Sól (Germanic Mythology) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sól (
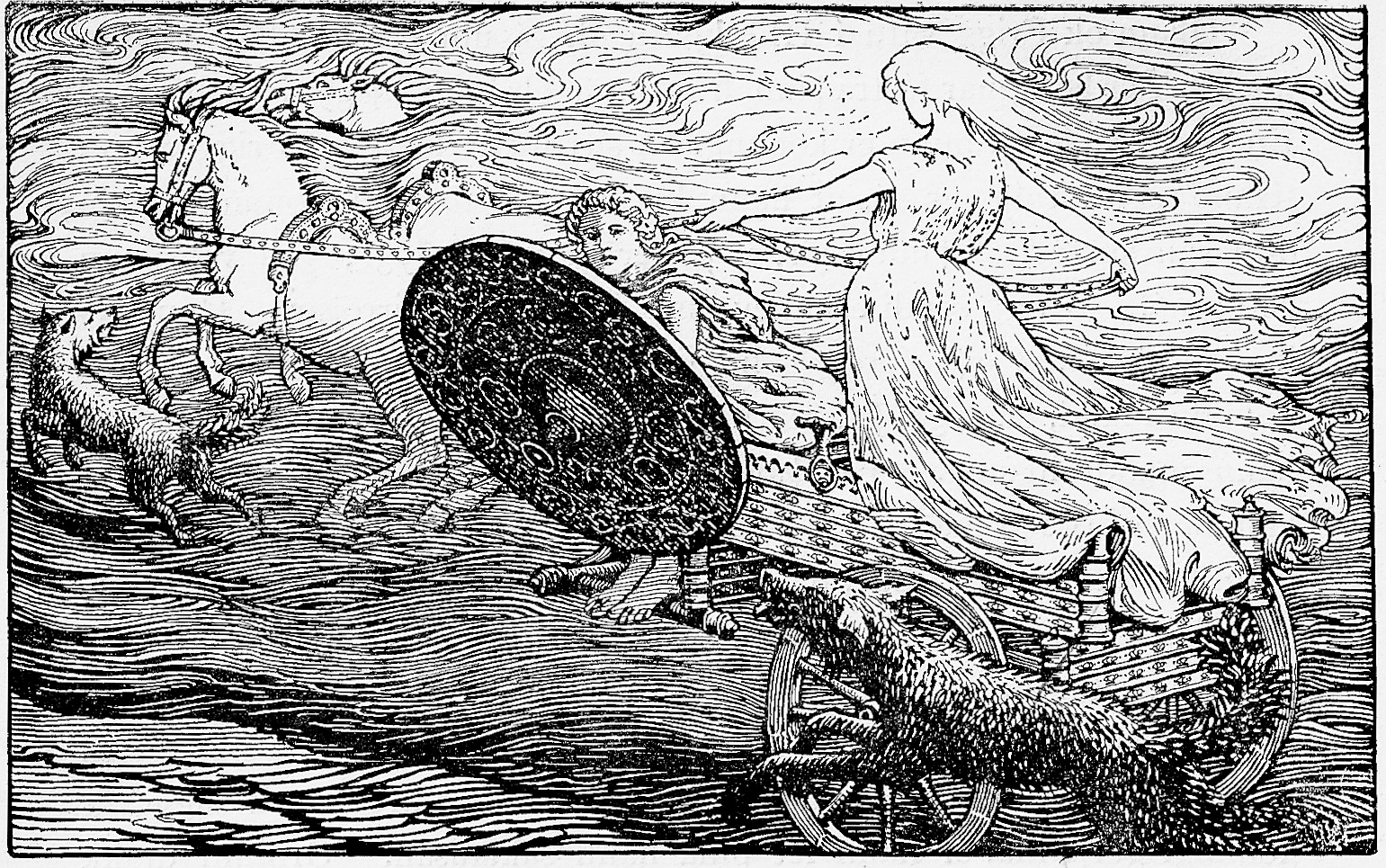 In a stanza of the poem ''
In a stanza of the poem ''

 Sól is referenced in the ''Prose Edda'' book ''
Sól is referenced in the ''Prose Edda'' book ''
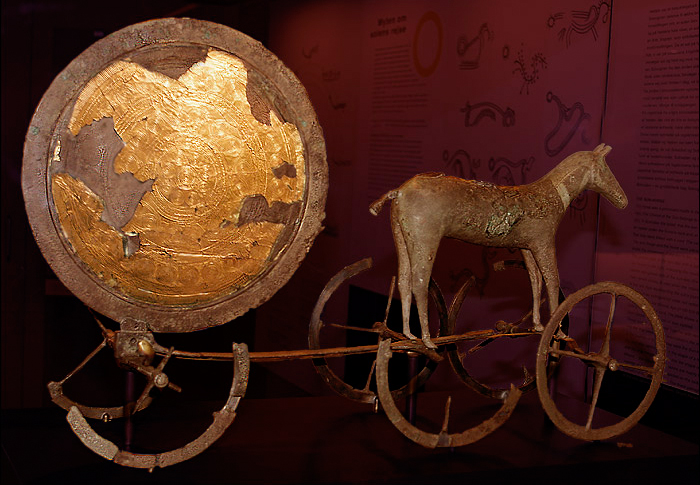 Scholars have proposed that Sól, as a goddess, may represent an extension of an earlier
Scholars have proposed that Sól, as a goddess, may represent an extension of an earlier
Norse Mythology: A Guide to the Gods, Heroes, Rituals, and Beliefs
'.
Old Norse
Old Norse, also referred to as Old Nordic or Old Scandinavian, was a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants ...
: , "Sun")Orchard (1997:152). or Sunna (Old High German
Old High German (OHG; ) is the earliest stage of the German language, conventionally identified as the period from around 500/750 to 1050. Rather than representing a single supra-regional form of German, Old High German encompasses the numerous ...
, and existing as an Old Norse and Icelandic synonym
A synonym is a word, morpheme, or phrase that means precisely or nearly the same as another word, morpheme, or phrase in a given language. For example, in the English language, the words ''begin'', ''start'', ''commence'', and ''initiate'' are a ...
: see Wiktionary sunna, "Sun") is the Sun personified in Germanic mythology
Germanic mythology consists of the body of myths native to the Germanic peoples, including Norse mythology, Anglo-Saxon paganism#Mythology, Anglo-Saxon mythology, and Continental Germanic mythology. It was a key element of Germanic paganism.
O ...
. One of the two Old High German
Old High German (OHG; ) is the earliest stage of the German language, conventionally identified as the period from around 500/750 to 1050. Rather than representing a single supra-regional form of German, Old High German encompasses the numerous ...
Merseburg Incantations
The Merseburg charms, Merseburg spells, or Merseburg incantations () are two medieval magic spells, charms or incantations, written in Old High German. They are the only known examples of Germanic pagan belief preserved in the language. They were ...
, written in the 9th or 10th century CE, attests that Sunna is the sister of Sinthgunt
Sinthgunt is a figure in Germanic mythology, attested solely in the Old High German 9th- or 10th-century "horse cure" Merseburg Incantation. In the incantation, Sinthgunt is referred to as the sister of the personified sun, Sunna (whose name is ...
. In Norse mythology
Norse, Nordic, or Scandinavian mythology, is the body of myths belonging to the North Germanic peoples, stemming from Old Norse religion and continuing after the Christianization of Scandinavia as the Nordic folklore of the modern period. The ...
, Sól is attested in the ''Poetic Edda
The ''Poetic Edda'' is the modern name for an untitled collection of Old Norse anonymous narrative poems in alliterative verse. It is distinct from the closely related ''Prose Edda'', although both works are seminal to the study of Old Norse ...
'', compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources, and the ''Prose Edda
The ''Prose Edda'', also known as the ''Younger Edda'', ''Snorri's Edda'' () or, historically, simply as ''Edda'', is an Old Norse textbook written in Iceland during the early 13th century. The work is often considered to have been to some exten ...
'', written in the 13th century by Snorri Sturluson
Snorri Sturluson ( ; ; 1179 – 22 September 1241) was an Icelandic historian, poet, and politician. He was elected twice as lawspeaker of the Icelandic parliament, the Althing. He is commonly thought to have authored or compiled portions of th ...
.
In both the ''Poetic Edda'' and the ''Prose Edda'' she is described as the sister of the personified moon, Máni
Máni (Old Norse: ; "Moon"Orchard (1997:109).) is the Lunar deity, Moon personified in Germanic mythology. Máni, personified, is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources, and the ''Prose Edd ...
, is the daughter of Mundilfari
In Norse mythology Mundilfari (Old Norse: ; rendered variously ''Mundilfari'', ''Mundilföri'' and ''Mundilfœri'') (Old Norse, possibly "the one moving according to particular times"Simek (2007:222).) is the father of Sól, goddess associated ...
, is at times referred to as '' Álfröðull'', and is foretold to be killed by a monstrous wolf during the events of Ragnarök
In Norse mythology, (also Ragnarok; or ; ) is a foretold series of impending events, including a great battle in which numerous great Norse mythological figures will perish (including the Æsir, gods Odin, Thor, Týr, Freyr, Heimdall, a ...
, though beforehand she will have given birth to a daughter who continues her mother's course through the heavens. In the ''Prose Edda'', she is additionally described as the wife of Glenr. As a proper noun
A proper noun is a noun that identifies a single entity and is used to refer to that entity ('' Africa''; ''Jupiter''; '' Sarah''; ''Walmart'') as distinguished from a common noun, which is a noun that refers to a class of entities (''continent, ...
, Sól appears throughout Old Norse literature. Scholars have produced theories about the development of the goddess from potential Nordic Bronze Age
The Nordic Bronze Age (also Northern Bronze Age, or Scandinavian Bronze Age) is a period of Scandinavian prehistory from .
The Nordic Bronze Age culture emerged about 1750 BC as a continuation of the Late Neolithic Dagger period, which is root ...
and Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists; its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-Euro ...
roots.
"Horse cure" Merseburg Incantation
One of the two Merseburg Incantations (the "horse cure"), recorded inOld High German
Old High German (OHG; ) is the earliest stage of the German language, conventionally identified as the period from around 500/750 to 1050. Rather than representing a single supra-regional form of German, Old High German encompasses the numerous ...
, mentions Sunna, who is described as having a sister, Sinthgunt
Sinthgunt is a figure in Germanic mythology, attested solely in the Old High German 9th- or 10th-century "horse cure" Merseburg Incantation. In the incantation, Sinthgunt is referred to as the sister of the personified sun, Sunna (whose name is ...
. The incantation describes how ''Phol'' and Wodan
Odin (; from ) is a widely revered god in Norse mythology and Germanic paganism. Most surviving information on Odin comes from Norse mythology, but he figures prominently in the recorded history of Northern Europe. This includes the Roman Emp ...
rode to a wood, and there Balder's foal
A foal is an equine up to one year old; this term is used mainly for horses, but can be used for donkeys. More specific terms are colt (horse), colt for a male foal and filly for a female foal, and are used until the horse is three or four. Whe ...
sprained its foot. Sinthgunt sang charms, her sister Sunna sang charms, '' Friia'' sang charms, her sister '' Volla'' sang charms, and finally Wodan sang charms, followed by a verse describing the healing of the foal's bone.Lindow (2001:227).
Norse attestations
''Poetic Edda''
In the poem ''Völuspá
''Völuspá'' (also ''Vǫluspá'', ''Vǫlospá'', or ''Vǫluspǫ́''; Old Norse: 'Prophecy of the völva, a seeress') is the best known poem of the ''Poetic Edda''. It dates back to the tenth century and tells the story from Norse Mythology of ...
'', a dead völva
In Germanic paganism, a seeress is a woman said to have the ability to foretell future events and perform sorcery. They are also referred to with many other names meaning "prophetess", "staff bearer" and "sorceress", and they are frequently calle ...
recounts the history of the universe and foretells the future to the disguised god Odin. In doing so, the völva recounts the early days of the universe, in which:
In the poem ''
Vafþrúðnismál
''Vafþrúðnismál'' (Old Norse: "The Lay of Vafþrúðnir") is the third poem in the ''Poetic Edda''. It is a conversation in verse form conducted initially between the Æsir Odin and Frigg, and subsequently between Odin and the jötunn Vafþrú ...
'', the god Odin
Odin (; from ) is a widely revered god in Norse mythology and Germanic paganism. Most surviving information on Odin comes from Norse mythology, but he figures prominently in the recorded history of Northern Europe. This includes the Roman Em ...
tasks the jötunn
A (also jotun; plural ; in the normalised scholarly spelling of Old Norse, ; or, in Old English, , plural ) is a type of being in Germanic mythology. In Norse mythology, are often contrasted with gods (the Æsir and Vanir) and with other no ...
Vafþrúðnir
Vafþrúðnir (Old Norse "mighty weaver"Orchard (1997:170).) is a wise jötunn in Norse mythology. His name comes from ''Vaf'', which means weave or entangle, and ''thrudnir'', which means strong or mighty. Some interpret it to mean "mighty in rid ...
with a question about the origins of the sun and the moon. Vafþrúðnir responds that Mundilfari
In Norse mythology Mundilfari (Old Norse: ; rendered variously ''Mundilfari'', ''Mundilföri'' and ''Mundilfœri'') (Old Norse, possibly "the one moving according to particular times"Simek (2007:222).) is the father of Sól, goddess associated ...
is the father of both Sól and Máni, and that they must pass through the heavens every day to count the years for man:
In a stanza ''Vafþrúðnismál'', Odin asks Vafþrúðnir from where another sun will come from once
Fenrir
Fenrir (Old Norse 'fen-dweller')Orchard (1997:42). or Fenrisúlfr (Old Norse "Fenrir's wolf", often translated "Fenris-wolf"),Simek (2007:81). also referred to as Hróðvitnir (Old Norse "fame-wolf")Simek (2007:160). and Vánagandr (Old Nors ...
has assailed the current sun. Vafþrúðnir responds in a further stanza, stating that before Álfröðull (Sól) is assailed by Fenrir, she will bear a daughter who will ride on her mother's paths after the events of Ragnarök.Larrington (1999:47).
Grímnismál
''Grímnismál'' (Old Norse: ; 'The Lay of Grímnir') is one of the mythological poems of the '' Poetic Edda''. It is preserved in the Codex Regius manuscript and the AM 748 I 4to fragment. It is spoken through the voice of ''Grímnir'', one ...
'', Odin says that before the Sun (referred to as "the shining god") is a shield named Svalinn, and if the shield were to fall from its frontal position, mountain and sea "would burn up". In stanza 39 Odin (disguised as '' Grimnir'') says that both the Sun and the Moon are pursued through the heavens by wolves; the Sun, referred to as the "bright bride" of the heavens, is pursued by Sköll
In Norse mythology, Sköll (Old Norse: , "Treachery"Orchard (1997:150). or "Mockery"Simek (2007:292)) is a wolf that, according to Snorri Sturluson's ''Prose Edda'', chases the Sun (personified as a goddess, Sól) riding her chariot across th ...
, while the Moon is pursued by Hati Hróðvitnisson
In Norse mythology, Hati Hróðvitnisson (first name meaning "He Who Hates", or "Enemy"Byock, Jesse. (Trans.) ''The Prose Edda'', page 164. (2006) Penguin Classics ) is a warg; a wolf that, according to Snorri Sturluson's ''Prose Edda'', chases ...
.Larrington (1999:57).
In the poem ''Alvíssmál
Alvíssmál (Old Norse: 'The Song of All-wise' or 'The Words of All-wise') is a poem collected in the ''Poetic Edda'', probably dating to the 12th century, that describes how the god Thor outwits a dwarf called Alvíss ("All-Wise") who seeks to ...
'', the god Thor
Thor (from ) is a prominent list of thunder gods, god in Germanic paganism. In Norse mythology, he is a hammer-wielding æsir, god associated with lightning, thunder, storms, sacred trees and groves in Germanic paganism and mythology, sacred g ...
questions the dwarf
Dwarf, dwarfs or dwarves may refer to:
Common uses
*Dwarf (folklore), a supernatural being from Germanic folklore
* Dwarf, a human or animal with dwarfism
Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities
* Dwarf (''Dungeons & Dragons''), a sh ...
Alvíss about the Sun, asking him what the Sun is called in each of the worlds. Alvíss responds that it is called "sun" by mankind, "sunshine" by the gods, " Dvalinn's deluder" by the dwarves, "everglow" by the jötnar, "the lovely wheel" by the elves
An elf (: elves) is a type of humanoid supernatural being in Germanic folklore. Elves appear especially in North Germanic mythology, being mentioned in the Icelandic ''Poetic Edda'' and the ''Prose Edda''.
In medieval Germanic-speakin ...
, and "all-shining" by the "sons of the Æsir
Æsir (Old Norse; singular: ) or ēse (Old English; singular: ) are deities, gods in Germanic paganism. In Old Nordic religion and Nordic mythology, mythology, the precise meaning of the term "" is debated, as it can refer either to the gods i ...
".Larrington (1999:111).
''Prose Edda''

 Sól is referenced in the ''Prose Edda'' book ''
Sól is referenced in the ''Prose Edda'' book ''Gylfaginning
''Gylfaginning'' (Old Norse: 'The Beguiling of Gylfi' or 'The Deluding of Gylfi'; 13th century Old Norse pronunciation ) is the first main part of the 13th century ''Prose Edda'', after the initial Prologue. The ''Gylfaginning'' takes the form of ...
'', where she is introduced in chapter 8 in a quote from stanza 5 of ''Völuspá''. In chapter 11 of ''Gylfaginning'', Gangleri (described as King Gylfi in disguise) asks the enthroned figure of High
High may refer to:
Science and technology
* Height
* High (atmospheric), a high-pressure area
* High (computability), a quality of a Turing degree, in computability theory
* High (tectonics), in geology an area where relative tectonic uplift t ...
how the Sun and Moon are steered. High describes that Sól is one of the two children of Mundilfari, and states that the children were so beautiful they were named after the Sun (Sól) and the Moon (Máni). Mundilfari has Sól married to a man named Glenr.
High says that the gods were "angered by this arrogance" and that the gods had the two placed in the heavens. There, the children were made to drive the horses Árvakr and Alsviðr that drew the chariot
A chariot is a type of vehicle similar to a cart, driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid Propulsion, motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk O ...
of the sun. High says that the gods had created the chariot to illuminate the worlds from burning embers flying from the fiery world of Muspelheim. In order to cool the horses, the gods placed two bellows
A bellows or pair of bellows is a device constructed to furnish a strong blast of air. The simplest type consists of a flexible bag comprising a pair of rigid boards with handles joined by flexible leather sides enclosing an approximately airtig ...
beneath their shoulders, and that "according to the same lore" these bellows are called Ísarnkol.Byock (2005:19–20).
In chapter 12 of ''Gylfaginning'', Gangleri tells High that the sun moves quickly, almost as if she were moving so quickly that she fears something, that she could not go faster even if she were afraid of her own death. High responds that "It is not surprising that she moves with such speed. The one chasing her comes close, and there is no escape for her except to run." Gangleri asks who chases her, to which High responds that two wolves give chase to Sól and Máni. The first wolf, Sköll
In Norse mythology, Sköll (Old Norse: , "Treachery"Orchard (1997:150). or "Mockery"Simek (2007:292)) is a wolf that, according to Snorri Sturluson's ''Prose Edda'', chases the Sun (personified as a goddess, Sól) riding her chariot across th ...
, chases Sól, and despite her fear, Sköll will eventually catch her. Hati Hróðvitnisson
In Norse mythology, Hati Hróðvitnisson (first name meaning "He Who Hates", or "Enemy"Byock, Jesse. (Trans.) ''The Prose Edda'', page 164. (2006) Penguin Classics ) is a warg; a wolf that, according to Snorri Sturluson's ''Prose Edda'', chases ...
, the second wolf, runs ahead of Sól to chase after Máni, whom Hati Hróðvitnisson will also catch. In chapter 35, Sól's status as a goddess is stated by High, along with Bil.Byock (2005:35).
In chapter 53, High says that after the events of Ragnarök
In Norse mythology, (also Ragnarok; or ; ) is a foretold series of impending events, including a great battle in which numerous great Norse mythological figures will perish (including the Æsir, gods Odin, Thor, Týr, Freyr, Heimdall, a ...
, Sól's legacy will be continued by a daughter that is no less beautiful than she, who will follow the path she once rode, and, in support, ''Vafþrúðnismál'' stanza 47 is then quoted.Byock (2005:78).
In the ''Prose Edda'' book ''Skáldskaparmál
''Skáldskaparmál'' (Old Norse: 'Poetic Diction' or 'The Language of Poetry'; ; ) is the second part of the ''Prose Edda'', compiled by Snorri Sturluson. It consists of a dialogue between Ægir, the divine personification of the sea, and Bra ...
'', Sól is first presented in chapter 93, where the kenning
A kenning ( Icelandic: ) is a figure of speech, a figuratively-phrased compound term that is used in place of a simple single-word noun. For instance, the Old English kenning () means , as does ().
A kenning has two parts: a base-word (a ...
s "daughter of Mundilfæri", "sister of Máni", "wife of Glen", "fire of sky and air" are given for her, followed by an excerpt of a work by the 11th century skald Skúli Þórsteinsson
Skúli Þórsteinsson was an 11th-century Icelandic poet and warrior. He was the grandson of Egill Skallagrímsson and a courtier of Jarl Eiríkr Hákonarson. A short account of his life is given at the end of ''Egils saga'':
:Of Thorstein's sons ...
:
:God-blithe bedfellow of Glen :steps to her divine sanctuary :with brightness; then descends the good :light of grey-clad moon.Faulkes (1995:93). Divided into four lines.In chapter 56, additional names for Sól are given; "day-star", "disc", "ever-glow", "all-bright seen", "fair-wheel", "grace-shine", " Dvalinn's toy", "elf-disc", "doubt-disc", and "ruddy".Faulkes (1995:133). Here '' Álfröðull'' is translated as "elf-disc". In chapter 58, following a list of horses, the horses Arvakr and Alsviðr are listed as drawing the sun,Faulkes (1995:137) and, in chapter 75, Sól is again included in a list of goddesses.Faulkes (1995:157).
Theories
 Scholars have proposed that Sól, as a goddess, may represent an extension of an earlier
Scholars have proposed that Sól, as a goddess, may represent an extension of an earlier Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists; its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-Euro ...
deity due to Indo-European linguistic connections between Norse ''Sól'', Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
''Surya
Surya ( ; , ) is the Sun#Dalal, Dalal, p. 399 as well as the solar deity in Hinduism. He is traditionally one of the major five deities in the Smarta tradition, Smarta tradition, all of whom are considered as equivalent deities in the Panchaya ...
'', Common Brittonic
Common Brittonic (; ; ), also known as British, Common Brythonic, or Proto-Brittonic, is a Celtic language historically spoken in Britain and Brittany from which evolved the later and modern Brittonic languages.
It is a form of Insular Cel ...
'' Sulis'', Lithuanian '' Saulė'', Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
'' Sol'', and Slavic '' Tsar Solnitse''.Mallory (1989:129).
Regarding Sól's attested personifications in Norse mythology, John Lindow
John Frederick Lindow (born July 23, 1946) is an American philologist who is Professor Emeritus of Old Norse and Folklore at University of California, Berkeley. He is a well known authority on Old Norse religion and literature.
Biography
John Lin ...
states that "even kenning
A kenning ( Icelandic: ) is a figure of speech, a figuratively-phrased compound term that is used in place of a simple single-word noun. For instance, the Old English kenning () means , as does ().
A kenning has two parts: a base-word (a ...
s like 'hall of the sun' for sky may not suggest personification, given the rules of kenning formation"; that in poetry only stanzas associated with Sól in the poem ''Vafþrúðnismál'' are certain in their personification of the goddess; and "that Sól is female and Máni male probably has to do with the grammatical gender of the nouns: Sól is feminine and Máni is masculine." Lindow states that, while the Sun seems to have been a focus of older Scandinavian religious practices, it is difficult to make a case for the placement of the sun in a central role in surviving sources for Norse mythology.Lindow (2001:198–199).
Rudolf Simek
Rudolf Simek (born 21 February 1954) is an Austrian philologist and religious studies scholar who is Professor and Chair of Ancient German and Nordic Studies at the University of Bonn. Simek specializes in Germanic studies, and is the author ...
states that Nordic Bronze Age
The Nordic Bronze Age (also Northern Bronze Age, or Scandinavian Bronze Age) is a period of Scandinavian prehistory from .
The Nordic Bronze Age culture emerged about 1750 BC as a continuation of the Late Neolithic Dagger period, which is root ...
archaeological finds, such as rock carvings and the Trundholm sun chariot, provide ample evidence of the Sun having been viewed as a life-giving heavenly body to the Bronze Age Scandinavians, and that the Sun likely always received an amount of veneration. Simek states that the only evidence of the Sun assuming a personification stems from the Old High German Incantation reference and from ''Poetic Edda'' poems, and that both of these references do not provide enough information to assume a Germanic sun cult. "On the other hand", Simek posits, the "great age of the concept is evident" by the Trundholm sun chariot, which specifically supports the notion of the Sun being drawn across the sky by horses. Simek further theorizes that the combination of sun symbols with ships in religious practices, which occur with frequency from the Bronze Age into Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, seem to derive from religious practices surrounding a fertility god (such as the Vanir
In Norse mythology, the Vanir (; Old Norse:, singular Vanr) are a group of gods associated with fertility, wisdom, and the ability to see the future. The Vanir are one of two groups of gods (the other being the Æsir) and are the namesake of the ...
gods Njörðr
In Norse mythology, Njörðr (Old Norse: ) is a god among the Vanir. Njörðr, father of the deities Freyr and Freyja by Sister-wife of Njörðr, his unnamed sister, was in an ill-fated marriage with the goddess Skaði, lives in Nóatún (myth ...
or Freyr
Freyr (Old Norse: 'Lord'), sometimes anglicized as Frey, is a widely attested Æsir, god in Norse mythology, associated with kingship, fertility, peace, prosperity, fair weather, and good harvest. Freyr, sometimes referred to as Yngvi-Freyr, was ...
), and not to a personified sun.Simek (2007:297).
See also
*Dagr
Dagr (Old Norse 'day')Lindow (2001:91). is the divine personification of the day in Norse mythology. He appears in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources, and the ''Prose Edda'', written in the 13th cen ...
, the personified day in Norse mythology
* Solveig, an Old Norse female given name that may involve the Sun
* Sowilo rune, the ''s'' rune
Runes are the letters in a set of related alphabets, known as runic rows, runic alphabets or futharks (also, see '' futhark'' vs ''runic alphabet''), native to the Germanic peoples. Runes were primarily used to represent a sound value (a ...
, named after the Sun
* Sunday
Sunday (Latin: ''dies solis'' meaning "day of the sun") is the day of the week between Saturday and Monday. Sunday is a Christian sabbath, day of rest in most Western countries and a part of the Workweek and weekend, weekend. In some Middle Ea ...
, a day of the week named after the Sun in Germanic societies
* List of solar deities
Notes
References
* Bellows, Henry Adams (1923). ''The Poetic Edda''.The American-Scandinavian Foundation
The American-Scandinavian Foundation (ASF) is an American non-profit foundation dedicated to promoting international understanding through educational and cultural exchange between the United States and Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Swe ...
* Byock, Jesse (Trans.) (2005). ''The Prose Edda''. Penguin Classics
Penguin Classics is an imprint (trade name), imprint of Penguin Books under which classic works of literature are published in English language, English, Spanish language, Spanish, Portuguese language, Portuguese, and Korean language, Korean amon ...
.
* Mallory, J.P. (1989). ''In Search of the Indo-Europeans: Language, Archaeology and Myth.'' Thames & Hudson
Thames & Hudson (sometimes T&H for brevity) is a publisher of illustrated books in all visually creative categories: art, architecture, design, photography, fashion, film, and the performing arts. It also publishes books on archaeology, history, ...
.
* Faulkes, Anthony (Trans.) (1995). ''Edda''. Everyman
The everyman is a stock character of fiction. An ordinary and humble character, the everyman is generally a protagonist whose benign conduct fosters the audience's identification with them.
Origin and history
The term ''everyman'' was used ...
.
* Larrington, Carolyne (Trans.) (1999). ''The Poetic Edda''. Oxford World's Classics
Oxford World's Classics is an imprint of Oxford University Press. First established in 1901 by Grant Richards and purchased by OUP in 1906, this imprint publishes primarily dramatic and classic literature for students and the general public. ...
.
* Lindow, John (2001). Norse Mythology: A Guide to the Gods, Heroes, Rituals, and Beliefs
'.
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books ...
. .
* Orchard, Andy (1997). ''Dictionary of Norse Myth and Legend''. Cassell.
* Simek, Rudolf (2007) translated by Angela Hall. ''Dictionary of Northern Mythology''. D.S. Brewer.
* Thorpe, Benjamin (Trans.) (1907). ''The Elder Edda of Saemund Sigfusson''. Norrœna Society.
Further reading
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Sol (Sun) Germanic goddesses Solar goddesses Ásynjur Personifications in Norse mythology Personifications