Surface energy transfer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Surface energy transfer (SET) is a
Surface energy transfer (SET) is a
 Surface energy transfer (SET) is a
Surface energy transfer (SET) is a dipole
In physics, a dipole () is an electromagnetic phenomenon which occurs in two ways:
*An electric dipole deals with the separation of the positive and negative electric charges found in any electromagnetic system. A simple example of this system ...
-surface energy transfer
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat ...
process involving a metallic surface and a molecular dipole.
Formula
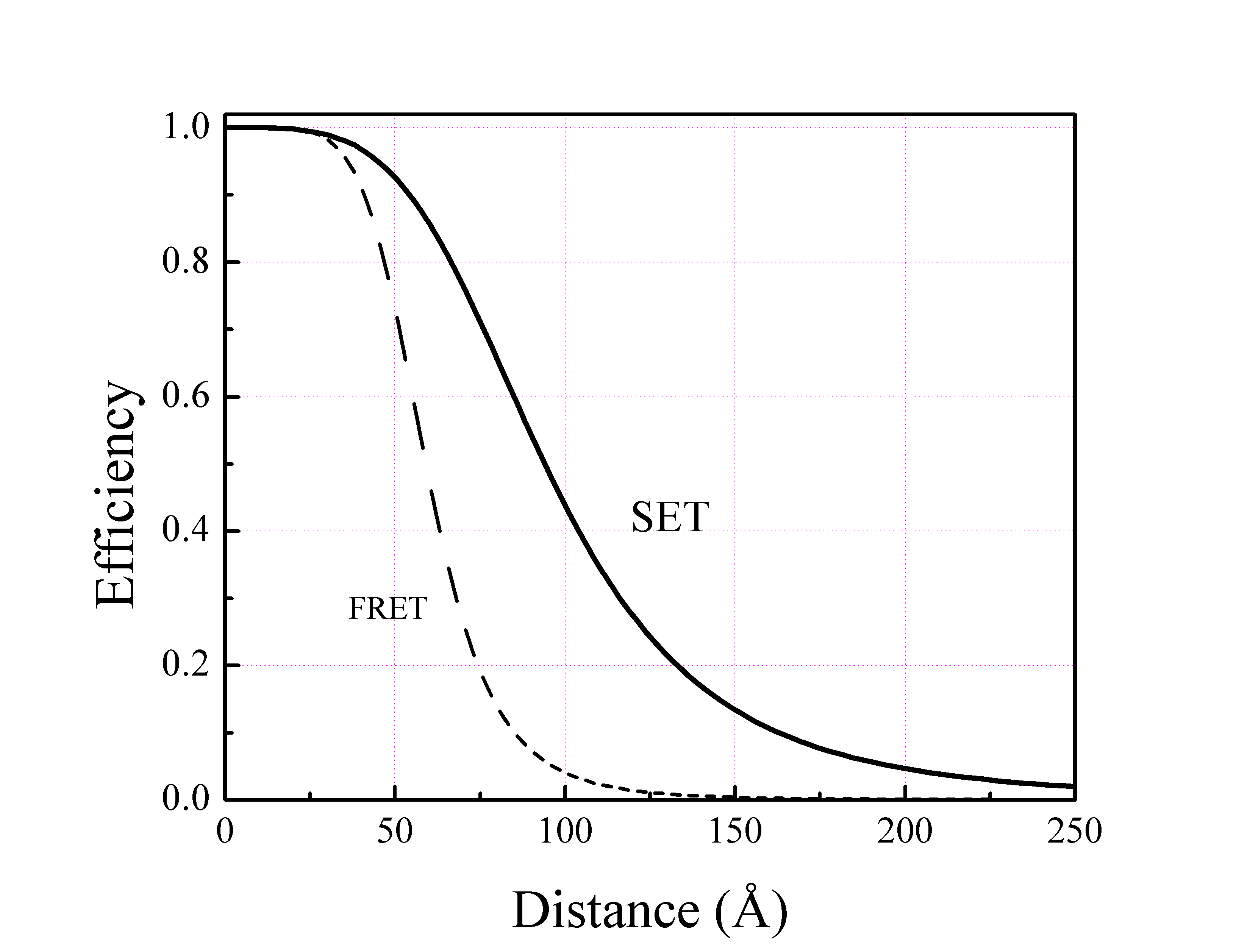
The SET rate follows the inverse of the fourth power of the distance : where * is the donor emission lifetime; * is the distance between donor-acceptor; * is the distance at which SET efficiency decreases to 50% (i.e., equal probability of energy transfer andspontaneous emission
Spontaneous emission is the process in which a quantum mechanical system (such as a molecule, an atom or a subatomic particle) transits from an excited energy state to a lower energy state (e.g., its ground state) and emits a quantized amount ...
).
Efficiency
The energy transfer efficiency also follows a similar form : Due to the fourth power dependence SET can cover a distance more than 15 nm, which is almost twice the efficiency ofFRET
A fret is any of the thin strips of material, usually metal wire, inserted laterally at specific positions along the neck or fretboard of a stringed instrument. Frets usually extend across the full width of the neck. On some historical instru ...
. Theoretically predicted in 1978 by Chance ''et al.'' it was proved experimentally in 2000s by different workers.
Applications
The efficiency of SET as nanoruler has been used in live cells. Gold nano particles are frequently used in these studies as the nanoparticle surface.See also
*Dexter electron transfer
Dexter electron transfer (also called Dexter electron exchange and Dexter energy transfer) is a fluorescence quenching mechanism in which an excited electron is transferred from one molecule (a donor) to a second molecule (an acceptor) via a non ...
*Förster resonance energy transfer
Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET), fluorescence resonance energy transfer, resonance energy transfer (RET) or electronic energy transfer (EET) is a mechanism describing energy transfer between two light-sensitive molecules (chromophores). ...
References
{{Reflist Energy transfer Fluorescence