Shinetsu Main Line on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The is a railway line, consisting of three geographically separated sections, operated by the
 ;Limited express, Rapid
, the following services are operated.
;Local
:Naoetsu–Nagaoka: every 60–120 minutes
:Nagaoka–Niitsu: every 60 minutes (every 20 minutes during peaks)
:Niitsu–Niigata: every 20 minutes (every 5–10 minutes during peaks)
;Excursion train (
;Limited express, Rapid
, the following services are operated.
;Local
:Naoetsu–Nagaoka: every 60–120 minutes
:Nagaoka–Niitsu: every 60 minutes (every 20 minutes during peaks)
:Niitsu–Niigata: every 20 minutes (every 5–10 minutes during peaks)
;Excursion train (
, ".
File:JNR 211-3000 Series C6 20190901.jpg, 211 series in Takasaki area (Isobe - Matsuida)
File:Shinano-Railway-115-S4.jpg, Shinano Railway 115 series
File:運用を開始した211系3000番台長野色.jpg, 211 series in Nagano area
File:Jreast E127 A8.jpg, E127-100 series
File:Shinetsu 115 fixed.jpg, 115 series in Niigata area (Furutsu - Niitsu)
File:Series-E129-JReast.jpg, E129 series (Nagatori - Tsukayama)
File:E653-1100 H202 20150302.jpg, E653-1100 series (Naoetsu Station)
File:JNR 115-1000 shonan-calor Taka.JPG, 115 series (Yokokawa Station)
File:JR_East_107-100.jpg, 107 series (Gumma-Yawata - Annaka)
File:485 T12 Hokuetsu 4 Naoetsu 20100903.jpg, 485-1000 series ''Hokuetsu'' (Naoetsu Station)
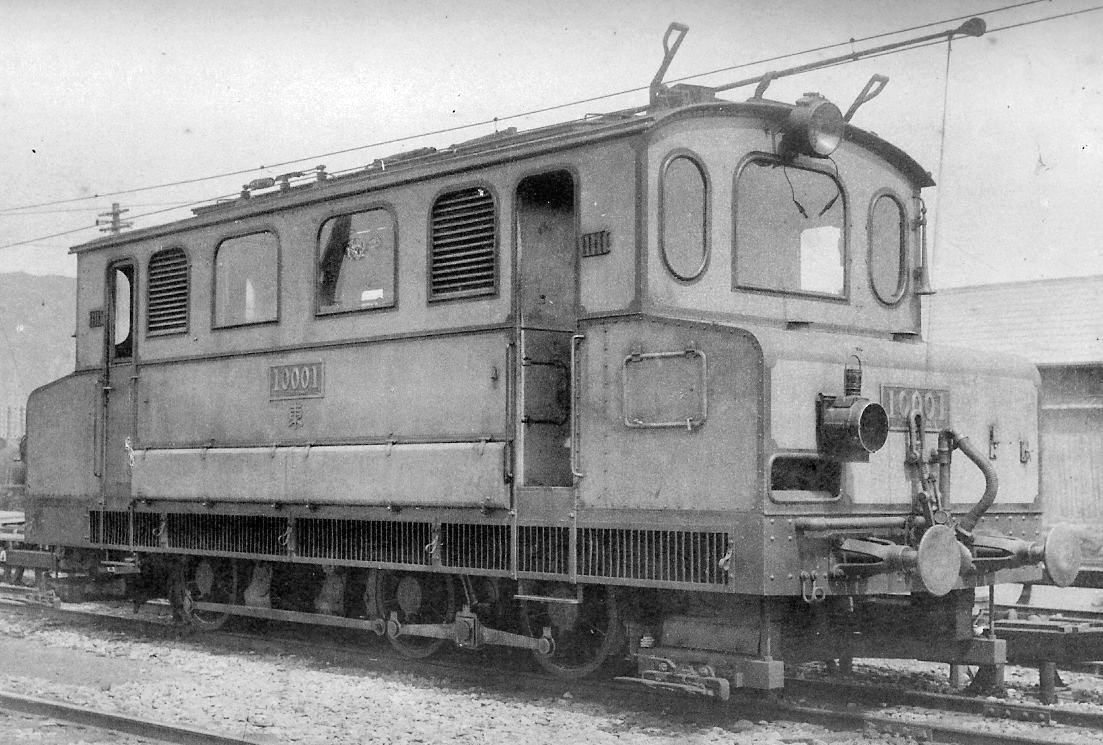 The Japanese Government Railways opened the Takasaki to Yokokawa section in 1885, the Naoetsu to Sekiyama section the following year, and the Sekiyama–Nagano–Karuizawa section in 1888. In order to surmount the 552 metre altitude difference between Yokokawa and Karuizawa (which are apart), it then constructed an Abt rack section through the Usui Pass, which opened in 1893, and was double-tracked for from Karuizawa to the top of the rack section. A horse-drawn tramway operated between Yokokawa and Karuizawa until the rack section opened.
The Japanese Government Railways opened the Takasaki to Yokokawa section in 1885, the Naoetsu to Sekiyama section the following year, and the Sekiyama–Nagano–Karuizawa section in 1888. In order to surmount the 552 metre altitude difference between Yokokawa and Karuizawa (which are apart), it then constructed an Abt rack section through the Usui Pass, which opened in 1893, and was double-tracked for from Karuizawa to the top of the rack section. A horse-drawn tramway operated between Yokokawa and Karuizawa until the rack section opened.
 The Hokuetsu Railway opened the Naoetsu to Nagaoka section in 1897, extending the line to Niigata in 1904. That company was nationalised in 1907. In 1909, the Imperial Japanese Railway authorities invited bids for the electrification of the route. A German company was selected to provide the engines and
The Hokuetsu Railway opened the Naoetsu to Nagaoka section in 1897, extending the line to Niigata in 1904. That company was nationalised in 1907. In 1909, the Imperial Japanese Railway authorities invited bids for the electrification of the route. A German company was selected to provide the engines and
A link to archival footage of the rack section operation is available here
 Shinano Railway Kita-Shinano Line (37.3 km, to )
*
Shinano Railway Kita-Shinano Line (37.3 km, to )
*  Echigo Tokimeki Railway Myōkō Haneuma Line (37.7 km, Myōkō-Kōgen to )
Echigo Tokimeki Railway Myōkō Haneuma Line (37.7 km, Myōkō-Kōgen to )

 (Note - for the connections at stations between Karuizawa and Shinonoi, see Shinano Railway Line)
* Nagano Station: The Zenkoji Hakuba Railway Co. opened a line to Susohana Guchi in 1936. A proposal for the line to be extended to Hakuba on the Oito Line did not eventuate, and the line closed in 1944.
* Kuroi Station: The Kubiki Railway Co. opened a gauge line to Uragawara between 1914 and 1916, with the line closing in 1971.
*Raikoji Station: The Nagaoka Railway Co. opened a line to Teradomari (on the Echigo Line) between 1915 and 1921. This company introduced Japan's first diesel railcar in 1928, and in 1951 electrified of the line at 750 V DC in 70 days, completing the balance the following year. Significant typhoon damage occurred in 1966, and in 1972, passenger services ceased between Raikoji and Nishinagaoka, with the entire line becoming freight-only three years later. The line closed in 1995.
:The 13 km gauge Uonuma Railway to Nishiojiya was opened in 1911, and nationalised in 1922. It was converted to gauge in 1954, freight services ceased in 1960, and the line closed in 1984.
*Nagaoka Station: The Tochio Railway opened a 27 km gauge line to Tochio and Yūkyūzan between 1915 and 1924. The line was electrified at 600 V DC in 1948, with this being raised to 750 V DC in 1956. CTC signalling was commissioned in 1961, freight services ceased in 1967, and the line closed between 1973 and 1975.
* Higashi Sanjo Station: The Echigo Railway Co. opened the 8 km line to Echigo Nagasawa in 1927, and was nationalised two months later. Freight services ceased in 1960, and the line closed in 1985.
* Kamo Station: The Kanbara Railway Co. operated a line to Gosen on the
(Note - for the connections at stations between Karuizawa and Shinonoi, see Shinano Railway Line)
* Nagano Station: The Zenkoji Hakuba Railway Co. opened a line to Susohana Guchi in 1936. A proposal for the line to be extended to Hakuba on the Oito Line did not eventuate, and the line closed in 1944.
* Kuroi Station: The Kubiki Railway Co. opened a gauge line to Uragawara between 1914 and 1916, with the line closing in 1971.
*Raikoji Station: The Nagaoka Railway Co. opened a line to Teradomari (on the Echigo Line) between 1915 and 1921. This company introduced Japan's first diesel railcar in 1928, and in 1951 electrified of the line at 750 V DC in 70 days, completing the balance the following year. Significant typhoon damage occurred in 1966, and in 1972, passenger services ceased between Raikoji and Nishinagaoka, with the entire line becoming freight-only three years later. The line closed in 1995.
:The 13 km gauge Uonuma Railway to Nishiojiya was opened in 1911, and nationalised in 1922. It was converted to gauge in 1954, freight services ceased in 1960, and the line closed in 1984.
*Nagaoka Station: The Tochio Railway opened a 27 km gauge line to Tochio and Yūkyūzan between 1915 and 1924. The line was electrified at 600 V DC in 1948, with this being raised to 750 V DC in 1956. CTC signalling was commissioned in 1961, freight services ceased in 1967, and the line closed between 1973 and 1975.
* Higashi Sanjo Station: The Echigo Railway Co. opened the 8 km line to Echigo Nagasawa in 1927, and was nationalised two months later. Freight services ceased in 1960, and the line closed in 1985.
* Kamo Station: The Kanbara Railway Co. operated a line to Gosen on the
Stations of the Shin'etsu Main Line (Gumma)
(JR East)
Stations of the Shin'etsu Main Line (Nagano/Niigata)
(JR East) {{DEFAULTSORT:Shinetsu Main Line Lines of East Japan Railway Company Rail transport in Gunma Prefecture Railway lines in Nagano Prefecture Rail transport in Niigata Prefecture 1067 mm gauge railways in Japan 1500 V DC railway electrification
East Japan Railway Company
The is a major passenger railway company in Japan and the largest of the seven Japan Railways Group companies. The company name is officially abbreviated as JR-EAST or JR East in English, and as in Japanese. The company's headquarters are in ...
(JR East) in Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
. It was originally one continuous line connecting and via . Since the opening and later extension of the Hokuriku Shinkansen
The Hokuriku Shinkansen () is a high-speed Shinkansen railway line connecting Tokyo with Tsuruga, Fukui, Tsuruga in the Hokuriku region of Japan. It is jointly operated by East Japan Railway Company (JR East) and West Japan Railway Company (JR ...
, sections running in parallel have either been discontinued or transferred to third-sector railway companies.
The name of the line refers to the old names for Nagano and Niigata prefectures, Shinano (), and Echigo ().
The discontinued section through the Usui Pass was famous for its steep 66.7 ‰ (6.67 %) gradient
In vector calculus, the gradient of a scalar-valued differentiable function f of several variables is the vector field (or vector-valued function) \nabla f whose value at a point p gives the direction and the rate of fastest increase. The g ...
.
Sections
From 14 March 2015, the line consists of the following three sections. * – (29.7 km): inGunma Prefecture
is a landlocked Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Kantō region of Honshu. Gunma Prefecture has a population of 1,937,626 (1 October 2019) and has a geographic area of . Gunma Prefecture borders Niigata Prefecture and Fuk ...
* – (9.3 km): in Nagano Prefecture
is a Landlocked country, landlocked Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Chūbu region of Honshu. Nagano Prefecture has a population of 2,007,682 () and has a geographic area of . Nagano Prefecture borders Niigata Prefecture ...
* – (136.3 km): in Niigata Prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture in the Chūbu region of Honshu of Japan. Niigata Prefecture has a population of 2,131,009 (1 July 2023) and is the List of Japanese prefectures by area, fifth-largest prefecture of Japan by geographic area ...
There are three small freight branches; from Echigo-Ishiyama Station to Niigata Freight Terminal, from Kami-Nuttari Junction to Nuttari Station (discontinued on 25 March 2010), and from Kami-Nuttari Junction to Higashi-Niigata-kō Station.
Services
Takasaki–Yokokawa
*Local: 1 or 2 trains per hour * Excursion train: ''SL Gunma Yokokawa'' and ''SL YOGISHA Yokokawa'' ()Shinonoi–Nagano
All trains run through on the Shinonoi Line or the Shinano Railway Line.Naoetsu–Niigata
Joyful Train
is the name given to railway rolling stock or train sets operated by the JR Group in Japan primarily for charters, special events, tourist excursions, and other similar purposes. Traditionally, this term is only used for chartered trains dedicate ...
)
:'' Koshino Shu*Kura''
Stations
Takasaki–Yokokawa
All stations are in Gunma Prefecture.Yokokawa–Shinonoi
The section between Yokokawa and was closed and the section between Karuizawa and Shinonoi was transferred to the ownership of the third-sector railway operator Shinano Railway from 1 October 1997 with the opening of theHokuriku Shinkansen
The Hokuriku Shinkansen () is a high-speed Shinkansen railway line connecting Tokyo with Tsuruga, Fukui, Tsuruga in the Hokuriku region of Japan. It is jointly operated by East Japan Railway Company (JR East) and West Japan Railway Company (JR ...
( Nagano Shinkansen) between Takasaki and Nagano.
Shinonoi–Nagano
All stations are in Nagano, Nagano Prefecture.Nagano–Naoetsu
The section between Nagano and Naoetsu was transferred to the ownership of the third-sector railway operators Shinano Railway and Echigo Tokimeki Railway from 14 March 2015 with the opening of theHokuriku Shinkansen
The Hokuriku Shinkansen () is a high-speed Shinkansen railway line connecting Tokyo with Tsuruga, Fukui, Tsuruga in the Hokuriku region of Japan. It is jointly operated by East Japan Railway Company (JR East) and West Japan Railway Company (JR ...
extension north of Nagano.
Naoetsu–Niigata
All stations are in Niigata Prefecture. :A: Limited Express '' Shirayuki'' :B: Rapid ''Ohayo-Shinetsu'' :C: Rapid ''Rakuraku-Train-Shinetsu'' :D: Rapid :Trains stop at stations marked "O", skip at stations marked "Rolling Stock
Present
Takasaki–Yokokawa
*211 series
The is a suburban electric multiple unit (EMU) train type introduced in 1985 by the Japanese National Railways (JNR). The trains are still being used by the East Japan Railway Company (JR East). They were formerly used by the West Japan Railwa ...
4/6-car DC EMUs
Shinonoi–Nagano
*115 series 115 may refer to:
*115 (number), the number
*AD 115, a year in the 2nd century AD
*115 BC, a year in the 2nd century BC
*115 (Hampshire Fortress) Corps Engineer Regiment, Royal Engineers, a unit in the UK Territorial Army
*115 (Leicestershire) Field ...
2/3-car DC EMUs ( Shinano Railway)
* 211 series
The is a suburban electric multiple unit (EMU) train type introduced in 1985 by the Japanese National Railways (JNR). The trains are still being used by the East Japan Railway Company (JR East). They were formerly used by the West Japan Railwa ...
3-car DC EMUs
* E127-100 series 2-car DC EMUs
* 383 series 6-car DC EMUs ('' Shinano'')
Naoetsu–Niigata
*115 series 115 may refer to:
*115 (number), the number
*AD 115, a year in the 2nd century AD
*115 BC, a year in the 2nd century BC
*115 (Hampshire Fortress) Corps Engineer Regiment, Royal Engineers, a unit in the UK Territorial Army
*115 (Leicestershire) Field ...
3-car DC EMUs (rapid only)
* E129 series 2/4 car DC EMUs (since December 2014)
* ET127 series 2-car DC EMUs (Naoetsu–Nagaoka, late night/early morning only)
* E653-1100 series 4-car DC/AC EMUs ( ''Shirayuki'', ''Ohayo-Shinetsu'', ''Rakuraku-Train-Shinetsu'')
Former
Takasaki–Yokokawa
*115 series 115 may refer to:
*115 (number), the number
*AD 115, a year in the 2nd century AD
*115 BC, a year in the 2nd century BC
*115 (Hampshire Fortress) Corps Engineer Regiment, Royal Engineers, a unit in the UK Territorial Army
*115 (Leicestershire) Field ...
(until March 2018)
* 107 series (until September 2017)
Naoetsu–Niigata
*485 series
The (and the earlier 481 and 483 series variants) was a Japanese limited express electric multiple unit (EMU) type introduced in 1964 by Japanese National Railways (JNR), and later operated by the East Japan Railway Company (JR East), West Jap ...
(Until March 2017) - '' Hokuetsu'', '' Kubikino'', ''Ohayo-Shinetsu'', ''Rakuraku-Train-Shinetsu'', '' Moonlight Echigo'', '' Minori'', '' Hakuchō'', etc.
* 489 series - '' Noto'' etc.
* 583 series
The were limited express electric multiple unit (EMU) train types introduced in 1967 by Japanese National Railways and later operated by East Japan Railway Company (JR East) and West Japan Railway Company (JR West) on the through services expr ...
(Until January 2013) - '' Kitaguni''
* 181 series, 183 series - '' Toki'' etc.
* 165 series
* 70 series
History
 The Japanese Government Railways opened the Takasaki to Yokokawa section in 1885, the Naoetsu to Sekiyama section the following year, and the Sekiyama–Nagano–Karuizawa section in 1888. In order to surmount the 552 metre altitude difference between Yokokawa and Karuizawa (which are apart), it then constructed an Abt rack section through the Usui Pass, which opened in 1893, and was double-tracked for from Karuizawa to the top of the rack section. A horse-drawn tramway operated between Yokokawa and Karuizawa until the rack section opened.
The Japanese Government Railways opened the Takasaki to Yokokawa section in 1885, the Naoetsu to Sekiyama section the following year, and the Sekiyama–Nagano–Karuizawa section in 1888. In order to surmount the 552 metre altitude difference between Yokokawa and Karuizawa (which are apart), it then constructed an Abt rack section through the Usui Pass, which opened in 1893, and was double-tracked for from Karuizawa to the top of the rack section. A horse-drawn tramway operated between Yokokawa and Karuizawa until the rack section opened.
 The Hokuetsu Railway opened the Naoetsu to Nagaoka section in 1897, extending the line to Niigata in 1904. That company was nationalised in 1907. In 1909, the Imperial Japanese Railway authorities invited bids for the electrification of the route. A German company was selected to provide the engines and
The Hokuetsu Railway opened the Naoetsu to Nagaoka section in 1897, extending the line to Niigata in 1904. That company was nationalised in 1907. In 1909, the Imperial Japanese Railway authorities invited bids for the electrification of the route. A German company was selected to provide the engines and General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) was an American Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1892, incorporated in the New York (state), state of New York and headquartered in Boston.
Over the year ...
supplied the turbines at the power station. In 1912, the rack section was electrified using third rail
A third rail, also known as a live rail, electric rail or conductor rail, is a method of providing electric power to a railway locomotive or train, through a semi-continuous rigid conductor placed alongside or between the rails of a track (r ...
at 600 V DC, this being the first use of this method in Japan. The electrification allowed for the use of faster and longer trains which reduced journey times and also pollution from the steam enginesA link to archival footage of the rack section operation is available here
Double-tracking
The Karuizawa to Nagano section was double-tracked between 1917 and 1920, with the Nagaoka to Miyauchi section double-tracked in 1931, and the Niitsu–Kamo section in 1944. Double-tracking of the remainder of the Niigata to Naoetsu line was undertaken in sections between 1958 and 1973. Double-tracking of the remainder of the Takasaki to Kaminagano line was undertaken in sections between 1963 and 1973, commencing with the replacement of the rack mechanism with an adhesion only electrified (1,500 V DCcatenary
In physics and geometry, a catenary ( , ) is the curve that an idealized hanging chain or wire rope, cable assumes under its own weight when supported only at its ends in a uniform gravitational field.
The catenary curve has a U-like shape, ...
) operation on the 1 in 15 (6.7%) grade. The rack equipment was initially kept as a contingency, and removed two months after the adhesion-only operation commenced and had proved its reliability.
The Kurohime to Myoko-Kogen section was double-tracked in conjunction with a realignment in 1980. The Mure to Kurohime section was also realigned and prepared for double-tracking (including new double-track size tunnels), but the second track was not laid.
Electrification
The Miyauchi to Nagaoka section was electrified in 1947 at 1,500 V DC in conjunction with the electrification of the Joetsu Line, with the Nagaoka to Niigata section electrified in 1962, the same year the Takasaki to Yokokawa section was commissioned to facilitate the extension to Nagano the following year via the new adhesion line through the Usui Pass mentioned above. The Nagano to Naoetsu section was electrified in 1966, and extended to Miyauchi in 1969.Separation into sections
In 1997, following the opening of the Nagano Shinkansen, the Yokokawa to Karuizawa section was closed, and the Karuizawa to Shinonoi section transferred to the third-sector Shinano Railway. On 14 March 2015, following the extension of theHokuriku Shinkansen
The Hokuriku Shinkansen () is a high-speed Shinkansen railway line connecting Tokyo with Tsuruga, Fukui, Tsuruga in the Hokuriku region of Japan. It is jointly operated by East Japan Railway Company (JR East) and West Japan Railway Company (JR ...
to , the to section was also spun off to the following two third-sector operating companies owned primarily by the respective prefectures and municipalities.
* Station numbering
Station numbering was introduced on the Shinonoi–Nagano section from February 2025, with Shinonoi station being assigned SE09. Numbers increase towards Nagano.Former connecting lines
 (Note - for the connections at stations between Karuizawa and Shinonoi, see Shinano Railway Line)
* Nagano Station: The Zenkoji Hakuba Railway Co. opened a line to Susohana Guchi in 1936. A proposal for the line to be extended to Hakuba on the Oito Line did not eventuate, and the line closed in 1944.
* Kuroi Station: The Kubiki Railway Co. opened a gauge line to Uragawara between 1914 and 1916, with the line closing in 1971.
*Raikoji Station: The Nagaoka Railway Co. opened a line to Teradomari (on the Echigo Line) between 1915 and 1921. This company introduced Japan's first diesel railcar in 1928, and in 1951 electrified of the line at 750 V DC in 70 days, completing the balance the following year. Significant typhoon damage occurred in 1966, and in 1972, passenger services ceased between Raikoji and Nishinagaoka, with the entire line becoming freight-only three years later. The line closed in 1995.
:The 13 km gauge Uonuma Railway to Nishiojiya was opened in 1911, and nationalised in 1922. It was converted to gauge in 1954, freight services ceased in 1960, and the line closed in 1984.
*Nagaoka Station: The Tochio Railway opened a 27 km gauge line to Tochio and Yūkyūzan between 1915 and 1924. The line was electrified at 600 V DC in 1948, with this being raised to 750 V DC in 1956. CTC signalling was commissioned in 1961, freight services ceased in 1967, and the line closed between 1973 and 1975.
* Higashi Sanjo Station: The Echigo Railway Co. opened the 8 km line to Echigo Nagasawa in 1927, and was nationalised two months later. Freight services ceased in 1960, and the line closed in 1985.
* Kamo Station: The Kanbara Railway Co. operated a line to Gosen on the
(Note - for the connections at stations between Karuizawa and Shinonoi, see Shinano Railway Line)
* Nagano Station: The Zenkoji Hakuba Railway Co. opened a line to Susohana Guchi in 1936. A proposal for the line to be extended to Hakuba on the Oito Line did not eventuate, and the line closed in 1944.
* Kuroi Station: The Kubiki Railway Co. opened a gauge line to Uragawara between 1914 and 1916, with the line closing in 1971.
*Raikoji Station: The Nagaoka Railway Co. opened a line to Teradomari (on the Echigo Line) between 1915 and 1921. This company introduced Japan's first diesel railcar in 1928, and in 1951 electrified of the line at 750 V DC in 70 days, completing the balance the following year. Significant typhoon damage occurred in 1966, and in 1972, passenger services ceased between Raikoji and Nishinagaoka, with the entire line becoming freight-only three years later. The line closed in 1995.
:The 13 km gauge Uonuma Railway to Nishiojiya was opened in 1911, and nationalised in 1922. It was converted to gauge in 1954, freight services ceased in 1960, and the line closed in 1984.
*Nagaoka Station: The Tochio Railway opened a 27 km gauge line to Tochio and Yūkyūzan between 1915 and 1924. The line was electrified at 600 V DC in 1948, with this being raised to 750 V DC in 1956. CTC signalling was commissioned in 1961, freight services ceased in 1967, and the line closed between 1973 and 1975.
* Higashi Sanjo Station: The Echigo Railway Co. opened the 8 km line to Echigo Nagasawa in 1927, and was nationalised two months later. Freight services ceased in 1960, and the line closed in 1985.
* Kamo Station: The Kanbara Railway Co. operated a line to Gosen on the Ban'etsu West Line
The is a railway line in Japan operated by East Japan Railway Company (JR East). It connects Kōriyama Station (Fukushima), Kōriyama Station in Kōriyama, Fukushima Prefecture, and Niitsu Station in Akiha-ku, Niigata, Akiha Ward, Niigata (cit ...
from 1923 until 2002.
References
External links
Stations of the Shin'etsu Main Line (Gumma)
(JR East)
Stations of the Shin'etsu Main Line (Nagano/Niigata)
(JR East) {{DEFAULTSORT:Shinetsu Main Line Lines of East Japan Railway Company Rail transport in Gunma Prefecture Railway lines in Nagano Prefecture Rail transport in Niigata Prefecture 1067 mm gauge railways in Japan 1500 V DC railway electrification