Sternocleidomastoid muscle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The sternocleidomastoid muscle is one of the largest and most superficial cervical muscles. The primary actions of the muscle are rotation of the head to the opposite side and
 The two heads are separated from one another at their origins by a triangular interval (''lesser supraclavicular fossa'') but gradually blend, below the middle of the neck, into a thick, rounded muscle which is inserted, by a strong tendon, into the lateral surface of the mastoid process, from its apex to its superior border, and by a thin
The two heads are separated from one another at their origins by a triangular interval (''lesser supraclavicular fossa'') but gradually blend, below the middle of the neck, into a thick, rounded muscle which is inserted, by a strong tendon, into the lateral surface of the mastoid process, from its apex to its superior border, and by a thin
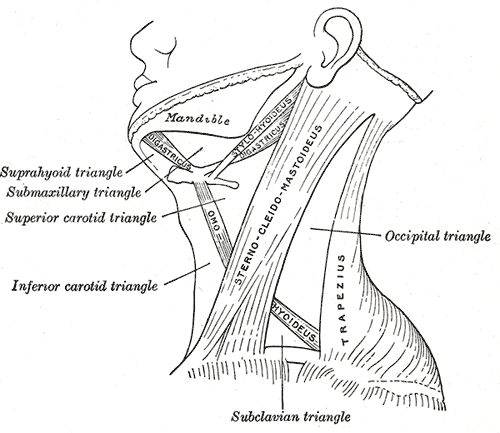 The sternocleidomastoid is within the investing fascia of the neck, along with the
The sternocleidomastoid is within the investing fascia of the neck, along with the
flexion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terminology, anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of Organ (anatomy), organs, joints, Limb (anatomy), limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used de ...
of the neck. The sternocleidomastoid is innervated by the accessory nerve
The accessory nerve, also known as the eleventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve XI, or simply CN XI, is a cranial nerve that supplies the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. It is classified as the eleventh of twelve pairs of cranial nerv ...
.
Etymology and location
It is given the name ''sternocleidomastoid'' because it originates at themanubrium
The sternum (: sternums or sterna) or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, human lung, lungs, and ma ...
of the sternum
The sternum (: sternums or sterna) or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major bl ...
(''sterno-'') and the clavicle
The clavicle, collarbone, or keybone is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately long that serves as a strut between the scapula, shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on each side of the body. The clavic ...
(''cleido-'') and has an insertion at the mastoid process of the temporal bone
The temporal bone is a paired bone situated at the sides and base of the skull, lateral to the temporal lobe of the cerebral cortex.
The temporal bones are overlaid by the sides of the head known as the temples where four of the cranial bone ...
of the skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
.
Structure
The sternocleidomastoid muscle originates from two locations: themanubrium
The sternum (: sternums or sterna) or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, human lung, lungs, and ma ...
of the sternum
The sternum (: sternums or sterna) or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major bl ...
and the clavicle
The clavicle, collarbone, or keybone is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately long that serves as a strut between the scapula, shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on each side of the body. The clavic ...
, hence it is said to have two heads: sternal head and clavicular head. It travels obliquely across the side of the neck and inserts at the mastoid process of the temporal bone
The temporal bone is a paired bone situated at the sides and base of the skull, lateral to the temporal lobe of the cerebral cortex.
The temporal bones are overlaid by the sides of the head known as the temples where four of the cranial bone ...
of the skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
by a thin aponeurosis
An aponeurosis (; : aponeuroses) is a flattened tendon by which muscle attaches to bone or fascia. Aponeuroses exhibit an ordered arrangement of collagen fibres, thus attaining high tensile strength in a particular direction while being vulnerable ...
. The sternocleidomastoid is thick and narrow at its center, and broader and thinner at either end.
The sternal head is a round fasciculus
''Fasciculus vesanus'' is an extinct species of stem-group ctenophores known from the Burgess Shale of British Columbia, Canada. It is dated to and belongs to middle Cambrian strata.
The species is remarkable for its two sets of long and sho ...
, tendinous in front, fleshy behind, arising from the upper part of the front of the manubrium sterni. It travels superiorly, laterally, and posteriorly.
The clavicular head is composed of fleshy and aponeurotic fibers, arises from the upper, frontal surface of the medial third of the clavicle
The clavicle, collarbone, or keybone is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately long that serves as a strut between the scapula, shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on each side of the body. The clavic ...
; it is directed almost vertically upward.
 The two heads are separated from one another at their origins by a triangular interval (''lesser supraclavicular fossa'') but gradually blend, below the middle of the neck, into a thick, rounded muscle which is inserted, by a strong tendon, into the lateral surface of the mastoid process, from its apex to its superior border, and by a thin
The two heads are separated from one another at their origins by a triangular interval (''lesser supraclavicular fossa'') but gradually blend, below the middle of the neck, into a thick, rounded muscle which is inserted, by a strong tendon, into the lateral surface of the mastoid process, from its apex to its superior border, and by a thin aponeurosis
An aponeurosis (; : aponeuroses) is a flattened tendon by which muscle attaches to bone or fascia. Aponeuroses exhibit an ordered arrangement of collagen fibres, thus attaining high tensile strength in a particular direction while being vulnerable ...
into the lateral half of the superior nuchal line
The nuchal lines are four curved lines on the external surface of the occipital bone:
* The upper, often faintly marked, is named the highest nuchal line, but is sometimes referred to as the Mempin line or linea suprema, and it attaches to the e ...
of the occipital bone
The occipital bone () is a neurocranium, cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone lies over the occipital lob ...
.
Nerve supply
The sternocleidomastoid is innervated byaccessory nerve
The accessory nerve, also known as the eleventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve XI, or simply CN XI, is a cranial nerve that supplies the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. It is classified as the eleventh of twelve pairs of cranial nerv ...
of the same side. It supplies only motor fibres. The cervical plexus supplies sensation, including proprioception
Proprioception ( ) is the sense of self-movement, force, and body position.
Proprioception is mediated by proprioceptors, a type of sensory receptor, located within muscles, tendons, and joints. Most animals possess multiple subtypes of propri ...
, from the ventral primary rami of C2 and C3.
Variation
The clavicular origin of the sternocleidomastoid varies greatly: in some cases the clavicular head may be as narrow as the sternal; in others it may be as much as in breadth. When the clavicular origin is broad, it is occasionally subdivided into several slips, separated by narrow intervals. More rarely, the adjoining margins of the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius are in contact. This would leave no posterior triangle. The supraclavicularis muscle arises from the manubrium behind the sternocleidomastoid and passes behind the sternocleidomastoid to the upper surface of the clavicle.Function
The function of this muscle is to rotate the head to the opposite side or obliquely rotate the head. It also flexes the neck. When both sides of the muscle act together, it flexes the neck and extends the head. When one side acts alone, it causes the head to rotate to the opposite side and flexes laterally to the same side (ipsilaterally). It also acts as an accessory muscle of respiration, along with the scalene muscles of the neck.Contraction
The signaling process to contract or relax the sternocleidomastoid begins in Cranial Nerve XI, theaccessory nerve
The accessory nerve, also known as the eleventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve XI, or simply CN XI, is a cranial nerve that supplies the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. It is classified as the eleventh of twelve pairs of cranial nerv ...
. The accessory nerve nucleus is in the anterior horn of the spinal cord around C1-C3, where lower motor neuron fibers mark its origin. The fibers from the accessory nerve nucleus travel upward to enter the cranium via the foramen magnum. The internal carotid artery to reach both the sternocleidomastoid muscles and the trapezius. After a signal reaches the accessory nerve nucleus in the anterior horn of the spinal cord, the signal is conveyed to motor endplates on the muscle fibers located at the clavicle. Acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic compound that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Par ...
(ACH) is released from vesicles and is sent over the synaptic cleft to receptors on the postsynaptic bulb. The ACH causes the resting potential to increase above -55mV, thus initiating an action potential which travels along the muscle fiber. Along the muscle fibers are t-tubule openings which facilitate the spread of the action potential into the muscle fibers. The t-tubule meets with the sarcoplasmic reticulum at locations throughout the muscle fiber, at these locations the sarcoplasmic reticulum releases calcium ions that results in the movement of troponin
Troponin, or the troponin complex, is a complex of three regulatory proteins (troponin C, troponin I, and troponin T) that are integral to muscle contraction in skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle, but not smooth muscle. Measurements of cardiac-spe ...
and tropomyosin on thin filaments. The movement of troponin and tropomyosin is key in facilitating the myosin head to move along the thin filament, resulting in a contraction of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
Anatomical landmark
 The sternocleidomastoid is within the investing fascia of the neck, along with the
The sternocleidomastoid is within the investing fascia of the neck, along with the trapezius muscle
The trapezius is a large paired trapezoid-shaped surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the human spine, spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula. It moves the scapula and ...
, with which it shares its nerve supply (the accessory nerve
The accessory nerve, also known as the eleventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve XI, or simply CN XI, is a cranial nerve that supplies the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. It is classified as the eleventh of twelve pairs of cranial nerv ...
). It is thick and thus serves as a primary landmark
A landmark is a recognizable natural or artificial feature used for navigation, a feature that stands out from its near environment and is often visible from long distances.
In modern-day use, the term can also be applied to smaller structures ...
of the neck, as it divides the neck into anterior and posterior cervical triangles (in front and behind the muscle, respectively) which helps define the location of structures, such as the lymph nodes for the head and neck.
Many important structures relate to the sternocleidomastoid, including the common carotid artery
In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) () are artery, arteries that supply the head and neck with oxygenated blood; they divide in the neck to form the external carotid artery, external and internal carotid artery, inte ...
, accessory nerve, and brachial plexus
The brachial plexus is a network of nerves (nerve plexus) formed by the anterior rami of the lower four Spinal nerve#Cervical nerves, cervical nerves and first Spinal nerve#Thoracic nerves, thoracic nerve (cervical spinal nerve 5, C5, Cervical spi ...
.
Clinical significance
Examination of the sternocleidomastoid muscle forms part of the examination of the cranial nerves. It can be felt on each side of the neck when a person moves their head to the opposite side. The triangle formed by the clavicle and the sternal and clavicular heads of the sternocleidomastoid muscle is used as a landmark in identifying the correct location for central venous catheterization. Contraction of the muscle gives rise to a condition called torticollis or ''wry neck'', and this can have a number of causes, including rheumatic, reflex or congenital causes. Torticollis gives the appearance of a tilted head on the side involved. Treatment involves physiotherapy exercises to stretch the involved muscle and strengthen the muscle on the opposite side of the neck. Congenital torticollis can have an unknown cause or result from birth trauma that gives rise to a mass or tumor that can be palpated within the muscle.References
{{Authority control Muscles of the head and neck Otorhinolaryngology Human head and neck