Sengoku Period on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The was the period in Japanese history in which civil wars and social upheavals took place almost continuously in the 15th and 16th centuries. The Ky┼Źtoku incident (1454),  This period was characterized by the overthrow of a superior power by a subordinate one. The Ashikaga shogunate, the '' de facto'' central government, declined and the , a local power, seized wider political influence. The people rebelled against the feudal lords in revolts known as .
The period saw a breakdown in the traditional master-servant relationship between a lord and his vassals, with many instances of vassals rebelling against their lords, internal dynastic conflict over lordships within noble families (in which vassals would take sides), and the installation of figurehead lords by cadet branches of noble families. The period was also marked by the loosening of samurai culture, with people born into other social strata sometimes making a name for themselves as warriors and thus becoming samurai. In turn, events sometimes allowed common
This period was characterized by the overthrow of a superior power by a subordinate one. The Ashikaga shogunate, the '' de facto'' central government, declined and the , a local power, seized wider political influence. The people rebelled against the feudal lords in revolts known as .
The period saw a breakdown in the traditional master-servant relationship between a lord and his vassals, with many instances of vassals rebelling against their lords, internal dynastic conflict over lordships within noble families (in which vassals would take sides), and the installation of figurehead lords by cadet branches of noble families. The period was also marked by the loosening of samurai culture, with people born into other social strata sometimes making a name for themselves as warriors and thus becoming samurai. In turn, events sometimes allowed common
 The Ky┼Źtoku incident in 1454,
The Ky┼Źtoku incident in 1454,  However, even if 1568 is the end date of the Sengoku period, there are also various theories about the beginning and end dates of the following Azuchi-Momoyama period. The Azuchi-Momoyama period refers to the period when
However, even if 1568 is the end date of the Sengoku period, there are also various theories about the beginning and end dates of the following Azuchi-Momoyama period. The Azuchi-Momoyama period refers to the period when
 Ashikaga Yoshihisa, who had become the ninth shogun during the Onin War, died at the age of 25, and Ashikaga Yoshitane became the 10th shogun. However, in 1493, Hosokawa Masamoto raised an army while shogun Yoshitane was away in Kyoto and installed the 11th shogun, Ashikaga Yoshizumi, in a de facto coup known as the . Masamoto held the position of , second only to the shogun in the Ashikaga shogunate, and the equivalent of in the Kamakura shogunate. This made the shogun a puppet of the
Ashikaga Yoshihisa, who had become the ninth shogun during the Onin War, died at the age of 25, and Ashikaga Yoshitane became the 10th shogun. However, in 1493, Hosokawa Masamoto raised an army while shogun Yoshitane was away in Kyoto and installed the 11th shogun, Ashikaga Yoshizumi, in a de facto coup known as the . Masamoto held the position of , second only to the shogun in the Ashikaga shogunate, and the equivalent of in the Kamakura shogunate. This made the shogun a puppet of the

 In 1546, H┼Źj┼Ź Ujiyasu defeated Uesugi Tomosada at the siege of Kawagoe Castle, and the
In 1546, H┼Źj┼Ź Ujiyasu defeated Uesugi Tomosada at the siege of Kawagoe Castle, and the
 When the Portuguese brought the
When the Portuguese brought the
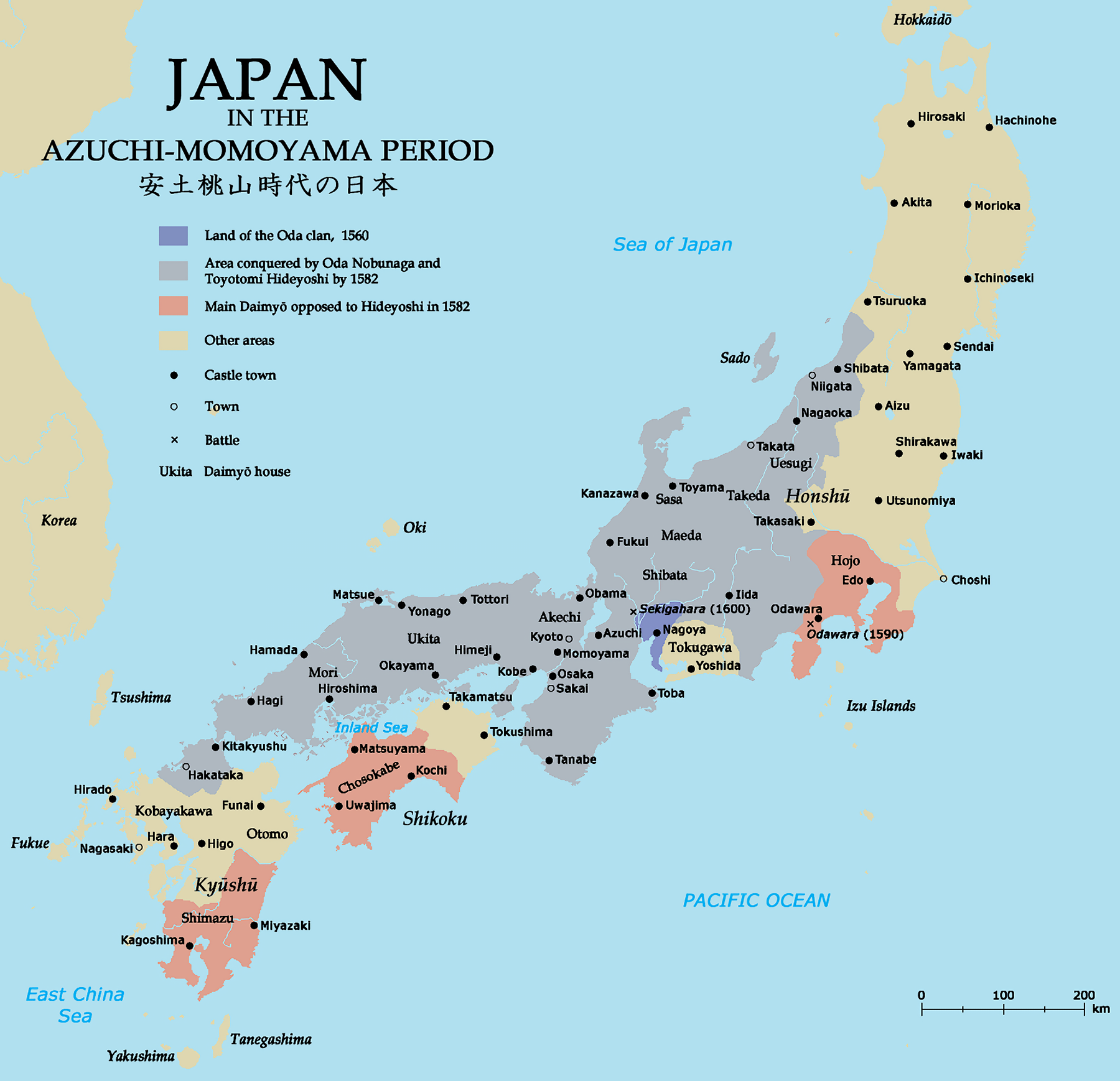
 In and around the
In and around the

 The upheaval resulted in the further weakening of central authority, and throughout Japan, regional lords, called ''
The upheaval resulted in the further weakening of central authority, and throughout Japan, regional lords, called ''
Sengoku Period
ŌĆō ''
Samurai Archives Japanese History page
*
held in Gifu Prefecture, 2000ŌĆō2001 *
{{Authority control * * * * * 1460s establishments in Japan 1467 establishments in Asia 1573 disestablishments in Japan Civil wars in Japan Muromachi period Wars of succession involving the states and peoples of Asia
┼īnin War
The , also known as the Upheaval of ┼īnin and ┼īnin-Bunmei war, was a civil war that lasted from 1467 to 1477, during the Muromachi period in Japan. ''┼īnin'' refers to the Japanese era name, Japanese era during which the war started; the war ende ...
(1467), or (1493) are generally chosen as the period's start date, but there are many competing historiographies for its end date, ranging from 1568, the date of Oda Nobunaga's march on Kyoto, to the suppression of the Shimabara Rebellion
The , also known as the or , was an rebellion, uprising that occurred in the Shimabara Domain of the Tokugawa shogunate in Japan from 17 December 1637 to 15 April 1638.
Matsukura Katsuie, the ''daimy┼Ź'' of the Shimabara Domain, enforced unpo ...
in 1638, deep into what was traditionally considered the Edo period
The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengok ...
. Regardless of the dates chosen, the Sengoku period overlaps substantially with the Muromachi period
The , also known as the , is a division of Japanese history running from approximately 1336 to 1573. The period marks the governance of the Muromachi or Ashikaga shogunate ( or ), which was officially established in 1338 by the first Muromachi ...
(1336ŌĆō1573).
 This period was characterized by the overthrow of a superior power by a subordinate one. The Ashikaga shogunate, the '' de facto'' central government, declined and the , a local power, seized wider political influence. The people rebelled against the feudal lords in revolts known as .
The period saw a breakdown in the traditional master-servant relationship between a lord and his vassals, with many instances of vassals rebelling against their lords, internal dynastic conflict over lordships within noble families (in which vassals would take sides), and the installation of figurehead lords by cadet branches of noble families. The period was also marked by the loosening of samurai culture, with people born into other social strata sometimes making a name for themselves as warriors and thus becoming samurai. In turn, events sometimes allowed common
This period was characterized by the overthrow of a superior power by a subordinate one. The Ashikaga shogunate, the '' de facto'' central government, declined and the , a local power, seized wider political influence. The people rebelled against the feudal lords in revolts known as .
The period saw a breakdown in the traditional master-servant relationship between a lord and his vassals, with many instances of vassals rebelling against their lords, internal dynastic conflict over lordships within noble families (in which vassals would take sides), and the installation of figurehead lords by cadet branches of noble families. The period was also marked by the loosening of samurai culture, with people born into other social strata sometimes making a name for themselves as warriors and thus becoming samurai. In turn, events sometimes allowed common samurai
The samurai () were members of the warrior class in Japan. They were originally provincial warriors who came from wealthy landowning families who could afford to train their men to be mounted archers. In the 8th century AD, the imperial court d ...
to rise to the rank of ''sengoku daimyo''; these included H┼Źj┼Ź S┼Źun (the first to do so), and Uesugi Kenshin
, later known as , was a Japanese ''daimy┼Ź'' (magnate). He was born in Nagao clan, and after adoption into the Uesugi clan, ruled Echigo Province in the Sengoku period of Japan. He was one of the most powerful ''daimy┼Ź'' of the Sengoku period ...
, a who attained power by weakening and eventually replacing his lord. The most spectacular example of a ''sengoku''-era rise is often considered to be that of Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and ''daimy┼Ź'' (feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period, Sengoku and Azuchi-Momoyama periods and regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: ...
, who rose from a peasant background to successively become a samurai, ''sengoku daimyo'', and '' kampaku'' (Imperial Regent).
Modern Japan recognizes Oda Nobunaga
was a Japanese ''daimy┼Ź'' and one of the leading figures of the Sengoku period, Sengoku and Azuchi-Momoyama periods. He was the and regarded as the first "Great Unifier" of Japan. He is sometimes referred as the "Demon Daimy┼Ź" and "Demo ...
, Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and ''daimy┼Ź'' (feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period, Sengoku and Azuchi-Momoyama periods and regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: ...
, and Tokugawa Ieyasu
Tokugawa Ieyasu (born Matsudaira Takechiyo; 31 January 1543 ŌĆō 1 June 1616) was the founder and first ''sh┼Źgun'' of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan, which ruled from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was the third of the three "Gr ...
as for their restoration of Japan's central government
A central government is the government that is a controlling power over a unitary state. Another distinct but sovereign political entity is a federal government, which may have distinct powers at various levels of government, authorized or deleg ...
.
Background
During this period, although theEmperor of Japan
The emperor of Japan is the hereditary monarch and head of state of Japan. The emperor is defined by the Constitution of Japan as the symbol of the Japanese state and the unity of the Japanese people, his position deriving from "the will of ...
was officially the ruler of the state and every lord swore loyalty to him, he was largely a marginalized, ceremonial, and religious figure who delegated power to the ''sh┼Źgun
, officially , was the title of the military rulers of Japan during most of the period spanning from 1185 to 1868. Nominally appointed by the Emperor, shoguns were usually the de facto rulers of the country, except during parts of the Kamak ...
'', a noble who was roughly equivalent to a military dictator.
From 1346 to 1358, during the Nanboku-cho period, the Ashikaga shogunate gradually expanded the authority of the , the local military and police officials established by the Kamakura shogunate
The was the feudal military government of Japan during the Kamakura period from 1185 to 1333. Nussbaum, Louis-Fr├®d├®ric. (2005)"''Kamakura-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 459.
The Kamakura shogunate was established by Minamoto no Yori ...
, giving the ''Shugo'' jurisdiction over land disputes between and allowing the ''Shugo'' to receive half of all taxes from the areas they controlled. The ''Shugo'' shared their newfound wealth with the local samurai, creating a hierarchical relationship between the ''Shugo'' and the samurai, and the first early , called , appeared.
In 1428, Ashikaga Yoshimochi, the fourth shogun, was ill and the question of his succession arose. Ashikaga Yoshikazu, the 5th shogun, died of illness at the age of 19, so the 6th shogun was chosen from among Yoshimochi's four brothers, and to ensure fairness, a lottery was held. The sixth shogun was Ashikaga Yoshinori. But he was not educated to be a shogun, and his temperamental and despotic behavior caused resentment. Akamatsu Mitsusuke assassinated him during the Kakitsu Rebellion. This led to instability in the Ashikaga shogunate system. The shogunate gradually lost influence and control over the ''daimyo''.
Beginning of the Sengoku period
The beginning of the Sengoku Period is considered to be the Ky┼Źtoku incident,┼īnin War
The , also known as the Upheaval of ┼īnin and ┼īnin-Bunmei war, was a civil war that lasted from 1467 to 1477, during the Muromachi period in Japan. ''┼īnin'' refers to the Japanese era name, Japanese era during which the war started; the war ende ...
, or Mei┼Ź incident.
The Ky┼Źtoku Incident was a major war in the Kanto region
Japanese
Kanto is a simplified spelling of , a Japanese word, only omitting the diacritics.
In Japan
Kant┼Ź may refer to:
*Kant┼Ź Plain
*Kant┼Ź region
* Kant┼Ź-kai, organized crime group
* Kanto (Pok├®mon), a geographical region in the ''Pok├®m ...
that lasted from 1454 to 1482. The war began when Ashikaga Shigeuji of , the office of the Ashikaga shogunate in charge of the Kanto region, killed Uesugi Noritada of , Kant┼Ź kub┼Ź's assistant. The various forces in the Kanto region divided and fought between the ''Kub┼Ź'' and ''Kanrei'' sides, with the Ashikaga shogunate supporting the ''Kanrei'' side.
Ashikaga Yoshimasa
"Ashikaga Yoshimasa" in ''Encyclop├”dia Britannica, The New Encyclop├”dia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclop├”dia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 625. was the eighth ''sh┼Źgun'' of the Ashikaga shogunate who reigned from 1449 to 1473 du ...
, the 8th shogun, tried to strengthen the power of the shogun, but his close associates did not follow his instructions, leading to political chaos and increasing social unrest. Since he had no sons, he tried to install his younger brother Ashikaga Yoshimi as the ninth shogun, but when his wife Hino Tomiko gave birth to Ashikaga Yoshihisa, a conflict arose among the ''shugo daimyo'' as to whether Yoshimi or Yoshihisa would be the next shogun. The Hatakeyama and Shiba clans were also divided into two opposing factions over succession within their own clans, and Hosokawa Katsumoto
was one of the Kanrei, the deputies to the Ashikaga shogunate, Sh┼Źgun, during Japan's Muromachi period. He is famous for his involvement in the creation of Ry┼Źan-ji, a temple famous for its rock garden, and for his involvement in the ┼īnin War ...
and Yamana S┼Źzen
was originally before becoming a monk. Due to his red complexion, he was sometimes known as ''Aka-ny┼½d┼Ź'', "the Red Monk". He was one of the ''shogun'' ''daimy┼Źs'' who fought against Hosokawa Katsumoto during the ┼īnin War in Heian-ky┼Ź.
Bi ...
, who were father-in-law and son-in-law, were politically at odds with each other.
In 1467, these conflicts finally led to the ┼īnin War
The , also known as the Upheaval of ┼īnin and ┼īnin-Bunmei war, was a civil war that lasted from 1467 to 1477, during the Muromachi period in Japan. ''┼īnin'' refers to the Japanese era name, Japanese era during which the war started; the war ende ...
(1467ŌĆō1477) between the Eastern Army, led by Hosokawa Katsumoto and including Hatakeyama Masanaga, Shiba Yoshitoshi, and Ashikaga Yoshimi, and the Western Army, led by Yamana S┼Źzen and including Hatakeyama Yoshinari, Shiba Yoshikado, and Ashikaga Yoshihisa. In 1469, the war spread to the provinces, but in 1473, Hosokawa Katsumoto and Yamana S┼Źzen, the leaders of both armies, died. In 1477, the war ended when the western lords, including Hatakeyama Yoshinari and ┼īuchi Masahiro
was a member of the ┼īuchi clan and general in the ┼īnin War, serving Yamana S┼Źzen.
He battled numerous times with Yamana's rival, Hosokawa Katsumoto, at one point commanding 20,000 men and 2,000 boats, moving his troops by land as well as by s ...
, withdrew their armies from Kyoto.
The war devastated two-thirds of Kyoto, destroying many aristocratic and samurai residences, Shinto shrine
A Stuart D. B. Picken, 1994. p. xxiii is a structure whose main purpose is to house ("enshrine") one or more kami, , the deities of the Shinto religion.
The Also called the . is where a shrine's patron is or are enshrined.Iwanami Japanese dic ...
s, and Buddhist temples, and undermining the authority of the Ashikaga shoguns, greatly reducing their control over the various regions. The war caused disarray which rippled across Japan. In addition to the military confrontations between separate states, there was also domestic fallout. In contempt of the shogunate, the daimyo who were subjected to remain in Kyoto instead returned to their provinces
A province is an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman , which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outside Italy. The term ''provi ...
. Consequentially, some of these daimyo found that their designated retainers or ''shugodai
were officials during feudal Japan. Shugodai were representatives of provincial shugo when the shugo could not virtually exercise his power, being often away from his province. Unlike shugo, who were appointed from the central power of the sa ...
'', representatives of their states appointed in a daimyo's absence, rose in power either to seize control of the domain or proclaim independence as a separate domain.
Thus began the Sengoku period, a period of civil war in which the ''daimyo'' of various regions fought to expand their own power. ''Daimyo'' who became more powerful as the shogunate's control weakened were called , and they often came from ''shugo daimyo'', ''Shugodai'', and . In other words, ''sengoku daimyo'' differed from ''shugo daimyo'' in that ''sengoku daimyo'' was able to rule the region on his own, without being appointed by the shogun.
Historians often consider the ┼īnin War, a ten-year conflict wrought by political turmoil, to be the trigger for what would come to be known as the Sengoku period. This civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
would clearly reveal the Ashikaga shogunate's reduced authority over its shogunal administration, the provincial ''daimyo'' and Japan as a whole; thereby a wave of unbridled conflict would spread across Japan and consume the states in an age of war. Furthermore, weariness of war, socioeconomic unrest and poor treatment by aristocrats provoked the wrath of the peasant class. Farmers, craftsmen, merchants and even villages would organize uprisings (known as ''"ikki")'' against the ruling class. An extraordinary example is the Kaga Rebellion, in which the local ''ikki'' had staged a large-scale revolt with the support of the True Pure Land sect (thereby establishing the term '' ikk┼Ź ikki)'' and assumed control of the entire province of Kaga. It is suggested by both scholars and authors that "''these succession disputes still might not have led to war were it not for the sh┼Źgun's lack of leadership''."Streich, Philip. "┼īnin War (1467ŌĆō1477)." ''Japan at War'': ''An Encyclopedia'', edited by Louis G. Perez, ABC-CLIO, 2013, pp. 296ŌĆō297. ''Gale eBooks'', link.gale.com/apps/doc/CX2789100191/GVRL?u=psucic&sid=bookmark-GVRL&xid=56a79408. Accessed 21 Mar. 2023.Streich, Philip. "Civil Wars, Sengoku Era (1467ŌĆō1570)." ''Japan at War'': ''An Encyclopedia'', edited by Louis G. Perez, ABC-CLIO, 2013, pp. 53ŌĆō55. ''Gale eBooks'', link.gale.com/apps/doc/CX2789100045/GVRL?u=psucic&sid=bookmark-GVRL&xid=3f87bd69. Accessed 21 Mar. 2023.
Timeline
Start and end dates
 The Ky┼Źtoku incident in 1454,
The Ky┼Źtoku incident in 1454, ┼īnin War
The , also known as the Upheaval of ┼īnin and ┼īnin-Bunmei war, was a civil war that lasted from 1467 to 1477, during the Muromachi period in Japan. ''┼īnin'' refers to the Japanese era name, Japanese era during which the war started; the war ende ...
in 1467, or Mei┼Ź incident in 1493 is usually considered the starting point of the Sengoku period. There are several events which could be considered the end of it: Nobunaga's entry to Kyoto
Kyoto ( or ; Japanese language, Japanese: , ''Ky┼Źto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in the Kansai region of Japan's largest and most populous island of Honshu. , the city had a population of 1.46 million, making it t ...
(1568) or abolition of the Muromachi shogunate (1573) or entry into Azuchi Castle (1576), Hideyoshi's promulgation of the ''S┼Źbujirei'' ( ja) law prohibiting war (1587), the siege of Odawara (1590)
The third occurred in 1590, and was the primary action in Toyotomi Hideyoshi's campaign to eliminate the H┼Źj┼Ź clan as a threat to his power. The months leading up to it saw hasty but major improvements in the defense of the castle, as H ...
, the Battle of Sekigahara
The Battle of Sekigahara (Shinjitai: ; Ky┼½jitai: , Hepburn romanization: ''Sekigahara no Tatakai'') was an important battle in Japan which occurred on October 21, 1600 (Keich┼Ź 5, 15th day of the 9th month) in what is now Gifu Prefecture, ...
(1600), the establishment of the Tokugawa shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate, also known as the was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868.
The Tokugawa shogunate was established by Tokugawa Ieyasu after victory at the Battle of Sekigahara, ending the civil wars ...
(1603), the siege of Osaka
A siege () . is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or by well-prepared assault. Siege warfare (also called siegecrafts or poliorcetics) is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict charact ...
(1615), or the suppression of the Shimabara Rebellion
The , also known as the or , was an rebellion, uprising that occurred in the Shimabara Domain of the Tokugawa shogunate in Japan from 17 December 1637 to 15 April 1638.
Matsukura Katsuie, the ''daimy┼Ź'' of the Shimabara Domain, enforced unpo ...
(1638). The old, well-known definition is that the Onin War initiated the Sengoku period in 1467; and that it ended in 1568, when Oda Nobunaga entered Kyoto in support of Ashikaga Yoshiaki
"Ashikaga Yoshiaki" in '' The New Encyclop├”dia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclop├”dia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 625. was the 15th and final ''sh┼Źgun'' of the Ashikaga shogunate in Japan who reigned from 1568 to 1573 when he ...
.
 However, even if 1568 is the end date of the Sengoku period, there are also various theories about the beginning and end dates of the following Azuchi-Momoyama period. The Azuchi-Momoyama period refers to the period when
However, even if 1568 is the end date of the Sengoku period, there are also various theories about the beginning and end dates of the following Azuchi-Momoyama period. The Azuchi-Momoyama period refers to the period when Oda Nobunaga
was a Japanese ''daimy┼Ź'' and one of the leading figures of the Sengoku period, Sengoku and Azuchi-Momoyama periods. He was the and regarded as the first "Great Unifier" of Japan. He is sometimes referred as the "Demon Daimy┼Ź" and "Demo ...
and Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and ''daimy┼Ź'' (feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period, Sengoku and Azuchi-Momoyama periods and regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: ...
were in power. They and Tokugawa Ieyasu
Tokugawa Ieyasu (born Matsudaira Takechiyo; 31 January 1543 ŌĆō 1 June 1616) was the founder and first ''sh┼Źgun'' of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan, which ruled from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was the third of the three "Gr ...
are the three unifiers of Japan. The name "Azuchi-Momoyama" comes from the fact that Nobunaga's castle, Azuchi Castle, was located in Azuchi, Shiga, and Fushimi Castle, where Hideyoshi lived after his retirement, was located in Momoyama. The beginning date could be either when Oda Nobunaga entered Kyoto in 1568 to support Ashikaga Yoshiaki, or when Nobunaga expelled Ashikaga Yoshiaki from Kyoto in 1573 and destroyed the Muromachi Shogunate, or when Nobunaga moved to Azuchi Castle in 1576. It ended either when Toyotomi Hideyoshi died in 1598, or at the Battle of Sekigahara in 1600, or with the opening of the Tokugawa shogunate in 1603.
Kaga ikki
The Kaga ''ikki'', also known as The Peasants' Kingdom, was a theocratic feudal confederacy that emerged in Kaga Province (present-day southern Ishikawa Prefecture), Japan, during the late 15th and early 16th centuries. The Kaga ''ikki'' wa ...
occurred in 1488, H┼Źj┼Ź S┼Źun conquered Izu province
was a province of Japan in the area now part of Shizuoka Prefecture and Tokyo. Nussbaum, Louis-Fr├®d├®ric. (2005). "''Izu''" in . Izu bordered on Sagami and Suruga Provinces. Its abbreviated form name was .
The mainland portion of Izu Prov ...
in 1491, and in 1492 Hosokawa Masamoto
was a deputy-'' sh┼Źgun,'' daimyo and shugo of the Hosokawa clan of Japan, and son of Hosokawa Katsumoto. Masamoto was appointed to the rank of deputy-shogun in 1486, but lost this status to his rival Hatakeyama Masanaga. His childhood name ...
banished the 10th shogun Ashikaga Yoshitane from Kyoto and installed Ashikaga Yoshizumi as the 11th shogun. Around this time, civil wars began to occur frequently throughout the country, and Buddhist temples in various regions grew as armed forces.
Kansai region and Kyoto
Puppetization of the Ashikaga Shogunate by the Hosokawa clan
 Ashikaga Yoshihisa, who had become the ninth shogun during the Onin War, died at the age of 25, and Ashikaga Yoshitane became the 10th shogun. However, in 1493, Hosokawa Masamoto raised an army while shogun Yoshitane was away in Kyoto and installed the 11th shogun, Ashikaga Yoshizumi, in a de facto coup known as the . Masamoto held the position of , second only to the shogun in the Ashikaga shogunate, and the equivalent of in the Kamakura shogunate. This made the shogun a puppet of the
Ashikaga Yoshihisa, who had become the ninth shogun during the Onin War, died at the age of 25, and Ashikaga Yoshitane became the 10th shogun. However, in 1493, Hosokawa Masamoto raised an army while shogun Yoshitane was away in Kyoto and installed the 11th shogun, Ashikaga Yoshizumi, in a de facto coup known as the . Masamoto held the position of , second only to the shogun in the Ashikaga shogunate, and the equivalent of in the Kamakura shogunate. This made the shogun a puppet of the Hosokawa clan
The is a Japanese samurai kin group or Japanese clan, clan. The clan descends from the Seiwa Genji, a branch of the Minamoto clan, and ultimately from Emperor Seiwa, through the Ashikaga clan. It produced many prominent officials in the Ashikaga ...
, which served as the ''Kanrei''. In recent years, it has been theorized that this incident marked the beginning of the Sengoku period.
Hosokawa Masamoto remained a bachelor for the rest of his life and adopted three people as his heirs. Following the advice of his vassals, Masamoto named Hosokawa Sumimoto as his successor instead of Hosokawa Sumiyuki, who had been adopted first. As a result, Masamoto was killed by Sumiyuki in 1507. This incident is called . This triggered a struggle for the succession of the Hosokawa clan, which was divided into the Hosokawa Sumimoto faction and the Hosokawa Takakuni faction, and started a war called , which was won by Hosokawa Takakuni.
Hosokawa Takakuni installed Ashikaga Yoshiharu as the 12th shogun. Meanwhile, Hosokawa Harumoto, son of Hosokawa Sumimoto, who had lost the war, collaborated with Miyoshi Motonaga to defeat Takakuni at the in 1527 and expel him from Kyoto. The authority of the ''Kanrei'' was thus destroyed, and with almost no support for Hosokawa Takakuni, he was forced to move from place to place. He gained the ''sengoku daimyo'' Uragami Muramune as an ally and fought Hosokawa Harumoto in a war called in 1531, but was defeated.
Hosokawa Harumoto seized power, but he alienated Miyoshi Motonaga, who was his retainer but still held a strong position of power. Harumoto seduced the Ikk┼Ź-sh┼½ into a ''Ikk┼Ź-ikki
were armed military leagues that formed in several regions of Japan in the 15th-16th centuries, composed entirely of members of the J┼Źdo Shinsh┼½ sect of Buddhism. In the early phases, these ''ikki'' leagues opposed the rule of local Shugo, go ...
'' against Motonaga, which resulted in Motonaga's death in 1532.
The rise of the Miyoshi clan
Miyoshi Motonaga's son, Miyoshi Nagayoshi, fought against Hosokawa Harumoto, but chose to subordinate himself to Harumoto. As a follower of Harumoto, Miyoshi Nagayoshi defeated Kizawa Nagamasa, the most powerful member of the Hatakeyama clan who served as ''Kanrei'', and in 1547 defeated the 12th shogun, Ashikaga Yoshiharu and Hosokawa Ujitusna, son of Hosokawa Takakuni, in the . This further reduced the power of the Ashikaga Shogunate. Miyoshi Nagayoshi was told by a retainer of the Hosokawa family that Miyoshi Masanaga had played a dark role in his father's death, and he petitioned his lord Hosokawa Harumoto to overthrow Masanaga, but this petition was not accepted, and, in turn, Nagayoshi was almost eliminated by Harumoto. In response, Miyoshi Nagayoshi attacked and defeated Miyoshi Masanaga, expelled Hosokawa Harumoto, Ashikaga Yoshiharu, the 12th shogun, and his son Ashikaga Yoshiteru from Kyoto, and established control over the Kyoto area in 1549. After that, he fought several times against Ashikaga Yoshiteru, who became the 13th shogun, for control of the Kyoto area. However, one by one, his sons died in war or from disease, and the Miyoshi clan began to decline rapidly. By the time of the 13th shogun, Ashikaga Yoshiteru, the shogun already had few direct fiefs and direct military forces, and his sphere of influence was limited to a few lands around Kyoto, losing both economic and military power. As a result, Ashikaga Yoshiteru was often chased out of Kyoto by the ''sengoku daimyo'' Miyoshi Nagayoshi and his forces, and was finally killed in an attack by the forces of Miyoshi Yoshitsugu and Matsunaga Hisahide. Ashikaga Yoshiteru was known as a great swordsman and was a student of Tsukahara Bokuden, who was known as one of the strongest swordsmen. According to Yagy┼½ Munenori, a swordsmanship instructor in the Tokugawa Shogunate, Ashikaga Yoshiteru was one of the five best swordsmen of his time. According to several historical books, including Lu├Łs Fr├│is' ''Historia de Japam'', he fought hard with ''naginata
The ''naginata'' (, , ) is a polearm and one of several varieties of traditionally made Japanese blades ('' nihont┼Ź''). ''Naginata'' were originally used by the samurai class of feudal Japan, as well as by ashigaru (foot soldiers) and s┼Źhei ( ...
'' and ''tachi
A is a type of sabre-like traditionally made Japanese sword (''nihonto'') worn by the samurai class of feudal Japan. ''Tachi'' and '' uchigatana'' ("''katana''") generally differ in length, degree of curvature, and how they were worn when she ...
'' during a raid, defeating many of his enemies, but eventually ran out of strength and was killed.
of Miyoshi Nagayasu, Miyoshi Soui, and Iwanari Tomomichi supported the young head of the clan, Miyoshi Yoshitsugu, in leading the Miyoshi clan. However, after the assassination of the 13th Shogun, the trio fell out with another Miyoshi follower, Matsunaga Hisashige, over the 14th Shogun, Ashikaga Yoshihide, and war broke out. The latter three also came into conflict with Yoshitsugu. The Miyoshi regime virtually collapsed when Oda Nobunaga
was a Japanese ''daimy┼Ź'' and one of the leading figures of the Sengoku period, Sengoku and Azuchi-Momoyama periods. He was the and regarded as the first "Great Unifier" of Japan. He is sometimes referred as the "Demon Daimy┼Ź" and "Demo ...
entered Kyoto in 1568. Miyoshi Yoshitugu and Matsunaga Hisahide submitted to Nobunaga, but were later killed by Nobunaga's forces. The trio was weakened and the Miyoshi clan declined.
Other regions
Ch┼½goku region (M┼Źri Motonari)

M┼Źri Motonari
was a prominent ''daimy┼Ź'' (feudal lord) in the western Ch┼½goku region of Japan during the Sengoku period of the 16th century. The M┼Źri clan claimed descent from ┼īe no Hiromoto (Õż¦µ▒¤Õ║āÕģā), an adviser to Minamoto no Yoritomo. Motonari w ...
was a ''sengoku daimyo'' who pacified the Chūgoku region
The , also known as the region, is the westernmost region of Honshū, the largest island of Japan. It consists of the prefectures of Hiroshima, Okayama, Shimane, Tottori and Yamaguchi. As of the 2020 census, it has a population of 7,328,339 ...
and is famous for his parable of the "Three Arrows", which explains the importance of clan unity. In his first battle, the Battle of Arita-Nakaide in 1517, he defeated the overwhelming majority of the Aki-Takeda clan with a small force, which later became known as the " Battle of Okehazama in the West" as a battle in which a small force defeated a large army. Motonari became head of the M┼Źri clan
The was a Japanese clan, Japanese samurai clan descended from ┼īe no Hiromoto. ┼īe no Hiromoto was descended from the Fujiwara clan. The family's most illustrious member, M┼Źri Motonari, greatly expanded the clan's power in Aki Province. Durin ...
in 1523 at the age of 27. The Amago and ┼īuchi clan
was one of the most powerful and important families in Western Japan during the reign of the Ashikaga shogunate in the 14th to 16th centuries. Their domains, ruled from the castle town of Yamaguchi in the western tip of Honshu island, compris ...
s were sharing power in the Ch┼½goku region at the time, and he switched the M┼Źri clan's allegiance from the Amago to the ┼īuchi clan in 1525. Motonari destroyed the Takahashi clan by 1535 and ruled Aki province
or Geishū () was a province in the Chūgoku region of western Honshu, comprising the western part of what is today Hiroshima Prefecture.
History
When Emperor Sh┼Źmu ordered two official temples for each province (one for male Buddhist prie ...
, Iwami province, and Bingo province, and destroyed the Aki-Takeda clan at the siege of Koriyama
The took place from 5 October 1540 (6th day of 9th month of Tenbun 9) until 8 February 1541 (13th day of 1st month of Tenbun 10) in Yoshida, Aki Province, Japan during the Sengoku period. Amago Haruhisa, with 30,000 men, attacked K┼Źriyama Ca ...
in 1541. Motonaga adopted his sons into the Kikkawa clan and Kobayakawa clans to expand the power of the M┼Źri clan, and the three clans cooperated with each other. In 1554, Motonaga became independent of the ┼īuchi clan, and after inciting the ┼īuchi clan to internal divisions through political maneuvering, he defeated Sue Harukata
was a samurai who served as a senior retainer of the ┼īuchi clan in the Sengoku period in Japan. He was the second son of Sue Okifusa, a senior retainer of the ┼īuchi clan. His childhood name was Goro, and he previously had the name Takafusa ...
, who had been in control of the ┼īuchi clan, at the Battle of Itsukushima
The 1555 was the only battle to be fought on the sacred island of Miyajima; the entire island is considered to be a Shinto shrine, and no birth or death is allowed on the island. Extensive purification rituals took place after the battle, to cl ...
in 1555, and defeated ┼īuchi Yoshinaga in 1557, destroying the ┼īuchi clan and pacifying Nagato and Suou provinces.
Motonari destroyed the Amago clan at the siege of Gassantoda Castle in 1567, and then pacified Izumo, Oki, and H┼Źki provinces, thus pacifying the Ch┼½goku region, and later extended his power to parts of Shikoku
is the smallest of the List of islands of Japan#Main islands, four main islands of Japan. It is long and between at its widest. It has a population of 3.8 million, the least populated of Japan's four main islands. It is south of Honshu ...
. He died in 1571 at the age of 75.
Hokuriku, Kant┼Ź, and Ch┼½bu regions (Uesugi Kenshin)
 In 1546, H┼Źj┼Ź Ujiyasu defeated Uesugi Tomosada at the siege of Kawagoe Castle, and the
In 1546, H┼Źj┼Ź Ujiyasu defeated Uesugi Tomosada at the siege of Kawagoe Castle, and the Later H┼Źj┼Ź clan
The was one of the most powerful samurai families in Japan in the Sengoku period and held domains primarily in the Kant┼Ź region. Their last name was simply , but were called "Later H┼Źj┼Ź" to differentiate between the earlier H┼Źj┼Ź clan who h ...
established its power in the Kant┼Ź region
The is a geography, geographical region of Honshu, the largest island of Japan. In a common definition, the region includes the Greater Tokyo Area and encompasses seven prefectures of Japan, prefectures: Chiba Prefecture, Chiba, Gunma Prefe ...
.
Uesugi Kenshin
, later known as , was a Japanese ''daimy┼Ź'' (magnate). He was born in Nagao clan, and after adoption into the Uesugi clan, ruled Echigo Province in the Sengoku period of Japan. He was one of the most powerful ''daimy┼Ź'' of the Sengoku period ...
(Nagao Kagetora) was a ''sengoku daimyo'' based in Echigo Province
was an old provinces of Japan, old province in north-central Japan, on the shores of the Sea of Japan. It bordered on Uzen Province, Uzen, Iwashiro Province, Iwashiro, K┼Źzuke Province, K┼Źzuke, Shinano Province, Shinano, and Etch┼½ Province, ...
who fought various ''sengoku daimyo'' and increased his power through aggressive invasions. After unifying Echigo in 1551, he invaded the Kant┼Ź region several times from 1552 to 1569 and fought against H┼Źj┼Ź Ujiyasu. He also invaded the territory of Takeda Shingen
was daimy┼Ź, daimyo of Kai Province during the Sengoku period of Japan. Known as "the Tiger of Kai", he was one of the most powerful daimyo of the late Sengoku period, and credited with exceptional military prestige. Shingen was based in a p ...
, who ruled Kai and Shinano Province
or is an old province of Japan that is now Nagano Prefecture.
Shinano bordered Echigo, Etch┼½, Hida, Kai, K┼Źzuke, Mikawa, Mino, Musashi, Suruga, and T┼Źt┼Źmi Provinces. The ancient capital was located near modern-day Matsumoto, whi ...
s from 1553 to 1573, and fought in the Battle of Kawanakajima
The were a series of battles fought in the Sengoku period of Japan between Takeda Shingen of Kai Province and Uesugi Kenshin of Echigo Province from 1553 to 1564.
Shingen and Kenshin contested each other for control of the plain of Kawanakaj ...
five times between 1553 and 1564. In 1559, Kenshin had an audience with Emperor ┼īgimachi and the 13th Shogun, Ashikaga Yoshiteru. When Imagawa Yoshimoto
was a Japanese ''daimy┼Ź'' (feudal lord) of the Sengoku period. Based in Suruga Province, he was known as ; he was one of the three ''daimy┼Ź'' that dominated the T┼Źkaid┼Ź region. He died in 1560 while marching to Kyoto to become Shogun. He ...
was killed by Oda Nobunaga
was a Japanese ''daimy┼Ź'' and one of the leading figures of the Sengoku period, Sengoku and Azuchi-Momoyama periods. He was the and regarded as the first "Great Unifier" of Japan. He is sometimes referred as the "Demon Daimy┼Ź" and "Demo ...
's forces at the Battle of Okehazama in 1560, the Alliance Kai-Sagami-Suruga formed in 1554 between Takeda Shingen in Kai, Hojo Ujiyasu in Sagami, and Imagawa Yoshimoto in Suruga was broken. Kenshin used this as an opportunity to seize Hojo Ujiyasu's territories one by one, and cornered the Later H┼Źj┼Ź clan at the siege of Odawara in 1561, but was unable to defeat them. On his return from the siege of Odawara, he performed a ceremony at the Tsurugaoka Hachimang┼½
is the most important Shinto shrine in the city of Kamakura, Kanagawa, Kamakura, Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan. The shrine is a cultural center of the city of Kamakura and serves as the venue of many of its most important festivals with two museum ...
and assumed the position of '' kant┼Ź kanrei''. Kenshin made peace with H┼Źj┼Ź Ujiyasu, who ceded part of his territory to him in 1569, and made Takeda Shingen a common enemy of Kenshin and Ujiyasu, but Shingen died of illness in 1573. After Takeda Shingen's death, he fell out with Oda Nobunaga and destroyed the Noto Hatakeyama clan, which was close to Nobunaga, at the siege of Nanao in 1577, pacifying Noto Province. He then defeated Oda Nobunaga's forces at the Battle of Tedorigawa. However, he died of a cerebral hemorrhage in 1578 at the young age of 49.
Social changes with the advent of matchlock guns
 When the Portuguese brought the
When the Portuguese brought the matchlock
A matchlock or firelock is a historical type of firearm wherein the gunpowder is ignited by a burning piece of flammable cord or twine that is in contact with the gunpowder through a mechanism that the musketeer activates by pulling a lever or Tri ...
gun to Japan in 1543, it was mass-produced in Japan, and a gun called the ''tanegashima
is one of the ┼īsumi Islands belonging to Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan. The island, in area, is the second largest of the ┼īsumi Islands, and has a population of 33,000 people. Access to the island is by ferry, or by air to New Tanegashima Airp ...
'' began to be used in wars. With the introduction of guns, a standing army of became essential to victory in war, making it impossible for small local lords to remain independent, and lands were consolidated under ''sengoku daimyo'' with vast territories, and battles between ''sengoku daimyo'' became more intense.
During this period, the organized use of large numbers of ''tanegashima'' (guns) was essential to winning the war. In order for the ''daimyo'' to win the war, they had to secure a large number of gunsmiths and arms dealers, import large quantities of lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
, the raw material for bullets, and nitre, the raw material for gunpowder, conduct routine marksmanship training, and secure large quantities of materials for building war positions. It was Oda Nobunaga who did this most successfully. He built Azuchi Castle at a strategic distribution point, brought several gunsmithing centers under his control, and established friendly relations with the Portuguese and merchants in Sakai
is a city located in Osaka Prefecture, Japan. It has been one of the largest and most important seaports of Japan since the medieval era. Sakai is known for its '' kofun'', keyhole-shaped burial mounds dating from the fifth century. The ''kofun ...
, which had become an international port. He examined the rice yields of the lands under his control and did not allow his retainers to take private ownership of the lands, leaving the management of the lands to his retainers. This made it possible to efficiently change territories according to the performance of the vassals, thus eliminating land disputes. In addition, he made it possible to form a standing army by assigning military service to each region according to rice production. He encouraged the economic activities of the common people. In this way, he rapidly increased his power.
Oda Nobunaga

 In and around the
In and around the Kinai
is a Japanese term denoting an ancient division of the country. ''Kinai'' is a name for the ancient provinces around the capital Nara and Heian-ky┼Ź. Nussbaum, Louis-Fr├®d├®ric. (2005). "''Kinai''" in . The five provinces were called ''go-kin ...
, the most politically important region in Japan, Oda Nobunaga allied with Tokugawa Ieyasu
Tokugawa Ieyasu (born Matsudaira Takechiyo; 31 January 1543 ŌĆō 1 June 1616) was the founder and first ''sh┼Źgun'' of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan, which ruled from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was the third of the three "Gr ...
to increase his power. Nobunaga defeated Imagawa Yoshimoto
was a Japanese ''daimy┼Ź'' (feudal lord) of the Sengoku period. Based in Suruga Province, he was known as ; he was one of the three ''daimy┼Ź'' that dominated the T┼Źkaid┼Ź region. He died in 1560 while marching to Kyoto to become Shogun. He ...
at the Battle of Okehazama in 1560 and moved to Kyoto in 1568 to support the 15th shogun, Ashikaga Yoshiaki
"Ashikaga Yoshiaki" in '' The New Encyclop├”dia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclop├”dia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 625. was the 15th and final ''sh┼Źgun'' of the Ashikaga shogunate in Japan who reigned from 1568 to 1573 when he ...
. Nobunaga defeated Miyoshi Yoshitsugu in 1569, laid siege to Mount Hiei in 1571, defeated Asakura Yoshikage at the siege of Ichij┼Źdani Castle in 1573, defeated Asai Nagamasa at the siege of Odani Castle in the same year, and expelled Ashikaga Yoshiaki from Kyoto in 1573, thus destroying the Ashikaga shogunate. He overpowered the Nagashima ikko ikki in 1574, defeated Takeda Katsuyori
was a Japanese ''daimy┼Ź'' (military lord) of the Sengoku period, who was famed as the head of the Takeda clan and the successor to the legendary warlord Takeda Shingen. He was son-in-law of Hojo Ujiyasu, ''daimy┼Ź'' of Hojo clan.
Early life
H ...
at the Battle of Nagashino
The was a famous battle in History of Japan, Japanese history, fought in 1575 at Nagashino Castle, Nagashino in Mikawa Province (present-day Nagashino, Shinshiro, Aichi Prefecture). The allied forces of Oda Nobunaga and Tokugawa Ieyasu (38,000) ...
in 1575, and defeated Ishiyama Hongan-ji in the Ishiyama Hongan-ji War
The was a ten-year military campaign that took place from 1570 to 1580 in Sengoku period Japan, carried out by lord Oda Nobunaga against a network of fortifications, temples, and communities belonging to the Ikk┼Ź-ikki, a powerful faction of J ...
in 1580. However, he was betrayed by his vassal Akechi Mitsuhide
, first called J┼½bei from his clan and later from his title, was a Japanese ''samurai'' general of the Sengoku period. Mitsuhide was originally a bodyguard of the last Ashikaga shogunate, Ashikaga ''sh┼Źgun'' Ashikaga Yoshiaki and later, one of ...
, who drove him to suicide in the Honn┼Ź-ji Incident
The was the assassination of Japanese daimyo Oda Nobunaga at Honn┼Ź-ji, a temple in Kyoto, on 21 June 1582 (2nd day of the sixth month, Tensh┼Ź 10). Nobunaga was on the verge of unifying the country, but died in the unexpected rebellion of ...
of 1582.
At the same time, the M┼Źri clan
The was a Japanese clan, Japanese samurai clan descended from ┼īe no Hiromoto. ┼īe no Hiromoto was descended from the Fujiwara clan. The family's most illustrious member, M┼Źri Motonari, greatly expanded the clan's power in Aki Province. Durin ...
overthrew the Ouchi clan in the Chūgoku region
The , also known as the region, is the westernmost region of Honshū, the largest island of Japan. It consists of the prefectures of Hiroshima, Okayama, Shimane, Tottori and Yamaguchi. As of the 2020 census, it has a population of 7,328,339 ...
, and the Shimazu and Otomo clans became major powers in Kyushu
is the third-largest island of Japan's Japanese archipelago, four main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands (i.e. excluding Okinawa Island, Okinawa and the other Ryukyu Islands, Ryukyu (''Nansei'') Ryukyu Islands, Islands ...
. In this way, regional unification was promoted.
Toyotomi (Hashiba) Hideyoshi
Though a peasant by birth,Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and ''daimy┼Ź'' (feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period, Sengoku and Azuchi-Momoyama periods and regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: ...
had risen through the ranks of , samurai, and ''sengoku daimyo'' under Nobunaga to become the most capable general of them all. When he learned that his lord Nobunaga had been effectively killed by Akechi Mitsuhide, he immediately made peace with the M┼Źri clan, who were in the midst of a battle, and turned his army back faster than anyone could have predicted, defeating Akechi Mitsuhide at the Battle of Yamazaki. Hideyoshi avenged his lord's death only 11 days after Nobunaga's death. The men who had been Nobunaga's chief vassals discussed future policy at the Kiyosu Conference, and Hideyoshi began his path to becoming Nobunaga's successor. In 1582, Hideyoshi defeated Shibata Katsuie and Oda Nobutaka, who had been enemies over Nobunaga's succession, at the Battle of Shizugatake
The took place during the Sengoku period of Japan between Toyotomi Hideyoshi (then Hashiba Hideyoshi) and Shibata Katsuie in Nagahama, Shiga, Shizugatake, ┼īmi Province over a period of two days beginning on the 20th day of the fourth month of ...
, and in 1583 he began construction of Osaka Castle
is a Japanese castle in Ch┼½┼Ź-ku, Osaka, Ch┼½┼Ź-ku, Osaka, Japan. The castle is one of Japan's most famous landmarks and played a major role in the unification of Japan during the sixteenth century of the AzuchiŌĆōMomoyama period.
Layout
Th ...
. In 1584, he fought bitterly against the allied forces of Tokugawa Ieyasu and Oda Nobuo at the Battle of Komaki and Nagakute
The , also known as the Komaki Campaign (Õ░Åńē¦Ńü«ÕĮ╣ ''Komaki no Eki''), was a series of battles in 1584 between the forces of Hashiba Hideyoshi (who would become Toyotomi Hideyoshi in 1586) and the forces of Oda Nobukatsu and Tokugawa Ieyasu ...
, but was able to make a truce with Nobuo by making peace with him. In 1585, he defeated Ch┼Źsokabe Motochika
was a prominent ''daimy┼Ź'' in Japanese Sengoku period, Sengoku-period.
He was the 21st chief of the Ch┼Źsokabe clan of Tosa Province (present-day K┼Źchi Prefecture), the ruler of Shikoku, Shikoku region.
Early life and rise
He was the son and ...
in an Invasion of Shikoku and pacified Shikoku
is the smallest of the List of islands of Japan#Main islands, four main islands of Japan. It is long and between at its widest. It has a population of 3.8 million, the least populated of Japan's four main islands. It is south of Honshu ...
. In 1586, he became and for the first time in history, although he was not a native-born aristocrat. In 1586, he also succeeded in getting Ieyasu to swear allegiance to him. In 1587, he defeated the Shimazu clan
The were the ''daimy┼Ź'' of the Satsuma han, which spread over Satsuma, ┼īsumi and Hy┼½ga provinces in Japan.
The Shimazu were identified as one of the '' tozama'' or outsider ''daimy┼Ź'' familiesAppert, Georges ''et al.'' (1888). in contr ...
in a Kyūshū campaign and pacified Kyūshū
is the third-largest island of Japan's four main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands (i.e. excluding Okinawa and the other Ryukyu (''Nansei'') Islands). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regio ...
. In 1590, he defeated the Later H┼Źj┼Ź clan in the siege of Odawara and pacified the Kant┼Ź region. In the same year, he forced the clans of the T┼Źhoku region
The , Northeast region, , or consists of the northeastern portion of Honshu, the largest island of Japan. This traditional region consists of six prefectures (): Akita, Aomori, Fukushima, Iwate, Miyagi, and Yamagata.
T┼Źhoku retains ...
to swear allegiance to him and finally achieved the unification of Japan.
T┼Źhoku region (Date Masamune)

Date Masamune
was a Japanese ''daimy┼Ź'' during the AzuchiŌĆōMomoyama period through the early Edo period. Heir to a long line of powerful feudal lords in the T┼Źhoku region, he went on to found the modern-day city of Sendai. An outstanding tactician, he w ...
was a one-eyed warlord, a famous ''sengoku daimyo'' who is often said to have had the potential to unite the country if only he had been born 20 years earlier. He became the head of the Date clan
The is a Japanese samurai kin group.Edmond Papinot, Papinot, Jacques Edmond Joseph. (1906). ''Dictionnaire dŌĆÖhistoire et de g├®ographie du Japon''; Papinot, (2003)"Date", ''Nobiliare du Japon'', p. 5 retrieved 2013-5-5.
History
The Date fam ...
in 1584, two years after the death of Oda Nobunaga, destroyed the Nihonmatsu clan and other clans, and then in 1589, at the Battle of Suriagehara, defeated the Ashina clan to conquer the Aizu province, and continued to expand his territory to conquer most of the T┼Źhoku region
The , Northeast region, , or consists of the northeastern portion of Honshu, the largest island of Japan. This traditional region consists of six prefectures (): Akita, Aomori, Fukushima, Iwate, Miyagi, and Yamagata.
T┼Źhoku retains ...
. On the other hand, Toyotomi Hideyoshi, who had only the Kant┼Ź and T┼Źhoku regions left to unify Japan, enacted a law called the in 1587, which prohibited ''sengoku daimyo'' from waging war against each other, and Masamune's conquest of the T┼Źhoku region was a serious violation of this law. After destroying the Later H┼Źj┼Ź clan at the siege of Odawara, Hideyoshi wanted to destroy the Date clan and other ''sengoku daimyo'' in the T┼Źhoku region who were reluctant to show their deference. Hideyoshi had his subordinate Maeda Toshiie question Masamune, who had arrived late to give the order to participate in the siege of Odawara, but after hearing Masamune's bold attitude, he decided to meet with Masamune. Masamune showed his reverence by appearing before Hideyoshi in a pure white death robe, ready to be executed. Hideyoshi placed his staff on Masamune's neck and said, "If you had come a little later, you would have been beheaded," and Masamune pledged his reverence to Hideyoshi. He did not lose his life, only some of his territory was confiscated. He was later interrogated by Hideyoshi on suspicion of inciting a peasant uprising and participating in the rebellion of Toyotomi Hidetsugu
was a during the Sengoku period of Japan. He was the nephew and retainer of Toyotomi Hideyoshi, the unifier and ruler of Japan from 1590 to 1598. Despite being Hideyoshi's closest adult, male relative, Hidetsugu was accused of atrocities and at ...
, but he defended himself with his usual courage and dignity and was not punished.
He was on the side of Tokugawa Ieyasu at the Battle of Sekigahara
The Battle of Sekigahara (Shinjitai: ; Ky┼½jitai: , Hepburn romanization: ''Sekigahara no Tatakai'') was an important battle in Japan which occurred on October 21, 1600 (Keich┼Ź 5, 15th day of the 9th month) in what is now Gifu Prefecture, ...
, and as the first lord of the Sendai Domain
The , also known as the , was a domain of the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan during the Edo period from 1600 to 1871.
The Sendai Domain was based at Aoba Castle in Mutsu Province, in the modern city of Sendai, located in the T┼Źhoku region of ...
during the Edo period
The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengok ...
, he developed Sendai
is the capital Cities of Japan, city of Miyagi Prefecture and the largest city in the T┼Źhoku region. , the city had a population of 1,098,335 in 539,698 households, making it the List of cities in Japan, twelfth most populated city in Japan.
...
and laid the foundations of the city as the center of the present-day T┼Źhoku region. In 1613, he sent Hasekura Tsunenaga
was a kirishitan Japanese samurai and retainer of Date Masamune, the daimy┼Ź of Sendai. He was of Japanese imperial descent with ancestral ties to Emperor Kanmu. Other names include Philip Francis Faxicura, Felipe Francisco Faxicura, and Ph ...
as an ambassador to Europe, where he was granted an audience with the Pope Paul V
Pope Paul V (; ) (17 September 1552 ŌĆō 28 January 1621), born Camillo Borghese, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 16 May 1605 to his death, in January 1621. In 1611, he honored Galileo Galilei as a mem ...
.
Events
''Gekokuj┼Ź''
daimy┼Ź
were powerful Japanese magnates, feudal lords who, from the 10th century to the early Meiji era, Meiji period in the middle 19th century, ruled most of Japan from their vast hereditary land holdings. They were subordinate to the shogun and no ...
s'', rose to fill the vacuum. In the course of this power shift, well-established clans
A clan is a group of people united by actual or perceived kinship
and descent. Even if lineage details are unknown, a clan may claim descent from a founding member or apical ancestor who serves as a symbol of the clan's unity. Many societie ...
such as the Takeda and the Imagawa
was a Japanese samurai clan that claimed descent from the Seiwa Genji by way of the Kawachi Genji. It was a branch of the Minamoto clan by the Ashikaga clan.
Origins
Ashikaga Kuniuji, grandson of Ashikaga Yoshiuji, established himself in t ...
, who had ruled under the authority of both the Kamakura and Muromachi ''bakufu'', were able to expand their spheres of influence. There were many, however, whose positions eroded and were eventually usurped by more capable underlings. This phenomenon of social meritocracy, in which capable subordinates rejected the status quo and forcefully overthrew an emancipated aristocracy, became known as , which means "low conquers high".
One of the earliest instances of this was H┼Źj┼Ź S┼Źun, who rose from relatively humble origins and eventually seized power in Izu Province
was a province of Japan in the area now part of Shizuoka Prefecture and Tokyo. Nussbaum, Louis-Fr├®d├®ric. (2005). "''Izu''" in . Izu bordered on Sagami and Suruga Provinces. Its abbreviated form name was .
The mainland portion of Izu Prov ...
in 1493. Building on the accomplishments of S┼Źun, the H┼Źj┼Ź clan
The was a Japanese samurai family who controlled the hereditary title of '' shikken'' (regent) of the Kamakura shogunate between 1203 and 1333. Despite the title, in practice the family wielded actual political power in Japan during this perio ...
remained a major power in the Kant┼Ź region
The is a geography, geographical region of Honshu, the largest island of Japan. In a common definition, the region includes the Greater Tokyo Area and encompasses seven prefectures of Japan, prefectures: Chiba Prefecture, Chiba, Gunma Prefe ...
until its subjugation by Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and ''daimy┼Ź'' (feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period, Sengoku and Azuchi-Momoyama periods and regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: ...
late in the Sengoku period. Other notable examples include the supplanting of the Hosokawa clan
The is a Japanese samurai kin group or Japanese clan, clan. The clan descends from the Seiwa Genji, a branch of the Minamoto clan, and ultimately from Emperor Seiwa, through the Ashikaga clan. It produced many prominent officials in the Ashikaga ...
by the Miyoshi, the Toki by the Sait┼Ź, and the Shiba clan
was a Japanese clan.Edmond Papinot, Papinot, Jacques Edmond Joseph. (1906). ''Dictionnaire dŌĆÖhistoire et de g├®ographie du Japon''; Papinot, (2003)("Shiba," ''Nobiliare du Japon'', p. 54 DF 58 of 80/nowiki> retrieved 2013-05-03.
History ...
by the Oda clan
The is a Japanese samurai family who were daimyo and an important political force in the unification of Japan in the mid-16th century. Though they reached the peak of their power under Oda Nobunaga and fell soon after, several branches of the ...
, which was in turn replaced by its underling, Toyotomi Hideyoshi, a son of a peasant with no family name.
Well-organized religious groups also gained political power at this time by uniting farmers in resistance and rebellion against the rule of the ''daimy┼Źs''. The monks of the Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
True Pure Land sect formed numerous ''Ikk┼Ź-ikki
were armed military leagues that formed in several regions of Japan in the 15th-16th centuries, composed entirely of members of the J┼Źdo Shinsh┼½ sect of Buddhism. In the early phases, these ''ikki'' leagues opposed the rule of local Shugo, go ...
'', the most successful of which, in Kaga Province
was a province of Japan in the area that is today the south and western portion of Ishikawa Prefecture in the Hokuriku region of Japan. Kaga bordered on Echizen, Etch┼½, Hida, and Noto Provinces. It was part of Hokurikud┼Ź Circuit. Its ...
, remained independent for nearly 100 years.
See also
*Crisis of the Third Century
The Crisis of the Third Century, also known as the Military Anarchy or the Imperial Crisis, was a period in History of Rome, Roman history during which the Roman Empire nearly collapsed under the combined pressure of repeated Barbarian invasions ...
ŌĆō a similar period in Roman history
* Horses in East Asian warfare
Horses in East Asian warfare are inextricably linked with the strategic and tactical evolution of armed conflict throughout the course of East Asian military history. A warrior on horseback or horse-drawn chariot changed the Balance of power (i ...
* Kabukimono
or were gangs of samurai in feudal Japan. First appearing in the AzuchiŌĆōMomoyama period (between the end of the Muromachi period in 1573 and the beginning of the Edo period in 1603) as the turbulent Sengoku period drew to a close, were ei ...
* List of Japanese battles
* Warring States period
The Warring States period in history of China, Chinese history (221 BC) comprises the final two and a half centuries of the Zhou dynasty (256 BC), which were characterized by frequent warfare, bureaucratic and military reforms, and ...
ŌĆō a similar period in Chinese history
Notes
References
* * * * * * *External links
* Warring-States Japan Battle Dataset ŌĆō 2,889 battles occurring within Japan during the Sengoku periodSengoku Period
ŌĆō ''
World History Encyclopedia
World History Encyclopedia (formerly Ancient History Encyclopedia) is a nonprofit educational company created in 2009 by Jan van der Crabben. The organization publishes and maintains articles, images, videos, podcasts, and interactive educational ...
''
Samurai Archives Japanese History page
*
held in Gifu Prefecture, 2000ŌĆō2001 *
{{Authority control * * * * * 1460s establishments in Japan 1467 establishments in Asia 1573 disestablishments in Japan Civil wars in Japan Muromachi period Wars of succession involving the states and peoples of Asia