|
Flea
Flea, the common name for the order (biology), order Siphonaptera, includes 2,500 species of small flightless insects that live as external parasites of mammals and birds. Fleas live by hematophagy, ingesting the blood of their hosts. Adult fleas grow to about long, are usually dark in color, and have bodies that are "flattened" sideways or narrow, enabling them to move through their hosts' fur or feathers. They lack wings; their hind legs are extremely well adapted for jumping. Their claws keep them from being dislodged, and their mouthparts are adapted for piercing skin and sucking blood. Some species can leap 50 times their body length, a feat second only to jumps made by another group of insects, the superfamily (taxonomy), superfamily of froghoppers. Flea larvae are worm-like, with no limbs; they have chewing mouthparts and feed on organic debris left on their hosts' skin. Genetic evidence indicates that fleas are a specialised lineage of parasitic scorpionflies (Mecopte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Flea Circus
A flea circus is a circus sideshow attraction in which fleas are attached (or appear to be attached) to miniature carts and other items, and encouraged to perform circus acts within a small housing. History The first records of flea performances were from watchmakers who were demonstrating their metalworking skills. In 1578, the London blacksmith Mark Scaliot produced a lock and chain that were attached to a flea. The first recorded flea circus dates back to the early 1820s, when an Italian impresario named Louis Bertolotto advertised an "extraordinary exhibition of industrious fleas" on Regent Street, London. Bertolotto's flea shows included "four card-playing fleas, a flea orchestra (allegedly playing audibly), and a reenactment of Napoleon's defeat at Waterloo". Bertolotto's book ''The History of the Flea'' (c. 1833) also promoted flea circuses. Flea performances with military themes such as staged "sword fights" among fleas, were popular in the 19th century. Some flea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Xenopsylla Cheopis
The Oriental rat flea (''Xenopsylla cheopis''), also known as the tropical rat flea or the rat flea, is a parasite of rodents, primarily of the genus ''Rattus'', and is a primary Vector (epidemiology), vector for bubonic plague, plague and murine typhus. This occurs when a flea that has fed on an infected rodent bites a human, although this flea can live on any warm blooded mammal. Body structure The Oriental rat flea has no genal or pronotal combs. This characteristic can be used to differentiate the Oriental rat flea from the cat flea, dog flea, and other fleas. The flea's body is about one tenth of an inch long (about ). Its body is constructed to make it easier to jump long distances. The flea's body consists of three regions: head, thorax, and abdomen. The head and the thorax have rows of bristles (called combs), and the abdomen consists of eight visible segments. A flea's mouth has two functions: one for squirting saliva or partly digested blood into the bite, and one for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Black Death
The Black Death was a bubonic plague pandemic that occurred in Europe from 1346 to 1353. It was one of the list of epidemics, most fatal pandemics in human history; as many as people perished, perhaps 50% of Europe's 14th century population. The disease is caused by the Bacteria, bacterium ''Yersinia pestis'' and spread by Flea, fleas and through the air. One of the most significant events in European history, the Black Death had far-reaching population, economic, and cultural impacts. It was the beginning of the second plague pandemic. The plague created religious, social and economic upheavals, with profound effects on the course of European history. The origin of the Black Death is disputed. Genetic analysis suggests ''Yersinia pestis'' bacteria evolved approximately 7,000 years ago, at the beginning of the Neolithic, with flea-mediated strains emerging around 3,800 years ago during the late Bronze Age. The immediate territorial origins of the Black Death and its outbreak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Yersinia Pestis
''Yersinia pestis'' (''Y. pestis''; formerly ''Pasteurella pestis'') is a Gram-negative bacteria, gram-negative, non-motile bacteria, non-motile, coccobacillus Bacteria, bacterium without Endospore, spores. It is related to pathogens ''Yersinia enterocolitica'', and ''Yersinia pseudotuberculosis'', from which it evolved. ''Yersinia pestis'' is responsible for the disease plague (disease), plague, which caused the Plague of Justinian and the Black Death, one of the deadliest pandemics in recorded history. Plague takes three main forms: Pneumonic plague, pneumonic, Septicemic plague, septicemic, and bubonic plague, bubonic. ''Y. pestis'' is a facultative anaerobic organism, facultative anaerobic Parasitism, parasitic bacterium that can infect humans primarily via its host the Oriental rat flea (''Xenopsylla cheopis''), but also through airborne transmission , aerosols and airborne droplets for its pneumonic form. As a parasite of its host, the rat flea, which is also a parasit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
The Flea (poem)
"The Flea" is an erotic metaphysical poem (first published posthumously in 1633) by John Donne (1572–1631). The exact date of its composition is unknown, but it is probable that Donne wrote this poem in the 1590s when he was a young law student at Lincoln's Inn, before he became a respected religious figure as Dean of St Paul's Cathedral. The poem uses the conceit of a flea, which has sucked blood from the male speaker and his female lover, to serve as an extended metaphor for the relationship between them. The speaker tries to convince a lady to sleep with him, arguing that if their blood mingling in the flea is innocent, then sexual mingling would also be innocent. His argument hinges on the belief that bodily fluids mix during sexual intercourse. According to Laurence Perrine, this poem, along with many other of Donne's poems, solidifies his place in the literary movement, creating what is now known as metaphysical poetry. Although the term was not found until after his death ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
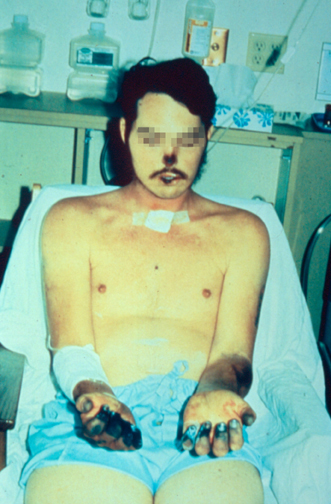
Bubonic Plague
Bubonic plague is one of three types of Plague (disease), plague caused by the Bacteria, bacterium ''Yersinia pestis''. One to seven days after exposure to the bacteria, flu-like symptoms develop. These symptoms include fever, headaches, and vomiting, as well as Lymphadenopathy, swollen and painful lymph nodes occurring in the area closest to where the bacteria entered the skin. Acral necrosis, the dark discoloration of skin, is another symptom. Occasionally, swollen lymph nodes, known as "buboes", may break open. The three types of plague are the result of the route of infection: bubonic plague, septicemic plague, and pneumonic plague. Bubonic plague is mainly spread by infected fleas from small animals. It may also result from exposure to the body fluids from a dead plague-infected animal. Mammals such as rabbits, hares, and some cat species are susceptible to bubonic plague, and typically die upon contraction. In the bubonic form of plague, the bacteria enter through the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Scorpionflies
Mecoptera (from the Greek language, Greek: ''mecos'' = "long", ''ptera'' = "wings") is an Order (biology), order of insects in the superorder Holometabola with about six hundred species in nine Family (biology), families worldwide. Mecopterans are sometimes called scorpionflies after their largest family, Panorpidae, in which the males have enlarged genitals raised over the body that look similar to the stingers of scorpions, and long beaklike Rostrum (anatomy), rostra. The Bittacidae, or hangingflies, are another prominent family and are known for their elaborate mating rituals, in which females choose mates based on the quality of gift prey offered to them by the males. A smaller group is the snow scorpionflies, family Boreidae, adults of which are sometimes seen walking on snowfields. In contrast, the majority of species in the order inhabit moist environments in tropical locations. The Mecoptera are closely related to the Siphonaptera (fleas), and a little more distantly to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Parasites
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson characterised parasites' way of feeding as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the broomrapes. There are six major parasitic strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropredation. One major axis of classification concerns invasiveness: an endo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pseudopulicidae
Pseudopulicidae is an extinct family of stem-group fleas from the Middle Jurassic to Early Cretaceous of China. They represent the oldest known group of stem-fleas. Like other stem-group "giant fleas", they are much larger and lack the specialised morphology of modern fleas. Description Pseudopulicids are much larger than modern fleas, varying from 8 mm to over 2 cm in body length. The females of the species are always larger than the males. The body is flattened, with a non-reduced thorax, and covered in posterior-facing hairs (setae). The antennae are relatively compact, with at least 16 antennomeres and 14-17 flagellomeres. The mouthparts are siphonate, with a piercing-suctorial function, and are serrated and longer in females. The distal (outer) part of the tibia is covered in comb-like ctenidia. The tarsi are elongate, at least as long as the femora and tibiae combined. The male abdominal sternites are sclerotized, and the penis of the males is large and exposed. Eco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Saurophthiridae
''Saurophthirus'' is an extinct genus of giant stem-group flea, and the only member of the family Saurophthiridae. The type species, ''S. longipes'' is found in early Cretaceous strata of Baissa, Siberia. Two other species ''S. exquisitus'' and ''S. laevigatus'' are from the Lower Cretaceous Yixian Formation of China.Gao, Taiping, et al. "New Transitional Fleas from China Highlighting Diversity of Early Cretaceous Ectoparasitic Insects." Current Biology 23.13 (2013): 1261-1266. Description Body length of largest species, ''S. longipes'' is long. They are generally seen as transitional between more primitive stem-fleas such as Pseudopulicidae Pseudopulicidae is an extinct family of stem-group fleas from the Middle Jurassic to Early Cretaceous of China. They represent the oldest known group of stem-fleas. Like other stem-group "giant fleas", they are much larger and lack the specialise ... and '' Tarwinia'' and modern fleas. References Siphonaptera genera Cretaceous ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nannochoristidae
Nannochoristidae is a family of scorpionflies with many unusual traits. It is a tiny, relict family with a single extant genus, ''Nannochorista'', with eight species occurring in New Zealand, southeastern Australia, Tasmania, Argentina and Chile. Due to the group's distinctiveness from other scorpionflies, it is sometimes placed in its own order, the Nannomecoptera. Some studies have placed them as the closest living relatives of fleas. Most mecopteran larvae are eruciform, or shaped like caterpillars. Nannochoristid larvae, however, are elateriform, and have elongated and slender bodies. The larvae are aquatic, which is unique among mecopterans. The larvae are predatory, hunting on the beds of shallow streams, primarily on the larvae of aquatic Diptera like chironomids. The adults are thought probably to be adapted to liquid feeding, likely on flower nectar and/or the juice of fruits. Adults of Australian and South American species are often found in habitats like the edges of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tarwiniidae
''Tarwinia'' is an extinct genus of stem-group flea known from a single species, ''T. australis'', from the Early Cretaceous (Aptian The Aptian is an age (geology), age in the geologic timescale or a stage (stratigraphy), stage in the stratigraphic column. It is a subdivision of the Early Cretaceous, Early or Lower Cretaceous epoch (geology), Epoch or series (stratigraphy), S ...) Koonwarra Fossil Bed of Victoria, Australia, it is the only member of the family Tarwiniidae, and the only stem-group flea known from the Southern Hemisphere. References {{Taxonbar, from1=Q21315090, from2=Q21334053, from3=Q35082361 Prehistoric invertebrates of Australia Fleas Monotypic prehistoric insect genera Early Cretaceous insects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |