|
Jadid
The Jadid movement or Jadidism was an Turco-Islamic modernist political, religious, and cultural movement in the Russian Empire in the late 19th and early 20th century. They normally referred to themselves by the Tatar terms ''Taraqqiparvarlar'' ("progressives"), ''Ziyalilar'' ("intellectuals"), or simply ''Yäşlär/Yoshlar'' ("youth"). The Jadid movement advocated for an Islamic social and cultural reformation through the revival of pristine Islamic beliefs and teachings, while simultaneously engaging with modernity. Jadids maintained that Muslim peoples in Tsarist Russia had entered a period of moral and societal decay that could only be rectified by the acquisition of a new kind of knowledge and modernist, European-modeled cultural reform. Modern technologies of communication and transportation such as telegraph, printing press, postal system, and railways, as well as the spread of Islamic literature through print media such as periodicals, journals, newspapers, etc. pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munawwar Qari
Munawwar Qari Abdurrashidkhan ogli (, , ; 1878 – 1931) was a prominent Jadid in Russian Turkestan. Like other Jadids, Munnawwar Qari worked as author, poet, teacher, journalist and in other occupations. Life Munawwar Qari was of an ethnic Uzbek origin. He was the youngest child in a family of Islamic scholars and received his education in Tashkent and Bukhara. In 1901, he opened Tashkent's first Maktab to follow the Jadids' new method of teaching. He also wrote textbooks for use in schools and published literary works of other authors, while publishing and editing ''The Sun'', one of the first independent newspapers in Russian Turkestan.Charles Kurzman: ''Modernist Islam, 1840–1940. A Sourcebook'', New York 2002, p. 33. After the Russian Revolution, he continued working as a teacher, but was arrested and deported to a Gulag camp in 1925Adeeb Khalid: '' The Politics of Muslim Cultural Reform: Jadidism in Central Asia'', Berkeley 1998, p. 300. and shot in 1931 after being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahmudkhodja Behbudiy
Mahkmudkhodja Behbudiy (Cyrillic Маҳмудхўжа Беҳбудий; Arabic script ; born as Mahmudkhodja ibn Behbud Chodscha) (20 January 1875 in Samarkand; 25 March 1919 in Qarshi) was an Uzbek Jadid activist, writer, journalist and leading public figure in Imperial Russian and Soviet Turkestan. Life Mehmudkhodja Behbudiy was born on 20 January 1875 ( new calendar) on the outskirts of Samarkand in Russian Turkestan. Many members of his family were Islamic scholars, and Behbudiy too became a Qazi following his madrasah education. After an eight-month trip to Arabia, Transcaucasia, Istanbul and Cairo in 1899, which brought him into contact with the cultural movements in Islam in the wider world, he started his public career in Central Asia in 1903. He subscribed to Ismail Gaspirali's '' Tercüman'' and changed his name from ''ibn Behbud Chodscha'' to ''Behbudiy''. He also wrote articles in support of Jadidism in all Central Asian newspapers and in 1913 launched ''Ayina'' (" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musa Bigiev
Musa Jarullah Bigiev (born – 28 October 1949), sometimes known as Luther of Islam, was Tatars, Tatar Hanafi Maturidi scholar, theologian philosopher, publicist and one of the leaders of the Jadid, Jadid movement. After receiving his education in Kazan, Bukhara, Istanbul and Cairo, he became a political activist for the Ittifaq al-Muslimin, Ittifaq, the political organisation of the Muslims of Russia. He also taught in Orenburg, wrote journalistic texts and translated classic works into Tatar language, Tatar. After emigrating from the Soviet Union, he travelled Europe and the Middle and Far East while writing and publishing. Naming variations In modern Tatar alphabet#Cyrillic version, Tatar, Bigievs name is written as Бигиев Муса Җарулла, ''Bigiev Musa Carulla'', or Муса Ярулла улы Бигиев, ''Musa Jarulla ulı Bigiev''. He had various names in Arabic; for example, ''Musa Jarullah ibn Fatima at-Turkistani Kazan, al-Qazani at-Tatari ar-Rostofdoni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ismail Gasprinsky
Ismail bey Gasprinsky (also written as Gaspirali and Gasprinski; , ; ''Ismail Gasprinskii''; – ) was a Crimean Tatar intellectual, educator, publisher and Pan-Turkist politician who inspired the Jadidist movement in Central Asia. He was one of the first Muslim intellectuals in the Russian Empire, who realized the need for education and cultural reform and modernization of the Turkic and Islamic communities. His last name comes from the town of Gaspra in Crimea. Biography Ismail communicated his ideas mainly through the newspaper '' Terciman'' he founded in 1883, which existed till 1918. In his publications he called for unity and solidarity among the Turkic peoples and advocated their modernization through Europeanization. Ismail believed that the only way for modernization was through education. He widely advocated for the introduction of an education reform, and criticized the traditional education system in Muslim schools focusing much on religion and devised a new method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaynulla Rasulev
Zaynulla Rasulev (''Zaynulla bin Khabibulla bin Rasūl''; , , 25 March 1833 – 2 February 1917) was a Bashkir religious leader in the 19th and early 20th century. Zaynulla is also embraced by the closely related Tatars as part of their religious legacy. Zaynulla is notable as one of the most important representatives of Jadidism and the organizer of one of the first Jadidi madrasah. Zaynulla belonged to the Naqshandi Sufi order. Life Born in 1833 in the village of Sharip in Verkheuralsk province, Orenburg Governorate (these days in the Uchalinsky District, Republic of Bashkortostan, Russia) to the family of mullah of the local Islamic community. Received instruction in a medrese in his home village, then in the medrese in Troitsk. Upon instruction, began a clerical career. Since 1858, served as Imam khatib in the village of Yuldash (currently in Uchalinsky District, Bashkortostan) . While still in his student years, Zaynulla Rasulev (Zeynullah Resûlî in Turkish) became in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkestan
Turkestan,; ; ; ; also spelled Turkistan, is a historical region in Central Asia corresponding to the regions of Transoxiana and East Turkestan (Xinjiang). The region is located in the northwest of modern day China and to the northwest of its borders, and extends directly to the east of the Caspian Sea. Turkestan is primarily inhabited by Turkic peoples, as well as Russian and Tajik-Persian minorities. Turkestan is subdivided into Afghan Turkestan, Russian Turkestan, and East Turkistan (the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in China). Throughout history, the region has been exposed to the invasion of several different groups and kingdoms, including the Huns, Hepthalites, Bactrians, Sogdians also for a short period of time the Imperial China, Arab Caliphate, Hellenistic Macedonian Empire, as well as Achaemenid Empire, various Turkic forces and the Mongol Empire. The Qara Khitai also briefly controlled the majority of Turkestan's land. Overview Known as Turan to the Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
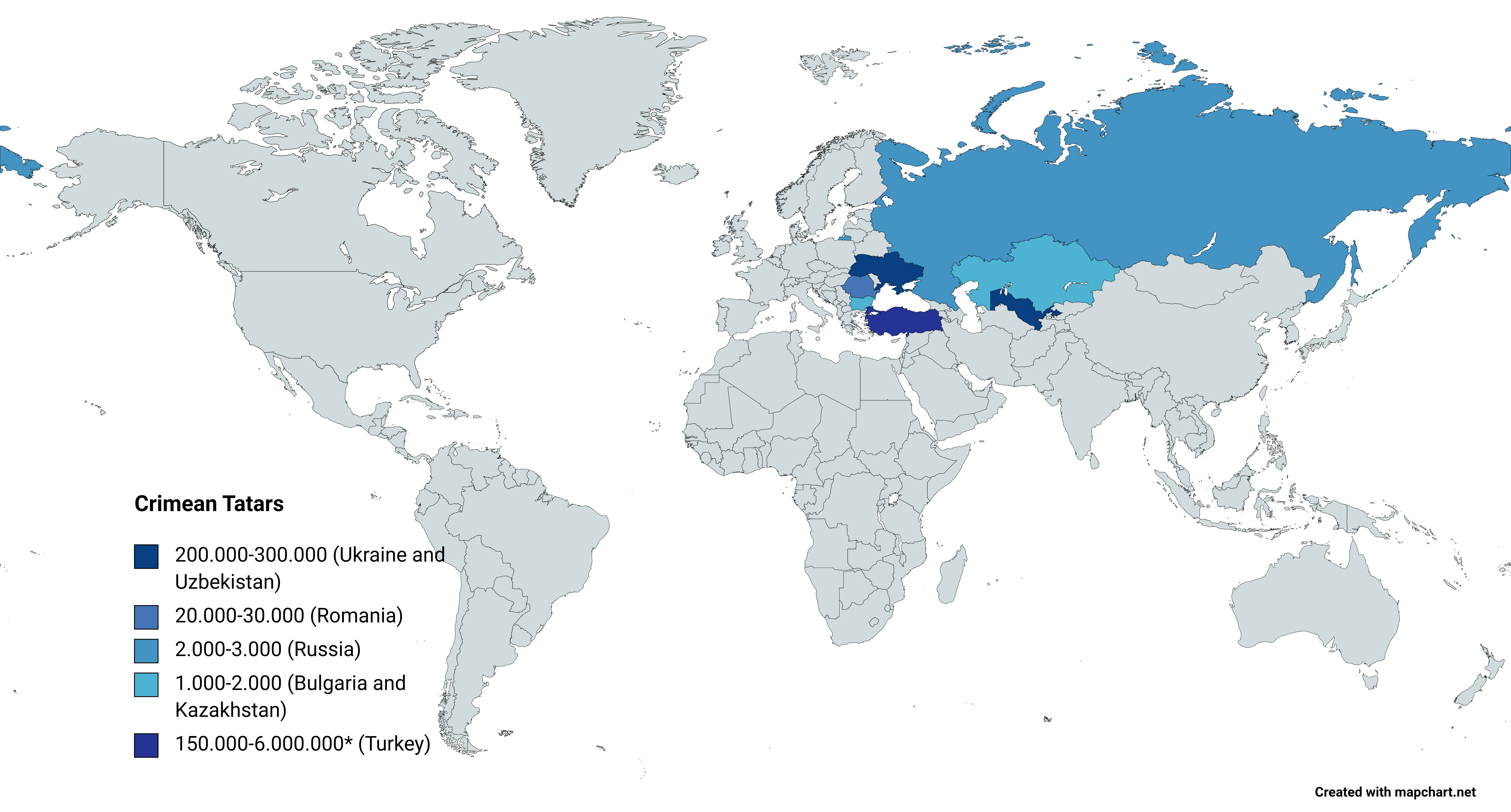
Crimean Tatars
Crimean Tatars (), or simply Crimeans (), are an Eastern European Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group and nation indigenous to Crimea. Their ethnogenesis lasted thousands of years in Crimea and the northern regions along the coast of the Black Sea, uniting Mediterranean basin, Mediterranean populations with those of the Eurasian Steppe.''Агджоян А. Т., Схаляхо Р. А., Утевская О. М., Жабагин М. К., Тагирли Ш. Г., Дамба Л. Д., Атраментова Л. А., Балановский О. П.'Генофонд крымских татар в сравнении с тюркоязычными народами Европы, 2015 Genome-wide study of the Crimean Tatars unveiled connections between them and the genomes of individuals from the Steppe during the Bronze Age, specifically those associated with the Yamnaya culture, Yamnaya archaeological culture. Until the 20th century, Crimean Tatars were the most populous demographic cohort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God in Abrahamic religions, God of Abraham (or ''Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the last Islamic prophet. Alongside the Quran, Muslims also believe in previous Islamic holy books, revelations, such as the Tawrat (Torah), the Zabur (Psalms), and the Injeel (Gospel). These earlier revelations are associated with Judaism and Christianity, which are regarded by Muslims as earlier versions of Islam. The majority of Muslims also follow the teachings and practices attributed to Muhammad (''sunnah'') as recorded in traditional accounts (hadith). With an estimated population of almost 2 billion followers, Muslims comprise around 26% of the world's total population. In descending order, the percentage of people who identify as Muslims on each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telegraph
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas pigeon post is not. Ancient signalling systems, although sometimes quite extensive and sophisticated as in China, were generally not capable of transmitting arbitrary text messages. Possible messages were fixed and predetermined, so such systems are thus not true telegraphs. The earliest true telegraph put into widespread use was the Chappe telegraph, an optical telegraph invented by Claude Chappe in the late 18th century. The system was used extensively in France, and European nations occupied by France, during the Napoleonic era. The electric telegraph started to replace the optical telegraph in the mid-19th century. It was first taken up in Britain in the form of the Cooke and Wheatstone telegraph, initially used mostly as an aid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Persian suffix "-stan" (meaning ) in both respective native languages and most other languages. The region is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the southwest, European Russia to the northwest, China and Mongolia to the east, Afghanistan and Iran to the south, and Siberia to the north. Together, the five Central Asian countries have a total population of around million. In the pre-Islamic and early Islamic eras ( and earlier) Central Asia was inhabited predominantly by Iranian peoples, populated by Eastern Iranian-speaking Bactrians, Sogdians, Khwarezmian language, Chorasmians, and the semi-nomadic Scythians and Dahae. As the result of Turkic migration, Central Asia also became the homeland for the Kazakhs, Kyrgyzs, Volga Tatars, Tatars, Turkmens, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Print Media
Mass media include the diverse arrays of media that reach a large audience via mass communication. Broadcast media transmit information electronically via media such as films, radio, recorded music, or television. Digital media comprises both Internet and mobile mass communication. Internet media comprise such services as email, social media sites, websites, and Internet-based radio and television. Many other mass media outlets have an additional presence on the web, by such means as linking to or running TV ads online, or distributing QR codes in outdoor or print media to direct mobile users to a website. In this way, they can use the easy accessibility and outreach capabilities the Internet affords, as thereby easily broadcast information throughout many different regions of the world simultaneously and cost-efficiently. Outdoor media transmits information via such media as augmented reality (AR) advertising; billboards; blimps; flying billboards (signs in tow of airpl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |