Sing Uturnallowed on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Singing is the art of creating
 In its physical aspect, singing has a well-defined technique that depends on the use of the lungs, which act as an air supply or
In its physical aspect, singing has a well-defined technique that depends on the use of the lungs, which act as an air supply or
 Vocal resonation is the process by which the basic product of
Vocal resonation is the process by which the basic product of
 Vocal music is written in many different forms and styles which are often labeled within a particular genre of music. These genres include
Vocal music is written in many different forms and styles which are often labeled within a particular genre of music. These genres include
A Brief History of Singing
Singing and Health: A systematic mapping and review of non-clinical research
{{Authority control Occupations in music Music performance Articles containing video clips
music
Music is the arrangement of sound to create some combination of Musical form, form, harmony, melody, rhythm, or otherwise Musical expression, expressive content. Music is generally agreed to be a cultural universal that is present in all hum ...
with the voice
The human voice consists of sound made by a human being using the vocal tract, including talking, singing, laughing, crying, screaming, shouting, humming or yelling. The human voice frequency is specifically a part of human sound produ ...
. It is the oldest form of musical expression, and the human voice can be considered the first musical instrument. The definition of singing varies across sources. Some sources define singing as the act of creating music
Music is the arrangement of sound to create some combination of Musical form, form, harmony, melody, rhythm, or otherwise Musical expression, expressive content. Music is generally agreed to be a cultural universal that is present in all hum ...
al sound
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid.
In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the br ...
s with the voice
The human voice consists of sound made by a human being using the vocal tract, including talking, singing, laughing, crying, screaming, shouting, humming or yelling. The human voice frequency is specifically a part of human sound produ ...
. Other common definitions include "the utterance of words or sounds in tuneful succession" or "the production of musical tones by means of the human voice".
A person whose profession is singing is called a singer or a vocalist (in jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Its roots are in blues, ragtime, European harmony, African rhythmic rituals, spirituals, h ...
or popular music
Popular music is music with wide appeal that is typically distributed to large audiences through the music industry. These forms and styles can be enjoyed and performed by people with little or no musical training.Popular Music. (2015). ''Fun ...
). Singers perform music (aria
In music, an aria (, ; : , ; ''arias'' in common usage; diminutive form: arietta, ; : ariette; in English simply air (music), air) is a self-contained piece for one voice, with or without instrument (music), instrumental or orchestral accompan ...
s, recitative
Recitative (, also known by its Italian name recitativo () is a style of delivery (much used in operas, oratorios, and cantatas) in which a singer is allowed to adopt the rhythms and delivery of ordinary speech. Recitative does not repeat lines ...
s, song
A song is a musical composition performed by the human voice. The voice often carries the melody (a series of distinct and fixed pitches) using patterns of sound and silence. Songs have a structure, such as the common ABA form, and are usu ...
s, etc.) that can be sung with
With or WITH may refer to:
* With, a preposition in English
* Carl Johannes With (1877–1923), Danish doctor and arachnologist
* With (character), a character in ''D. N. Angel''
* ''With'' (novel), a novel by Donald Harrington
* ''With'' (album ...
or without accompaniment by musical instrument
A musical instrument is a device created or adapted to make Music, musical sounds. In principle, any object that produces sound can be considered a musical instrument—it is through purpose that the object becomes a musical instrument. A person ...
s. Singing is often done in an ensemble of musicians, such as a choir
A choir ( ), also known as a chorale or chorus (from Latin ''chorus'', meaning 'a dance in a circle') is a musical ensemble of singers. Choral music, in turn, is the music written specifically for such an ensemble to perform or in other words ...
. Singers may perform as soloists or accompanied by anything from a single instrument (as in art song
An art song is a Western world, Western vocal music Musical composition, composition, usually written for one voice with piano accompaniment, and usually in the classical music, classical art music tradition. By extension, the term "art song" is ...
s or some jazz styles) up to a symphony orchestra
An orchestra (; ) is a large instrumental ensemble typical of classical music, which combines instruments from different families. There are typically four main sections of instruments:
* String instruments, such as the violin, viola, cello, ...
or big band
A big band or jazz orchestra is a type of musical ensemble of jazz music that usually consists of ten or more musicians with four sections: saxophones, trumpets, trombones, and a rhythm section. Big bands originated during the early 1910s and ...
. Many styles of singing exist throughout the world.
Singing can be formal or informal, arranged, or improvised. It may be done as a form of religious devotion, as a hobby, as a source of pleasure, comfort, as part of a ritual, during music education
Music education is a field of practice in which educators are trained for careers as primary education, elementary or secondary education, secondary music teachers, school or music conservatory ensemble directors. Music education is also a rese ...
or as a profession. Excellence in singing requires time, dedication, instruction, and regular practice. If practice is done regularly then the sounds can become clearer and stronger. Professional singers usually build their career
A career is an individual's metaphorical "journey" through learning, work (human activity), work and other aspects of personal life, life. There are a number of ways to define career and the term is used in a variety of ways.
Definitions
The ...
s around one specific musical genre
A music genre is a conventional category that identifies some pieces of music as belonging to a shared tradition or set of conventions. Genre is to be distinguished from musical form and musical style, although in practice these terms are sometim ...
, such as classical or rock
Rock most often refers to:
* Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids
* Rock music, a genre of popular music
Rock or Rocks may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wale ...
, although there are singers with crossover success (singing in more than one genre). Professional singers typically receive voice training from vocal coaches or voice teachers throughout their careers.
Singing should not be confused with rapping
Rapping (also rhyming, flowing, spitting, emceeing, or MCing) is an artistic form of vocal delivery and emotive expression that incorporates " rhyme, rhythmic speech, and ommonlystreet vernacular". It is usually performed over a backin ...
as they are not the same. According to music scholar and rap historian Martin E. Connor, "Rap is often defined by its very opposition to singing." While also a form of vocal music
Vocal music is a type of singing performed by one or more singers, either with instrumental accompaniment, or without instrumental accompaniment (a cappella), in which singing provides the main focus of the piece. Music which employs singing but ...
, rap differs from singing in that it does not engage with tonality
Tonality is the arrangement of pitch (music), pitches and / or chord (music), chords of a musical work in a hierarchy of perceived ''relations'', ''stabilities'', ''attractions'', and ''directionality''.
In this hierarchy, the single pitch or ...
in the same way and does not require pitch accuracy. Like singing, rap does use rhythm in connection to words but these are spoken rather than sung on specific pitches. ''Grove Music Online
''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' is an encyclopedic dictionary of music and musicians. Along with the German-language '' Die Musik in Geschichte und Gegenwart'', it is one of the largest reference works on the history and t ...
'' states that "Within the historical context of popular music in the United States, rap can be seen as an alternative to singing that could connect directly with stylistic speech practices in African American English." However, some rap artists do employ singing as well as rapping in their music; using the switch between the rhythmic speech of rapping and the sung pitches of singing as a striking contrast to grab the attention of the listener.
Voices
 In its physical aspect, singing has a well-defined technique that depends on the use of the lungs, which act as an air supply or
In its physical aspect, singing has a well-defined technique that depends on the use of the lungs, which act as an air supply or bellows
A bellows or pair of bellows is a device constructed to furnish a strong blast of air. The simplest type consists of a flexible bag comprising a pair of rigid boards with handles joined by flexible leather sides enclosing an approximately airtig ...
; on the larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ (anatomy), organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal ...
, which acts as a reed
Reed or Reeds may refer to:
Science, technology, biology, and medicine
* Reed bird (disambiguation)
* Reed pen, writing implement in use since ancient times
* Reed (plant), one of several tall, grass-like wetland plants of the order Poales
* Re ...
or vibrator; on the chest
The thorax (: thoraces or thoraxes) or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen.
In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main di ...
, head cavities and the skeleton, which have the function of an amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal (a time-varying voltage or current). It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power su ...
, as the tube in a wind instrument
A wind instrument is a musical instrument that contains some type of resonator (usually a tube) in which a column of air is set into vibration by the player blowing into (or over) a mouthpiece set at or near the end of the resonator. The pitch ...
; and on the tongue
The tongue is a Muscle, muscular organ (anatomy), organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for chewing and swallowing as part of the digestive system, digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper s ...
, which together with the palate
The palate () is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity.
A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly sep ...
, teeth
A tooth (: teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tear ...
, and lip
The lips are a horizontal pair of soft appendages attached to the jaws and are the most visible part of the mouth of many animals, including humans. Mammal lips are soft, movable and serve to facilitate the ingestion of food (e.g. sucklin ...
s articulate and impose consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract, except for the h sound, which is pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Examples are and pronou ...
s and vowel
A vowel is a speech sound pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract, forming the nucleus of a syllable. Vowels are one of the two principal classes of speech sounds, the other being the consonant. Vowels vary in quality, in loudness a ...
s on the amplified sound. Though these four mechanisms function independently, they are nevertheless coordinated in the establishment of a vocal technique and are made to interact upon one another. During passive breathing, air is inhaled with the diaphragm while exhalation occurs without any effort. Exhalation may be aided by the abdominal
The abdomen (colloquially called the gut, belly, tummy, midriff, tucky, or stomach) is the front part of the torso between the thorax (chest) and pelvis in humans and in other vertebrates. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal ...
, internal intercostal and lower pelvis/pelvic muscles. Inhalation is aided by use of external intercostals
The external intercostal muscles or external intercostals (intercostales externi) are eleven in number on both sides.
Structure
The muscles extend from the tubercles of the ribs behind, to the cartilages of the ribs in front, where they end ...
, scalenes
The scalene muscles are a group of three muscles on each side of the neck, identified as the anterior, the middle, and the posterior. They are innervated by the third to the eighth cervical spinal nerves (C3-C8).
The anterior and middle scale ...
, and sternocleidomastoid muscles. The pitch is altered with the vocal cords
In humans, the vocal cords, also known as vocal folds, are folds of throat tissues that are key in creating sounds through Speech, vocalization. The length of the vocal cords affects the pitch of voice, similar to a violin string. Open when brea ...
. With the lips closed, this is called humming
A hum ( /hʌm/ ) Latin: murmur, The sound of giraffes humming () is a sound made by producing a wordless tone with the mouth closed, forcing the sound to emerge from the nose. To hum is to produce such a sound, often with a melody. It is also ...
.
The sound of each individual's singing voice is entirely unique not only because of the actual shape and size of an individual's vocal cords
In humans, the vocal cords, also known as vocal folds, are folds of throat tissues that are key in creating sounds through Speech, vocalization. The length of the vocal cords affects the pitch of voice, similar to a violin string. Open when brea ...
, but also due to the size and shape of the rest of that person's body. Humans have vocal folds which can loosen, tighten, or change their thickness, and over which breath can be transferred at varying pressures. The shape of the chest and neck
The neck is the part of the body in many vertebrates that connects the head to the torso. It supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that transmit sensory and motor information between the brain and the rest of the body. Addition ...
, the position of the tongue
The tongue is a Muscle, muscular organ (anatomy), organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for chewing and swallowing as part of the digestive system, digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper s ...
, and the tightness of otherwise unrelated muscles can be altered. Any one of these actions results in a change in pitch, volume (loudness
In acoustics, loudness is the subjectivity, subjective perception of sound pressure. More formally, it is defined as the "attribute of auditory sensation in terms of which sounds can be ordered on a scale extending from quiet to loud". The relat ...
), timbre
In music, timbre (), also known as tone color or tone quality (from psychoacoustics), is the perceived sound of a musical note, sound or tone. Timbre distinguishes sounds according to their source, such as choir voices and musical instrument ...
, or tone of the sound produced. Sound also resonates within different parts of the body and an individual's size and bone structure can affect the sound produced by an individual.
Singers can also learn to project sound in certain ways so that it resonates better within their vocal tract. This is known as vocal resonation
Vocal resonance may be defined as "the process by which the basic product of phonation is enhanced in timbre and/or intensity by the air-filled cavities through which it passes on its way to the outside air." Throughout the vocal literature, variou ...
. Another major influence on vocal sound and production is the function of the larynx which people can manipulate in different ways to produce different sounds. These different kinds of laryngeal function are described as different kinds of vocal registers
A vocal register is a range of tones in the human voice produced by a particular vibratory pattern of the vocal folds. These registers include modal voice (or normal voice), vocal fry, falsetto, and the whistle register.
Registers originate in ...
.polka dots
The primary method for singers to accomplish this is through the use of the singer's formant; which has been shown to match particularly well to the most sensitive part of the ear
In vertebrates, an ear is the organ that enables hearing and (in mammals) body balance using the vestibular system. In humans, the ear is described as having three parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The outer ear co ...
's frequency range.
It has also been shown that a more powerful voice may be achieved with a fatter and fluid-like vocal fold mucosa. The more pliable the mucosa, the more efficient the transfer of energy from the airflow to the vocal folds.
Vocal classification
InEuropean classical music
Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be #Relationship to other music traditions, distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical mu ...
and opera
Opera is a form of History of theatre#European theatre, Western theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by Singing, singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically ...
, voices are treated like musical instrument
A musical instrument is a device created or adapted to make Music, musical sounds. In principle, any object that produces sound can be considered a musical instrument—it is through purpose that the object becomes a musical instrument. A person ...
s. Composers
A composer is a person who writes music. The term is especially used to indicate composers of Western classical music, or those who are composers by occupation. Many composers are, or were, also skilled performers of music.
Etymology and defi ...
who write vocal music must have an understanding of the skills, talents, and vocal properties of singers. Voice classification is the process by which human singing voices are evaluated and are thereby designated into voice types
A voice type is a classification of the human singing voice into perceivable categories or groups. Particular human singing voices are identified as having certain qualities or characteristics of vocal range, vocal weight, tessitura, vocal timb ...
. These qualities include but are not limited to vocal range
Vocal range is the range of pitches that a human voice can phonate. A common application is within the context of singing, where it is used as a defining characteristic for classifying singing voices into voice types. It is also a topic of stud ...
, vocal weight
Vocal weight refers to the perceived "lightness" or "heaviness" of a singing voice. This quality of the voice is one of the major determining factors in voice classification within classical music. Lighter voices are often associated with the ter ...
, vocal tessitura, vocal timbre
In music, timbre (), also known as tone color or tone quality (from psychoacoustics), is the perceived sound of a musical note, sound or tone. Timbre distinguishes sounds according to their source, such as choir voices and musical instrument ...
, and vocal transition points such as breaks and lifts within the voice. Other considerations are physical characteristics, speech level, scientific testing, and vocal registration
A vocal register is a range of tones in the human voice produced by a particular vibratory pattern of the vocal folds. These registers include modal voice (or normal voice), vocal fry, falsetto, and the whistle register.
Registers originate in ...
. The science behind voice classification developed within European classical music
Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be #Relationship to other music traditions, distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical mu ...
has been slow in adapting to more modern forms of singing. Voice classification is often used within opera
Opera is a form of History of theatre#European theatre, Western theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by Singing, singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically ...
to associate possible roles with potential voices. There are currently several different systems in use within classical music including the German ''Fach
The German system (; literally "compartment" or "subject of study", here in the sense of "vocal specialization") is a method of classifying singers, primarily opera singers, according to the range, weight, and color of their voices. It is used ...
'' system and the choral music system among many others. No system is universally applied or accepted.
However, most classical music systems acknowledge seven different major voice categories. Women are typically divided into three groups: soprano
A soprano () is a type of classical singing voice and has the highest vocal range of all voice types. The soprano's vocal range (using scientific pitch notation) is from approximately middle C (C4) = 261 Hertz, Hz to A5 in Choir, choral ...
, mezzo-soprano
A mezzo-soprano (, ), or mezzo ( ), is a type of classical music, classical female singing human voice, voice whose vocal range lies between the soprano and the contralto voice types. The mezzo-soprano's vocal range usually extends from the A bel ...
, and contralto
A contralto () is a classical music, classical female singing human voice, voice whose vocal range is the lowest of their voice type, voice types.
The contralto's vocal range is fairly rare, similar to the mezzo-soprano, and almost identical to ...
. Men are usually divided into four groups: countertenor
A countertenor (also contra tenor) is a type of classical male singing voice whose vocal range is equivalent to that of the female contralto or mezzo-soprano voice types, generally extending from around G3 to D5 or E5, although a sopranist (a ...
, tenor
A tenor is a type of male singing voice whose vocal range lies between the countertenor and baritone voice types. It is the highest male chest voice type. Composers typically write music for this voice in the range from the second B below m ...
, baritone
A baritone is a type of classical music, classical male singing human voice, voice whose vocal range lies between the bass (voice type), bass and the tenor voice type, voice-types. It is the most common male voice. The term originates from the ...
, and bass
Bass or Basses may refer to:
Fish
* Bass (fish), various saltwater and freshwater species
Wood
* Bass or basswood, the wood of the tilia americana tree
Music
* Bass (sound), describing low-frequency sound or one of several instruments in th ...
. With regard to voices of pre-pubescent children, an eighth term, treble, can be applied. Within each of these major categories, several sub-categories identify specific vocal qualities like coloratura
Coloratura ( , , ; , from ''colorata'', the past participle of the verb ''colorare'', 'to color') is a passage of music holding elaboration to a melody. The elaboration usually takes the form of runs, trills, wide leaps or other virtuoso ma ...
facility and vocal weight
Vocal weight refers to the perceived "lightness" or "heaviness" of a singing voice. This quality of the voice is one of the major determining factors in voice classification within classical music. Lighter voices are often associated with the ter ...
to differentiate between voices.
Within choral music
A choir ( ), also known as a chorale or chorus (from Latin ''chorus'', meaning 'a dance in a circle') is a musical ensemble of singers. Choral music, in turn, is the music written specifically for such an ensemble to perform or in other words ...
, singers' voices are divided solely on the basis of vocal range. Choral music most commonly divides vocal parts into high and low voices within each sex (SATB, or soprano, alto, tenor, and bass). As a result, the typical choral situation gives many opportunities for misclassification to occur. Since most people have medium voices, they must be assigned to a part that is either too high or too low for them; the mezzo-soprano must sing soprano or alto and the baritone must sing tenor or bass. Either option can present problems for the singer, but for most singers, there are fewer dangers in singing too low than in singing too high.
Within contemporary forms of music (sometimes referred to as contemporary commercial music), singers are classified by the style of music they sing, such as jazz, pop, blues, soul, country, folk, and rock styles. There is currently no authoritative voice classification system within non-classical music. Attempts have been made to adopt classical voice type terms to other forms of singing but such attempts have been met with controversy. The development of voice categorizations were made with the understanding that the singer would be using classical vocal technique within a specified range using unamplified (no microphones) vocal production. Since contemporary musicians use different vocal techniques and microphones and are not forced to fit into a specific vocal role, applying such terms as soprano, tenor, baritone, etc. can be misleading or even inaccurate.
Vocal registration
''Vocal registration'' refers to the system of vocal registers within the voice. A register in the voice is a particular series of tones, produced in the same vibratory pattern of thevocal fold
In humans, the vocal cords, also known as vocal folds, are folds of throat tissues that are key in creating sounds through Speech, vocalization. The length of the vocal cords affects the pitch of voice, similar to a violin string. Open when brea ...
s, and possessing the same quality. Registers originate in laryngeal function. They occur because the vocal folds are capable of producing several different vibratory patterns. Each of these vibratory patterns appears within a particular range of pitches and produces certain characteristic sounds. The occurrence of registers has also been attributed to the effects of the acoustic interaction between the vocal fold oscillation and the vocal tract. The term "register" can be somewhat confusing as it encompasses several aspects of the voice. The term register can be used to refer to any of the following:
* A particular part of the vocal range
Vocal range is the range of pitches that a human voice can phonate. A common application is within the context of singing, where it is used as a defining characteristic for classifying singing voices into voice types. It is also a topic of stud ...
such as the upper, middle, or lower registers.
* A resonance
Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when an object or system is subjected to an external force or vibration whose frequency matches a resonant frequency (or resonance frequency) of the system, defined as a frequency that generates a maximu ...
area such as chest voice
Chest voice is a term used within vocal music. The use of this term varies widely within vocal pedagogical circles. There is no consistent opinion among vocal music professionals regarding the term. Chest voice can be used in relation to:
* A part ...
or head voice.
* A phonatory
The term phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, ''phonation'' is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the defin ...
process (phonation is the process of producing vocal sound by the vibration of the vocal folds that is in turn modified by the resonance of the vocal tract)
* A certain vocal timbre
In music, timbre (), also known as tone color or tone quality (from psychoacoustics), is the perceived sound of a musical note, sound or tone. Timbre distinguishes sounds according to their source, such as choir voices and musical instrument ...
or vocal "color"
* A region of the voice which is defined or delimited by vocal breaks.
In linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds ...
, a register language is a language which combines tone
Tone may refer to:
Visual arts and color-related
* Tone (color theory), a mix of tint and shade, in painting and color theory
* Tone (color), the lightness or brightness (as well as darkness) of a color
* Toning (coin), color change in coins
* ...
and vowel phonation
The term phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, ''phonation'' is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the defi ...
into a single phonological
Phonology (formerly also phonemics or phonematics: "phonemics ''n.'' 'obsolescent''1. Any procedure for identifying the phonemes of a language from a corpus of data. 2. (formerly also phonematics) A former synonym for phonology, often prefer ...
system. Within speech pathology
Speech is the use of the human voice as a medium for language. Spoken language combines vowel and consonant sounds to form units of meaning like words, which belong to a language's lexicon. There are many different intentional speech acts, suc ...
, the term vocal register has three constituent elements: a certain vibratory pattern of the vocal folds, a certain series of pitches, and a certain type of sound. Speech pathologists identify four vocal registers based on the physiology of laryngeal function: the vocal fry register
The vocal fry register is the lowest vocal register and is produced through a loose glottal closure that permits air to bubble through slowly with a popping or rattling sound of a very low frequency. During this phonation, the arytenoid cartilage ...
, the modal register, the falsetto register, and the whistle register
The whistle register (also called the flute register or flageolet register) is the highest register of the human voice, lying above the modal register and falsetto register. This register has a specific physiological production that is differe ...
. This view is also adopted by many vocal pedagogues.
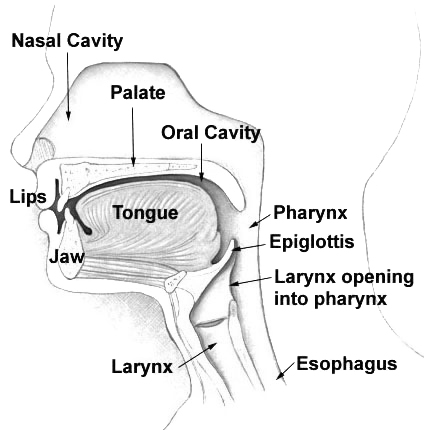
Vocal resonation
 Vocal resonation is the process by which the basic product of
Vocal resonation is the process by which the basic product of phonation
The term phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, ''phonation'' is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the defi ...
is enhanced in timbre or intensity by the air-filled cavities through which it passes on its way to the outside air. Various terms related to the resonation process include amplification, enrichment, enlargement, improvement, intensification, and prolongation, although in strictly scientific usage acoustic authorities would question most of them. The main point to be drawn from these terms by a singer or speaker is that the result of resonation is, or should be, to make a better sound. There are seven areas that may be listed as possible vocal resonators. In sequence from the lowest within the body to the highest, these areas are the chest
The thorax (: thoraces or thoraxes) or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen.
In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main di ...
, the tracheal tree, the larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ (anatomy), organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal ...
itself, the pharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates ...
, the oral cavity
A mouth also referred to as the oral is the body orifice through which many animals ingest food and vocalize. The body cavity immediately behind the mouth opening, known as the oral cavity (or in Latin), is also the first part of the alime ...
, the nasal cavity
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nas ...
, and the sinuses
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoi ...
.
Chest voice and head voice
''Chest voice'' and ''head voice'' are terms used withinvocal music
Vocal music is a type of singing performed by one or more singers, either with instrumental accompaniment, or without instrumental accompaniment (a cappella), in which singing provides the main focus of the piece. Music which employs singing but ...
. The use of these terms varies widely within vocal pedagogical circles and there is currently no one consistent opinion among vocal music professionals in regards to these terms. Chest voice can be used in relation to a particular part of the vocal range
Vocal range is the range of pitches that a human voice can phonate. A common application is within the context of singing, where it is used as a defining characteristic for classifying singing voices into voice types. It is also a topic of stud ...
or type of vocal register
A vocal register is a range of tones in the human voice produced by a particular vibratory pattern of the vocal folds. These registers include modal voice (or normal voice), vocal fry, falsetto, and the whistle register.
Registers originate in lar ...
; a vocal resonance
Vocal resonance may be defined as "the process by which the basic product of phonation is enhanced in timbre and/or intensity by the air-filled cavities through which it passes on its way to the outside air." Throughout the vocal literature, variou ...
area; or a specific vocal timbre. Head voice can be used in relation to a particular part of the vocal range or type of vocal register or a vocal resonance area. In Men, the head voice is commonly referred to as the falsetto. The transition from and combination of chest voice and head voice is referred to as vocal mix or vocal mixing in the singer's performance. Vocal mixing can be inflected in specific modalities of artists who may concentrate on smooth transitions between chest voice and head voice, and those who may use a "flip" to describe the sudden transition from chest voice to head voice for artistic reasons and enhancement of vocal performances.
History and development
The first recorded mention of the terms chest voice and head voice was around the 13th century when it was distinguished from the "throat voice" (pectoris, guttoris, capitis—at this time it is likely that head voice referred to the falsetto register) by the writers Johannes de Garlandia and Jerome of Moravia. The terms were later adopted withinbel canto
, )—with several similar constructions (, , , pronounced in English as )—is a term with several meanings that relate to Italian singing, and whose definitions have often been misunderstood. ''Bel canto'' was not only seen as a vocal technique ...
, the Italian opera singing method, where chest voice was identified as the lowest and head voice the highest of three vocal registers: the chest, passagio, and head registers. This approach is still taught by some vocal pedagogists today. Another current popular approach that is based on the bel canto model is to divide both men and women's voices into three registers. Men's voices are divided into "chest register", "head register", and "falsetto register" and woman's voices into "chest register", "middle register", and "head register". Such pedagogists teach that the head register is a vocal
The human voice consists of sound made by a human being using the vocal tract, including talking, singing, laughing, crying, screaming, shouting, humming or yelling. The human voice frequency is specifically a part of human sound producti ...
technique used in singing to describe the resonance felt in the singer's head.
However, as knowledge of physiology has increased over the past two hundred years, so has the understanding of the physical process of singing and vocal production. As a result, many vocal pedagogists, such as Ralph Appelman at Indiana University
Indiana University (IU) is a state university system, system of Public university, public universities in the U.S. state of Indiana. The system has two core campuses, five regional campuses, and two regional centers under the administration o ...
and William Vennard at the University of Southern California
The University of Southern California (USC, SC, or Southern Cal) is a Private university, private research university in Los Angeles, California, United States. Founded in 1880 by Robert M. Widney, it is the oldest private research university in ...
, have redefined or even abandoned the use of the terms chest voice and head voice. In particular, the use of the terms ''chest register'' and ''head register'' have become controversial since vocal registration
A vocal register is a range of tones in the human voice produced by a particular vibratory pattern of the vocal folds. These registers include modal voice (or normal voice), vocal fry, falsetto, and the whistle register.
Registers originate in ...
is more commonly seen today as a product of laryngeal function that is unrelated to the physiology of the chest, lungs, and head. For this reason, many vocal pedagogists argue that it is meaningless to speak of registers being produced in the chest or head. They argue that the vibratory sensations which are felt in these areas are resonance phenomena and should be described in terms related to vocal resonance
Vocal resonance may be defined as "the process by which the basic product of phonation is enhanced in timbre and/or intensity by the air-filled cavities through which it passes on its way to the outside air." Throughout the vocal literature, variou ...
, not to registers. These vocal pedagogists prefer the terms ''chest voice'' and ''head voice'' over the term register. This view believes that the problems which people identify as register problems are really problems of resonance adjustment. This view is also in alignment with the views of other academic fields that study vocal registration including speech pathology
Speech is the use of the human voice as a medium for language. Spoken language combines vowel and consonant sounds to form units of meaning like words, which belong to a language's lexicon. There are many different intentional speech acts, suc ...
, phonetics
Phonetics is a branch of linguistics that studies how humans produce and perceive sounds or, in the case of sign languages, the equivalent aspects of sign. Linguists who specialize in studying the physical properties of speech are phoneticians ...
, and linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds ...
. Although both methods are still in use, current vocal pedagogical practice tends to adopt the newer more scientific view. Also, some vocal pedagogists take ideas from both viewpoints.
The contemporary use of the term chest voice often refers to a specific kind of vocal coloration or vocal timbre. In classical singing, its use is limited entirely to the lower part of the modal register or normal voice. Within other forms of singing, chest voice is often applied throughout the modal register. Chest timbre can add a wonderful array of sounds to a singer's vocal interpretive palette.
However, the use of an overly strong chest voice in the higher registers in an attempt to hit higher notes in the chest can lead to forcing. Forcing can lead consequently to vocal deterioration.
Vocal registers: General discussion of transitions
Passaggio () is a term used in classical singing to describe the transition area between thevocal registers
A vocal register is a range of tones in the human voice produced by a particular vibratory pattern of the vocal folds. These registers include modal voice (or normal voice), vocal fry, falsetto, and the whistle register.
Registers originate in ...
. The ''passaggi'' (plural) of the voice lie between the different vocal registers, such as the chest voice
Chest voice is a term used within vocal music. The use of this term varies widely within vocal pedagogical circles. There is no consistent opinion among vocal music professionals regarding the term. Chest voice can be used in relation to:
* A part ...
, where any singer can produce a powerful sound, the middle voice, and the head voice, where a penetrating sound is accessible, but usually only through vocal training. The historic Italian school of singing describes a ''primo passaggio'' and a ''secondo passaggio'' connected through a ''zona di passaggio'' in the male voice and a ''primo passaggio'' and ''secondo passaggio'' in the female voice. A major goal of classical voice training in classical styles is to maintain an even timbre
In music, timbre (), also known as tone color or tone quality (from psychoacoustics), is the perceived sound of a musical note, sound or tone. Timbre distinguishes sounds according to their source, such as choir voices and musical instrument ...
throughout the passaggio. Through proper training, it is possible to produce a resonant and powerful sound.
Vocal registers and transitions
One cannot adequately discuss the vocal ''passaggio'' without having a basic understanding of the different vocal registers. In his book ''The Principles of Voice Production'', Ingo Titze states, "The term ''register'' has been used to describe perceptually distinct regions of vocal quality that can be maintained over some ranges of pitch and loudness." Discrepancies in terminology exist between different fields of vocal study, such as teachers and singers, researchers, and clinicians. As Marilee David points out, "Voice scientists see registration primarily as acoustic events." For singers, it is more common to explain registration events based on the physical sensations they feel when singing. Titze also explains that there are discrepancies in the terminology used to talk about vocal registration between speech pathologists and singing teachers. Since this article discusses the ''passaggio'', which is a term used by classical singers, the registers will be discussed as they are in the field of singing rather than speech pathology and science. The three main registers, described as head, middle (mixed), and chest voice, are described as having a rich timbre, because of the overtones due to thesympathetic resonance
Sympathetic resonance or sympathetic vibration is a harmonic phenomenon wherein a passive string or vibratory body responds to external vibrations to which it has a harmonic likeness. The classic example is demonstrated with two similarly-tuned ...
within the human body. Their names are derived from the area in which the singer feels these resonant vibration in the body. The chest register, more commonly referred to as the chest voice, is the lowest of the registers. When singing in the chest voice the singer feels sympathetic vibration in the chest. This is the register that people most commonly use while speaking. The middle voice falls in between the chest voice and head voice. The head register, or the head voice, is the highest of the main vocal registers. When singing in the head voice, the singer may feel sympathetic vibration occurring in the face or another part of the head. Where these registers lie in the voice is dependent on sex and the voice type within each sex.
There are an additional two registers called falsetto
Falsetto ( , ; Italian language, Italian diminutive of , "false") is the vocal register occupying the frequency range just above the modal voice register and overlapping with it by approximately one octave.
It is produced by the vibration of the ...
and flageolet
__NOTOC__
The flageolet is a woodwind instrument and a member of the family of fipple, duct flutes that includes Recorder (musical instrument), recorders and tin whistles. There are two basic forms of the instrument: the French, having four fing ...
register, which lie above their head register. Training is often required to access the pitches within these registers. Men and women with lower voices rarely sing in these registers. Lower-voiced women in particular receive very little if any training in the flageolet register. Men have one more additional register called the ''strohbass'', which lies below the chest voice. Singing in this register is hard on the vocal cords, and therefore, is hardly ever used.
Vocal pedagogy
Vocal pedagogy is the study of the teaching of singing. The art and science of vocal pedagogy has a long history that began inAncient Greece
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically r ...
and continues to develop and change today. Professions that practice the art and science of vocal pedagogy include vocal coaches, choral directors, vocal music educators, opera directors, and other teachers of singing.
Vocal pedagogy concepts are a part of developing proper vocal technique. Typical areas of study include the following:
* Anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old scien ...
and physiology as it relates to the physical process of singing
** Vocal health and voice disorders
Voice disordersTitze, I.R. (1994). Principles of Voice Production, Prentice Hall, . are medical conditions involving abnormal pitch, loudness or quality of the sound produced by the larynx and thereby affecting speech production. These include:
* ...
related to singing
** Breathing and air support for singing
** Phonation
The term phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, ''phonation'' is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the defi ...
** Vocal resonation
Vocal resonance may be defined as "the process by which the basic product of phonation is enhanced in timbre and/or intensity by the air-filled cavities through which it passes on its way to the outside air." Throughout the vocal literature, variou ...
or Voice projection
** Vocal registration
A vocal register is a range of tones in the human voice produced by a particular vibratory pattern of the vocal folds. These registers include modal voice (or normal voice), vocal fry, falsetto, and the whistle register.
Registers originate in ...
: a particular series of tones, produced in the same vibratory pattern of the vocal folds, and possessing the same quality, which originate in laryngeal function, because each of these vibratory patterns appears within a particular range of pitches and produces certain characteristic sounds.
** Voice classification
* Vocal styles: for classical singers, this includes styles ranging from Lieder
In the Western classical music tradition, ( , ; , ; ) is a term for setting poetry to classical music. The term is used for any kind of song in contemporary German and Dutch, but among English and French speakers, is often used interchangea ...
to opera
Opera is a form of History of theatre#European theatre, Western theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by Singing, singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically ...
; for pop singers, styles can include "belted out" a blues ballads; for jazz singers, styles can include Swing ballads and scatting.
** Techniques used in styles such as sostenuto
Piano pedals are foot-operated levers at the base of a piano that change the instrument's sound in various ways. Modern pianos usually have three pedals, from left to right, the soft pedal (or una corda), the sostenuto pedal, and the sustaini ...
and legato
In music performance and notation, legato (; Italian for "tied together"; French ''lié''; German ''gebunden'') indicates that musical notes are played or sung smoothly, such that the transition from note to note is made with no intervening si ...
, range extension, tone quality, vibrato
Vibrato (Italian language, Italian, from past participle of "wikt:vibrare, vibrare", to vibrate) is a musical effect consisting of a regular, pulsating change of pitch (music), pitch. It is used to add expression to vocal and instrumental music. ...
, and coloratura
Coloratura ( , , ; , from ''colorata'', the past participle of the verb ''colorare'', 'to color') is a passage of music holding elaboration to a melody. The elaboration usually takes the form of runs, trills, wide leaps or other virtuoso ma ...
Vocal technique
Singing when done with proper vocal technique is an integrated and coordinated act that effectively coordinates the physical processes of singing. There are four physical processes involved in producing vocal sound:respiration
Respiration may refer to:
Biology
* Cellular respiration, the process in which nutrients are converted into useful energy in a cell
** Anaerobic respiration, cellular respiration without oxygen
** Maintenance respiration, the amount of cellul ...
, phonation
The term phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, ''phonation'' is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the defi ...
, resonation, and articulation. These processes occur in the following sequence:
# Breath is taken
# Sound is initiated in the larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ (anatomy), organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal ...
# The vocal resonators receive the sound and influence it
# The articulators shape the sound into recognizable units
Although these four processes are often considered separately when studied, in actual practice, they merge into one coordinated function. With an effective singer or speaker, one should rarely be reminded of the process involved as their mind and body are so coordinated that one only perceives the resulting unified function. Many vocal problems result from a lack of coordination within this process.
Since singing is a coordinated act, it is difficult to discuss any of the individual technical areas and processes without relating them to others. For example, phonation only comes into perspective when it is connected with respiration; the articulators affect resonance; the resonators affect the vocal folds; the vocal folds affect breath control; and so forth. Vocal problems are often a result of a breakdown in one part of this coordinated process which causes voice teachers to frequently focus intensively on one area of the process with their student until that issue is resolved. However, some areas of the art of singing are so much the result of coordinated functions that it is hard to discuss them under a traditional heading like phonation, resonation, articulation, or respiration.
Once the voice student has become aware of the physical processes that make up the act of singing and of how those processes function, the student begins the task of trying to coordinate them. Inevitably, students and teachers will become more concerned with one area of the technique than another. The various processes may progress at different rates, with a resulting imbalance or lack of coordination. The areas of vocal technique which seem to depend most strongly on the student's ability to coordinate various functions are:
# Extending the vocal range
Vocal range is the range of pitches that a human voice can phonate. A common application is within the context of singing, where it is used as a defining characteristic for classifying singing voices into voice types. It is also a topic of stud ...
to its maximum potential
# Developing consistent vocal production with a consistent tone quality
# Developing flexibility and agility
# Achieving a balanced vibrato
Vibrato (Italian language, Italian, from past participle of "wikt:vibrare, vibrare", to vibrate) is a musical effect consisting of a regular, pulsating change of pitch (music), pitch. It is used to add expression to vocal and instrumental music. ...
# A blend of chest and head voice on every note of the range
Developing the singing voice
Singing is a skill that requires highly developed muscle reflexes. Singing does not require much muscle strength but it does require a high degree of muscle coordination. Individuals can develop their voices further through the careful and systematic practice of both songs and vocal exercises. Vocal exercises have several purposes, including warming up the voice; extending the vocal range; "lining up" the voice horizontally and vertically; and acquiring vocal techniques such as legato, staccato, control of dynamics, rapid figurations, learning to sing wide intervals comfortably, singing trills, singing melismas and correcting vocal faults. Vocal pedagogists instruct their students to exercise their voices in an intelligent manner. Singers should be thinking constantly about the kind of sound they are making and the kind of sensations they are feeling while they are singing. Learning to sing is an activity that benefits from the involvement of an instructor. A singer does not hear the same sounds inside his or her head that others hear outside. Therefore, having a guide who can tell a student what kinds of sounds he or she is producing guides a singer to understand which of the internal sounds correspond to the desired sounds required by the style of singing the student aims to re-create.Extending vocal range
An important goal of vocal development is to learn to sing to the natural limits of one's vocal range without any obvious or distracting changes of quality or technique. Vocal pedagogists teach that a singer can only achieve this goal when all of the physical processes involved in singing (such as laryngeal action, breath support, resonance adjustment, and articulatory movement) are effectively working together. Most vocal pedagogists believe in coordinating these processes by (1) establishing good vocal habits in the most comfortable tessitura of the voice, and then (2) slowly expanding the range. There are three factors that significantly affect the ability to sing higher or lower: # The ''energy'' factor – "energy" has several connotations. It refers to the total response of the body to the making of sound; to a dynamic relationship between the breathing-in muscles and the breathing-out muscles known as the breath support mechanism; to the amount of breath pressure delivered to the vocal folds and their resistance to that pressure; and to the dynamic level of the sound. # The ''space'' factor – "space" refers to the size of the inside of the mouth and the position of the palate and larynx. Generally speaking, a singer's mouth should be opened wider the higher he or she sings. The internal space or position of the soft palate and larynx can be widened by relaxing the throat. Vocal pedagogists describe this as feeling like the "beginning of a yawn". # The ''depth'' factor – "depth" has two connotations. It refers to the actual physical sensations of depth in the body and vocal mechanism, and to mental concepts of depth that are related to tone quality. McKinney says, "These three factors can be expressed in three basic rules: (1) As you sing higher, you must use more energy; as you sing lower, you must use less. (2) As you sing higher, you must use more space; as you sing lower, you must use less. (3) As you sing higher, you must use more depth; as you sing lower, you must use less."Posture
The singing process functions best when certain physical conditions of the body are put in place. The ability to move air in and out of the body freely and to obtain the needed quantity of air can be seriously affected by the posture of the various parts of the breathing mechanism. A sunken chest position will limit the capacity of the lungs, and a tense abdominal wall will inhibit the downward travel of the diaphragm. Good posture allows the breathing mechanism to fulfill its basic function efficiently without any undue expenditure of energy. Good posture also makes it easier to initiate phonation and to tune the resonators as proper alignment prevents unnecessary tension in the body. Vocal pedagogists have also noted that when singers assume good posture it often provides them with a greater sense of self-assurance and poise while performing. Audiences also tend to respond better to singers with good posture. Habitual good posture also ultimately improves the overall health of the body by enabling better blood circulation and preventing fatigue and stress on the body. There are eight components of the ideal singing posture: # Feet slightly apart # Legs straight but knees slightly bent # Hips facing straight forward # Spine aligned # Abdomen flat # Chest comfortably forward # Shoulders down and back # Head facing straight forwardBreathing and breath support
Natural breathing has three stages: a breathing-in period, breathing out period, and a resting or recovery period; these stages are not usually consciously controlled. Within singing, there are four stages of breathing: a breathing-in period (inhalation); a setting up controls period (suspension); a controlled exhalation period (phonation); and a recovery period. These stages must be under conscious control by the singer until they become conditioned reflexes. Many singers abandon conscious controls before their reflexes are fully conditioned which ultimately leads to chronic vocal problems.Vibrato
Vibrato
Vibrato (Italian language, Italian, from past participle of "wikt:vibrare, vibrare", to vibrate) is a musical effect consisting of a regular, pulsating change of pitch (music), pitch. It is used to add expression to vocal and instrumental music. ...
is a technique in which a sustained note wavers very quickly and consistently between a higher and a lower pitch, giving the note a slight quaver. Vibrato is the pulse or wave in a sustained tone. Vibrato occurs naturally and is the result of proper breath support and a relaxed vocal apparatus. Some studies have shown that vibrato is the result of a neuromuscular tremor in the vocal folds. In 1922 Max Schoen was the first to make the comparison of vibrato to a tremor due to change in amplitude, lack of automatic control and it being half the rate of normal muscular discharge. Some singers use vibrato as a means of expression. Many successful artists can sing a deep, rich vibrato.
Extended vocal technique
Extended vocal technique
Vocalists are capable of producing a variety of extended technique sounds. These alternative singing techniques have been used extensively in the 20th century, especially in art song and opera. Particularly famous examples of extended vocal techniq ...
s include rapping, screaming, growling, overtones, sliding, falsetto
Falsetto ( , ; Italian language, Italian diminutive of , "false") is the vocal register occupying the frequency range just above the modal voice register and overlapping with it by approximately one octave.
It is produced by the vibration of the ...
, yodeling
Yodeling (also jodeling) is a form of singing which involves repeated and rapid changes of pitch between the low-pitch chest register (or "chest voice") and the high-pitch head register or falsetto. The English word ''yodel'' is derived from t ...
, belting, use of vocal fry register
The vocal fry register is the lowest vocal register and is produced through a loose glottal closure that permits air to bubble through slowly with a popping or rattling sound of a very low frequency. During this phonation, the arytenoid cartilage ...
, using sound reinforcement system
A sound reinforcement system is the combination of microphones, signal processors, amplifiers, and loudspeakers in Loudspeaker enclosure, enclosures all controlled by a mixing console that makes live or pre-recorded sounds louder and may also ...
s, among others. A sound reinforcement system is the combination of microphones, signal processors, amplifiers, and loudspeakers. The combination of such units may also use reverb, echo chambers and Auto-Tune
Auto-Tune is audio processor software released on September 19, 1997, by the American company Antares Audio Technologies. It uses a proprietary device to measure and Pitch correction, correct pitch in music. It operates on different principles ...
among other devices.
Vocal music
Vocal music ismusic
Music is the arrangement of sound to create some combination of Musical form, form, harmony, melody, rhythm, or otherwise Musical expression, expressive content. Music is generally agreed to be a cultural universal that is present in all hum ...
performed by one or more singers, which are typically called song
A song is a musical composition performed by the human voice. The voice often carries the melody (a series of distinct and fixed pitches) using patterns of sound and silence. Songs have a structure, such as the common ABA form, and are usu ...
s, and which may be performed with or without instrumental
An instrumental or instrumental song is music without any vocals, although it might include some inarticulate vocals, such as shouted backup vocals in a big band setting. Through Semantic change, semantic widening, a broader sense of the word s ...
accompaniment, in which singing provides the main focus of the piece. Vocal music is probably the oldest form of music since it does not require any instrument or equipment besides the voice. All musical culture
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
s have some form of vocal music and there are many long-standing singing traditions throughout the world's cultures. Music which employs singing but does not feature it prominently is generally considered instrumental music. For example, some blues rock
Blues rock is a fusion music genre, genre and form of rock music, rock and blues music that relies on the chords/scales and instrumental improvisation of blues. It is mostly an electric ensemble-style music with instrumentation similar to electri ...
songs may have a short, simple call-and-response chorus, but the emphasis in the song is on the instrumental melodies and improvisation. Vocal music typically features sung words called lyrics
Lyrics are words that make up a song, usually consisting of verses and choruses. The writer of lyrics is a lyricist. The words to an extended musical composition such as an opera are, however, usually known as a "libretto" and their writer, ...
, although there are notable examples of vocal music that are performed using non-linguistic syllables or noises, sometimes as musical onomatopoeia
Onomatopoeia (or rarely echoism) is a type of word, or the process of creating a word, that phonetics, phonetically imitates, resembles, or suggests the sound that it describes. Common onomatopoeias in English include animal noises such as Oin ...
. A short piece of vocal music with lyrics is broadly termed a song, although, in classical music
Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be #Relationship to other music traditions, distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical mu ...
, terms such as aria
In music, an aria (, ; : , ; ''arias'' in common usage; diminutive form: arietta, ; : ariette; in English simply air (music), air) is a self-contained piece for one voice, with or without instrument (music), instrumental or orchestral accompan ...
are typically used.
Genres of vocal music
 Vocal music is written in many different forms and styles which are often labeled within a particular genre of music. These genres include
Vocal music is written in many different forms and styles which are often labeled within a particular genre of music. These genres include popular music
Popular music is music with wide appeal that is typically distributed to large audiences through the music industry. These forms and styles can be enjoyed and performed by people with little or no musical training.Popular Music. (2015). ''Fun ...
, art music
Art music (alternatively called classical music, cultivated music, serious music, and canonic music) is music considered to be of high culture, high phonoaesthetic value. It typically implies advanced structural and theoretical considerationsJa ...
, religious music
Religious music (also sacred music) is a type of music that is performed or composed for Religion, religious use or through religious influence. It may overlap with ritual music, which is music, sacred or not, performed or composed for or as a ri ...
, secular music
Non-religious secular music and Religious music, sacred music were the two main genres of Western world, Western music during the Middle Ages and Renaissance music, Renaissance era. The oldest written examples of secular music are songs with Lat ...
, and fusions of such genres. Within these larger genres are many subgenres. For example, popular music would encompass blues
Blues is a music genre and musical form that originated among African Americans in the Deep South of the United States around the 1860s. Blues has incorporated spiritual (music), spirituals, work songs, field hollers, Ring shout, shouts, cha ...
, jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Its roots are in blues, ragtime, European harmony, African rhythmic rituals, spirituals, h ...
, country music
Country (also called country and western) is a popular music, music genre originating in the southern regions of the United States, both the American South and American southwest, the Southwest. First produced in the 1920s, country music is p ...
, easy listening
Easy listening (including mood music) is a popular music genre and radio format that was most popular during the 1950s to the 1970s. It is related to middle of the road (MOR) music and encompasses instrumental recordings of standards, hit s ...
, hip hop
Hip-hop or hip hop (originally disco rap) is a popular music genre that emerged in the early 1970s from the African-American community of New York City. The style is characterized by its synthesis of a wide range of musical techniques. Hip- ...
, rock music
Rock is a Music genre, genre of popular music that originated in the United States as "rock and roll" in the late 1940s and early 1950s, developing into a range of styles from the mid-1960s, primarily in the United States and the United Kingdo ...
, and several other genres. There may also be a subgenre within a subgenre such as vocalese
Vocalese is a style of jazz singing in which words are added to an instrumental soloist's improvisation.
Definition
Vocalese uses recognizable lyrics that are sung to pre-existing instrumental solos, as opposed to scat singing, which uses nonsen ...
and scat singing
Originating in vocal jazz, scat singing or scatting is vocal Musical improvisation, improvisation with Non-lexical vocables in music, wordless vocables, Pseudoword#Nonsense syllables, nonsense syllables or without words at all. In scat singing, t ...
in jazz.
Popular and traditional music
In many modern popmusical group
A musical ensemble, also known as a music group, musical group, or a band is a group of people who perform instrumental and/or vocal music, with the ensemble typically known by a distinct name. Some music ensembles consist solely of instrumen ...
s, a lead singer performs the primary vocals or melody
A melody (), also tune, voice, or line, is a linear succession of musical tones that the listener perceives as a single entity. In its most literal sense, a melody is a combination of Pitch (music), pitch and rhythm, while more figurativel ...
of a song
A song is a musical composition performed by the human voice. The voice often carries the melody (a series of distinct and fixed pitches) using patterns of sound and silence. Songs have a structure, such as the common ABA form, and are usu ...
, as opposed to a backing singer who sings backup vocals or the harmony
In music, harmony is the concept of combining different sounds in order to create new, distinct musical ideas. Theories of harmony seek to describe or explain the effects created by distinct pitches or tones coinciding with one another; harm ...
of a song. Backing vocalists sing some, but usually, not all, parts of the song often singing only in a song's refrain or humming
A hum ( /hʌm/ ) Latin: murmur, The sound of giraffes humming () is a sound made by producing a wordless tone with the mouth closed, forcing the sound to emerge from the nose. To hum is to produce such a sound, often with a melody. It is also ...
in the background. An exception is five-part gospel
Gospel originally meant the Christianity, Christian message ("the gospel"), but in the second century Anno domino, AD the term (, from which the English word originated as a calque) came to be used also for the books in which the message w ...
a cappella
Music performed a cappella ( , , ; ), less commonly spelled acapella in English, is music performed by a singer or a singing group without instrumental accompaniment. The term ''a cappella'' was originally intended to differentiate between Rena ...
music, where the lead is the highest of the five voices and sings a descant
A descant, discant, or is any of several different things in music, depending on the period in question; etymologically, the word means a voice (''cantus'') above or removed from others. The ''Harvard Dictionary of Music'' states:
A descant ...
and not the melody
A melody (), also tune, voice, or line, is a linear succession of musical tones that the listener perceives as a single entity. In its most literal sense, a melody is a combination of Pitch (music), pitch and rhythm, while more figurativel ...
. Some artists may sing both the lead and backing vocals on audio recordings by overlapping recorded vocal tracks.
Popular music includes a range of vocal styles. Hip hop
Hip-hop or hip hop (originally disco rap) is a popular music genre that emerged in the early 1970s from the African-American community of New York City. The style is characterized by its synthesis of a wide range of musical techniques. Hip- ...
uses rapping
Rapping (also rhyming, flowing, spitting, emceeing, or MCing) is an artistic form of vocal delivery and emotive expression that incorporates " rhyme, rhythmic speech, and ommonlystreet vernacular". It is usually performed over a backin ...
, the rhythm
Rhythm (from Greek , ''rhythmos'', "any regular recurring motion, symmetry") generally means a " movement marked by the regulated succession of strong and weak elements, or of opposite or different conditions". This general meaning of regular r ...
ic delivery of rhyme
A rhyme is a repetition of similar sounds (usually the exact same phonemes) in the final Stress (linguistics), stressed syllables and any following syllables of two or more words. Most often, this kind of rhyming (''perfect rhyming'') is consciou ...
s in a rhythmic speech over a beat
Beat, beats, or beating may refer to:
Common uses
* Assault, inflicting physical harm or unwanted physical contact
* Battery (crime), a criminal offense involving unlawful physical contact
* Battery (tort), a civil wrong in common law of inte ...
or without accompaniment. Some types of rapping consist mostly or entirely of speech and chanting, like the Jamaican " toasting". In some types of rapping, the performers may interpolate short sung or half-sung passages. Blues
Blues is a music genre and musical form that originated among African Americans in the Deep South of the United States around the 1860s. Blues has incorporated spiritual (music), spirituals, work songs, field hollers, Ring shout, shouts, cha ...
singing is based on the use of the blue note
Blue Note Records is an American jazz record label now owned by Universal Music Group and operated under Capitol Music Group. Established in 1939 by German-Jewish emigrants Alfred Lion and Max Margulis, it derived its name from the blue no ...
s – notes sung at a slightly lower pitch than that of the major scale for expressive purposes. In heavy metal and hardcore punk
Hardcore punk (commonly abbreviated to hardcore or hXc) is a punk rock music genre#subtypes, subgenre and subculture that originated in the late 1970s. It is generally faster, harder, and more aggressive than other forms of punk rock. Its roots ...
subgenres, vocal styles can include techniques such as screams, shouts, and unusual sounds such as the "death growl
The death growl, or simply growl, is an extended vocal technique usually employed in extreme styles of music, particularly in death metal and other Extreme metal, extreme Heavy metal genres, subgenres of heavy metal music. Sometimes death gro ...
".
One difference between live performances in the popular and Classical genres is that whereas Classical performers often sing without amplification in small- to mid-size halls, in popular music, a microphone
A microphone, colloquially called a mic (), or mike, is a transducer that converts sound into an electrical signal. Microphones are used in many applications such as telephones, hearing aids, public address systems for concert halls and publi ...
and PA system
A public address system (or PA system) is an electronic system comprising microphones, amplifiers, loudspeakers, and related equipment. It increases the apparent volume (loudness) of a human voice, musical instrument, or other acoustic sound sou ...
(amplifier and speakers) are used in almost all performance venues, even a small coffee house. The use of the microphone has had several impacts on popular music. For one, it facilitated the development of intimate, expressive singing styles such as "crooning
A crooner is a singer who performs with a smooth, intimate style that originated in the 1920s. The crooning style was made possible by better microphones that picked up quieter sounds and a wider range of frequencies, allowing the singer to acce ...
" which would not have enough projection and volume if done without a microphone. As well, pop singers who use microphones can do a range of other vocal styles that would not project without amplification, such as making whispering sounds, humming, and mixing half-sung and sung tones. As well, some performers use the microphone's response patterns to create effects, such as bringing the mic very close to the mouth to get an enhanced bass response, or, in the case of hip-hop beatboxer
Beatboxing (also, and sometimes, called beat boxing) is a form of vocal percussion primarily involving the art of mimicking drum machines (usually a TR-808), using one's mouth, lips, tongue, and voice.
s, doing plosive "p" and "b" sounds into the mic to create percussive effects. In the 2000s, controversy arose over the widespread use of electronic Auto-Tune
Auto-Tune is audio processor software released on September 19, 1997, by the American company Antares Audio Technologies. It uses a proprietary device to measure and Pitch correction, correct pitch in music. It operates on different principles ...
pitch correction
Pitch correction is an electronic effects unit or audio software that changes the intonation (highness or lowness in pitch) of an audio signal so that all pitches will be notes from the equally tempered system (i.e., like the pitches on a piano) ...
devices with recorded and live popular music vocals. Controversy has also arisen due to cases where pop singers have been found to be lip-syncing
Lip sync or lip synch (pronounced , like the word ''sink'', despite the spelling of the participial forms ''synced'' and ''syncing''), short for lip synchronization, is a technical term for matching a speaking or singing person's lip movements ...
to a pre-recorded recording of their vocal performance or, in the case of the controversial act Milli Vanilli
Milli Vanilli ( ) was a German duo R&B music act from Munich. The act was created in 1988 by Frank Farian, founder of Boney M., and consisted of Fab Morvan and Rob Pilatus as the lip-syncing performers, with the two actual main studio sing ...
, lip-syncing to tracks recorded by other uncredited singers.
While some bands use backup singers who only sing when they are on stage, it is common for backup singers in popular music to have other roles. In many rock
Rock most often refers to:
* Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids
* Rock music, a genre of popular music
Rock or Rocks may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wale ...
and metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
bands, the musicians doing backup vocals also play instruments, such as rhythm guitar
In music performances, rhythm guitar is a guitar technique and role that performs a combination of two functions: to provide all or part of the rhythmic pulse (music), pulse in conjunction with other instruments from the rhythm section (e.g., d ...
, electric bass, or drums. In Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
or Afro-Cuban
Afro-Cubans () or Black Cubans are Cubans of full or partial sub-Saharan African ancestry. The term ''Afro-Cuban'' can also refer to historical or cultural elements in Cuba associated with this community, and the combining of native African a ...
groups, backup singers may play percussion instruments or shakers while singing. In some pop and hip hop groups and in musical theater
Musical theatre is a form of theatrical performance that combines songs, spoken dialogue, acting and dance. The story and emotional content of a musical – humor, pathos, love, anger – are communicated through words, music, moveme ...
, the backup singers may be required to perform elaborately choreographed dance routines while they sing through headset microphones.
Careers
The salaries and working conditions for vocalists vary a great deal. While jobs in other music fields such as music education choir conductors tend to be based on full-time, salaried positions, singing jobs tend to be based on contracts for individual shows or performances, or for a sequence of shows. Aspiring singers and vocalists must have musical skills, an excellent voice, the ability to work with people, and a sense of showmanship and drama. Additionally, singers need to have the ambition and drive to continually study and improve. Professional singers continue to seek outvocal coach
A vocal coach, also known as a voice coach (though this term often applies to those working with speech and communication rather than singing), is a music teacher, usually a piano accompanist, who helps singers prepare for a performance, often al ...
ing to hone their skills, extend their range, and learn new styles. As well, aspiring singers need to gain specialized skills in the vocal techniques used to interpret songs, learn about the vocal literature from their chosen style of music, and gain skills in choral music techniques, sight singing
Visual perception is the ability to detect light and use it to form an image of the surrounding environment. Photodetection without image formation is classified as ''light sensing''. In most vertebrates, visual perception can be enabled by ph ...
and memorizing songs, and vocal exercises.
Some singers learn other music jobs, such as the composing, music producing and songwriting
A songwriter is a person who creates musical compositions or writes lyrics for songs, or both. The writer of the music for a song can be called a composer, although this term tends to be used mainly in the classical music genre and film scoring. ...
. Some singers put videos on YouTube
YouTube is an American social media and online video sharing platform owned by Google. YouTube was founded on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim who were three former employees of PayPal. Headquartered in ...
and streaming
Streaming media refers to multimedia delivered through a network for playback using a media player. Media is transferred in a ''stream'' of packets from a server to a client and is rendered in real-time; this contrasts with file downl ...
apps. Singers market themselves to buyers of vocal talent, by doing audition
An audition is a sample performance by an actor, singer, musician, dancer or other performer. It typically involves the performer displaying their talent through a previously memorized and rehearsed solo piece or by performing a work or piece gi ...
s in front of a music director
A music director, musical director or director of music is a person responsible for the musical aspects of a performance, production, or organization. This would include the artistic director and usually chief conductor of an orchestra or concert ...
. Depending on the style of vocal music that a person has trained in, the "talent buyers" that they seek out may be record company
"Big Three" music labels
A record label or record company is a brand or trademark of music recordings and music videos, or the company that owns it. Sometimes, a record label is also a publishing company that manages such brands and t ...
, A&R representatives, music directors, choir directors, nightclub managers, or concert promoters. A CD or DVD with excerpts of vocal performances is used to demonstrate a singer's skills. Some singers hire an agent or manager to help them to seek out paid engagements and other performance opportunities; the agent or manager is often paid by receiving a percentage of the fees that the singer gets from performing onstage.
Singing competitions
There are several television shows that showcase singing. ''American Idol
''American Idol'' is an American Music competition, singing competition television series created by Simon Fuller, produced by Fremantle (company), Fremantle North America and 19 Entertainment, and distributed by Fremantle North America. It a ...
'' was launched in 2002. The first singing reality show was ''Sa Re Ga Ma Pa
''Sa Re Ga Ma Pa'' is an Indian Hindi-language reality singing television show. It started airing on Zee TV in 1995 as ''Sa Re Ga Ma''. It is the oldest running game show in India as well as the oldest show on private television in India. The ...
'' launched by Zee TV
ZEE TV also known as Z TV is an Indian Hindi language general entertainment pay television channel owned by Zee Entertainment Enterprises. It was launched on 1 October 1992 as the oldest privately owned television channel in India.
History ...
in 1995. At the ''American Idol
''American Idol'' is an American Music competition, singing competition television series created by Simon Fuller, produced by Fremantle (company), Fremantle North America and 19 Entertainment, and distributed by Fremantle North America. It a ...
'' Contestants audition in front of a panel of judges to see if they can move on to the next round in Hollywood, from then, the competition begins. The field of contestants is narrowed down week by week until a winner is chosen. To move on to the next round, the contestants' fate is determined by a vote by viewers. '' The Voice'' is another singing competition program. Similar to ''American Idol'', the contestants audition in front of a panel of judges, however, the judges' chairs are faced towards the audience during the performance. If the coaches are interested in the artist, they will press their button signifying they want to coach them. Once the auditions conclude, coaches have their team of artists and the competition begins. Coaches then mentor their artists and they compete to find the best singer. Other well-known singing competitions include ''The X Factor
''The X Factor'' is a television music competition franchise created by British producer Simon Cowell and his company Syco Entertainment. It originated in the United Kingdom, where it was devised as a replacement for '' Pop Idol'' (2001–200 ...
'', ''America's Got Talent
''America's Got Talent'' (often abbreviated as ''AGT'') is an American talent show competition, and is part of the global ''Got Talent'' franchise created by Simon Cowell. The program is produced by Fremantle (as well as distributed by) and ...
'', '' Rising Star'' and ''The Sing-Off
''The Sing-Off'' is an American television singing competition featuring a cappella groups. It debuted on NBC on December 14, 2009, and was produced by Sony Pictures Television and Outlaw Productions, with Mark Burnett's One Three Media (for a t ...
''.
A different example of a singing competition is ''Don't Forget the Lyrics!
''Don't Forget the Lyrics!'' is an international music game show. The original American show aired on Fox from July 11, 2007, to June 19, 2009, and after a year off the air, a third overall season, and first as a syndicated show, began on June ...
'', where the show's contestants compete to win cash prizes by correctly recalling song lyrics from a variety of genres. The show contrasts to many other music-based game shows in that artistic talent (such as the ability to sing or dance in an aesthetically pleasing way) is irrelevant to the contestants' chances of winning; in the words of one of their commercials prior to the first airing, "You don't have to sing it well; you just have to sing it right." In a similar vein, '' The Singing Bee'' combines karaoke singing with a spelling bee-style competition, with the show featuring contestants trying to remember the lyrics to popular songs.
Singing and language
Every spoken language, natural or non-natural language has its own intrinsic musicality which affects singing by means of pitch, phrasing, and accent.American Sign Language: Artistic Song Signing
An artistic signer, a signer who translates the lyrics of a song into American Sign Language (ASL), can modify existing signs, create new signs from the three basic parameters of sign language, and manipulate the typical signing space, thus deliberately expressing "rhythm, pitch, phrasing, and timbre." Moreover, an artistic signer can be a person who is "Deaf, hearing, or hard of hearing" such as Justina Miles, a Deaf performer who used ASL to interpret Rihanna's 2023 Super Bowl Halftime Show performance, and Stephen Torrence, a hearing person who created signed songs on YouTube.Neurological aspects
Much research has been done recently on the link between music and language, especially singing. It is becoming increasingly clear that these two processes are very much alike, and yet also different. Levitin describes how, beginning with the eardrum, sound waves are translated into pitch, or a tonotopic map, and then shortly thereafter "speech and music probably diverge into separate processing circuits" (130). There is evidence that neural circuits used for music and language may start out in infants undifferentiated. There are several areas of the brain that are used for both language and music. For example,Brodmann area 47
Brodmann area 47, or BA47, is part of the frontal cortex in the human brain. It curves from the lateral surface of the frontal lobe into the ventral (orbital) frontal cortex. It is inferior to BA10 and BA45, and lateral to BA11. This cytoarc ...
, which has been implicated in the processing of syntax
In linguistics, syntax ( ) is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituenc ...
in oral and sign languages, as well as musical syntax and semantic aspects of language. Levitin recounts how in certain studies, "listening to music and attending its syntactic features", similar to the syntactic processes in language, activated this part of the brain. In addition, "musical syntax ... has been localized to ... areas adjacent to and overlapping with those regions that process speech syntax, such as Broca's area
Broca's area, or the Broca area (, also , ), is a region in the frontal lobe of the dominant Cerebral hemisphere, hemisphere, usually the left, of the Human brain, brain with functions linked to speech production.
Language processing in the brai ...
" and "the regions involved in musical semantics ... appear to be ocalizednear Wernicke's area
Wernicke's area (; ), also called Wernicke's speech area, is one of the two parts of the cerebral cortex that are linked to speech, the other being Broca's area. It is involved in the comprehension of written and spoken language, in contrast to ...
." Both Broca's area and Wernicke's area are important steps in language processing and production.
Singing has been shown to help stroke victims recover speech. According to neurologist Gottfried Schlaug, there is a corresponding area to that of speech, which resides in the left hemisphere, on the right side of the brain. This is casually known as the "singing center". By teaching stroke victims to sing their words, this can help train this area of the brain for speech. In support of this theory, Levitin asserts that "regional specificity", such as that for speech, "may be temporary, as the processing centers for important mental functions actually move to other regions after trauma or brain damage." Thus in the right hemisphere of the brain, the "singing center" may be retrained to help produce speech.
Accents and singing
The speaking dialect or accent of a person may differ greatly from the general singing accent that a person uses while singing. When people sing, they generally use the accent or neutral accent that is used in the style of music they are singing in, rather than a regional accent or dialect; the style of music and the popular center/region of the style has more influence on the singing accent of a person than where they come from. For example, in the English language, British singers of rock or popular music often sing in an American accent or neutral accent instead of an English accent.Legal
In Iran women are not allowed to sing.See also
* List of multilingual bands and artists * Sign singingArt music
*A cappella
Music performed a cappella ( , , ; ), less commonly spelled acapella in English, is music performed by a singer or a singing group without instrumental accompaniment. The term ''a cappella'' was originally intended to differentiate between Rena ...
* Aria
In music, an aria (, ; : , ; ''arias'' in common usage; diminutive form: arietta, ; : ariette; in English simply air (music), air) is a self-contained piece for one voice, with or without instrument (music), instrumental or orchestral accompan ...
* Bel canto
, )—with several similar constructions (, , , pronounced in English as )—is a term with several meanings that relate to Italian singing, and whose definitions have often been misunderstood. ''Bel canto'' was not only seen as a vocal technique ...
* Chanson
A (, ; , ) is generally any Lyrics, lyric-driven French song. The term is most commonly used in English to refer either to the secular polyphonic French songs of late medieval music, medieval and Renaissance music or to a specific style of ...
* Chiaroscuro (music)
* Choir
A choir ( ), also known as a chorale or chorus (from Latin ''chorus'', meaning 'a dance in a circle') is a musical ensemble of singers. Choral music, in turn, is the music written specifically for such an ensemble to perform or in other words ...
* Fach
The German system (; literally "compartment" or "subject of study", here in the sense of "vocal specialization") is a method of classifying singers, primarily opera singers, according to the range, weight, and color of their voices. It is used ...
* Musician
A musician is someone who Composer, composes, Conducting, conducts, or Performing arts#Performers, performs music. According to the United States Employment Service, "musician" is a general Terminology, term used to designate a person who fol ...
* Opera
Opera is a form of History of theatre#European theatre, Western theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by Singing, singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically ...
* Overtone singing
Overtone singing, also known as overtone chanting, harmonic singing, polyphonic overtone singing, or diphonic singing, is a set of singing techniques in which the vocalist manipulates the resonances of the vocal tract to arouse the perception ...
* Recitative
Recitative (, also known by its Italian name recitativo () is a style of delivery (much used in operas, oratorios, and cantatas) in which a singer is allowed to adopt the rhythms and delivery of ordinary speech. Recitative does not repeat lines ...
* Sing-along
Sing-along, also called community singing or group singing, is an event of singing together at gatherings or parties, less formally than choir singing, sometimes with a songbook. Common genres are folk songs, patriotic songs, kids' songs, spirit ...
* Singer-songwriter
A singer-songwriter is a musician who writes, composes, and performs their own musical material, including lyrics and melodies. In the United States, the category is built on the folk- acoustic tradition with a guitar, although this role has ...
* Sprechgesang
(, "spoken singing") and (, "spoken voice"), more commonly known as speak-singing in English, are expressionist musical vocal techniques between singing and speaking. Though sometimes used interchangeably, is directly related to the operatic re ...
* Throat singing
Throat singing refers to several vocal practices found in different cultures worldwide. These vocal practices are generally associated with a certain type of guttural voice that contrasts with the most common types of voices employed in singing, wh ...
* Vocal pedagogy
Vocal pedagogy is the study of the art and science of voice instruction. It is used in the teaching of singing and assists in defining what singing is, how singing works, and how singing technique is accomplished.
Vocal pedagogy covers a broad r ...
* Voice projection
* Voice type
A voice type is a classification of the human singing voice into perceivable categories or groups. Particular human singing human voice, voices are identified as having certain qualities or characteristics of vocal range, vocal weight, tessitura ...
* Yodeling
Yodeling (also jodeling) is a form of singing which involves repeated and rapid changes of pitch between the low-pitch chest register (or "chest voice") and the high-pitch head register or falsetto. The English word ''yodel'' is derived from t ...
* Winsingad
Other music
*Beatboxing
Beatboxing (also, and sometimes, called beat boxing) is a form of vocal percussion primarily involving the art of mimicking drum machines (usually a Roland TR-808, TR-808), using one's mouth, lips, tongue, and voice.Belting (music)
Belting (or yell singing) is a specific technique of singing by which a singer carries their chest voice above their break or passaggio with a proportion of head voice. Belting is sometimes described as "high chest voice" or "mixed voice" (not ...
* Death growl
The death growl, or simply growl, is an extended vocal technique usually employed in extreme styles of music, particularly in death metal and other Extreme metal, extreme Heavy metal genres, subgenres of heavy metal music. Sometimes death gro ...
* Humming
A hum ( /hʌm/ ) Latin: murmur, The sound of giraffes humming () is a sound made by producing a wordless tone with the mouth closed, forcing the sound to emerge from the nose. To hum is to produce such a sound, often with a melody. It is also ...
* Isicathamiya
* Kulning
Kulning, also known as the Nordic herding call, refers to high-pitched herding calls that were developed centuries ago in Norway and Sweden. Different regions have different names for these calls, such as ''kauka'', ''lålla'', ''kula'', ''kulok ...
* Lead vocalist
The lead vocalist in popular music is typically the member of a group or band whose voice is the most prominent melody in a performance where multiple voices may be heard. The lead singer sets their voice against the accompaniment parts of t ...
* Mbube (genre)
* Rapping
Rapping (also rhyming, flowing, spitting, emceeing, or MCing) is an artistic form of vocal delivery and emotive expression that incorporates " rhyme, rhythmic speech, and ommonlystreet vernacular". It is usually performed over a backin ...
* Screaming (music)
Screaming is an extended vocal technique that is popular in "aggressive" music genres such as heavy metal, punk rock, and noise music. Screamed vocals are usually harsh, loud and aggressive, used to create an angry, emotional or intense tone. ...
* Songwriter
A songwriter is a person who creates musical compositions or writes lyrics for songs, or both. The writer of the music for a song can be called a composer, although this term tends to be used mainly in the classical music genre and film scoring. ...
* Vocoder
A vocoder (, a portmanteau of ''vo''ice and en''coder'') is a category of speech coding that analyzes and synthesizes the human voice signal for audio data compression, multiplexing, voice encryption or voice transformation.
The vocoder wa ...
Physiology
* ''N''-acylethanolamine (NAE)References
Further reading
* Blackwood, Alan. ''The Performing World of the Singer''. London: Hamish Hamilton, 1981. 113 p., amply ill. (mostly with photos.). * * Reid, Cornelius. ''A Dictionary of Vocal Terminology: an Analysis''. New York: J. Patelson Music House, 1983.External links
A Brief History of Singing
Singing and Health: A systematic mapping and review of non-clinical research
{{Authority control Occupations in music Music performance Articles containing video clips