|
Torticollis
Torticollis, also known as wry neck, is an extremely painful, dystonic condition defined by an abnormal, asymmetrical head or neck position, which may be due to a variety of causes. The term ''torticollis'' is derived . The most common case has no obvious cause, and the pain and difficulty in turning the head usually goes away after a few days, even without treatment in adults. Signs and symptoms Torticollis is a fixed or dynamic tilt, rotation, with flexion or extension of the head and/or neck. The type of torticollis can be described depending on the positions of the head and neck. * laterocollis: the head is tipped toward the shoulder * rotational torticollis: the head rotates along the longitudinal axis towards the shoulder * anterocollis: forward flexion of the head and neck and brings the chin towards the chest * retrocollis: hyperextension of head and neck backward bringing the back of the head towards the back A combination of these movements may often be observed. To ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benign Paroxysmal Torticollis
Benign paroxysmal torticollis (BPT) is a rare medical disorder affecting infants. Symptoms The defining characteristic of BPT is a tilting of an infant's head in recurrent episodes, for varying periods of time.Deonna, T. & Martin, D. (1981) Benign paroxysmal torticollis in infancy. Archives of Disease in Childhood. 56:956-959. Furthermore, the child's trunk may bend in the same direction as the head, giving the baby an overall curved shape; this complaint is known as tortipelvis.Drigo, P. Carli, G. & Laverda, A.M. (2000) Benign paroxysmal torticollis of infancy. Brain and Development. 22:169-172. In addition to this, the individual may also, but not necessarily, experience vomiting, pallor, ataxia, Psychomotor agitation, agitation, infantile migraine, unsteadiness of gait upon learning to walk, general malaise and nystagmus. The periods in which the child's head is tilted and other symptoms appear can last anywhere from a few minutes to a few weeks, with a frequency of anywhere f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dystonia
Dystonia is a neurology, neurological Hyperkinesia, hyperkinetic Movement disorders, movement disorder in which sustained or repetitive muscle contractions occur involuntarily, resulting in twisting and repetitive movements or abnormal fixed postures. The movements may resemble a tremor. Dystonia is often intensified or exacerbated by physical activity, and symptoms may progress into adjacent muscles. The disorder may be Heredity, hereditary or caused by other factors such as birth trauma (physical), birth-related or other Injury, physical trauma, infection, poisoning (e.g., lead poisoning) or reaction to Medication, pharmaceutical drugs, particularly Antipsychotic, neuroleptics, or stress. Treatment must be highly customized to the needs of the individual and may include oral medications, chemodenervation Botulinum toxin, botulinum neurotoxin injections, physical therapy, or other supportive therapies, and surgical procedures such as deep brain stimulation. Classification The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternocleidomastoid Muscle
The sternocleidomastoid muscle is one of the largest and most superficial cervical muscles. The primary actions of the muscle are rotation of the head to the opposite side and Anatomical terms of motion#Flexion and extension, flexion of the neck. The sternocleidomastoid is innervated by the accessory nerve. Etymology and location It is given the name ''sternocleidomastoid'' because it originates at the manubrium of the Human sternum, sternum (''sterno-'') and the clavicle (''cleido-'') and has an Insertion (anatomy), insertion at the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the human skull, skull. Structure The sternocleidomastoid muscle originates from two locations: the manubrium of the Human sternum, sternum and the clavicle, hence it is said to have two heads: sternal head and clavicular head. It travels obliquely across the side of the neck and inserts at the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the human skull, skull by a thin aponeurosis. The sternocleidomastoid is thick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossbills
Crossbills are birds of the genus ''Loxia'' within the finch family (Fringillidae), with six species. These birds are characterized by the mandibles with crossed tips, which gives the group its English name. Adult males tend to be red or orange in color, and females green or yellow, but there is much variation. Crossbills are specialist feeders on conifer cones, and the unusual bill shape is an adaptation which enables them to extract seeds from cones. These birds are typically found in higher northern hemisphere latitudes, where their food sources grow. They irrupt out of the breeding range when the cone crop fails. Crossbills breed very early in the year, often in winter months, to take advantage of maximum cone supplies. Systematics and evolution The genus ''Loxia'' was introduced by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in 1758 in the 10th edition of his ''Systema Naturae''. The name is from the Ancient Greek , "crosswise". The Swiss naturalist Conrad Gessner had used the wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trochlear Nerve
The trochlear nerve (), ( lit. ''pulley-like'' nerve) also known as the fourth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IV, or CN IV, is a cranial nerve that innervates a single muscle - the superior oblique muscle of the eye (which operates through the pulley-like trochlea). Unlike most other cranial nerves, the trochlear nerve is exclusively a motor nerve ( somatic efferent nerve). The trochlear nerve is unique among the cranial nerves in several respects: * It is the ''smallest'' nerve in terms of the number of axons it contains. * It has the greatest intracranial length. * It is the only cranial nerve that exits from the dorsal (rear) aspect of the brainstem. * It innervates a muscle, the superior oblique muscle, on the opposite side (contralateral) from its nucleus. The trochlear nerve decussates within the brainstem before emerging on the contralateral side of the brainstem (at the level of the inferior colliculus). An injury to the trochlear nucleus in the brainstem will result i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grisel's Syndrome
Grisel's syndrome is a non-traumatic subluxation of the atlanto-axial joint caused by inflammation of the adjacent tissues. This is a rare disease that usually affects children. Progressive throat and neck pain and neck stiffness can be followed by neurologic symptoms such as pain or numbness radiating to arms ( radiculopathies). In extreme cases, the condition can lead to quadriplegia and even death from acute respiratory failure. The condition often follows soft tissue inflammation in the neck such as in cases of upper respiratory tract infections, peritonsillar or retropharyngeal abscesses. Post-operative inflammation after certain procedures such as adenoidectomy can also lead to this condition in susceptible individuals such as those with Down syndrome. Pathophysiology Pathophysiology of this disease consists of relaxation of the transverse ligament of the atlanto-axial joint. Diagnosis Diagnosis can be established using plain film x-rays as well as CT scan of the neck ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plagiocephaly
Plagiocephaly, also known as flat head syndrome, is a condition characterized by an asymmetrical distortion (flattening of one side) of the skull. A mild and widespread form is characterized by a flat spot on the back or one side of the head caused by remaining in a supine position for prolonged periods. Plagiocephaly is a diagonal asymmetry across the head shape. Often it is a flattening which is to one side at the back of the head, and there is often some facial asymmetry. Depending on whether synostosis is involved, plagiocephaly divides into two groups: synostotic, with one or more fused cranial sutures, and non-synostotic (deformational). Surgical treatment of these groups includes the deference method; however, the treatment of deformational plagiocephaly is controversial. Brachycephaly describes a very wide head shape with a flattening across the whole back of the head. Causes Slight plagiocephaly is routinely diagnosed at birth and may be the result of a restrictive int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idiopathic Disease
An idiopathic disease is any disease with an unknown cause or mechanism of apparent spontaneous origin. For some medical conditions, one or more causes are somewhat understood, but in a certain percentage of people with the condition, the cause may not be readily apparent or characterized. In these cases, the origin of the condition is said to be idiopathic. With some other medical conditions, the root cause for a large percentage of all cases has not been established—for example, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis or ankylosing spondylitis; the majority of these cases are deemed idiopathic. Certain medical conditions, when idiopathic, notably some forms of epilepsy and stroke, are preferentially described by the synonymous term of cryptogenic. Derivation The term 'idiopathic' derives from Greek ''idios'' "one's own" and ''pathos'' "suffering", so ''idiopathy'' means approximately "a disease of its own kind". Examples Diseases where the cause is seen as wholly or partly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
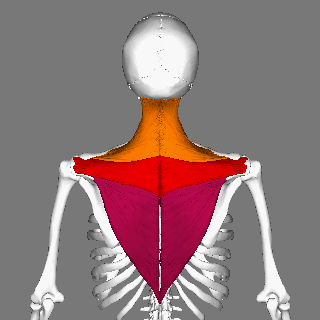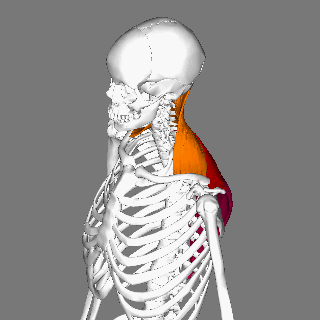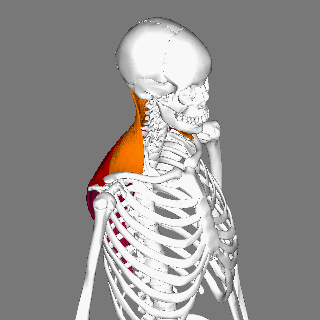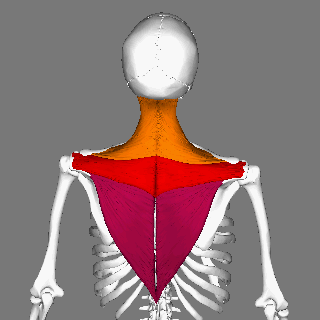
Trapezius Muscle
The trapezius is a large paired trapezoid-shaped surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the human spine, spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula. It moves the scapula and supports the arm. The trapezius has three functional parts: * an upper (descending) part which supports the weight of the arm; * a middle region (transverse), which retracts the scapula; and * a lower (ascending) part which medially rotates and depresses the scapula. Name and history The trapezius muscle resembles a trapezoid, trapezium, also known as a trapezoid, or diamond-shaped quadrilateral. The word "spinotrapezius" refers to the human trapezius, although it is not commonly used in modern texts. In other mammals, it refers to a portion of the analogous muscle. Structure The ''superior'' or ''upper'' (or descending) fibers of the trapezius originate from the spinous process of C7, the external occipital protuberance, the me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthopedics
Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics (American and British English spelling differences, alternative spelling orthopaedics) is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal Physical trauma, trauma, Spinal disease, spine diseases, Sports injury, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, tumors and congenital disorders. Etymology Nicholas Andry coined the word in French as ', derived from the Ancient Greek words ("correct", "straight") and ("child"), and published ''Orthopedie'' (translated as ''Orthopædia: Or the Art of Correcting and Preventing Deformities in Children'') in 1741. The word was Assimilation (linguistics), assimilated into English as ''orthopædics''; the Typographic ligature, ligature ''æ'' was common in that era for ''ae'' in Greek- and Latin-based words. As the name implies, the discipline was initially developed with atte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva
Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (; FOP), also called Münchmeyer disease or formerly myositis ossificans progressiva, is an extremely rare connective tissue disease in which fibrous connective tissue such as muscle, tendons, and ligaments turn into bone tissue (ossification). It is the only known medical condition in which tissue of one organ system changes into that of another. It is a severe, disabling disorder with no cure. FOP is caused by a mutation of the gene ACVR1. The mutation affects the body's repair mechanism, causing fibrous tissue including muscle, tendons, and ligaments to become ossified, either spontaneously or when damaged as the result of trauma. In many cases, otherwise minor injuries can cause joints to become permanently fused as new bone forms, replacing the damaged muscle tissue. This new bone formation (known as "heterotopic ossification") eventually forms a secondary skeleton and progressively restricts the patient's ability to move. Bone formed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenothiazine
Phenothiazine, abbreviated PTZ, is an organic compound that has the formula S(C6H4)2NH and is related to the thiazine-class of heterocyclic compounds. Derivatives of phenothiazine are highly bioactive and have widespread use and rich history. The derivatives chlorpromazine and promethazine revolutionized the fields of psychiatry and allergy treatment, respectively. An earlier derivative, methylene blue, was one of the first antimalarial drugs, and derivatives of phenothiazine are currently under investigation as possible anti-infective drugs. Phenothiazine is a prototypical pharmaceutical lead structure in medicinal chemistry. Uses Phenothiazine itself is only of theoretical interest, but derivatives of it revolutionized psychiatry, other fields of medicine, and pest management. Other derivatives have been studied for possible use in advanced batteries and fuel cells. Phenothiazine-derived drugs In 1876, methylene blue, a derivative of phenothiazine, was synthesized by H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |