scalpels on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A scalpel or bistoury is a small and extremely sharp bladed instrument used for
Sonic scalpel
{{Surgical instruments Medical knives Surgical instruments
surgery
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery s ...
, anatomical
Anatomy () is the branch of morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old scien ...
dissection
Dissection (from Latin ' "to cut to pieces"; also called anatomization) is the dismembering of the body of a deceased animal or plant to study its anatomical structure. Autopsy is used in pathology and forensic medicine to determine the cause of ...
, podiatry
Podiatry ( ), also know as podiatric medicine and surgery ( ), is a branch of medicine devoted to the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disorders of the foot, ankle and lower limb. The healthcare professional is known as a podiatrist. The US ...
and various handicraft
A handicraft is a traditional main sector of craft making and applies to a wide range of creative and design activities that are related to making things with one's hands and skill, including work with textiles, moldable and rigid material ...
s. A lancet is a double-edged scalpel.
Scalpel blades are usually made of hardened and tempered steel, stainless steel
Stainless steel, also known as inox, corrosion-resistant steel (CRES), or rustless steel, is an iron-based alloy that contains chromium, making it resistant to rust and corrosion. Stainless steel's resistance to corrosion comes from its chromi ...
, or high carbon steel; in addition, titanium
Titanium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in ...
, ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcela ...
, diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Diamond is tasteless, odourless, strong, brittle solid, colourless in pure form, a poor conductor of e ...
and even obsidian
Obsidian ( ) is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extrusive rock, extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock. Produced from felsic lava, obsidian is rich in the lighter element ...
knives are not uncommon. For example, when performing surgery under MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and rad ...
guidance, steel blades are unusable (the blades would be drawn to the magnets and would also cause image artifacts). Historically, the preferred material for surgical scalpels was silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
. Scalpel blades are also offered by some manufacturers with a zirconium nitride–coated edge to improve sharpness and edge retention. Others manufacture blades that are polymer-coated to enhance lubricity during a cut.
Scalpels may be single-use disposable or re-usable. Re-usable scalpels can have permanently attached blades that can be sharpened or, more commonly, removable single-use blades. Disposable scalpels usually have a plastic handle with an extensible blade (like a utility knife
A utility knife is any type of knife used for general manual work purposes.Peterson, Harold L., ''Daggers and Fighting Knives of the Western World'', London: Herbert Jenkins Ltd., , p. 1 Such knives were originally fixed-blade knives with dur ...
) and are used once, then the entire instrument is discarded. Scalpel blades are usually individually packed in sterile pouches but are also offered non-sterile.
Alternatives to scalpels in surgical applications include electrocautery and laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
s.
History
left, A lancet belonging to Edward Jenner Obsidian scalpels older than 2100 BC have been found in a Bronze Age settlement in Turkey. Skulls from the same time and place show signs of brain surgery.Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
ians made incisions for embalming with scalpels of sharpened obsidian
Obsidian ( ) is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extrusive rock, extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock. Produced from felsic lava, obsidian is rich in the lighter element ...
, a material that is still in use.
The first medical writings of ancient Greeks indicate they were commonly using tools identical to today's scalpels around 500 BC. The ''amphismela'' was an anatomical knife-edged on both sides. The term comes from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
''αμφι'' (''utrinque'', "on both sides"), and ''μελιζω'' (''inside'', "I cut").
Ancient Romans
The Roman people was the ethnicity and the body of Roman citizenship, Roman citizens
(; ) during the Roman Kingdom, the Roman Republic, and the Roman Empire. This concept underwent considerable changes throughout the long history of the Roman ...
used more than 150 different surgical instruments, including scalpels.
10th century Arab-Spanish surgeon Albucasis
Abū al-Qāsim Khalaf ibn al-'Abbās al-Zahrāwī al-Ansari (; c. 936–1013), popularly known as al-Zahrawi (), Latinised as Albucasis or Abulcasis (from Arabic ''Abū al-Qāsim''), was an Arab physician, surgeon and chemist from al-And ...
invented a retractable scalpel.
The French used an amphismela in the 1700s.
South African scientists showed that a blunt scalpel caused sharp cuts if the blade was subjected to ultrasound. Applications might be in energy-saving paper cutting.
Operation
In the ''palmar grip'', also called the "dinner knife" grip, the handle is held with the second through fourth fingers and secured along the base of the thumb, with the index finger extended along the top rear of the blade and the thumb along the side of the handle. This grip is best for initial incisions and larger cuts. In the ''pencil grip'', best used for more accurate cuts with smaller blades (e.g. #15) and the #7 handle, the scalpel is held with the tips of the first and second fingers and the tip of the thumb with the handle resting on the fleshy base of the index finger and thumb.Types
Surgical
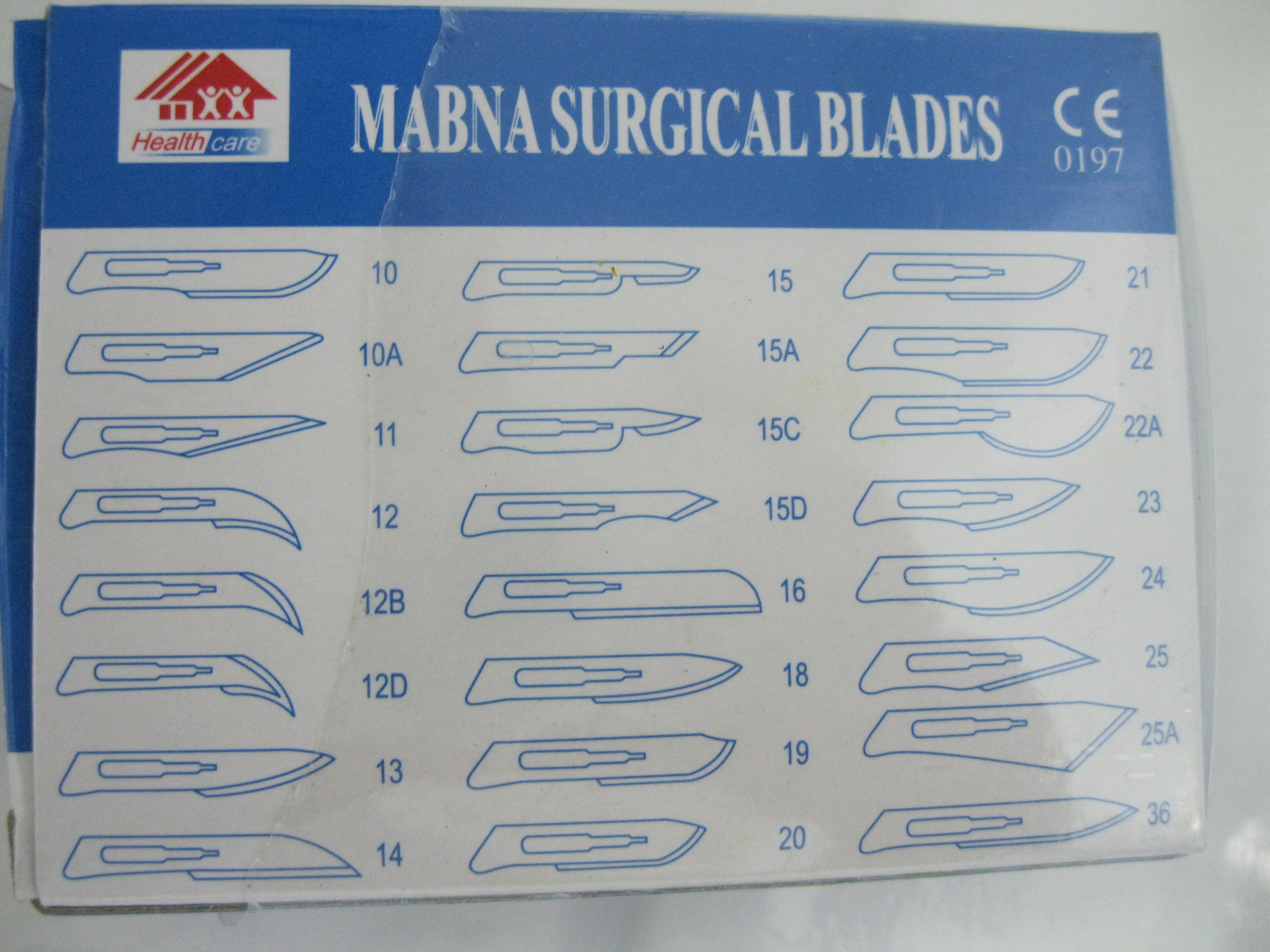
Surgical scalpels consist of two parts, a blade and a handle. The handles are often reusable, with the blades being replaceable. In medical applications, each blade is only used once (sometimes just for a single, small cut). The handle is also known as a "B.P. handle", named after Charles Russell Bard and Morgan Parker, founders of the Bard-Parker Company. Morgan Parker patented the 2-piece scalpel design in 1915 and Bard-Parker developed a method of cold sterilization that would not dull the blades, as did the heat-based method that was previously used. The handle of medical scalpels come in several basic types. The first is a flat handle used in the #3 and #4 handles. The #7 handle is more like a long writing pen, rounded at the front and flat at the back. A #4 handle is larger than a #3. #5 handles are also common, and are round, with a patterning to ensure a non-slip grip. Blades are manufactured with a corresponding fitment size so that they fit on only one size handle. The following table of blades is incomplete and some blades listed may work with handles not specified here. A lancet has a double-edged blade and a pointed end for making small incisions or drainage punctures.Handicraft
X-Acto knife Graphical and model-making scalpels tend to have round handles, with textured grips (either knurled metal or soft plastic). The blade is usually flat and straight, allowing it to be run easily against astraightedge
A straightedge or straight edge is a tool used for drawing straight lines, or checking their straightness. If it has equally spaced markings along its length, it is usually called a ruler.
Straightedges are used in the automotive service and ma ...
to produce straight cuts.
There are many kinds of graphic arts blades; the most common around the graphic design studio is the #11 blade which is very similar to a #11 surgical blade (q.v.). Other blade shapes are used for wood carving
Wood carving (or woodcarving) is a form of woodworking by means of a cutting tool (knife) in one hand or a chisel by two hands or with one hand on a chisel and one hand on a mallet, resulting in a wooden figure or figurine, or in the sculpture, ...
, cutting leather and heavy fabric.
Blades
Safety
Rising awareness of the dangers of sharps in a medical environment around the beginning of the 21st century led to the development of various methods of protecting healthcare workers from accidental cuts and puncture wounds. According to theCenters for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
, as many as 1,000 people were subject to accidental needle sticks and lacerations each day in the United States while providing medical care. Additionally, surgeons can expect to suffer hundreds of such injuries over the course of their career. Scalpel blade injuries were among the most frequent sharps injuries, second only to needlesticks. Scalpel injuries made up 7 percent to 8 percent of all sharps injuries in 2001.
"Scalpel Safety" is a term coined to inform users that there are choices available to them to ensure their protection from this common sharps injury.
Safety scalpels are becoming increasingly popular as their prices come down and also on account of legislation such as the Needle Stick Prevention Act, which requires hospitals to minimize the risk of pathogen transmission through needle or scalpel-related accidents.
There are essentially two kinds of disposable safety scalpels offered by various manufacturers. They can be either classified as retractable blade or retractable sheath type. The retractable blade version made by companies such as OX Med Tech, DeRoyal, Jai Surgicals, Swann Morton, and PenBlade are more intuitive to use due to their similarities to a standard box-cutter. Retractable sheath versions have much stronger ergonomic feel for the doctors and are made by companies such as Aditya Dispomed
Aditya may refer to:
* Ādityas, a group of Hindu deities
* An alternative name for Surya, the Sun in later Hinduism
* Aditya (name)
** Aditya (actor) (born 1978), Indian film producer and actor
* Aditya (boat), ''Aditya'' (boat), solar-powered fe ...
, Aspen Surgical and Southmedic. A few companies have also started to offer a safety scalpel with a reusable metal handle. In such models, the blade is usually protected in a cartridge. Such systems usually require a custom handle and the price of blades and cartridges is considerably more than for conventional surgical blades.
There are various scalpel blade removers on the market that allows users to safely remove blades from the handle, instead of dangerously using fingers or forceps. In the medical field, when taking into account activation rates, the combination of a single-handed scalpel blade remover with a passing tray or a neutral zone was as safe and up to five times safer than a safety scalpel.Fuentes, H., et al. (2008). "Scalpel Safety": Modeling the effectiveness of different safety devices' ability to reduce scalpel blade injuries." The International Journal of Risk & Safety in Medicine 20(1–2):83–89. There are companies which offer a single-handed scalpel blade remover that complies with regulatory requirements such as US Occupational Safety and Health Administration
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA; ) is a regulatory agency of the United States Department of Labor that originally had federal visitorial powers to inspect and examine workplaces. The United States Congress established ...
Standards.
The usage of both safety scalpels and a single-handed blade remover, combined with a hands-free passing technique, are potentially effective in reducing scalpel blade injuries. It is up to employers and scalpel users to consider and use safer and more effective scalpel safety measures when feasible.
See also
* * *References
External links
Sonic scalpel
{{Surgical instruments Medical knives Surgical instruments