Sodium Hydroxide on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an
Solid-Liquid Equilibrium (SLE) and Vapour-Liquid Equilibrium (VLE) of Aqueous NaOH
". Online report, accessed on 2017-04-29. When solutions with less than 18.4% NaOH are cooled, water
5th edition, John Wiley & Sons Historically, sodium hydroxide was produced by treating sodium carbonate with
Clean green finish that sends a loved one down the drain
Times Online. Retrieved 2013-02-20.Thacker, H. Leon; Kastner, Justin (August 2004)
''Carcass Disposal: A Comprehensive Review. Chapter 6''
. National Agricultural Biosecurity Center, Kansas State University, 2004. Retrieved 2010-03-08 and the only solids that remain are bone hulls, which can be crushed between one's fingertips.Roach, Mary (2004). ''Stiff: The Curious Lives of Human Cadavers'', New York: W.W. Norton & Company. . Sodium hydroxide is frequently used in the process of decomposing roadkill dumped in landfills by animal disposal contractors. Due to its availability and low cost, it has been used by criminals to dispose of corpses. Italian

 Sodium hydroxide is used in the home as a type of drain openers to unblock clogged drains, usually in the form of a dry crystal or as a thick liquid gel. The alkali reacts with greases to produce water soluble soap and
Sodium hydroxide is used in the home as a type of drain openers to unblock clogged drains, usually in the form of a dry crystal or as a thick liquid gel. The alkali reacts with greases to produce water soluble soap and
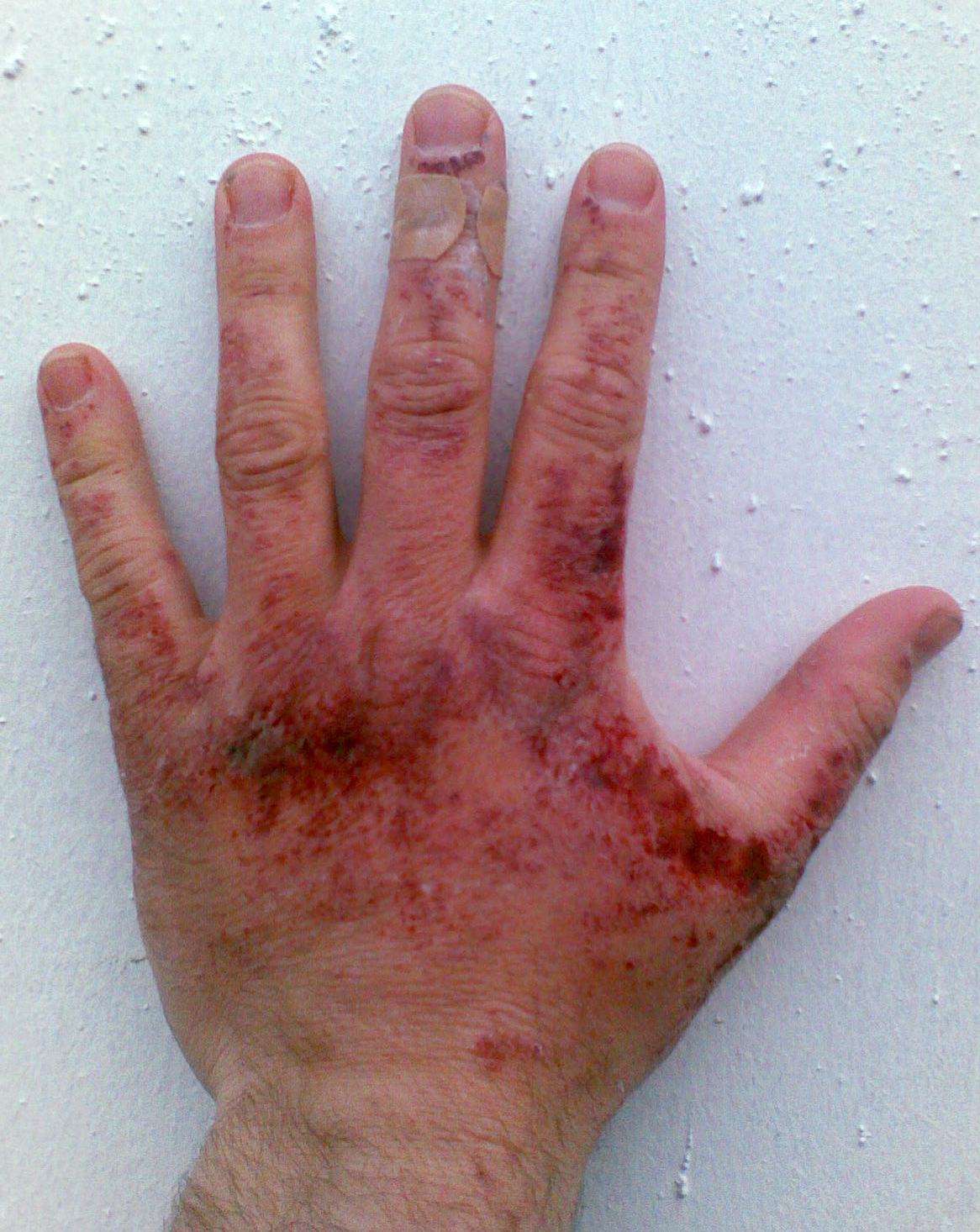 Like other
Like other
 Careful storage is needed when handling sodium hydroxide for use, especially bulk volumes. Following proper NaOH storage guidelines and maintaining worker/environment safety is always recommended given the chemical's burn hazard.
Sodium hydroxide is often stored in bottles for small-scale laboratory use, within intermediate bulk containers (medium volume containers) for cargo handling and transport, or within large stationary storage tanks with volumes up to 100,000 gallons for manufacturing or waste water plants with extensive NaOH use. Common materials that are compatible with sodium hydroxide and often utilized for NaOH storage include: polyethylene ( HDPE, usual, XLPE, less common),
Careful storage is needed when handling sodium hydroxide for use, especially bulk volumes. Following proper NaOH storage guidelines and maintaining worker/environment safety is always recommended given the chemical's burn hazard.
Sodium hydroxide is often stored in bottles for small-scale laboratory use, within intermediate bulk containers (medium volume containers) for cargo handling and transport, or within large stationary storage tanks with volumes up to 100,000 gallons for manufacturing or waste water plants with extensive NaOH use. Common materials that are compatible with sodium hydroxide and often utilized for NaOH storage include: polyethylene ( HDPE, usual, XLPE, less common),
/ref> A procedure for making sodium hydroxide appeared as part of a recipe for making soap in an Arab book of the late 13th century: (Inventions from the Various Industrial Arts), which was compiled by al-Muzaffar Yusuf ibn 'Umar ibn 'Ali ibn Rasul (d. 1295), a king of
International Chemical Safety Card 0360
* Euro Chlor-How is chlorine made
Chlorine Online
CDC – Sodium Hydroxide – NIOSH Workplace Safety and Health Topic
* Data sheets *
Technical charts (page 33—41)
for enthalpy, temperature and pressure *
Sodium Hydroxide MSDS
*
Certified Lye MSDS
*
Hill Brothers MSDS
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20150508191719/http://www.inclusive-science-engineering.com/inorganic-chemical-caustic-soda-production-process-description-and-flowsheet/ Caustic soda production in continuous causticising plant by lime soda process] {{DEFAULTSORT:Sodium Hydroxide Chemical engineering Cleaning products Deliquescent materials Desiccants Household chemicals Hydroxides Inorganic compounds Photographic chemicals Sodium compounds E-number additives Food acidity regulators
inorganic compound
An inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bondsthat is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemistry''.
Inorgan ...
with the formula . It is a white solid ionic compound
In chemistry, a salt or ionic compound is a chemical compound consisting of an assembly of positively charged ions (Cation, cations) and negatively charged ions (Anion, anions), which results in a compound with no net electric charge (electrica ...
consisting of sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
s and hydroxide anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conven ...
s .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly corrosive
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engine ...
base and alkali that decomposes lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing ...
s and protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s at ambient temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making ...
s and at high concentrations may cause severe chemical burns. It is highly soluble in water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
, and readily absorbs moisture
Moisture is the presence of a liquid, especially water, often in trace amounts. Moisture is defined as water in the adsorbed or absorbed phase. Small amounts of water may be found, for example, in the air (humidity), in foods, and in some comme ...
and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
from the air. It forms a series of hydrates . The monohydrate crystallizes from water solutions between 12.3 and 61.8 °C. The commercially available "sodium hydroxide" is often this monohydrate, and published data may refer to it instead of the anhydrous compound.
As one of the simplest hydroxides, sodium hydroxide is frequently used alongside neutral water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
and acidic hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid or spirits of salt, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride (HCl). It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungency, pungent smell. It is classified as a acid strength, strong acid. It is ...
to demonstrate the pH scale to chemistry students.
Sodium hydroxide is used in many industries: in the making of wood pulp
Pulp is a fibrous Lignocellulosic biomass, lignocellulosic material prepared by chemically, semi-chemically, or mechanically isolating the cellulose fiber, cellulosic fibers of wood, fiber crops, Paper recycling, waste paper, or cotton paper, rag ...
and paper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, Textile, rags, poaceae, grasses, Feces#Other uses, herbivore dung, or other vegetable sources in water. Once the water is dra ...
, textile
Textile is an Hyponymy and hypernymy, umbrella term that includes various Fiber, fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, Staple (textiles)#Filament fiber, filaments, Thread (yarn), threads, and different types of #Fabric, fabric. ...
s, drinking water
Drinking water or potable water is water that is safe for ingestion, either when drunk directly in liquid form or consumed indirectly through food preparation. It is often (but not always) supplied through taps, in which case it is also calle ...
, soap
Soap is a salt (chemistry), salt of a fatty acid (sometimes other carboxylic acids) used for cleaning and lubricating products as well as other applications. In a domestic setting, soaps, specifically "toilet soaps", are surfactants usually u ...
s and detergent
A detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with Cleanliness, cleansing properties when in Concentration, dilute Solution (chemistry), solutions. There are a large variety of detergents. A common family is the alkylbenzene sulfonate ...
s, and as a drain cleaner. Worldwide production in 2022 was approximately 83 million tons.
Properties
Physical properties
Pure sodium hydroxide is a colorless crystalline solid that melts at without decomposition and boils at . It is highly soluble in water, with a lower solubility in polarsolvent
A solvent (from the Latin language, Latin ''wikt:solvo#Latin, solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a Solution (chemistry), solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas ...
s such as ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the ps ...
and methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical compound and the simplest aliphatic Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with the chemical formula (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often ab ...
. Sodium hydroxide is insoluble in ether and other non-polar solvents.
Similar to the hydration of sulfuric acid, dissolution of solid sodium hydroxide in water is a highly exothermic reaction where a large amount of heat is liberated, posing a threat to safety through the possibility of splashing. The resulting solution is usually colorless and odorless. As with other alkaline solutions, it feels slippery with skin contact due to the process of saponification
Saponification is a process of cleaving esters into carboxylate salts and Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols by the action of aqueous alkali. Typically aqueous sodium hydroxide solutions are used. It is an important type of alkaline hydrolysis. When the ...
that occurs between and natural skin oils.
Viscosity
Concentrated (50%) aqueous solutions of sodium hydroxide have a characteristicviscosity
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's rate-dependent drag (physics), resistance to a change in shape or to movement of its neighboring portions relative to one another. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of ''thickness''; for e ...
, 78 m Pa·s, that is much greater than that of water (1.0 mPa·s) and near that of olive oil (85 mPa·s) at room temperature. The viscosity of aqueous , as with any liquid chemical, is inversely related to its temperature, i.e., its viscosity decreases as temperature increases, and vice versa. The viscosity of sodium hydroxide solutions plays a direct role in its application as well as its storage.
Hydrates
Sodium hydroxide can form several hydrates , which result in a complex solubility diagram that was described in detail by Spencer Umfreville Pickering in 1893. The known hydrates and the approximate ranges of temperature and concentration (mass percent of NaOH) of their saturated water solutions are: * Heptahydrate, : from −28 °C (18.8%) to −24 °C (22.2%). * Pentahydrate, : from −24 °C (22.2%) to −17.7 °C (24.8%). * Tetrahydrate, , α form: from −17.7 °C (24.8%) to 5.4 °C (32.5%). * Tetrahydrate, , β form: metastable. * Trihemihydrate, : from 5.4 °C (32.5%) to 15.38 °C (38.8%) and then to 5.0 °C (45.7%). * Trihydrate, : metastable. * Dihydrate, : from 5.0 °C (45.7%) to 12.3 °C (51%). * Monohydrate, : from 12.3 °C (51%) to 65.10 °C (69%) then to 62.63 °C (73.1%). Early reports refer to hydrates with ''n'' = 0.5 or ''n'' = 2/3, but later careful investigations failed to confirm their existence. The only hydrates with stable melting points are (65.10 °C) and (15.38 °C). The other hydrates, except the metastable ones and (β) can be crystallized from solutions of the proper composition, as listed above. However, solutions of NaOH can be easily supercooled by many degrees, which allows the formation of hydrates (including the metastable ones) from solutions with different concentrations. For example, when a solution of NaOH and water with 1:2 mole ratio (52.6% NaOH by mass) is cooled, the monohydrate normally starts to crystallize (at about 22 °C) before the dihydrate. However, the solution can easily be supercooled down to −15 °C, at which point it may quickly crystallize as the dihydrate. When heated, the solid dihydrate might melt directly into a solution at 13.35 °C; however, once the temperature exceeds 12.58 °C it often decomposes into solid monohydrate and a liquid solution. Even the ''n'' = 3.5 hydrate is difficult to crystallize, because the solution supercools so much that other hydrates become more stable. A hot water solution containing 73.1% (mass) of NaOH is a eutectic that solidifies at about 62.63 °C as an intimate mix of anhydrous and monohydrate crystals. A second stable eutectic composition is 45.4% (mass) of NaOH, that solidifies at about 4.9 °C into a mixture of crystals of the dihydrate and of the 3.5-hydrate. The third stable eutectic has 18.4% (mass) of NaOH. It solidifies at about −28.7 °C as a mixture of water ice and the heptahydrate .M. Conde Engineering:Solid-Liquid Equilibrium (SLE) and Vapour-Liquid Equilibrium (VLE) of Aqueous NaOH
". Online report, accessed on 2017-04-29. When solutions with less than 18.4% NaOH are cooled, water
ice
Ice is water that is frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 ° C, 32 ° F, or 273.15 K. It occurs naturally on Earth, on other planets, in Oort cloud objects, and as interstellar ice. As a naturally oc ...
crystallizes first, leaving the NaOH in solution.
The α form of the tetrahydrate has density 1.33 g/cm3. It melts congruously at 7.55 °C into a liquid with 35.7% NaOH and density 1.392 g/cm3, and therefore floats on it like ice on water. However, at about 4.9 °C it may instead melt incongruously into a mixture of solid and a liquid solution.
The β form of the tetrahydrate is metastable, and often transforms spontaneously to the α form when cooled below −20 °C. Once initiated, the exothermic transformation is complete in a few minutes, with a 6.5% increase in volume of the solid. The β form can be crystallized from supercooled solutions at −26 °C, and melts partially at −1.83 °C.
The "sodium hydroxide" of commerce is often the monohydrate (density 1.829 g/cm3). Physical data in technical literature may refer to this form, rather than the anhydrous compound.
Crystal structure
NaOH and its monohydrate form orthorhombic crystals with the space groups Cmcm ( oS8) and Pbca (oP24), respectively. The monohydrate cell dimensions are a = 1.1825, b = 0.6213, c = 0.6069 nm. The atoms are arranged in a hydrargillite-like layer structure, with each sodium atom surrounded by six oxygen atoms, three each from hydroxide ions and three from water molecules. The hydrogen atoms of the hydroxyls form strong bonds with oxygen atoms within each O layer. Adjacent O layers are held together byhydrogen bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (H-bond) is a specific type of molecular interaction that exhibits partial covalent character and cannot be described as a purely electrostatic force. It occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom, Covalent bond, covalently b ...
s between water molecules.
Chemical properties
Reaction with acids
Sodium hydroxide reacts with protic acids to produce water and the corresponding salts. For example, when sodium hydroxide reacts withhydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid or spirits of salt, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride (HCl). It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungency, pungent smell. It is classified as a acid strength, strong acid. It is ...
, sodium chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as Salt#Edible salt, edible salt, is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. It is transparent or translucent, brittle, hygroscopic, and occurs a ...
is formed:
:
In general, such neutralization reactions are represented by one simple net ionic equation:
:
This type of reaction with a strong acid releases heat, and hence is exothermic. Such acid–base reaction
In chemistry, an acid–base reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs between an acid and a base. It can be used to determine pH via titration. Several theoretical frameworks provide alternative conceptions of the reaction mechanisms an ...
s can also be used for titration
Titration (also known as titrimetry and volumetric analysis) is a common laboratory method of Quantitative research, quantitative Analytical chemistry, chemical analysis to determine the concentration of an identified analyte (a substance to be ...
s. However, sodium hydroxide is not used as a primary standard because it is hygroscopic
Hygroscopy is the phenomenon of attracting and holding water molecules via either absorption (chemistry), absorption or adsorption from the surrounding Natural environment, environment, which is usually at normal or room temperature. If water mol ...
and absorbs carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
from air.
Reaction with acidic oxides
Sodium hydroxide also reacts with acidic oxides, such assulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless gas with a pungent smell that is responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is r ...
. Such reactions are often used to " scrub" harmful acidic gases (like and ) produced in the burning of coal and thus prevent their release into the atmosphere. For example,
:
Reaction with metals and oxides
Glass reacts slowly with aqueous sodium hydroxide solutions at ambient temperatures to form solublesilicate
A silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used ...
s. Because of this, glass joints and stopcocks exposed to sodium hydroxide have a tendency to "freeze". Flasks and glass-lined chemical reactors are damaged by long exposure to hot sodium hydroxide, which also frosts the glass. Sodium hydroxide does not attack iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
at room temperature, since iron does not have amphoteric properties (i.e., it only dissolves in acid, not base).
Nevertheless, at high temperatures (e.g. above 500 °C), iron can react endothermic
An endothermic process is a chemical or physical process that absorbs heat from its surroundings. In terms of thermodynamics, it is a thermodynamic process with an increase in the enthalpy (or internal energy ) of the system.Oxtoby, D. W; Gillis, ...
ally with sodium hydroxide to form iron(III) oxide
Iron(III) oxide or ferric oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula . It occurs in nature as the mineral hematite, which serves as the primary source of iron for the steel industry. It is also known as red iron oxide, especially when use ...
, sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
metal, and hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
gas. This is due to the lower enthalpy of formation of iron(III) oxide (−824.2 kJ/mol) compared to sodium hydroxide (−500 kJ/mol) and positive entropy change of the reaction, which implies spontaneity at high temperatures (, ) and non-spontaneity at low temperatures (, ). Consider the following reaction between molten sodium hydroxide and finely divided iron filings:
:
A few transition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. The lanthanide and actinid ...
s, however, may react quite vigorously with sodium hydroxide under milder conditions.
In 1986, an aluminium road tanker in the UK was mistakenly used to transport 25% sodium hydroxide solution, causing pressurization of the contents and damage to tankers. The pressurization is due to the hydrogen gas which is produced in the reaction between sodium hydroxide and aluminium:
:
Precipitant
Unlike sodium hydroxide, which is soluble, the hydroxides of most transition metals are insoluble, and therefore sodium hydroxide can be used to precipitate transition metal hydroxides. The following colours are observed: * Copper - blue * Iron(II) - green * Iron(III) - yellow / brown Zinc and lead salts dissolve in excess sodium hydroxide to give a clear solution of or . Aluminium hydroxide is used as a gelatinous flocculant to filter out particulate matter inwater treatment
Water treatment is any process that improves the quality of water to make it appropriate for a specific end-use. The end use may be drinking, industrial water supply, irrigation, river flow maintenance, water recreation or many other uses, ...
. Aluminium hydroxide is prepared at the treatment plant from aluminium sulfate
Aluminium sulfate is a salt with the chemical formula, formula . It is soluble in water and is mainly used as a Coagulation (water treatment), coagulating agent (promoting particle collision by neutralizing charge) in the purification of drinking ...
by reacting it with sodium hydroxide or bicarbonate.
:
:
Saponification
Sodium hydroxide can be used for the base-driven hydrolysis of esters (also calledsaponification
Saponification is a process of cleaving esters into carboxylate salts and Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols by the action of aqueous alkali. Typically aqueous sodium hydroxide solutions are used. It is an important type of alkaline hydrolysis. When the ...
), amide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a chemical compound, compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent any group, typically organyl functional group, groups or hydrogen at ...
s and alkyl halides. However, the limited solubility of sodium hydroxide in organic solvents means that the more soluble potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which utili ...
(KOH) is often preferred. Touching a sodium hydroxide solution with bare hands, while not recommended, produces a slippery feeling. This happens because oils on the skin such as sebum
A sebaceous gland or oil gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur ...
are converted to soap.
Despite solubility in propylene glycol
Propylene glycol ( IUPAC name: propane-1,2-diol) is a viscous, colorless liquid. It is almost odorless and has a faintly sweet taste. Its chemical formula is CH3CH(OH)CH2OH.
As it contains two alcohol groups, it is classified as a diol. An al ...
it is unlikely to replace water in saponification due to propylene glycol's primary reaction with fat before reaction between sodium hydroxide and fat.
Production
Sodium hydroxide is industrially produced, first as a 32% solution, and then evaporated to a 50% solution by variations of the electrolyticchloralkali process
The chloralkali process (also chlor-alkali and chlor alkali) is an industrial process for the electrolysis of sodium chloride (NaCl) solutions. It is the technology used to produce chlorine and sodium hydroxide (caustic soda), which are commodi ...
. Chlorine gas is the main product from this process. Solid sodium hydroxide is obtained from this solution by the evaporation of water. Solid sodium hydroxide is most commonly sold as flakes, prills, and cast blocks.
In 2022, world production was estimated at 83 million dry tonnes of sodium hydroxide, and demand was estimated at 51 million tonnes. In 1998, total world production was around 45 million tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1,000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton in the United States to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the s ...
s. North America and Asia each contributed around 14 million tonnes, while Europe produced around 10 million tonnes. In the United States, the major producer of sodium hydroxide is Olin, which has annual production around 5.7 million tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1,000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton in the United States to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the s ...
s from sites at Freeport, Texas; Plaquemine, Louisiana
Plaquemine is a city in and the parish seat of Iberville Parish, Louisiana, Iberville Parish, Louisiana, United States. It is part of the Baton Rouge metropolitan area, Baton Rouge metropolitan statistical area. At the 2010 United States census, ...
; St. Gabriel, Louisiana; McIntosh, Alabama; Charleston, Tennessee; Niagara Falls, New York; and Bécancour, Canada. Other major US producers include Oxychem, Westlake, Shintek, and Formosa. All of these companies use the chloralkali process
The chloralkali process (also chlor-alkali and chlor alkali) is an industrial process for the electrolysis of sodium chloride (NaCl) solutions. It is the technology used to produce chlorine and sodium hydroxide (caustic soda), which are commodi ...
.''Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology''5th edition, John Wiley & Sons Historically, sodium hydroxide was produced by treating sodium carbonate with
calcium hydroxide
Calcium hydroxide (traditionally called slaked lime) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca( OH)2. It is a colorless crystal or white powder and is produced when quicklime ( calcium oxide) is mixed with water. Annually, approxim ...
(slaked lime) in a metathesis reaction which takes advantage of the fact that sodium hydroxide is soluble, while calcium carbonate is not. This process was called causticizing.
:
The sodium carbonate for this reaction was produced by the Leblanc process in the early 19th century, or the Solvay process in the late 19th century. The conversion of sodium carbonate to sodium hydroxide was superseded entirely by the chloralkali process
The chloralkali process (also chlor-alkali and chlor alkali) is an industrial process for the electrolysis of sodium chloride (NaCl) solutions. It is the technology used to produce chlorine and sodium hydroxide (caustic soda), which are commodi ...
, which produces sodium hydroxide in a single process.
Sodium hydroxide is also produced by combining pure sodium metal with water. The byproducts are hydrogen gas and heat, often resulting in a flame.
:
This reaction is commonly used for demonstrating the reactivity of alkali metals in academic environments; however, it is not used commercially aside from a reaction within the mercury cell chloralkali process where sodium amalgam is reacted with water.
Uses
Sodium hydroxide is a popular strong base used in industry. Sodium hydroxide is used in the manufacture of sodium salts and detergents, pH regulation, and organic synthesis. In bulk, it is most often handled as anaqueous solution
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, also known as sodium chloride (NaCl), in water ...
, since solutions are cheaper and easier to handle.
Sodium hydroxide is used in many scenarios where it is desirable to increase the alkalinity
Alkalinity (from ) is the capacity of water to resist Freshwater acidification, acidification. It should not be confused with base (chemistry), basicity, which is an absolute measurement on the pH scale. Alkalinity is the strength of a buffer s ...
of a mixture, or to neutralize acids. For example, in the petroleum industry, sodium hydroxide is used as an additive in drilling mud
In geotechnical engineering, drilling fluid, also known as drilling mud, is used to aid the drilling of boreholes into the earth. Used while drilling oil well, oil and natural gas wells and on exploration drilling rigs, drilling fluids are a ...
to increase alkalinity
Alkalinity (from ) is the capacity of water to resist Freshwater acidification, acidification. It should not be confused with base (chemistry), basicity, which is an absolute measurement on the pH scale. Alkalinity is the strength of a buffer s ...
in bentonite
Bentonite ( ) is an Absorption (chemistry), absorbent swelling clay consisting mostly of montmorillonite (a type of smectite) which can either be Na-montmorillonite or Ca-montmorillonite. Na-montmorillonite has a considerably greater swelli ...
mud systems, to increase the mud viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's rate-dependent drag (physics), resistance to a change in shape or to movement of its neighboring portions relative to one another. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of ''thickness''; for e ...
, and to neutralize any acid gas (such as hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is toxic, corrosive, and flammable. Trace amounts in ambient atmosphere have a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. Swedish chemist ...
and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
) which may be encountered in the geological formation
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics (lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock expo ...
as drilling progresses. Another use is in salt spray testing where pH needs to be regulated. Sodium hydroxide is used with hydrochloric acid to balance pH. The resultant salt, NaCl, is the corrosive agent used in the standard neutral pH salt spray test.
Poor quality crude oil can be treated with sodium hydroxide to remove sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms ...
ous impurities in a process known as ''caustic washing''. Sodium hydroxide reacts with weak acids such as hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is toxic, corrosive, and flammable. Trace amounts in ambient atmosphere have a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. Swedish chemist ...
and mercaptans to yield non-volatile sodium salts, which can be removed. The waste which is formed is toxic and difficult to deal with, and the process is banned in many countries because of this. In 2006, Trafigura used the process and then dumped the waste in Ivory Coast.
Other common uses of sodium hydroxide include:
* for making soaps and detergents. Sodium hydroxide is used for hard bar soap, while potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which utili ...
is used for liquid soaps. Sodium hydroxide is used more often than potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which utili ...
because it is cheaper and a smaller quantity is needed.
* as drain cleaners that convert pipe-clogging fats and grease into soap, which dissolves in water
* for making artificial textile fibres such as rayon
* in the manufacture of paper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, Textile, rags, poaceae, grasses, Feces#Other uses, herbivore dung, or other vegetable sources in water. Once the water is dra ...
. Around 56% of sodium hydroxide produced is used by industry, 25% of which is used in the paper industry.
* in purifying bauxite ore from which aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
metal is extracted. This is known as the Bayer process.
* de-greasing metals
* oil refining
* making dyes and bleaches
* in water treatment plants for pH regulation
* to treat bagels and pretzel dough, giving the distinctive shiny finish
Chemical pulping
Sodium hydroxide is also widely used in pulping of wood for making paper or regenerated fibers. Along with sodium sulfide, sodium hydroxide is a key component of the white liquor solution used to separatelignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidit ...
from cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of glycosidic bond, β(1→4) linked glucose, D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important s ...
fiber
Fiber (spelled fibre in British English; from ) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often inco ...
s in the kraft process
The kraft process (also known as kraft pulping or sulfate process) is a process for conversion of wood into wood pulp, which consists of almost pure cellulose fibres, the main component of paper. The kraft process involves treatment of wood chip ...
. It also plays a key role in several later stages of the process of bleaching the brown pulp resulting from the pulping process. These stages include oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
delignification, oxidative extraction, and simple extraction, all of which require a strong alkaline environment with a pH > 10.5 at the end of the stages.
Tissue digestion
In a similar fashion, sodium hydroxide is used to digest tissues, as in a process that was used with farm animals at one time. This process involved placing a carcass into a sealed chamber, then adding a mixture of sodium hydroxide and water (which breaks the chemical bonds that keep the flesh intact). This eventually turns the body into a liquid with a dark brown color,Ayres, Chris (27 February 2010Clean green finish that sends a loved one down the drain
Times Online. Retrieved 2013-02-20.Thacker, H. Leon; Kastner, Justin (August 2004)
''Carcass Disposal: A Comprehensive Review. Chapter 6''
. National Agricultural Biosecurity Center, Kansas State University, 2004. Retrieved 2010-03-08 and the only solids that remain are bone hulls, which can be crushed between one's fingertips.Roach, Mary (2004). ''Stiff: The Curious Lives of Human Cadavers'', New York: W.W. Norton & Company. . Sodium hydroxide is frequently used in the process of decomposing roadkill dumped in landfills by animal disposal contractors. Due to its availability and low cost, it has been used by criminals to dispose of corpses. Italian
serial killer
A serial killer (also called a serial murderer) is a person who murders three or more people,An offender can be anyone:
*
*
*
*
* (This source only requires two people) with the killings taking place over a significant period of time in separat ...
Leonarda Cianciulli used this chemical to turn dead bodies into soap. In Mexico, a man who worked for drug cartels admitted disposing of over 300 bodies with it.
Sodium hydroxide is a dangerous chemical due to its ability to hydrolyze protein. If a dilute solution is spilled on the skin, burns may result if the area is not washed thoroughly and for several minutes with running water. Splashes in the eye can be more serious and can lead to blindness.
Dissolving amphoteric metals and compounds
Strong bases attackaluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
. Sodium hydroxide reacts with aluminium and water to release hydrogen gas. The aluminium takes an oxygen atom from sodium hydroxide, which in turn takes an oxygen atom from water, and releases two hydrogen atoms. The reaction thus produces hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
gas and sodium aluminate. In this reaction, sodium hydroxide acts as an agent to make the solution alkaline, which aluminium can dissolve in.
: → 2 +
Sodium aluminate is an inorganic chemical that is used as an effective source of aluminium hydroxide for many industrial and technical applications. Pure sodium aluminate (anhydrous) is a white crystalline solid having a formula variously given as , , , or . Formation of sodium tetrahydroxoaluminate(III) or hydrated sodium aluminate is given by:
:O
This reaction can be useful in etching
Etching is traditionally the process of using strong acid or mordant to cut into the unprotected parts of a metal surface to create a design in intaglio (incised) in the metal. In modern manufacturing, other chemicals may be used on other type ...
, removing anodizing, or converting a polished surface to a satin-like finish, but without further passivation such as anodizing or alodining the surface may become degraded, either under normal use or in severe atmospheric conditions.
In the Bayer process, sodium hydroxide is used in the refining of alumina containing ores (bauxite
Bauxite () is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)), and diaspore (α-AlO(OH) ...
) to produce alumina (aluminium oxide
Aluminium oxide (or aluminium(III) oxide) is a chemical compound of aluminium and oxygen with the chemical formula . It is the most commonly occurring of several Aluminium oxide (compounds), aluminium oxides, and specifically identified as alum ...
) which is the raw material used to produce aluminium via the electrolytic Hall-Héroult process. Since the alumina is amphoteric, it dissolves in the sodium hydroxide, leaving impurities less soluble at high pH such as iron oxides
An iron oxide is a chemical compound composed of iron and oxygen. Several iron oxides are recognized. Often they are nonstoichiometric, non-stoichiometric. Ferric oxyhydroxides are a related class of compounds, perhaps the best known of which is ...
behind in the form of a highly alkaline red mud.
Other amphoteric metals are zinc and lead which dissolve in concentrated sodium hydroxide solutions to give sodium zincate and sodium plumbate respectively.
Esterification and transesterification reagent
Sodium hydroxide is traditionally used in soap making ( cold process soap,saponification
Saponification is a process of cleaving esters into carboxylate salts and Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols by the action of aqueous alkali. Typically aqueous sodium hydroxide solutions are used. It is an important type of alkaline hydrolysis. When the ...
). It was made in the nineteenth century for a hard surface rather than liquid product because it was easier to store and transport.
For the manufacture of biodiesel
Biodiesel is a renewable biofuel, a form of diesel fuel, derived from biological sources like vegetable oils, animal fats, or recycled greases, and consisting of long-chain fatty acid esters. It is typically made from fats.
The roots of bi ...
, sodium hydroxide is used as a catalyst for the transesterification of methanol and triglycerides. This only works with anhydrous sodium hydroxide, because combined with water the fat would turn into soap
Soap is a salt (chemistry), salt of a fatty acid (sometimes other carboxylic acids) used for cleaning and lubricating products as well as other applications. In a domestic setting, soaps, specifically "toilet soaps", are surfactants usually u ...
, which would be tainted with methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical compound and the simplest aliphatic Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with the chemical formula (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often ab ...
. NaOH is used more often than potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which utili ...
because it is cheaper and a smaller quantity is needed. Due to production costs, NaOH, which is produced using common salt is cheaper than potassium hydroxide.
Skincare ingredient
Sodium hydroxide is an ingredient used in some skin care and cosmetic products, such as facial cleansers, creams, lotions, and makeup. It is typically used in low concentration as a pH balancer, due its highly alkaline nature.Food preparation
Food uses of sodium hydroxide include washing or chemical peeling offruits
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (angiosperms) that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propaga ...
and vegetables
Vegetables are edible parts of plants that are consumed by humans or other animals as food. This original meaning is still commonly used, and is applied to plants collectively to refer to all edible plant matter, including flowers, fruits, ...
, chocolate
Chocolate is a food made from roasted and ground cocoa beans that can be a liquid, solid, or paste, either by itself or to flavoring, flavor other foods.
Cocoa beans are the processed seeds of the cacao tree (''Theobroma cacao''); unprocesse ...
and cocoa processing, caramel coloring production, poultry
Poultry () are domesticated birds kept by humans for the purpose of harvesting animal products such as meat, Eggs as food, eggs or feathers. The practice of animal husbandry, raising poultry is known as poultry farming. These birds are most typ ...
scalding, soft drink
A soft drink (see #Terminology, § Terminology for other names) is a class of non-alcoholic drink, usually (but not necessarily) Carbonated water, carbonated, and typically including added Sweetness, sweetener. Flavors used to be Natural flav ...
processing, and thickening ice cream. Olive
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'' ("European olive"), is a species of Subtropics, subtropical evergreen tree in the Family (biology), family Oleaceae. Originating in Anatolia, Asia Minor, it is abundant throughout the Mediterranean ...
s are often soaked in sodium hydroxide for softening; pretzels and German lye rolls are glazed with a sodium hydroxide solution before baking to make them crisp. Owing to the difficulty in obtaining food grade sodium hydroxide in small quantities for home use, sodium carbonate is often used in place of sodium hydroxide. It is known as E number
E numbers, short for Europe numbers, are codes for substances used as food additives, including those found naturally in many foods, such as vitamin C, for use within the European Union (EU) and European Free Trade Association (EFTA). Commonly ...
E524.
Specific foods processed with sodium hydroxide include:
* German pretzels are poached in a boiling sodium carbonate solution or cold sodium hydroxide solution before baking, which contributes to their unique crust.
* Lye water is an essential ingredient in the crust of the traditional baked Chinese moon cakes.
* Most yellow coloured Chinese noodles are made with lye water but are commonly mistaken for containing egg.
* One variety of zongzi uses lye water to impart a sweet flavor.
* Sodium hydroxide causes gelling of egg whites in the production of century eggs.
* Some methods of preparing olives involve subjecting them to a lye-based brine.
* The Filipino dessert () called uses a small quantity of lye water to help give the rice flour batter a jelly-like consistency. A similar process is also used in the kakanin known as or except that the mixture uses grated cassava
''Manihot esculenta'', common name, commonly called cassava, manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America, from Brazil, Paraguay and parts of the Andes. Although ...
instead of rice flour.
* The Norwegian dish known as lutefisk ().
* Bagels are often boiled in a lye solution before baking, contributing to their shiny crust.
* Hominy is dried maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native American ...
(corn) kernels reconstituted by soaking in lye-water. These expand considerably in size and may be further processed by frying to make corn nuts or by drying and grinding to make grits
Grits (stylized as GRITS) is an American Christian hip hop group from Nashville, Tennessee. Their name is an acronym, which stands for "Grammatical Revolution In the Spirit". GRITS is made up of Stacey "Coffee" Jones and Teron "Bonafide" Carter ...
. Hominy is used to create masa, a popular flour used in Mexican cuisine to make corn tortillas and tamales. Nixtamal
Hominy is a food item produced from dried maize (corn) kernels that have been treated with an alkali, in a process called nixtamalization ( is the Nahuatl word for "hominy"). "Lye hominy" is a type of hominy made with lye.
History
The process ...
is similar, but uses calcium hydroxide
Calcium hydroxide (traditionally called slaked lime) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca( OH)2. It is a colorless crystal or white powder and is produced when quicklime ( calcium oxide) is mixed with water. Annually, approxim ...
instead of sodium hydroxide.
Cleaning agent
Sodium hydroxide is frequently used as an industrialcleaning agent
Cleaning agents or hard-surface cleaners are substances (usually liquids, powders, sprays, or granules) used to remove dirt, including dust, stains, foul odors, and clutter on surfaces. Purposes of cleaning agents include health, beauty, removing ...
where it is often called "caustic". It is added to water, heated, and then used to clean process equipment, storage tanks, etc. It can dissolve grease, oils, fats and protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
-based deposits. It is also used for cleaning waste discharge pipes under sinks and drains in domestic properties. Surfactants can be added to the sodium hydroxide solution in order to stabilize dissolved substances and thus prevent redeposition. A sodium hydroxide soak solution is used as a powerful degreaser on stainless steel
Stainless steel, also known as inox, corrosion-resistant steel (CRES), or rustless steel, is an iron-based alloy that contains chromium, making it resistant to rust and corrosion. Stainless steel's resistance to corrosion comes from its chromi ...
and glass bakeware. It is also a common ingredient in oven cleaners.
A common use of sodium hydroxide is in the production of parts washer detergent
A detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with Cleanliness, cleansing properties when in Concentration, dilute Solution (chemistry), solutions. There are a large variety of detergents. A common family is the alkylbenzene sulfonate ...
s. Parts washer detergents based on sodium hydroxide are some of the most aggressive parts washer cleaning chemicals. The sodium hydroxide-based detergents include surfactants, rust inhibitors and defoamers. A parts washer heats water and the detergent in a closed cabinet and then sprays the heated sodium hydroxide and hot water at pressure against dirty parts for degreasing applications. Sodium hydroxide used in this manner replaced many solvent-based systems in the early 1990s when trichloroethane was outlawed by the Montreal Protocol
The Montreal Protocol on Substances That Deplete the Ozone Layer is an international treaty designed to protect the ozone layer by phasing out the production of numerous substances that are responsible for ozone depletion. It was agreed on 16 ...
. Water and sodium hydroxide detergent-based parts washers are considered to be an environmental improvement over the solvent-based cleaning methods.

 Sodium hydroxide is used in the home as a type of drain openers to unblock clogged drains, usually in the form of a dry crystal or as a thick liquid gel. The alkali reacts with greases to produce water soluble soap and
Sodium hydroxide is used in the home as a type of drain openers to unblock clogged drains, usually in the form of a dry crystal or as a thick liquid gel. The alkali reacts with greases to produce water soluble soap and glycerol
Glycerol () is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, sweet-tasting, viscous liquid. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known as glycerides. It is also widely used as a sweetener in the food industry and as a humectant in pha ...
. It also hydrolyzes proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, re ...
, such as those found in hair
Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals.
The human body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and ...
, which may block waste water pipes. Dissolving sodium hydroxide in water is an exothermic reaction producing considerable quantities of heat which assists in speeding up the reactions with grease and other organic matter. Such alkaline drain cleaners and their acidic versions are highly corrosive
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engine ...
and should be handled with great caution.
Relaxer
Sodium hydroxide is used in somerelaxer
A relaxer is a type of lotion or cream generally used by people with tight curls or very curly hair which makes hair easier to hair straightening, straighten by chemically "relaxing" the natural curls. The active agent is usually a strong alkali, ...
s to straighten hair. However, because of the high incidence and intensity of chemical burns, manufacturers of chemical relaxers use other alkaline chemicals in preparations available to consumers. Sodium hydroxide relaxers are still available, but they are used mostly by professionals.
Paint stripper
A solution of sodium hydroxide in water was traditionally used as the most common paint stripper on wooden objects. Its use has become less common, because it can damage the wood surface, raising the grain and staining the colour.Water treatment
Sodium hydroxide is sometimes used during water purification to raise the pH of water supplies. Increased pH makes the water less corrosive to plumbing and reduces the amount of lead, copper and other toxic metals that can dissolve into drinking water.Historical uses
Sodium hydroxide has been used for detection ofcarbon monoxide poisoning
Carbon monoxide poisoning typically occurs from breathing in carbon monoxide (CO) at excessive levels. Symptoms are often described as " flu-like" and commonly include headache, dizziness, weakness, vomiting, chest pain, and confusion. Large ...
, with blood samples of such patients turning to a vermilion color upon the addition of a few drops of sodium hydroxide. Today, carbon monoxide poisoning can be detected by CO oximetry
A CO-oximeter is a device that measures the oxygen carrying state of hemoglobin in a blood specimen, including oxygen-carrying hemoglobin (O2Hb), non-oxygen-carrying but normal hemoglobin (HHb) (formerly, but incorrectly, referred to as 'reduced ...
.
In cement mixes, mortars, concrete, grouts
Sodium hydroxide is used in some cement mix plasticisers. This helps homogenise cement mixes, preventing segregation of sands and cement, decreases the amount of water required in a mix and increases workability of the cement product, be it mortar, render or concrete.Safety
 Like other
Like other corrosive
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engine ...
acid
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis ...
s and alkalis, a few drops of sodium hydroxide solutions can readily decompose proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, re ...
and lipids
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins Vitamin A, A, Vitamin D, D, Vitamin E, E and Vitamin K, K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The fu ...
in living tissues via amide hydrolysis and ester hydrolysis, which consequently cause chemical burns and may induce permanent blindness
Visual or vision impairment (VI or VIP) is the partial or total inability of visual perception. In the absence of treatment such as corrective eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment, visual impairment may cause the individual difficul ...
upon contact with eyes. Solid alkali can also express its corrosive nature if there is water, such as water vapor. Thus, protective equipment, like rubber gloves, safety clothing and eye protection, should always be used when handling this chemical or its solutions. The standard first aid measures for alkali spills on the skin is, as for other corrosives, irrigation with large quantities of water. Washing is continued for at least ten to fifteen minutes.
Moreover, dissolution of sodium hydroxide is highly exothermic, and the resulting heat may cause heat burns or ignite flammables. It also produces heat when reacted with acids.
Sodium hydroxide is mildly corrosive to glass
Glass is an amorphous (non-crystalline solid, non-crystalline) solid. Because it is often transparency and translucency, transparent and chemically inert, glass has found widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in window pane ...
, which can cause damage to glazing or cause ground glass joints to bind. Sodium hydroxide is corrosive to several metals, like aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
which reacts with the alkali to produce flammable hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
gas on contact.
Sodium hydroxide's toxicity level for fish etc. is around 20—200 mg/l and associated with increased pH value. However as it is quickly neutralised and does not accumulate, its effect on the environment is usually easily handled.
Storage
 Careful storage is needed when handling sodium hydroxide for use, especially bulk volumes. Following proper NaOH storage guidelines and maintaining worker/environment safety is always recommended given the chemical's burn hazard.
Sodium hydroxide is often stored in bottles for small-scale laboratory use, within intermediate bulk containers (medium volume containers) for cargo handling and transport, or within large stationary storage tanks with volumes up to 100,000 gallons for manufacturing or waste water plants with extensive NaOH use. Common materials that are compatible with sodium hydroxide and often utilized for NaOH storage include: polyethylene ( HDPE, usual, XLPE, less common),
Careful storage is needed when handling sodium hydroxide for use, especially bulk volumes. Following proper NaOH storage guidelines and maintaining worker/environment safety is always recommended given the chemical's burn hazard.
Sodium hydroxide is often stored in bottles for small-scale laboratory use, within intermediate bulk containers (medium volume containers) for cargo handling and transport, or within large stationary storage tanks with volumes up to 100,000 gallons for manufacturing or waste water plants with extensive NaOH use. Common materials that are compatible with sodium hydroxide and often utilized for NaOH storage include: polyethylene ( HDPE, usual, XLPE, less common), carbon steel
Carbon steel is a steel with carbon content from about 0.05 up to 2.1 percent by weight. The definition of carbon steel from the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) states:
* no minimum content is specified or required for chromium, cobalt ...
, polyvinyl chloride
Polyvinyl chloride (alternatively: poly(vinyl chloride), colloquial: vinyl or polyvinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic polymer of plastic (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of ...
(PVC), stainless steel
Stainless steel, also known as inox, corrosion-resistant steel (CRES), or rustless steel, is an iron-based alloy that contains chromium, making it resistant to rust and corrosion. Stainless steel's resistance to corrosion comes from its chromi ...
, and fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP, with a resistant liner).
Sodium hydroxide must be stored in airtight containers to preserve its normality as it will absorb water and carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
History
Sodium hydroxide was first prepared by soap makers.Thorpe, Thomas Edward, ed., ''A Dictionary of Applied Chemistry'' (London, England: Longmans, Green, and Co., 1913), vol. 5/ref> A procedure for making sodium hydroxide appeared as part of a recipe for making soap in an Arab book of the late 13th century: (Inventions from the Various Industrial Arts), which was compiled by al-Muzaffar Yusuf ibn 'Umar ibn 'Ali ibn Rasul (d. 1295), a king of
Yemen
Yemen, officially the Republic of Yemen, is a country in West Asia. Located in South Arabia, southern Arabia, it borders Saudi Arabia to Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, the north, Oman to Oman–Yemen border, the northeast, the south-eastern part ...
.
The recipe called for passing water repeatedly through a mixture of '' alkali'' (Arabic: , where is ash from saltwort plants, which are rich in sodium; hence ''alkali'' was impure sodium carbonate) and quicklime ( calcium oxide, CaO), whereby a solution of sodium hydroxide was obtained. European soap makers also followed this recipe. When in 1791 the French chemist and surgeon Nicolas Leblanc (1742–1806) patented a process for mass-producing sodium carbonate, natural "soda ash" (impure sodium carbonate that was obtained from the ashes of plants that are rich in sodium) was replaced by this artificial version. However, by the 20th century, the electrolysis of sodium chloride had become the primary method for producing sodium hydroxide.O'Brien, Thomas F.; Bommaraju, Tilak V. and Hine, Fumio (2005) ''Handbook of Chlor-Alkali Technology'', vol. 1. Berlin, Germany: Springer. Chapter 2: History of the Chlor-Alkali Industry, p. 34.
See also
* Acid and base * HAZMAT Class 8 Corrosive Substances * List of cleaning agentsReferences
Bibliography
*External links
International Chemical Safety Card 0360
* Euro Chlor-How is chlorine made
Chlorine Online
CDC – Sodium Hydroxide – NIOSH Workplace Safety and Health Topic
* Data sheets *
Technical charts (page 33—41)
for enthalpy, temperature and pressure *
Sodium Hydroxide MSDS
*
Certified Lye MSDS
*
Hill Brothers MSDS
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20150508191719/http://www.inclusive-science-engineering.com/inorganic-chemical-caustic-soda-production-process-description-and-flowsheet/ Caustic soda production in continuous causticising plant by lime soda process] {{DEFAULTSORT:Sodium Hydroxide Chemical engineering Cleaning products Deliquescent materials Desiccants Household chemicals Hydroxides Inorganic compounds Photographic chemicals Sodium compounds E-number additives Food acidity regulators