Scabies on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Scabies (; also sometimes known as the seven-year itch) is a contagious human skin
 The characteristic symptoms of a scabies infection include intense
The characteristic symptoms of a scabies infection include intense
File:Acarodermatitis Fuß.jpg, Scabies of the foot
File:Acarodermatitis Arm.jpg, Scabies of the arm
File:Acarodermatitis Hand.jpg, Scabies of the hand
In most people, the trails of the burrowing mites are linear or S-shaped tracks in the skin, often accompanied by rows of small, pimple-like mosquito or insect bites. Lesions are symmetrical and mainly affect the hands, wrists, axillae, thighs, buttocks, waist, soles of the feet, areola, and vulva in females, and penis and scrotum in males. The neck and above are usually not affected, except in cases of crusted scabies and infestations of infants, the elderly, and the immunocompromised. With link to many images Symptoms typically appear two to six weeks after infestation for individuals never before exposed to scabies. For those having been previously exposed, the symptoms can appear within several days after infestation. However, symptoms may appear after several months or years.
 The elderly, disabled, and people with impaired immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, cancer, or those on
The elderly, disabled, and people with impaired immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, cancer, or those on
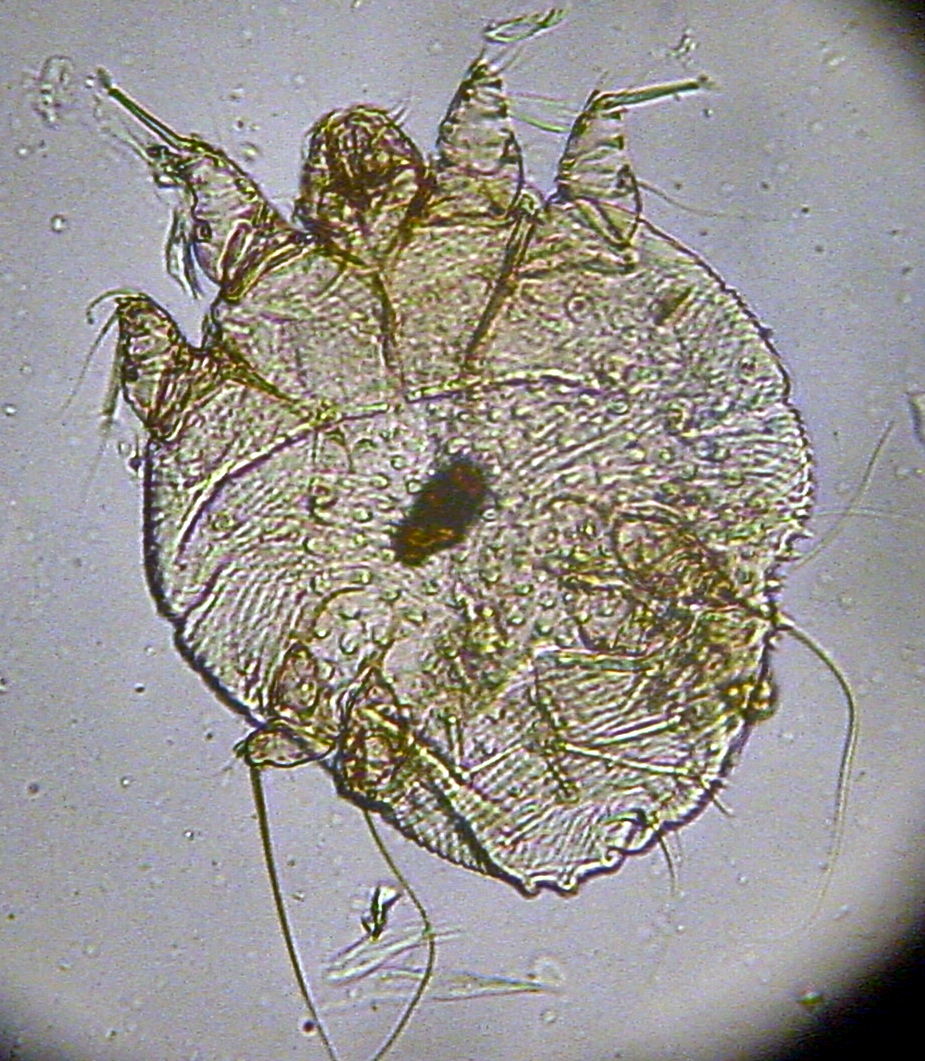 Scabies may be diagnosed clinically in geographical areas where it is common when diffuse itching presents along with either a lesion in two typical spots or itchiness is present in another household member. The classical sign of scabies is the burrow made by a mite within the skin. To detect the burrow, the suspected area is rubbed with ink from a fountain pen or a topical
Scabies may be diagnosed clinically in geographical areas where it is common when diffuse itching presents along with either a lesion in two typical spots or itchiness is present in another household member. The classical sign of scabies is the burrow made by a mite within the skin. To detect the burrow, the suspected area is rubbed with ink from a fountain pen or a topical
File:ScabiesD04.jpg, Day 4
File:ScabiesD08.JPG, Day 8 (treatment begins)
File:ScabiesD12.JPG, Day 12 (under treatment)
File:ScabiesHealed.JPG, Healed
 Scabies may occur in some domestic and wild animals; the mites that cause these infestations are of different subspecies from the one typically causing the human form. These subspecies can infest animals that are not their usual hosts, but such infections do not last long. Scabies-infected animals experience severe itching and secondary skin infections. They often lose weight and become frail.
The most frequently diagnosed form of scabies in domestic animals is sarcoptic mange, caused by the subspecies ''Sarcoptes scabiei canis'', most commonly in dogs and cats. Sarcoptic mange is transmissible to humans who come into prolonged contact with infested animals, and is distinguished from human scabies by its distribution on skin surfaces covered by clothing. Scabies-infected domestic fowl develop what is known as "scaly leg". Domestic animals that have gone feral and have no veterinary care are frequently affected by scabies. Nondomestic animals have also been observed to develop scabies. Gorillas, for instance, are known to be susceptible to infection by contact with items used by humans, and it is a fatal disease of wombats.
Scabies is also a concern for
Scabies may occur in some domestic and wild animals; the mites that cause these infestations are of different subspecies from the one typically causing the human form. These subspecies can infest animals that are not their usual hosts, but such infections do not last long. Scabies-infected animals experience severe itching and secondary skin infections. They often lose weight and become frail.
The most frequently diagnosed form of scabies in domestic animals is sarcoptic mange, caused by the subspecies ''Sarcoptes scabiei canis'', most commonly in dogs and cats. Sarcoptic mange is transmissible to humans who come into prolonged contact with infested animals, and is distinguished from human scabies by its distribution on skin surfaces covered by clothing. Scabies-infected domestic fowl develop what is known as "scaly leg". Domestic animals that have gone feral and have no veterinary care are frequently affected by scabies. Nondomestic animals have also been observed to develop scabies. Gorillas, for instance, are known to be susceptible to infection by contact with items used by humans, and it is a fatal disease of wombats.
Scabies is also a concern for
 The International Alliance for the Control of Scabies was started in 2012, and brings together over 150 researchers, clinicians, and public-health experts from more than 15 countries. It has managed to bring the global health implications of scabies to the attention of the
The International Alliance for the Control of Scabies was started in 2012, and brings together over 150 researchers, clinicians, and public-health experts from more than 15 countries. It has managed to bring the global health implications of scabies to the attention of the
American Academy of Dermatology pamphlet on Scabies
{{Authority control Arthropod infestations Articles containing video clips Mammal diseases Parasitic arthropods of humans Parasitic infestations, stings, and bites of the skin Tropical diseases Wikipedia infectious disease articles ready to translate Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate
infestation
Infestation is the state of being invaded or overrun by pests or parasites. It can also refer to the actual organisms living on or within a host.
Terminology
In general, the term "infestation" refers to parasitic diseases caused by animals su ...
by the tiny (0.2–0.45 mm) mite
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods) of two large orders, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari. However, most recent genetic analyses do not recover the two as eac ...
''Sarcoptes scabiei
''Sarcoptes scabiei'' (/sɑː''r''ˈkɒptiːz skeɪˈbiːaɪ/ Traditional English pronunciation of Latin) or the itch mite is a parasite, parasitic mite found in all parts of the world that burrows into skin and causes scabies. Humans become Inf ...
'', variety ''hominis''. The word is from . The most common symptoms are severe itchiness
An itch (also known as pruritus) is a sensation that causes a strong desire or reflex to scratch. Itches have resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of sensory experience. Itches have many similarities to pain, and while both ...
and a pimple
A pimple or zit is a kind of comedo that results from excess sebum and dead skin cells getting trapped in the pores of the skin. In its aggravated state, it may evolve into a pustule or papule. Pimples can be treated by acne medications, anti ...
-like rash. Occasionally, tiny burrow
file:Chipmunk-burrow (exits).jpg, An eastern chipmunk at the entrance of its burrow
A burrow is a hole or tunnel excavated into the ground by an animal to construct a space suitable for habitation or temporary refuge, or as a byproduct of Animal lo ...
s may appear on the skin. In a first-ever infection, the infected person usually develops symptoms within two to six weeks. During a second infection, symptoms may begin within 24 hours. These symptoms can be present across most of the body or just in certain areas such as the wrists, between fingers, or along the waistline. The head may be affected, but this is typically only in young children. The itch is often worse at night. Scratching may cause skin breakdown and an additional bacterial infection in the skin.
Various names have been given to this condition and the name 'seven year itch' has been recorded in many documents from the 1800's. Although the 1952 The_Seven_Year_Itch_(play) and modern treatment methods have generally changed this name to refer to human relationships, the condition was historically very difficult to treat.
Scabies is caused by infection with the female mite
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods) of two large orders, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari. However, most recent genetic analyses do not recover the two as eac ...
''Sarcoptes scabiei ''var.'' hominis'', an ectoparasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted str ...
. The mites burrow into the skin to live and deposit eggs. The symptoms of scabies are due to an allergic reaction
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are various conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include Allergic rhinitis, hay fever, Food allergy, food al ...
to the mites. Often, only between 10 and 15 mites are involved in an infection. Scabies most often spreads during a relatively long period of direct skin contact with an infected person (at least 10 minutes) such as that which may occur during sexual activity or living together. Spread of the disease may occur even if the person has not developed symptoms yet. Crowded living conditions, such as those found in child-care facilities, group homes, and prisons, increase the risk of spread. Areas with a lack of access to water also have higher disease rates. Crusted scabies is a more severe form of the disease, not essentially different but an infestation by huge numbers of mites that typically only affects those with a poor immune system; the number of mites also makes them much more contagious. In these cases, the spread of infection may occur during brief contact or by contaminated objects. The mite is tiny and at the limit of detection with the human eye. It is not readily obvious; factors that aid in detection are good lighting, magnification, and knowing what to look for. Diagnosis is based either on detecting the mite (confirmed scabies), detecting typical lesions in a typical distribution with typical historical features (clinical scabies), or detecting atypical lesions or atypical distribution of lesions with only some historical features present (suspected scabies).
Several medications are available to treat those infected, including oral and topical ivermectin
Ivermectin is an antiparasitic drug. After its discovery in 1975, its first uses were in veterinary medicine to prevent and treat heartworm and acariasis. Approved for human use in 1987, it is used to treat infestations including head lice ...
, permethrin
Permethrin is a medication and an insecticide. As a medication, it is used to treat scabies and lice. It is applied to the skin as a cream or lotion. As an insecticide, it can be sprayed onto outer clothing or mosquito nets to kill the insects ...
, crotamiton, and lindane creams. Sexual contacts within the last month and people who live in the same house should also be treated at the same time. Bedding and clothing used in the last three days should be washed in hot water and dried in a hot dryer. As the mite does not live for more than three days away from human skin, more washing is not needed. Symptoms may continue for two to four weeks following treatment. If after this time symptoms continue, retreatment may be needed.
Scabies is one of the three most common skin disorders in children, along with ringworm
Dermatophytosis, also known as tinea and ringworm, is a mycosis, fungal infection of the skin (a dermatomycosis), that may affect skin, hair, and nails. Typically it results in a red, itchy, scaly, circular rash. Hair loss may occur in the a ...
and bacterial skin infections. As of 2015, it affects about 204 million people (2.8% of the world population). It is equally common in both sexes. The young and the old are more commonly affected. It also occurs more commonly in the developing world
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreeme ...
and tropical climate
Tropical climate is the first of the five major climate groups in the Köppen climate classification identified with the letter A. Tropical climates are defined by a monthly average temperature of or higher in the coolest month, featuring hot te ...
s. Other animals do not spread human scabies; similar infection in other animals is known as sarcoptic mange, and is typically caused by slightly different but related mites.
Signs and symptoms
 The characteristic symptoms of a scabies infection include intense
The characteristic symptoms of a scabies infection include intense itching
An itch (also known as pruritus) is a sensation that causes a strong desire or reflex to scratch. Itches have resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of sensory experience. Itches have many similarities to pain, and while both ...
and superficial burrows. Because the host develops the symptoms as a reaction to the mites' presence over time, typically a delay of four to six weeks occurs between the onset of infestation and the onset of itching. Similarly, symptoms often persist for one to several weeks after successful eradication of the mites. As noted, those re-exposed to scabies after successful treatment may exhibit symptoms of the new infestation in a much shorter period—as little as one to four days.
Itching
In the classic scenario, the itch is made worse by warmth and is usually experienced as being worse at night, possibly because distractions are fewer. As a symptom, it is less common in the elderly.Rash
The superficial burrows of scabies usually occur in the area of the finger webs, feet, ventral wrists, elbows, back, buttocks, and external genitals. Except in infants and the immunosuppressed, infection generally does not occur in the skin of the face or scalp. The burrows are created by the excavation of the adult mite in theepidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and Subcutaneous tissue, hypodermis. The epidermal layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the ...
. Acropustulosis, or blisters and pustules on the palms and soles of the feet, are characteristic symptoms of scabies in infants.
Crusted scabies
 The elderly, disabled, and people with impaired immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, cancer, or those on
The elderly, disabled, and people with impaired immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, cancer, or those on immunosuppressive medications
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent the activity of the immune system.
Classification
Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified ...
, are susceptible to crusted scabies (also called Norwegian scabies). On those with weaker immune systems, the host becomes a more fertile breeding ground for the mites, which spread over the host's body, except the face. The mites in crusted scabies are not more virulent than in noncrusted scabies but are much more numerous, sometimes up to two million. People with crusted scabies exhibit scaly rashes, slight itching, and thick crusts of skin that contain large numbers of scabies mites. For this reason, persons with crusted scabies are more contagious to others than those with typical scabies. Such areas make eradication of mites particularly difficult, as the crusts protect the mites from topical miticides/scabicides, necessitating prolonged treatment of these areas.
Cause
Scabies mite
In the 18th century, Italian biologists Giovanni Cosimo Bonomo and Diacinto Cestoni (1637–1718) described the mite now called ''Sarcoptes scabiei
''Sarcoptes scabiei'' (/sɑː''r''ˈkɒptiːz skeɪˈbiːaɪ/ Traditional English pronunciation of Latin) or the itch mite is a parasite, parasitic mite found in all parts of the world that burrows into skin and causes scabies. Humans become Inf ...
'', variety ''hominis'', as the cause of scabies. ''Sarcoptes'' is a genus of skin parasites and part of the larger family of mites collectively known as scab mites. These organisms have eight legs as adults and are placed in the same phylogenetic class (Arachnida
Arachnids are arthropods in the class Arachnida () of the subphylum Chelicerata. Arachnida includes, among others, spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites, pseudoscorpions, harvestmen, camel spiders, whip spiders and vinegaroons.
Adult arachnids ...
) as spiders and ticks.
''S. scabiei'' mites are under 0.5 mm in size; they are sometimes visible as pinpoints of white. Gravid females tunnel into the dead, outermost layer (stratum corneum
The stratum corneum (Latin language, Latin for 'horny layer') is the outermost layer of the epidermis (skin), epidermis. Consisting of dead tissue, it protects underlying tissue from infection, dehydration, chemicals and mechanical stress. It is ...
) of a host's skin and deposit eggs in the shallow burrows. The eggs hatch into larva
A larva (; : larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into their next life stage. Animals with indirect development such as insects, some arachnids, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase ...
e in three to ten days. These young mites move about on the skin and molt
In biology, moulting (British English), or molting (American English), also known as sloughing, shedding, or in many invertebrates, ecdysis, is a process by which an animal casts off parts of its body to serve some beneficial purpose, either at ...
into a " nymphal" stage, before maturing as adults, which live three to four weeks in the host's skin. Males roam on top of the skin, occasionally burrowing into the skin. In general, the total number of adult mites infesting a healthy hygienic person with non-crusted scabies is small, about 11 females in burrows, on average.
The movement of mites within and on the skin produces an intense itch, which has the characteristics of a delayed cell-mediated inflammatory response to allergens. IgE antibodies are present in the serum and the site of infection, which react to multiple protein allergens in the body of the mite. Some of these cross-react to allergens from house dust mites
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air condi ...
. Immediate antibody-mediated allergic reactions (wheals) have been elicited in infected persons, but not in those not infected; immediate hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) is an abnormal physiological condition in which there is an undesirable and adverse immune response to an antigen. It is an abnormality in the immune system that causes Imm ...
of this type is thought to explain the observed far more rapid allergic skin response to reinfection seen in persons who have been infected previously, especially within the previous year or two.
Transmission
Scabies is contagious and can be contracted through prolonged physical contact with an infested person. This includessexual intercourse
Sexual intercourse (also coitus or copulation) is a sexual activity typically involving the insertion of the Erection, erect male Human penis, penis inside the female vagina and followed by Pelvic thrust, thrusting motions for sexual pleasure ...
, although a majority of cases are acquired through other forms of skin-to-skin contact. Less commonly, scabies infestation can happen through the sharing of clothes, towels, and bedding, but this is not a major mode of transmission; individual mites can survive for only two to three days, at most, away from human skin at room temperature. As with lice, a latex condom is ineffective against scabies transmission during intercourse, because mites typically migrate from one individual to the next at sites other than the sex organs.
Healthcare workers are at risk of contracting scabies from patients, because they may be in extended contact with them.
Pathophysiology
The symptoms are caused by anallergic reaction
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are various conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include Allergic rhinitis, hay fever, Food allergy, food al ...
of the host's body to mite proteins, though exactly which proteins remains a topic of study. The mite proteins are also present in the gut, and in mite feces, which are deposited under the skin. The allergic reaction is both of the delayed (cell-mediated) and immediate (antibody-mediated) type, and involves IgE (antibodies are presumed to mediate the very rapid symptoms on reinfection). The allergy-type symptoms (itching) continue for some days, and even several weeks, after all mites are killed. New lesions may appear for a few days after mites are eradicated. Nodular lesions from scabies may continue to be symptomatic for weeks after the mites have been killed.
Rates of scabies are negatively related to temperature and positively related to humidity.
Diagnosis
 Scabies may be diagnosed clinically in geographical areas where it is common when diffuse itching presents along with either a lesion in two typical spots or itchiness is present in another household member. The classical sign of scabies is the burrow made by a mite within the skin. To detect the burrow, the suspected area is rubbed with ink from a fountain pen or a topical
Scabies may be diagnosed clinically in geographical areas where it is common when diffuse itching presents along with either a lesion in two typical spots or itchiness is present in another household member. The classical sign of scabies is the burrow made by a mite within the skin. To detect the burrow, the suspected area is rubbed with ink from a fountain pen or a topical tetracycline
Tetracycline, sold under various brand names, is an antibiotic in the tetracyclines family of medications, used to treat a number of infections, including acne, cholera, brucellosis, plague, malaria, and syphilis. It is available in oral an ...
solution, which glows under a special light. The skin is then wiped with an alcohol pad. If the person is infected with scabies, the characteristic zigzag or S pattern of the burrow will appear across the skin; however, interpreting this test may be difficult, as the burrows are scarce and may be obscured by scratch marks. A definitive diagnosis is made by finding either the scabies mites or their eggs and fecal pellets. Searches for these signs involve either scraping a suspected area, mounting the sample in potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which utili ...
and examining it under a microscope, or using dermoscopy to examine the skin directly.
Differential diagnosis
Symptoms of early scabies infestation mirror other skin diseases, includingdermatitis
Dermatitis is a term used for different types of skin inflammation, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened ...
, syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms depend on the stage it presents: primary, secondary, latent syphilis, latent or tertiary. The prim ...
, erythema multiforme, various urticaria
Hives, also known as urticaria, is a kind of skin rash with red or flesh-colored, raised, itchy bumps. Hives may burn or sting. The patches of rash may appear on different body parts, with variable duration from minutes to days, and typically ...
-related syndromes, allergic reactions, ringworm-related diseases, and other ectoparasites such as lice
Louse (: lice) is the common name for any member of the infraorder Phthiraptera, which contains nearly 5,000 species of wingless parasitic insects. Phthiraptera was previously recognized as an order, until a 2021 genetic study determined th ...
and flea
Flea, the common name for the order (biology), order Siphonaptera, includes 2,500 species of small flightless insects that live as external parasites of mammals and birds. Fleas live by hematophagy, ingesting the blood of their hosts. Adult f ...
s.
Prevention of passing on scabies to other people
Mass-treatment programs that use topicalpermethrin
Permethrin is a medication and an insecticide. As a medication, it is used to treat scabies and lice. It is applied to the skin as a cream or lotion. As an insecticide, it can be sprayed onto outer clothing or mosquito nets to kill the insects ...
or oral ivermectin
Ivermectin is an antiparasitic drug. After its discovery in 1975, its first uses were in veterinary medicine to prevent and treat heartworm and acariasis. Approved for human use in 1987, it is used to treat infestations including head lice ...
have been effective in reducing the prevalence of scabies in several populations. No vaccine is available for scabies. The simultaneous treatment of all close contacts is recommended, even if they show no symptoms of infection (asymptomatic
Asymptomatic (or clinically silent) is an adjective categorising the medical conditions (i.e., injuries or diseases) that patients carry but without experiencing their symptoms, despite an explicit diagnosis (e.g., a positive medical test).
P ...
), to reduce rates of recurrence. Since mites can survive for only two to three days without a host, other objects in the environment pose little risk of transmission except in the case of crusted scabies. Therefore, cleaning is of little importance. Rooms used by those with crusted scabies require thorough cleaning.
Management
Treatment
Several medications are effective in treating scabies. Treatment should involve the entire household and any others who have had recent, prolonged contact with the infested individual. In addition to treating the infestation, options to control itchiness includeantihistamine
Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic (not patented) drug that can be bought without a prescription and provides ...
s and prescription anti-inflammatory agents. Bedding, clothing and towels used during the previous three days should be washed in hot water and dried in a hot dryer.
Treatment protocols for crusted scabies are significantly more intense than for common scabies.
Permethrin
Permethrin
Permethrin is a medication and an insecticide. As a medication, it is used to treat scabies and lice. It is applied to the skin as a cream or lotion. As an insecticide, it can be sprayed onto outer clothing or mosquito nets to kill the insects ...
, a pyrethroid
A pyrethroid is an organic compound similar to the natural pyrethrins, which are produced by the flowers of pyrethrums (''Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium'' and ''Chrysanthemum coccineum, C. coccineum''). Pyrethroids are used as commercial and hou ...
insecticide, is the most effective treatment for scabies, and remains the treatment of choice. It is applied from the neck down, usually before sleep, and left on for about 8 to 14 hours, then washed off in the morning. Care should be taken to coat the entire skin surface, not just symptomatic areas; any patch of skin left untreated can provide a "safe haven" for one or more mites to survive. One application is normally sufficient, as permethrin kills eggs, hatchlings, and adult mites, though many physicians recommend a second application three to seven days later as a precaution. Crusted scabies may require multiple applications or supplemental treatment with oral ivermectin (below). Permethrin may cause slight irritation of the skin that is usually tolerable. In recent years, concern is growing about permethrin-resistant scabies, although some researchers refer to this as pseudo-resistance.
Ivermectin
Oralivermectin
Ivermectin is an antiparasitic drug. After its discovery in 1975, its first uses were in veterinary medicine to prevent and treat heartworm and acariasis. Approved for human use in 1987, it is used to treat infestations including head lice ...
is effective in eradicating scabies, often in a single dose. It is the treatment of choice for crusted scabies, and is sometimes prescribed in combination with a topical agent. It has not been tested on infants, and is not recommended for children under six years of age.
Topical
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes ...
ivermectin preparations are effective for scabies in adults. It has also been useful for sarcoptic mange, the veterinary analog of human scabies.
One review found that the efficacy of permethrin is similar to that of systemic or topical ivermectin. A separate review found that although oral ivermectin is usually effective for the treatment of scabies, it does have a higher treatment failure rate than topical permethrin. Another review found that oral ivermectin provided a reasonable balance between efficacy and safety. A study has demonstrated that scabies is markedly reduced in populations taking ivermectin regularly; the drug is widely used for treating scabies and other parasitic diseases, particularly among the poor and disadvantaged in the tropics, beginning with the developer Merck providing the drug at no cost to treat onchocerciasis
Onchocerciasis, also known as river blindness, is a disease caused by infection with the parasitic worm ''Onchocerca volvulus''. Symptoms include severe itching, bumps under the skin, and blindness. It is the second-most common cause of blindne ...
from 1987.
Others
Other treatments include lindane, benzyl benzoate, crotamiton, malathion, andsulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms ...
preparations. Lindane is effective, but concerns over potential neurotoxicity have limited its availability in many countries. It is banned in California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
, but may be used in other states as a second-line treatment. Sulfur ointments or benzyl benzoate are often used in the developing world due to their low cost; some 10% sulfur solutions have been shown to be effective, and sulfur ointments are typically used for at least a week, though many people find the odor of sulfur products unpleasant. Crotamiton has been found to be less effective than permethrin in limited studies. Crotamiton or sulfur preparations are sometimes recommended instead of permethrin for children, due to concerns over dermal absorption of permethrin.
Communities
Scabies is endemic in many developing countries, where it tends to be particularly problematic in rural and remote areas. In such settings, community-wide control strategies are required to reduce the rate of disease, as treatment of only individuals is ineffective due to the high rate of reinfection. Large-scale mass drug administration strategies may be required where coordinated interventions aim to treat whole communities in one concerted effort. Although such strategies have shown to be able to reduce the burden of scabies in these kinds of communities, debate remains about the best strategy to adopt, including the choice of drug. The resources required to implement such large-scale interventions in a cost-effective and sustainable way are significant. Furthermore, since endemic scabies is largely restricted to poor and remote areas, it is a public health issue that has not attracted much attention from policymakers and international donors.Epidemiology
Scabies is one of the three most common skin disorders in children, along with tinea and pyoderma. As of 2010, it affects about 100 million people (1.5% of the population) and its frequency is not related to gender. The mites are distributed around the world and equally infect all ages, races, and socioeconomic classes in different climates. Scabies is more often seen in crowded areas with unhygienic living conditions. Globally as of 2009, an estimated 300 million cases of scabies occur each year, although various parties claim the figure is either over- or underestimated. About 1–10% of the global population is estimated to be infected with scabies, but in certain populations, the infection rate may be as high as 50–80%.History
Scabies has been observed in humans since ancient times. Archeological evidence from Egypt and the Middle East suggests scabies was present as early as 494 BC. In the fourth century BC,Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
reported on "lice" that "escape from little pimples if they are pricked" – a description consistent with scabies. Arab physician Ibn Zuhr
Abū Marwān ‘Abd al-Malik ibn Zuhr (), traditionally known by his Latinized name Avenzoar (; 1094–1162), was an Arab physician, surgeon, and poet. He was born at Seville in medieval Andalusia (present-day Spain), was a contemporary of A ...
is believed to have been the first to provide a clinical description of the scabies mites.
Roman encyclopedist and medical writer Aulus Cornelius Celsus
Aulus Cornelius Celsus ( 25 BC 50 AD) was a Roman encyclopedist, known for his extant medical work, '' De Medicina'', which is believed to be the only surviving section of a much larger encyclopedia. The ''De Medicina'' is a primary source on ...
(''circa'' 25 BC – 50 AD) is credited with naming the disease "scabies" and describing its characteristic features. The parasitic etiology of scabies was documented by Italian physician Giovanni Cosimo Bonomo (1663–1696) in his 1687 letter, "Observations concerning the fleshworms of the human body". Bonomo's description established scabies as one of the first human diseases with a well-understood cause.
In Europe in the late 19th through mid-20th centuries, a sulfur-bearing ointment
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes ...
called by the medical eponym of Wilkinson's ointment was widely used for topical treatment of scabies. The contents and origins of several versions of the ointment were detailed in correspondence published in the ''British Medical Journal
''The BMJ'' is a fortnightly peer-reviewed medical journal, published by BMJ Publishing Group Ltd, which in turn is wholly-owned by the British Medical Association (BMA). ''The BMJ'' has editorial freedom from the BMA. It is one of the world ...
'' in 1945.
In the 1995 documentary '' Anne Frank Remembered'', Bloeme Evers-Emden told of how she was selected from Auschwitz and sent to a work camp where conditions were sufficiently improved that she was able to survive until the liberation. She said Anne Frank was rejected for this transfer because she had contracted scabies.
Scabies in animals
 Scabies may occur in some domestic and wild animals; the mites that cause these infestations are of different subspecies from the one typically causing the human form. These subspecies can infest animals that are not their usual hosts, but such infections do not last long. Scabies-infected animals experience severe itching and secondary skin infections. They often lose weight and become frail.
The most frequently diagnosed form of scabies in domestic animals is sarcoptic mange, caused by the subspecies ''Sarcoptes scabiei canis'', most commonly in dogs and cats. Sarcoptic mange is transmissible to humans who come into prolonged contact with infested animals, and is distinguished from human scabies by its distribution on skin surfaces covered by clothing. Scabies-infected domestic fowl develop what is known as "scaly leg". Domestic animals that have gone feral and have no veterinary care are frequently affected by scabies. Nondomestic animals have also been observed to develop scabies. Gorillas, for instance, are known to be susceptible to infection by contact with items used by humans, and it is a fatal disease of wombats.
Scabies is also a concern for
Scabies may occur in some domestic and wild animals; the mites that cause these infestations are of different subspecies from the one typically causing the human form. These subspecies can infest animals that are not their usual hosts, but such infections do not last long. Scabies-infected animals experience severe itching and secondary skin infections. They often lose weight and become frail.
The most frequently diagnosed form of scabies in domestic animals is sarcoptic mange, caused by the subspecies ''Sarcoptes scabiei canis'', most commonly in dogs and cats. Sarcoptic mange is transmissible to humans who come into prolonged contact with infested animals, and is distinguished from human scabies by its distribution on skin surfaces covered by clothing. Scabies-infected domestic fowl develop what is known as "scaly leg". Domestic animals that have gone feral and have no veterinary care are frequently affected by scabies. Nondomestic animals have also been observed to develop scabies. Gorillas, for instance, are known to be susceptible to infection by contact with items used by humans, and it is a fatal disease of wombats.
Scabies is also a concern for cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, bovid ungulates widely kept as livestock. They are prominent modern members of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Mature female cattle are calle ...
.
Society and culture
 The International Alliance for the Control of Scabies was started in 2012, and brings together over 150 researchers, clinicians, and public-health experts from more than 15 countries. It has managed to bring the global health implications of scabies to the attention of the
The International Alliance for the Control of Scabies was started in 2012, and brings together over 150 researchers, clinicians, and public-health experts from more than 15 countries. It has managed to bring the global health implications of scabies to the attention of the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
(WHO). Consequently, the WHO has included scabies on its official list of neglected tropical diseases
Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) are a diverse group of tropical infections that are common in low-income populations in developing regions of Africa, Asia, and the Americas. They are caused by a variety of pathogens, such as viruses, bacteri ...
and other neglected conditions.
Research
Moxidectin
Moxidectin is an anthelmintic drug used in animals to prevent or control parasitic worms (helminths), such as heartworm and intestinal worms, in dogs, cats, horses, cattle, sheep and wombats. Moxidectin kills some of the most common internal ...
is being evaluated as a treatment for scabies. It is established in veterinary medicine to treat a range of parasites, including sarcoptic mange. Its advantage over ivermectin is its longer half-life in humans, thus the potential duration of action.
Tea tree oil
Tea tree oil, also known as melaleuca oil, is an essential oil with a fresh, camphoraceous odour and a colour that ranges from pale yellow to nearly colourless and clear. It is derived from the leaves of the tea tree, '' Melaleuca alternif ...
(TTO) exhibits scabicidal action in a laboratory setting.
References
Further reading
* * *External links
American Academy of Dermatology pamphlet on Scabies
{{Authority control Arthropod infestations Articles containing video clips Mammal diseases Parasitic arthropods of humans Parasitic infestations, stings, and bites of the skin Tropical diseases Wikipedia infectious disease articles ready to translate Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate