|
Salem, Tamil Nadu
Salem () is a major city in Salem district, located on the banks of the Thirumanimutharu river in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu surrounded by mountains. Salem is the List of cities in Tamil Nadu by population, fifth largest urban agglomeration in the state, and the List of metropolitan areas in Tamil Nadu, third largest metropolitan region. The city is large. History Early period Around the beginning of the common era, the existence of a culturally and economically advanced society in Salem two thousand years ago is evident from the discovery of silver coins of the Roman Emperor Nero, Tiberices Claudices Nero (37–68 CE) in Koneripatti of Salem in 1987. Later, the Pandya dynasty started ruling the region around Salem. Afterwards, the Pallava dynasty arose in Salem, followed by Mahendra Varma Pallava coming to Salem and the rise of Saivite principles. Mahendra Varma Pallava was succeeded by Narasimha Varma Pallava. Soon, the Pandya dynasty ruled over Salem. The Hoysala r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil Script
The Tamil script ( ) is an abugida script that is used by Tamils and Tamil language, Tamil speakers in India, Sri Lanka, Malaysia, Singapore and elsewhere to write the Tamil language. It is one of the official scripts of the Indian Republic. Certain minority languages such as Saurashtra language, Saurashtra, Badaga language, Badaga, Irula language, Irula and Paniya language, Paniya are also written in the Tamil script. Characteristics The Tamil script has 12 vowels (, , "soul-letters"), 18 consonants (, , "body-letters") and one special character, the (, ). is called "அக்கு", ''akku,'' and is classified in Tamil orthography as being neither a consonant nor a vowel. However, it is listed at the end of the vowel set. The script is Syllabary, syllabic, not alphabetic, and is written from left to right. History The Tamil script, like the other Brahmic scripts, is thought to have evolved from the original Brahmi script. The earliest inscriptions which are accepted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Million-plus Urban Agglomerations In India
India is a country in South Asia and is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the most-populous country with more than 1.4 billion people, home to nearly 17.5 percent of the world's population. India consists of twenty-eight states and eight union territories. Census The first official population census of India was conducted in 1872 and every ten years since 1951 by the office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner under the Ministry of Home Affairs. The last official census was conducted in 2011. The next census due in 2021 was delayed due to the COVID-19 pandemic and is scheduled for 2024. As per Government of India, an urban agglomeration (U.A.) is a continuous urban spread constituting a town and its adjoining outgrowths (OGs), or two or more physically contiguous towns together with or without outgrowths of such towns. An Urban Agglomeration must consist of at least a statutory town and its total population should not be less than 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities In Tamil Nadu By Population
The following are the cities in the state of States and territories of India, Tamil Nadu, India, which have a population of 1 lakh (100,000) and above (city / corporation area only), based on the Census of India, 2011, 2011 census conducted by Government of India. List of Cities in Tamil Nadu See also * List of metropolitan areas in Tamil Nadu * List of urban agglomerations in Tamil Nadu References {{DEFAULTSORT:Cities in Tamil Nadu by population Tamil Nadu-related lists Cities and towns in Tamil Nadu, Population Lists of cities in India by population, Tamil Nadu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian State
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, for a total of 36 subnational entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into 800 districts and smaller administrative divisions by the respective subnational government. The states of India are self-governing administrative divisions, each having a state government. The governing powers of the states are shared between the state government and the union government. On the other hand, the union territories are directly governed by the union government. History 1876–1919 The British Raj was a very complex political entity consisting of various imperial divisions and states and territories of varying autonomy. At the time of its establishment in 1876, it was made up of 584 constituent states and the directly ruled territories of the Crown. The entire empire was divided into provinces and agencies. A province consisted of territory under the direct rule of the Empe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirumanimutharu River
Thirumanimutharu River The Thirumanimutharu River originates from three reserved forests in the Eastern Ghats (Shevaroy Mountain) in Salem district, Tamil Nadu. It runs for 120 kilometers through Namakkal district before joining the Cauvery River near Paramathi Velur at Nanjai Edayar village in Namakkal district, Tamil Nadu. Source and Course The river originates from three reserved forests in the Eastern Ghats: * Velampatti Reserved Forest to the east, * Manjavadi Ghat Reserved Forest to the north, and * Kapputhu Reserved Forest to the west. Several streams flow southward from Velampatti Reserved Forest (), converging into a single river known as the East Thirumanimutharu. This river passes through several villages, including Kuttathupatti, Palapatti, Jalakandapuram, Sarkar Nattamangalam, and Karumapuram, before entering Karipatti village. From Karipatti village, the Thirumanimutharu flows westward, passing through Ayothiyapattinam on its way to Salem town. Three water st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Literacy In India
Literacy in India is a key for social-economic progress. The 2011 census, indicated a 2001–2011 literacy growth of 9.2%, which is slower than the growth seen during the previous decade. At the then-current rate of progress in 1990, one study projected that universal literacy might be reached by 2060. The census of India pegged the average literacy rate as 73% in 2011 while National Statistical Commission surveyed literacy to be 80.6% in 2017–18. Meanwhile, the National Sample Survey Office (India), National Sample Survey Office in its 2023–2024 annual PLFS report stated the total literacy rate of India to be 80.9%. Literacy rate in urban areas was 90%, higher than rural areas with 77%. There is a wide gender disparity in the literacy rate in India and effective literacy rates (age 7 and above) was 88% for men and 81% for women. The lower female literacy rate has a dramatically negative impact on Family planning in India, family planning and population stabilisation efforts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Sex Ratio
The human sex ratio is the ratio of males to females in a population in the context of anthropology and demography. In humans, the natural sex ratio at birth is slightly biased towards the male sex. It is estimated to be about 1.05 worldwide or within a narrow range from 1.03 to 1.06 males per female at birth. The sex ratio for the entire world population (all ages) is approximately 101 males to 100 females . The sex ratios at birth and of the total population are affected by various factors including natural factors, exposure to pesticides and environmental contaminants, war casualties, returning soldier effect, effects of war on men, sex-selective abortions, infanticides, aging, gendercide, problems with birth registration and Life expectancy#Sex differences, sex differences in life expectancy. Human sex ratios, either at birth or in the population as a whole, can be reported in any of four ways: the ratio of males to females, the ratio of females to males, the proportion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Male
Male (Planet symbols, symbol: ♂) is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete (sex cell) known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or Egg cell, ovum, in the process of fertilisation. A male organism cannot sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually without access to at least one ovum from a female, but some organisms can reproduce both sexually and Asexual reproduction, asexually. Most male mammals, including male humans, have a Y chromosome, which codes for the production of larger amounts of testosterone to develop male reproductive organs. In humans, the word ''male'' can also be used to refer to gender, in the social sense of gender role or gender identity. Overview The existence of separate sexes has evolved independently at different times and in different lineage (evolution), lineages, an example of convergent evolution. The repeated pattern is sexual reproduction in isogamy, isogamous species with two or more mating types with gametes of identic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Female
An organism's sex is female ( symbol: ♀) if it produces the ovum (egg cell), the type of gamete (sex cell) that fuses with the male gamete (sperm cell) during sexual reproduction. A female has larger gametes than a male. Females and males are results of the anisogamous reproduction system, wherein gametes are of different sizes (unlike isogamy where they are the same size). The exact mechanism of female gamete evolution remains unknown. In species that have males and females, sex-determination may be based on either sex chromosomes, or environmental conditions. Most female mammals, including female humans, have two X chromosomes. Characteristics of organisms with a female sex vary between different species, having different female reproductive systems, with some species showing characteristics secondary to the reproductive system, as with mammary glands in mammals. In humans, the word ''female'' can also be used to refer to gender in the social sense of gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistical composite index of life expectancy, Education Index, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, which is used to rank countries into four tiers of Human development (humanity), human development. A country scores a higher level of HDI when the life expectancy at birth, lifespan is higher, the education level is higher, and the gross national income GNI (PPP) per capita is higher. It was developed by Pakistani economist Mahbub ul-Haq and was further used to measure a country's development by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)'s Human Development Report Office. The 2010 Human Development Report introduced an List of countries by inequality-adjusted Human Development Index, inequality-adjusted Human Development Index (IHDI). While the simple HDI remains useful, it stated that "the IHDI is the actual level of huma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
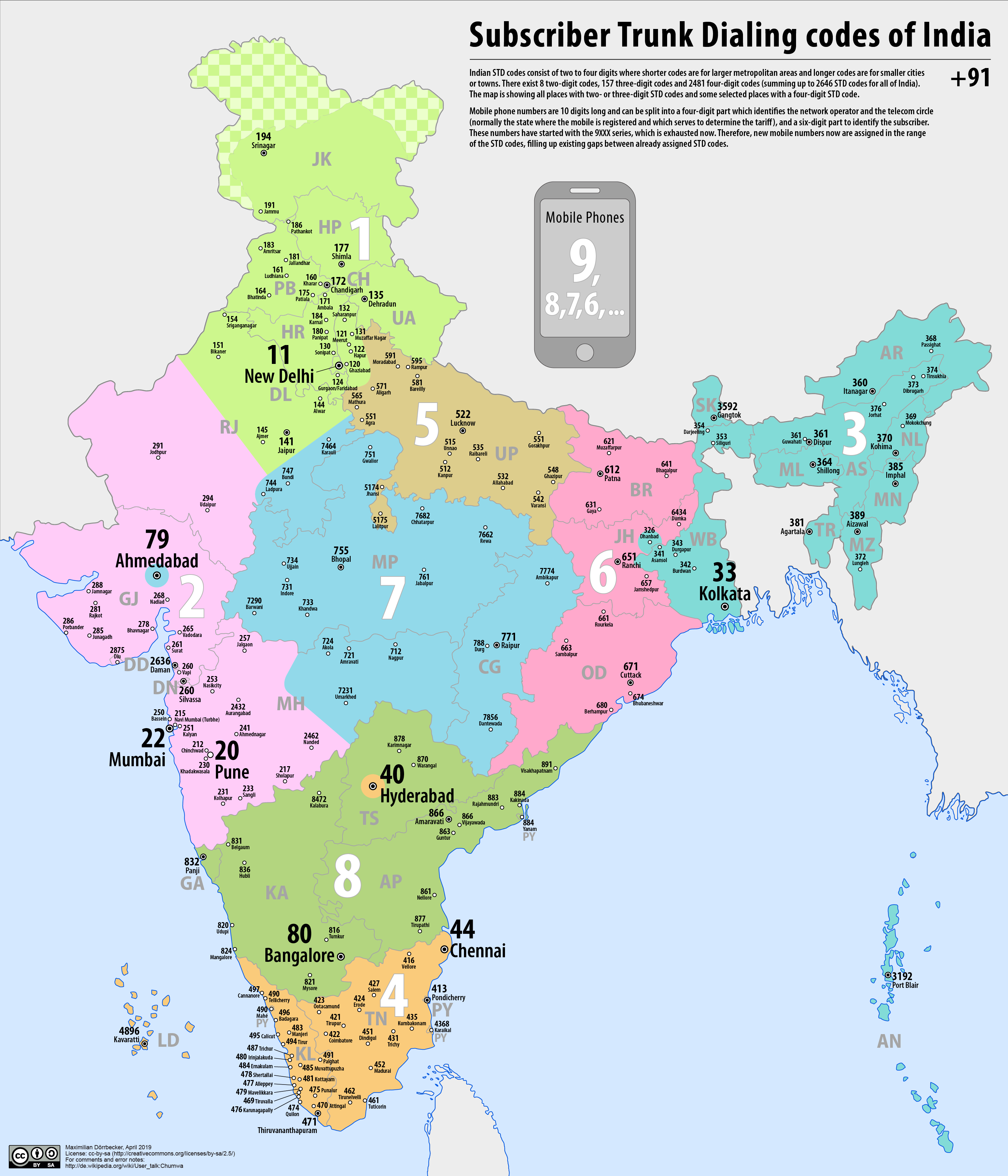
Telephone Numbers In India
Telephone numbers in India are administered under the ''National Numbering Plan of 2003'' by the Department of Telecommunications of the Government of India. The numbering plan was last updated in 2015. The country code "91" was assigned to India by the International Telecommunication Union in the 1960s. Fixed-line (landline) numbers Subscriber trunk dialling (STD) codes are assigned to each city, town and village. These codes can be between 2 and 8 digits long, with the largest metropolitan areas and cities having the shortest (two-digit) codes: *11 - New Delhi, Delhi *22 - Mumbai, Maharashtra *33 - Kolkata, West Bengal *44 - Chennai, Tamil Nadu *20 - Pune, Maharashtra *40 - Hyderabad, Telangana *79 - Ahmedabad, Gujarat *80 - Bengaluru, Karnataka Second-tier cities and metropolitan areas, as well as large or particularly significant towns have three-digit area codes: *120 - Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh, Ghaziabad and Noida, Uttar Pradesh *124 - Gurugram, Haryana *129 - Farida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postal Index Number
A Postal Index Number (PIN; sometimes redundantly a PIN code) refers to a six-digit code in the Indian postal code system used by India Post. On 15 August 2022, the PIN system celebrated its 50th anniversary. History The PIN system was introduced on 15 August 1972 by Shriram Bhikaji Velankar, an additional secretary in the Government of India, Government of India's Ministry of Communications (India), Ministry of Communications. The system was introduced to simplify the manual sorting and delivery of mail by eliminating confusion over incorrect addresses, similar place names, and different languages used by the public. PIN structure The first digit of a PIN indicates the zone, the second indicates the sub-zone, and the third, combined with the first two, indicates the sorting district within that zone. The final three digits are assigned to individual post offices within the sorting district. Postal zones There are nine postal zones in India, including eight regional zon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |