Sinornithoides on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Sinornithoides'' (meaning "Chinese bird form") is a
 In 1988, a Chinese-Canadian expedition discovered the remains of a small theropod near Huamuxiao, in the
In 1988, a Chinese-Canadian expedition discovered the remains of a small theropod near Huamuxiao, in the
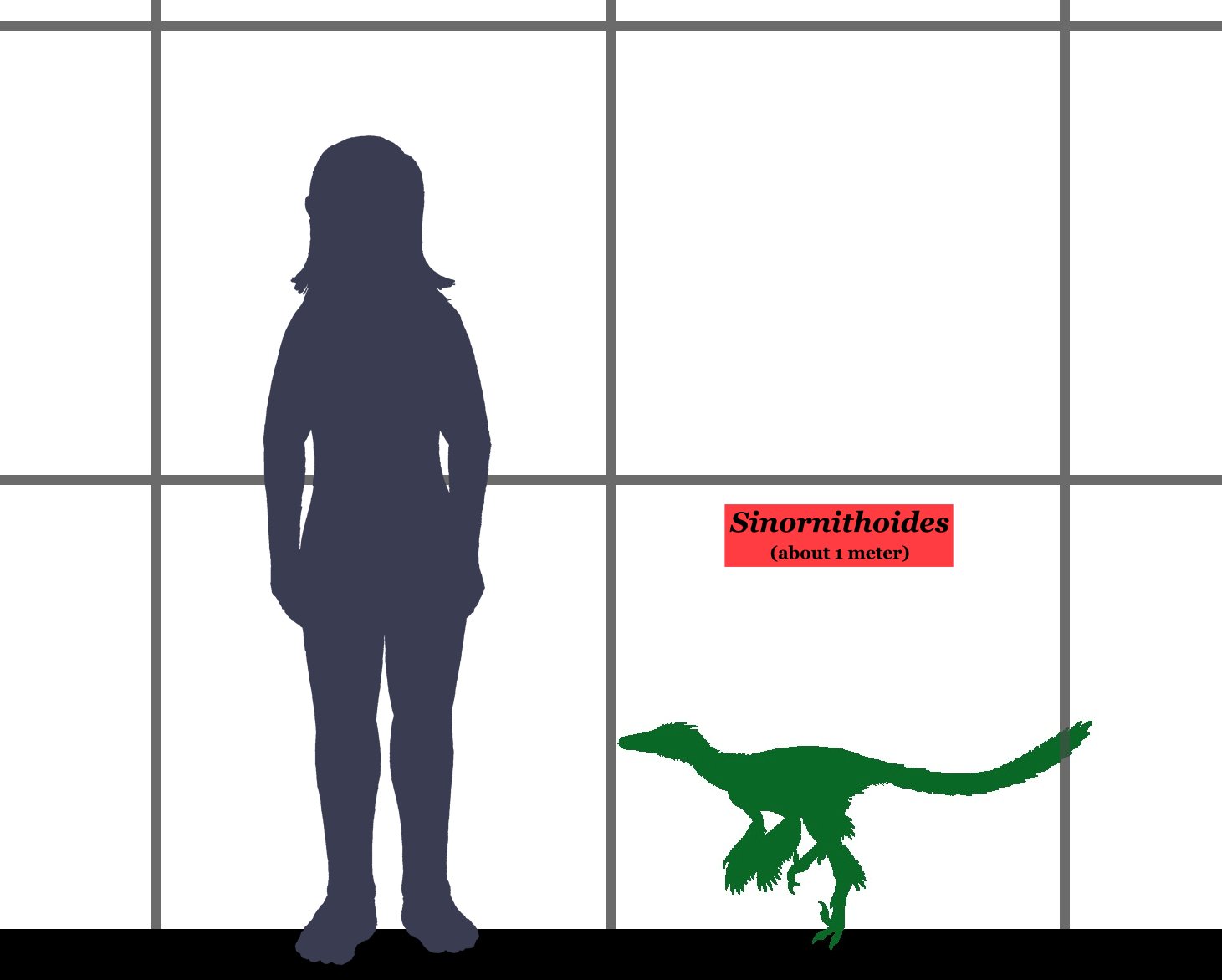 ''Sinornithoides'' is a
''Sinornithoides'' is a  In 1994, ''Sinornithoides'' was one of the most completely known troodontids, especially as regarded the palate, but the lack of sufficient fossil material to compare it with induced Russell and Dong not to indicate any diagnostic traits.
The skull of ''Sinornithoides'' is elongated and pointed. However, the head is relatively short compared to the body as a whole. The praemaxilla is short. There is a ''fenestra promaxillaris'', a small opening in the front of the
In 1994, ''Sinornithoides'' was one of the most completely known troodontids, especially as regarded the palate, but the lack of sufficient fossil material to compare it with induced Russell and Dong not to indicate any diagnostic traits.
The skull of ''Sinornithoides'' is elongated and pointed. However, the head is relatively short compared to the body as a whole. The praemaxilla is short. There is a ''fenestra promaxillaris'', a small opening in the front of the

genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
of troodontid theropod
Theropoda (; from ancient Greek , (''therion'') "wild beast"; , (''pous, podos'') "foot"">wiktionary:ποδός"> (''pous, podos'') "foot" is one of the three major groups (clades) of dinosaurs, alongside Ornithischia and Sauropodom ...
dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutio ...
s containing the single species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
''Sinornithoides youngi''. ''S. youngi'' lived during the Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous (geochronology, geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphy, chronostratigraphic name) is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 143.1 ...
(Aptian
The Aptian is an age (geology), age in the geologic timescale or a stage (stratigraphy), stage in the stratigraphic column. It is a subdivision of the Early Cretaceous, Early or Lower Cretaceous epoch (geology), Epoch or series (stratigraphy), S ...
/Albian
The Albian is both an age (geology), age of the geologic timescale and a stage (stratigraphy), stage in the stratigraphic column. It is the youngest or uppermost subdivision of the Early Cretaceous, Early/Lower Cretaceous epoch (geology), Epoch/s ...
stage
Stage, stages, or staging may refer to:
Arts and media Acting
* Stage (theatre), a space for the performance of theatrical productions
* Theatre, a branch of the performing arts, often referred to as "the stage"
* ''The Stage'', a weekly Brit ...
, around 113 million years ago
Million years ago, abbreviated as Mya, Myr (megayear) or Ma (megaannum), is a unit of time equal to (i.e. years), or approximately 31.6 teraseconds.
Usage
Myr is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used w ...
).Sereno, P.C. (2010). "Taxonomy, cranial morphology, and relationships of parrot-beaked dinosaurs (Ceratopsia: ''Psittacosaurus'')." ''New Perspectives on Horned Dinosaurs''. Bloomington: Indiana, 21-58. It measured approximately one meter
The metre (or meter in US spelling; symbol: m) is the base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI). Since 2019, the metre has been defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of of ...
long (3.3 ft). It lived in Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of China. Its border includes two-thirds of the length of China's China–Mongolia border, border with the country of Mongolia. ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, and probably ate invertebrates and other small prey. They lived in what is now Mongolia, which was part of Laurasia.
Discovery
 In 1988, a Chinese-Canadian expedition discovered the remains of a small theropod near Huamuxiao, in the
In 1988, a Chinese-Canadian expedition discovered the remains of a small theropod near Huamuxiao, in the Ordos Basin
The Ordos Plateau, also known as the Ordos Basin or simply the Ordos, is a highland sedimentary basin in parts of most Northern China with an elevation of , and consisting mostly of land enclosed by the Ordos Loop, a large northerly rectangular ...
of Inner Mongolia. ''Sinornithoides youngi'', the type species
In International_Code_of_Zoological_Nomenclature, zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the spe ...
, was named and described in 1993/1994 by Dale Russell
Dale Alan Russell (27 December 1937 – 21 December 2019)
was an American-Canadian geologist and palaeontologist. Throughout his career Russell worked as the Curator of Fossil Vertebrates at the Canadian Museum of Nature, Research Professor at ...
and Dong Zhiming
Dong Zhiming (Chinese language, Chinese: 董枝明, Pinyin: ''Dǒng Zhimíng''; January 1937 – 20 October 2024) was a Chinese vertebrate paleontologist formerly employed at the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP) ...
based on this fossil specimen from the Lower Cretaceous Ejinhoro Formation. The generic name is derived from Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
''Sinae'', "Chinese", and Greek ὄρνις, ''ornis'', "bird", en ~ειδής, ''~eides'', a suffix meaning "~like", in reference to the bird-like build. The specific name honours Yang Zhongjian
Yang Zhongjian, also Yang Chung-chien (; 1 June 1897 – 15 January 1979), courtesy name Keqiang (), also known as C.C. (Chung Chien) Young, was a Chinese paleontologist and zoologist. He was one of China's foremost vertebrate paleontologists. ...
.Russell, D. and Dong, Z. (1993). "A nearly complete skeleton of a new troodontid dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous of the Ordos Basin, Inner Mongolia, People's Republic of China." ''Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences'', 30: 2163-2173. doi:10.1139/e93-187
It is represented by a holotype
A holotype (Latin: ''holotypus'') is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of s ...
, IVPP V9612, an almost complete skeleton with skull, which is articulated and nearly complete except for the roof of the skull, some cervical and many dorsal vertebrae, along with some other referred skeletal elements. The holotype is preserved in much the same roosting position as another troodontid fossil, that of '' Mei long'', with its snout tucked under its left hand. It represents a subadult individual.Currie, P. and Dong, Z. (2001). "New information on Cretaceous troodontids from the People's Republic of China." ''Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences'', 38: 1753–1766.
Description
 ''Sinornithoides'' is a
''Sinornithoides'' is a troodontid
Troodontidae is a clade of bird-like theropod dinosaurs from the Late Jurassic to Late Cretaceous. During most of the 20th century, troodontid fossils were few and incomplete and they have therefore been allied, at various times, with many dinos ...
, a group of small, bird-like, gracile maniraptora
Maniraptora is a clade of coelurosaurian dinosaurs which includes the birds and the non-avian dinosaurs that were more closely related to them than to ''Ornithomimus velox''. It contains the major subgroups Avialae, Dromaeosauridae, Troodontidae, ...
ns. All troodontids have many unique features of the skull, such as closely spaced teeth
A tooth (: teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tear ...
in the lower jaw, and large numbers of teeth. Troodontids have sickle-claws and raptorial
In biology (specifically the anatomy of arthropods), the term ''raptorial'' implies much the same as ''predatory'' but most often refers to modifications of an arthropod leg, arthropod's foreleg that make it function for the grasping of prey whi ...
hands
A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the koala (which has two opposable thumbs on each "han ...
, and some of the highest non- avian encephalization quotient
Encephalization quotient (EQ), encephalization level (EL), or just encephalization is a relative brain size measure that is defined as the ratio between observed and predicted brain mass for an animal of a given size, based on nonlinear regre ...
s, meaning they were behaviourally advanced and had keen senses. In 2010, Gregory S. Paul
Gregory Scott Paul (born December 24, 1954) is an American freelance researcher, author and illustrator who works in paleontology. He is best known for his work and research on theropoda, theropod dinosaurs and his detailed illustrations, both l ...
estimated its body length at 1.1 metres, its weight at 2.5 kilogrammes.Paul, G.S., 2010, ''The Princeton Field Guide to Dinosaurs'', Princeton University Press p. 139
 In 1994, ''Sinornithoides'' was one of the most completely known troodontids, especially as regarded the palate, but the lack of sufficient fossil material to compare it with induced Russell and Dong not to indicate any diagnostic traits.
The skull of ''Sinornithoides'' is elongated and pointed. However, the head is relatively short compared to the body as a whole. The praemaxilla is short. There is a ''fenestra promaxillaris'', a small opening in the front of the
In 1994, ''Sinornithoides'' was one of the most completely known troodontids, especially as regarded the palate, but the lack of sufficient fossil material to compare it with induced Russell and Dong not to indicate any diagnostic traits.
The skull of ''Sinornithoides'' is elongated and pointed. However, the head is relatively short compared to the body as a whole. The praemaxilla is short. There is a ''fenestra promaxillaris'', a small opening in the front of the maxilla
In vertebrates, the maxilla (: maxillae ) is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxil ...
side, which is rare among troodontids. There are four premaxillary and about twenty-three maxillary teeth. The maxillary teeth have no serrations on their front edge; the denticles on the concavely curved rear edge are small. The maxillary teeth are rather recurved. The lacrimal bone
The lacrimal bones are two small and fragile bones of the facial skeleton; they are roughly the size of the little fingernail and situated at the front part of the medial wall of the orbit. They each have two surfaces and four borders. Several bon ...
lacks a pneumatic channel. In the braincase the subotic recess is large. The tips of the lower jaws do not curve towards each other but touch at their inner sides. The external mandibular fenestra is large. The dentary, lower jaw, teeth are quite pointed and have no front edge denticles; their rear edge is very straight. The holotype preserves a furcula and a basket of fifteen pairs of gastralia
Gastralia (: gastralium) are dermal bones found in the ventral body wall of modern crocodilians and tuatara, and many prehistoric tetrapods. They are found between the sternum and pelvis, and do not articulate with the vertebrae. In these reptil ...
. The arms are weakly developed, with a slender humerus
The humerus (; : humeri) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius (bone), radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extrem ...
and ulna
The ulna or ulnar bone (: ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone in the forearm stretching from the elbow to the wrist. It is on the same side of the forearm as the little finger, running parallel to the Radius (bone), radius, the forearm's other long ...
. The front top of the third metatarsal
The metatarsal bones or metatarsus (: metatarsi) are a group of five long bones in the midfoot, located between the tarsal bones (which form the heel and the ankle) and the phalanges ( toes). Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are ...
is not fully overgrown by the second and fourth metatarsals. The sickle claw of the second toe is relatively large and long for a troodontid.
Classification
''Sinornithoides'' was in 1994 assigned to theTroodontidae
Troodontidae is a clade of bird-like theropod dinosaurs from the Late Jurassic to Late Cretaceous. During most of the 20th century, troodontid fossils were few and incomplete and they have therefore been allied, at various times, with many dinos ...
.
A possible position of ''Sinornithoides'' in the evolutionary tree of the Paraves
Paraves are a widespread group of theropod dinosaurs that originated in the Middle Jurassic period. In addition to the extinct dromaeosauridae, dromaeosaurids, troodontidae, troodontids, Anchiornithidae, anchiornithids, and possibly the scansor ...
is shown by the cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not s ...
below, following a 2012 analysis by Turner, Makovicky and Norell.

See also
* Timeline of troodontid researchReferences
{{Taxonbar, from=Q134725 Troodontidae Dinosaur genera Aptian dinosaurs Taxa named by Dale Russell Taxa named by Dong Zhiming Fossil taxa described in 1993 Dinosaurs of China