Typeface Simple Zilla Slab on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A typeface (or font family) is a design of
A typeface (or font family) is a design of
 Font ''superfamilies'' began to emerge when foundries began to include typefaces with significant structural differences, but some design relationship, under the same general family name. Arguably the first superfamily was created when Morris Fuller Benton created Clearface Gothic for ATF in 1910, a sans serif companion to the existing (serifed) Clearface. The superfamily label does not include quite different designs given the same family name for what would seem to be purely marketing, rather than design, considerations:
Font ''superfamilies'' began to emerge when foundries began to include typefaces with significant structural differences, but some design relationship, under the same general family name. Arguably the first superfamily was created when Morris Fuller Benton created Clearface Gothic for ATF in 1910, a sans serif companion to the existing (serifed) Clearface. The superfamily label does not include quite different designs given the same family name for what would seem to be purely marketing, rather than design, considerations:
 Digital type became the dominant form of type in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Digital fonts store the image of each character either as a
Digital type became the dominant form of type in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Digital fonts store the image of each character either as a
 Serif, or ''Roman'', typefaces are named for the features at the ends of their strokes. Times New Roman and Garamond are common examples of serif typefaces. Serif fonts are probably the most used class in printed materials, including most books, newspapers and magazines. Serif fonts are often classified into three subcategories: Old Style, Transitional, and Didone (typography), Didone (or Modern), representative examples of which are Garamond, Baskerville, and Bodoni respectively.
Old Style typefaces are influenced by early Italian lettering design. Modern fonts often exhibit a bracketed serif and a substantial difference in weight within the strokes. Though some argument exists as to whether Transitional fonts exist as a discrete category among serif fonts, Transitional fonts lie somewhere between Old Style and Modern style typefaces. Transitional fonts exhibit a marked increase in the variation of stroke weight and a more horizontal serif compared to Old Style. Slab serif designs have particularly large serifs, and date to the early nineteenth century. The earliest known slab serif font was first shown around 1817 by the English typefounder Vincent Figgins.
''Roman'', ''italic'', and ''oblique'' are also terms used to differentiate between upright and two possible slanted forms of a typeface. Italic and oblique fonts are similar (indeed, oblique fonts are often simply called italics) but there is strictly a difference: ''italic'' applies to fonts where the letter forms are redesigned, not just slanted. Almost all serif faces have italic forms; some sans-serif faces have oblique designs. (Most faces do not offer both as this is an artistic choice by the font designer about how the slanted form should look.)
Serif, or ''Roman'', typefaces are named for the features at the ends of their strokes. Times New Roman and Garamond are common examples of serif typefaces. Serif fonts are probably the most used class in printed materials, including most books, newspapers and magazines. Serif fonts are often classified into three subcategories: Old Style, Transitional, and Didone (typography), Didone (or Modern), representative examples of which are Garamond, Baskerville, and Bodoni respectively.
Old Style typefaces are influenced by early Italian lettering design. Modern fonts often exhibit a bracketed serif and a substantial difference in weight within the strokes. Though some argument exists as to whether Transitional fonts exist as a discrete category among serif fonts, Transitional fonts lie somewhere between Old Style and Modern style typefaces. Transitional fonts exhibit a marked increase in the variation of stroke weight and a more horizontal serif compared to Old Style. Slab serif designs have particularly large serifs, and date to the early nineteenth century. The earliest known slab serif font was first shown around 1817 by the English typefounder Vincent Figgins.
''Roman'', ''italic'', and ''oblique'' are also terms used to differentiate between upright and two possible slanted forms of a typeface. Italic and oblique fonts are similar (indeed, oblique fonts are often simply called italics) but there is strictly a difference: ''italic'' applies to fonts where the letter forms are redesigned, not just slanted. Almost all serif faces have italic forms; some sans-serif faces have oblique designs. (Most faces do not offer both as this is an artistic choice by the font designer about how the slanted form should look.)
 Sans serif (lit. without serif) designs appeared relatively recently in the history of type design. The first, similar to slab serif designs, was shown in 1816 by William Caslon IV. Many have minimal variation in stroke width, creating the impression of a minimal, simplified design. When first introduced, the faces were disparaged as "grotesque" (or ) and "gothic": but by the late nineteenth century were commonly used for san-serif without negative implication.
The major Sans-serif#Classification, sub-classes of Sans-serif are "Sans-serif#Grotesque, Grotesque", "Sans-serif#Neo-grotesque, Neo-grotesque", "Sans-serif#Geometric, Geometric" and "Sans-serif#Humanist, Humanist".
Sans serif (lit. without serif) designs appeared relatively recently in the history of type design. The first, similar to slab serif designs, was shown in 1816 by William Caslon IV. Many have minimal variation in stroke width, creating the impression of a minimal, simplified design. When first introduced, the faces were disparaged as "grotesque" (or ) and "gothic": but by the late nineteenth century were commonly used for san-serif without negative implication.
The major Sans-serif#Classification, sub-classes of Sans-serif are "Sans-serif#Grotesque, Grotesque", "Sans-serif#Neo-grotesque, Neo-grotesque", "Sans-serif#Geometric, Geometric" and "Sans-serif#Humanist, Humanist".
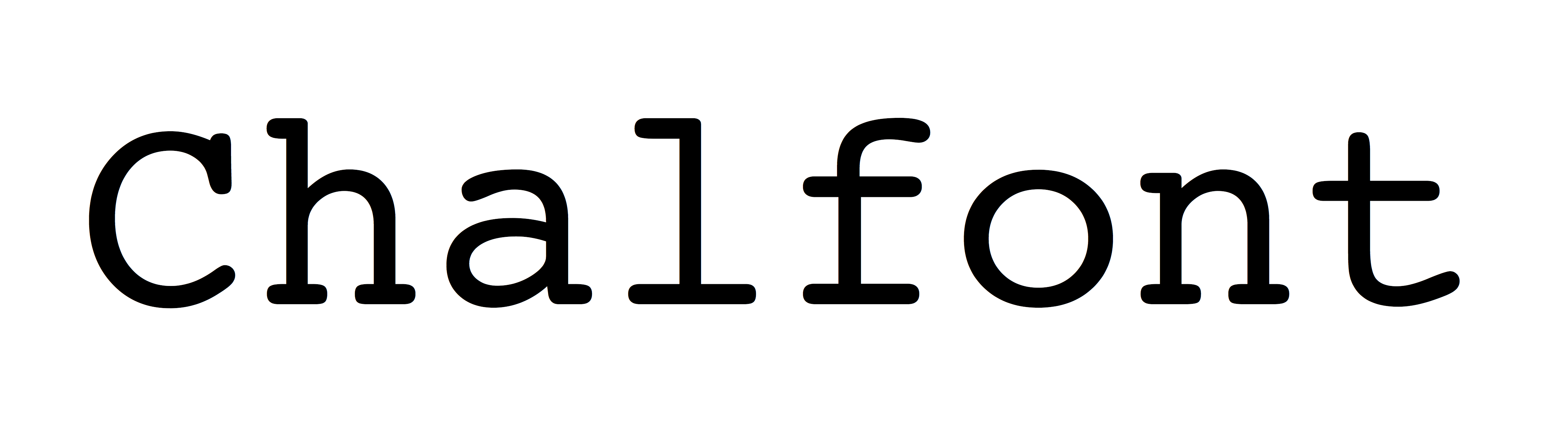 Monospaced fonts are typefaces in which every glyph is the same width (as opposed to variable-width fonts, where the ''w'' and ''m'' are wider than most letters, and the ''i'' is narrower). The first monospaced typefaces were designed for typewriters, which could only move the same distance forward with each letter typed. Their use continued with early computers, which could only display a single font. Although modern computers can display any desired typeface, monospaced fonts are still important for computer programming, terminal emulation, and for laying out tabulated data in plain text documents; they may also be particularly legible at small sizes due to all characters being quite wide. List of typefaces#Monospaced, Examples of monospaced typefaces are
Monospaced fonts are typefaces in which every glyph is the same width (as opposed to variable-width fonts, where the ''w'' and ''m'' are wider than most letters, and the ''i'' is narrower). The first monospaced typefaces were designed for typewriters, which could only move the same distance forward with each letter typed. Their use continued with early computers, which could only display a single font. Although modern computers can display any desired typeface, monospaced fonts are still important for computer programming, terminal emulation, and for laying out tabulated data in plain text documents; they may also be particularly legible at small sizes due to all characters being quite wide. List of typefaces#Monospaced, Examples of monospaced typefaces are
 Display type refers to the use of type at large sizes, perhaps 30 points or larger. Some typefaces are considered useful solely at display sizes, and are known as display faces. Most effect typefaces are display types. Common features of display type include tighter default letter spacing, finer details and serifs, slightly more condensed letter shapes and larger differences between thick and thin strokes; many of these are most visible in serif designs. Many display typefaces in the past such as those intended for posters and newspaper headlines were also only cut in capitals, since it was assumed lower-case would not be needed, or at least with no italics. This was true of many early sans-serif fonts.
Display type refers to the use of type at large sizes, perhaps 30 points or larger. Some typefaces are considered useful solely at display sizes, and are known as display faces. Most effect typefaces are display types. Common features of display type include tighter default letter spacing, finer details and serifs, slightly more condensed letter shapes and larger differences between thick and thin strokes; many of these are most visible in serif designs. Many display typefaces in the past such as those intended for posters and newspaper headlines were also only cut in capitals, since it was assumed lower-case would not be needed, or at least with no italics. This was true of many early sans-serif fonts.
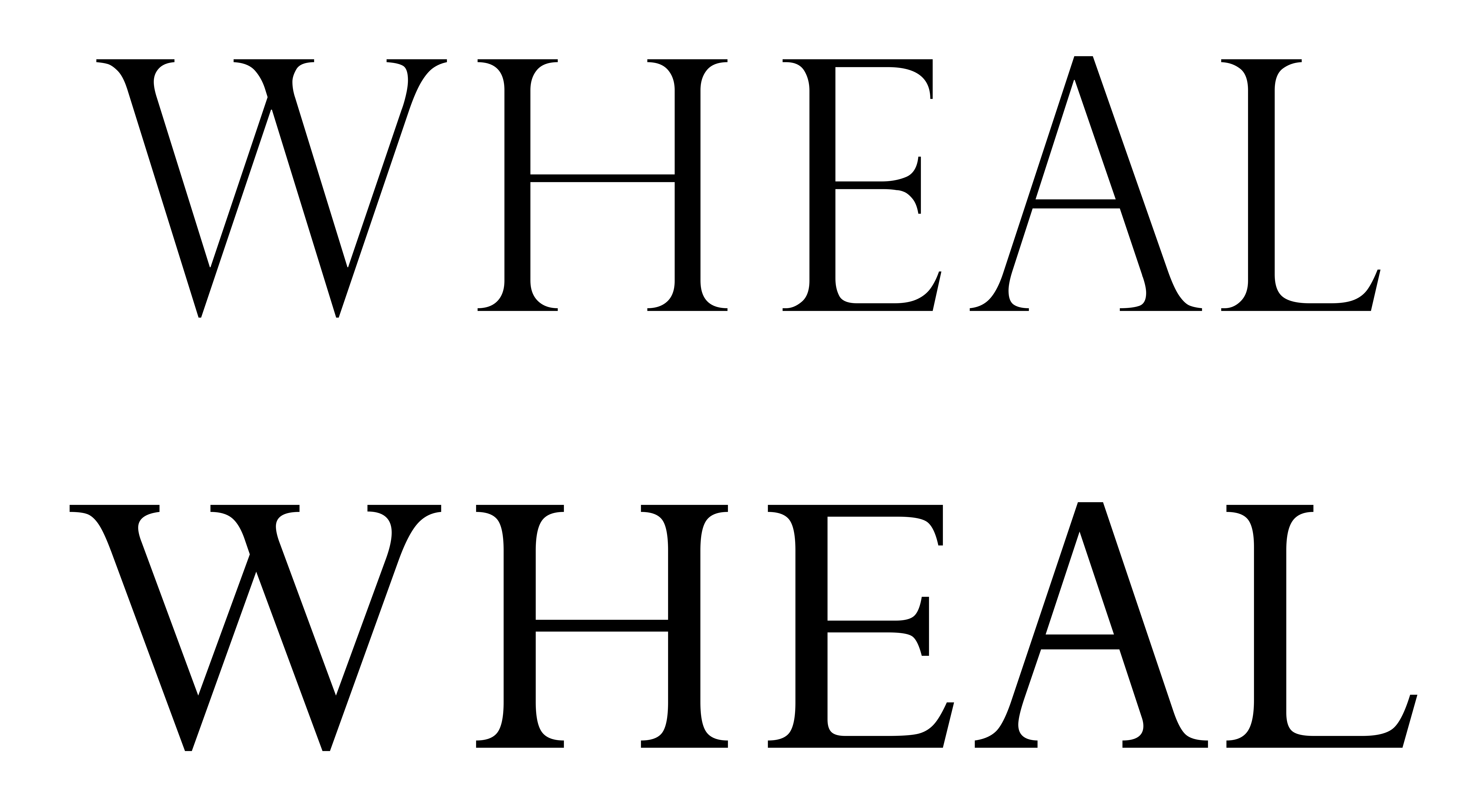 In the days of metal type, when each size was cut individually, types intended for display use were often adjusted accordingly. These modifications continued to be made even after fonts started to be made by scaling using a pantograph, but began to fade away with the advent of phototypesetting and then digital fonts, which can both be printed at any size. Premium digital fonts used for magazines, books and newspapers do often include display variants, but they are often not included with typefaces bundled with operating systems and desktop publishing software. Display typefaces in the letterpress period were often made as wood type, being lighter than metal.
Decades into the desktop publishing revolution, few typographers with metal foundry type experience are still working, and few digital typefaces are optimized specifically for different sizes, so the misuse of the term display typeface as a synonym for ornamental type has become widespread; properly speaking, ornamental typefaces are a subcategory of display typefaces. At the same time, with new printing techniques, typefaces have largely replaced hand-lettering for very large signs and notices that would once have been painted or carved by hand.
In the days of metal type, when each size was cut individually, types intended for display use were often adjusted accordingly. These modifications continued to be made even after fonts started to be made by scaling using a pantograph, but began to fade away with the advent of phototypesetting and then digital fonts, which can both be printed at any size. Premium digital fonts used for magazines, books and newspapers do often include display variants, but they are often not included with typefaces bundled with operating systems and desktop publishing software. Display typefaces in the letterpress period were often made as wood type, being lighter than metal.
Decades into the desktop publishing revolution, few typographers with metal foundry type experience are still working, and few digital typefaces are optimized specifically for different sizes, so the misuse of the term display typeface as a synonym for ornamental type has become widespread; properly speaking, ornamental typefaces are a subcategory of display typefaces. At the same time, with new printing techniques, typefaces have largely replaced hand-lettering for very large signs and notices that would once have been painted or carved by hand.
 A reverse-contrast type is a typeface in which the stress is reversed from the norm: instead of the vertical lines being the same width or thicker than horizontals, which is normal in Latin-alphabet printing, the horizontal lines are the thickest. Reverse-contrast types are rarely used for body text, and are particularly common in Typeface#Display type, display applications such as headings and posters, in which their unusual structure may be particularly eye-catching. First seen in London in 1821, they were particularly common in the mid- to late nineteenth century in American and British printing and have been revived occasionally since then. They effectively become slab serif designs because of the serifs becoming thick, and are often characterised as part of that genre. In recent times, the reverse-contrast effect has been extended to other kinds of typeface, such as
A reverse-contrast type is a typeface in which the stress is reversed from the norm: instead of the vertical lines being the same width or thicker than horizontals, which is normal in Latin-alphabet printing, the horizontal lines are the thickest. Reverse-contrast types are rarely used for body text, and are particularly common in Typeface#Display type, display applications such as headings and posters, in which their unusual structure may be particularly eye-catching. First seen in London in 1821, they were particularly common in the mid- to late nineteenth century in American and British printing and have been revived occasionally since then. They effectively become slab serif designs because of the serifs becoming thick, and are often characterised as part of that genre. In recent times, the reverse-contrast effect has been extended to other kinds of typeface, such as
 Some typefaces have a structure that suggests a three-dimensional letter, such as letters carved into stone. An example of this is the genre known as 'inline', 'block' 'outline' or 'shadowed' typefaces. This renders the interior of glyphs in the background color, with a thin line around the edges of the glyphs. In some cases, the outline shows the glyph filled in with the foreground color, surrounded a thin outline mirroring the edges separated by a small gap. (This latter style is often used with "college" typefaces.) Colorized block lettering is often seen in carefully rendered graffiti.
A "shadow" effect can also be either designed into a typeface or added to an existing typeface. Designed-in shadows can be stylized or connected to the foreground. An after-market shadow effect can be created by making two copies of each glyph, slightly offset in a diagonal direction and possibly in different colors. Drop shadows can also be dynamically created by rendering software. The shadow effect is often combined with the outline effect, where the top layer is shown in white with black outline and the bottom layer in black, for greater contrast. An example typeface with an 'inline' effect is Imprint (typeface), Imprint Shadowed, where the shadowed version is more widely distributed than the regular design.
Some typefaces have a structure that suggests a three-dimensional letter, such as letters carved into stone. An example of this is the genre known as 'inline', 'block' 'outline' or 'shadowed' typefaces. This renders the interior of glyphs in the background color, with a thin line around the edges of the glyphs. In some cases, the outline shows the glyph filled in with the foreground color, surrounded a thin outline mirroring the edges separated by a small gap. (This latter style is often used with "college" typefaces.) Colorized block lettering is often seen in carefully rendered graffiti.
A "shadow" effect can also be either designed into a typeface or added to an existing typeface. Designed-in shadows can be stylized or connected to the foreground. An after-market shadow effect can be created by making two copies of each glyph, slightly offset in a diagonal direction and possibly in different colors. Drop shadows can also be dynamically created by rendering software. The shadow effect is often combined with the outline effect, where the top layer is shown in white with black outline and the bottom layer in black, for greater contrast. An example typeface with an 'inline' effect is Imprint (typeface), Imprint Shadowed, where the shadowed version is more widely distributed than the regular design.
 The process of printing typefaces has historically been far simpler than commissioning and engraving custom illustrations, especially as many non-text features of printed works like symbols and borders were likely to be reused by a printer in future. Non-character typefaces have therefore been created for elements of documents that are not letters but are likely to be reused regularly. These include:
The process of printing typefaces has historically been far simpler than commissioning and engraving custom illustrations, especially as many non-text features of printed works like symbols and borders were likely to be reused by a printer in future. Non-character typefaces have therefore been created for elements of documents that are not letters but are likely to be reused regularly. These include:
 Symbol, or dingbat, typefaces consist of symbols (such as decorative bullets, clock faces, railroad timetable symbols, CD-index, or TV-channel enclosed numbers) rather than normal text characters. Common, widely used symbol typeface releases include Zapf Dingbats and Wingdings, though many may be created internally by a publication for its own use and some typefaces may have a symbol range included. Marlett is an example of a font used by Microsoft Windows, Windows to draw elements of windows and icons.
Symbol, or dingbat, typefaces consist of symbols (such as decorative bullets, clock faces, railroad timetable symbols, CD-index, or TV-channel enclosed numbers) rather than normal text characters. Common, widely used symbol typeface releases include Zapf Dingbats and Wingdings, though many may be created internally by a publication for its own use and some typefaces may have a symbol range included. Marlett is an example of a font used by Microsoft Windows, Windows to draw elements of windows and icons.
Monotype printed borders specimens
ArchLinux list of Metric-compatible fonts
* {{Authority control Typefaces, Articles containing video clips Typography Typesetting
 A typeface (or font family) is a design of
A typeface (or font family) is a design of letter
Letter, letters, or literature may refer to:
Characters typeface
* Letter (alphabet), a character representing one or more of the sounds used in speech or none in the case of a silent letter; any of the symbols of an alphabet
* Letterform, the g ...
s, number
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The most basic examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can ...
s and other symbol
A symbol is a mark, Sign (semiotics), sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, physical object, object, or wikt:relationship, relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by cr ...
s, to be used in printing or for electronic display. Most typefaces include variations in size (e.g., 24 point), weight (e.g., light, bold), slope (e.g., italic), width (e.g., condensed), and so on. Each of these variations of the typeface is a font
In metal typesetting, a font is a particular size, weight and style of a ''typeface'', defined as the set of fonts that share an overall design.
For instance, the typeface Bauer Bodoni (shown in the figure) includes fonts " Roman" (or "regul ...
.
There are thousands of different typefaces in existence, with new ones being developed constantly.
The art and craft of designing typefaces is called type design
Type design is the art and process of designing typefaces. This involves drawing each letterform using a consistent style. The basic concepts and design variables are described below.
A typeface differs from other modes of graphic production su ...
. Designers of typefaces are called type designer
Type design is the art and process of designing typefaces. This involves drawing each letterform using a consistent style. The basic concepts and design variables are described below.
A typeface differs from other modes of graphic production su ...
s and are often employed by type foundries
A type foundry is a company that designs or distributes typefaces. Before digital typography, type foundries manufactured and sold metal and wood typefaces for hand typesetting, and matrices for line-casting machines like the Linotype and Mono ...
. In desktop publishing
Desktop publishing (DTP) is the creation of documents using dedicated software on a personal ("desktop") computer. It was first used almost exclusively for print publications, but now it also assists in the creation of various forms of online co ...
, type designers are sometimes also called "font developers" or "font designers" (a typographer
Typography is the art and technique of Typesetting, arranging type to make written language legibility, legible, readability, readable and beauty, appealing when displayed. The arrangement of type involves selecting typefaces, Point (typogra ...
is someone who ''uses'' typefaces to design a page layout).
Every typeface is a collection of glyph
A glyph ( ) is any kind of purposeful mark. In typography, a glyph is "the specific shape, design, or representation of a character". It is a particular graphical representation, in a particular typeface, of an element of written language. A ...
s, each of which represents an individual letter, number, punctuation mark, or other symbol. The same glyph may be used for characters from different writing systems
A writing system comprises a set of symbols, called a ''script'', as well as the rules by which the script represents a particular language. The earliest writing appeared during the late 4th millennium BC. Throughout history, each independe ...
, e.g. Roman uppercase A looks the same as Cyrillic
The Cyrillic script ( ) is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Ea ...
uppercase А and Greek uppercase alpha
Alpha (uppercase , lowercase ) is the first letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of one. Alpha is derived from the Phoenician letter ''aleph'' , whose name comes from the West Semitic word for ' ...
(Α). There are typefaces tailored for special applications, such as cartography
Cartography (; from , 'papyrus, sheet of paper, map'; and , 'write') is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an imagined reality) can ...
, astrology
Astrology is a range of Divination, divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that propose that information about human affairs and terrestrial events may be discerned by studying the apparent positions ...
or mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
.
Terminology
In professionaltypography
Typography is the art and technique of Typesetting, arranging type to make written language legibility, legible, readability, readable and beauty, appealing when displayed. The arrangement of type involves selecting typefaces, Point (typogra ...
, the term ''typeface'' is not interchangeable with the word ''font
In metal typesetting, a font is a particular size, weight and style of a ''typeface'', defined as the set of fonts that share an overall design.
For instance, the typeface Bauer Bodoni (shown in the figure) includes fonts " Roman" (or "regul ...
,'' because the term font has historically been defined as a given alphabet and its associated characters in a single size. For example, 8-point Caslon Italic was one font, and 10-point Caslon Italic was another. Historically, a font came from a type foundry
A type foundry is a company that designs or distributes typefaces. Before digital typography, type foundries manufactured and sold metal and wood typefaces for hand typesetting, and matrices for line-casting machines like the Linotype and ...
as a set of "sort
Sort may refer to:
* Sorting, any process of arranging items in sequence or in sets
** Sorting algorithm, any algorithm for ordering a list of elements
** Mainframe sort merge, sort utility for IBM mainframe systems
** Sort (Unix), which sorts the ...
s", with number of copies of each character included.
As the range of typeface designs increased and requirements of publishers broadened over the centuries, fonts of specific weight
In science and engineering, the weight of an object is a quantity associated with the gravitational force exerted on the object by other objects in its environment, although there is some variation and debate as to the exact definition.
Some sta ...
(blackness or lightness) and stylistic variants (most commonly ''regular'' or ''roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
'' as distinct from '' italic'', as well as ''condensed'') have led to ''font families'', collections of closely related typeface designs that can include hundreds of styles. A typeface family is typically a group of related typefaces which vary only in weight, orientation, width
Length is a measure of distance. In the International System of Quantities, length is a quantity with dimension distance. In most systems of measurement a base unit for length is chosen, from which all other units are derived. In the Intern ...
, etc., but not design. For example, Times is a typeface family, whereas Times Roman, Times Italic and Times Bold are individual typefaces making up the Times family. Typeface families typically include several typefaces, though some, such as Helvetica
Helvetica, also known by its original name Neue Haas Grotesk, is a widely-used sans-serif typeface developed in 1957 by Swiss typeface designer Max Miedinger and Eduard Hoffmann.
Helvetica is a neo-grotesque design, one influenced by the f ...
, may consist of dozens of fonts. In traditional typography, a font family is a set of fonts within the same typeface: for example Times Roman 8, Times Roman 10, Times Roman 12 etc. In web typography
Web typography, like typography generally, is the design of pages their layout and typeface choices. Unlike traditional print-based typography (where the page is fixed once typeset), pages intended for display on the World Wide Web have additiona ...
, the term 'font family' (as specified using the HTML
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It defines the content and structure of web content. It is often assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets ( ...
code ) may equate to a 'typeface family' or even to a very broad category such as sans-serif
In typography and lettering, a sans-serif, sans serif (), gothic, or simply sans letterform is one that does not have extending features called "serifs" at the end of strokes. Sans-serif typefaces tend to have less stroke width variation than ...
that encompass many typeface families.
Another way to look at the distinction between font and typeface is that a font is the vessel (e.g. the software) that allows you to use a set of characters with a given appearance, whereas a typeface is the actual design of such characters. Therefore, a given typeface, such as Times, may be rendered by different fonts, such as computer font
A computer font is implemented as a digital data file containing a set of graphically related glyphs. A computer font is designed and created using a font editor. A computer font specifically designed for the computer screen, and not for printi ...
files created by this or that vendor, a set of metal type characters etc. In the metal type
In physical typesetting, a sort or type is a block with a typographic character etched on it, used—when lined up with others—to print text. In movable-type printing, the sort or type is cast from a matrix mold and assembled by hand wit ...
era, a font also meant a specific point size, but with digital scalable outline fonts this distinction is no longer valid, as a single font may be scaled to any size.
The first "extended" font families, which included a wide range of widths and weights in the same general style emerged in the early 1900s, starting with ATF
The Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (BATFE), commonly referred to as ATF, is a domestic law enforcement agency within the United States Department of Justice. Its responsibilities include the investigation and prevention ...
's Cheltenham
Cheltenham () is a historic spa town and borough adjacent to the Cotswolds in Gloucestershire, England. Cheltenham became known as a health and holiday spa town resort following the discovery of mineral springs in 1716, and claims to be the mo ...
(1902–1913), with an initial design by Bertram Grosvenor Goodhue, and many additional faces designed by Morris Fuller Benton. Later examples include Futura, Lucida, ITC Officina
ITC Officina is a font superfamily designed by Erik Spiekermann and released in 1990. It consists of ITC Officina Sans, ITC Officina Serif and ITC Officina Display, with bold, italic, and small-caps variations of each.
Sources
Typedia ...
. Some became superfamilies as a result of revival, such as Linotype Syntax, Linotype Univers; while others have alternate styling designed as compatible replacements of each other, such as Compatil
Compatil is a large typeface
A typeface (or font family) is a design of Letter (alphabet), letters, Numerical digit, numbers and other symbols, to be used in printing or for electronic display. Most typefaces include variations in size (e.g., ...
, Generis.
 Font ''superfamilies'' began to emerge when foundries began to include typefaces with significant structural differences, but some design relationship, under the same general family name. Arguably the first superfamily was created when Morris Fuller Benton created Clearface Gothic for ATF in 1910, a sans serif companion to the existing (serifed) Clearface. The superfamily label does not include quite different designs given the same family name for what would seem to be purely marketing, rather than design, considerations:
Font ''superfamilies'' began to emerge when foundries began to include typefaces with significant structural differences, but some design relationship, under the same general family name. Arguably the first superfamily was created when Morris Fuller Benton created Clearface Gothic for ATF in 1910, a sans serif companion to the existing (serifed) Clearface. The superfamily label does not include quite different designs given the same family name for what would seem to be purely marketing, rather than design, considerations: Caslon Antique
Caslon Antique is a decorative American typeface that was designed in 1894 by Berne Nadall. It was originally called "Fifteenth Century", but was renamed "Caslon Antique" by Nadall's foundry, Barnhart Bros. & Spindler, in the mid-1920s.
The ...
, Futura Black and Futura Display are structurally unrelated to the Caslon and Futura families, respectively, and are generally not considered part of those families by typographers, despite their names.
Additional or supplemental glyph
A glyph ( ) is any kind of purposeful mark. In typography, a glyph is "the specific shape, design, or representation of a character". It is a particular graphical representation, in a particular typeface, of an element of written language. A ...
s intended to match a main typeface have been in use for centuries. In some formats they have been marketed as separate fonts. In the early 1990s, the Adobe Systems type group introduced the idea of ''expert set'' fonts, which had a standardized set of additional glyphs, including small caps
In typography, small caps (short for small capitals) are grapheme, characters typeset with glyphs that resemble uppercase letters but reduced in height and weight close to the surrounding lowercase letters or text figures. Small caps are used i ...
, old style figures
Text figures (also known as non-lining, lowercase, old style, ranging, hanging, medieval, billing, or antique figures or numerals) are numerals designed with varying heights in a fashion that resembles a typical line of running text, hence the ...
, and additional superior letters, fractions
A fraction (from , "broken") represents a part of a whole or, more generally, any number of equal parts. When spoken in everyday English, a fraction describes how many parts of a certain size there are, for example, one-half, eight-fifths, thre ...
and ligatures not found in the main fonts for the typeface. Supplemental fonts have also included alternate letters such as swashes, dingbat
In typography, a dingbat (sometimes more formally known as a printer's ornament or printer's character) is an ornament, specifically, a glyph used in typesetting, often employed to create box frames (similar to box-drawing characters), or a ...
s, and alternate character sets, complementing the regular fonts under the same family. However, with introduction of font formats such as OpenType
OpenType is a format for scalable computer fonts. Derived from TrueType, it retains TrueType's basic structure but adds many intricate data structures for describing typographic behavior. OpenType is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corpora ...
, those supplemental glyphs were merged into the main fonts, relying on specific software capabilities to access the alternate glyphs.
Since Apple's and Microsoft's operating systems supported different character sets in the platform related fonts, some foundries used expert fonts in a different way. These fonts included the characters which were missing on either Macintosh or Windows computers, e.g. fractions, ligatures or some accented glyphs. The goal was to deliver the whole character set to the customer regardless of which operating system was used.
Sizing
The size of typefaces andfont
In metal typesetting, a font is a particular size, weight and style of a ''typeface'', defined as the set of fonts that share an overall design.
For instance, the typeface Bauer Bodoni (shown in the figure) includes fonts " Roman" (or "regul ...
s is traditionally measured in points
A point is a small dot or the sharp tip of something. Point or points may refer to:
Mathematics
* Point (geometry), an entity that has a location in space or on a plane, but has no extent; more generally, an element of some abstract topologica ...
; ''point'' has been defined differently at different times, but now the most popular is the Desktop Publishing point of in (). When specified in typographic sizes (points, kyus), the height of an ''em-square'', an invisible box which is typically a bit larger than the distance from the tallest ascender to the lowest descender
In typography and handwriting, a descender is the portion of a grapheme that extends below the Baseline (typography), baseline of a typeface, font.
For example, in the letter ''y'', the descender is the "tail", or that portion of the diagonal li ...
, is scaled to equal the specified size. For example, when setting Helvetica
Helvetica, also known by its original name Neue Haas Grotesk, is a widely-used sans-serif typeface developed in 1957 by Swiss typeface designer Max Miedinger and Eduard Hoffmann.
Helvetica is a neo-grotesque design, one influenced by the f ...
at 12 point, the em square defined in the Helvetica font is scaled to 12 points or . Yet no particular element of 12-point Helvetica need measure exactly 12 points.
Frequently measurement in non-typographic units (feet, inches, meters) will be of the ''cap-height'', the height of the capital letters. Font size is also commonly measured in millimeters (mm) and ''q''s (a quarter of a millimeter, ''kyu'' in romanized Japanese) and inches.
History
Type foundries have cast fonts inlead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
alloys from the 1450s until the present, although wood served as the material for some large fonts called wood type during the 19th century, particularly in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
. In the 1890s, the mechanization of typesetting allowed automated casting of fonts on the fly as lines of type in the size and length needed. This was known as continuous casting, and remained profitable and widespread until its demise in the 1970s. The first machine of this type was the Linotype machine
The Linotype machine ( ) is a "line casting" machine used in printing which is manufactured and sold by the former Mergenthaler Linotype Company and related It was a hot metal typesetting system that cast lines of metal type for one-time use. Li ...
, invented by Ottmar Mergenthaler.
During a brief transitional period (–1990s), photographic technology, known as ''phototypesetting
Phototypesetting is a method of Typesetting, setting type which uses photography to make columns of Sort (typesetting), type on a scroll of photographic paper.
It has been made obsolete by the popularity of the personal computer and desktop publ ...
'', utilized tiny high-resolution images of individual glyphs on a film strip (in the form of a film negative, with the letters as clear areas on an opaque black background). A high-intensity light source behind the film strip projected the image of each glyph through an optical system, which focused the desired letter onto the light-sensitive phototypesetting paper at a specific size and position. This photographic typesetting process permitted optical scaling
Scaling may refer to:
Science and technology
Mathematics and physics
* Scaling (geometry), a linear transformation that enlarges or diminishes objects
* Scale invariance, a feature of objects or laws that do not change if scales of length, energ ...
, allowing designers to produce multiple sizes from a single font, although physical constraints on the reproduction system used still required design changes at different sizes; for example, ink traps and spikes to allow for spread of ink
Ink is a gel, sol, or solution that contains at least one colorant, such as a dye or pigment, and is used to color a surface to produce an image, text, or design. Ink is used for drawing or writing with a pen, brush, reed pen, or quill. ...
encountered in the printing stage. Manually operated photocomposition systems using fonts on filmstrips allowed fine kerning
In typography, kerning is the process of adjusting the spacing between Character (symbol), characters in a Typeface#Proportion, proportional font, usually to achieve a visually pleasing result. Kerning adjusts the space between individual le ...
between letters without the physical effort of manual typesetting, and spawned an enlarged type design industry in the 1960s and 1970s.
By the mid-1970s, all of the major typeface technologies and all their fonts were in use: letterpress; continuous casting machines; phototypositors; computer-controlled phototypesetters; and the earliest digital typesetters – bulky machines with primitive processors and CRT outputs. From the mid-1980s, as digital typography has grown, users have almost universally adopted the American spelling ''font'', which has come to primarily refer to a computer file
A computer file is a System resource, resource for recording Data (computing), data on a Computer data storage, computer storage device, primarily identified by its filename. Just as words can be written on paper, so too can data be written to a ...
containing scalable outline letterforms (''digital font''), in one of several common formats. Some typefaces, such as Verdana, are designed primarily for use on computer screen
A computer monitor is an output device that displays information in pictorial or textual form. A discrete monitor comprises a visual display, support electronics, power supply, housing, electrical connectors, and external user controls.
The ...
s.
Digital type
 Digital type became the dominant form of type in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Digital fonts store the image of each character either as a
Digital type became the dominant form of type in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Digital fonts store the image of each character either as a bitmap
In computing, a bitmap (also called raster) graphic is an image formed from rows of different colored pixels. A GIF is an example of a graphics image file that uses a bitmap.
As a noun, the term "bitmap" is very often used to refer to a partic ...
in a ''bitmap font
A computer font is implemented as a digital data file containing a set of graphically related glyphs. A computer font is designed and created using a font editor. A computer font specifically designed for the computer screen, and not for print ...
'', or by mathematical description of lines and curves in an ''outline font'', also called a '' vector font''. Bitmap fonts were more commonly used in the earlier stages of digital type, and are rarely used today. These bitmapped typefaces were first produced by Casady & Greene, Inc. and were also known as Fluent Fonts. Fluent Fonts became mostly obsolete with the creation of downloadable PostScript fonts, and these new fonts are called Fluent Laser Fonts (FLF).
When an outline font is used, a rasterizing routine (in the application software, operating system or printer) renders the character outlines, interpreting the vector instructions to decide which pixels should be black and which ones white. Rasterization is straightforward at high resolutions such as those used by laser printer
Laser printing is an electrostatic digital printing process. It produces high-quality text and graphics (and moderate-quality photographs) by repeatedly passing a laser beam back and forth over a Electric charge, negatively charged cylinder call ...
s and in high-end publishing systems. For computer screen
A computer monitor is an output device that displays information in pictorial or textual form. A discrete monitor comprises a visual display, support electronics, power supply, housing, electrical connectors, and external user controls.
The ...
s, where each individual pixel can mean the difference between legible and illegible characters, some digital fonts use hinting algorithms to make readable bitmaps at small sizes.
Digital fonts may also contain data representing the ''metrics'' used for composition, including kerning
In typography, kerning is the process of adjusting the spacing between Character (symbol), characters in a Typeface#Proportion, proportional font, usually to achieve a visually pleasing result. Kerning adjusts the space between individual le ...
pairs, component creation data for accented characters, glyph substitution rules for Arabic typography and for connecting script faces, and for simple everyday ligature Ligature may refer to:
Language
* Ligature (writing), a combination of two or more letters into a single symbol (typography and calligraphy)
* Ligature (grammar), a morpheme that links two words
Medicine
* Ligature (medicine), a piece of suture us ...
s like "". Common font formats include TrueType
TrueType is an Computer font#Outline fonts, outline font standardization, standard developed by Apple Inc., Apple in the late 1980s as a competitor to Adobe Inc., Adobe's PostScript fonts#Type 1, Type 1 fonts used in PostScript. It has become the ...
, OpenType
OpenType is a format for scalable computer fonts. Derived from TrueType, it retains TrueType's basic structure but adds many intricate data structures for describing typographic behavior. OpenType is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corpora ...
and PostScript
PostScript (PS) is a page description language and dynamically typed, stack-based programming language. It is most commonly used in the electronic publishing and desktop publishing realm, but as a Turing complete programming language, it c ...
Type 1, while Metafont
Metafont is a page description language, description language used to define raster fonts. It is also the name of the interpreter (computer software), interpreter that executes Metafont code, generating the bitmap fonts that can be embedded into ...
is still used by TeX
Tex, TeX, TEX, may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Tex (nickname), a list of people and fictional characters with the nickname
* Tex Earnhardt (1930–2020), U.S. businessman
* Joe Tex (1933–1982), stage name of American soul singer ...
and its variants. Applications using these font formats, including the rasterizers, appear in Microsoft and Apple Computer operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
s, Adobe Systems
Adobe Inc. ( ), formerly Adobe Systems Incorporated, is an American software, computer software company based in San Jose, California. It offers a wide range of programs from web design tools, photo manipulation and vector creation, through to ...
products and those of several other companies. Digital fonts are created with font editors such as FontForge
FontForge is a FOSS font editor which supports many common font formats. Developed primarily by George Williams until 2012, FontForge is free software and is distributed under a mix of the GNU General Public License Version 3 and the 3-clause ...
, RoboFont, Glyphs, Fontlab
FontLab is a font editor developed by Fontlab Ltd. FontLab is available for Windows and macOS.
History
The software was initially developed by the company SoftUnion Ltd. of Saint Petersburg, Russia, under lead programmer Yuri Yarmola. In 1992 ...
's TypeTool, FontLab Studio, Fontographer, or AsiaFont Studio.
Typeface anatomy
Typographers have developed a comprehensive vocabulary for describing the many aspects of typefaces and typography. Some vocabulary applies only to a subset of all scripts. ''Serifs'', for example, are a purely decorative characteristic of typefaces used for European scripts, whereas the glyphs used in Arabic or East Asian scripts have characteristics (such as stroke width) that may be similar in some respects but cannot reasonably be called serifs and may not be purely decorative.Serifs
Typefaces can be divided into two main categories:serif
In typography, a serif () is a small line or stroke regularly attached to the end of a larger stroke in a letter or symbol within a particular font or family of fonts. A typeface or "font family" making use of serifs is called a serif typeface ( ...
and sans serif
In typography and lettering, a sans-serif, sans serif (), gothic, or simply sans letterform is one that does not have extending features called "serifs" at the end of strokes. Sans-serif typefaces tend to have less stroke width variation than ...
. Serif
In typography, a serif () is a small line or stroke regularly attached to the end of a larger stroke in a letter or symbol within a particular font or family of fonts. A typeface or "font family" making use of serifs is called a serif typeface ( ...
s comprise the small features at the end of strokes within letters. The printing industry refers to typeface without serifs as sans serif (from French ''sans'', meaning ''without''), or as ''grotesque'' (or, in German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
, ''grotesk'').
Great variety exists among both serif and sans serif typefaces. Both groups contain faces designed for setting large amounts of body text, and others intended primarily as decorative. The presence or absence of serifs represents only one of many factors to consider when choosing a typeface.
Typefaces with serifs are often considered easier to read in long passages than those without. Studies on the matter are ambiguous, suggesting that most of this effect is due to the greater familiarity of serif typefaces. As a general rule, printed works such as newspapers and books almost always use serif typefaces, at least for the text body. Websites do not have to specify a font and can simply respect the browser settings of the user. But of those web sites that do specify a font, most use modern sans serif fonts, because it is commonly believed that, in contrast to the case for printed material, sans serif fonts are easier than serif fonts to read on the low-resolution computer screen.
Proportion
A proportional typeface, also called variable-width typeface, contains glyphs of varying widths, while amonospaced
A monospaced font, also called a fixed-pitch, fixed-width, or non-proportional font, is a font whose letters and characters each occupy the same amount of horizontal space. This contrasts with Typeface#Proportion, variable-width fonts, where t ...
(non-proportional or fixed-width) typeface uses a single standard width for all glyphs in the font. Duospaced font
A duospaced font (also called a duospace font) is a fixed-width font whose letters and characters occupy either of two integer multiples of a specified, fixed horizontal space. Traditionally, this means either a single or double character width, a ...
s are similar to monospaced fonts, but characters can also be two character widths instead of a single character width.
Many people generally find proportional typefaces nicer-looking and easier to read, and thus they appear more commonly in professionally published printed material. For the same reason, GUI computer applications (such as word processor A word processor (WP) is a device or computer program that provides for input, editing, formatting, and output of text, often with some additional features.
Early word processors were stand-alone devices dedicated to the function, but current word ...
s and web browser
A web browser, often shortened to browser, is an application for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's scr ...
s) typically use proportional fonts. However, many proportional fonts contain fixed-width (tabular) numerals so that columns of numbers stay aligned.
Monospaced typefaces function better for some purposes because their glyphs line up in neat, regular columns. No glyph is given any more weight than another. Most manually operated typewriter
A typewriter is a Machine, mechanical or electromechanical machine for typing characters. Typically, a typewriter has an array of Button (control), keys, and each one causes a different single character to be produced on paper by striking an i ...
s use monospaced fonts. So do text-only computer displays and third- and fourth-generation game console graphics processors, which treat the screen as a uniform grid of character cells. Most computer programs which have a text-based interface (terminal emulator
A terminal emulator, or terminal application, is a computer program that emulates a video terminal within some other display architecture. Though typically synonymous with a shell or text terminal, the term ''terminal'' covers all remote term ...
s, for example) use only monospaced fonts (or add additional spacing to proportional fonts to fit them in monospaced cells) in their configuration. Monospaced fonts are commonly used by computer programmer
A programmer, computer programmer or coder is an author of computer source code someone with skill in computer programming.
The professional titles ''software developer'' and ''software engineer'' are used for jobs that require a progr ...
s for displaying and editing source code
In computing, source code, or simply code or source, is a plain text computer program written in a programming language. A programmer writes the human readable source code to control the behavior of a computer.
Since a computer, at base, only ...
so that certain characters (for example parentheses
A bracket is either of two tall fore- or back-facing punctuation marks commonly used to isolate a segment of text or data from its surroundings. They come in four main pairs of shapes, as given in the box to the right, which also gives their n ...
used to group arithmetic expressions) are easy to see.
ASCII art
ASCII art is a graphic design technique that uses computers for presentation and consists of pictures pieced together from the 95 printable (from a total of 128) character (computing), characters defined by the ASCII Standard from 1963 and ASCI ...
usually requires a monospaced font for proper viewing, with the exception of Shift JIS art which takes advantage of the proportional characters in the MS PGothic font. In a web page
A web page (or webpage) is a World Wide Web, Web document that is accessed in a web browser. A website typically consists of many web pages hyperlink, linked together under a common domain name. The term "web page" is therefore a metaphor of pap ...
, the <tt> </tt>, <code> </code> or <pre> </pre> HTML
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It defines the content and structure of web content. It is often assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets ( ...
tags most commonly specify monospaced fonts. In LaTeX
Latex is an emulsion (stable dispersion) of polymer microparticles in water. Latices are found in nature, but synthetic latices are common as well.
In nature, latex is found as a wikt:milky, milky fluid, which is present in 10% of all floweri ...
, the ''verbatim'' environment or the Teletype
A teleprinter (teletypewriter, teletype or TTY) is an electromechanical device that can be used to send and receive typed messages through various communications channels, in both point-to-point and point-to-multipoint configurations.
Init ...
font family (e.g., \texttt or TeX
Tex, TeX, TEX, may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Tex (nickname), a list of people and fictional characters with the nickname
* Tex Earnhardt (1930–2020), U.S. businessman
* Joe Tex (1933–1982), stage name of American soul singer ...
, use manuscript
A manuscript (abbreviated MS for singular and MSS for plural) was, traditionally, any document written by hand or typewritten, as opposed to mechanically printed or reproduced in some indirect or automated way. More recently, the term has ...
s in monospaced fonts (typically Courier
A courier is a person or organization that delivers a message, package or letter from one place or person to another place or person. Typically, a courier provides their courier service on a commercial contract basis; however, some couriers are ...
) for ease of editing and word count estimates, and it was considered discourteous to submit a manuscript in a proportional font. This has become less universal in recent years, such that authors need to check with editors as to their preference, though monospaced fonts are still the norm.
Font metrics
Most scripts share the notion of a baseline: an imaginary horizontal line on which characters rest. In some scripts, parts of glyphs lie below the baseline. The ''descent'' spans the distance between the baseline and the lowest descending glyph in a typeface, and the part of a glyph that descends below the baseline has the name ''descender
In typography and handwriting, a descender is the portion of a grapheme that extends below the Baseline (typography), baseline of a typeface, font.
For example, in the letter ''y'', the descender is the "tail", or that portion of the diagonal li ...
''. Conversely, the ''ascent'' spans the distance between the baseline and the top of the glyph that reaches farthest from the baseline. The ascent and descent may or may not include distance added by accents or diacritical marks.
In the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
, Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
and Cyrillic
The Cyrillic script ( ) is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Ea ...
(sometimes collectively referred to as LGC) scripts, one can refer to the distance from the baseline to the top of regular lowercase glyphs ( mean line) as the ''x-height
upright 2.0, alt=A diagram showing the line terms used in typography
In typography, the x-height, or corpus size, is the distance between the baseline and the mean line of lowercase letters in a typeface. Typically, this is the height of the le ...
'', and the part of a glyph rising above the x-height as the '' ascender''. The distance from the baseline to the top of the ascent or a regular uppercase glyphs (cap line) is also known as the cap height. The height of the ascender can have a dramatic effect on the readability and appearance of a font. The ratio between the x-height and the ascent or cap height often serves to characterize typefaces.
Typefaces that can be substituted for one another in a document without changing the document's text flow are said to be "metrically identical" (or "metrically compatible"). Several typefaces have been created to be metrically compatible with widely used proprietary typefaces to allow the editing of documents set in such typefaces in digital typesetting environments where these typefaces are not available. For instance, the free and open-source Liberation fonts
Liberation is the collective name of four TrueType font families: ''Liberation Sans'', ''Liberation Sans Narrow'', ''Liberation Serif'', and ''Liberation Mono''. These fonts are metrically compatible with the most popular fonts on the Microsof ...
and Croscore fonts
The ChromeOS core fonts, also known as the Croscore fonts, are a collection of three TrueType font families: Arimo (sans-serif), Tinos (serif) and Cousine ( monospace). These fonts are metrically compatible with Monotype Corporation’s Ari ...
have been designed as metrically compatible substitutes for widely used Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
fonts.
Optical sizing
During the metal type era, all type was cut in metal and could only be printed at a specific size. It was a natural process to vary a design at different sizes, making it chunkier and clearer to read at smaller sizes. Many digital typefaces are offered with a range of fonts (or a variable font axis) for different sizes, especially designs sold for professional design use. The art of designing fonts for a specific size is known as optical sizing. Others will be offered in only one style, but optimised for a specific size. Optical sizes are particularly common for serif fonts, since the fine detail of serif fonts can need to be bulked up for smaller sizes. Typefaces may also be designed differently considering the type of paper on which they will be printed. Designs to be printed on absorbentnewsprint
Newsprint is a low-cost, non-archival paper consisting mainly of wood pulp and most commonly used to print newspapers and other publications and advertising material. Invented in 1844 by Charles Fenerty of Nova Scotia, Canada, it usually has ...
paper will be more slender as the ink will naturally spread out as it absorbs into the paper, and may feature ink traps: areas left blank into which the ink will soak as it dries. These corrections will not be needed for printing on high-gloss cardboard or display on-screen. Fonts designed for low-resolution displays, meanwhile, may avoid pure circles, fine lines and details a screen cannot render.
Typesetting numbers
Most typefaces, especially modern designs, include a complementary set of numeric digits. Numbers can be typeset in two main independent sets of ways: ''lining'' and '' non-lining figures'', and ''proportional'' and ''tabular'' styles. Most modern typefaces set numeric digits by default as lining figures, which are the height of upper-case letters. Non-lining figures, styled to match lower-case letters, are often common in fonts intended for body text, as they are thought to be less disruptive to the style of running text. They are also called ''lower-case numbers'' or ''text figures'' for the same reason.Tabular figures
The horizontal spacing of digits can also be ''proportional'', with a character width tightly matching the width of the figure itself, or ''tabular'', where all digits have the same width. Proportional spacing places the digits closely together, reducing empty space in a document, and is thought to allow the numbers to blend into the text more effectively. As tabular spacing makes all numbers with the same number of digits the same width, it is used for typesetting documents such as price lists, stock listings and sums in mathematics textbooks, all of which require columns of numeric figures to line up on top of each other for easier comparison. Tabular spacing is also a common feature of simple printing devices such as cash registers and date-stamps. Characters of uniform width are a standard feature of so-called monospaced fonts, used in programming and on typewriters. However, many fonts that are not monospaced use tabular figures. More complex font designs may include two or more combinations with one as the default and others as alternate characters. Of the four possibilities, non-lining tabular figures are particularly rare since there is no common use for them. Fonts intended for professional use in documents such as business reports may also make the bold-style tabular figures take up the same width as the regular (non-bold) numbers, so a bold-style total would appear just as wide as the same sum in regular style.Style of typefaces
Because an abundance of typefaces has been created over the centuries, they are commonly categorized according to their appearance. At the highest level (in the context of Latin-script fonts), one can differentiate Roman, Blackletter, and Gaelic types. Roman types are in the most widespread use today, and are sub-classified as serif, sans serif, ornamental, and script types. Historically, the first European fonts were blackletter, followed by Roman serif, then sans serif and then the other types. The use of Gaelic faces was restricted to the Irish language, though these form a unique if minority class. Typefaces may be monospaced regardless of whether they are Roman, Blackletter, or Gaelic. Symbol typefaces are non-alphabetic. The Cyrillic script comes in two varieties, Roman-appearance type (called гражданский шрифт ''graždanskij šrift'') and traditional Slavonic type (called славянский шрифт ''slavjanskij šrift'').Roman typefaces
Serif typefaces
 Serif, or ''Roman'', typefaces are named for the features at the ends of their strokes. Times New Roman and Garamond are common examples of serif typefaces. Serif fonts are probably the most used class in printed materials, including most books, newspapers and magazines. Serif fonts are often classified into three subcategories: Old Style, Transitional, and Didone (typography), Didone (or Modern), representative examples of which are Garamond, Baskerville, and Bodoni respectively.
Old Style typefaces are influenced by early Italian lettering design. Modern fonts often exhibit a bracketed serif and a substantial difference in weight within the strokes. Though some argument exists as to whether Transitional fonts exist as a discrete category among serif fonts, Transitional fonts lie somewhere between Old Style and Modern style typefaces. Transitional fonts exhibit a marked increase in the variation of stroke weight and a more horizontal serif compared to Old Style. Slab serif designs have particularly large serifs, and date to the early nineteenth century. The earliest known slab serif font was first shown around 1817 by the English typefounder Vincent Figgins.
''Roman'', ''italic'', and ''oblique'' are also terms used to differentiate between upright and two possible slanted forms of a typeface. Italic and oblique fonts are similar (indeed, oblique fonts are often simply called italics) but there is strictly a difference: ''italic'' applies to fonts where the letter forms are redesigned, not just slanted. Almost all serif faces have italic forms; some sans-serif faces have oblique designs. (Most faces do not offer both as this is an artistic choice by the font designer about how the slanted form should look.)
Serif, or ''Roman'', typefaces are named for the features at the ends of their strokes. Times New Roman and Garamond are common examples of serif typefaces. Serif fonts are probably the most used class in printed materials, including most books, newspapers and magazines. Serif fonts are often classified into three subcategories: Old Style, Transitional, and Didone (typography), Didone (or Modern), representative examples of which are Garamond, Baskerville, and Bodoni respectively.
Old Style typefaces are influenced by early Italian lettering design. Modern fonts often exhibit a bracketed serif and a substantial difference in weight within the strokes. Though some argument exists as to whether Transitional fonts exist as a discrete category among serif fonts, Transitional fonts lie somewhere between Old Style and Modern style typefaces. Transitional fonts exhibit a marked increase in the variation of stroke weight and a more horizontal serif compared to Old Style. Slab serif designs have particularly large serifs, and date to the early nineteenth century. The earliest known slab serif font was first shown around 1817 by the English typefounder Vincent Figgins.
''Roman'', ''italic'', and ''oblique'' are also terms used to differentiate between upright and two possible slanted forms of a typeface. Italic and oblique fonts are similar (indeed, oblique fonts are often simply called italics) but there is strictly a difference: ''italic'' applies to fonts where the letter forms are redesigned, not just slanted. Almost all serif faces have italic forms; some sans-serif faces have oblique designs. (Most faces do not offer both as this is an artistic choice by the font designer about how the slanted form should look.)
Sans-serif typefaces
Blackletter typefaces
"Blackletter" is the name of the class of typefaces used with the earliest printing presses in Europe, which imitated the calligraphy style of that time and place. Various forms exist including textualis, rotunda (script), rotunda, schwabacher and Fraktur (typeface), fraktur. (Some people refer to Blackletter as "gothic script (disambiguation), gothic script" or "gothic font", though the term "Gothic" in typography refers tosans serif
In typography and lettering, a sans-serif, sans serif (), gothic, or simply sans letterform is one that does not have extending features called "serifs" at the end of strokes. Sans-serif typefaces tend to have less stroke width variation than ...
typefaces.)
Gaelic typefaces
Gaelic fonts were first used for the Irish language in 1571, and were used regularly for Irish until the early 1960s, though they continue to be used in display type and type for signage. Their use was effectively confined to Ireland, though Gaelic typefaces were designed and produced in France, Belgium, and Italy. Gaelic typefaces make use of insular script, insular letterforms, and early fonts made use of a variety of abbreviations deriving from the manuscript tradition. Various forms exist, including manuscript, traditional, and modern styles, chiefly distinguished as having angular or uncial features.Monospaced typefaces
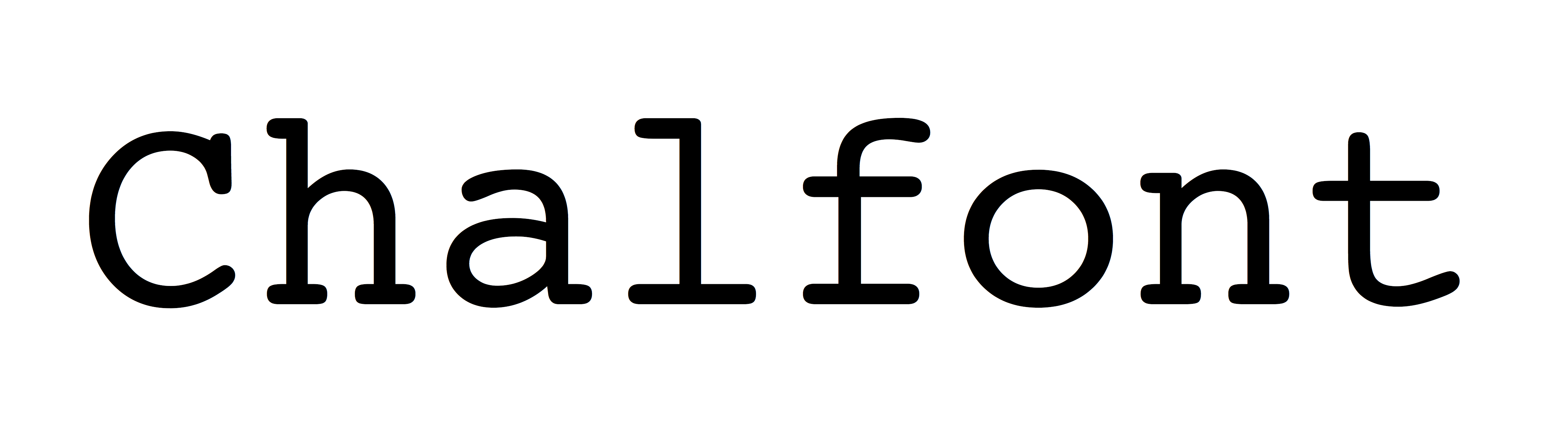 Monospaced fonts are typefaces in which every glyph is the same width (as opposed to variable-width fonts, where the ''w'' and ''m'' are wider than most letters, and the ''i'' is narrower). The first monospaced typefaces were designed for typewriters, which could only move the same distance forward with each letter typed. Their use continued with early computers, which could only display a single font. Although modern computers can display any desired typeface, monospaced fonts are still important for computer programming, terminal emulation, and for laying out tabulated data in plain text documents; they may also be particularly legible at small sizes due to all characters being quite wide. List of typefaces#Monospaced, Examples of monospaced typefaces are
Monospaced fonts are typefaces in which every glyph is the same width (as opposed to variable-width fonts, where the ''w'' and ''m'' are wider than most letters, and the ''i'' is narrower). The first monospaced typefaces were designed for typewriters, which could only move the same distance forward with each letter typed. Their use continued with early computers, which could only display a single font. Although modern computers can display any desired typeface, monospaced fonts are still important for computer programming, terminal emulation, and for laying out tabulated data in plain text documents; they may also be particularly legible at small sizes due to all characters being quite wide. List of typefaces#Monospaced, Examples of monospaced typefaces are Courier
A courier is a person or organization that delivers a message, package or letter from one place or person to another place or person. Typically, a courier provides their courier service on a commercial contract basis; however, some couriers are ...
, Prestige Elite, Fixedsys, and Monaco (typeface), Monaco. Most monospaced fonts are sans-serif or slab-serif as these designs are easiest to read printed small or display on low-resolution screens, though many exceptions exist.
CJK typefaces
CJK, or Chinese, Japanese and Korean typefaces consist of large sets of glyphs. These typefaces originate in the glyphs found in brush calligraphy during the Tang dynasty. These later evolved into the Song style (宋体字) which used thick vertical strokes and thin horizontal strokes in wood block printing. The glyphs found in CJK fonts are designed to fit within a square. This allows for regular vertical, horizontal, right-to-left and left-to-right orientations. CJK fonts can also include an extended set of monospaced Latin characters. This commonly results in complex, sometimes contradictory rules and conventions for mixing languages in type.Mincho
With CJK typefaces, Mincho style tends to be something like Serifs for the end of stems, and in fact includes Serifed glyphs for Extended Latin and Cyrillic sets within a typeface.Gothic
With CJK typefaces, Goth style tends to be something like Sans Serifs with squarish, cut off end-caps for the end of stems, and in fact includes Sans Serif glyphs for Extended Latin and Cyrillic sets within a typeface.Maru
With CJK typefaces, Maru style tends to be something like Sans Serifs with rounded end-caps for the end of stems, and in fact includes Rounded Sans Serif glyphs for Extended Latin and Cyrillic sets within a typeface.Display type
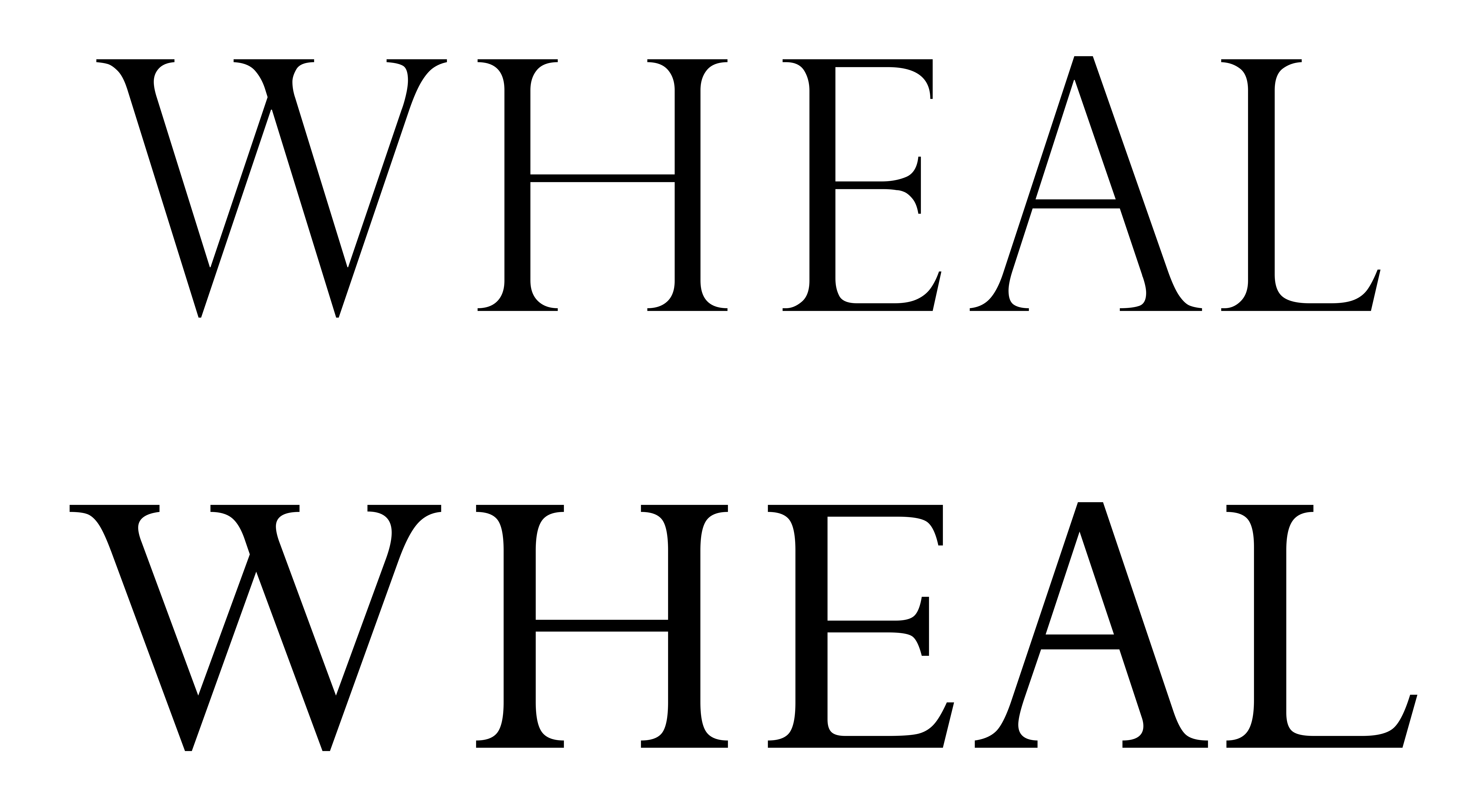 In the days of metal type, when each size was cut individually, types intended for display use were often adjusted accordingly. These modifications continued to be made even after fonts started to be made by scaling using a pantograph, but began to fade away with the advent of phototypesetting and then digital fonts, which can both be printed at any size. Premium digital fonts used for magazines, books and newspapers do often include display variants, but they are often not included with typefaces bundled with operating systems and desktop publishing software. Display typefaces in the letterpress period were often made as wood type, being lighter than metal.
Decades into the desktop publishing revolution, few typographers with metal foundry type experience are still working, and few digital typefaces are optimized specifically for different sizes, so the misuse of the term display typeface as a synonym for ornamental type has become widespread; properly speaking, ornamental typefaces are a subcategory of display typefaces. At the same time, with new printing techniques, typefaces have largely replaced hand-lettering for very large signs and notices that would once have been painted or carved by hand.
In the days of metal type, when each size was cut individually, types intended for display use were often adjusted accordingly. These modifications continued to be made even after fonts started to be made by scaling using a pantograph, but began to fade away with the advent of phototypesetting and then digital fonts, which can both be printed at any size. Premium digital fonts used for magazines, books and newspapers do often include display variants, but they are often not included with typefaces bundled with operating systems and desktop publishing software. Display typefaces in the letterpress period were often made as wood type, being lighter than metal.
Decades into the desktop publishing revolution, few typographers with metal foundry type experience are still working, and few digital typefaces are optimized specifically for different sizes, so the misuse of the term display typeface as a synonym for ornamental type has become widespread; properly speaking, ornamental typefaces are a subcategory of display typefaces. At the same time, with new printing techniques, typefaces have largely replaced hand-lettering for very large signs and notices that would once have been painted or carved by hand.
Script typefaces
Script typefaces imitate handwriting or calligraphy. They do not lend themselves to quantities of body text, as people find them harder to read than many serif and sans-serif typefaces; they are typically used for logos or invitations. Historically, most lettering on logos, displays, shop frontages did not use fonts but was rather custom-designed by signpainters and engravers, so many emulate the styles of hand-drawn signs from different historical periods. The genre has developed rapidly in recent years due to modern font formats allowing more complex simulations of handwriting. Examples include Coronet (typeface), Coronet (a quite simple design from 1937) and Zapfino (a much more complicated digital design).Mimicry typefaces
Mimicry typefaces are decorative typefaces that have been designed to represent characters of one alphabet but at the same time evoke another writing system. This group includes Roman typefaces designed to appear as Arabic, Chinese characters (Wonton fonts),Cyrillic
The Cyrillic script ( ) is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Ea ...
(Faux Cyrillic), Indic scripts, Greek alphabet, Greek (an example being Lithos), Hebrew alphabet, Hebrew (Faux Hebrew), Kana, or Thai alphabet, Thai. These are used largely for the purpose of novelty to make something appear foreign, or to make businesses offering foreign products, such as restaurants, clearly stand out. This typographic mimicry is also known as a faux font (named faux x, where x is usually a language script), pseudoscript, ethnic typeface, simulation typeface or a "foreign look" font.
Reverse-contrast typefaces
 A reverse-contrast type is a typeface in which the stress is reversed from the norm: instead of the vertical lines being the same width or thicker than horizontals, which is normal in Latin-alphabet printing, the horizontal lines are the thickest. Reverse-contrast types are rarely used for body text, and are particularly common in Typeface#Display type, display applications such as headings and posters, in which their unusual structure may be particularly eye-catching. First seen in London in 1821, they were particularly common in the mid- to late nineteenth century in American and British printing and have been revived occasionally since then. They effectively become slab serif designs because of the serifs becoming thick, and are often characterised as part of that genre. In recent times, the reverse-contrast effect has been extended to other kinds of typeface, such as
A reverse-contrast type is a typeface in which the stress is reversed from the norm: instead of the vertical lines being the same width or thicker than horizontals, which is normal in Latin-alphabet printing, the horizontal lines are the thickest. Reverse-contrast types are rarely used for body text, and are particularly common in Typeface#Display type, display applications such as headings and posters, in which their unusual structure may be particularly eye-catching. First seen in London in 1821, they were particularly common in the mid- to late nineteenth century in American and British printing and have been revived occasionally since then. They effectively become slab serif designs because of the serifs becoming thick, and are often characterised as part of that genre. In recent times, the reverse-contrast effect has been extended to other kinds of typeface, such as sans-serif
In typography and lettering, a sans-serif, sans serif (), gothic, or simply sans letterform is one that does not have extending features called "serifs" at the end of strokes. Sans-serif typefaces tend to have less stroke width variation than ...
designs.
Effect typefaces
 Some typefaces have a structure that suggests a three-dimensional letter, such as letters carved into stone. An example of this is the genre known as 'inline', 'block' 'outline' or 'shadowed' typefaces. This renders the interior of glyphs in the background color, with a thin line around the edges of the glyphs. In some cases, the outline shows the glyph filled in with the foreground color, surrounded a thin outline mirroring the edges separated by a small gap. (This latter style is often used with "college" typefaces.) Colorized block lettering is often seen in carefully rendered graffiti.
A "shadow" effect can also be either designed into a typeface or added to an existing typeface. Designed-in shadows can be stylized or connected to the foreground. An after-market shadow effect can be created by making two copies of each glyph, slightly offset in a diagonal direction and possibly in different colors. Drop shadows can also be dynamically created by rendering software. The shadow effect is often combined with the outline effect, where the top layer is shown in white with black outline and the bottom layer in black, for greater contrast. An example typeface with an 'inline' effect is Imprint (typeface), Imprint Shadowed, where the shadowed version is more widely distributed than the regular design.
Some typefaces have a structure that suggests a three-dimensional letter, such as letters carved into stone. An example of this is the genre known as 'inline', 'block' 'outline' or 'shadowed' typefaces. This renders the interior of glyphs in the background color, with a thin line around the edges of the glyphs. In some cases, the outline shows the glyph filled in with the foreground color, surrounded a thin outline mirroring the edges separated by a small gap. (This latter style is often used with "college" typefaces.) Colorized block lettering is often seen in carefully rendered graffiti.
A "shadow" effect can also be either designed into a typeface or added to an existing typeface. Designed-in shadows can be stylized or connected to the foreground. An after-market shadow effect can be created by making two copies of each glyph, slightly offset in a diagonal direction and possibly in different colors. Drop shadows can also be dynamically created by rendering software. The shadow effect is often combined with the outline effect, where the top layer is shown in white with black outline and the bottom layer in black, for greater contrast. An example typeface with an 'inline' effect is Imprint (typeface), Imprint Shadowed, where the shadowed version is more widely distributed than the regular design.
Small print typefaces
Some typefaces are specifically designed to be printed at small sizes, for example in telephone directories or on newsprint paper. Bell Gothic and Bell Centennial, commissioned for telephone directories, are notable examples of this. Small-print designs often feature a largex-height
upright 2.0, alt=A diagram showing the line terms used in typography
In typography, the x-height, or corpus size, is the distance between the baseline and the mean line of lowercase letters in a typeface. Typically, this is the height of the le ...
, and a chunky design. Some fonts used at such sizes may be members of a larger typeface family joining members for normal sizes. For example, the Times New Roman family contains some designs intended for small print use, as do many families with optical sizes such as Minion (typeface), Minion.
In the metal type era, typefaces intended to be printed small contained ink traps, small indentations at the junctions of strokes that would be filled up with ink spreading out, maintaining the intended appearance of the type design. Without ink traps, the excess ink would blob and ruin the crisp edge. At larger sizes, these ink traps were not necessary, so display faces did not have them. They have also been removed from most digital fonts, as these will normally be viewed on screen or printed through inkjet printing, laser printing, offset lithography, electrophotographic printing or other processes that do not show the ink spread of letterpress. Ink traps have remained common on designs intended to be printed on low-quality, absorbent paper, especially newsprint
Newsprint is a low-cost, non-archival paper consisting mainly of wood pulp and most commonly used to print newspapers and other publications and advertising material. Invented in 1844 by Charles Fenerty of Nova Scotia, Canada, it usually has ...
and telephone directories.
Typeface family
A typeface family (or type family) is a set of typefaces that share a common design concept. The simplest typeface family has just a 'regular' face and an 'oblique' face (or 'Roman' and 'Italic'); the next step up adds boldface versions of these types. A modern professional typeface family (such as Danish Standard no. 737) might have as many as 54 different styles: Font#Width, condensed, normal and Font#Width, expanded forms of each of 'thin', 'extralight', 'light', 'regular', 'medium', 'demibold', 'bold', 'extrabold' and 'heavy' types, in regular and italic.Texts used to demonstrate typefaces
A sentence that uses all of the alphabet (a pangram), such as "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog", is often used as a design aesthetic tool to demonstrate the personality of a typeface's characters in a setting (because it displays all the letters of the alphabet). For extended settings of typefaces graphic designers often use nonsense text (commonly referred to as ''greeking''), such as ''lorem ipsum'' or Latin text such as the beginning of Cicero's ''In Catilinam''. Greeking is used in typography to determine a typeface's ''Type color, colour'', or weight and style, and to demonstrate an overall typographic aesthetic prior to actual type setting. Another common demonstration word is "Hamburgevons".Non-character typefaces
 The process of printing typefaces has historically been far simpler than commissioning and engraving custom illustrations, especially as many non-text features of printed works like symbols and borders were likely to be reused by a printer in future. Non-character typefaces have therefore been created for elements of documents that are not letters but are likely to be reused regularly. These include:
The process of printing typefaces has historically been far simpler than commissioning and engraving custom illustrations, especially as many non-text features of printed works like symbols and borders were likely to be reused by a printer in future. Non-character typefaces have therefore been created for elements of documents that are not letters but are likely to be reused regularly. These include:
Ornamental typefaces
Ornamental (also known as ''novelty'' or sometimes ''display'') typefaces are used to decorate a page. Historically complex interlocking patterns known as Arabesque (European art), arabesques were common in fine printing, as were floral borders known as Fleuron (typography), fleurons evoking hand-drawn manuscripts. In the metal type era, type-founding companies often would offer pre-formed illustrations as fonts showing objects and designs likely to be useful for printing and advertisements, the equivalent of modern clip art and stock photographs. As examples, the American Type Founders specimen of 1897 offered designs including baseball players, animals, Christmas wreaths, designs for cheques, and emblems such as Seals of the U.S. states, state seals for government printing. The practice has declined as printing custom illustrations and colour printing using processes such as lithography has become cheaper, although illustration typefaces are still sold by some companies. #Display type, See above for the historical definition of ''display typeface''.Symbol typefaces
 Symbol, or dingbat, typefaces consist of symbols (such as decorative bullets, clock faces, railroad timetable symbols, CD-index, or TV-channel enclosed numbers) rather than normal text characters. Common, widely used symbol typeface releases include Zapf Dingbats and Wingdings, though many may be created internally by a publication for its own use and some typefaces may have a symbol range included. Marlett is an example of a font used by Microsoft Windows, Windows to draw elements of windows and icons.
Symbol, or dingbat, typefaces consist of symbols (such as decorative bullets, clock faces, railroad timetable symbols, CD-index, or TV-channel enclosed numbers) rather than normal text characters. Common, widely used symbol typeface releases include Zapf Dingbats and Wingdings, though many may be created internally by a publication for its own use and some typefaces may have a symbol range included. Marlett is an example of a font used by Microsoft Windows, Windows to draw elements of windows and icons.
Emoji
Emoji are pictograms that can be used and displayed inline with text. They are similar to previous symbol typefaces, but with a much larger range of characters, such as symbols for common objects, animals, food types, weather and emotions. Originally developed in Japan, they are now commonly installed on many computer and smartphone operating systems. Following standardisation and inclusion in the Unicode standard, allowing them to be used internationally, the number of Emoji characters has rapidly increased to meet the demands of an expanded range of cultures using them; unlike many previous symbol typefaces, they are interchangeable with the ability to display the pictures of the same meaning in a range of fonts on different operating systems. The popularity of emoji has meant that characters have sometimes gained culture-specific meanings not inherent to the design. Both colour and monochrome emoji typefaces exist, as well as at least one animated design.Music typefaces
Typefaces that include musical notes and other needed symbols have been developed to print sheet music.Intellectual property
See also
Explanatory notes
References
Further reading
* * * * Jaspert, W. P.; Berry, W. Turner; Alfred F. Johnson, Johnson, A. F. (1953, 1958, 1962, 1970, 1983, 1986, 1990, 1991, 1993, 2001, 2008). ''The Encyclopedia of Typefaces''. London: Blandford Press. *External links
*Monotype printed borders specimens
ArchLinux list of Metric-compatible fonts
* {{Authority control Typefaces, Articles containing video clips Typography Typesetting