Seal's Rock on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lundy is an English island in the
 The place-name ''Lundy'' is first attested in 1189 in the ''Records of the Templars in England'', where it appears as . It appears in the Charter Rolls as ''Lundeia'' again in 1199, and as ''Lunday'' in 1281. The name is Scandinavian and means '
The place-name ''Lundy'' is first attested in 1189 in the ''Records of the Templars in England'', where it appears as . It appears in the Charter Rolls as ''Lundeia'' again in 1199, and as ''Lunday'' in 1281. The name is Scandinavian and means '
 Beacon Hill Cemetery was excavated by Charles Thomas in 1969.Charles Thomas, ''And Shall These Mute Stones Speak?'' (1994) Cardiff: University of Wales Press The cemetery contains four inscribed stones, dated to the 5th or 6th century AD. The site was originally enclosed by a curvilinear bank and ditch, which is still visible in the southwest corner, however, the other walls were moved when the Old Light was constructed in 1819.
Beacon Hill Cemetery was excavated by Charles Thomas in 1969.Charles Thomas, ''And Shall These Mute Stones Speak?'' (1994) Cardiff: University of Wales Press The cemetery contains four inscribed stones, dated to the 5th or 6th century AD. The site was originally enclosed by a curvilinear bank and ditch, which is still visible in the southwest corner, however, the other walls were moved when the Old Light was constructed in 1819.
 Four
Four
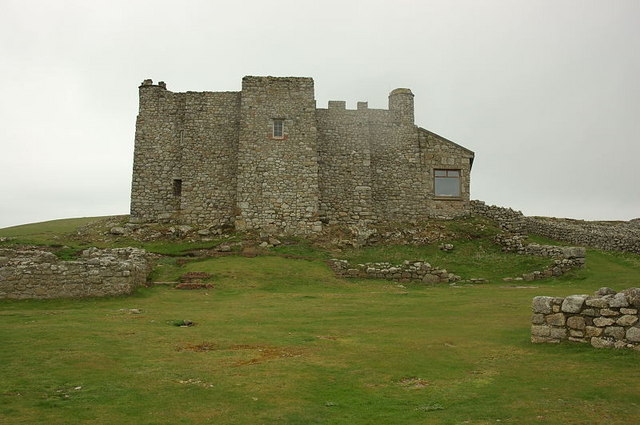 In 1235, William de Marisco was implicated in the murder of Henry Clement, a messenger of Henry III. Three years later, an attempt was made to kill Henry III by a man who later confessed to being an agent of the Marisco family. William de Marisco fled to Lundy where he lived as a virtual king. He built a stronghold in the area now known as Bulls' Paradise with walls thick.
In 1242, Henry III sent troops to the island. They scaled the island's cliff and captured William de Marisco and 16 of his "subjects". Henry III built the castle (sometimes referred to as the Marisco Castle) in an attempt to establish the rule of law on the island and its surrounding waters. In 1275, the island is recorded as being in the Lordship of King Edward I but by 1322 it was in the possession of
In 1235, William de Marisco was implicated in the murder of Henry Clement, a messenger of Henry III. Three years later, an attempt was made to kill Henry III by a man who later confessed to being an agent of the Marisco family. William de Marisco fled to Lundy where he lived as a virtual king. He built a stronghold in the area now known as Bulls' Paradise with walls thick.
In 1242, Henry III sent troops to the island. They scaled the island's cliff and captured William de Marisco and 16 of his "subjects". Henry III built the castle (sometimes referred to as the Marisco Castle) in an attempt to establish the rule of law on the island and its surrounding waters. In 1275, the island is recorded as being in the Lordship of King Edward I but by 1322 it was in the possession of
 Hudson Heaven died in 1916, and was succeeded by his nephew, Walter Charles Hudson Heaven. With the outbreak of the
Hudson Heaven died in 1916, and was succeeded by his nephew, Walter Charles Hudson Heaven. With the outbreak of the
 During the
During the
 The island of Lundy is long from north to south by a little over wide, with an area of . The highest point on Lundy is Beacon Hill, above sea level. A few yards off the northeastern coast is Seal's Rock which is so called after the
The island of Lundy is long from north to south by a little over wide, with an area of . The highest point on Lundy is Beacon Hill, above sea level. A few yards off the northeastern coast is Seal's Rock which is so called after the
 The vegetation on the plateau is mainly dry heath, with an area of waved
The vegetation on the plateau is mainly dry heath, with an area of waved
 As an isolated island on major migration routes, Lundy has a rich bird life and is a popular site for
As an isolated island on major migration routes, Lundy has a rich bird life and is a popular site for
 Lundy is home to an unusual range of introduced mammals, including a distinct breed of wild pony, the Lundy pony, as well as Soay sheep (''Ovis aries''), sika deer (''Cervus nippon''), feral goats (''Capra aegagrus hircus''), and European rabbit, some of which are Melanism, melanistic.
Other mammals which have made the island their home include the grey seal (''Halichoerus grypus'') and the Eurasian pygmy shrew (''Sorex minutus''). Until their elimination in 2006, in order to protect the nesting seabirds, Lundy was one of the few places in the UK where the
Lundy is home to an unusual range of introduced mammals, including a distinct breed of wild pony, the Lundy pony, as well as Soay sheep (''Ovis aries''), sika deer (''Cervus nippon''), feral goats (''Capra aegagrus hircus''), and European rabbit, some of which are Melanism, melanistic.
Other mammals which have made the island their home include the grey seal (''Halichoerus grypus'') and the Eurasian pygmy shrew (''Sorex minutus''). Until their elimination in 2006, in order to protect the nesting seabirds, Lundy was one of the few places in the UK where the
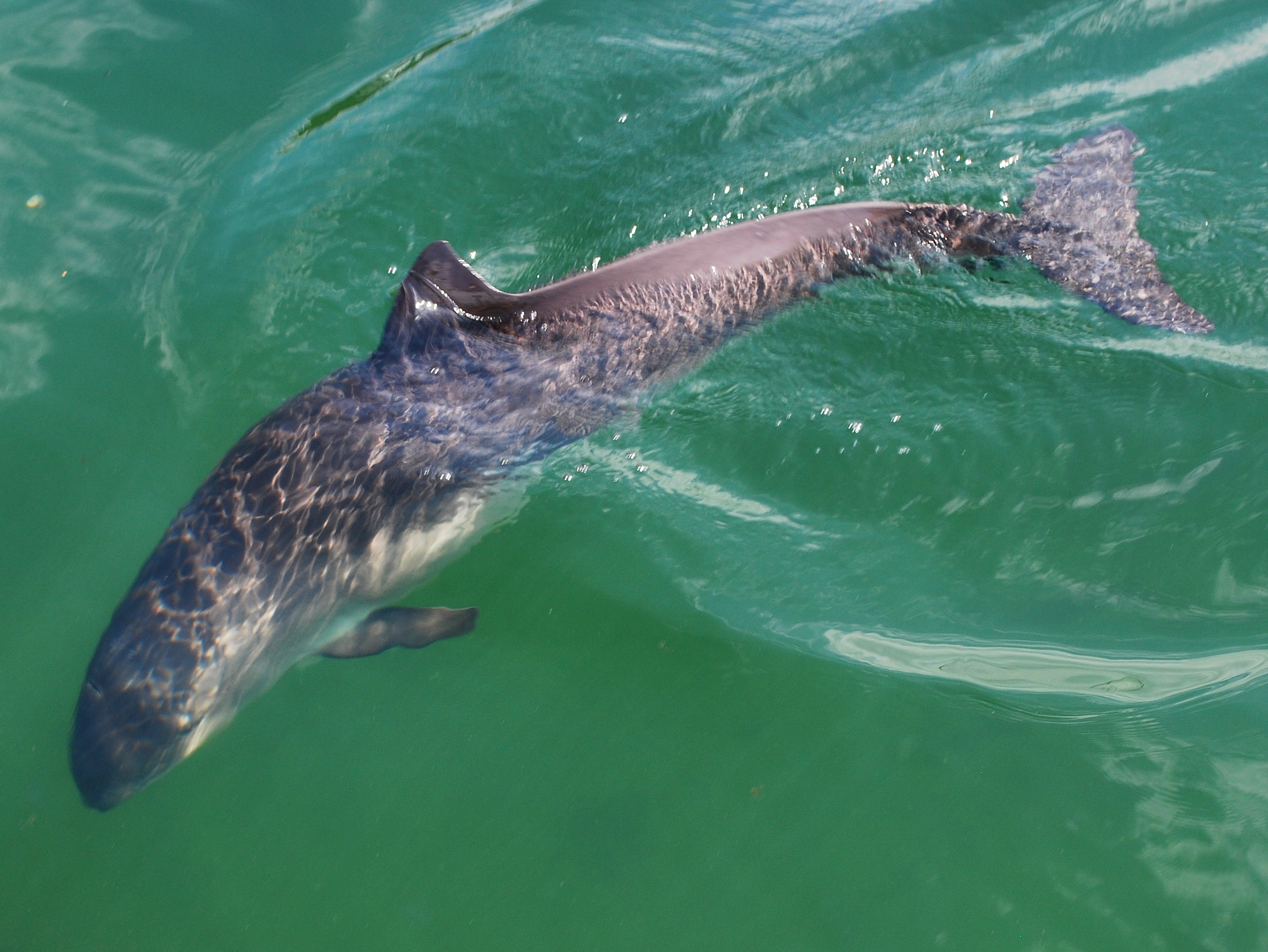 Three species of cetacean are regularly seen from the island; them being the common bottlenose dolphin, bottlenose dolphin (''Tursiops truncatrus''), common dolphin (''Delphinus delphis''), and harbour porpoise (''Phocoena phocoena''). Other cetacean species that are sighted from Lundy, albeit more rarely, are the Common minke whale, minke whale (''Balaenoptera acutorostrata''), Risso's dolphin (''Grampus griseus''), and long-finned pilot whale (''Globicephala melas''). Basking sharks (''Cetorhinus maximus''), ocean sunfish (''Mola mola''), and leatherback sea turtles (''Dermochelys coriacea'') are also seen around Lundy, especially off the more sheltered eastern coast and only during the warmer months. Furthermore, there is a grey seal (''Halichoerus grypus'') colony consisting of roughly 60 animals that live around the island.
Three species of cetacean are regularly seen from the island; them being the common bottlenose dolphin, bottlenose dolphin (''Tursiops truncatrus''), common dolphin (''Delphinus delphis''), and harbour porpoise (''Phocoena phocoena''). Other cetacean species that are sighted from Lundy, albeit more rarely, are the Common minke whale, minke whale (''Balaenoptera acutorostrata''), Risso's dolphin (''Grampus griseus''), and long-finned pilot whale (''Globicephala melas''). Basking sharks (''Cetorhinus maximus''), ocean sunfish (''Mola mola''), and leatherback sea turtles (''Dermochelys coriacea'') are also seen around Lundy, especially off the more sheltered eastern coast and only during the warmer months. Furthermore, there is a grey seal (''Halichoerus grypus'') colony consisting of roughly 60 animals that live around the island.

Election Maps It is part of the constituency electing the Member of Parliament for Torridge and Tavistock (UK Parliament constituency), Torridge and Tavistock and was from 1999 to 2020 part of the South West England (European Parliament constituency), South West England constituency for the European Parliament. In 2013, the island became a separate Church of England ecclesiastical parish.
Philatelic Research at the British Library
by David Beech
Lundy Marine Reserve at Protect Planet Ocean
* {{Authority control Lundy, Islands of the Bristol Channel Islands of Devon National nature reserves in England National Trust properties in Devon Nature reserves in Devon Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Devon Sites of Special Scientific Interest notified in 1987 Special Areas of Conservation in England Tourist attractions in Devon Ports and harbours of the Bristol Channel Barbary piracy Invasions of England Marine reserves of the United Kingdom Philately of the United Kingdom Natural regions of England Shipwrecks of England Aviation accidents and incidents locations in England Island restoration Car-free islands of Europe Former civil parishes in Devon Unparished areas in Devon Torridge District Pirate dens and locations Barbary slave raids
Bristol Channel
The Bristol Channel (, literal translation: "Severn Sea") is a major inlet in the island of Great Britain, separating South Wales (from Pembrokeshire to the Vale of Glamorgan) and South West England (from Devon to North Somerset). It extends ...
. It forms part of the district of Torridge
Torridge may refer to:
* Torridge District
Torridge is a Non-metropolitan district, local government district in north-west Devon, England. Its council is based in the town of Bideford. The district also includes the towns of Great Torringt ...
in the county of Devon
Devon ( ; historically also known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial county in South West England. It is bordered by the Bristol Channel to the north, Somerset and Dorset to the east, the English Channel to the south, and Cornwall to the west ...
.
About long and wide, Lundy has had a long and turbulent history, frequently changing hands between the British crown and various usurpers. In the 1920s, the island's owner, Martin Harman, tried to issue his own coinage and was fined. In 1941, two German Heinkel He 111
The Heinkel He 111 is a German airliner and medium bomber designed by Siegfried and Walter Günter at Heinkel Flugzeugwerke in 1934. Through development, it was described as a wolf in sheep's clothing. Due to restrictions placed on Germany a ...
bombers crash landed on the island, and their crews were captured.
In 1969, Lundy was purchased by British millionaire Jack Hayward
Sir Jack Arnold Hayward (14 June 1923 – 13 January 2015) was an English businessman, property developer, philanthropist, and president of English football club Wolverhampton Wanderers.
Biography
Early life
The only son of Charles Willi ...
, who donated it to the National Trust
The National Trust () is a heritage and nature conservation charity and membership organisation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland.
The Trust was founded in 1895 by Octavia Hill, Sir Robert Hunter and Hardwicke Rawnsley to "promote the ...
. It is now managed by the Landmark Trust
The Landmark Trust is a British architectural conservation, building conservation charitable organization, charity, founded in 1965 by John Smith (Conservative politician), Sir John and Lady Smith, that rescues buildings of historic interest or ...
, a conservation charity that derives its income from day trips and holiday lettings, most visitors arriving by boat from Bideford
Bideford ( ) is a historic port town on the estuary of the River Torridge in north Devon, South West England. It is the main town of the Torridge District, Torridge Districts of England, local government district.
Toponymy
In ancient records Bi ...
or Ilfracombe
Ilfracombe ( ) is a seaside resort and civil parishes in England, civil parish on the North Devon coast, England, with a small harbour surrounded by cliffs.
The parish stretches along the coast from the 'Coastguard Cottages' in Hele Bay towar ...
. A local tourist curiosity is the special "Puffin" postage stamp, a category known by philatelists as "local carriage labels", a collectors' item.
As a steep, rocky island, often shrouded by fog, Lundy has been the scene of many shipwrecks, and the remains of its old lighthouse installations are of both historic and scientific interest. Its present-day lighthouses, one of which is solar-powered, are fully automated. Lundy has a rich bird life, as it lies on major migration routes, and attracts many vagrant as well as indigenous species. It also boasts a variety of marine habitats, with rare seaweeds, sponges and corals. In 2010, the island became Britain's first Marine Conservation Zone.
Profile
Lundy is the largest island in theBristol Channel
The Bristol Channel (, literal translation: "Severn Sea") is a major inlet in the island of Great Britain, separating South Wales (from Pembrokeshire to the Vale of Glamorgan) and South West England (from Devon to North Somerset). It extends ...
. It lies off the coast of Devon
Devon ( ; historically also known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial county in South West England. It is bordered by the Bristol Channel to the north, Somerset and Dorset to the east, the English Channel to the south, and Cornwall to the west ...
, England, about a third of the distance across the channel from Devon
Devon ( ; historically also known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial county in South West England. It is bordered by the Bristol Channel to the north, Somerset and Dorset to the east, the English Channel to the south, and Cornwall to the west ...
to Pembrokeshire
Pembrokeshire ( ; ) is a Principal areas of Wales, county in the South West Wales, south-west of Wales. It is bordered by Carmarthenshire to the east, Ceredigion to the northeast, and otherwise by the sea. Haverfordwest is the largest town and ...
in Wales. Lundy gives its name to a British sea area. Lundy is included in the district of Torridge
Torridge may refer to:
* Torridge District
Torridge is a Non-metropolitan district, local government district in north-west Devon, England. Its council is based in the town of Bideford. The district also includes the towns of Great Torringt ...
in Devon. In 2007, it had a resident population of 28 people. These include a warden, a ranger, an island manager, a farmer, bar and housekeeping staff, and volunteers. Most live in and around the village at the south of the island. Visitors include day-tripper
A day trip is a visit to a tourist destination or visitor attraction from a person's home, hotel, or hostel in the morning, returning to the same lodging in the evening. The day trip is a form of recreational travel and leisure to a location tha ...
s and holiday makers staying overnight in rental properties or camping.
In a 2005 opinion poll of ''Radio Times
''Radio Times'' is a British weekly listings magazine devoted to television and radio programme schedules, with other features such as interviews, film reviews and lifestyle items. Founded in September 1923 by John Reith, then general manage ...
'' readers, Lundy was named as Britain's tenth greatest natural wonder. The island has been designated a Site of Special Scientific Interest
A Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) in Great Britain, or an Area of Special Scientific Interest (ASSI) in the Isle of Man and Northern Ireland, is a conservation designation denoting a protected area in the United Kingdom and Isle ...
and it was England's first statutory Marine Nature reserve Marine nature reserve (MNR) is a conservation designation officially awarded by a government to a marine reserve of national significance. Republic of Ireland
Lough Hyne, a marine lake off of County Cork, is Ireland's only marine nature reserve. Un ...
, and the first Marine Conservation Zone
A Marine Conservation Zone (MCZ) is a type of marine nature reserve in United Kingdom, UK waters. They were established under the Marine and Coastal Access Act 2009, Marine and Coastal Access Act (2009) and are areas designated with the aim to prot ...
, because of its unique flora and fauna. It is managed by the Landmark Trust
The Landmark Trust is a British architectural conservation, building conservation charitable organization, charity, founded in 1965 by John Smith (Conservative politician), Sir John and Lady Smith, that rescues buildings of historic interest or ...
on behalf of the National Trust
The National Trust () is a heritage and nature conservation charity and membership organisation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland.
The Trust was founded in 1895 by Octavia Hill, Sir Robert Hunter and Hardwicke Rawnsley to "promote the ...
.
Etymology
 The place-name ''Lundy'' is first attested in 1189 in the ''Records of the Templars in England'', where it appears as . It appears in the Charter Rolls as ''Lundeia'' again in 1199, and as ''Lunday'' in 1281. The name is Scandinavian and means '
The place-name ''Lundy'' is first attested in 1189 in the ''Records of the Templars in England'', where it appears as . It appears in the Charter Rolls as ''Lundeia'' again in 1199, and as ''Lunday'' in 1281. The name is Scandinavian and means 'puffin
Puffins are any of three species of small alcids (auks) in the bird genus ''Fratercula''. These are pelagic seabirds that feed primarily by diving in the water. They breed in large colonies on coastal cliffs or offshore islands, nesting in crev ...
island', from the Old Norse
Old Norse, also referred to as Old Nordic or Old Scandinavian, was a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants ...
meaning 'puffin' (compare Lundey in Iceland
Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the regi ...
); it appears in the 12th-century ''Orkneyinga saga
The ''Orkneyinga saga'' (Old Norse: ; ; also called the ''History of the Earls of Orkney'' and ''Jarls' Saga'') is a narrative of the history of the Orkney and Shetland islands and their relationship with other local polities, particularly No ...
'' as .
Lundy is known in Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, of or about Wales
* Welsh language, spoken in Wales
* Welsh people, an ethnic group native to Wales
Places
* Welsh, Arkansas, U.S.
* Welsh, Louisiana, U.S.
* Welsh, Ohio, U.S.
* Welsh Basin, during t ...
as , 'Gwair's Island', in reference to an alternative name for the wizard Gwydion
Gwydion fab Dôn () is a magician, hero and trickster of Welsh mythology, appearing most prominently in the Fourth Branch of the ''Mabinogi'', which focuses largely on his relationship with his young nephew, Lleu Llaw Gyffes. He also appears ...
.
History
Lundy has evidence of visitation or occupation from theMesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic i ...
period onward, with Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
flintwork, Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
burial mounds
A tumulus (: tumuli) is a mound of earth and stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds, mounds, howes, or in Siberia and Central Asia as ''kurgans'', and may be found throughout much of the world. ...
, four inscribed gravestones from the early medieval period,Lundy Field Society 40th Annual Report for 1989. pp. 34–47. and an early medieval monastery (possibly dedicated to St Elen or St Helen).
Beacon Hill Cemetery
Celtic Christian
Celtic Christianity is a form of Christianity that was common, or held to be common, across the Celtic-speaking world during the Early Middle Ages. The term Celtic Church is deprecated by many historians as it implies a unified and identifiab ...
enclosures of this type were common in Western Britain and are known as in Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, of or about Wales
* Welsh language, spoken in Wales
* Welsh people, an ethnic group native to Wales
Places
* Welsh, Arkansas, U.S.
* Welsh, Louisiana, U.S.
* Welsh, Ohio, U.S.
* Welsh Basin, during t ...
and in Cornish. There are surviving examples in Luxulyan
Luxulyan (; ), also spelt Luxullian or Luxulian, is a village and civil parish in mid Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The village lies four miles (6.5 km) northeast of St Austell and six miles (10 km) south of Bodmin. The population ...
, in Cornwall; Mathry, Meidrim
Meidrim is a village and community some west of Carmarthen and north of St Clears in Carmarthenshire, Wales. Meidrim (formerly also spelled 'Mydrim') and its twin village of Drefach are situated either side of the Afon Dewi Fawr at the point ...
and Clydau
Clydau (sometimes Clydaï or Clydey) is a community (Wales), community and parish in Pembrokeshire, Wales.
Name
The meaning of the Welsh placename is uncertain, although the church is now dedicated to St. Clydaï, an alleged daughter of Brychan. ...
in the south of Wales; and Stowford
Stowford is a village and civil parish in the district of West Devon in the English county of Devon. It is situated to the west of Dartmoor. Stowford is about 1 mile west of the village of Lewdown and about 11 miles south-west of Okehampton in ...
, Jacobstowe, Lydford
Lydford, sometimes spelled Lidford, is a village and civil parish, in Devon, north of Tavistock on the western fringe of Dartmoor in the West Devon district. The parish covers an area of , and at the 2021 census had a population of 370.
The ...
and Instow
Instow is a village in north Devon, England. It is on the estuary where the rivers Taw and Torridge meet, between the villages of Westleigh and Yelland and on the opposite bank to Appledore. There is an electoral ward with the same name. The ...
, in Devon.
Thomas proposed the following sequence of site usage:
# An area of round huts and fields. These huts may have fallen into disuse before the construction of the cemetery.
# The construction of the focal grave, an rectangular stone enclosure containing a single cist
In archeology, a cist (; also kist ;
ultimately from ; cognate to ) or cist grave is a small stone-built coffin-like box or ossuary used to hold the bodies of the dead. In some ways, it is similar to the deeper shaft tomb. Examples occur ac ...
grave. The interior of the enclosure was filled with small granite pieces. Two more cist graves located to the west of the enclosure may also date from this time.
# Perhaps 100 years later, the focal grave was opened and the infill removed. The body may have been moved to a church at this time.
# Two further stages of cist grave construction around the focal grave.
Twenty-three cist graves were found during this excavation. Considering that the excavation only uncovered a small area of the cemetery, there may be as many as 100 graves.
Inscribed stones
 Four
Four Celtic inscribed stone
Celtic inscribed stones are stone monuments dating from 400 to 1000 AD which have inscriptions in Celtic languages, Celtic or Latin text. These can be written in Ogham inscription, Ogham or Latin script, Roman letters. Some stones have both Ogham ...
s have been found in Beacon Hill Cemetery:
* 1400 OPTIMI, or TIMI;Elisabeth Okasha
Elisabeth Okasha (née Barty) is an expert in early medieval language and inscribed objects, and professor emerita of English language at University College Cork, where she served as Acting Director of UCC Language Centre between 2007-2019. She i ...
, (1993) ''Corpus of Early Christian Inscribed Stones of South-west Britain''. Leicester: University Press the name (or perhaps epithet) Optimus is Latin and male. Discovered in 1962 by D. B. Hague.
* 1401 RESTEVTAE, or RESGEVT Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
, female i.e. Resteuta or Resgeuta. Discovered in 1962 by D. B. Hague.
* 1402 POTIT or OIT, Latin, male. Discovered in 1961 by K. S. Gardener and A. Langham.
* 1403 --]IGERNI IL TIGERNI, or—I]GERNI ILI
Ili, ILI, Illi may refer to:
Abbreviations
* Indian Law Institute
* Influenza-like illness
* Intelligent Land Investments
* Intensive lifestyle intervention, a type of lifestyle medicine
* International Law Institute, a non-profit organization ...
RNI, Brittonic, male i.e. Tigernus son of Tigernus. Discovered in 1905.
Knights Templar
Lundy was granted to theKnights Templar
The Poor Fellow-Soldiers of Christ and of the Temple of Solomon, mainly known as the Knights Templar, was a Military order (religious society), military order of the Catholic Church, Catholic faith, and one of the most important military ord ...
by Henry II
Henry II may refer to:
Kings
* Saint Henry II, Holy Roman Emperor (972–1024), crowned King of Germany in 1002, of Italy in 1004 and Emperor in 1014
*Henry II of England (1133–89), reigned from 1154
*Henry II of Jerusalem and Cyprus (1271–1 ...
in 1160. The Templars were a major international maritime force at this time, with interests in North Devon, and almost certainly an important port at Bideford
Bideford ( ) is a historic port town on the estuary of the River Torridge in north Devon, South West England. It is the main town of the Torridge District, Torridge Districts of England, local government district.
Toponymy
In ancient records Bi ...
or on the River Taw
The River Taw () in England rises at Taw Head, a spring on the central northern flanks of Dartmoor, crosses North Devon and at the town of Barnstaple, formerly a significant port, empties into Barnstaple Bay in the Bristol Channel, having form ...
in Barnstaple
Barnstaple ( or ) is a river-port town and civil parish in the North Devon district of Devon, England. The town lies at the River Taw's lowest crossing point before the Bristol Channel. From the 14th century, it was licensed to export wool from ...
. This was probably because of the increasing threat posed by the Norse sea raiders; however, it is unclear whether they ever took possession of the island. Ownership was disputed by the Marisco family who may have already been on the island during King Stephen's reign. The Mariscos were fined, and the island was cut off from necessary supplies. Evidence of the Templars' weak hold on the island came when King John, on his accession in 1199, confirmed the earlier grant.
Marisco family
 In 1235, William de Marisco was implicated in the murder of Henry Clement, a messenger of Henry III. Three years later, an attempt was made to kill Henry III by a man who later confessed to being an agent of the Marisco family. William de Marisco fled to Lundy where he lived as a virtual king. He built a stronghold in the area now known as Bulls' Paradise with walls thick.
In 1242, Henry III sent troops to the island. They scaled the island's cliff and captured William de Marisco and 16 of his "subjects". Henry III built the castle (sometimes referred to as the Marisco Castle) in an attempt to establish the rule of law on the island and its surrounding waters. In 1275, the island is recorded as being in the Lordship of King Edward I but by 1322 it was in the possession of
In 1235, William de Marisco was implicated in the murder of Henry Clement, a messenger of Henry III. Three years later, an attempt was made to kill Henry III by a man who later confessed to being an agent of the Marisco family. William de Marisco fled to Lundy where he lived as a virtual king. He built a stronghold in the area now known as Bulls' Paradise with walls thick.
In 1242, Henry III sent troops to the island. They scaled the island's cliff and captured William de Marisco and 16 of his "subjects". Henry III built the castle (sometimes referred to as the Marisco Castle) in an attempt to establish the rule of law on the island and its surrounding waters. In 1275, the island is recorded as being in the Lordship of King Edward I but by 1322 it was in the possession of Thomas, 2nd Earl of Lancaster
Thomas, 2nd Earl of Lancaster ( 1278 – 22 March 1322) was an English nobleman of the first House of Lancaster of the royal Plantagenet Dynasty. He was Earl of Lancaster, Leicester, and Derby from 1296 to 1322, and Earl of Lincoln and Sa ...
and was among the large number of lands seized by Edward II following Lancaster's execution for rebelling against the King. At some point in the 13th century the monks of the Cistercian
The Cistercians (), officially the Order of Cistercians (, abbreviated as OCist or SOCist), are a Catholic religious order of monks and nuns that branched off from the Benedictines and follow the Rule of Saint Benedict, as well as the contri ...
order at Cleeve Abbey
Cleeve Abbey is a medieval monastery located near the Washford River and village of Washford, in the English county of Somerset. It is a Grade I listed building and has been scheduled as an ancient monument.
The abbey was founded in the late ...
held the rectory of the island.
Piracy
Over the next few centuries, the island was hard to govern. Trouble followed as both English and foreign pirates andprivateer
A privateer is a private person or vessel which engages in commerce raiding under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign o ...
s – including other members of the Marisco family – took control of the island for short periods. Ships were forced to navigate close to Lundy because of the dangerous shingle banks in the fast flowing River Severn
The River Severn (, ), at long, is the longest river in Great Britain. It is also the river with the most voluminous flow of water by far in all of England and Wales, with an average flow rate of at Apperley, Gloucestershire. It rises in t ...
and Bristol Channel
The Bristol Channel (, literal translation: "Severn Sea") is a major inlet in the island of Great Britain, separating South Wales (from Pembrokeshire to the Vale of Glamorgan) and South West England (from Devon to North Somerset). It extends ...
, with its tidal range of , one of the greatest in the world. This made the island a profitable location from which to prey on passing Bristol
Bristol () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city, unitary authority area and ceremonial county in South West England, the most populous city in the region. Built around the River Avon, Bristol, River Avon, it is bordered by t ...
-bound merchant ships bringing back valuable goods from overseas.
In 1627, a group known as the Salé Rovers
The Salé Rovers, also known as the Sallee Rovers, were a group of Barbary pirates active during the 17th and 18th centuries in the Mediterranean Sea and Atlantic Ocean. Like other Barbary pirates, they attacked Christianity, Christian merchant s ...
, from the Republic of Salé
The Republic of Salé, also known as the Bou Regreg Republic and the Republic of the Two Banks, was a city-state maritime Barbary pirates, corsair republic based at Salé in Morocco during the 17th century, located at the mouth of the Bou Regre ...
(now Salé
Salé (, ) is a city in northwestern Morocco, on the right bank of the Bou Regreg river, opposite the national capital Rabat, for which it serves as a commuter town. Along with some smaller nearby towns, Rabat and Salé form together a single m ...
in Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
) occupied Lundy for five years. These Barbary pirates
The Barbary corsairs, Barbary pirates, Ottoman corsairs, or naval mujahideen (in Muslim sources) were mainly Muslim corsairs and privateers who operated from the largely independent Barbary states. This area was known in Europe as the Barba ...
, under the command of a Dutch
Dutch or Nederlands commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
** Dutch people as an ethnic group ()
** Dutch nationality law, history and regulations of Dutch citizenship ()
** Dutch language ()
* In specific terms, i ...
renegade named Jan Janszoon
Jan Janszoon van Haarlem, commonly known as Reis Mourad the Younger (c. 1570 – c. 1641), was a Dutch pirate who later became a Barbary corsair in the Regency of Algiers and the Republic of Salé. After being captured by Algerian corsairs o ...
, flew a Moorish
The term Moor is an exonym used in European languages to designate the Muslim populations of North Africa (the Maghreb) and the Iberian Peninsula (particularly al-Andalus) during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a single, distinct or self-defi ...
flag over the island. Slaving raids were made embarking from Lundy by the Barbary Pirates, and captured Europeans were held on Lundy before being sent to Salé
Salé (, ) is a city in northwestern Morocco, on the right bank of the Bou Regreg river, opposite the national capital Rabat, for which it serves as a commuter town. Along with some smaller nearby towns, Rabat and Salé form together a single m ...
and Algiers
Algiers is the capital city of Algeria as well as the capital of the Algiers Province; it extends over many Communes of Algeria, communes without having its own separate governing body. With 2,988,145 residents in 2008Census 14 April 2008: Offi ...
to be sold as slave to slavery on the Barbary coast
Slavery on the Barbary Coast refers to the enslavement of people taken captive by the Barbary corsairs of North Africa.
According to Robert Davis, author of '' Christian Slaves, Muslim Masters'', between 1 million and 1.2 million Europeans wer ...
.
From 1628 to 1634, in addition to the Barbary Pirates, the island was plagued by privateers of French, Basque, English and Spanish origin targeting the lucrative shipping routes passing through the Bristol Channel. These incursions were eventually ended by John Penington
Sir John Penington (1584?–1646) was an English admiral who served under Charles I of England.
Biography
John Penington was the second cousin of Sir Isaac Penington or Pennington, and the son of Robert Penington of Henham in Essex, describe ...
, but in the 1660s and as late as the 1700s the island still fell prey to French privateers.
Civil war
In theEnglish Civil War
The English Civil War or Great Rebellion was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Cavaliers, Royalists and Roundhead, Parliamentarians in the Kingdom of England from 1642 to 1651. Part of the wider 1639 to 1653 Wars of th ...
, Thomas Bushell held Lundy for King Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
, rebuilding Marisco Castle and garrisoning the island at his own expense. He was a friend of Francis Bacon
Francis Bacon, 1st Viscount St Alban (; 22 January 1561 – 9 April 1626) was an English philosopher and statesman who served as Attorney General and Lord Chancellor of England under King James I. Bacon argued for the importance of nat ...
, a strong supporter of the Royalist
A royalist supports a particular monarch as head of state for a particular kingdom, or of a particular dynastic claim. In the abstract, this position is royalism. It is distinct from monarchism, which advocates a monarchical system of gove ...
cause and an expert on mining and coining. It was the last Royalist territory held between the first
First most commonly refers to:
* First, the ordinal form of the number 1
First or 1st may also refer to:
Acronyms
* Faint Images of the Radio Sky at Twenty-Centimeters, an astronomical survey carried out by the Very Large Array
* Far Infrared a ...
and second
The second (symbol: s) is a unit of time derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes, and finally to 60 seconds each (24 × 60 × 60 = 86400). The current and formal definition in the International System of U ...
civil wars. After receiving permission from Charles I, Bushell surrendered the island on 24 February 1647 to Richard Fiennes, representing General Fairfax
Sir Thomas Fairfax (17 January 1612 – 12 November 1671) was an English army officer and politician who commanded the New Model Army from 1645 to 1650 during the English Civil War. Because of his dark hair, he was known as "Black Tom" to his l ...
. In 1656, the island was acquired by Lord Saye and Sele.

18th and 19th centuries
The late 18th and early 19th centuries were years of lawlessness on Lundy, particularly during the ownership of Thomas Benson (1708–1772), a Member of Parliament for Barnstaple in 1747 andSheriff of Devon
The High Sheriff of Devon is the Kings's representative for the County of Devon, a territory known as his/her bailiwick. Selected from three nominated people, they hold the office for one year. They have judicial, ceremonial and administrative f ...
, who notoriously used the island for housing convicts whom he was supposed to be deporting. Benson leased Lundy from its owner, John Leveson-Gower, 1st Earl Gower
John Leveson-Gower, 1st Earl Gower, PC (10 August 1694 – 25 December 1754) was a British Tory politician who served as Lord Privy Seal from 1742 to 1743 and again from 1744 to 1754. Leveson-Gower also served in the Parliament of Great Brita ...
(1694–1754) (who was an heir of the Grenville family of Bideford and of Stowe, Kilkhampton
Stowe House in the parish of Kilkhampton in Cornwall, United Kingdom, was a mansion built in 1679 by John Grenville, 1st Earl of Bath (1628–1701) and demolished in 1739. The Grenville family were for many centuries lords of the manor of Kil ...
in Cornwall), at a rent of £60 per annum and contracted with the Government to transport a shipload of convicts to Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
, but diverted the ship to Lundy to use the convicts as his personal slaves. Later Benson was involved in an insurance swindle. He purchased and insured the ship ''Nightingale'' and loaded it with a valuable cargo of pewter and linen. Having cleared the port on the mainland, the ship put into Lundy, where the cargo was removed and stored in a cave built by the convicts, before setting sail again. Some days afterwards, when a homeward-bound vessel was sighted, the ''Nightingale'' was set on fire and scuttled. The crew were taken off the stricken ship by the other ship, which landed them safely at Clovelly
Clovelly () is a privately owned harbour village in the Torridge District, Torridge district of Devon, England. The settlement and surrounding land belongs to John Rous, who inherited it from his mother in 1983. He belongs to the Hamlyn family ...
.
Sir Vere Hunt, 1st Baronet of Curragh, a rather eccentric Irish politician and landowner, and unsuccessful man of business, purchased the island from John Cleveland in 1802 for £5,270. Hunt planted in the island a small, self-contained Irish colony with its own constitution and divorce laws, coinage, and stamps. The tenants came from Hunt's Irish estate and they experienced agricultural difficulties while on the island. This led Hunt to seek someone who would take the island off his hands, failing in his attempt to sell the island to the British government as a base for troops.
After the 1st Baronet's death his son, Sir Aubrey (Hunt) de Vere, 2nd Baronet, also had great difficulty in securing any profit from the property. In the 1820s, John Benison agreed to purchase the island for £4,500 but then refused to complete the sale, as he felt that de Vere could not make out a good title in respect of the sale terms, namely that the island was free from tithes and taxes.
William Hudson Heaven purchased Lundy in 1834, as a summer retreat and for hunting
Hunting is the Human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, and killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to obtain the animal's body for meat and useful animal products (fur/hide (sk ...
, at a cost of 9,400 guineas
The guinea (; commonly abbreviated gn., or gns. in plural) was a coin, minted in Great Britain between 1663 and 1814, that contained approximately one-quarter of an ounce of gold. The name came from the Guinea region in West Africa, from where m ...
(£9,870). He claimed it to be a "free island", and successfully resisted the jurisdiction of the mainland magistrates. Lundy was in consequence sometimes referred to as "the kingdom of Heaven". It belonged in law to the county of Devon, and had long been part of the hundred
100 or one hundred (Roman numerals, Roman numeral: C) is the natural number following 99 (number), 99 and preceding 101 (number), 101.
In mathematics
100 is the square of 10 (number), 10 (in scientific notation it is written as 102). The standar ...
of Braunton
Braunton is a large village, civil parishes in England, civil parish, ecclesiastical parish and former Manorialism, manor in Devon. The village is situated west of Barnstaple. It is one of the largest villages in Devon with a population at th ...
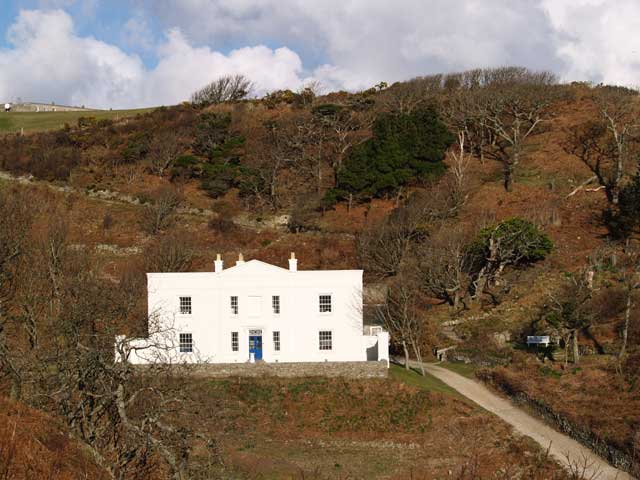
. Many of the buildings on the island, including St. Helen's Church, designed by the architect John Norton, and Millcombe House (originally known simply as "the Villa"), date from the Heaven period. The Georgian-style
Georgian architecture is the name given in most English-speaking countries to the set of architectural styles current between 1714 and 1830. It is named after the first four British monarchs of the House of Hanover, George I, George II, Ge ...
villa was built in 1836. However, the expense of building the road from the beach (no financial assistance being provided by Trinity House
The Corporation of Trinity House of Deptford Strond, also known as Trinity House (and formally as The Master, Wardens and Assistants of the Guild Fraternity or Brotherhood of the most glorious and undivided Trinity and of St Clement in the ...
, despite their frequent use of the road following the construction of the lighthouses), maintaining the villa, and the general cost of running the island had a ruinous effect on the family's finances, which had been diminished by reduced profits from their sugar plantations, rum production, and livestock rearing in Jamaica
Jamaica is an island country in the Caribbean Sea and the West Indies. At , it is the third-largest island—after Cuba and Hispaniola—of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean. Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, west of Hispaniola (the is ...
.
In 1957, a message in a bottle from one of the seamen of was washed ashore between Babbacombe
Babbacombe is a district of Torquay, Devon, England. It is notable for Babbacombe Model Village, the Babbacombe Theatre and its clifftop green, Babbacombe Downs, from which Oddicombe Beach is accessed via Babbacombe Cliff Railway. Frequent ...
and Peppercombe in Devon
Devon ( ; historically also known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial county in South West England. It is bordered by the Bristol Channel to the north, Somerset and Dorset to the east, the English Channel to the south, and Cornwall to the west ...
. The letter, dated 15 August 1843, read: "Dear Brother, Please e God i be with y against Michaelmas. Prepare y search Lundy for y Jenny ivories. Adiue William, Odessa". The bottle and letter are on display at the Portledge Hotel at Fairy Cross, in Devon, England. was a three-masted full-rigged ship
A full-rigged ship or fully rigged ship is a sailing ship, sailing vessel with a sail plan of three or more mast (sailing), masts, all of them square rig, square-rigged. Such a vessel is said to have a ship rig or be ship-rigged, with each mas ...
reputed to be carrying ivory and gold dust that was wrecked on Lundy on 20 January 1797 at a place thereafter called Jenny's Cove. Some ivory was apparently recovered some years later but the leather bags supposed to contain gold dust were never found.
20th and 21st centuries
William Heaven was succeeded by his son the Reverend Hudson Grosset Heaven who, thanks to a legacy from Sarah Langworthy (née Heaven), was able to fulfill his life's ambition of building a stone church on the island. St Helen's was completed in 1896, and stands today as a lasting memorial to the Heaven period. It has been designated byEnglish Heritage
English Heritage (officially the English Heritage Trust) is a charity that manages over 400 historic monuments, buildings and places. These include prehistoric sites, a battlefield, medieval castles, Roman forts, historic industrial sites, Lis ...
a Grade II listed building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building is a structure of particular architectural or historic interest deserving of special protection. Such buildings are placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Hi ...
. He is said to have been able to afford either a church or a new harbour. His choice of the church was not however in the best financial interests of the island. The unavailability of the money for re-establishing the family's financial soundness, coupled with disastrous investment and speculation in the early 20th century, caused severe financial hardship.
First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
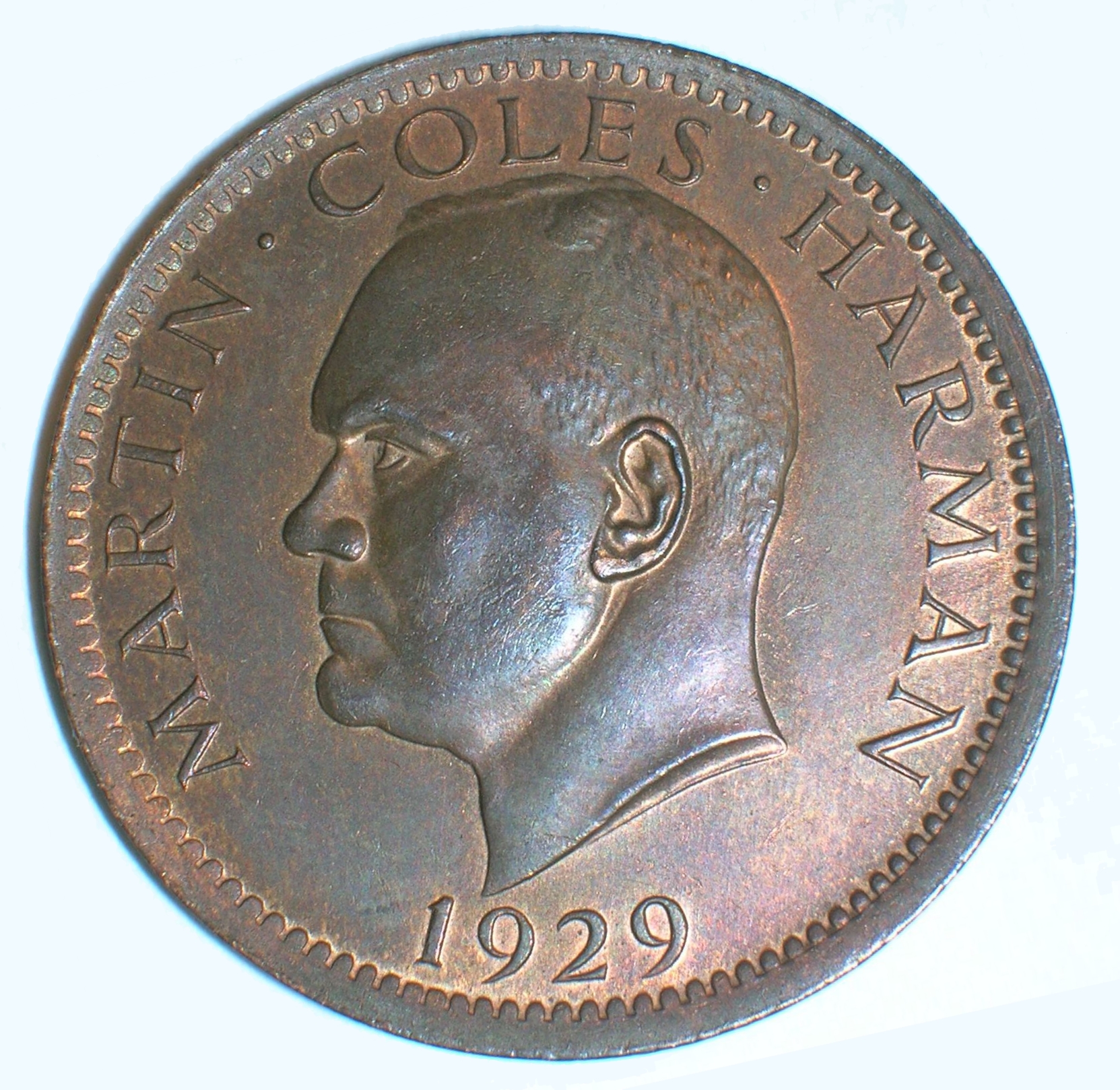
, matters deteriorated seriously, and in 1918 the family sold Lundy to Augustus Langham Christie. In 1924, the Christie family sold the island along with the mail contract and the MV ''Lerina'' to Martin Coles Harman
Martin Coles Harman (1885 – 5 December 1954) was an English businessman who, in 1925, bought the island of Lundy.
Born in Steyning in Sussex and educated at Whitgift School in Croydon, Harman had six brothers and five sisters. At the age of 1 ...
. Harman issued two coins of Half Puffin and One Puffin denominations in 1929, nominally equivalent to the British halfpenny and penny, resulting in his prosecution under the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
's Coinage Act of 1870. His case was heard by Devon magistrates
The term magistrate is used in a variety of systems of governments and laws to refer to a civilian officer who administers the law. In ancient Rome, a ''magistratus'' was one of the highest ranking government officers, and possessed both judici ...
in April 1930, and he was fined £5 and ordered to pay £15 15 shillings (£15.75 in decimal currency
Decimalisation or decimalization (see spelling differences) is the conversion of a system of currency or of weights and measures to units related by powers of 10.
Most countries have decimalised their currencies, converting them from non-decimal ...
) costs
Cost is the value of money that has been used up to produce something or deliver a service, and hence is not available for use anymore. In business, the cost may be one of acquisition, in which case the amount of money expended to acquire it is ...
. He appealed to the King's Bench Division
The King's Bench Division (or Queen's Bench Division when the monarch is female) of the High Court of Justice deals with a wide range of common law cases and has supervisory responsibility over certain lower courts.
It hears appeals on point ...
of the High Court of Justice
The High Court of Justice in London, known properly as His Majesty's High Court of Justice in England, together with the Court of Appeal (England and Wales), Court of Appeal and the Crown Court, are the Courts of England and Wales, Senior Cour ...
in 1931, but the appeal was dismissed. The coins were withdrawn and became collectors' items. In 1965, a "fantasy" restrike four-coin set, a few in gold, was issued to commemorate 40 years since Harman purchased the island. Harman's son, John Pennington Harman
Lance Corporal John Pennington Harman VC (20 July 1914 – 9 April 1944) was a British Army soldier and an English recipient of the Victoria Cross (VC), the highest and most prestigious award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be ...
was awarded a posthumous Victoria Cross
The Victoria Cross (VC) is the highest and most prestigious decoration of the Orders, decorations, and medals of the United Kingdom, British decorations system. It is awarded for valour "in the presence of the enemy" to members of the British ...
during the Battle of Kohima
The Battle of Kohima was the turning point of the Imperial Japan, Japanese Operation U-Go, U-Go offensive into British Raj, India in 1944 during the World War II, Second World War. The battle took place in three stages from 4 April to 22 June 19 ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
in 1944. There is a memorial to him at the VC Quarry on Lundy. Martin Coles Harman died in 1954.
Residents did not pay taxes to the United Kingdom and had to pass through customs when they travelled to and from Lundy Island. Although the island was ruled as a virtual fiefdom
A fief (; ) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal alle ...
, its owner never claimed to be independent of the United Kingdom, in contrast to later territorial "micronation
A micronation is a polity, political entity whose representatives claim that they belong to an independent nation or sovereign state, but which lacks legal recognition by any sovereign state. Micronations are classified separately from list o ...
s".
Following the death of Harman's son Albion in 1968, Lundy was put up for sale in 1969. Jack Hayward
Sir Jack Arnold Hayward (14 June 1923 – 13 January 2015) was an English businessman, property developer, philanthropist, and president of English football club Wolverhampton Wanderers.
Biography
Early life
The only son of Charles Willi ...
, a British millionaire, purchased the island for £150,000 (£ today) and gave it to the National Trust
The National Trust () is a heritage and nature conservation charity and membership organisation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland.
The Trust was founded in 1895 by Octavia Hill, Sir Robert Hunter and Hardwicke Rawnsley to "promote the ...
, who leased it to the Landmark Trust
The Landmark Trust is a British architectural conservation, building conservation charitable organization, charity, founded in 1965 by John Smith (Conservative politician), Sir John and Lady Smith, that rescues buildings of historic interest or ...
. The Landmark Trust has managed the island since then, deriving its income from arranging day trips, letting out holiday cottages and from donations. In May 2015 a sculpture by Antony Gormley
Sir Antony Mark David Gormley (born 30 August 1950) is a British sculptor. His works include the ''Angel of the North'', a public sculpture in Gateshead in the north of England, commissioned in 1994 and erected in February 1998; ''Another Pl ...
was erected on Lundy. It is one of five life-sized sculptures, ''Land'', placed near the centre and at four compass points of the UK in a commission by the Landmark Trust, to celebrate its 50th anniversary. The others are at Lowsonford
Lowsonford is a small village within the parish of Rowington in Warwickshire, England. The village lies north-east of Henley-in-Arden.
General information
The most famous of Lowsonford's buildings is the " Fleur de Lys" pub which is known fo ...
(Warwickshire
Warwickshire (; abbreviated Warks) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in the West Midlands (region), West Midlands of England. It is bordered by Staffordshire and Leicestershire to the north, Northamptonshire to the east, Ox ...
), Saddell Bay
Saddell Bay is an embayment along the eastern side of the Kintyre Peninsula of Scotland. Saddell Bay is an element of Kilbrannan Sound that separates the Kintyre Peninsula from the Isle of Arran. Other bays along the east side of the Kintyre Pen ...
(Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
), the Martello Tower (Aldeburgh
Aldeburgh ( ) is a coastal town and civil parish in the East Suffolk District, East Suffolk district, in the English county, county of Suffolk, England, north of the River Alde. Its estimated population was 2,276 in 2019. It was home to the comp ...
, Suffolk
Suffolk ( ) is a ceremonial county in the East of England and East Anglia. It is bordered by Norfolk to the north, the North Sea to the east, Essex to the south, and Cambridgeshire to the west. Ipswich is the largest settlement and the county ...
), and Clavell Tower
Clavell Tower, also known as Clavell Folly or the Kimmeridge Tower, is a Grade II listed Tuscan style tower built in 1830. It lies on the Jurassic Coast, on the top of Hen Cliff just east of Kimmeridge Bay in the Isle of Purbeck in Dorset, En ...
(Kimmeridge Bay
Kimmeridge Bay () is a bay on the Isle of Purbeck, a peninsula on the English Channel coast in Dorset, England, close to and southeast of the village of Kimmeridge, on the Smedmore Estate. The area is renowned for its fossils, with The Etche ...
, Dorset
Dorset ( ; Archaism, archaically: Dorsetshire , ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is bordered by Somerset to the north-west, Wiltshire to the north and the north-east, Hampshire to the east, t ...
).
The island is visited by over 20,000 day trippers a year, but during September 2007 had to be closed for several weeks owing to an outbreak of norovirus
Norovirus, also known as Norwalk virus and sometimes referred to as the winter vomiting disease, is the most common cause of gastroenteritis. Infection is characterized by non-bloody diarrhea, vomiting, and stomach pain. Fever or headaches may ...
.
An inaugural Lundy Island half-marathon took place on 8 July 2018 with 267 competitors.
Wrecked ships and aircraft
Wreck of ''Jenny''
Near the end of a voyage fromAfrica
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
to Bristol
Bristol () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city, unitary authority area and ceremonial county in South West England, the most populous city in the region. Built around the River Avon, Bristol, River Avon, it is bordered by t ...
, the British merchant ship
A merchant ship, merchant vessel, trading vessel, or merchantman is a watercraft that transports cargo or carries passengers for hire. This is in contrast to pleasure craft, which are used for personal recreation, and naval ships, which are ...
was wrecked on the coast of Lundy on 20 January 1797. Only the first mate
A chief mate (C/M) or chief officer, usually also synonymous with the first mate or first officer, is a licensed mariner and head of the deck department of a merchant ship. The chief mate is customarily a watchstander and is in charge of the shi ...
survived. The site of the tragedy () has since been known as Jenny's Cove.
Wreck of Battleship ''Montagu''
Steaming in heavyfog
Fog is a visible aerosol consisting of tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. Reprint from Fog can be considered a type of low-lying cloud usually resembling stratus and is heavily influenc ...
, the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
battleship
A battleship is a large, heavily naval armour, armored warship with a main battery consisting of large naval gun, guns, designed to serve as a capital ship. From their advent in the late 1880s, battleships were among the largest and most form ...
ran hard aground near Shutter Rock on Lundy's southwest corner at about 2:00 a.m. on 30 May 1906. Thinking they were aground at Hartland Point
Hartland Point is a high rocky outcrop of land on the north-western tip of the Devon coast in England. It is three miles (5 km) north-west of the village of Hartland. The point marks the western limit (on the English side) of the Bristol C ...
on the English mainland, a landing party went ashore for help, only finding out where they were after encountering the lighthouse
A lighthouse is a tower, building, or other type of physical structure designed to emit light from a system of lamps and lens (optics), lenses and to serve as a beacon for navigational aid for maritime pilots at sea or on inland waterways.
Ligh ...
keeper at the island's north light.
Strenuous efforts by the Royal Navy to salvage the badly damaged battleship during the summer of 1906 failed, and in 1907 it was decided to give up and sell her for scrap. ''Montagu'' was scrapped at the scene over the next fifteen years. Diving clubs still visit the site, where armour plating remains among the rocks and kelp.
Remains of a German Heinkel 111H bomber
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
two German Heinkel He 111
The Heinkel He 111 is a German airliner and medium bomber designed by Siegfried and Walter Günter at Heinkel Flugzeugwerke in 1934. Through development, it was described as a wolf in sheep's clothing. Due to restrictions placed on Germany a ...
bombers crash landed on the island in 1941. The first was on 3 March, when all the crew survived and were taken prisoner.
The second was on 1 April when the pilot was killed and the other crew members were taken prisoner. This plane had bombed a British ship and one engine was damaged by anti aircraft
Anti-aircraft warfare (AAW) is the counter to aerial warfare and includes "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action".AAP-6 It encompasses surface-based, subsurface ( submarine-launched), and air-bas ...
fire, forcing it to crash land. Most of the metal was salvaged, although a few remains can be found at the crash site to date. Reportedly, to avoid reprisals, the crew concocted the story that they were on a reconnaissance mission.
Geography
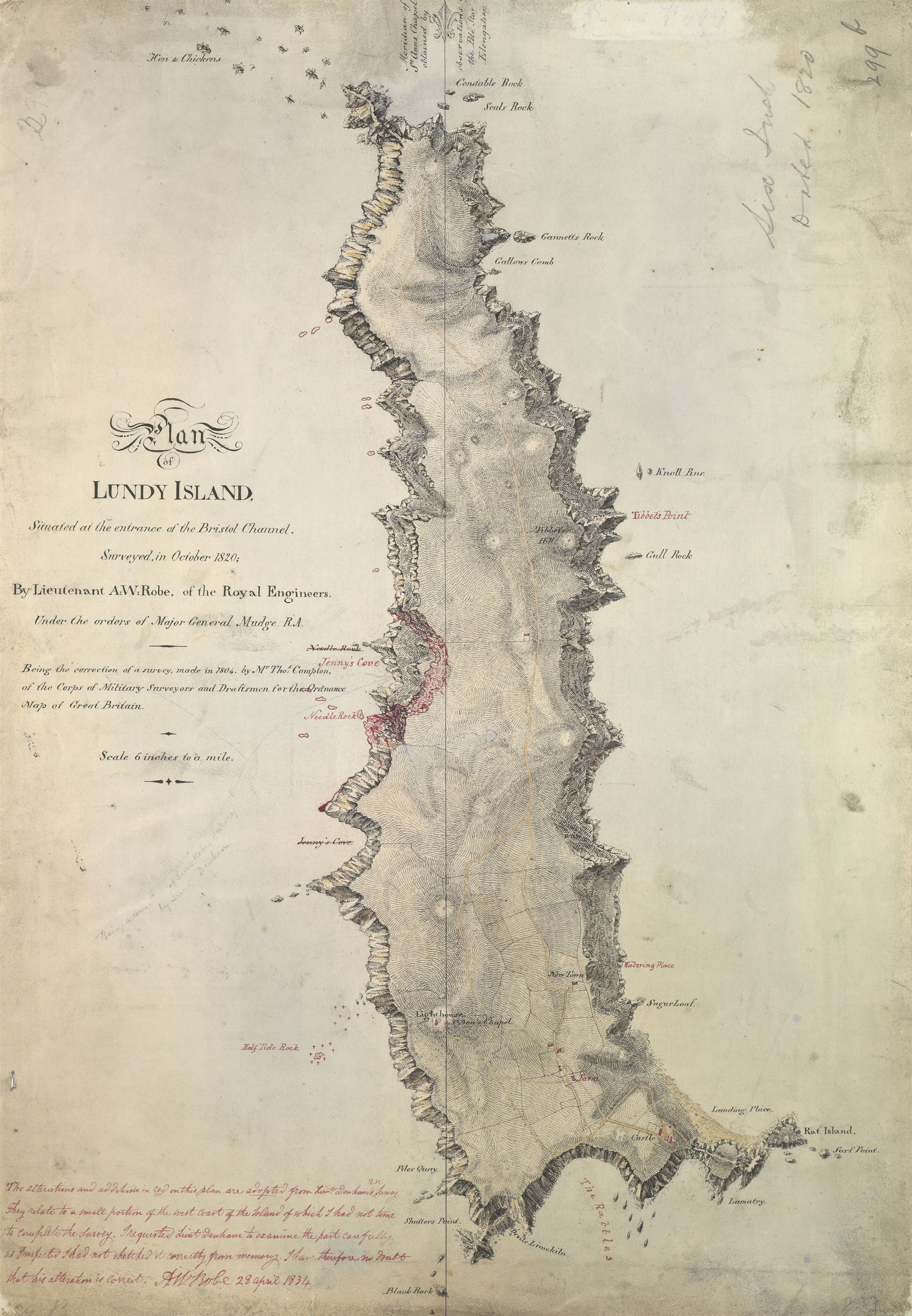
 The island of Lundy is long from north to south by a little over wide, with an area of . The highest point on Lundy is Beacon Hill, above sea level. A few yards off the northeastern coast is Seal's Rock which is so called after the
The island of Lundy is long from north to south by a little over wide, with an area of . The highest point on Lundy is Beacon Hill, above sea level. A few yards off the northeastern coast is Seal's Rock which is so called after the seals
Seals may refer to:
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, or "true seal"
** Fur seal
* Seal (emblem), a device to impress an emblem, used as a means of a ...
which rest on and inhabit the islet
An islet ( ) is generally a small island. Definitions vary, and are not precise, but some suggest that an islet is a very small, often unnamed, island with little or no vegetation to support human habitation. It may be made of rock, sand and/ ...
. It is less than wide. Near the jetty is a small pocket beach
A pocket beach is usually a small beach that is isolated between two headlands. There is typically very little or no exchange of sediment between the pocket beach and adjacent shorelines.
Pocket beaches can be natural or artificial. Many natural ...
. One of the Meteorological Office's 31 sea areas announced on the BBC Radio 4 shipping forecast
The ''Shipping Forecast'' is a BBC Radio broadcast of weather reports and forecasts for the seas around the British Isles. It is produced by the Met Office and broadcast by BBC Radio 4 on behalf of the Maritime and Coastguard Agency. The for ...
is named Lundy.
Geology
The island is primarily composed ofgranite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly coo ...
of 59.8 ± 0.4 – 58.4 ± 0.4 million years (from the Palaeocene
The Paleocene ( ), or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''palai ...
epoch
In chronology and periodization, an epoch or reference epoch is an instant in time chosen as the origin of a particular calendar era. The "epoch" serves as a reference point from which time is measured.
The moment of epoch is usually decided b ...
), with slate
Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous, metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade, regional metamorphism. It is the finest-grained foliated metamorphic ro ...
at the southern end; the plateau soil is mainly loam
Loam (in geology and soil science) is soil composed mostly of sand (particle size > ), silt (particle size > ), and a smaller amount of clay (particle size < ). By weight, its mineral composition is about 40–40–20% concentration of sand–si ...
, with some peat
Peat is an accumulation of partially Decomposition, decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, Moorland, moors, or muskegs. ''Sphagnum'' moss, also called peat moss, is one of the most ...
. Among the igneous
Igneous rock ( ), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava.
The magma can be derived from partial ...
dykes cutting the granite are a small number composed of a unique orthophyre. This was given the name Lundyite in 1914, although the term – never precisely defined – has since fallen into disuse.
It is possible, based on emplacement of magmas of the basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
, trachyte
Trachyte () is an extrusive igneous rock composed mostly of alkali feldspar. It is usually light-colored and aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained), with minor amounts of mafic minerals, and is formed by the rapid cooling of lava (or shallow intrus ...
and rhyolite
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture (geology), texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals (phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained matri ...
types at a high levels in Earth's crust, that a volcano
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most oft ...
system existed above Lundy.
Climate
Lundy lies on the line where the NorthAtlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
and the Bristol Channel meet, so it has quite a mild climate. The island has cool, wet winters and mild, wet summers. It is often windy and fog is frequently experienced. The record high temperature is on 2 August 1990, and the record low temperature is recorded just six months later on 7 February 1991. Lundy is in the USDA 9a plant hardiness zone.
Ecology
Flora
Calluna
''Calluna vulgaris'', common heather, ling, or simply heather, is the sole species in the genus ''Calluna'' in the flowering plant family Ericaceae. It is a low-growing evergreen shrub growing to tall, or rarely to and taller, and is found wide ...
heath; the northern end of the island is largely bare rock. This area is also rich in lichen
A lichen ( , ) is a hybrid colony (biology), colony of algae or cyanobacteria living symbiotically among hypha, filaments of multiple fungus species, along with yeasts and bacteria embedded in the cortex or "skin", in a mutualism (biology), m ...
s, such as ''Teloschistes flavicans'' and several species of Cladonia
''Cladonia'' is a genus of moss-like lichenized fungi in the family Cladoniaceae. They are the primary food source for reindeer/caribou. ''Cladonia'' species are of economic importance to reindeer-herders, such as the Sami in Scandinavia or th ...
and Parmelia.
Other areas are either a dry heath/acidic grassland mosaic, characterised by heaths and western gorse
''Ulex gallii'', the western gorse or dwarf furzeA R Clapham, T G Tutin, E F Warburg, ''Flora of the British Isles'', Cambridge, 1962, p. 332 is an evergreen shrub in the pea family (Fabaceae), native to the Atlantic coasts of western Europe: sou ...
(''Ulex gallii''), or semi-improved acidic grassland in which Yorkshire fog
''Holcus lanatus'' is a perennial flowering plant in the grass family Poaceae. The specific epithet ' is Latin for 'woolly' which describes the plant's hairy texture. Common names include Yorkshire fog, tufted grass, and meadow soft grass. In Nor ...
(''Holcus lanatus'') is abundant. Tussocky (Thrift) (Holcus/Armeria) communities occur mainly on the western side, and some patches of bracken
Bracken (''Pteridium'') is a genus of large, coarse ferns in the family (biology), family Dennstaedtiaceae. Ferns (Pteridophyta) are vascular plants that undergo alternation of generations, having both large plants that produce spores and small ...
(''Pteridium aquilinum'') on the eastern side.
There is one endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
plant species, the Lundy cabbage ''(Coincya wrightii)'', a species of primitive brassica
''Brassica'' () is a genus of plants in the cabbage and mustard family (Brassicaceae). The members of the genus are informally known as cruciferous vegetables, cabbages, mustard plants, or simply brassicas. Crops from this genus are sometim ...
.
By the 1980s, the eastern side of the island had become overgrown by rhododendron
''Rhododendron'' (; : ''rhododendra'') is a very large genus of about 1,024 species of woody plants in the Ericaceae, heath family (Ericaceae). They can be either evergreen or deciduous. Most species are native to eastern Asia and the Himalayan ...
s (''Rhododendron ponticum'') which had spread from a few specimens planted in the garden of Millcombe House in Victorian times
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the reign of Queen Victoria, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. Slightly different definitions are sometimes used. The era followed th ...
, but in recent years significant efforts have been made to eradicate this non-native plant.
Fauna
Terrestrial invertebrates
Two invertebrate taxa areendemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
to Lundy, with both feeding on the endemic Lundy cabbage ('' Coincya wrightii''). These are the Lundy cabbage flea beetle (''Psylliodes luridipennis
''Psylliodes luridipennis'', commonly known as the Lundy cabbage flea beetle or the bronze Lundy cabbage flea beetle, is a species of flea beetle endemic to the island of Lundy, where it lives and feeds upon the endemic Lundy cabbage (''Coincya ...
''), a species of leaf beetle
The beetle family Chrysomelidae, commonly known as leaf beetles, includes over 37,000 (and probably at least 50,000) species in more than 2,500 genera, making it one of the largest and most commonly encountered of all beetle families. Numerous s ...
(family Chrysomelidae) and the Lundy cabbage weevil (''Ceutorhynchus contractus
''Ceutorhynchus'' is a genus of true weevils in the tribe Ceutorhynchini. There are at least 400 described species in ''Ceutorhynchus''.
''Ceutorhynchus succinus'' Legalov, 2013 is a species from the Eocene of Europe found in Baltic amber.New an ...
'' var. ''pallipes''), a variety of true weevil
The Curculionidae are a family of weevils, commonly called snout beetles or true weevils. They are one of the largest animal families with 6,800 genera and 83,000 species described worldwide. They are the sister group to the family Brentidae
...
(family Curculionidae). In addition, the Lundy cabbage is the main host of a flightless form
Form is the shape, visual appearance, or configuration of an object. In a wider sense, the form is the way something happens.
Form may also refer to:
*Form (document), a document (printed or electronic) with spaces in which to write or enter dat ...
of ''Psylliodes napi
''Psylliodes napi'' is a species of flea beetle in the family Chrysomelidae
The beetle family Chrysomelidae, commonly known as leaf beetles, includes over 37,000 (and probably at least 50,000) species in more than 2,500 genera, making it one o ...
'' (another species of flea beetle) and a wide variety of other invertebrate species which are not endemic to the island. Another resident invertebrate of note is ''Atypus affinis
''Atypus affinis'', the purseweb spider, is a mygalomorph spider from Europe and North Africa.
Distribution
''A. affinis'' is found throughout much of the European mainland, in Great Britain and in North Africa, where this fossorial spider typi ...
'', the only British species of purseweb spider
Atypidae, also known as atypical tarantulas or purseweb spiders, is a spider family containing only three genera. They are accomplished ambush predators that spend most of their time in a sock-like, silken retreat on the ground from where they kil ...
.
Birds
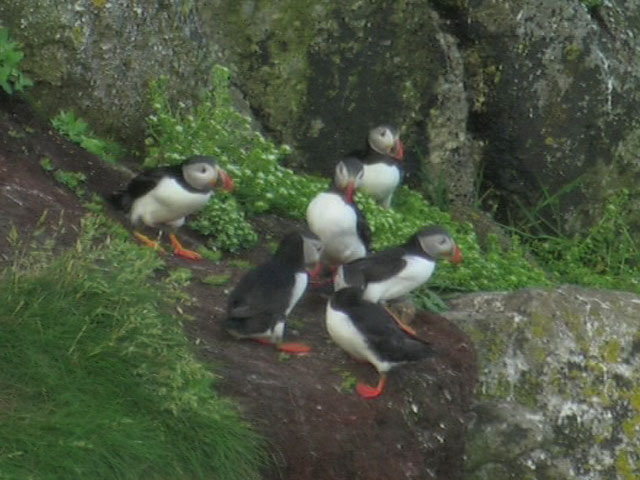
The population ofpuffins
Puffins are any of three species of small alcids (auks) in the bird genus ''Fratercula''. These are pelagic seabirds that feed primarily by diving in the water. They breed in large colonies on coastal cliffs or offshore islands, nesting in crev ...
(''Fratercula arctica'') on the island declined in the late 20th and early 21st centuries as a consequence of depredations by brown and black rat
The black rat (''Rattus rattus''), also known as the roof rat, ship rat, or house rat, is a common long-tailed rodent of the stereotypical rat genus ''Rattus'', in the subfamily Murinae. It likely originated in the Indian subcontinent, but is n ...
s (''Rattus rattus'') and possibly also as a result of commercial fishing for sand eel
Sand eel or sandeel is the common name used for a considerable number of species of fish. While they are not true eels, they are eel-like in their appearance and can grow up to in length. Many species are found off the western coasts of Europe ...
s, the puffins' principal prey. Since the elimination of rats in 2006, seabird numbers have increased. By 2023 the number of puffins had risen to 1,355 and the number of Manx shearwater
The Manx shearwater (''Puffinus puffinus'') is a medium-sized shearwater in the seabird family Procellariidae. The scientific name of this species records a name shift: Manx shearwaters were called Manks puffins in the 17th century. Puffin is an ...
to 25,000, representing 95% of England's breeding population of this seabird. The island has since 2014 become colonised by European storm petrel
The European storm petrel (''Hydrobates pelagicus''), also known as British storm petrel, or just storm petrel, is a species of seabird in the northern storm petrel family, Hydrobatidae. The small, square-tailed bird is entirely black except f ...
.
 As an isolated island on major migration routes, Lundy has a rich bird life and is a popular site for
As an isolated island on major migration routes, Lundy has a rich bird life and is a popular site for birdwatching
Birdwatching, or birding, is the observing of birds, either as a recreational activity or as a form of citizen science. A birdwatcher may observe by using their naked eye, by using a visual enhancement device such as binoculars or a telescop ...
. Large numbers of black-legged kittiwake (''Rissa tridactyla'') nest on the cliffs, as do razorbill
The razorbill (''Alca torda'') is a North Atlantic colonial seabird and the only extant member of the genus ''Alca (bird), Alca'' of the family Alcidae, the auks. It is the closest living relative of the extinct great auk (''Pinguinus impennis' ...
(''Alca torda''), common guillemot
The common murre or common guillemot (''Uria aalge'') is a large auk. It has a circumpolar distribution, occurring in low-Arctic and boreal waters in the North Atlantic and North Pacific. It spends most of its time at sea, only coming to land to ...
(''Uria aalge''), European herring gull
The European herring gull (''Larus argentatus'') is a large gull, up to long. It breeds throughout the northern and western coasts of Europe. Some European herring gulls, especially those resident in colder areas, bird migration, migrate furthe ...
(''Larus argentatus''), lesser black-backed gull
The lesser black-backed gull (''Larus fuscus'') is a large gull that breeds on the Atlantic coasts of Europe. It is migratory, wintering from the British Isles south to West Africa. However, it has increased dramatically in North America, especi ...
(''Larus fuscus''), northern fulmar
The northern fulmar (''Fulmarus glacialis''), fulmar, or Arctic fulmar is an abundant seabird found primarily in subarctic regions of the North Atlantic and North Pacific oceans. There has been one confirmed sighting in the Southern Hemisphere, ...
(''Fulmarus glacialis''), European shag
The European shag or common shag (''Gulosus aristotelis'') is a species of cormorant. It is the only member of the monotypic genus ''Gulosus''. It breeds around the rocky coasts of western and southern Europe, southwest Asia and north Africa, ma ...
(''Phalacrocorax aristotelis''), Eurasian oystercatcher
The Eurasian oystercatcher (''Haematopus ostralegus'') also known as the common pied oystercatcher, or (in Europe) just oystercatcher, is a wader in the oystercatcher bird family Haematopodidae. It has striking black and white plumage, a long st ...
(''Haematopus ostralegus''), Eurasian skylark
The Eurasian skylark (''Alauda arvensis'') is a passerine bird in the lark family, Alaudidae. It is a widespread species found across Europe and the Palearctic with introduced populations in Australia, New Zealand and on the Hawaiian Islands. I ...
(''Alauda arvensis''), meadow pipit
The meadow pipit (''Anthus pratensis'') is a small passerine bird that breeds throughout much of the Palearctic, from south-eastern Greenland and Iceland east to just east of the Ural Mountains in Russia, and south to central France and Romania; ...
(''Anthus pratensis''), common blackbird
The common blackbird (''Turdus merula'') is a species of true thrush. It is also called the Eurasian blackbird (especially in North America, to distinguish it from the unrelated New World blackbirds), or simply the blackbird. It breeds in Europ ...
(''Turdus merula''), European robin
The European robin (''Erithacus rubecula''), known simply as the robin or robin redbreast in the British Isles, is a small insectivorous passerine bird that belongs to the Old World flycatcher family Muscicapidae. It is found across Europe, ea ...
(''Erithacus rubecula''), and linnet
The common linnet (''Linaria cannabina'') is a small passerine bird of the finch family, Fringillidae. It derives its common name and the scientific name, ''Linaria'', from its fondness for hemp seeds and flax seeds—flax being the English na ...
(''Carduelis cannabina''). There are also smaller populations of peregrine falcon
The peregrine falcon (''Falco peregrinus''), also known simply as the peregrine, is a Cosmopolitan distribution, cosmopolitan bird of prey (raptor) in the family (biology), family Falconidae renowned for its speed. A large, Corvus (genus), cro ...
(''Falco peregrinus'') and raven
A raven is any of several large-bodied passerine bird species in the genus '' Corvus''. These species do not form a single taxonomic group within the genus. There is no consistent distinction between crows and ravens; the two names are assigne ...
(''Corvus corax'').
Lundy has attracted many vagrant birds, in particular species from North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
. As of 2007, the island's bird list totals 317 species. This has included the following species, each of which represents the sole British record: Ancient murrelet
The ancient murrelet (') is a bird in the auk family. The English term "murrelet" is a diminutive of "murre", a word of uncertain origins, but which may imitate the call of the common guillemot. Ancient murrelets are called "ancient" because t ...
, eastern phoebe
The eastern phoebe (''Sayornis phoebe'') is a small passerine bird. The genus name ''Sayornis'' is constructed from the specific part of Charles Lucien Bonaparte's name for Say's phoebe, ''Muscicapa saya'', and Ancient Greek ''ornis'', "bird". '' ...
, and eastern towhee
The eastern towhee (''Pipilo erythrophthalmus''), also known as chewink, joree, or joree bird, is a large American sparrow, New World sparrow. The taxonomy of the towhees has been under debate in recent decades, and formerly this bird and the spo ...
. Records of bimaculated lark, American robin
The American robin (''Turdus migratorius'') is a migratory bird of the true thrush genus and Turdidae, the wider thrush family. It is named after the European robin because of its reddish-orange breast, though the two species are not clos ...
, and common yellowthroat
The common yellowthroat (''Geothlypis trichas'') is a New World warbler. It is an abundant breeder in North America, ranging from southern Canada to central Mexico. The genus name ''Geothlypis'' is from Ancient Greek ''geo'', "ground", and ''thl ...
were also firsts for Britain (American robin has also occurred two further times on Lundy). Veery
The veery (''Catharus fuscescens'') is a small North American Thrush (bird), thrush species, a member of a group of closely related and similar species in the genus ''Catharus'', also including the gray-cheeked thrush (''C. minimus''), Bicknell's ...
s in 1987 and 1997 were Britain's second and fourth records, a Rüppell's warbler in 1979 was Britain's second, an eastern Bonelli's warbler in 2004 was Britain's fourth, and a black-faced bunting in 2001 Britain's third.
Other British Birds rarities that have been sighted (single records unless otherwise indicated) are: little bittern; gyrfalcon
The gyrfalcon ( or ) (), also abbreviated as gyr, is a bird of prey from the genus ''Falco'' (falcons and kestrels) and the largest species of the family Falconidae. A high-latitude species, the gyrfalcon breeds on the Arctic coasts and tundra, ...
(3 records); little
Little is a synonym for small size and may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Little'' (album), 1990 debut album of Vic Chesnutt
* ''Little'' (film), 2019 American comedy film
*The Littles, a series of children's novels by American author John P ...
and Baillon's crake
Baillon's crake (''Zapornia pusilla''), also known as the marsh crake, is a small waterbird of the family Rallidae.
Distribution
Their breeding habitat is sedge beds in Europe, mainly in the east, and across the Palearctic. They used to breed in ...
s; collared pratincole
The collared pratincole (''Glareola pratincola''), also known as the common pratincole or red-winged pratincole, is a wader in the pratincole family, Glareolidae. As with other pratincoles, it is native to the Old World.
Taxonomy
The collared p ...
; semipalmated (5 records), least (2 records), white-rumped, and Baird's (2 records) sandpipers; Wilson's phalarope
Wilson's phalarope (''Phalaropus tricolor'') is a small wader. This bird, the largest of the phalaropes, breeds in the prairies of North America in western Canada and the western United States. It is migratory, wintering in inland salt lakes n ...
; laughing gull
The laughing seagull (''Leucophaeus atricilla'') is a medium-sized gull of North America, North and South America. Named for its laugh-like call, it is an opportunistic omnivore and scavenger. It breeds in large colonies mostly along the Atlantic ...
; bridled tern
The bridled tern (''Onychoprion anaethetus'')Sometimes the name is (wrongly?) spelled as ''S. anaestheta'', for instance in: is a seabird of the family Laridae. It is a bird of the tropical oceans. The scientific name is from Ancient Greek. Th ...
; Pallas's sandgrouse; great spotted, black-billed, and yellow-billed (3 records) cuckoos; European roller
The European roller (''Coracias garrulus'') is the only member of the Coraciidae, roller family breeding in Europe. Its range extends into the Maghreb, West Asia and Central Asia. It winters in southern Africa, primarily in dry wooded savanna and ...
; olive-backed pipit
The olive-backed pipit (''Anthus hodgsoni'') is a small passerine bird of the pipit (''Anthus'') genus, which breeds across southern, north central and eastern Asia, as well as in the north-eastern European Russia. It is a long-distance bird migr ...
; citrine wagtail
The citrine wagtail (''Motacilla citreola'') is a small songbird in the family Motacillidae.
Etymology
The term ''citrine'', and the specific name ''citreola'', refers to its yellowish colouration.
Taxonomy
Its systematics, phylogeny and taxon ...
; Alpine accentor
The alpine accentor (''Prunella collaris'') is a small passerine bird in the family Prunellidae, which is native to Eurasia and North Africa.
Taxonomy
The Alpine accentor was described by the Austrian naturalist Giovanni Antonio Scopoli in 176 ...
; thrush nightingale
The thrush nightingale (''Luscinia luscinia''), also known as the sprosser, is a small passerine bird that was formerly classed as a member of the thrush family Turdidae, but is now more generally considered to be an Old World flycatcher, Muscic ...
; red-flanked bluetail
The red-flanked bluetail (''Tarsiger cyanurus''), also known as the orange-flanked bush-robin, is a small passerine bird that was formerly classed as a member of the thrush family Turdidae, but is now more generally considered to be an Old World ...
; western black-eared (2 records) and desert
A desert is a landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions create unique biomes and ecosystems. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About one-third of the la ...
wheatears; White's
White's is a gentlemen's club in St James's, London. Founded in 1693 as a hot chocolate shop in Mayfair, it is London's oldest club and therefore the oldest private members' club in the world. It moved to its current premises on St James's St ...
, Swainson's (3 records), and grey-cheeked (2 records) thrushes; Sardinian (2 records), Arctic
The Arctic (; . ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the North Pole, lying within the Arctic Circle. The Arctic region, from the IERS Reference Meridian travelling east, consists of parts of northern Norway ( ...
(3 records), Radde's warbler, Radde's, and western Bonelli's warblers; Isabelline shrike, Isabelline and lesser grey shrikes; red-eyed vireo (7 records); two-barred crossbill; yellow-rumped warbler, yellow-rumped and blackpoll warblers; yellow-breasted bunting, yellow-breasted (2 records) and black-headed buntings (3 records); rose-breasted grosbeak (2 records); bobolink; and Baltimore oriole (2 records).
Mammals
 Lundy is home to an unusual range of introduced mammals, including a distinct breed of wild pony, the Lundy pony, as well as Soay sheep (''Ovis aries''), sika deer (''Cervus nippon''), feral goats (''Capra aegagrus hircus''), and European rabbit, some of which are Melanism, melanistic.
Other mammals which have made the island their home include the grey seal (''Halichoerus grypus'') and the Eurasian pygmy shrew (''Sorex minutus''). Until their elimination in 2006, in order to protect the nesting seabirds, Lundy was one of the few places in the UK where the
Lundy is home to an unusual range of introduced mammals, including a distinct breed of wild pony, the Lundy pony, as well as Soay sheep (''Ovis aries''), sika deer (''Cervus nippon''), feral goats (''Capra aegagrus hircus''), and European rabbit, some of which are Melanism, melanistic.
Other mammals which have made the island their home include the grey seal (''Halichoerus grypus'') and the Eurasian pygmy shrew (''Sorex minutus''). Until their elimination in 2006, in order to protect the nesting seabirds, Lundy was one of the few places in the UK where the black rat
The black rat (''Rattus rattus''), also known as the roof rat, ship rat, or house rat, is a common long-tailed rodent of the stereotypical rat genus ''Rattus'', in the subfamily Murinae. It likely originated in the Indian subcontinent, but is n ...
(''Rattus rattus'') could be found regularly.
Marine habitat
In 1971, a proposal was made by the Lundy Field Society to establish a marine reserve, and the survey was led by Dr Keith Hiscock, supported by a team of students from Bangor University. Provision for the establishment of statutory Marine Nature Reserves was included in the Wildlife and Countryside Act 1981, and on 21 November 1986 the Secretary of State for the Environment announced the designation of a statutory reserve at Lundy. There is an outstanding variety of marine habitats and wildlife, and a large number of rare and unusual species in the waters around Lundy, including some species of seaweed, Sponge, branching sponges, Gorgonian, sea fans, and Coral, cup corals. In 2003, the first statutory No Take Zone (NTZ) for marine nature conservation in the UK was set up in the waters to the east of Lundy island. In 2008, this was declared as having been successful in several ways including the increasing size and number of Homarus gammarus, lobsters within the reserve, and potential benefits for other marine wildlife. However, the no take zone has received a mixed reaction from local fishermen. On 12 January 2010 the island became Britain's first Marine protected area, Marine Conservation Zone designated under the Marine and Coastal Access Act 2009, designed to help to preserve important habitats and species. Three species of cetacean are regularly seen from the island; them being the common bottlenose dolphin, bottlenose dolphin (''Tursiops truncatrus''), common dolphin (''Delphinus delphis''), and harbour porpoise (''Phocoena phocoena''). Other cetacean species that are sighted from Lundy, albeit more rarely, are the Common minke whale, minke whale (''Balaenoptera acutorostrata''), Risso's dolphin (''Grampus griseus''), and long-finned pilot whale (''Globicephala melas''). Basking sharks (''Cetorhinus maximus''), ocean sunfish (''Mola mola''), and leatherback sea turtles (''Dermochelys coriacea'') are also seen around Lundy, especially off the more sheltered eastern coast and only during the warmer months. Furthermore, there is a grey seal (''Halichoerus grypus'') colony consisting of roughly 60 animals that live around the island.
Three species of cetacean are regularly seen from the island; them being the common bottlenose dolphin, bottlenose dolphin (''Tursiops truncatrus''), common dolphin (''Delphinus delphis''), and harbour porpoise (''Phocoena phocoena''). Other cetacean species that are sighted from Lundy, albeit more rarely, are the Common minke whale, minke whale (''Balaenoptera acutorostrata''), Risso's dolphin (''Grampus griseus''), and long-finned pilot whale (''Globicephala melas''). Basking sharks (''Cetorhinus maximus''), ocean sunfish (''Mola mola''), and leatherback sea turtles (''Dermochelys coriacea'') are also seen around Lundy, especially off the more sheltered eastern coast and only during the warmer months. Furthermore, there is a grey seal (''Halichoerus grypus'') colony consisting of roughly 60 animals that live around the island.
Transport

To the island
There are two ways to get to Lundy, depending on the time of year. In the summer months (April to October) visitors are carried on theLandmark Trust
The Landmark Trust is a British architectural conservation, building conservation charitable organization, charity, founded in 1965 by John Smith (Conservative politician), Sir John and Lady Smith, that rescues buildings of historic interest or ...
's own vessel, MS Oldenburg, MS ''Oldenburg'', which sails from both Bideford
Bideford ( ) is a historic port town on the estuary of the River Torridge in north Devon, South West England. It is the main town of the Torridge District, Torridge Districts of England, local government district.
Toponymy
In ancient records Bi ...
and Ilfracombe
Ilfracombe ( ) is a seaside resort and civil parishes in England, civil parish on the North Devon coast, England, with a small harbour surrounded by cliffs.
The parish stretches along the coast from the 'Coastguard Cottages' in Hele Bay towar ...
. Sailings are usually three days a week, on Tuesdays, Thursdays and Saturdays, with additional sailings on Wednesdays during July and August. The voyage takes on average two hours, depending on ports, tides and weather. The ''Oldenburg'' was first registered in Bremen, Germany, in 1958 and has been sailing to Lundy since being bought by the Lundy Company Ltd in 1985.
In the winter months (November to March) the island is served by a scheduled helicopter service from Hartland Point
Hartland Point is a high rocky outcrop of land on the north-western tip of the Devon coast in England. It is three miles (5 km) north-west of the village of Hartland. The point marks the western limit (on the English side) of the Bristol C ...
. The helicopter operates on Mondays and Fridays.
A grass runway of is available, allowing access to small STOL aircraft.
On the island
In 2007, Derek Green, Lundy's general manager, launched an appeal to raise £250,000 to save the Beach Road, which had been damaged by heavy rain and high seas. The road was built in the first half of the 19th century to provide people and goods with safe access to the top of the island, above the only jetty. The fund-raising was completed on 10 March 2009.Lighthouses
The island has a pair of active lights built in 1897 and an older lighthouse no longer in service.Electricity supply
There is a small power station comprising three Cummins (corporation), Cummins B and C series diesel engines, offering an approximately 150 kVA 3-phase supply to most of the island buildings. Waste heat from the engine jackets is cogeneration, used for a district heating pipe. There are also plans to collect the waste heat from the engine exhaust heat gases to feed into the district heat network to improve the efficiency further. The power is normally switched off between 00:00 and 06:30.Administration
The island is an unparished area of Torridge District, Torridge district in the county ofDevon
Devon ( ; historically also known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial county in South West England. It is bordered by the Bristol Channel to the north, Somerset and Dorset to the east, the English Channel to the south, and Cornwall to the west ...
. It forms part of the Wards and electoral divisions of the United Kingdom, ward of Clovelly, Clovelly Bay.Ordnance SurveyElection Maps It is part of the constituency electing the Member of Parliament for Torridge and Tavistock (UK Parliament constituency), Torridge and Tavistock and was from 1999 to 2020 part of the South West England (European Parliament constituency), South West England constituency for the European Parliament. In 2013, the island became a separate Church of England ecclesiastical parish.
Stamps
Owing to a decline in population and lack of interest in the mail contract, the General Post Office, GPO ended its presence on Lundy at the end of 1927. For the next two years Harman handled the mail to and from the island without charge. On 1 November 1929, he decided to offset the expense by issuing two postage stamps ( puffin in pink and 1 puffin in blue). One puffin is equivalent to one English penny. The printing of Puffin stamps continues to this day and they are available at face value from the Lundy Post Office. One used to have to stick Lundy stamps on the back of the envelope; but from 1962 Royal Mail allowed their use on the front of the envelope, but placed on the left side, with the right side reserved for the Royal Mail postage stamp or stamps. Lundy stamps are cancelled by a circular Lundy hand stamp. In 1974, the face value of the Lundy Island stamps was increased to include Royal Mail charges in addition to the charge for transporting mail to the mainland and so from that year it has not been necessary to affix a separate Royal Mail postage stamp. Lundy stamps are a type of postage stamp known to philatelists as "local carriage labels" or "local stamps". Issues of increasing value were made over the years, including air mail, featuring a variety of subjects. The market value of the early issues has risen substantially over the years. For the many thousands of annual visitors Lundy stamps have become part of the collection of the many British Local Posts collectors. The first catalogues of these stamps included Gerald Rosen's 1970 ''Catalogue of British Local Stamps''. Later specialist catalogues include ''Stamps of Lundy Island'' by Stanley Newman, first published in 1984, ''Phillips Modern British Locals CD Catalogue'', published since 2003, and ''Labbe's Specialised Guide to Lundy Island Stamps'', published since 2005 and now in its 11th Edition. Labbe's Guide is considered the gold standard of Lundy catalogues owing to its extensive approach to varieties, errors, specialised items, and "fantasy" issues. There is a comprehensive collection of these stamps in the Chinchen Collection, donated by Barry Chinchen to the British Library Philatelic Collections in 1977 and now held by the British Library. This is also the home of the Landmark Trust Lundy Island Philatelic Archive which includes artwork, texts and essays as well as postmarking devices and issued stamps.by David Beech
See also
* Barbara Kathleen Snow, Barbara Whitaker, former warden * Coins of Lundy * Puffin Island (Anglesey), Puffin IslandReferences
Further reading
* *External links
*Lundy Marine Reserve at Protect Planet Ocean
* {{Authority control Lundy, Islands of the Bristol Channel Islands of Devon National nature reserves in England National Trust properties in Devon Nature reserves in Devon Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Devon Sites of Special Scientific Interest notified in 1987 Special Areas of Conservation in England Tourist attractions in Devon Ports and harbours of the Bristol Channel Barbary piracy Invasions of England Marine reserves of the United Kingdom Philately of the United Kingdom Natural regions of England Shipwrecks of England Aviation accidents and incidents locations in England Island restoration Car-free islands of Europe Former civil parishes in Devon Unparished areas in Devon Torridge District Pirate dens and locations Barbary slave raids