Ur III period on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Third Dynasty of Ur or Ur III was a
 Following Utu-Hengal's reign,
Following Utu-Hengal's reign,
 When Kings of the Third Ur dynasty ruled they had specific dates and names for each period of their rule. One example was "the year of Ur-nammu king," which marked Ur-Nammu's coronation. Another important time was the year named "The threshed grain of Largas." This year name references an event in which Ur-Nammu attacked the territory of Largas and took grain back to Ur. Another year-name that has been discovered was the year that Ur-Nammu's daughter became ''en'' of the god Nanna and was renamed with the priestess-name of En-Nirgal-ana. This designation as ''en'' of Nanna makes the year's designation almost certain.
When Kings of the Third Ur dynasty ruled they had specific dates and names for each period of their rule. One example was "the year of Ur-nammu king," which marked Ur-Nammu's coronation. Another important time was the year named "The threshed grain of Largas." This year name references an event in which Ur-Nammu attacked the territory of Largas and took grain back to Ur. Another year-name that has been discovered was the year that Ur-Nammu's daughter became ''en'' of the god Nanna and was renamed with the priestess-name of En-Nirgal-ana. This designation as ''en'' of Nanna makes the year's designation almost certain.
 The Ur III state followed a patrimonial system. The state was organized into a hierarchical pyramid of households with the royal household at the top. As described by Steinkeller it was a network of households linked together by mutual rights and obligations. All resources of the state were exclusively owned by the royal household. All inferior households were considered dependants of the higher ones. Inferior households contributed corvee labour to the royal household and received economic support, land, and protection in return.
In each province, administrative and economic responsibility were split between two households: one headed by a governor (ensi) and one headed by a general (Šagina) who represented the crown.
Each province had a redistribution center where provincial taxes, called bala, would all go to be shipped to the capital. The bala tax worked on a rotating basis, with only one province supporting the kingdom at a time. Each province would support the kingdom for an amount of time determined by the size of their economy. Taxes could be paid in various forms, from crops to livestock to land. The government would then apportion out goods as needed, including funding temples and giving food rations to the needy.
The Ur III state followed a patrimonial system. The state was organized into a hierarchical pyramid of households with the royal household at the top. As described by Steinkeller it was a network of households linked together by mutual rights and obligations. All resources of the state were exclusively owned by the royal household. All inferior households were considered dependants of the higher ones. Inferior households contributed corvee labour to the royal household and received economic support, land, and protection in return.
In each province, administrative and economic responsibility were split between two households: one headed by a governor (ensi) and one headed by a general (Šagina) who represented the crown.
Each province had a redistribution center where provincial taxes, called bala, would all go to be shipped to the capital. The bala tax worked on a rotating basis, with only one province supporting the kingdom at a time. Each province would support the kingdom for an amount of time determined by the size of their economy. Taxes could be paid in various forms, from crops to livestock to land. The government would then apportion out goods as needed, including funding temples and giving food rations to the needy.
 This is an area where scholars have many different views. It had long been posited that the common laborer was nothing more than a serf, but new analysis and documents reveal a possible different picture. Gangs of labourers can be divided into various groups.
Certain groups indeed seem to work under compulsion. Others work in order to keep property or get rations from the state. Still other laborers were free men and women for whom social mobility was a possibility. Many families travelled together in search of labor. Such laborers could amass private property and even be promoted to higher positions. This is quite a different picture of a laborer's life than the previous belief that they were afforded no way to move out of the social group they were born into.
Slaves also made up a crucial group of labor for the state. One scholar estimates that 2/5 of chattel slaves mentioned in documents were not born slaves but became slaves due to accumulating debt, being sold by family members, or other reasons. However, one surprising feature of this period is that slaves seem to have been able to accumulate some assets and even property during their lifetimes such that they could buy their freedom. Extant documents give details about specific deals for slaves' freedoms negotiated with slaveowners.
This is an area where scholars have many different views. It had long been posited that the common laborer was nothing more than a serf, but new analysis and documents reveal a possible different picture. Gangs of labourers can be divided into various groups.
Certain groups indeed seem to work under compulsion. Others work in order to keep property or get rations from the state. Still other laborers were free men and women for whom social mobility was a possibility. Many families travelled together in search of labor. Such laborers could amass private property and even be promoted to higher positions. This is quite a different picture of a laborer's life than the previous belief that they were afforded no way to move out of the social group they were born into.
Slaves also made up a crucial group of labor for the state. One scholar estimates that 2/5 of chattel slaves mentioned in documents were not born slaves but became slaves due to accumulating debt, being sold by family members, or other reasons. However, one surprising feature of this period is that slaves seem to have been able to accumulate some assets and even property during their lifetimes such that they could buy their freedom. Extant documents give details about specific deals for slaves' freedoms negotiated with slaveowners.

 The Ur III kings oversaw many substantial state-run projects, including intricate
The Ur III kings oversaw many substantial state-run projects, including intricate
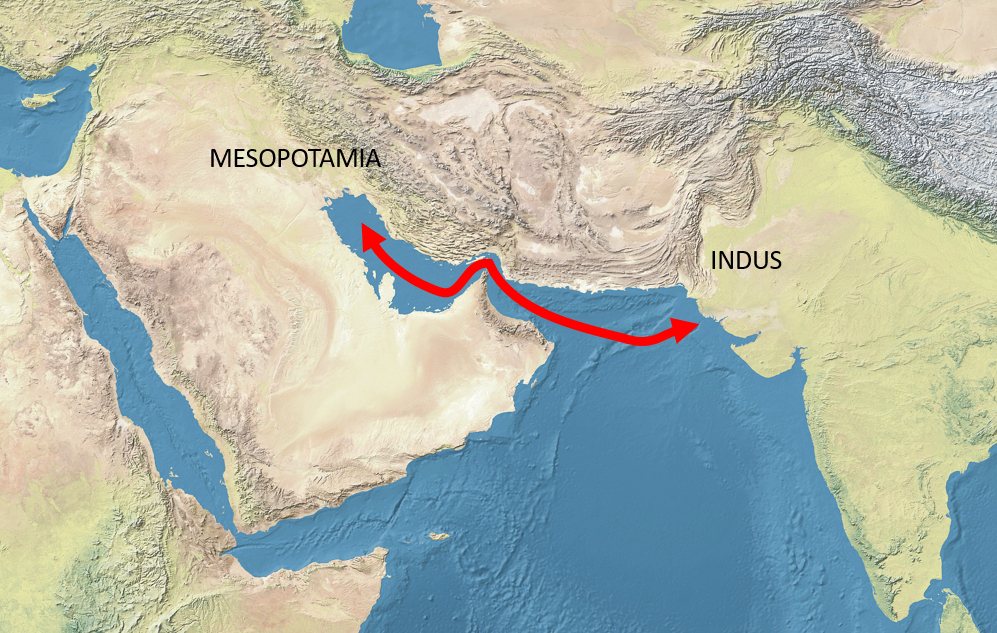 Evidence for imports from the Indus to Ur can be found from around 2350 BC. Various objects made with shell species that are characteristic of the Indus coast, particularly ''Trubinella Pyrum'' and ''Fasciolaria Trapezium'', have been found in the archaeological sites of Mesopotamia dating from around 2500-2000 BC. Several Indus seals with Harappan script have also been found in Mesopotamia, particularly in Ur and
Evidence for imports from the Indus to Ur can be found from around 2350 BC. Various objects made with shell species that are characteristic of the Indus coast, particularly ''Trubinella Pyrum'' and ''Fasciolaria Trapezium'', have been found in the archaeological sites of Mesopotamia dating from around 2500-2000 BC. Several Indus seals with Harappan script have also been found in Mesopotamia, particularly in Ur and
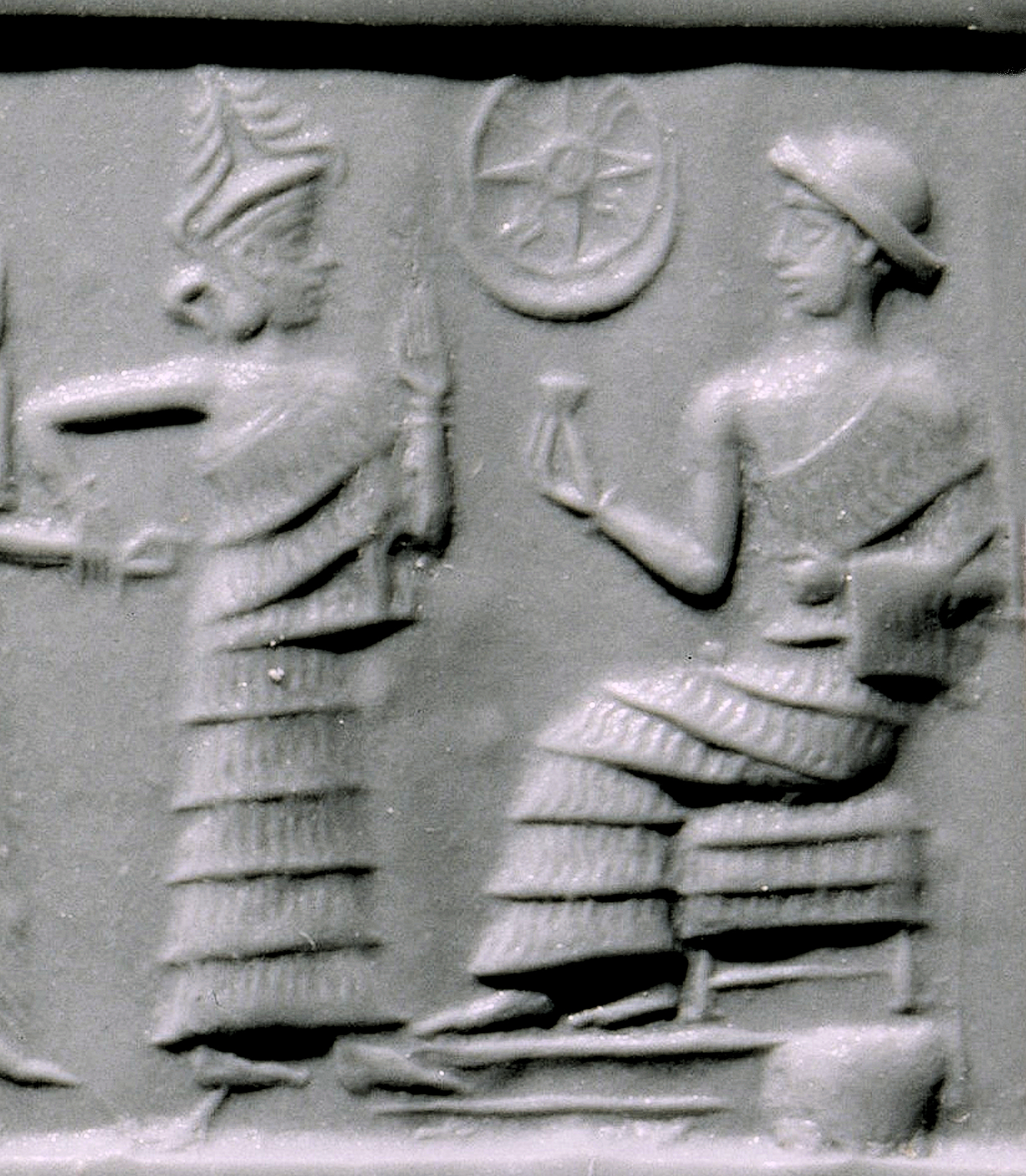 Sumerian dominated the cultural sphere and was the language of legal, administrative, and economic documents, while signs of the spread of Akkadian could be seen elsewhere. New towns that arose in this period were virtually all given Akkadian names. Culture also thrived through many different types of art forms.
Sumerian dominated the cultural sphere and was the language of legal, administrative, and economic documents, while signs of the spread of Akkadian could be seen elsewhere. New towns that arose in this period were virtually all given Akkadian names. Culture also thrived through many different types of art forms.
File:Stele of Ur-Nammu (front and back).jpg, Stele of
The State of Ur III Research - CDLI
{{DEFAULTSORT:Third Dynasty Of Ur States and territories established in the 3rd millennium BC States and territories disestablished in the 3rd millennium BC States and territories disestablished in the 20th century BC Sumer Ur Middle Eastern royal families 22nd-century BC establishments Former empires in Asia Former monarchies
Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age, early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. ...
ian dynasty based in the city of Ur in the 22nd and 21st centuries BC (middle chronology
The chronology of the ancient Near East is a framework of dates for various events, rulers and dynasties. Historical inscriptions and texts customarily record events in terms of a succession of officials or rulers: "in the year X of king Y". Com ...
). For a short period they were the preeminent power in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
and their realm is sometimes referred to by historians as the Neo-Sumerian Empire.
The Third Dynasty of Ur is commonly abbreviated as "Ur III" by historians studying the period. It is numbered in reference to previous dynasties, such as the First Dynasty of Ur (26-25th century BC), but it seems the once supposed Second Dynasty of Ur was never recorded.
The Third Dynasty of Ur was the last Sumerian dynasty which came to preeminent power in Mesopotamia. It began after several centuries of control, exerted first by the Akkadian Empire
The Akkadian Empire () was the first known empire, succeeding the long-lived city-states of Sumer. Centered on the city of Akkad (city), Akkad ( or ) and its surrounding region, the empire united Akkadian language, Akkadian and Sumerian languag ...
, and then, after its fall, by Gutian and independent Sumerian city-state kings. It controlled the cities of Isin
Isin (, modern Arabic language, Arabic: Ishan al-Bahriyat) is an archaeological site in Al-Qādisiyyah Governorate, Iraq which was the location of the Ancient Near East city of Isin, occupied from the late 4th millennium Uruk period up until at ...
, Larsa
Larsa (, read ''Larsamki''), also referred to as Larancha/Laranchon (Gk. Λαραγχων) by Berossus, Berossos and connected with the biblical Arioch, Ellasar, was an important city-state of ancient Sumer, the center of the Cult (religious pra ...
, and Eshnunna
Eshnunna (also Esnunak) (modern Tell Asmar in Diyala Governorate, Iraq) was an ancient Sumerian (and later Akkadian) city and city-state in central Mesopotamia 12.6 miles northwest of Tell Agrab and 15 miles northwest of Tell Ishchali. Althou ...
and extended as far north as Upper Mesopotamia
Upper Mesopotamia constitutes the Upland and lowland, uplands and great outwash plain of northwestern Iraq, northeastern Syria and southeastern Turkey, in the northern Middle East. Since the early Muslim conquests of the mid-7th century, the regio ...
. The Ur III provinces, from north to south were Sippar, Tiwe, Urum, Puö, Gudua, Babylon, Kis, Kazallu, Apiak, Marad, Nippur, Uru-sagrig, Isin, Adab, Suruppak, Umma, Girsu, Uruk, and Ur.
History
The Third Dynasty of Ur arose some time after the fall of the Akkad Dynasty. The period between the last powerful king of the Akkad Dynasty, Shar-Kali-Sharri, and the first king of Ur III,Ur-Nammu
Ur-Nammu (or Ur-Namma, Ur-Engur, Ur-Gur, Sumerian language, Sumerian: ; died 2094 BC) founded the Sumerian Third Dynasty of Ur, in southern Mesopotamia, following several centuries of Akkadian Empire, Akkadian and Gutian period, Gutian rule. Thou ...
, is not well documented, but most Assyriologists posit that there was a brief "Dark Age", followed by a power struggle among the most powerful city-states. On the king-lists, Shar-Kali-Sharri is followed by two more kings of Akkad and six in Uruk; however, there are no year names surviving for any of these, nor even any artifacts confirming that any of these reigns was historical — save one artifact for Dudu of Akkad (Shar-Kali-Sharri's immediate successor on the list). Akkad's primacy, instead, seems to have been usurped by Gutian invaders from the Zagros Mountains
The Zagros Mountains are a mountain range in Iran, northern Iraq, and southeastern Turkey. The mountain range has a total length of . The Zagros range begins in northwestern Iran and roughly follows Iran's western border while covering much of s ...
, whose kings ruled in Mesopotamia for an indeterminate period (124 years according to some copies of the king list, only 25 according to others). An illiterate and nomadic people, their rule was not conducive to agriculture, nor record-keeping, and by the time they were expelled, the region was crippled by severe famine and skyrocketing grain prices. Their last king, Tirigan, was driven out by Utu-hengal of Uruk
Uruk, the archeological site known today as Warka, was an ancient city in the Near East, located east of the current bed of the Euphrates River, on an ancient, now-dried channel of the river in Muthanna Governorate, Iraq. The site lies 93 kilo ...
.
Ur-Nammu
Ur-Nammu (or Ur-Namma, Ur-Engur, Ur-Gur, Sumerian language, Sumerian: ; died 2094 BC) founded the Sumerian Third Dynasty of Ur, in southern Mesopotamia, following several centuries of Akkadian Empire, Akkadian and Gutian period, Gutian rule. Thou ...
(originally a general) founded the Third Dynasty of Ur, but the precise events surrounding his rise are unclear. The ''Sumerian King List
The ''Sumerian King List'' (abbreviated ''SKL'') or ''Chronicle of the One Monarchy'' is an ancient Composition (language), literary composition written in Sumerian language, Sumerian that was likely created and redacted to legitimize the claims ...
'' states that Utu-hengal had reigned for seven years (or 426, or 26 in other copies), although only one year-name for him is known from records, that of his accession, suggesting a shorter reign.
It is possible that Ur-Nammu was originally his governor. There are two stelae
A stele ( ) or stela ( )The plural in English is sometimes stelai ( ) based on direct transliteration of the Greek, sometimes stelae or stelæ ( ) based on the inflection of Greek nouns in Latin, and sometimes anglicized to steles ( ) or stela ...
discovered in Ur that include this detail in an inscription about Ur-Nammu's life.
Ur-Nammu rose to prominence as a warrior-king when he crushed the ruler of Lagash
Lagash (; cuneiform: LAGAŠKI; Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''Lagaš'') was an ancient city-state located northwest of the junction of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers and east of Uruk, about east of the modern town of Al-Shatrah, Iraq. Lagash ( ...
in battle, killing the king himself. After this battle, Ur-Nammu seems to have earned the title 'king of Sumer and Akkad.'
Ur's dominance over the Neo-Sumerian Empire was consolidated with the famous Code of Ur-Nammu, probably the first such law-code for Mesopotamia since that of Urukagina
Uru-ka-gina, Uru-inim-gina, or Iri-ka-gina ( ; died 2370 BC) was King of the city-states of Lagash and Girsu in Mesopotamia, and the last ruler of the 1st Dynasty of Lagash. He assumed the title of king, claiming to have been divinely appointe ...
of Lagash
Lagash (; cuneiform: LAGAŠKI; Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''Lagaš'') was an ancient city-state located northwest of the junction of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers and east of Uruk, about east of the modern town of Al-Shatrah, Iraq. Lagash ( ...
centuries earlier.
Many significant changes occurred in the empire under Shulgi
Shulgi ( dšul-gi,(died c. 2046 BC) formerly read as Dungi) of Ur was the second king of the Third Dynasty of Ur. He reigned for 48 years, from (Middle Chronology). His accomplishments include the completion of construction of the Great ...
's reign. He took steps to centralize and standardize the procedures of the empire. He is credited with standardizing administrative processes, archival documentation, the tax system, and the national calendar. He captured the city of Susa
Susa ( ) was an ancient city in the lower Zagros Mountains about east of the Tigris, between the Karkheh River, Karkheh and Dez River, Dez Rivers in Iran. One of the most important cities of the Ancient Near East, Susa served as the capital o ...
and the surrounding region, toppling Elamite
Elamite, also known as Hatamtite and formerly as Scythic, Median, Amardian, Anshanian and Susian, is an extinct language that was spoken by the ancient Elamites. It was recorded in what is now southwestern Iran from 2600 BC to 330 BC. Elamite i ...
king Kutik-Inshushinak, while the rest of Elam fell under control of Shimashki dynasty.
The military and conquests of Ur III
In the last century of the 3rd millennium BCE, it is believed that the kings of Ur waged several conflicts around the frontiers of the kingdom. These conflicts are believed to have been influenced by the king of Akkad. As there is little evidence of how the kings organized their forces, it is unclear whether defensive forces were in the center or outside the kingdom. What is known is that the second ruler of the dynasty, Šulgi achieved some expansion and conquest. These were continued by his three successors but their conquests are less frequent with time. At the very height of the expansion of Ur, they had taken territory from southeasternAnatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
(modern Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
) to the Iranian shore of the Persian Gulf, a testimony to the strength of the dynasty. There are hundreds of texts that explain how treasures were seized by the Ur III armies and brought back to the kingdom after many victories. In some texts, it also appears that the Shulgi campaigns were the most profitable for the kingdom, although it is likely that the kings and temples of Ur were primarily those that benefited from the spoils of war.
Conflicts with northeastern mountain tribes
The rulers of Ur III were often in conflict with the highland tribes of the Zagros mountain area who dwelled in the northeastern portion of Mesopotamia. The most important of these tribes were the Simurrum and theLullubi
Lullubi, Lulubi (: ''Lu-lu-bi'', : ''Lu-lu-biki'' "Country of the Lullubi"), more commonly known as Lullu, were a group of Bronze Age tribes of Hurrian and Semitic languages, Semitic origin who existed and disappeared during the 3rd millennium BC ...
tribal kingdoms. They were also often in conflict with Elam
Elam () was an ancient civilization centered in the far west and southwest of Iran, stretching from the lowlands of what is now Khuzestan and Ilam Province as well as a small part of modern-day southern Iraq. The modern name ''Elam'' stems fr ...
.
Military rulers of Mari
In the northern area of Mari, Semitic military rulers called the Shakkanakkus apparently continued to rule contemporaneously with the Third Dynasty of Ur, or possibly in the period that just preceded it, with rulers such as military governors like Puzur-Ishtar, who was probably contemporary with Amar-Sin.List of rulers
Assyriologists employ many complicated methods for establishing the most precise dates possible for this period, but controversy still exists. Generally, scholars use either the conventional (middle, generally preferred) or the low (short) chronologies. They are as follows: The list of the Kings of the Third Dynasty of Ur with the length of their reigns, appears on a cuneiform document listing the kings of Ur andIsin
Isin (, modern Arabic language, Arabic: Ishan al-Bahriyat) is an archaeological site in Al-Qādisiyyah Governorate, Iraq which was the location of the Ancient Near East city of Isin, occupied from the late 4th millennium Uruk period up until at ...
, the "List of Reigns of Kings of Ur and Isin" (MS 1686). The list explains: "18 years Ur-Namma asking, 48 years Shulgi
Shulgi ( dšul-gi,(died c. 2046 BC) formerly read as Dungi) of Ur was the second king of the Third Dynasty of Ur. He reigned for 48 years, from (Middle Chronology). His accomplishments include the completion of construction of the Great ...
asking, 9 years Amar-Suen, 9 years Su-Suen, 24 years Ibbi-Suen."
Fall of Ur III
The power of the Neo-Sumerians was waning.Ibbi-Sin
Ibbi-Sin (, ), (died c. 2004 BC) son of Shu-Sin, was king of Sumer and Akkad and last king of the Ur III dynasty, and reigned c. 2028–2004 BC (Middle chronology). During his reign, the Sumerian empire was attacked repeatedly by Amorites. As f ...
in the 21st century launched military campaigns into Elam
Elam () was an ancient civilization centered in the far west and southwest of Iran, stretching from the lowlands of what is now Khuzestan and Ilam Province as well as a small part of modern-day southern Iraq. The modern name ''Elam'' stems fr ...
, but did not manage to penetrate far into the country. In 2004/1940 BC (middle/short chronology respectively), the Elamites, allied with the people of Susa
Susa ( ) was an ancient city in the lower Zagros Mountains about east of the Tigris, between the Karkheh River, Karkheh and Dez River, Dez Rivers in Iran. One of the most important cities of the Ancient Near East, Susa served as the capital o ...
and led by Kindattu, king of the Elamite Shimashki dynasty, was able to surround Ur and managed to sack Ur(early summer?) and lead Ibbi-Sin
Ibbi-Sin (, ), (died c. 2004 BC) son of Shu-Sin, was king of Sumer and Akkad and last king of the Ur III dynasty, and reigned c. 2028–2004 BC (Middle chronology). During his reign, the Sumerian empire was attacked repeatedly by Amorites. As f ...
into captivity, ending the third dynasty of Ur
The Third Dynasty of Ur or Ur III was a Sumerian dynasty based in the city of Ur in the 22nd and 21st centuries BC ( middle chronology). For a short period they were the preeminent power in Mesopotamia and their realm is sometimes referred to by ...
. After this victory, the Elamites destroyed the kingdom, and ruled through military occupation for the next 21 years.
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
then fell under Amorite
The Amorites () were an ancient Northwest Semitic-speaking Bronze Age people from the Levant. Initially appearing in Sumerian records c. 2500 BC, they expanded and ruled most of the Levant, Mesopotamia and parts of Egypt from the 21st century BC ...
influence. The Amorite kings of the Dynasty of Isin
The Dynasty of Isin refers to the final ruling dynasty listed on the ''Sumerian King List'' (''SKL''). The list of the Kings of Isin with the length of their reigns, also appears on a cuneiform document listing the kings of Ur and Isin, the ''Li ...
formed successor state
Succession of states is a concept in international relations regarding a successor state that has become a sovereign state over a territory (and populace) that was previously under the sovereignty of another state. The theory has its roots in 19th ...
s to Ur III, starting the Isin-Larsa period
The Isin-Larsa period (–1763 BCE, Middle Chronology, or 1961–1699 BCE, Short Chronology) is a phase in the history of ancient Mesopotamia, which extends between the end of the Third Dynasty of Ur and the conquest of Mesopotamia by King Hammur ...
. They managed to drive the Elamites out of Ur, rebuilt the city, and returned the statue of Nanna that the Elamites had plundered. The Amorites were nomadic tribes from the northern Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
who were Northwest Semitic
Northwest Semitic is a division of the Semitic languages comprising the indigenous languages of the Levant. It emerged from Proto-Semitic language, Proto-Semitic in the Early Bronze Age. It is first attested in proper names identified as Amorite l ...
speakers, unlike the native Akkadians
The Akkadian Empire () was the first known empire, succeeding the long-lived city-states of Sumer. Centered on the city of Akkad ( or ) and its surrounding region, the empire united Akkadian and Sumerian speakers under one rule and exercised ...
of southern Mesopotamia and Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
, who spoke East Semitic
The East Semitic languages are one of three divisions of the Semitic languages. The East Semitic group is attested by three distinct languages, Akkadian, Eblaite and possibly Kishite, all of which have been long extinct. They were influenced ...
. By around the 19th century BC, much of southern Mesopotamia was occupied by the Amorites. The Amorites at first did not practice agriculture, preferring a semi-nomadic lifestyle, herding sheep. Over time, Amorite grain merchants rose to prominence and established their own independent dynasties in several south Mesopotamian city-states, most notably Isin
Isin (, modern Arabic language, Arabic: Ishan al-Bahriyat) is an archaeological site in Al-Qādisiyyah Governorate, Iraq which was the location of the Ancient Near East city of Isin, occupied from the late 4th millennium Uruk period up until at ...
, Larsa
Larsa (, read ''Larsamki''), also referred to as Larancha/Laranchon (Gk. Λαραγχων) by Berossus, Berossos and connected with the biblical Arioch, Ellasar, was an important city-state of ancient Sumer, the center of the Cult (religious pra ...
, Eshnunna
Eshnunna (also Esnunak) (modern Tell Asmar in Diyala Governorate, Iraq) was an ancient Sumerian (and later Akkadian) city and city-state in central Mesopotamia 12.6 miles northwest of Tell Agrab and 15 miles northwest of Tell Ishchali. Althou ...
, Lagash
Lagash (; cuneiform: LAGAŠKI; Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''Lagaš'') was an ancient city-state located northwest of the junction of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers and east of Uruk, about east of the modern town of Al-Shatrah, Iraq. Lagash ( ...
, and later, founding Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-s ...
as a state.
Dating systems
 When Kings of the Third Ur dynasty ruled they had specific dates and names for each period of their rule. One example was "the year of Ur-nammu king," which marked Ur-Nammu's coronation. Another important time was the year named "The threshed grain of Largas." This year name references an event in which Ur-Nammu attacked the territory of Largas and took grain back to Ur. Another year-name that has been discovered was the year that Ur-Nammu's daughter became ''en'' of the god Nanna and was renamed with the priestess-name of En-Nirgal-ana. This designation as ''en'' of Nanna makes the year's designation almost certain.
When Kings of the Third Ur dynasty ruled they had specific dates and names for each period of their rule. One example was "the year of Ur-nammu king," which marked Ur-Nammu's coronation. Another important time was the year named "The threshed grain of Largas." This year name references an event in which Ur-Nammu attacked the territory of Largas and took grain back to Ur. Another year-name that has been discovered was the year that Ur-Nammu's daughter became ''en'' of the god Nanna and was renamed with the priestess-name of En-Nirgal-ana. This designation as ''en'' of Nanna makes the year's designation almost certain.
Social and political organization
Political organization
 The Ur III state followed a patrimonial system. The state was organized into a hierarchical pyramid of households with the royal household at the top. As described by Steinkeller it was a network of households linked together by mutual rights and obligations. All resources of the state were exclusively owned by the royal household. All inferior households were considered dependants of the higher ones. Inferior households contributed corvee labour to the royal household and received economic support, land, and protection in return.
In each province, administrative and economic responsibility were split between two households: one headed by a governor (ensi) and one headed by a general (Šagina) who represented the crown.
Each province had a redistribution center where provincial taxes, called bala, would all go to be shipped to the capital. The bala tax worked on a rotating basis, with only one province supporting the kingdom at a time. Each province would support the kingdom for an amount of time determined by the size of their economy. Taxes could be paid in various forms, from crops to livestock to land. The government would then apportion out goods as needed, including funding temples and giving food rations to the needy.
The Ur III state followed a patrimonial system. The state was organized into a hierarchical pyramid of households with the royal household at the top. As described by Steinkeller it was a network of households linked together by mutual rights and obligations. All resources of the state were exclusively owned by the royal household. All inferior households were considered dependants of the higher ones. Inferior households contributed corvee labour to the royal household and received economic support, land, and protection in return.
In each province, administrative and economic responsibility were split between two households: one headed by a governor (ensi) and one headed by a general (Šagina) who represented the crown.
Each province had a redistribution center where provincial taxes, called bala, would all go to be shipped to the capital. The bala tax worked on a rotating basis, with only one province supporting the kingdom at a time. Each province would support the kingdom for an amount of time determined by the size of their economy. Taxes could be paid in various forms, from crops to livestock to land. The government would then apportion out goods as needed, including funding temples and giving food rations to the needy.
The city of Nippur and its importance
The city ofNippur
Nippur (Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''Nibru'', often logogram, logographically recorded as , EN.LÍLKI, "Enlil City;"I. E. S. Edwards, C. J. Gadd, N. G. L. Hammond, ''The Cambridge Ancient History: Prolegomena & Prehistory'': Vol. 1, Part 1, Ca ...
was one of the most important cities in the Third Dynasty of Ur. Nippur is believed to be the religious center of Mesopotamia. It was home to the shrine of Enlil
Enlil, later known as Elil and Ellil, is an List of Mesopotamian deities, ancient Mesopotamian god associated with wind, air, earth, and storms. He is first attested as the chief deity of the Sumerian pantheon, but he was later worshipped by t ...
, who was the lord of all gods. This was where the God Enlil spoke the king's name and was calling the king to his existence. This was used as a legitimacy for every king in order to secure power. The city is also believed to be a place where people would often take disputes according to some tablets that were found near the city. Politically it is hard to say how significant Nippur was because the city had no status as a dynastic or military power. However, the fact that Nippur never really gave kings any real political or military advantages suggests to some that it was never really conquered. The city itself was more viewed as "national Cult Center." Because it was viewed this way it was thought that any conquest of the city would give the Mesopotamian rulers unacceptable political risks. Also as the city was seen as a holy site this enabled Nippur to survive numerous conflicts that wiped out many other cities in the region.
Social system
 This is an area where scholars have many different views. It had long been posited that the common laborer was nothing more than a serf, but new analysis and documents reveal a possible different picture. Gangs of labourers can be divided into various groups.
Certain groups indeed seem to work under compulsion. Others work in order to keep property or get rations from the state. Still other laborers were free men and women for whom social mobility was a possibility. Many families travelled together in search of labor. Such laborers could amass private property and even be promoted to higher positions. This is quite a different picture of a laborer's life than the previous belief that they were afforded no way to move out of the social group they were born into.
Slaves also made up a crucial group of labor for the state. One scholar estimates that 2/5 of chattel slaves mentioned in documents were not born slaves but became slaves due to accumulating debt, being sold by family members, or other reasons. However, one surprising feature of this period is that slaves seem to have been able to accumulate some assets and even property during their lifetimes such that they could buy their freedom. Extant documents give details about specific deals for slaves' freedoms negotiated with slaveowners.
This is an area where scholars have many different views. It had long been posited that the common laborer was nothing more than a serf, but new analysis and documents reveal a possible different picture. Gangs of labourers can be divided into various groups.
Certain groups indeed seem to work under compulsion. Others work in order to keep property or get rations from the state. Still other laborers were free men and women for whom social mobility was a possibility. Many families travelled together in search of labor. Such laborers could amass private property and even be promoted to higher positions. This is quite a different picture of a laborer's life than the previous belief that they were afforded no way to move out of the social group they were born into.
Slaves also made up a crucial group of labor for the state. One scholar estimates that 2/5 of chattel slaves mentioned in documents were not born slaves but became slaves due to accumulating debt, being sold by family members, or other reasons. However, one surprising feature of this period is that slaves seem to have been able to accumulate some assets and even property during their lifetimes such that they could buy their freedom. Extant documents give details about specific deals for slaves' freedoms negotiated with slaveowners.
An early code of law
One salient feature of Ur III is its establishment of one of the earliest known law-codes, the '' Code of Ur-Nammu''. It is quite similar to the famousCode of Hammurabi
The Code of Hammurabi is a Babylonian legal text composed during 1755–1750 BC. It is the longest, best-organized, and best-preserved legal text from the ancient Near East. It is written in the Old Babylonian dialect of Akkadian language, Akkadi ...
, resembling its prologue and bodily structure. Extant copies, written in Old Babylonian, exist from Nippur
Nippur (Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''Nibru'', often logogram, logographically recorded as , EN.LÍLKI, "Enlil City;"I. E. S. Edwards, C. J. Gadd, N. G. L. Hammond, ''The Cambridge Ancient History: Prolegomena & Prehistory'': Vol. 1, Part 1, Ca ...
, Sippar
Sippar (Sumerian language, Sumerian: , Zimbir) (also Sippir or Sippara) was an ancient Near Eastern Sumerian and later Babylonian city on the east bank of the Euphrates river. Its ''Tell (archaeology), tell'' is located at the site of modern Tell ...
, and also Ur itself. Although the prologue credits Ur-Nammu
Ur-Nammu (or Ur-Namma, Ur-Engur, Ur-Gur, Sumerian language, Sumerian: ; died 2094 BC) founded the Sumerian Third Dynasty of Ur, in southern Mesopotamia, following several centuries of Akkadian Empire, Akkadian and Gutian period, Gutian rule. Thou ...
, the author is still somewhat under dispute; some scholars attribute it to his son, Shulgi
Shulgi ( dšul-gi,(died c. 2046 BC) formerly read as Dungi) of Ur was the second king of the Third Dynasty of Ur. He reigned for 48 years, from (Middle Chronology). His accomplishments include the completion of construction of the Great ...
.
The prologue to the law-code, written in the first person, established the king as the beacon of justice for his land, a role that previous kings normally did not play. He claims to want justice for all, including traditionally unfortunate groups in the kingdom like the widower or the orphan.
Most legal disputes were dealt with locally by government officials called mayors, although their decision could be appealed and eventually overturned by the provincial governor. Sometimes legal disputes were publicly aired with witnesses present at a place like the town square or in front of the temple. However, the image of the king as the supreme judge of the land took hold, and this image appears in many literary works and poems. Citizens sometimes wrote letters of prayer to the king, either present or past.
Industry and commerce

 The Ur III kings oversaw many substantial state-run projects, including intricate
The Ur III kings oversaw many substantial state-run projects, including intricate irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering of plants) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has bee ...
systems and centralization of agriculture. An enormous labor force was amassed to work in agriculture, particularly in irrigation, harvesting, and sowing.
Textiles were a particularly important industry in Ur during this time. The textile industry
The textile industry is primarily concerned with the design, production and distribution of textiles: yarn, cloth and clothing.
Industry process
Cotton manufacturing
Cotton is the world's most important natural fibre. In the year 2007, th ...
was run by the state. Many men, women, and children alike were employed to produce wool
Wool is the textile fiber obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have some properties similar to animal w ...
and linen
Linen () is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant.
Linen is very strong and absorbent, and it dries faster than cotton. Because of these properties, linen is comfortable to wear in hot weather and is valued for use in garments. Lin ...
clothing
Clothing (also known as clothes, garments, dress, apparel, or attire) is any item worn on a human human body, body. Typically, clothing is made of fabrics or textiles, but over time it has included garments made from animal skin and other thin s ...
. The detailed documents from the administration of this period exhibit a startling amount of centralization; some scholars have gone so far as to say no other period in Mesopotamian history reached the same level.
Trade with the Gulf Region
Trade was very important to the Ur Dynasty because it was a way to ensure that the empire had enough ways to grow its wealth and care for those Ur ruled. One of the areas that Mesopotamia traded with was the Persian Gulf area, trading mostly raw materials such as metal, wood, ivory, and also semi-precious stones. One specific kind of item traded with the two regions were conch shells. These were made by craftsmen who would turn them into lamps and cups dating back to the 3rd millennium. They have been discovered in graves, palaces, temples, and even residential homes. The fact that this item was mostly found in upper class contexts could show that only the wealthy at the time had access to the item. Additionally, Ur consumed jewelry, inlays, carvings, and cylinder seals in significant amounts. The high demand for these items shows a heavy trade relationship with the Gulf region.Commercial relations with the Indus
 Evidence for imports from the Indus to Ur can be found from around 2350 BC. Various objects made with shell species that are characteristic of the Indus coast, particularly ''Trubinella Pyrum'' and ''Fasciolaria Trapezium'', have been found in the archaeological sites of Mesopotamia dating from around 2500-2000 BC. Several Indus seals with Harappan script have also been found in Mesopotamia, particularly in Ur and
Evidence for imports from the Indus to Ur can be found from around 2350 BC. Various objects made with shell species that are characteristic of the Indus coast, particularly ''Trubinella Pyrum'' and ''Fasciolaria Trapezium'', have been found in the archaeological sites of Mesopotamia dating from around 2500-2000 BC. Several Indus seals with Harappan script have also been found in Mesopotamia, particularly in Ur and Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-s ...
. About twenty seals have been found from the Akkadian and Ur III sites, that have connections with Harappa
Harappa () is an archaeological site in Punjab, Pakistan, about west of Sahiwal, that takes its name from a modern village near the former course of the Ravi River, which now runs to the north. Harappa is the type site of the Bronze Age Indus ...
and often use the Indus script
The Indus script, also known as the Harappan script and the Indus Valley script, is a corpus of symbols produced by the Indus Valley Civilisation. Most inscriptions containing these symbols are extremely short, making it difficult to judge whe ...
.
These exchanges came to a halt with the decline of the Indus valley civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation, was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form from 2600 BCE ...
after around 1900 BC.
Art and culture
 Sumerian dominated the cultural sphere and was the language of legal, administrative, and economic documents, while signs of the spread of Akkadian could be seen elsewhere. New towns that arose in this period were virtually all given Akkadian names. Culture also thrived through many different types of art forms.
Sumerian dominated the cultural sphere and was the language of legal, administrative, and economic documents, while signs of the spread of Akkadian could be seen elsewhere. New towns that arose in this period were virtually all given Akkadian names. Culture also thrived through many different types of art forms.
Literature
Sumerian texts were mass-produced in the Ur III period; however, the word 'revival' or 'renaissance' to describe this period is misleading because archaeological evidence does not offer evidence of a previous period of decline. Instead, Sumerian began to take on a different form. As the Semitic Akkadian language became the common spoken language, Sumerian continued to dominate literature and also administrative documents. Government officials learned to write at special schools that used only Sumerian literature. Some scholars believe that the Uruk ''Epic of Gilgamesh
The ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' () is an epic poetry, epic from ancient Mesopotamia. The literary history of Gilgamesh begins with five Sumerian language, Sumerian poems about Gilgamesh (formerly read as Sumerian "Bilgames"), king of Uruk, some of ...
'' was written down during this period into its classic Sumerian form. The Ur III Dynasty attempted to establish ties to the early kings of Uruk by claiming to be their familial relations.
For example, the Ur III kings often claimed Gilgamesh's divine parents, Ninsun and Lugalbanda, as their own, probably to evoke a comparison to the epic hero.
Another text from this period, known as "The Death of Urnammu", contains an underworld scene in which Ur-Nammu showers "his brother Gilgamesh" with gifts.
Ur-Nammu
Ur-Nammu (or Ur-Namma, Ur-Engur, Ur-Gur, Sumerian language, Sumerian: ; died 2094 BC) founded the Sumerian Third Dynasty of Ur, in southern Mesopotamia, following several centuries of Akkadian Empire, Akkadian and Gutian period, Gutian rule. Thou ...
, University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archeology and Anthropology.
File:Cuneiform tablet impressed with cylinder seal. Receipt of goats,ca. 2040 B.C. Neo-Summerian.jpg, Cuneiform tablet impressed with cylinder seal. Receipt of goats, , year 7 of Amar-Sin. Neo-Sumerian.
File:Cuneiform tablet impressed with cylinder seal. Receipt of goats,ca. 2040 B.C. Neo-Summerian (drawing).jpg, Cuneiform tablet impressed with cylinder seal. Receipt of goats, . Neo-Sumerian (drawing).
File:Administrative Tablet, Third Dynasty of Ur, 2026 BC.jpg, Administrative Tablet, Third Dynasty of Ur, 2026 BC.
See also
* List of Mesopotamian dynasties * Renaissance of SumerReferences
Further reading
* * * * *External links
The State of Ur III Research - CDLI
{{DEFAULTSORT:Third Dynasty Of Ur States and territories established in the 3rd millennium BC States and territories disestablished in the 3rd millennium BC States and territories disestablished in the 20th century BC Sumer Ur Middle Eastern royal families 22nd-century BC establishments Former empires in Asia Former monarchies