septum on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
 *
*  *
*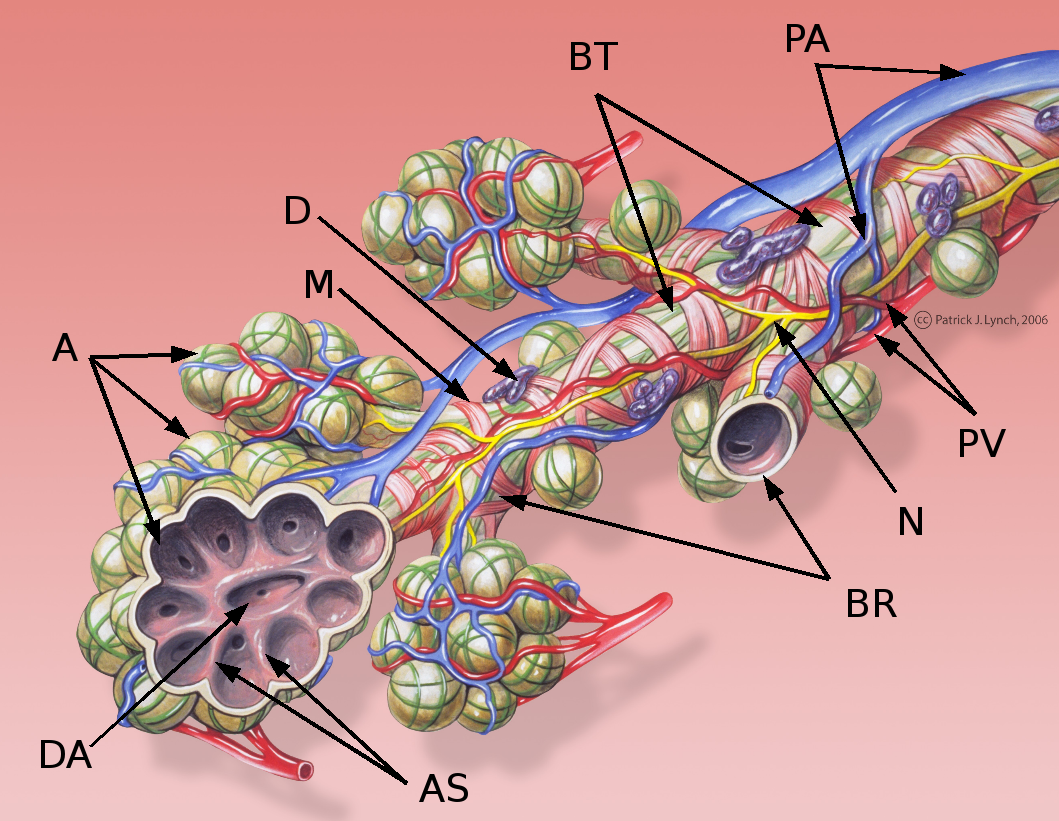 * Alveolar septum: the thin wall which separates the alveoli from each other in the lungs
*
* Alveolar septum: the thin wall which separates the alveoli from each other in the lungs
*

 *A partition dividing filamentous
*A partition dividing filamentous
 *A partition that separates the
*A partition that separates the
biology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and ...
, a septum (Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
for ''something that encloses''; septa) is a wall, dividing a cavity or structure into smaller ones. A cavity or structure divided in this way may be referred to as septate.
Examples
Human anatomy
*Interatrial septum
The interatrial septum is the wall of tissue that separates the right and left atria of the heart.
Structure
The interatrial septum is a that lies between the left atrium and right atrium of the human heart. The interatrial septum lies at ang ...
, the wall of tissue that is a sectional part of the left and right atria of the heart
Interventricular septum
The interventricular septum (IVS, or ventricular septum, or during development septum inferius) is the stout wall separating the ventricle (heart), ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another.
The interventricular septum is di ...
, the wall separating the left and right ventricles of the heart
* Lingual septum, a vertical layer of fibrous tissue that separates the halves of the tongue
 *
*Nasal septum
The nasal septum () separates the left and right airways of the Human nose, nasal cavity, dividing the two nostrils.
It is Depression (kinesiology), depressed by the depressor septi nasi muscle.
Structure
The fleshy external end of the nasal s ...
: the cartilage wall separating the nostrils of the nose
 * Alveolar septum: the thin wall which separates the alveoli from each other in the lungs
*
* Alveolar septum: the thin wall which separates the alveoli from each other in the lungs
* Orbital septum
In anatomy, the orbital septum (palpebral fascia) is a membranous sheet that acts as the anterior (frontal) boundary of the orbit. It extends from the orbital rims to the eyelids. It forms the fibrous portion of the eyelids.
Structure
In the ...
, a palpebral ligament in the upper and lower eyelids
* Septum pellucidum
The septum pellucidum (Latin for "translucent wall") is a thin, triangular, vertical double membrane separating the anterior horns of the left and right lateral ventricles of the brain. It runs as a sheet from the corpus callosum down to the f ...
or septum lucidum, a thin structure separating two fluid pockets in the brain
* Uterine septum
A uterine septum is a congenital uterine malformation where the uterine cavity is partitioned by a longitudinal septum; the outside of the uterus has a normal typical shape. The wedge-like partition may involve only the superior part of the cav ...
, a malformation of the uterus
* Penile septum, a fibrous wall between the two corpora cavernosa penis
* Septum glandis
The septum glandis, also septum of the glans, refers to the fibrous partition of the ventral aspect of the glans penis that separates the two glans wings in the ventral midline. The septum extends from the urethral meatus through the glanular ur ...
, partition of the ventral aspect of the glans penis
* Scrotal septum
The septum of scrotum or scrotal septum is an incomplete vertical wall (septum) that divides the scrotum into two compartments –each containing a single testis. It consists of flexible connective tissue and nonstriated muscle (dartos fascia
...
, layer of tissue dividing the scrotum
* Vaginal septum
A vaginal septum is a vaginal anomaly that is partition within the vagina; such a septum could be either longitudinal or transverse. In some affected women, the septum is partial or does not extend the length or width of the vagina. Pain during ...
, a lateral or transverse partition inside the vagina
* Intermuscular septa separating the muscles of the arms and legs
Histological septa are seen throughout most tissues of the body, particularly where they are needed to stiffen soft cellular tissue, and they also provide planes of ingress for small blood vessels. Because the dense collagen fibres of a septum usually extend out into the softer adjacent tissues, microscopic fibrous septa are less clearly defined than the macroscopic types of septa listed above. In rare instances, a septum is a cross-wall. Thus it divides a structure into smaller parts.
Cell biology
Theseptum (cell biology)
A septum in cell biology is the new cell wall that forms between two daughter cells as a result of cell division. Cell division is an extremely complex process that contains four different subprocesses. These processes included the growth of a ce ...
is the boundary formed between dividing cells in the course of cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell (biology), cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukar ...
.

Fungus
 *A partition dividing filamentous
*A partition dividing filamentous hypha
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium.
Structure
A hypha consists of one o ...
e into discrete cells in fungi.
Botany
 *A partition that separates the
*A partition that separates the locule
A locule (: locules) or loculus (; : loculi) is a small cavity or compartment within an organ or part of an organism (animal, plant, or fungus).
In angiosperms (flowering plants), the term ''locule'' usually refers to a chamber within an ovary ...
s of a fruit, anther
The stamen (: stamina or stamens) is a part consisting of the male reproductive organs of a flower. Collectively, the stamens form the androecium., p. 10
Morphology and terminology
A stamen typically consists of a stalk called the filament ...
, or sporangium
A sporangium (from Late Latin, ; : sporangia) is an enclosure in which spores are formed. It can be composed of a unicellular organism, single cell or can be multicellular organism, multicellular. Virtually all plants, fungus, fungi, and many ot ...
.
Zoology
A coral septum is one of the radial calcareous plates in thecorallite
A corallite is the skeletal cup, formed by an individual stony coral polyp, in which the polyp sits and into which it can retract. The cup is composed of aragonite, a crystalline form of calcium carbonate, and is secreted by the polyp. Corallit ...
s of a coral
Corals are colonial marine invertebrates within the subphylum Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact Colony (biology), colonies of many identical individual polyp (zoology), polyps. Coral species include the important Coral ...
.
Annelid
The annelids (), also known as the segmented worms, are animals that comprise the phylum Annelida (; ). The phylum contains over 22,000 extant species, including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to vario ...
s have septa that divide their coelom
The coelom (or celom) is the main body cavity in many animals and is positioned inside the body to surround and contain the digestive tract and other organs. In some animals, it is lined with mesothelium. In other animals, such as molluscs, i ...
into segmented chambers.
Many shelled organisms have septa subdividing their shell chamber, including rhizopods, cephalopods
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan Taxonomic rank, class Cephalopoda (Greek language, Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral symm ...
and gastropod
Gastropods (), commonly known as slugs and snails, belong to a large Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda ().
This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, freshwater, and fro ...
s, the latter seemingly serving as a defence against shell-boring predators.
Laboratory technology
* A rubber septum is an engineered membrane that permits transfer of a substance (usually liquid or gas) without contact with air, usually using a syringe with needle.{{Citation needed, date=August 2024References