Tetiʻaroa on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tetiaroa (
 Tetiaroa is administratively part of the commune of Arue, whose main part is in the northeastern part of
Tetiaroa is administratively part of the commune of Arue, whose main part is in the northeastern part of
 The atoll of Tetiaroa was a special place for the
The atoll of Tetiaroa was a special place for the
Tetiaroa Island
at
French
French may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France
** French people, a nation and ethnic group
** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices
Arts and media
* The French (band), ...
: ''Tetiaroa'') is an atoll
An atoll () is a ring-shaped island, including a coral rim that encircles a lagoon. There may be coral islands or cays on the rim. Atolls are located in warm tropical or subtropical parts of the oceans and seas where corals can develop. Most ...
in the Windward group of the Society Islands
The Society Islands ( , officially ; ) are an archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean that includes the major islands of Tahiti, Mo'orea, Moorea, Raiatea, Bora Bora and Huahine. Politically, they are part of French Polynesia, an overseas country ...
of French Polynesia
French Polynesia ( ; ; ) is an overseas collectivity of France and its sole #Governance, overseas country. It comprises 121 geographically dispersed islands and atolls stretching over more than in the Pacific Ocean, South Pacific Ocean. The t ...
, an overseas territorial collectivity
A territorial collectivity (, previously '), or territorial authority, in many francophone countries, is a Legal person, legal entity governed by public law that exercises within its territory certain powers devolved to it by the State as part of a ...
of France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
in the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
. Once a holiday location for Tahitian royalty, the islets are under a 99-year lease signed by Marlon Brando
Marlon Brando Jr. (April 3, 1924 – July 1, 2004) was an American actor. Widely regarded as one of the greatest cinema actors of the 20th century,''Movies in American History: An Encyclopedia''
, and are home to The Brando Resort.
Geography
 Tetiaroa is administratively part of the commune of Arue, whose main part is in the northeastern part of
Tetiaroa is administratively part of the commune of Arue, whose main part is in the northeastern part of Tahiti
Tahiti (; Tahitian language, Tahitian , ; ) is the largest island of the Windward Islands (Society Islands), Windward group of the Society Islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France. It is located in the central part of t ...
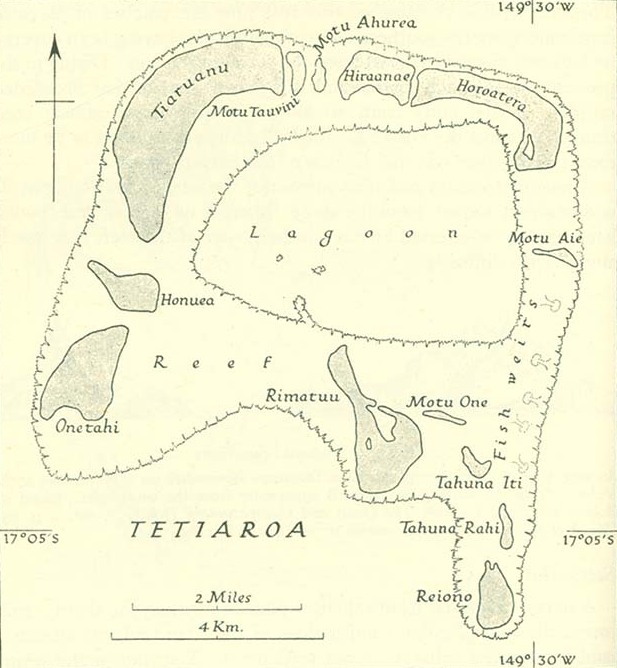
. The atoll is located north of Tahiti. The atoll has a total surface area of ; approximately of sand divided by 12 motus (islets) with varying surface areas. The lagoon is approximately wide and deep. The atoll has no reef opening, making access by boat nearly impossible.
The islets (or motus), in clockwise order starting from the southwest corner, include: Onetahi (with regulated airstrip and site of The Brando Resort), Honuea, Tiaruanu, Motu Tauvini (Tauini), Motu Ahurea (Auroa), Hiraanae, Horoatera (Oroatera), Motu 'Ā'ie, Tahuna Iti, Tahuna Rahi, Reiono, Motu One (emerging sandbank) and Rimatu'u (with an ornithology reserve).
Climate
Tetiaroa has atropical rainforest climate
A tropical rainforest climate or equatorial climate is a tropical climate sub-type usually found within 10 to 15 degrees latitude of the equator. There are some other areas at higher latitudes, such as the coast of southeast Florida, United States ...
(Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (1951–2014), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author ...
''Af''), slightly above a tropical monsoon climate
An area of tropical monsoon climate (occasionally known as a sub-equatorial, tropical wet climate or a tropical monsoon and trade-wind littoral climate) is a tropical climate subtype that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification category ' ...
(''Am''). The average annual temperature in Tetiaroa is . The average annual rainfall is with December as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in March, at around , and lowest in August, at around . The highest temperature ever recorded in Tetiaroa was on 20 March 1995; the coldest temperature ever recorded was on 25 July 1987.
History
Early years
 The atoll of Tetiaroa was a special place for the
The atoll of Tetiaroa was a special place for the Tahiti
Tahiti (; Tahitian language, Tahitian , ; ) is the largest island of the Windward Islands (Society Islands), Windward group of the Society Islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France. It is located in the central part of t ...
an chiefs, as a place to entertain themselves with song, dance, fishing and feasting. It was also a special place for the ''ariori'' to practice their custom of ''haaporia''. This custom included eating to gain weight, and staying out of the sun to whiten their skin. Plump and pale was a sign of "well-being and prosperity" for the ''ariori'' and chiefs. Tetiaroa was controlled by the chiefs of Pare-'Arue, and later, by members of the Pōmare Dynasty Pōmare or Pomare may refer to:
Tahiti
* Pōmare dynasty, the dynasty of the Tahitian monarchs
* Pōmare I (c. 1742–1803), first king of the Kingdom of Tahiti
* Pōmare II (c. 1774–1821), second king of Tahiti
* Pōmare III (1820–1827), third ...
.
In 1789, William Bligh
William Bligh (9 September 1754 – 7 December 1817) was a Vice-admiral (Royal Navy), Royal Navy vice-admiral and colonial administrator who served as the governor of New South Wales from 1806 to 1808. He is best known for his role in the Muti ...
is said to have been the first European to visit the atoll while looking for early mutineers prior to the departure of which eventually suffered a full mutiny. The United States Exploring Expedition
The United States Exploring Expedition of 1838–1842 was an exploring and surveying expedition of the Pacific Ocean and surrounding lands conducted by the United States. The original appointed commanding officer was Commodore Thomas ap Catesby ...
visited the island on 10 September 1839.
Williams and Brando
In 1904, the royal family sold Tetiaroa to Johnston Walter Williams, a Canadian national and the only dentist in Tahiti. Williams later became Consul of theUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
from 1916 to 1935. Williams managed Tetiaroa as a residence and a copra
Copra (from ; ; ; ) is the dried, white flesh of the coconut from which coconut oil is extracted. Traditionally, the coconuts are sun-dried, especially for export, before the oil, also known as copra oil, is pressed out. The oil extracted ...
plantation.
In 1960, Marlon Brando
Marlon Brando Jr. (April 3, 1924 – July 1, 2004) was an American actor. Widely regarded as one of the greatest cinema actors of the 20th century,''Movies in American History: An Encyclopedia''
"discovered" Tetiaroa while scouting filming locations for ''Mutiny on the Bounty
The mutiny on the ''Bounty'' occurred in the South Pacific Ocean on 28 April 1789. Disaffected crewmen, led by acting-Lieutenant Fletcher Christian, seized control of the ship, , from their captain, Lieutenant (navy), Lieutenant William Bli ...
'', which was shot on Tahiti and neighbouring Mo'orea. After filming was completed, Brando hired a local fisherman to ferry him to Tetiaroa. It was "more gorgeous than anything I had anticipated," he marveled in his 1994 autobiography ''Songs My Mother Taught Me.'' Brando eventually purchased Tetiaroa's islets (motus) from one of Williams's direct descendants, Mrs. (Madame) Duran. Williams and his wife are buried on Motu Rimatuu. Brando decided on the purchase in 1966, having to endure political interference and local resistance to secure the atoll, reef and lagoon, all of which is now the property of French Polynesia. Many important archaeological sites have been located, identified, and studied on Tetiaroa. Thus, the historical significance of Tetiaroa to the people (and the government) of French Polynesia continues to make future development questionable at best.
Wanting to live on the atoll, Brando built a small village on Motu Onetahi in 1970. It consisted of an airstrip to arrive without breaching the reef, 12 simple bungalows, a kitchen hut, dining hall and bar, all built from local materials: coconut wood, thatch roofs and even large sea shells for sinks. The village became a place for friends, family and researchers studying the atoll's ecology and archaeology. Over the years, Brando spent as much time on the atoll as he could, and valued it as a getaway from his hectic life in Hollywood. Although, ultimately, he didn't spend as much time there as he'd wished to, it is said that he always cherished his moments on Tetiaroa. During his stays on the island, he was often visited by his children, grandchildren and great-grandchildren. Upon his death, Brando's son Teihotu lived on the island for some time. Eventually the village became a modest hotel managed by his Tahitian wife, Tarita Teriipaia
Tarita Teriipaia (born 30 December 1941) is a retired actress of French Polynesian and Chinese descent who was the third wife of actor Marlon Brando; the couple divorced in 1972.
Biography
Born in Bora Bora, French Polynesia, she played Maimit ...
, who had played his on-screen love in ''Mutiny on the Bounty''. The hotel operated for more than 25 years, even after Brando had to leave French Polynesia to return to Los Angeles. Many hotel guests, arriving with higher expectations, lamented the lack of amenities normally found at an island "resort".
In 1980, the maxi yacht
A maxi yacht usually refers to a racing yacht of at least in length.
Origin
The term ''maxi'' originated with the International Offshore Rule (IOR) rating system, which in the 1970s and 1980s measured offshore racing yachts and applied a single ...
SY ran aground on the Onetahi reef, which caused it to be shipwrecked and written off by insurers. Purportedly, Brando and the owner of the yacht engaged in a brief bidding-war over rights to the vessel's polished mahogany hull (as reported by the owner in the New Zealand yachting magazine ''Sail'', in 1981), which Brando (allegedly) wanted to use as a bar at a new resort he planned to build on the island. The yacht was salvaged, and sent to New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
for repair. In 2002, two years before the actor's death, Brando signed a new will and trust agreement that left no instructions for Tetiaroa. Following his death in 2004, the TetiAroa Village Hotel was closed and the staff was evicted from the atoll. The atoll was closed to tourism. In August 2004, French Polynesian vice-president Hiro Tefaarerea Hiro may refer to:
People
* Hiro (given name), includes lists of people with the given name
* Hiro (photographer) (1930–2021), Japanese-born American photographer
* Hiro (singer) (born 1991), French singer
* Hiroko Shimabukuro (born 1984), Japa ...
advocated for the atoll to be declared a nature reserve to prevent development. Eventually, executors of the estate granted development rights to Pacific Beachcomber SC, a Tahitian company that owns hotels throughout French Polynesia. The Brando Resort was opened in July 2014.
Flora and fauna
The island provides habitat for the following seabird species:Brown booby
The brown booby (''Sula leucogaster'') is a large seabird of the booby family Sulidae, of which it is perhaps the most common and widespread species. It has a pantropical range, which overlaps with that of other booby species. The gregarious bro ...
, red-footed booby
The red-footed booby (''Sula sula'') is a large seabird of the booby family, Sulidae. Adults always have red feet, but the colour of the plumage varies. They are powerful and agile fliers, but they are clumsy in takeoffs and landings. They are ...
, great crested tern
The greater crested tern Retrieved 28 February 2012 (''Thalasseus bergii''), also called crested tern, swift tern, or great crested tern, is a tern in the family Laridae that nests in dense colonies on coastlines and islands in the tropical and ...
, white tern
The white tern or common white tern (''Gygis alba'') is a small seabird found across the tropical oceans of the world. It is sometimes known as the fairy tern, although this name is potentially confusing as it is also the common name of ''Sternul ...
, great frigatebird
The great frigatebird (''Fregata minor'') is a large seabird in the frigatebird family (biology), family. There are major nesting populations in the tropical Pacific Ocean, such as Hawaii and the Galápagos Islands; in the Indian Ocean, colonies ...
, lesser frigatebird
The lesser frigatebird (''Fregata ariel'') is a seabird of the frigatebird family Fregatidae. At around 75 cm (30 in) in length, it is the smallest species of frigatebird. It occurs over tropical and subtropical waters across the Indian ...
, brown noddy
The brown noddy or common noddy (''Anous stolidus'') is a seabird in the family Laridae. The largest of the noddies, it can be told from the closely related black noddy by its larger size and plumage, which is dark brown rather than black. The ...
, black noddy
The black noddy (''Anous minutus''), also known as white-capped noddy, is a species of tern in the family Laridae. It is a medium-sized seabird with black plumage and a white cap that closely resembles the lesser noddy with which it was at one ...
, sooty tern
The sooty tern (''Onychoprion fuscatus'') is a tern in the family Laridae. It is a seabird of the tropical oceans, and remarkably, has evolved the ability to fly for years at a time, skimming the sea surface for food, and returning to land only ...
, and the grey-backed or spectacled tern
The spectacled tern (''Onychoprion lunatus''), also known as the grey-backed tern, is a seabird in the family Laridae.
Description
A close relative of the bridled and sooty terns (with which it is sometimes confused), the spectacled tern is l ...
. Shore and terrestrial birds include the Pacific reef egret, Pacific golden plover
The Pacific golden plover (''Pluvialis fulva'') is a migratory shorebird that breeds during summer in Alaska and Siberia. During nonbreeding season, this medium-sized plover migrates widely across the Pacific.
Taxonomy
The Pacific golden plove ...
, wandering tattler
The wandering tattler (''Tringa incana''; formerly ''Heteroscelus incanus'': Pereira & Baker, 2005; Banks ''et al.'', 2006), is a medium-sized wading bird. It is similar in appearance to the closely related gray-tailed tattler, ''T. brevipes'' ...
, Pacific long-tailed cuckoo
The long-tailed koel (''Urodynamis taitensis''), also known as the long-tailed cuckoo, Pacific long-tailed cuckoo, sparrow hawk, home owl, screecher, screamer or in Māori, is a species of the Cuculidae bird family (the cuckoos). It is the onl ...
, and the bristle-thighed curlew
The bristle-thighed curlew (''Numenius tahitiensis'') is a medium-sized shorebird that breeds in Alaska and winters on tropical Pacific islands.
It is known in Mangareva as ''kivi'' or ''kivikivi'' and in Rakahanga as ''kihi''; it is said to b ...
.
Tetiaroa hosts five of the seven marine species of turtle, namely the Hawksbill turtle
The hawksbill sea turtle (''Eretmochelys imbricata'') is a critically endangered sea turtle belonging to the family Cheloniidae. It is the only extant species in the genus ''Eretmochelys''. The species has a global distribution that is largely ...
, green turtle
The green sea turtle (''Chelonia mydas''), also known as the green turtle, black (sea) turtle or Pacific green turtle, is a species of large sea turtle of the family Cheloniidae. It is the only species in the genus ''Chelonia''. Its range exte ...
, leatherback turtle, olive Ridley turtle
The olive ridley sea turtle (''Lepidochelys olivacea''), also known commonly as the Pacific ridley sea turtle, is a species of turtle in the family Cheloniidae. The species is the second-smallest and most abundant of all sea turtles found in t ...
, and loggerhead turtle
The loggerhead sea turtle (''Caretta caretta'') is a species of oceanic turtle distributed throughout the world. It is a marine reptile, belonging to the family Cheloniidae. The average loggerhead measures around in carapace length when ful ...
.
Tetiaroa hosts numerous marine mammals, including the humpback whale
The humpback whale (''Megaptera novaeangliae'') is a species of baleen whale. It is a rorqual (a member of the family Balaenopteridae) and is the monotypic taxon, only species in the genus ''Megaptera''. Adults range in length from and weigh u ...
, short-finned pilot whale
The short-finned pilot whale (''Globicephala macrorhynchus'') is one of the two species of cetaceans in the genus ''Pilot whale, Globicephala'', which it shares with the long-finned pilot whale (''G. melas''). It is part of the oceanic dolphin ...
, rough-toothed dolphin
The rough-toothed dolphin (''Steno bredanensis'') is a species of dolphin that can be found in deep warm and tropical waters around the world.
The species was first described by Georges Cuvier in 1823. The genus name ''Steno'', of which this spe ...
, spinner dolphin
The spinner dolphin (''Stenella longirostris'') is a small dolphin found in off-shore tropical waters around the world. It is famous for its acrobatic displays in which it rotates around its longitudinal axis as it leaps through the air. It is a ...
, Risso's dolphin
Risso's dolphin (''Grampus griseus'') is a marine mammal and dolphin, the only species of the genus ''Grampus''. Some of the most closely related species to these dolphins include: pilot whales (''Globicephala'' spp.), pygmy killer whales (''Fere ...
, melon-headed whale
The melon-headed whale (''Peponocephala electra''), also known less commonly as the electra dolphin, little killer whale, or many-toothed blackfish, is a toothed whale of the oceanic dolphin family (Delphinidae). The common name is derived from t ...
, Blainville's beaked whale
Blainville's beaked whale (''Mesoplodon densirostris''), or the dense-beaked whale, is believed to be the widest ranging mesoplodont whale. The French zoologist Henri de Blainville first described the species in 1817 from a small piece of jaw— ...
, Cuvier's beaked whale
Cuvier's beaked whale, goose-beaked whale, or ziphius (''Ziphius cavirostris'') is the most widely distributed of all beaked whales in the family Beaked whale, Ziphiidae. It is smaller than most baleen whales—and indeed the larger Toothed whal ...
, and even some migrating pods of orca
The orca (''Orcinus orca''), or killer whale, is a toothed whale and the largest member of the oceanic dolphin family. The only extant species in the genus '' Orcinus'', it is recognizable by its black-and-white-patterned body. A cosmopol ...
.
Numerous bony fishes
Osteichthyes ( ; ), also known as osteichthyans or commonly referred to as the bony fish, is a diverse clade of vertebrate animals that have endoskeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondrichthyes (cartila ...
, sharks
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by a ribless endoskeleton, dermal denticles, five to seven gill slits on each side, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the ...
, and rays
Ray or RAY may refer to:
Fish
* Ray (fish), any cartilaginous fish of the superorder Batoidea
* Ray (fish fin anatomy), the bony or horny spine on ray-finned fish
Science and mathematics
* Half-line (geometry) or ray, half of a line split at an ...
are also present.
Plants include the fish-poison tree, Pacific ironwood
Ironwood is a common name for many woods that have a reputation for hardness, or specifically a wood density that is denser than water (approximately 1000 kg/m3, or 62 pounds per cubic foot), although usage of the name ironwood in English ma ...
, Alexandrian laurel, coconut palm
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (biology), family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, ...
, island walnut
A walnut is the edible seed of any tree of the genus '' Juglans'' (family Juglandaceae), particularly the Persian or English walnut, '' Juglans regia''. They are accessory fruit because the outer covering of the fruit is technically an i ...
, dye fig, beach gardenia
''Gardenia'' is a genus of flowering plants in the coffee family, Rubiaceae, native to the tropical and subtropical regions of Africa, Asia, Madagascar, Pacific Islands, and Australia.
The genus was named by Carl Linnaeus and John Ellis after ...
, beach heliotrope, lantern tree Lantern tree is a common name for several plants and may refer to:
*''Crinodendron hookerianum'', or Chilean lantern tree
*''Dichrostachys cinerea'', or Chinese lantern tree, native to Africa and widely introduced
*''Hernandia nymphaeifolia
''He ...
, breadfruit
Breadfruit (''Artocarpus altilis'') is a species of flowering tree in the mulberry and jackfruit family ( Moraceae) believed to have been selectively bred in Polynesia from the breadnut ('' Artocarpus camansi''). Breadfruit was spread into ...
, lime tree
''Tilia'' is a genus of about 30 species of trees or bushes, native throughout most of the temperate Northern Hemisphere. The tree is known as linden for the European species, and basswood for North American species. In Great Britain and Irelan ...
, sea lettuce
The sea lettuces comprise the genus ''Ulva'', a group of edible green algae that is widely distributed along the coasts of the world's oceans. The type species within the genus ''Ulva'' is ''Ulva lactuca'', wikt:lactuca, ''lactuca'' being Latin ...
, and vanilla orchids, amongst others.
Conservation and restoration
The presence of two invasive rat species significantly impacted the native vegetation, nesting seabird populations, sea turtle hatchlings, andland crabs
A number of lineages of crabs have evolved to live predominantly on land. Examples of terrestrial crabs are found in the families Gecarcinidae and Gecarcinucidae, as well as in selected genera from other families, such as '' Sesarma'', althou ...
. The Tetiaroa Society, Island Conservation
Island Conservation is a non-profit organization with the mission to "restore islands for nature and people worldwide" and has therefore focused its efforts on islands with species categorized as Critically Endangered and Endangered on the IUCN' ...
, and the Brando Resort (among other partners) initiated an invasive rat-eradication project in the summer of 2022. After repeated pandemic-related disruptions, the operation took place over June and July 2022, covering 520 hectares of land and requiring more than 60 members of staff, plus volunteers. The hope is that this project will restore the terrestrial ecosystems, protect endangered native birds and turtles, and enhance the resilience of surrounding coral reefs, making them more resistant to climate change. Additional benefits may be ensuring food security for the local population, as well as eliminating reservoirs and vectors for human disease. In time, the atoll could become a translocation habitat for the Polynesian ground dove
The Polynesian ground dove or Society Islands ground dove (''Pampusana erythroptera'') or ''Tutururu'' is a Critically Endangered, critically endangered species of bird in the family Columbidae. Originally Endemism, endemic to the Society Islands ...
and the Tuamotu sandpiper
The Tuamotu sandpiper (''Prosobonia parvirostris'') is an endangered member of the large wader family Scolopacidae, that is endemic to the Tuamotu Islands in French Polynesia. It is sometimes placed in the monotypic genus ''Aechmorhynchus''. A na ...
. The next phase of the restoration program will be extensive research and monitoring, to record the subsequent benefits to the terrestrial and marine ecosystems.
Airport
Tetiaroa Airport is an airport on the atoll. The airport is served by Air Tetiaroa, acharter airline
Air charter is the business of renting an entire aircraft (i.e., chartering) as opposed to individual aircraft seats (i.e., purchasing a ticket through a traditional airline).
Regulation
Charter – also called air taxi or ad hoc – flight ...
who primarily operate flights for guests of the Brando Resort to Faa'a International Airport. The airport currently has no scheduled commercial service.
References
External links
Tetiaroa Island
at
NASA Earth Observatory
NASA Earth Observatory is an online publishing outlet for NASA which was created in 1999. It is the principal source of satellite imagery and other scientific information about the climate and the environment which are being provided by NASA for ...
{{Society Islands
Atolls of the Society Islands
Marlon Brando
Island restoration