Solar Eclipse Of June 8, 1918 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A total
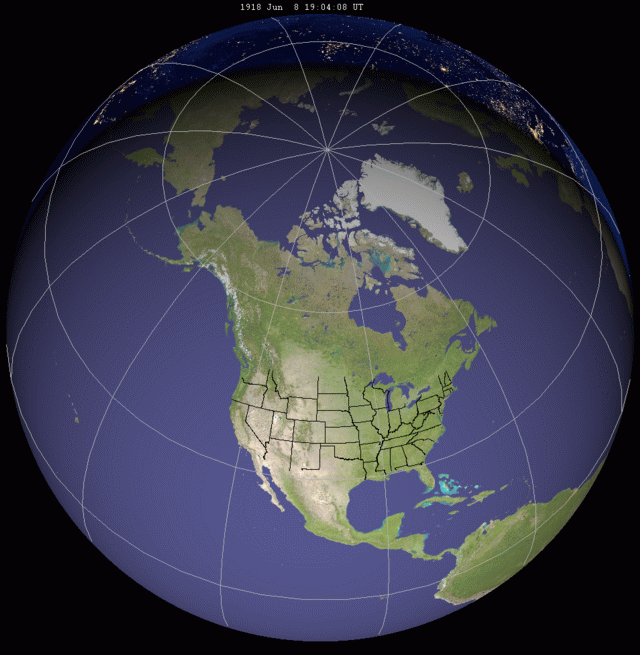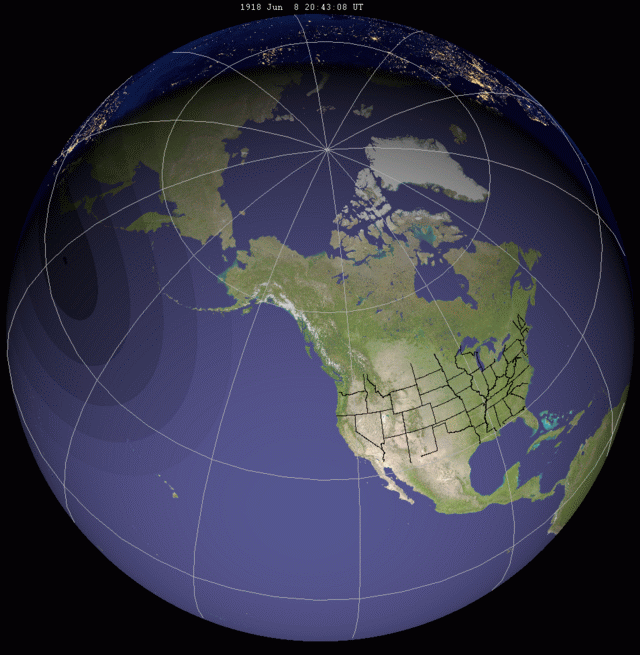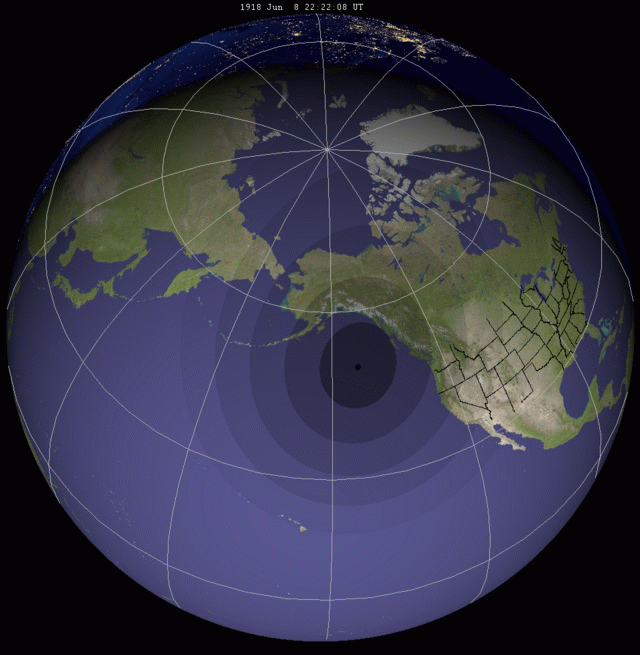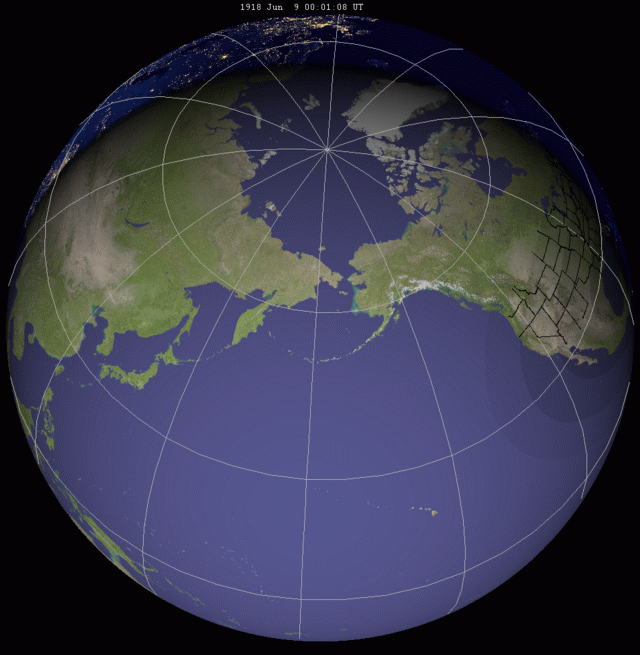 The path of totality started south of
The path of totality started south of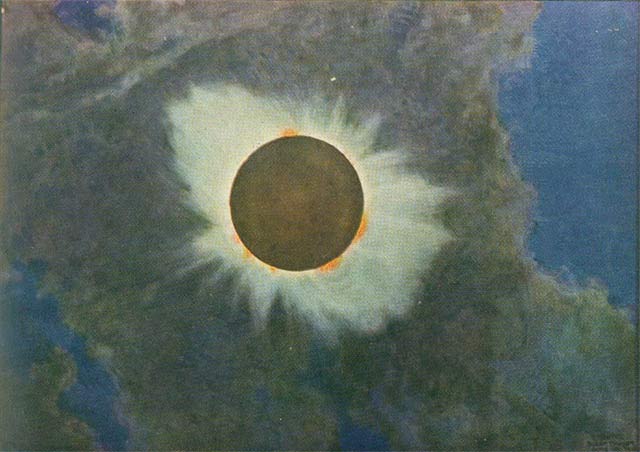 
 The path of the eclipse clipped
The path of the eclipse clipped
NASA graphic
* ttp://xjubier.free.fr/en/site_pages/solar_eclipses/Solar_Corona_Shape_pg02.html Foto and sketch of Solar Corona June 8, 1918 {{Commons category, Solar eclipse of 1918 June 8 1918 in science 1918 06 8 June 1918 1918 06 8
solar eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs approximately every six months, during the eclipse season i ...
occurred at the Moon's descending node
An orbital node is either of the two points where an orbit intersects a plane of reference to which it is inclined. A non-inclined orbit, which is contained in the reference plane, has no nodes.
Planes of reference
Common planes of referenc ...
of orbit between Saturday, June 8 and Sunday, June 9, 1918, with a magnitude
Magnitude may refer to:
Mathematics
*Euclidean vector, a quantity defined by both its magnitude and its direction
*Magnitude (mathematics), the relative size of an object
*Norm (mathematics), a term for the size or length of a vector
*Order of ...
of 1.0292. A solar eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs approximately every six months, during the eclipse season i ...
occurs when the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
passes between Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
and the Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter
The angular diameter, angular size, apparent diameter, or apparent size is an angular separation (in units of angle) describing how large a sphere or circle appears from a given point of view. In the vision sciences, it is called the '' visual ...
is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring 3.7 days after perigee
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. The line of apsides (also called apse line, or major axis of the orbit) is the line connecting the two extreme values.
Apsides perta ...
(on June 5, 1918, at 8:40 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.
The eclipse was viewable across the entire contiguous United States
The contiguous United States, also known as the U.S. mainland, officially referred to as the conterminous United States, consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the District of Columbia of the United States in central North America. The te ...
, an event which would not occur again until the solar eclipse of August 21, 2017
The solar eclipse of August 21, 2017, dubbed the "Great American Eclipse" by some media, was a total solar eclipse visible within a band that spanned the contiguous United States from the Pacific Ocean, Pacific to the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic c ...
.
The Path
 The path of totality started south of
The path of totality started south of Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
, went across the Pacific Ocean, passing northern part of Kitadaitō, Okinawa
is a List of villages in Japan, village consisting of the islands of Kitadaitōjima and Okidaitōjima of Shimajiri District, Okinawa, Shimajiri District, Okinawa Prefecture, Japan.
As of October 2016, the village has an estimated population of 61 ...
and the whole Tori-shima in Izu Islands
The are a group of volcanic islands stretching south and east from the Izu Peninsula of Honshū, Japan. Administratively, they form two towns and six villages; all part of Tokyo Prefecture. The largest is Izu Ōshima, usually called simply Ōsh ...
on June 9 (Sunday), and then acrossed the contiguous United States
The contiguous United States, also known as the U.S. mainland, officially referred to as the conterminous United States, consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the District of Columbia of the United States in central North America. The te ...
and British Bahamas (today's Bahamas
The Bahamas, officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an archipelagic and island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean. It contains 97 per cent of the archipelago's land area and 88 per cent of its population. ...
) on June 8 (Saturday). The largest city to see totality was Denver
Denver ( ) is a List of municipalities in Colorado#Consolidated city and county, consolidated city and county, the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Colorado, most populous city of the U.S. state of ...
, although many could theoretically see it as the size of the shadow was between across as it traveled across America. The longest duration of totality was in the Pacific at a point south of Alaska. The path of the eclipse finished near Bermuda
Bermuda is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean. The closest land outside the territory is in the American state of North Carolina, about to the west-northwest.
Bermuda is an ...
.
Besides the path where a total solar eclipse was visible, a partial solar eclipse was visible in the eastern part of East Asia
East Asia is a geocultural region of Asia. It includes China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan, plus two special administrative regions of China, Hong Kong and Macau. The economies of Economy of China, China, Economy of Ja ...
, northern part of Northern Europe
The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54th parallel north, 54°N, or may be based on other ge ...
, eastern part of Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of approximately 2,000 small islands in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: Maritime Southeast Asia to the west, Poly ...
, Hawaii Islands
The Hawaiian Islands () are an archipelago of eight major volcanic islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the Pacific Ocean, North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the Hawaii (island), island of Hawaii in the south to nort ...
, northeastern Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
, the entire North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
except the Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles is a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea, forming part of the West Indies in Caribbean, Caribbean region of the Americas. They are distinguished from the larger islands of the Greater Antilles to the west. They form an arc w ...
, and the northwestern tip of South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
.
U.S. Observation team
 The path of the eclipse clipped
The path of the eclipse clipped Washington state
Washington, officially the State of Washington, is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is often referred to as Washington State to distinguish it from the national capital, both named after George Washington ...
, and then moved across the whole of Oregon through the rest of the country, exiting over Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
. The U.S. Naval Observatory
The United States Naval Observatory (USNO) is a scientific and military facility that produces geopositioning, navigation and timekeeping data for the United States Navy and the United States Department of Defense. Established in 1830 as the ...
(USNO) obtained a special grant of $3,500 from Congress for a team to observe the eclipse in Baker City, Oregon
Oregon ( , ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is a part of the Western U.S., with the Columbia River delineating much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while t ...
. The team had been making preparations since the year before, and John C. Hammond led the first members to Baker City on April 11. The location was important, as it influenced the probability of cloud cover and the duration and angle of the sun during the eclipse. The team included Samuel Alfred Mitchell
Samuel Alfred Mitchell (April 29, 1874 – February 22, 1960) was a Canadian-American astronomer who studied solar eclipses and set up a program to use photographic techniques to determine the distance to stars at McCormick Observatory, where h ...
as its expert on eclipses, and Howard Russell Butler
Howard Russell Butler (March 3, 1856 – May 20, 1934) was an American painter and founder of the American Fine Arts Society. Butler persuaded Andrew Carnegie to fund the construction of Carnegie Lake near Princeton University, supervised the cons ...
, an artist and physicist. In a time before reliable colour photography, Butler's role was to paint the eclipse at totality after observing it for 112.1 seconds. He noted later that he used a system of taking notes of the colours using skills he had learned for transient effects.
Joel Stebbins
Joel Stebbins (July 30, 1878 – March 16, 1966) was an American astronomer who pioneered photoelectric photometry in astronomy. He was director of the University of Illinois Observatory from 1903 to 1922 where he performed innovative work with t ...
and Jakob Kunz from the University of Illinois Observatory
The University of Illinois Astronomical Observatory, located at 901 S. Mathews Avenue in Urbana, Illinois, on the campus of the University of Illinois Urbana–Champaign, was built in 1896, and was designed by Charles A. Gunn. It was listed on t ...
made the first photoelectric photometric observations of the solar corona from their observing site near Rock Springs, Wyoming
Observation
As the total eclipse approached, the team watched as clouds obscured the Sun. The clouds did clear, but during their most important observations the Sun was covered by a thin cloud; the Sun was completely visible five minutes later. This was not unusual, as cloudy conditions were reported across the country, where the eclipse was also observed from theYerkes Observatory
Yerkes Observatory ( ) is an astronomical observatory located in Williams Bay, Wisconsin, United States. The observatory was operated by the University of Chicago Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics from its founding in 1897 until 2018. O ...
, Lick Observatory
The Lick Observatory is an astronomical observatory owned and operated by the University of California. It is on the summit of Mount Hamilton (California), Mount Hamilton, in the Diablo Range just east of San Jose, California, United States. The ...
, and Mount Wilson Observatory
The Mount Wilson Observatory (MWO) is an Observatory#Astronomical observatories, astronomical observatory in Los Angeles County, California, United States. The MWO is located on Mount Wilson (California), Mount Wilson, a peak in the San Gabrie ...
.
Following the 1915 prediction of Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein (14 March 187918 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist who is best known for developing the theory of relativity. Einstein also made important contributions to quantum mechanics. His mass–energy equivalence f ...
's General theory of relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity, and as Einstein's theory of gravity, is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physi ...
that light would be deflected when passing near a massive object such as the Sun, the USNO expedition attempted to validate Einstein's prediction by measuring the position of stars near the Sun. The cloud cover during totality obscured observations of stars, though, preventing this test of the validity of general relativity from being completed until the solar eclipse of May 29, 1919
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Thursday, May 29, 1919, with a magnitude of 1.0719. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of ...
.
Eclipse details
Shown below are two tables displaying details about this particular solar eclipse. The first table outlines times at which the moon's penumbra or umbra attains the specific parameter, and the second table describes various other parameters pertaining to this eclipse.Eclipse season
This eclipse is part of aneclipse season
An eclipse season is a period, roughly every six months, when eclipses occur. Eclipse seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of the Orbit of the Moon, Moon's orbital plane (orbital inclination, tilted five degrees to the ecliptic, Earth ...
, a period, roughly every six months, when eclipses occur. Only two (or occasionally three) eclipse seasons occur each year, and each season lasts about 35 days and repeats just short of six months (173 days) later; thus two full eclipse seasons always occur each year. Either two or three eclipses happen each eclipse season. In the sequence below, each eclipse is separated by a fortnight
A fortnight is a unit of time equal to 14 days (two weeks). The word derives from the Old English term , meaning "" (or "fourteen days", since the Anglo-Saxons counted by nights).
Astronomy and tides
In astronomy, a ''lunar fortnight'' is hal ...
.
Related eclipses
Eclipses in 1918
* A total solar eclipse on June 8. * A partial lunar eclipse on June 24. * An annular solar eclipse on December 3. * A penumbral lunar eclipse on December 17.Metonic
* Preceded by:Solar eclipse of August 21, 1914
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Friday, August 21, 1914, with a magnitude of 1.0328. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of t ...
* Followed by: Solar eclipse of March 28, 1922
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Tuesday, March 28, 1922, with a magnitude of 0.9381. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image o ...
Tzolkinex
* Preceded by: Solar eclipse of April 28, 1911 * Followed by:Solar eclipse of July 20, 1925
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's Lunar node, ascending node of orbit between Monday, July 20 and Tuesday, July 21, 1925, with a Magnitude of eclipse, magnitude of 0.9436. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and ...
Half-Saros
* Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of June 4, 1909 * Followed by: Lunar eclipse of June 15, 1927Tritos
* Preceded by: Solar eclipse of July 10, 1907 * Followed by: Solar eclipse of May 9, 1929Solar Saros 126
* Preceded by:Solar eclipse of May 28, 1900
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Monday, May 28, 1900, with a magnitude of 1.0249. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the ...
* Followed by: Solar eclipse of June 19, 1936
file:1936 uludag.jpg, left, Astronomers in Turkey observing the 1936 eclipse
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's Lunar node, descending node of orbit on Friday, June 19, 1936, with a Magnitude of eclipse, magnitude of 1.0329. A solar ecl ...
Inex
* Preceded by: Solar eclipse of June 28, 1889 * Followed by: Solar eclipse of May 20, 1947Triad
* Preceded by: Solar eclipse of August 7, 1831 * Followed by: Solar eclipse of April 8, 2005Solar eclipses of 1916–1920
Saros 126
Metonic series
Tritos series
Inex series
Notes
Other links
NASA graphic
* ttp://xjubier.free.fr/en/site_pages/solar_eclipses/Solar_Corona_Shape_pg02.html Foto and sketch of Solar Corona June 8, 1918 {{Commons category, Solar eclipse of 1918 June 8 1918 in science 1918 06 8 June 1918 1918 06 8