Syphilis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Tertiary syphilis may occur approximately 3 to 15 years after the initial infection and may be divided into three different forms: gummatous syphilis (15%), late neurosyphilis (6.5%), and cardiovascular syphilis (10%). Without treatment, a third of infected people develop tertiary disease. People with tertiary syphilis are not infectious.
Gummatous syphilis or late
Tertiary syphilis may occur approximately 3 to 15 years after the initial infection and may be divided into three different forms: gummatous syphilis (15%), late neurosyphilis (6.5%), and cardiovascular syphilis (10%). Without treatment, a third of infected people develop tertiary disease. People with tertiary syphilis are not infectious.
Gummatous syphilis or late
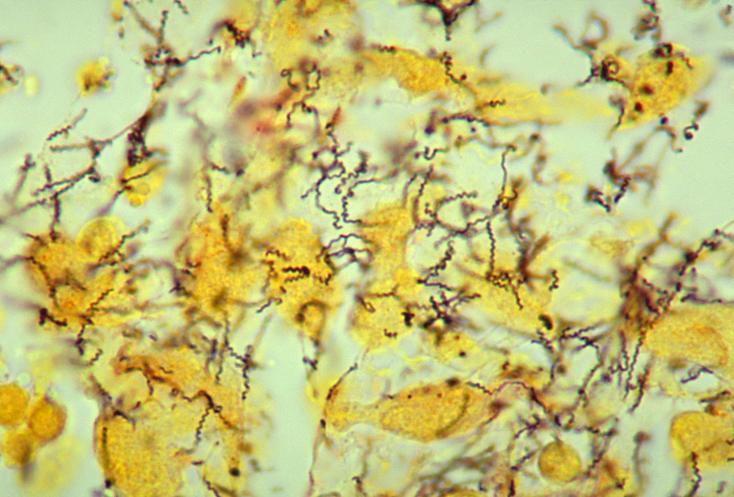 ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum'' is a spiral-shaped,
''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum'' is a spiral-shaped,
 Syphilis is difficult to diagnose clinically during early infection. Confirmation is either via
Syphilis is difficult to diagnose clinically during early infection. Confirmation is either via
 In 2012, about 0.5% of adults were infected with syphilis, with 6 million new cases. In 1999, it is believed to have infected 12 million additional people, with greater than 90% of cases in the
In 2012, about 0.5% of adults were infected with syphilis, with 6 million new cases. In 1999, it is believed to have infected 12 million additional people, with greater than 90% of cases in the
 In 2020, a group of leading paleopathologists concluded that enough evidence had been collected to prove that treponemal disease, almost certainly including syphilis, had existed in Europe prior to the voyages of Columbus. There is an outstanding issue, however. Damaged teeth and bones may seem to hold proof of pre-Columbian syphilis, but there is a possibility that they point to an endemic form of treponemal disease instead. As syphilis, bejel, and yaws vary considerably in mortality rates and the level of human disease they elicit, it is important to know which one is under discussion in any given case, but it remains difficult for paleopathologists to distinguish among them. (The fourth of the treponemal diseases is pinta, a skin disease and therefore unrecoverable through paleopathology.) Ancient
In 2020, a group of leading paleopathologists concluded that enough evidence had been collected to prove that treponemal disease, almost certainly including syphilis, had existed in Europe prior to the voyages of Columbus. There is an outstanding issue, however. Damaged teeth and bones may seem to hold proof of pre-Columbian syphilis, but there is a possibility that they point to an endemic form of treponemal disease instead. As syphilis, bejel, and yaws vary considerably in mortality rates and the level of human disease they elicit, it is important to know which one is under discussion in any given case, but it remains difficult for paleopathologists to distinguish among them. (The fourth of the treponemal diseases is pinta, a skin disease and therefore unrecoverable through paleopathology.) Ancient
 The earliest known depiction of an individual with syphilis is
The earliest known depiction of an individual with syphilis is
 The "Tuskegee Study of Untreated Syphilis in the Negro Male" was an infamous, unethical and racist
The "Tuskegee Study of Untreated Syphilis in the Negro Male" was an infamous, unethical and racist
"Syphilis - CDC Fact Sheet"
UCSF HIV InSite Knowledge Base Chapter: Syphilis and HIV
Recommendations for Public Health Surveillance of Syphilis in the United States
* {{Authority control Bacterial diseases Bacterium-related cutaneous conditions Infectious diseases Infectious diseases with eradication efforts Infections with a predominantly sexual mode of transmission Sexually transmitted diseases and infections Spirochaetes Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate (full) Wikipedia infectious disease articles ready to translate
Syphilis () is a
 Primary syphilis is typically acquired by direct sexual contact with the infectious lesions of another person. Approximately 2–6 weeks after contact (with a range of 10–90 days) a skin lesion, called a chancre, appears at the site and this contains infectious bacteria. This is classically (40% of the time) a single, firm, painless, non-itchy skin ulceration with a clean base and sharp borders approximately 0.3–3.0 cm in size. The lesion may take on almost any form. In the classic form, it evolves from a macule to a
Primary syphilis is typically acquired by direct sexual contact with the infectious lesions of another person. Approximately 2–6 weeks after contact (with a range of 10–90 days) a skin lesion, called a chancre, appears at the site and this contains infectious bacteria. This is classically (40% of the time) a single, firm, painless, non-itchy skin ulceration with a clean base and sharp borders approximately 0.3–3.0 cm in size. The lesion may take on almost any form. In the classic form, it evolves from a macule to a
, mucous membranes, and lymph nodes. There may be a symmetrical, reddish-pink, non-itchy sexually transmitted infection
A sexually transmitted infection (STI), also referred to as a sexually transmitted disease (STD) and the older term venereal disease (VD), is an infection that is Transmission (medicine), spread by Human sexual activity, sexual activity, e ...
caused by the bacterium
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the ...
''Treponema pallidum
''Treponema pallidum'', formerly known as ''Spirochaeta pallida'', is a Microaerophile, microaerophilic, Gram-negative bacteria, gram-negative, spirochaete bacterium with subspecies that cause the diseases syphilis, bejel (also known as endemic ...
'' subspecies
In Taxonomy (biology), biological classification, subspecies (: subspecies) is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (Morphology (biology), morpholog ...
''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms depend on the stage it presents: primary, secondary, latent or tertiary. The primary stage classically presents with a single chancre (a firm, painless, non-itchy skin ulceration usually between 1 cm and 2 cm in diameter), though there may be multiple sores. In secondary syphilis, a diffuse rash
A rash is a change of the skin that affects its color, appearance, or texture.
A rash may be localized in one part of the body, or affect all the skin. Rashes may cause the skin to change color, itch, become warm, bumpy, chapped, dry, cracke ...
occurs, which frequently involves the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There may also be sores in the mouth or vagina. Latent syphilis has no symptoms and can last years. In tertiary syphilis, there are gummas (soft, non-cancerous growths), neurological problems, or heart symptoms. Syphilis has been known as " the great imitator", because it may cause symptoms similar to many other diseases.
Syphilis is most commonly spread through sexual activity
Human sexual activity, human sexual practice or human sexual behaviour is the manner in which humans experience and express their sexuality. People engage in a variety of sexual acts, ranging from activities done alone (e.g., masturbation) t ...
. It may also be transmitted from mother to baby during pregnancy or at birth, resulting in congenital syphilis
Congenital syphilis is syphilis that occurs when a mother with untreated syphilis passes the infection to her baby during pregnancy or at childbirth, birth. It may present in the fetus, infant, or later. Clinical features vary and differ between ...
. Other diseases caused by '' Treponema'' bacteria include yaws ('' T. pallidum'' subspecies ''pertenue''), pinta ('' T. carateum''), and nonvenereal endemic syphilis (''T. pallidum'' subspecies ''endemicum''). These three diseases are not typically sexually transmitted. Diagnosis is usually made by using blood tests
A blood test is a laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose test or a cho ...
; the bacteria can also be detected using dark field microscopy
Dark-field microscopy, also called dark-ground microscopy, describes microscopy methods, in both light microscopy, light and electron microscopy, which exclude the unscattered beam from the image. Consequently, the field around the specimen (i.e ...
. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
(U.S.) recommends for all pregnant women to be tested.
The risk of sexual transmission of syphilis can be reduced by using a latex
Latex is an emulsion (stable dispersion) of polymer microparticles in water. Latices are found in nature, but synthetic latices are common as well.
In nature, latex is found as a wikt:milky, milky fluid, which is present in 10% of all floweri ...
or polyurethane
Polyurethane (; often abbreviated PUR and PU) is a class of polymers composed of organic chemistry, organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethane term ...
condom
A condom is a sheath-shaped Barrier contraception, barrier device used during sexual intercourse to reduce the probability of pregnancy or a Sexually transmitted disease, sexually transmitted infection (STI). There are both external condo ...
. Syphilis can be effectively treated with antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
. The preferred antibiotic for most cases is benzathine benzylpenicillin injected into a muscle. In those who have a severe penicillin allergy, doxycycline
Doxycycline is a Broad-spectrum antibiotic, broad-spectrum antibiotic of the Tetracycline antibiotics, tetracycline class used in the treatment of infections caused by bacteria and certain parasites. It is used to treat pneumonia, bacterial p ...
or tetracycline may be used. In those with neurosyphilis, intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutr ...
benzylpenicillin or ceftriaxone is recommended. During treatment, people may develop fever, headache, and muscle pains, a reaction known as Jarisch–Herxheimer.
In 2015, about 45.4 million people had syphilis infections, of which six million were new cases. During 2015, it caused about 107,000 deaths, down from 202,000 in 1990. After decreasing dramatically with the availability of penicillin in the 1940s, rates of infection have increased since the turn of the millennium in many countries, often in combination with human immunodeficiency virus
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause AIDS, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of th ...
(HIV). This is believed to be partly due to unsafe drug use, increased prostitution
Prostitution is a type of sex work that involves engaging in sexual activity in exchange for payment. The definition of "sexual activity" varies, and is often defined as an activity requiring physical contact (e.g., sexual intercourse, no ...
, and decreased use of condom
A condom is a sheath-shaped Barrier contraception, barrier device used during sexual intercourse to reduce the probability of pregnancy or a Sexually transmitted disease, sexually transmitted infection (STI). There are both external condo ...
s.
Signs and symptoms
Syphilis canpresent
The present is the period of time that is occurring now. The present is contrasted with the past, the period of time that has already occurred; and the future, the period of time that has yet to occur.
It is sometimes represented as a hyperplan ...
in one of four different stages: primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary, and may also occur congenital
A birth defect is an abnormal condition that is present at childbirth, birth, regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disability, disabilities that may be physical disability, physical, intellectual disability, intellectual, or dev ...
ly. There may be no symptoms. It was referred to as "the great imitator" by Sir William Osler due to its varied presentations.
Primary
 Primary syphilis is typically acquired by direct sexual contact with the infectious lesions of another person. Approximately 2–6 weeks after contact (with a range of 10–90 days) a skin lesion, called a chancre, appears at the site and this contains infectious bacteria. This is classically (40% of the time) a single, firm, painless, non-itchy skin ulceration with a clean base and sharp borders approximately 0.3–3.0 cm in size. The lesion may take on almost any form. In the classic form, it evolves from a macule to a
Primary syphilis is typically acquired by direct sexual contact with the infectious lesions of another person. Approximately 2–6 weeks after contact (with a range of 10–90 days) a skin lesion, called a chancre, appears at the site and this contains infectious bacteria. This is classically (40% of the time) a single, firm, painless, non-itchy skin ulceration with a clean base and sharp borders approximately 0.3–3.0 cm in size. The lesion may take on almost any form. In the classic form, it evolves from a macule to a papule
A papule is a small, well-defined bump in the skin lesion, skin. It may have a rounded, pointed or flat top, and may have a umbilication, dip. It can appear with a Peduncle (anatomy), stalk, be thread-like or look warty. It can be soft or firm a ...
and finally to an erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as Surface runoff, water flow or wind) that removes soil, Rock (geology), rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust#Crust, Earth's crust and then sediment transport, tran ...
or ulcer
An ulcer is a discontinuity or break in a bodily membrane that impedes normal function of the affected organ. According to Robbins's pathology, "ulcer is the breach of the continuity of skin, epithelium or mucous membrane caused by sloughin ...
. Occasionally, multiple lesions may be present (~40%), with multiple lesions being more common when coinfected with HIV. Lesions may be painful or tender (30%), and they may occur in places other than the genitals (2–7%). The most common location in women is the cervix
The cervix (: cervices) or cervix uteri is a dynamic fibromuscular sexual organ of the female reproductive system that connects the vagina with the uterine cavity. The human female cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the time ...
(44%), the penis
A penis (; : penises or penes) is a sex organ through which male and hermaphrodite animals expel semen during copulation (zoology), copulation, and through which male placental mammals and marsupials also Urination, urinate.
The term ''pen ...
in heterosexual men (99%), and anally and rectal
The rectum (: rectums or recta) is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the Gastrointestinal tract, gut in others. Before expulsion through the anus or cloaca, the rectum stores the feces te ...
ly in men who have sex with men
Men who have sex with men (MSM) are men who engage in sexual activity with other men, regardless of their sexual orientation or sexual identity. The term was created by epidemiologists in the 1990s, to better study and communicate the spre ...
(34%). Lymph node enlargement frequently (80%) occurs around the area of infection, occurring seven to 10 days after chancre formation. The lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by injury or diseases. The term ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin meaning "injury". Lesions may occur in both plants and animals.
Types
There is no de ...
may persist for three to six weeks if left untreated.
Secondary
upright=1.4, Reddish nodules over much of the body due to secondary syphilis">nodule_(dermatology)#Primary_lesions.html" ;"title="papules and nodule (dermatology)#Primary lesions">nodules over much of the body due to secondary syphilis Secondary syphilis occurs approximately four to ten weeks after the primary infection. While secondary disease is known for the many different ways it can manifest, symptoms most commonly involve the Human skin">skin Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation. Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...rash
A rash is a change of the skin that affects its color, appearance, or texture.
A rash may be localized in one part of the body, or affect all the skin. Rashes may cause the skin to change color, itch, become warm, bumpy, chapped, dry, cracke ...
on the trunk and extremities, including the palms and soles. The rash may become maculopapular or pustular
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body, usually caused by bacterial infection. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pre ...
. It may form flat, broad, whitish, wart-like lesions on mucous membranes, known as condyloma latum. All of these lesions harbor bacteria and are infectious. Other symptoms may include fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
, sore throat
Sore throat, also known as throat pain, is pain or irritation of the throat. The majority of sore throats are caused by a virus, for which antibiotics are not helpful.
For sore throat caused by bacteria (GAS), treatment with antibiotics may hel ...
, malaise
In medicine, malaise is a feeling of general discomfort, uneasiness or lack of wellbeing and often the first sign of an infection or other disease. It is considered a vague termdescribing the state of simply not feeling well. The word has exist ...
, weight loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, by a mean loss of fluid, body fat (adipose tissue), or lean mass (namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other conn ...
, hair loss
Hair loss, also known as alopecia or baldness, refers to a loss of hair from part of the head or body. Typically at least the head is involved. The severity of hair loss can vary from a small area to the entire body. Inflammation or scarring ...
, and headache
A headache, also known as cephalalgia, is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of Depression (mood), depression in those with severe ...
. Rare manifestations include liver inflammation, kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and rig ...
disease, joint inflammation, periostitis, inflammation of the optic nerve, uveitis
Uveitis () is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and ...
, and interstitial keratitis. The acute symptoms usually resolve after three to six weeks; about 25% of people may present with a recurrence of secondary symptoms. Many people who present with secondary syphilis (40–85% of women, 20–65% of men) do not report previously having had the classical chancre of primary syphilis.
Latent
Latent syphilis is defined as having serologic proof of infection without symptoms of disease. It develops after secondary syphilis and is divided into early latent and late latent stages. Early latent syphilis is defined by theWorld Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
as less than 2 years after original infection. Early latent syphilis is infectious as up to 25% of people can develop a recurrent secondary infection (during which bacteria are actively replicating and are infectious). Two years after the original infection the person will enter late latent syphilis and is not as infectious as in the early phase. The latent phase of syphilis can last many years after which, without treatment, approximately 15–40% of people can develop tertiary syphilis.
Tertiary
benign
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer.
A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous benign tumor, ''benign'' tumor in that a malig ...
syphilis usually occurs 1 to 46 years after the initial infection, with an average of 15 years. This stage is characterized by the formation of chronic gummas, which are soft, tumor-like balls of inflammation which may vary considerably in size. They typically affect the skin, bone, and liver, but can occur anywhere.
Cardiovascular syphilis usually occurs 10–30 years after the initial infection. The most common complication is syphilitic aortitis, which may result in aortic aneurysm formation.
Neurosyphilis refers to an infection involving the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
. Involvement of the central nervous system in syphilis (either asymptomatic or symptomatic) can occur at any stage of the infection. It may occur early, being either asymptomatic or in the form of syphilitic meningitis; or late as meningovascular syphilis, manifesting as general paresis or tabes dorsalis.
Meningovascular syphilis involves inflammation of the small and medium arteries of the central nervous system. It can present between 1–10 years after the initial infection. Meningovascular syphilis is characterized by stroke, cranial nerve palsies and spinal cord inflammation. Late symptomatic neurosyphilis can develop decades after the original infection and includes 2 types; general paresis and tabes dorsalis. General paresis presents with dementia, personality changes, delusions, seizures, psychosis and depression. Tabes dorsalis is characterized by gait instability, sharp pains in the trunk and limbs, impaired positional sensation of the limbs as well as having a positive Romberg's sign. Both tabes dorsalis and general paresis may present with Argyll Robertson pupil which are pupils that constrict when the person focuses on near objects ( accommodation reflex) but do not constrict when exposed to bright light ( pupillary reflex).
Congenital
Congenital syphilis is that which is transmitted during pregnancy or during birth. Two-thirds of syphilitic infants are born without symptoms. Common symptoms that develop over the first couple of years of life include enlargement of the liver and spleen (70%), rash (70%), fever (40%), neurosyphilis (20%), and lung inflammation (20%). If untreated, late congenital syphilis may occur in 40%, including saddle nose deformation, Higouménakis' sign, saber shin, or Clutton's joints among others. Infection during pregnancy is also associated withmiscarriage
Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spontaneous abortion, is an end to pregnancy resulting in the loss and expulsion of an embryo or fetus from the womb before it can fetal viability, survive independently. Miscarriage before 6 weeks ...
. The main dental defects seen in congenital syphilis are the peg-shaped, notched incisors known as Hutchinson's teeth
Hutchinson's teeth is a sign of congenital syphilis. Affected people have Human tooth, teeth that are smaller and more widely spaced than normal and which have notches on their biting surfaces.
It is named for Jonathan Hutchinson, Sir Jonathan ...
and so-called mulberry molars (also known as Moon or Fournier molars), defective permanent molars with rounded, deformed crowns resembling a mulberry
''Morus'', a genus of flowering plants in the family Moraceae, consists of 19 species of deciduous trees commonly known as mulberries, growing wild and under cultivation in many temperate world regions. Generally, the genus has 64 subordinat ...
.
Cause
Bacteriology
 ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum'' is a spiral-shaped,
''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum'' is a spiral-shaped, Gram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelope consists ...
, highly mobile bacterium. Two other human diseases are caused by related ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies, yaws (subspecies ''pertenue'') and bejel (subspecies ''endemicum''), and one further caused by the very closely related ''Treponema carateum'', pinta. Unlike subspecies ''pallidum'', they do not cause neurological disease. Humans are the only known natural reservoir
In Infection, infectious disease ecology and epidemiology, a natural reservoir, also known as a disease reservoir or a reservoir of infection, is the population of organisms or the specific environment in which an infectious pathogen naturally li ...
for subspecies ''pallidum''. It is unable to survive more than a few days without a host. This is due to its small genome (1.14 Mbp) failing to encode the metabolic pathways necessary to make most of its macronutrients. It has a slow doubling time of greater than 30 hours. The bacterium is known for its ability to evade the immune system and its invasiveness.
Transmission
Syphilis is transmitted primarily by sexual contact or duringpregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
from a mother to her baby; the bacterium is able to pass through intact mucous membranes or compromised skin. It is thus transmissible by kissing near a lesion, as well as manual, oral
The word oral may refer to:
Relating to the mouth
* Relating to the mouth, the first portion of the alimentary canal that primarily receives food and liquid
**Oral administration of medicines
** Oral examination (also known as an oral exam or ora ...
, vaginal, and anal sex
Anal sex or anal intercourse principally means the insertion and pelvic thrusting, thrusting of the Erection, erect human penis, penis into a person's Human anus, anus, or anus and rectum, for sexual pleasure.Sepages 270–271for anal sex inform ...
. Approximately 30% to 60% of those exposed to primary or secondary syphilis will get the disease. Its infectivity
In epidemiology, infectivity is the ability of a pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be refer ...
is exemplified by the fact that an individual inoculated with only 57 organisms has a 50% chance of being infected. Most new cases in the United States (60%) occur in men who have sex with men; and in this population 20% of syphilis cases were due to oral sex alone. Syphilis can be transmitted by blood products, but the risk is low due to screening of donated blood in many countries. The risk of transmission from sharing needles appears to be limited.
It is not generally possible to contract syphilis through toilet seats, daily activities, hot tubs, or sharing eating utensils or clothing. This is mainly because the bacteria die very quickly outside of the body, making transmission by objects extremely difficult.
Diagnosis
 Syphilis is difficult to diagnose clinically during early infection. Confirmation is either via
Syphilis is difficult to diagnose clinically during early infection. Confirmation is either via blood tests
A blood test is a laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose test or a cho ...
or direct visual inspection using dark field microscopy
Dark-field microscopy, also called dark-ground microscopy, describes microscopy methods, in both light microscopy, light and electron microscopy, which exclude the unscattered beam from the image. Consequently, the field around the specimen (i.e ...
. Blood tests are more commonly used, as they are easier to perform. Diagnostic tests are unable to distinguish between the stages of the disease.
Blood tests
Blood tests are divided into nontreponemal and treponemal tests. Nontreponemal tests are used initially and include venereal disease research laboratory (VDRL) and rapid plasma reagin (RPR) tests.False positives
A false positive is an error in binary classification in which a test result incorrectly indicates the presence of a condition (such as a disease when the disease is not present), while a false negative is the opposite error, where the test res ...
on the nontreponemal tests can occur with some viral infections, such as varicella (chickenpox) and measles
Measles (probably from Middle Dutch or Middle High German ''masel(e)'', meaning "blemish, blood blister") is a highly contagious, Vaccine-preventable diseases, vaccine-preventable infectious disease caused by Measles morbillivirus, measles v ...
. False positives can also occur with lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). The name typically refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enlarged lymph node ...
, tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
, malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
, endocarditis
Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium. It usually involves the heart valves. Other structures that may be involved include the interventricular septum, the chordae tendineae, the mural endocardium, o ...
, connective tissue disease, and pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
.
Because of the possibility of false positives with nontreponemal tests, confirmation is required with a treponemal test, such as ''Treponema pallidum'' particle agglutination assay (TPHA) or fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption test (FTA-Abs). Treponemal antibody tests usually become positive two to five weeks after the initial infection and remain positive for many years. Neurosyphilis is diagnosed by finding high numbers of leukocytes
White blood cells (scientific name leukocytes), also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign entities. White blood cells are genera ...
(predominately lymphocytes
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells (for cell-mediated and cytotoxic adaptive immunity), B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity), and ...
) and high protein levels in the cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ven ...
in the setting of a known syphilis infection.
Direct testing
Dark field microscopy
Dark-field microscopy, also called dark-ground microscopy, describes microscopy methods, in both light microscopy, light and electron microscopy, which exclude the unscattered beam from the image. Consequently, the field around the specimen (i.e ...
of serous fluid from a chancre may be used to make an immediate diagnosis. Hospitals do not always have equipment or experienced staff members, and testing must be done within 10 minutes of acquiring the sample. Two other tests can be carried out on a sample from the chancre: direct fluorescent antibody (DFA) and polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to make millions to billions of copies of a specific DNA sample rapidly, allowing scientists to amplify a very small sample of DNA (or a part of it) sufficiently to enable detailed st ...
(PCR) tests. DFA uses antibodies
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that caus ...
tagged with fluorescein
Fluorescein is an organic compound and dye based on the xanthene tricyclic structural motif, formally belonging to Triarylmethane dye, triarylmethine dyes family. It is available as a dark orange/red powder slightly soluble in water and alcohol. ...
, which attach to specific syphilis proteins, while PCR uses techniques to detect the presence of specific syphilis gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
s. These tests are not as time-sensitive, as they do not require living bacteria to make the diagnosis.
Prevention
Vaccine
, there is novaccine
A vaccine is a biological Dosage form, preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verifi ...
effective for prevention. Several vaccines based on treponemal proteins reduce lesion development in an animal model but research continues.
Sex
Condom
A condom is a sheath-shaped Barrier contraception, barrier device used during sexual intercourse to reduce the probability of pregnancy or a Sexually transmitted disease, sexually transmitted infection (STI). There are both external condo ...
use reduces the likelihood of transmission during sex, but does not eliminate the risk. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
(CDC) states, "Correct and consistent use of latex condoms can reduce the risk of syphilis only when the infected area or site of potential exposure is protected. However, a syphilis sore outside of the area covered by a latex condom can still allow transmission, so caution should be exercised even when using a condom."
Abstinence
Abstinence is the practice of self-enforced restraint from indulging in bodily activities that are widely experienced as giving pleasure. Most frequently, the term refers to sexual abstinence, but it can also mean abstinence from alcohol (drug), ...
from intimate physical contact with an infected person is effective at reducing the transmission of syphilis. The CDC states, "The surest way to avoid transmission of sexually transmitted diseases, including syphilis, is to abstain from sexual contact or to be in a long-term mutually monogamous
Monogamy ( ) is a relationship of two individuals in which they form a mutual and exclusive intimate partnership. Having only one partner at any one time, whether for life or serial monogamy, contrasts with various forms of non-monogamy (e.g. ...
relationship with a partner who has been tested and is known to be uninfected."
Congenital disease
Congenital syphilis in the newborn can be prevented by screening mothers during early pregnancy and treating those who are infected. TheUnited States Preventive Services Task Force
The United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) is "an independent panel of experts in primary care and prevention that systematically reviews the evidence of effectiveness and develops recommendations for clinical preventive services". ...
(USPSTF) strongly recommends universal screening of all pregnant women, while the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
(WHO) recommends all women be tested at their first antenatal visit and again in the third trimester. If they are positive, it is recommended their partners also be treated. Congenital syphilis is still common in the developing world, as many women do not receive antenatal care at all, and the antenatal care others receive does not include screening. It still occasionally occurs in the developed world, as those most likely to acquire syphilis are least likely to receive care during pregnancy. Several measures to increase access to testing appear effective at reducing rates of congenital syphilis in low- to middle-income countries. Point-of-care testing to detect syphilis appeared to be reliable, although more research is needed to assess its effectiveness and into improving outcomes in mothers and babies.
Screening
The CDC recommends that sexually active men who have sex with men be tested at least yearly. The USPSTF also recommends screening among those at high risk. Syphilis is anotifiable disease
A notifiable disease is any disease that is required by law to be reported to government authorities. The collation of information allows the authorities to monitor the disease, and provides early warning of possible outbreaks. In the case of lives ...
in many countries, including Canada, the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
, and the United States. This means health care providers are required to notify public health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the de ...
authorities, which will then ideally provide partner notification to the person's partners. Physicians may also encourage patients to send their partners to seek care. Several strategies have been found to improve follow-up for STI testing, including email and text messaging of reminders for appointments.
Treatment
Historic use of mercury
As a form ofchemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
, elemental mercury had been used to treat skin diseases in Europe as early as 1363. As syphilis spread, preparations of mercury were among the first medicines used to combat it. Mercury is in fact highly anti-microbial: by the 16th century it was sometimes found to be sufficient to halt development of the disease when applied to ulcers as an inunction or when inhaled as a suffumigation. It was also treated by ingestion of mercury compounds. Once the disease had gained a strong foothold, however, the amounts and forms of mercury necessary to control its development exceeded the human body's ability to tolerate it, and the treatment became worse and more lethal than the disease. Nevertheless, medically directed mercury poisoning became widespread through the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries in Europe, North America, and India. Mercury salts such as mercury (II) chloride were still in prominent medical use as late as 1916, and considered effective and worthwhile treatments.
Early infections
The first-line treatment for uncomplicated syphilis (primary or secondary stages) remains a single dose of intramuscular benzathine benzylpenicillin. The bacterium is highly vulnerable to penicillin when treated early, and a treated individual is typically rendered non-infective in about 24 hours.Doxycycline
Doxycycline is a Broad-spectrum antibiotic, broad-spectrum antibiotic of the Tetracycline antibiotics, tetracycline class used in the treatment of infections caused by bacteria and certain parasites. It is used to treat pneumonia, bacterial p ...
and tetracycline are alternative choices for those allergic to penicillin; due to the risk of birth defect
A birth defect is an abnormal condition that is present at birth, regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth de ...
s, these are not recommended for pregnant women. Resistance to macrolide
Macrolides are a class of mostly natural products with a large macrocyclic lactone ring to which one or more deoxy sugars, usually cladinose and desosamine, may be attached. Macrolides belong to the polyketide class of natural products. ...
s, rifampicin, and clindamycin is often present. Ceftriaxone, a third-generation cephalosporin
The cephalosporins (sg. ) are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from the fungus '' Acremonium'', which was previously known as ''Cephalosporium''.
Together with cephamycins, they constitute a subgroup of β-lactam antibio ...
antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
, may be as effective as penicillin-based treatment. It is recommended that a treated person avoid sex until the sores are healed. In comparison to azithromycin for treatment in early infection, there is lack of strong evidence for superiority of azithromycin to benzathine penicillin G.
Late infections
For neurosyphilis, due to the poor penetration of benzathine penicillin into thecentral nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
, those affected are given large doses of intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutr ...
penicillin G for a minimum of 10 days. If a person is allergic to penicillin, ceftriaxone may be used or penicillin desensitization attempted. Other late presentations may be treated with once-weekly intramuscular benzathine penicillin for three weeks. Treatment at this stage solely limits further progression of the disease and has a limited effect on damage which has already occurred. Serologic cure can be measured when the non-treponemal titers decline by a factor of 4 or more in 6–12 months in early syphilis or 12–24 months in late syphilis.
Jarisch–Herxheimer reaction
One of the potential side effects of treatment is the Jarisch–Herxheimer reaction. It frequently starts within one hour and lasts for 24 hours, with symptoms of fever, muscle pains, headache, and a fast heart rate. It is results from the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines by the immune system in response to lipoproteins released from rupturing syphilis bacteria.Pregnancy
Penicillin is an effective treatment for syphilis in pregnancy but there is no agreement on which dose or route of delivery is most effective.Epidemiology
developing world
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreeme ...
. It affects between 700,000 and 1.6 million pregnancies a year, resulting in miscarriage
Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spontaneous abortion, is an end to pregnancy resulting in the loss and expulsion of an embryo or fetus from the womb before it can fetal viability, survive independently. Miscarriage before 6 weeks ...
s, stillbirth
Stillbirth is typically defined as fetus, fetal death at or after 20 or 28 weeks of pregnancy, depending on the source. It results in a baby born without vital signs, signs of life. A stillbirth can often result in the feeling of guilt (emotio ...
s, and congenital syphilis. During 2015, it caused about 107,000 deaths, down from 202,000 in 1990. In sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lie south of the Sahara. These include Central Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa, and West Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the list of sovereign states and ...
, syphilis contributes to approximately 20% of perinatal deaths. Rates are proportionally higher among intravenous drug users, those who are infected with HIV, and men who have sex with men. In the United States about 55,400 people are newly infected each year . African American
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an Race and ethnicity in the United States, American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from an ...
s accounted for almost half of all cases in 2010. As of 2014, syphilis infections continue to increase in the United States. In the United States as of 2020, rates of syphilis have increased by more than threefold; in 2018 approximately 86% of all cases of syphilis in the United States were in men. In 2021, preliminary CDC data illustrated that 2,677 cases of congenital syphilis were found in the population of 332 million in the United States.
Syphilis was very common in Europe during the 18th and 19th centuries. Flaubert found it universal among 19th-century Egyptian prostitutes. In the developed world during the early 20th century, infections declined rapidly with the widespread use of antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
s, until the 1980s and 1990s. Since 2000, rates of syphilis have been increasing in the US, Canada, the UK, Australia and Europe, primarily among men who have sex with men. Rates of syphilis among US women have remained stable during this time, while rates among UK women have increased, but at a rate less than that of men. Increased rates among heterosexuals have occurred in China and Russia since the 1990s. This has been attributed to unsafe sexual practices, such as sexual promiscuity, prostitution, and decreasing use of barrier protection.
Left untreated, it has a mortality rate of 8% to 58%, with a greater death rate among males. The symptoms of syphilis have become less severe over the 19th and 20th centuries, in part due to widespread availability of effective treatment, and partly due to virulence of the bacteria. With early treatment, few complications result. Syphilis increases the risk of HIV transmission by two to five times, and coinfection is common (30–60% in some urban centers). In 2015, Cuba
Cuba, officially the Republic of Cuba, is an island country, comprising the island of Cuba (largest island), Isla de la Juventud, and List of islands of Cuba, 4,195 islands, islets and cays surrounding the main island. It is located where the ...
became the first country to eliminate mother-to-child transmission of syphilis.
History
Origin, spread and discovery
Paleopathologists have known for decades that syphilis was present in the Americas before European contact. The situation inAfro-Eurasia
Afro-Eurasia (also Afroeurasia and Eurafrasia) is a landmass comprising the continents of Africa, Asia, and Europe. The terms are compound (linguistics), compound words of the names of its constituent parts. Afro-Eurasia has also been called th ...
has been murkier and caused considerable debate. According to the Columbian theory, syphilis was brought to Spain by the men who sailed with Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus (; between 25 August and 31 October 1451 – 20 May 1506) was an Italians, Italian explorer and navigator from the Republic of Genoa who completed Voyages of Christopher Columbus, four Spanish-based voyages across the At ...
in 1492 and spread from there, with a serious epidemic in Naples
Naples ( ; ; ) is the Regions of Italy, regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 908,082 within the city's administrative limits as of 2025, while its Metropolitan City of N ...
beginning as early as 1495. Contemporaries believed the disease sprang from American roots, and in the 16th century physicians wrote extensively about the new disease inflicted on them by the returning explorers.
Most evidence supports the Columbian origin hypothesis. However, beginning in the 1960s, examples of probable treponematosis—the parent disease of syphilis, bejel, and yaws—in skeletal remains shifted the opinion of some towards a "pre-Columbian" origin. A 2024 study published in ''Nature
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the Ecosphere (planetary), ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the Scientific law, laws, elements and phenomenon, phenomena of the physic ...
'' supported an emergence postdating human occupation in the Americas.
When living conditions changed with urbanization, elite social groups began to practice basic hygiene and started to separate themselves from other social tiers. Consequently, treponematosis was driven out of the age group in which it had become endemic. It then began to appear in adults as syphilis. Because they had never been exposed as children, they were not able to fend off serious illness. Spreading the disease via sexual contact also led to victims being infected with a massive bacterial load from open sores on the genitalia. Adults in higher socioeconomic groups then became very sick with painful and debilitating symptoms lasting for decades. Often, they died of the disease, as did their children who were infected with congenital syphilis. The difference between rural and urban populations was first noted by Ellis Herndon Hudson, a clinician who published extensively about the prevalence of treponematosis, including syphilis, in times past. The importance of bacterial load was first noted by the physician Ernest Grin in 1952 in his study of syphilis in Bosnia.
The most compelling evidence for the validity of the pre-Columbian hypothesis is the presence of syphilitic-like damage to bones and teeth in medieval skeletal remains. While the absolute number of cases is not large, new ones are continually discovered, most recently in 2015. At least fifteen cases of acquired treponematosis based on evidence from bones, and six examples of congenital treponematosis based on evidence from teeth, are now widely accepted. In several of the twenty-one cases the evidence may also indicate syphilis.
 In 2020, a group of leading paleopathologists concluded that enough evidence had been collected to prove that treponemal disease, almost certainly including syphilis, had existed in Europe prior to the voyages of Columbus. There is an outstanding issue, however. Damaged teeth and bones may seem to hold proof of pre-Columbian syphilis, but there is a possibility that they point to an endemic form of treponemal disease instead. As syphilis, bejel, and yaws vary considerably in mortality rates and the level of human disease they elicit, it is important to know which one is under discussion in any given case, but it remains difficult for paleopathologists to distinguish among them. (The fourth of the treponemal diseases is pinta, a skin disease and therefore unrecoverable through paleopathology.) Ancient
In 2020, a group of leading paleopathologists concluded that enough evidence had been collected to prove that treponemal disease, almost certainly including syphilis, had existed in Europe prior to the voyages of Columbus. There is an outstanding issue, however. Damaged teeth and bones may seem to hold proof of pre-Columbian syphilis, but there is a possibility that they point to an endemic form of treponemal disease instead. As syphilis, bejel, and yaws vary considerably in mortality rates and the level of human disease they elicit, it is important to know which one is under discussion in any given case, but it remains difficult for paleopathologists to distinguish among them. (The fourth of the treponemal diseases is pinta, a skin disease and therefore unrecoverable through paleopathology.) Ancient DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
(aDNA) holds the answer, because just as only aDNA suffices to distinguish between syphilis and other diseases that produce similar symptoms in the body, it alone can differentiate spirochetes that are 99.8 percent identical with absolute accuracy. Progress on uncovering the historical extent of syndromes through aDNA remains slow, however, because the bacterium responsible for treponematosis is rare in skeletal remains and fragile, making it notoriously difficult to recover and analyse. Precise dating to the medieval period is not yet possible but work by Kettu Majander et al. uncovering the presence of several different kinds of treponematosis at the beginning of the early modern period argues against its recent introduction from elsewhere. Therefore, they argue, treponematosis—possibly including syphilis—almost certainly existed in medieval Europe.
Despite significant progress in tracing the presence of syphilis in past historic periods, definitive findings from paleopathology and aDNA studies are still lacking for the medieval period. Evidence from art is therefore helpful in settling the issue. Research by Marylynn Salmon has demonstrated that deformities in medieval subjects can be identified by comparing them to those of modern victims of syphilis in medical drawings and photographs. One of the most typical deformities, for example, is a collapsed nasal bridge called saddle nose. Salmon discovered that it appeared often in medieval illuminations, especially among the men tormenting Christ in scenes of the crucifixion. The association of saddle nose with evil is an indication that the artists were thinking of syphilis, which is typically transmitted through sexual intercourse with promiscuous partners, a mortal sin in medieval times.
It remains mysterious why the authors of medieval medical treatises so uniformly refrained from describing syphilis or commenting on its existence in the population. Many may have confused it with other diseases such as leprosy ( Hansen's disease) or elephantiasis. The great variety of symptoms of treponematosis, the different ages at which the various diseases appear, and its widely divergent outcomes depending on climate and culture, would have added greatly to the confusion of medical practitioners, as indeed they did right down to the middle of the 20th century. In addition, evidence indicates that some writers on disease feared the political implications of discussing a condition more fatal to elites than to commoners. Historian Jon Arrizabalaga has investigated this question for Castile with startling results revealing an effort to hide its association with elites.
The first written records of an outbreak of syphilis in Europe occurred in 1495 in Naples, Italy, during a French invasion ( Italian War of 1494–98). Since it was claimed to have been spread by French troops, it was initially called the "French disease" by the people of Naples. The disease reached London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
in 1497 and was recorded at St Bartholomew's Hospital as infecting 10 out of the 20 patients. In 1530, the pastoral name "syphilis" (the name of a character) was first used by the Italian physician and poet Girolamo Fracastoro as the title of his Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
poem in dactylic hexameter '' Syphilis sive morbus gallicus'' (''Syphilis or The French Disease'') describing the ravages of the disease in Italy. In Great Britain it was also called the "Great Pox".
In the 16th through 19th centuries, syphilis was one of the largest public health burdens in prevalence
In epidemiology, prevalence is the proportion of a particular population found to be affected by a medical condition (typically a disease or a risk factor such as smoking or seatbelt use) at a specific time. It is derived by comparing the number o ...
, symptoms, and disability, although records of its true prevalence were generally not kept because of the fearsome and sordid status of sexually transmitted infections
A sexually transmitted infection (STI), also referred to as a sexually transmitted disease (STD) and the older term venereal disease (VD), is an infection that is spread by sexual activity, especially vaginal intercourse, anal sex, or ...
in those centuries. According to a 2020 study, more than 20% of individuals in the age range 15–34 years in late 18th-century London were treated for syphilis. At the time the causative agent was unknown but it was well known that it was spread sexually and also often from mother to child. Its association with sex, especially sexual promiscuity and prostitution
Prostitution is a type of sex work that involves engaging in sexual activity in exchange for payment. The definition of "sexual activity" varies, and is often defined as an activity requiring physical contact (e.g., sexual intercourse, no ...
, made it an object of fear and revulsion and a taboo. The magnitude of its morbidity and mortality in those centuries reflected that, unlike today, there was no adequate understanding of its pathogenesis
In pathology, pathogenesis is the process by which a disease or disorder develops. It can include factors which contribute not only to the onset of the disease or disorder, but also to its progression and maintenance. The word comes .
Descript ...
and no truly effective treatments. Its damage was caused not so much by great sickness or death early in the course of the disease but rather by its gruesome effects decades after infection as it progressed to neurosyphilis with tabes dorsalis. Mercury compounds and isolation were commonly used, with treatments often worse than the disease.
The causative organism, ''Treponema pallidum'', was first identified by Fritz Schaudinn
Fritz Richard Schaudinn (19 September 1871 – 22 June 1906) was a German zoologist.
Born in Röseningken (now in Ozyorsky District) in the Province of Prussia, he co-discovered, with Erich Hoffmann in 1905, the causative agent of syphilis, ' ...
and Erich Hoffmann, in 1905. The first effective treatment for syphilis was arsphenamine, discovered by Sahachiro Hata in 1909, during a survey of hundreds of newly synthesized organic arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is not ...
al compounds led by Paul Ehrlich
Paul Ehrlich (; 14 March 1854 – 20 August 1915) was a Nobel Prize-winning German physician and scientist who worked in the fields of hematology, immunology and antimicrobial chemotherapy. Among his foremost achievements were finding a cure fo ...
. It was manufactured and marketed from 1910 under the trade name Salvarsan by Hoechst AG
Hoechst AG () was a German chemicals, later life sciences, company that became Aventis Deutschland after its merger with France's Rhône-Poulenc S.A. in 1999. With the new company's 2004 merger with Sanofi-Synthélabo, it became a subsidiar ...
. This organoarsenic compound
Organoarsenic chemistry is the chemistry of Chemical compound, compounds containing a chemical bond between arsenic and carbon. A few organoarsenic compounds, also called "organoarsenicals," are produced industrially with uses as insecticides, herb ...
was the first modern chemotherapeutic agent.
During the 20th century, as both microbiology
Microbiology () is the branches of science, scientific study of microorganisms, those being of unicellular organism, unicellular (single-celled), multicellular organism, multicellular (consisting of complex cells), or non-cellular life, acellula ...
and pharmacology
Pharmacology is the science of drugs and medications, including a substance's origin, composition, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, therapeutic use, and toxicology. More specifically, it is the study of the interactions that occur betwee ...
advanced greatly, syphilis, like many other infectious diseases, became more of a manageable burden than a scary and disfiguring mystery, at least in developed countries
A developed country, or advanced country, is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy, and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for eval ...
among those people who could afford to pay for timely diagnosis and treatment. Penicillin was discovered in 1928, and effectiveness of treatment with penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of beta-lactam antibiotic, β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' Mold (fungus), moulds, principally ''Penicillium chrysogenum, P. chrysogenum'' and ''Penicillium rubens, P. ru ...
was confirmed in trials in 1943, at which time it became the main treatment.
Many famous historical figures, including Franz Schubert
Franz Peter Schubert (; ; 31 January 179719 November 1828) was an Austrian composer of the late Classical period (music), Classical and early Romantic music, Romantic eras. Despite his short life, Schubert left behind a List of compositions ...
, Arthur Schopenhauer
Arthur Schopenhauer ( ; ; 22 February 1788 – 21 September 1860) was a German philosopher. He is known for his 1818 work ''The World as Will and Representation'' (expanded in 1844), which characterizes the Phenomenon, phenomenal world as ...
, Édouard Manet
Édouard Manet (, ; ; 23 January 1832 – 30 April 1883) was a French Modernism, modernist painter. He was one of the first 19th-century artists to paint modern life, as well as a pivotal figure in the transition from Realism (art movement), R ...
, Charles Baudelaire
Charles Pierre Baudelaire (, ; ; 9 April 1821 – 31 August 1867) was a French poet, essayist, translator and art critic. His poems are described as exhibiting mastery of rhythm and rhyme, containing an exoticism inherited from the Romantics ...
, and Guy de Maupassant are believed to have had the disease. Friedrich Nietzsche
Friedrich Wilhelm Nietzsche (15 October 1844 – 25 August 1900) was a German philosopher. He began his career as a classical philology, classical philologist, turning to philosophy early in his academic career. In 1869, aged 24, Nietzsche bec ...
was long believed to have gone mad as a result of tertiary syphilis, but that diagnosis has recently come into question.
Arts and literature
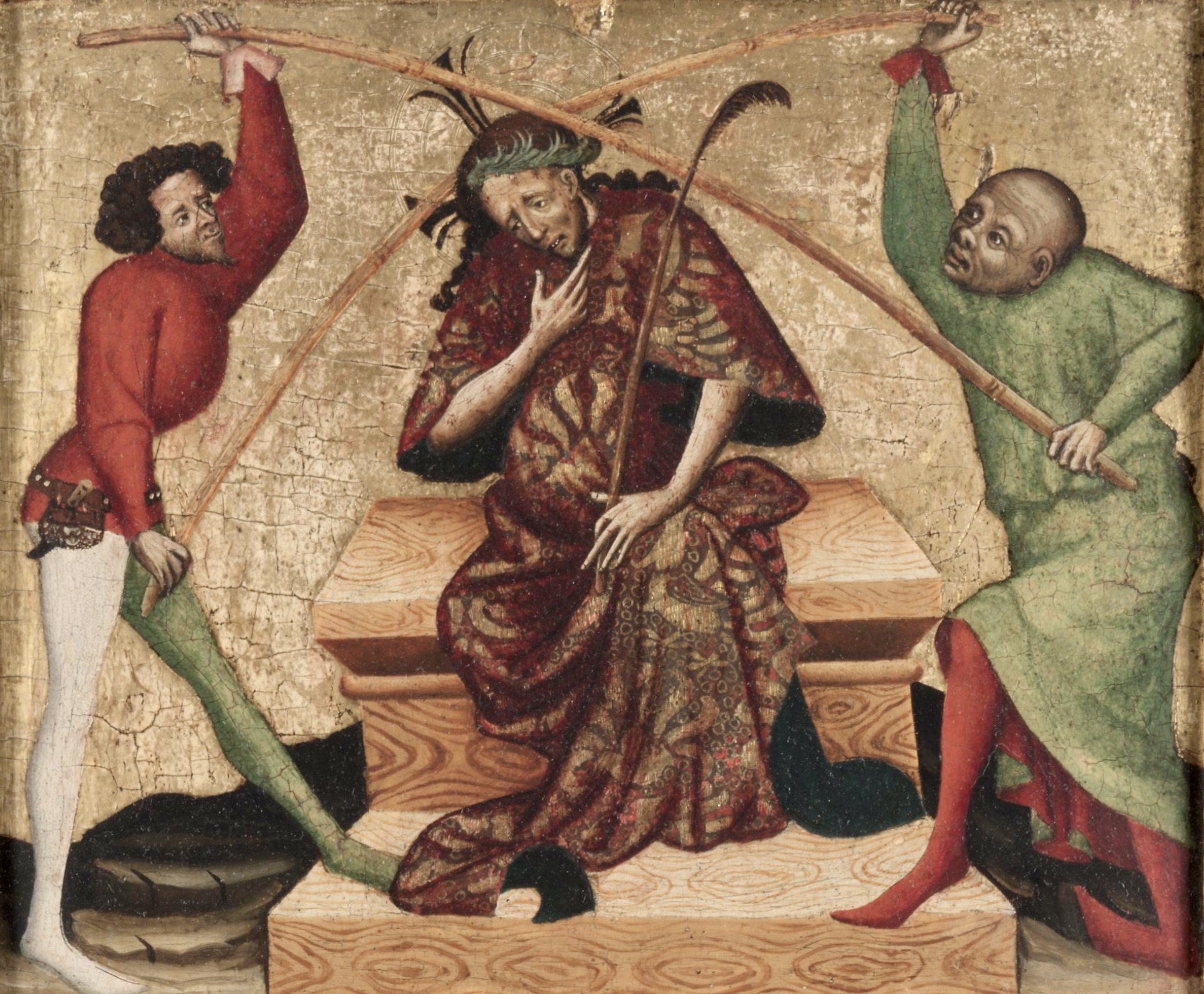
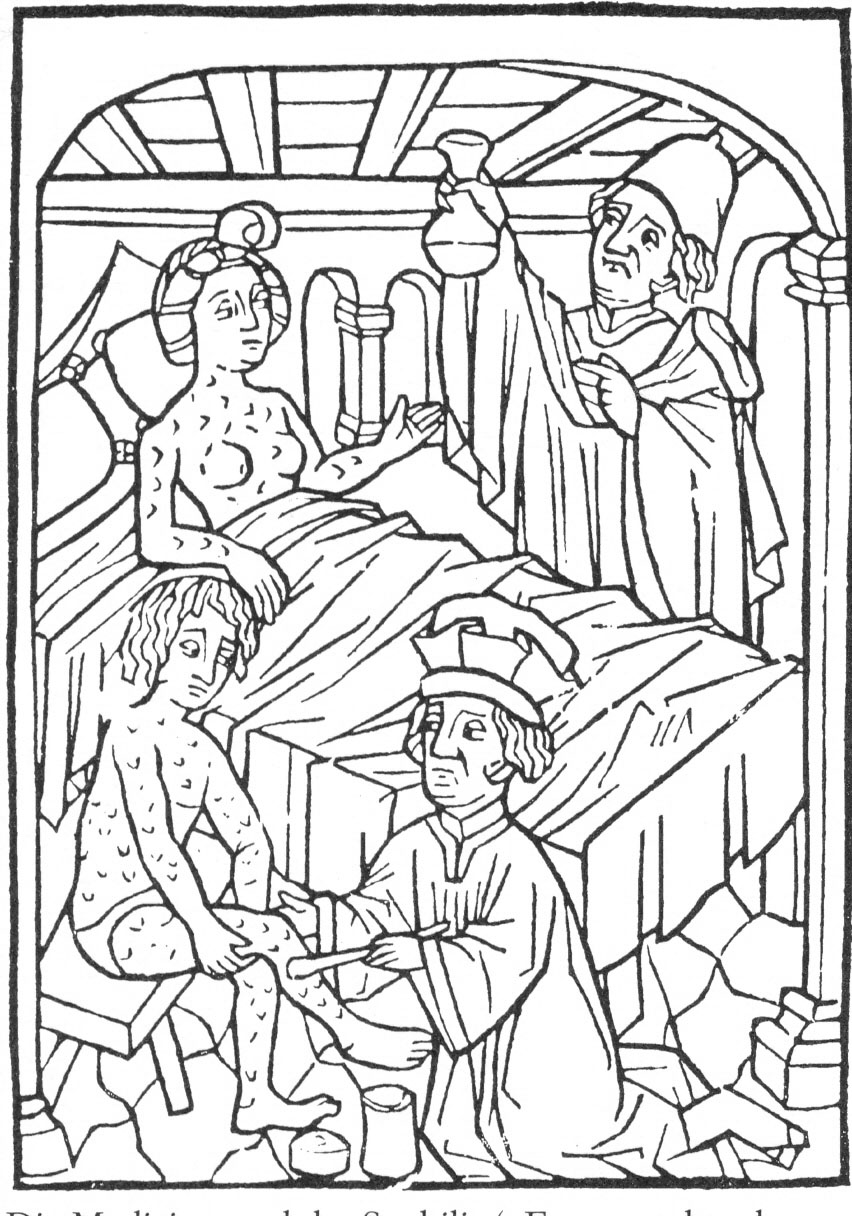
 The earliest known depiction of an individual with syphilis is
The earliest known depiction of an individual with syphilis is Albrecht Dürer
Albrecht Dürer ( , ;; 21 May 1471 – 6 April 1528),Müller, Peter O. (1993) ''Substantiv-Derivation in Den Schriften Albrecht Dürers'', Walter de Gruyter. . sometimes spelled in English as Durer or Duerer, was a German painter, Old master prin ...
's '' Syphilitic Man'' (1496), a woodcut believed to represent a Landsknecht
The (singular: , ), also rendered as Landsknechts or Lansquenets, were German mercenaries used in pike and shot formations during the early modern period. Consisting predominantly of pikemen and supporting foot soldiers, their front line was ...
, a Northern European mercenary
A mercenary is a private individual who joins an armed conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a member of any other official military. Mercenaries fight for money or other forms of payment rather t ...
. The myth of the ''femme fatale
A ( , ; ), sometimes called a maneater, Mata Hari, or vamp, is a stock character of a mysterious, beautiful, and Seduction, seductive woman whose charms ensnare her lovers, often leading them into compromising, deadly traps. She is an archetype ...
'' or "poison women" of the 19th century is believed to be partly derived from the devastation of syphilis, with classic examples in literature including John Keats' " La Belle Dame sans Merci".
The Flemish artist Stradanus designed a print called ''Preparation and Use of Guayaco for Treating Syphilis'', a scene of a wealthy man receiving treatment for syphilis with the tropical wood guaiacum sometime around 1590.
Tuskegee and Guatemala studies
 The "Tuskegee Study of Untreated Syphilis in the Negro Male" was an infamous, unethical and racist
The "Tuskegee Study of Untreated Syphilis in the Negro Male" was an infamous, unethical and racist clinical study
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human subject research, human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel v ...
conducted between 1932 and 1972 by the U.S. Public Health Service. Whereas the purpose of this study was to observe the natural history
Natural history is a domain of inquiry involving organisms, including animals, fungi, and plants, in their natural environment, leaning more towards observational than experimental methods of study. A person who studies natural history is cal ...
of untreated syphilis; the African-American men in the study were told they were receiving free treatment for "bad blood" from the United States government.
The Public Health Service started working on this study in 1932 in collaboration with Tuskegee University
Tuskegee University (Tuskegee or TU; formerly known as the Tuskegee Institute) is a private, historically black land-grant university in Tuskegee, Alabama, United States. It was founded as a normal school for teachers on July 4, 1881, by the ...
, a historically black college
Historically Black colleges and universities (HBCUs) are institutions of higher education in the United States that were established before the Civil Rights Act of 1964 with the intention of serving African Americans. Most are in the Southern U ...
in Alabama. Researchers enrolled 600 poor, African American sharecroppers from Macon County, Alabama
Alabama ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South, Deep Southern regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gu ...
in the study. Of these men, 399 had contracted syphilis before the study began, and 201 did not have the disease. Medical care, hot meals and free burial insurance were given to those who participated. The men were told that the study would last six months, but in the end, it continued for 40 years. After funding for treatment was lost, the study was continued without informing the men that they were only being studied and would not be treated. Facing insufficient participation, the Macon County Health Department nevertheless wrote to subjects to offer them a "last chance" to get a special "treatment", which was not a treatment at all, but a spinal tap administered exclusively for diagnostic purposes. None of the men infected were ever told that they had the disease, and none were treated with penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of beta-lactam antibiotic, β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' Mold (fungus), moulds, principally ''Penicillium chrysogenum, P. chrysogenum'' and ''Penicillium rubens, P. ru ...
even after the antibiotic had been proven to successfully treat syphilis. According to the Centers for Disease Control
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency under the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and is headquartered in Atlanta, ...
, the men were told they were being treated for "bad blood"—a colloquialism describing various conditions such as fatigue, anemia
Anemia (also spelt anaemia in British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen. This can be due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin availabl ...
and syphilis—which was a leading cause of death among southern African American men.
The 40-year study became a textbook example of criminally negligent medical ethics
Medical ethics is an applied branch of ethics which analyzes the practice of clinical medicine and related scientific research. Medical ethics is based on a set of values that professionals can refer to in the case of any confusion or conflict. T ...
because researchers had knowingly withheld treatment with penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of beta-lactam antibiotic, β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' Mold (fungus), moulds, principally ''Penicillium chrysogenum, P. chrysogenum'' and ''Penicillium rubens, P. ru ...
and because the subjects had been misled concerning the purposes of the study. The revelation in 1972 of these study failures by a whistleblower
Whistleblowing (also whistle-blowing or whistle blowing) is the activity of a person, often an employee, revealing information about activity within a private or public organization that is deemed illegal, immoral, illicit, unsafe, unethical or ...
, Peter Buxtun, led to major changes in U.S. law and regulation on the protection of participants in clinical studies. Now studies require informed consent
Informed consent is an applied ethics principle that a person must have sufficient information and understanding before making decisions about accepting risk. Pertinent information may include risks and benefits of treatments, alternative treatme ...
, communication of diagnosis
Diagnosis (: diagnoses) is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in a lot of different academic discipline, disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " ...
, and accurate reporting of test results.
Similar experiments were carried out in Guatemala
Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is hydrologically b ...
from 1946 to 1948. It was done during the administration of American President Harry S. Truman
Harry S. Truman (May 8, 1884December 26, 1972) was the 33rd president of the United States, serving from 1945 to 1953. As the 34th vice president in 1945, he assumed the presidency upon the death of Franklin D. Roosevelt that year. Subsequen ...
and Guatemalan President Juan José Arévalo with the cooperation of some Guatemalan health ministries and officials. Doctors infected soldiers, prostitutes, prisoners and mental patients with syphilis and other sexually transmitted infection
A sexually transmitted infection (STI), also referred to as a sexually transmitted disease (STD) and the older term venereal disease (VD), is an infection that is Transmission (medicine), spread by Human sexual activity, sexual activity, e ...
s, without the informed consent
Informed consent is an applied ethics principle that a person must have sufficient information and understanding before making decisions about accepting risk. Pertinent information may include risks and benefits of treatments, alternative treatme ...
of the subjects and treated most subjects with antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
s. The experiment resulted in at least 83 deaths. In October 2010, the U.S. formally apologized to Guatemala for the ethical violations that took place. Secretary of State Hillary Clinton
Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton ( Rodham; born October 26, 1947) is an American politician, lawyer and diplomat. She was the 67th United States secretary of state in the administration of Barack Obama from 2009 to 2013, a U.S. senator represent ...
and Health and Human Services Secretary Kathleen Sebelius stated "Although these events occurred more than 64 years ago, we are outraged that such reprehensible research could have occurred under the guise of public health. We deeply regret that it happened, and we apologize to all the individuals who were affected by such abhorrent research practices." The experiments were led by physician John Charles Cutler who also participated in the late stages of the Tuskegee syphilis experiment.
Names
Syphilis was first called ''grande verole'' or the "great pox" by the French. Other historical names have included "button scurvy", sibbens, frenga and dichuchwa, among others. Since it was a disgraceful disease, the disease was known in several countries by the name of their neighbouring, often hostile country. The English, the Germans, and the Italians called it "the French disease", while the French referred to it as the "Neapolitan disease". The Dutch called it the "Spanish/Castilian disease". To the Turks it was known as the "Christian disease", whilst in India, the Hindus and Muslims named the disease after each other.References
Further reading
* *External links
"Syphilis - CDC Fact Sheet"
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
(CDC)UCSF HIV InSite Knowledge Base Chapter: Syphilis and HIV
Recommendations for Public Health Surveillance of Syphilis in the United States
* {{Authority control Bacterial diseases Bacterium-related cutaneous conditions Infectious diseases Infectious diseases with eradication efforts Infections with a predominantly sexual mode of transmission Sexually transmitted diseases and infections Spirochaetes Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate (full) Wikipedia infectious disease articles ready to translate