November 1946) is an ethnic Uyghur businesswoman and political activist. Born in Altay City, Xinjiang, Kadeer became a millionaire in the 1980s through her real estate ...
mainly tried to garner international support for the "rights and interests of the Uyghurs", including the right to demonstrate, although the Chinese government has accused her of orchestrating the deadly July 2009 Ürümqi riots.
Eric Enno Tamm's 2011 book states that, "Authorities have censored Uyghur writers and 'lavished funds' on official histories that depict Chinese territorial expansion into ethnic borderlands as 'unifications (tongyi), never as conquests (zhengfu) or annexations (tunbing)' "
Genocide of Uyghurs in Xinjiang<