Saurashtra (region) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Saurashtra, also known as Sorath or
 In earliest foreign mention, Egyptian mathematician, geographer, astrologer Claudius Ptolemy and Greek manuscript Periplus both call this region "Surastrene"
Saurashtra and its
In earliest foreign mention, Egyptian mathematician, geographer, astrologer Claudius Ptolemy and Greek manuscript Periplus both call this region "Surastrene"
Saurashtra and its
 After India's independence in 1947, 217
After India's independence in 1947, 217
 Saurashtra has been a flourishing region and rich in natural resources since ancient times, while having gone through several droughts especially during the 20th century. Water resources and its related dynamics have influenced the region and its agro-economy to a certain extent. It is found that water was easily available in the region 10 to 15 years ago. Ashvin A. Shah, a US-based engineering consultant who conducted a survey in 1998 on water availability in the region, says, "The presence of 700,000 dugwells in Saurashtra region indicates the presence of extensive groundwater aquifers throughout the region. This means there is one well for fewer than 20 people or one well every 300 metres".
Amri Saurashtra went through severe droughts over the years to the extent that people could no longer grow crops, nor did they have drinking water available. There has been in recent times a campaign to take up rain water harvesting.
Significantly, the Check dam campaign from the late 1990s brought almost a drastic change resulting in raising water tables in Saurashtra. However, in 2019, the region was hit with a severe drought, affecting 20 districts in Gujarat, and water had to be brought in by tanker from the Sardar Sarovar Dam on the Narmada River.
Saurashtra has been a flourishing region and rich in natural resources since ancient times, while having gone through several droughts especially during the 20th century. Water resources and its related dynamics have influenced the region and its agro-economy to a certain extent. It is found that water was easily available in the region 10 to 15 years ago. Ashvin A. Shah, a US-based engineering consultant who conducted a survey in 1998 on water availability in the region, says, "The presence of 700,000 dugwells in Saurashtra region indicates the presence of extensive groundwater aquifers throughout the region. This means there is one well for fewer than 20 people or one well every 300 metres".
Amri Saurashtra went through severe droughts over the years to the extent that people could no longer grow crops, nor did they have drinking water available. There has been in recent times a campaign to take up rain water harvesting.
Significantly, the Check dam campaign from the late 1990s brought almost a drastic change resulting in raising water tables in Saurashtra. However, in 2019, the region was hit with a severe drought, affecting 20 districts in Gujarat, and water had to be brought in by tanker from the Sardar Sarovar Dam on the Narmada River.
Kathiawar
Kathiawar () is a peninsula, near the far north of India's west coast, of about bordering the Arabian Sea. It is bounded by the Gulf of Kutch in the northwest and by the Gulf of Khambhat (Gulf of Cambay) in the east. In the northeast, it ...
, is a peninsular region of Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the nin ...
, India, located on the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel ...
coast. It covers about a third of Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the nin ...
state, notably 11 districts of Gujarat, including Rajkot District. It was formerly a state of India before it merged with Bombay state. In 1961 it separated from Bombay and joined Gujarat.
Location
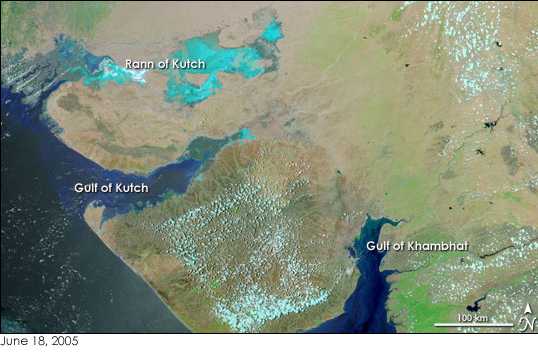
Saurashtra peninsula is bound on the south and south-west by the Arabian sea, on the north-west by theGulf of Kutch
The Gulf of Kutch is located between the peninsula regions of Kutch and Saurashtra, bounded in the state of Gujarat that borders Pakistan. It opens towards the Arabian Sea facing the Osman Gulf.
It is about 50 km wide at the entrance be ...
and on the east by the Gulf of Khambhat. From the apex of these two gulfs, the Little Rann of Kutch and Khambhat, waste tracts half salt morass half sandy desert, stretch inland towards each other and complete the isolation of Kathiawar, except one narrow neck which connects it on the north-east with the mainland of Gujarat.
The peninsula is sometimes referred to as Kathiawar
Kathiawar () is a peninsula, near the far north of India's west coast, of about bordering the Arabian Sea. It is bounded by the Gulf of Kutch in the northwest and by the Gulf of Khambhat (Gulf of Cambay) in the east. In the northeast, it ...
after the Kathi Darbar, which once ruled most of the region. However, Saurashtra is not entirely synonymous with Kathiawar, since a small portion of the historical Saurashtra region extends beyond the Kathiawar peninsula. Sorath forms the southern portion of the peninsula.
"sau" means 100 and "rasthra" means languages and sourasthra is made up with 100 languages so there isn't one original word.
According to few experts, the name Saurashtra is derived from Saura Rashtra. In Sanskrit, Saura means Sun and Rashtra means country. It means, country of Sun, and there were 12 sun temples in ancient times in this region. Due to continued Islamic invasions, the idols of deities of these temples were moved to other places, one of those is located at Kanakaditya Temple at Kasheli near Pawas in Ratnagiri district
Ratnagiri District (Marathi pronunciation: �ət̪n̪aːɡiɾiː is a district in the state of Maharashtra, India. The administrative headquarter of the district is located in the town of Ratnagiri. The district is 11.33% urban. The district ...
of Maharashtra. The location of other 11 idols are currently unknown.
Districts
The Saurashtra region comprises the south western part of modern Gujarat state and the districts included in this region are: * Devbhoomi Dwarka * Jamnagar * Morbi * Rajkot * Porbandar * Junagadh * Gir Somnath * Amreli *Bhavnagar
Bhavnagar is a city in the Bhavnagar district of the Saurashtra region of Gujarat, a state of India. It was founded in 1723 by Bhavsinhji Takhtasinhji Gohil (1703–1764). It was the capital of Bhavnagar State, which was a princely state befo ...
* Botad
* Surendranagar
* Ahmedabad (part)
The region also historically encompassed the Diu district of the Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu union territory.
History
Referred to as Saurashtra and as some other names as well over a period of time, since theMahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the '' Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the K ...
and Vedic period
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (ca. 1300–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, bet ...
, this region is mentioned again as Surastrene, or Saraostus in the first century CE Periplus of the Erythraean Sea:
 In earliest foreign mention, Egyptian mathematician, geographer, astrologer Claudius Ptolemy and Greek manuscript Periplus both call this region "Surastrene"
Saurashtra and its
In earliest foreign mention, Egyptian mathematician, geographer, astrologer Claudius Ptolemy and Greek manuscript Periplus both call this region "Surastrene"
Saurashtra and its Prakrit
The Prakrits (; sa, prākṛta; psu, 𑀧𑀸𑀉𑀤, ; pka, ) are a group of vernacular Middle Indo-Aryan languages that were used in the Indian subcontinent from around the 3rd century BCE to the 8th century CE. The term Prakrit is usu ...
name Sorath, literally means "good country". The name finds mentions in the Junagadh Rock inscription dating 150 CE, attributed to Rudradaman I. Prior to this, during the rule of Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, ...
(268–232 BCE), the region was under Yavana Tushaspa, and governed by Pushyagupta during Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya (350-295 BCE) was a ruler in Ancient India who expanded a geographically-extensive kingdom based in Magadha and founded the Maurya dynasty. He reigned from 320 BCE to 298 BCE. The Maurya kingdom expanded to become an emp ...
's reign (322BC – 298BC). From the 8th to 11th century, Brahmin
Brahmin (; sa, ब्राह्मण, brāhmaṇa) is a varna as well as a caste within Hindu society. The Brahmins are designated as the priestly class as they serve as priests ( purohit, pandit, or pujari) and religious teachers ( ...
merchant
A merchant is a person who trades in commodities produced by other people, especially one who trades with foreign countries. Historically, a merchant is anyone who is involved in business or trade. Merchants have operated for as long as indust ...
s from Saurashtra region started migrating towards Southern India due to the frequent Muslim invasions, these merchants upon the invitation of Chola, Pandya, Vijayanagara, Nayak and Thanjavur Maratha Kings set up mercantile silk-weaving guild
A guild ( ) is an association of artisans and merchants who oversee the practice of their craft/trade in a particular area. The earliest types of guild formed as organizations of tradesmen belonging to a professional association. They sometimes ...
s throughout Southern India and were involved in the trade
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
An early form of trade, barter, saw the direct exch ...
of silk clothes and diamonds
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure, ...
to the royal families of ancient South India, as the silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the ...
became the attire of royal families after the period of Gupta dynasty
The Gupta Empire was an Outline of ancient India, ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period ...
. These Brahmins who trace their ancestry to the historical region of Saurashtra are now known as the Saurashtra people. Several historians believe that it was Saurashtrian textile
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not t ...
merchants who introduced idly to South India
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of India. It encompasses the States and union territories of India, Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and T ...
during the 10th and 12th centuries. There are even claims that a mix of rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly '' Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and ''Porteresia'', both wild and domestica ...
and urad dal ground together and later steamed to form cakes had its origins in Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the nin ...
. This was called ''Iddada''.
Gir
For a long time, the name ''Sorath'' referred to this region. From the 9th to 14th century ChudasamaRajput
Rajput (from Sanskrit ''raja-putra'' 'son of a king') is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating from the Indian subcontinent. The term Ra ...
ruled Sorath with their capitals Vanthali
Vamansthli (Vanthli)is a city and a municipality in Junagadh district in the Indian state of Gujarat.
Demographics
India census, Vanthali had a population of 21,891. Males constitute 53% of the population and females 47%. Vanthali has an avera ...
and Junagadh alternatively. The Chudasama Rajputs ruled Sorath longer than any others, until the Sorath area came under Muslim rule. Sorath, a Muslim name of Saurashtra, was initially one of ten prants, but by the colonial age it was one of only four surviving ones, the others being absorbed. The salute state Junagadh (alias "Junagarh" or the "Old Fort"), founded during British rule, and its neighbouring states were controlled by the Western India States Agency (WISA). In 1947, Junagadh's Muslim ruler desired to accede his territory to Pakistan, but the predominantly Hindu population rebelled.
Saurashtra State
 After India's independence in 1947, 217
After India's independence in 1947, 217 princely states
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to ...
of Kathiawar, including the former Junagadh State, were merged to form the state of Saurashtra on 15 February 1948. Initially, it was named United State of Kathiawar, which was renamed to Saurashtra State in November 1948. The exercise took up a lot of Shri Vallabhbhai Patel's time to convince the local princes and petty subas (totalling 222 in Saurashtra alone). However, Maharaja Krishnakumar Sinhji of Bhavnagar State readily extended to offer his large and royal empire of Bhavnagar / Gohilwar to Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel, and Bhavnagar became the first in the country to be merged into the union of India.
The capital of Saurashtra was Rajkot. Uchharangray Navalshankar Dhebar, who later went on to become President of the Indian National Congress between 1955 and 1959, became Saurashtra's first Chief Minister. He was succeeded by Rasiklal Umedchand Parikh on 19 December 1954.
On 1 November 1956, Saurashtra was merged into Bombay state. In 1960 Bombay state was divided along linguistic lines into the new states of Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the nin ...
and Maharashtra. The territory of Saurashtra, including Junagadh and all of Sorath, became part of the state of Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the nin ...
.
Language
Saurashtra (alternate names and spellings: Sourashtra, Sowrashtra, Palkar) is also the name of an Indo-Aryan language of Kathiawar-Saurashtra. Though the Saurashtra language is not spoken in the region now, people of this region who migrated to Southern India - especiallyKarnataka
Karnataka (; ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a state in the southwestern region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act. Originally known as Mysore State , it was renamed ''Kar ...
(Bengaluru
Bangalore (), officially Bengaluru (), is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It has a population of more than and a metropolitan population of around , making it the third most populous city and fifth most ...
), Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil languag ...
( Ambur, Madurai
Madurai ( , also , ) is a major city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is the cultural capital of Tamil Nadu and the administrative headquarters of Madurai District. As of the 2011 census, it was the third largest Urban agglomeration in ...
, Dindigul
Dindigul, also spelt Thindukkal (), is a city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is the administrative headquarters of the Dindigul district. Dindigul is located southwest from the state capital, Chennai, away from Tiruchirappalli, away ...
, Paramakudi, Salem
Salem may refer to: Places
Canada
Ontario
* Bruce County
** Salem, Arran–Elderslie, Ontario, in the municipality of Arran–Elderslie
** Salem, South Bruce, Ontario, in the municipality of South Bruce
* Salem, Dufferin County, Ontario, part ...
, Tanjore, Pudukkottai, Trichy, Namakkal, Kanyakumari
Kanniyakumari (; , referring to Devi Kanya Kumari), also known as Cape Comorin, is a city in Kanniyakumari district in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. It is the southern tip of the Indian subcontinent and the southernmost city in mainland I ...
, Kanchipuram, Walajapet, Arani, Chennai
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of ...
, Palayamkottai, Kumbakonam, Thirubuvanam
Thirubuvanam is a panchayat town in Thanjavur district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. The town is mainly known for the Kampaheswarar Temple.
Demographics
India census, Thirubuvanam had a population of 14,139. Males constitute 50% of the p ...
) and Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to t ...
- still preserve and speak the language. The script of this language is derived from the Devanagari script and shares similarities with modern-day Gujarati.
Postage stamps
The first postage stamps of the state were issued for Princely State of Junagadh in 1864. They consisted of three lines of Hindi script in colourless letters on black, and were produced by hand-stamping withwatercolor
Watercolor (American English) or watercolour (British English; see spelling differences), also ''aquarelle'' (; from Italian diminutive of Latin ''aqua'' "water"), is a painting method”Watercolor may be as old as art itself, going back to ...
ink. A second issue in 1868 used coloured letters, printed in black or red on several colours of paper.
The issue of 1877 was the first to include Latin letters; the circular design included the inscription "SORUTH POSTAGE" at the top, and "ONE ANNA OF A RUPEE" (or "FOUR ANNAS...") at the bottom. Some of these were surcharged in 1913–14, followed by redesigned stamps in 1914.
A set of eight stamps in 1929 included pictures of Junagadh, the Gir lion
The Asiatic lion is a population of ''Panthera leo leo'' that today survives in the wild only in India. Since the turn of the 20th century, its range has been restricted to Gir National Park and the surrounding areas in the Indian state of Gujarat ...
, and the Kathi horse in addition to the nawab. In 1937 the one anna value was reissued reading "POSTAGE AND REVENUE".
The Indian province of Saurashtra did not design any of its own stamps, but before adopting the stamps of India, Saurashtra issued a court fee stamp overprinted for postal use, then created more one anna stamps by surcharging three stamps of the 1929 issue.
Natural resources
 Saurashtra has been a flourishing region and rich in natural resources since ancient times, while having gone through several droughts especially during the 20th century. Water resources and its related dynamics have influenced the region and its agro-economy to a certain extent. It is found that water was easily available in the region 10 to 15 years ago. Ashvin A. Shah, a US-based engineering consultant who conducted a survey in 1998 on water availability in the region, says, "The presence of 700,000 dugwells in Saurashtra region indicates the presence of extensive groundwater aquifers throughout the region. This means there is one well for fewer than 20 people or one well every 300 metres".
Amri Saurashtra went through severe droughts over the years to the extent that people could no longer grow crops, nor did they have drinking water available. There has been in recent times a campaign to take up rain water harvesting.
Significantly, the Check dam campaign from the late 1990s brought almost a drastic change resulting in raising water tables in Saurashtra. However, in 2019, the region was hit with a severe drought, affecting 20 districts in Gujarat, and water had to be brought in by tanker from the Sardar Sarovar Dam on the Narmada River.
Saurashtra has been a flourishing region and rich in natural resources since ancient times, while having gone through several droughts especially during the 20th century. Water resources and its related dynamics have influenced the region and its agro-economy to a certain extent. It is found that water was easily available in the region 10 to 15 years ago. Ashvin A. Shah, a US-based engineering consultant who conducted a survey in 1998 on water availability in the region, says, "The presence of 700,000 dugwells in Saurashtra region indicates the presence of extensive groundwater aquifers throughout the region. This means there is one well for fewer than 20 people or one well every 300 metres".
Amri Saurashtra went through severe droughts over the years to the extent that people could no longer grow crops, nor did they have drinking water available. There has been in recent times a campaign to take up rain water harvesting.
Significantly, the Check dam campaign from the late 1990s brought almost a drastic change resulting in raising water tables in Saurashtra. However, in 2019, the region was hit with a severe drought, affecting 20 districts in Gujarat, and water had to be brought in by tanker from the Sardar Sarovar Dam on the Narmada River.
References
Sources and external links
* * Ron Wood, ''Soruth'' (Handbook of Indian Philately, Series 2, Hampshire, UK: The India Study Circle for Philately, 1999) * Sapovadia, Vrajlal K., Saurashtra: A Language, Region, Culture & Community (3 April 2012). Available at SSRN: http://ssrn.com/abstract=2033685 {{Gujarat Historical Indian regions Regions of Gujarat Gulf of Khambhat