Sun workstation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The SUN workstation was a modular computer system designed at
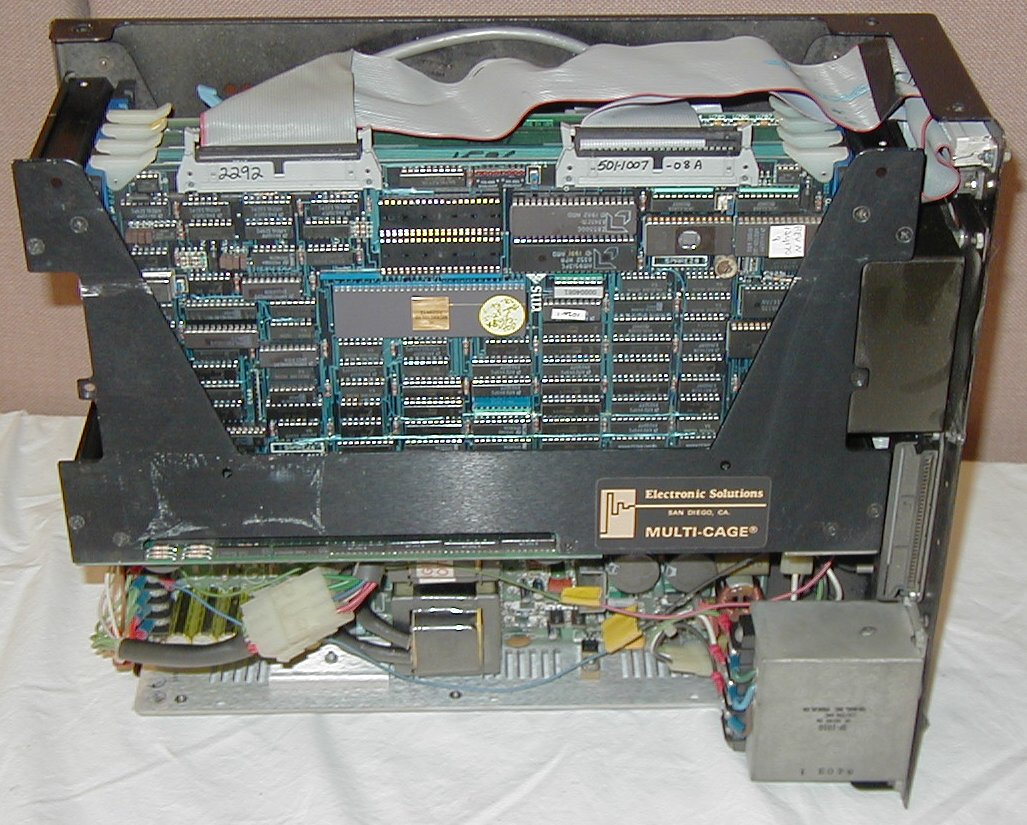 The Multibus computer interface made it possible to use standard enclosures, and to use circuit boards made by different vendors to create other configurations.
For example, the CPU board combined with a multi-port serial controller created a
The Multibus computer interface made it possible to use standard enclosures, and to use circuit boards made by different vendors to create other configurations.
For example, the CPU board combined with a multi-port serial controller created a
Stanford University
Leland Stanford Junior University, commonly referred to as Stanford University, is a Private university, private research university in Stanford, California, United States. It was founded in 1885 by railroad magnate Leland Stanford (the eighth ...
in the early 1980s. It became the seed technology for many commercial products, including the original workstations from Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems, Inc., often known as Sun for short, was an American technology company that existed from 1982 to 2010 which developed and sold computers, computer components, software, and information technology services. Sun contributed sig ...
.
History
In 1979Xerox
Xerox Holdings Corporation (, ) is an American corporation that sells print and electronic document, digital document products and services in more than 160 countries. Xerox was the pioneer of the photocopier market, beginning with the introduc ...
donated some Alto
The musical term alto, meaning "high" in Italian (Latin: '' altus''), historically refers to the contrapuntal part higher than the tenor and its associated vocal range. In four-part voice leading alto is the second-highest part, sung in ch ...
computers, developed at their Palo Alto Research Center
Future Concepts division (formerly Palo Alto Research Center, PARC and Xerox PARC) is a research and development company in Palo Alto, California. It was founded in 1969 by Jacob E. "Jack" Goldman, chief scientist of Xerox Corporation, as a div ...
, to Stanford's Computer Science Department, as well as other universities that were developing the early Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the Global network, global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a internetworking, network of networks ...
. The Altos were connected using Ethernet
Ethernet ( ) is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 198 ...
to form several local area network
A local area network (LAN) is a computer network that interconnects computers within a limited area such as a residence, campus, or building, and has its network equipment and interconnects locally managed. LANs facilitate the distribution of da ...
s. The SUN's design was inspired by that of the Alto, but used lower-cost modular components. (Many words are spelled phonetically) The project name was derived from the initials of the campus' Stanford University Network. CSL Technical Report 229 (First author name is misspelled on cover)
Professor Forest Baskett suggested the best-known configuration: a relatively low-cost personal workstation
A workstation is a special computer designed for technical or computational science, scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by a single user, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating syste ...
for computer-aided logic design work. The design created a 3M computer
The 3M computer industrial goal was first proposed in the early 1980s by Raj Reddy and his colleagues at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) as a minimum specification for academic and technical workstations. It requires at least one megabyte of m ...
: a 1 million instructions per second
Instructions per second (IPS) is a measure of a computer's Central processing unit, processor speed. For complex instruction set computers (CISCs), different Machine code, instructions take different amounts of time, so the value measured depen ...
(MIPS) processor, 1 Megabyte of memory and a 1 Megapixel raster scan
A raster scan, or raster scanning, is the rectangular pattern of image capture and reconstruction in television. By analogy, the term is used for raster graphics, the pattern of image storage and transmission used in most computer bitmap image s ...
bit-map graphics display. Sometimes the $10,000 estimated price was called the fourth "M" — a "Megapenny".
Director of Computer Facilities Ralph Gorin suggested other configurations and initially funded the project.
Graduate student Andy Bechtolsheim
Andreas Maria Maximilian Freiherr von Mauchenheim genannt Bechtolsheim (born 30 September 1955) is a German electrical engineer, entrepreneur and investor. He co-founded Sun Microsystems in 1982 and was its chief hardware designer. he's 68th w ...
designed the hardware, with several other students and staff members assisting with software and other aspects of the project. Vaughan Pratt
Vaughan Pratt (born April 12, 1944) is a Professor, Professor Emeritus at Stanford University, who was an early pioneer in the field of computer science. Since 1969, Pratt has made several contributions to foundational areas such as search algorit ...
became unofficial faculty leader of the project in 1980.
Three key technologies made the SUN workstation possible: very large-scale integration
Very may refer to:
* English's prevailing intensifier
Businesses
* The Very Group, a British retail/consumer finance corporation
** Very (online retailer), their main e-commerce brand
* VERY TV, a Thai television channel
Places
* Véry, ...
(VLSI) integrated circuits
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
, Multibus and ECAD
Electronic design automation (EDA), also referred to as electronic computer-aided design (ECAD), is a category of software tools for designing electronic systems such as integrated circuits and printed circuit boards. The tools work together ...
.
ECAD (Electronic Computer Assisted Design, now known as Electronic design automation) allowed a single designer to quickly develop systems of greater complexity.
The Stanford Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (SAIL) had pioneered personal display terminals, but the 1971 system was showing its age. Bechtolsheim used the Stanford University Drawing System (SUDS) to design the SUN boards on the SAIL system. SUDS had been originally developed for the Foonly
Foonly Inc. was an American computer company formed by Dave Poole in 1976, that produced a series of Digital Equipment Corporation, DEC PDP-10 compatible mainframe computer, mainframe computers.
The first and most famous Foonly machine, the F1, ...
computer.
The Structured Computer Aided Logic Design (SCALD) package was then used to verify the design, automate layout and produce wire-wrapped
Close-up of a wire-wrap connection
Typical wire wrap construction of crossbar_switch.html" ;"title="Bell System telephone crossbar switch">Bell System telephone crossbar switch. Some types of connection were soldered.
Wire wrap is an electron ...
prototypes and then printed circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a Lamination, laminated sandwich structure of electrical conduction, conductive and Insulator (electricity), insulating layers, each with a pattern of traces, planes ...
s. CSL Technical Report 201
VLSI integrated circuits finally allowed for a high-level of hardware functionality to be included in a single chip. The graphics display controller was the first board designed, published in 1980. A Motorola 68000
The Motorola 68000 (sometimes shortened to Motorola 68k or m68k and usually pronounced "sixty-eight-thousand") is a 16/32-bit complex instruction set computer (CISC) microprocessor, introduced in 1979 by Motorola Semiconductor Products Sector ...
CPU, along with memory, a parallel port controller and a serial port controller, were included on the main CPU board designed by Bechtolsheim. The third board was an interface to the 2.94 Mbits/second experimental Ethernet (before the speed was standardized at 10 Mbits/second).
 The Multibus computer interface made it possible to use standard enclosures, and to use circuit boards made by different vendors to create other configurations.
For example, the CPU board combined with a multi-port serial controller created a
The Multibus computer interface made it possible to use standard enclosures, and to use circuit boards made by different vendors to create other configurations.
For example, the CPU board combined with a multi-port serial controller created a terminal server
A terminal server connects devices with a serial port to a local area network (LAN). Products marketed as terminal servers can be very simple devices that do not offer any security functionality, such as data encryption and user authentication. ...
(called a TIP, for Terminal Interface Processor) which connected many terminals to the Digital Equipment Corporation
Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC ), using the trademark Digital, was a major American company in the computer industry from the 1960s to the 1990s. The company was co-founded by Ken Olsen and Harlan Anderson in 1957. Olsen was president until ...
time-sharing systems at Stanford or anywhere on the Internet.
Configuring multiple Ethernet controllers (including commercial ones, once they were available) with one CPU board created a router. William Yeager wrote the software, which was later adopted and evolved by Cisco Systems
Cisco Systems, Inc. (using the trademark Cisco) is an American multinational corporation, multinational digital communications technology conglomerate (company), conglomerate corporation headquartered in San Jose, California. Cisco develops, m ...
on its version of the hardware.
Les Earnest licensed the CPU board for one of the first commercial low-cost laser printer
Laser printing is an electrostatic digital printing process. It produces high-quality text and graphics (and moderate-quality photographs) by repeatedly passing a laser beam back and forth over a Electric charge, negatively charged cylinder call ...
controllers at a company called Imagen.
The processor board was combined with a prototype high performance graphics display by students of James H. Clark
James Henry Clark (born March 23, 1944) is an American entrepreneur and computer scientist. He founded several notable Silicon Valley technology companies, including Silicon Graphics, Netscape, myCFO, and Healtheon. His research work in compu ...
.
That group later formed Silicon Graphics Incorporated
Silicon Graphics, Inc. (stylized as SiliconGraphics before 1999, later rebranded SGI, historically known as Silicon Graphics Computer Systems or SGCS) was an American high-performance computing manufacturer, producing computer hardware and soft ...
.
Eventually about ten SUN workstations were built during 1981 and 1982, after which Stanford declined to build any more. Bechtolsheim then licensed the hardware design to several vendors, but was frustrated that none of them had chosen to build a workstation.
Vinod Khosla, also from Stanford, convinced Bechtolsheim along with Scott McNealy
Scott McNealy (born November 13, 1954) is an American businessman. He is most famous for co-founding the computer technology company Sun Microsystems in 1982 along with Vinod Khosla, Bill Joy, and Andy Bechtolsheim. In 2004, while still at Sun ...
to found Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems, Inc., often known as Sun for short, was an American technology company that existed from 1982 to 2010 which developed and sold computers, computer components, software, and information technology services. Sun contributed sig ...
in order to build the Sun-1
Sun-1 was the first generation of UNIX computer workstations and servers produced by Sun Microsystems, launched in May 1982. These were based on a CPU board designed by Andy Bechtolsheim while he was a graduate student at Stanford University an ...
workstation, which included some improvements to the earlier design. CSL Technical Report 1579
Other faculty members who did research using SUN workstations included David Cheriton
David Ross Cheriton (born March 29, 1951) is a Canadian computer scientist, businessman, philanthropist, and venture capitalist. He is a computer science professor at Stanford University, where he founded and leads the Distributed Systems Group.
...
, Brian Reid, and John Hennessy.
See also
* NuMachine, a similar MIT projectReferences
External links
* {{cite web , title= SUN display , publisher=Stanford University
Leland Stanford Junior University, commonly referred to as Stanford University, is a Private university, private research university in Stanford, California, United States. It was founded in 1885 by railroad magnate Leland Stanford (the eighth ...
, date= January 2001 , url= http://infolab.stanford.edu/pub/voy/museum/pictures/display/SUN.htm , accessdate= May 1, 2011
History of computing hardware
Sun Microsystems
Stanford University
Computer workstations
68k-based computers