|
Sun-1
Sun-1 was the first generation of UNIX computer workstations and servers produced by Sun Microsystems, launched in May 1982. These were based on a CPU board designed by Andy Bechtolsheim while he was a graduate student at Stanford University and funded by DARPA. The Sun-1 systems ran SunOS 0.9, a port of UniSoft's UniPlus V7 port of Seventh Edition UNIX to the Motorola 68000 microprocessor, with no window system. Affixed to the case of early Sun-1 workstations and servers is a red bas relief emblem with the word ''SUN'' spelled using only symbols shaped like the letter ''U''. This is the original Sun logo, rather than the more familiar purple diamond shape used later. The first Sun-1 workstation was sold to Solo Systems in May 1982. The Sun-1/100 was used in the original Lucasfilm EditDroid non-linear editing system. Models Hardware The Sun-1 workstation was based on the Stanford University SUN workstation designed by Andy Bechtolsheim (advised by Vaughan Pratt and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
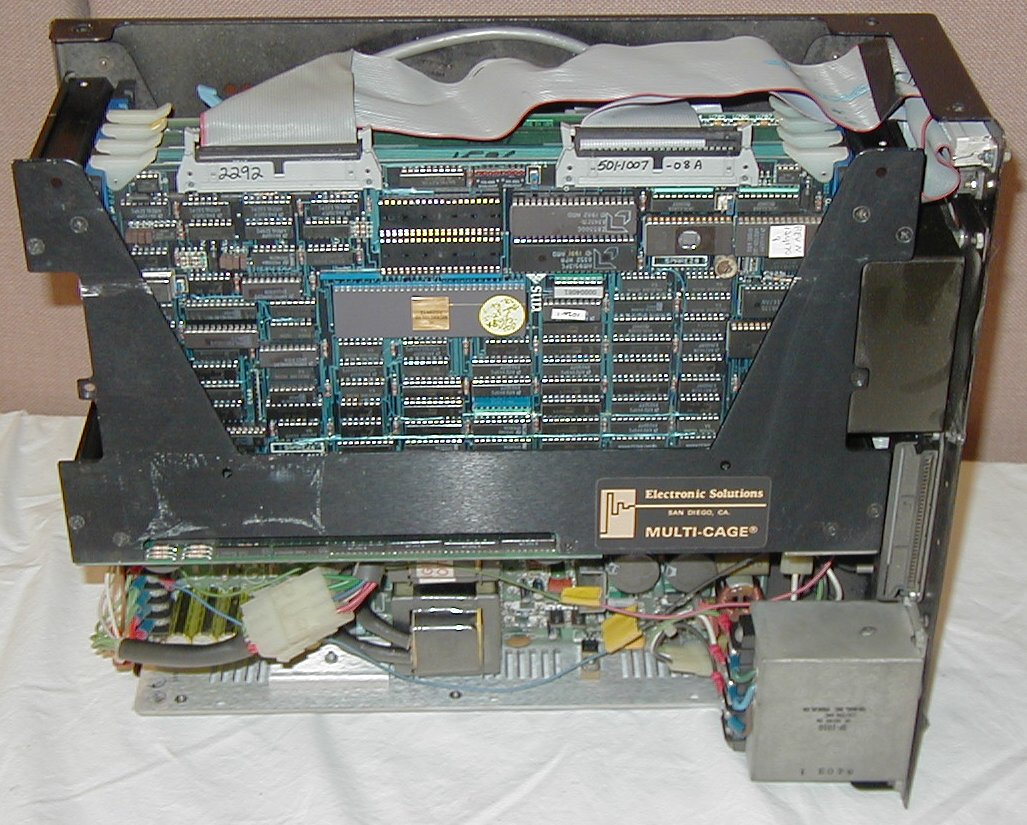
Sun100U Cardcage
Sun-1 was the first generation of UNIX computer workstations and servers produced by Sun Microsystems, launched in May 1982. These were based on a CPU board designed by Andy Bechtolsheim while he was a graduate student at Stanford University and funded by DARPA. The Sun-1 systems ran SunOS 0.9, a port of UniSoft's UniPlus V7 port of Seventh Edition UNIX to the Motorola 68000 microprocessor, with no window system. Affixed to the case of early Sun-1 workstations and servers is a red bas relief emblem with the word ''SUN'' spelled using only symbols shaped like the letter ''U''. This is the original Sun logo, rather than the more familiar purple diamond shape used later. The first Sun-1 workstation was sold to Solo Systems in May 1982. The Sun-1/100 was used in the original Lucasfilm EditDroid non-linear editing system. Models Hardware The Sun-1 workstation was based on the Stanford University SUN workstation designed by Andy Bechtolsheim (advised by Vaughan Pratt and Fores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun-2
The Sun-2 series of UNIX workstations and servers was launched by Sun Microsystems in November 1983. As the name suggests, the Sun-2 represented the second generation of Sun systems, superseding the original Sun-1 series. The Sun-2 series used a 10 MHz Motorola 68010 microprocessor with a proprietary Sun-2 Memory Management Unit (MMU), which enabled it to be the first Sun architecture to run a full virtual memory UNIX implementation, SunOS 1.0, based on 4.1BSD. Early Sun-2 models were based on the Intel Multibus architecture, with later models using VMEbus, which continued to be used in the successor Sun-3 and Sun-4 families. Sun-2 systems were supported in SunOS until version 4.0.3. A port to support Multibus Sun-2 systems in NetBSD was begun in January 2001 from the Sun-3 support in the NetBSD 1.5 release. Code supporting the Sun-2 began to be merged into the NetBSD tree in April 2001. sun2 is considered a tier 2 support platform as of NetBSD 7.0.1. Sun-2 models Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems, Inc., often known as Sun for short, was an American technology company that existed from 1982 to 2010 which developed and sold computers, computer components, software, and information technology services. Sun contributed significantly to the evolution of several key computing technologies, among them Unix, Reduced instruction set computer, RISC processors, thin client computing, and virtualization, virtualized computing. At its height, the Sun headquarters were in Santa Clara, California (part of Silicon Valley), on the former west campus of the Agnews Developmental Center. Sun products included computer servers and workstations built on its own Reduced instruction set computer, RISC-based SPARC processor architecture, as well as on x86-based AMD Opteron and Intel Xeon processors. Sun also developed its own computer storage, storage systems and a suite of software products, including the Unix-based SunOS and later Solaris operating system, Solaris operating s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
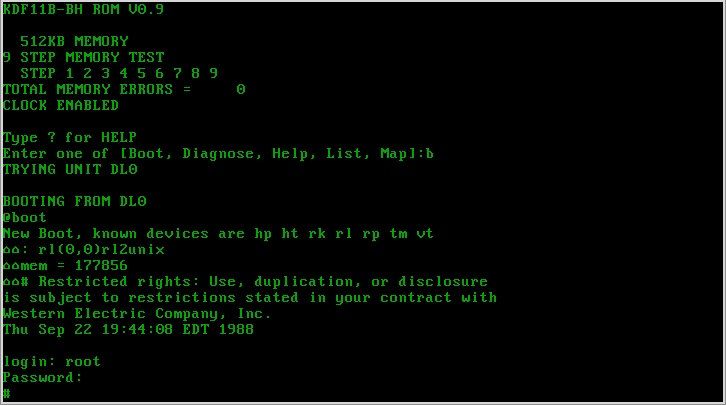
SunOS
SunOS is a Unix-branded operating system developed by Sun Microsystems for their workstation and server computer systems from 1982 until the mid-1990s. The ''SunOS'' name is usually only used to refer to versions 1.0 to 4.1.4, which were based on BSD, while versions 5.0 and later are based on UNIX System V Release 4 and are marketed under the brand name '' Solaris''. History SunOS 1 only supported the Sun-2 series systems, including Sun-1 systems upgraded with Sun-2 ( 68010) CPU boards. SunOS 2 supported Sun-2 and Sun-3 ( 68020) series systems. SunOS 4 supported Sun-2 (until release 4.0.3), Sun-3 (until 4.1.1), Sun386i (4.0, 4.0.1 and 4.0.2 only) and Sun-4 ( SPARC) architectures. Although SunOS 4 was intended to be the first release to fully support Sun's new SPARC processor, there was also a SunOS 3.2 release with preliminary support for Sun-4 systems. SunOS 4.1.2 introduced support for Sun's first sun4m-architecture multiprocessor machines (t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UniSoft
UniSoft Corporation is an American software developer established in 1981, originally focused on the development of Unix ports for various computer architectures. Based in Millbrae, California, it now builds standardization and conformance testing applications for the digital television market. History UniSoft was founded on October 5, 1981, in Emeryville, California. Their original business was Unix development, and they were soon recognized as one of the early implementers of Unix for the emerging 16-bit microcomputer market. By 1989, they had completed over 225 Unix implementations on various hardware platforms, which was estimated to have been about 65% of all such ports. UniSoft's port of Version 7 Unix was the first operating system for Sun Microsystems' Sun-1 workstations and servers. It also developed Apple Inc.'s Unix variant, A/UX, for the Apple Macintosh II. UniSoft UniPlus System V served as the basis of Silicon Graphics' GL2 operating system, which eventually e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Management Unit
A memory management unit (MMU), sometimes called paged memory management unit (PMMU), is a computer hardware unit that examines all references to computer memory, memory, and translates the memory addresses being referenced, known as virtual memory addresses, into physical addresses in main memory. In modern systems, programs generally have addresses that access the theoretical maximum memory of the computer architecture, 32 or 64 bits. The MMU maps the addresses from each program into separate areas in physical memory, which is generally much smaller than the theoretical maximum. This is possible because programs rarely use large amounts of memory at any one time. Most modern operating systems (OS) work in concert with an MMU to provide virtual memory (VM) support. The MMU tracks memory use in fixed-size blocks known as ''pages''. If a program refers to a location in a page that is not in physical memory, the MMU sends an interrupt to the operating system. The OS selects a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motorola 68000
The Motorola 68000 (sometimes shortened to Motorola 68k or m68k and usually pronounced "sixty-eight-thousand") is a 16/32-bit complex instruction set computer (CISC) microprocessor, introduced in 1979 by Motorola Semiconductor Products Sector. The design implements a 32-bit instruction set, with 32-bit registers and a 16-bit internal data bus. The address bus is 24 bits and does not use memory segmentation, which made it easier to program for. Internally, it uses a 16-bit data arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and two more 16-bit ALUs used mostly for addresses, and has a 16-bit external data bus. For this reason, Motorola termed it a 16/32-bit processor. As one of the first widely available processors with a 32-bit instruction set, large unsegmented address space, and relatively high speed for the era, the 68k was a popular design through the 1980s. It was widely used in a new generation of personal computers with graphical user interfaces, including the Macintosh 128K, Amiga, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multibus
Multibus is a computer bus standard used in industrial systems. It was developed by Intel Corporation and was adopted as the IEEE 796 bus. The Multibus specification was a robust industry standard with a relatively large form factor, allowing complex devices to be designed on it. Because it was well-defined and well-documented, a Multibus-compatible industry grew around it, with many companies making card cages and enclosures for it. Many others made CPU, memory, and other peripheral boards. In 1982 there were over 100 Multibus board and systems manufacturers. This allowed complex systems to be built from commercial off-the-shelf hardware, and also allowed companies to innovate by designing a proprietary Multibus board, then integrate it with another vendor's hardware to create a complete system. One example of this was Sun Microsystems with their Sun-1 and Sun-2 workstations. Sun built custom-designed CPU, memory, SCSI, and video display boards, and then added 3Com Ether ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andy Bechtolsheim
Andreas Maria Maximilian Freiherr von Mauchenheim genannt Bechtolsheim (born 30 September 1955) is a German electrical engineer, entrepreneur and investor. He co-founded Sun Microsystems in 1982 and was its chief hardware designer. he's 68th wealthiest according to Bloomberg Billionaires Index and ''Forbes'' with an estimated net worth of US$28.9billion.Andreas von Bechtolsheim profile Forbes.com, 14 December 2024. Early life and education Bechtolsheim was born at Hängeberg am Ammersee, located in Finning,[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EditDroid
The EditDroid is a computerized analog non-linear editing (NLE) system which was developed by Lucasfilm spin-off company, the Droid Works and Convergence Corporation who formed a joint venture company. The company existed up through the mid-'80s to the early '90s in an attempt to move from analog editing methods to digital. EditDroid debuted at the National Association of Broadcasters (NAB) 62nd Annual meeting in Las Vegas in 1984 concurrent with another editing tool that would compete with the EditDroid for all its years in production, the Montage Picture Processor. The EditDroid was never a commercial success and after the close of ''The Droid Works'' in 1987 and subsequent redevelopment of the product for seven years, the software was eventually sold to Avid Technology in 1993. Only 24 EditDroid systems were ever produced. Features The system is LaserDisc-based, relying on several LaserDisc players and a database system which queues up the clips in the order needed from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seventh Edition Unix
Version 7 Unix, also called Seventh Edition Unix, Version 7 or just V7, was an important early release of the Unix operating system. V7, released in 1979, was the last Bell Laboratories release to see widespread distribution before the commercialization of Unix by AT&T Corporation in the early 1980s. V7 was originally developed for Digital Equipment Corporation's PDP-11 minicomputers and was later ported to other platforms. Overview Unix versions from Bell Labs were designated by the edition of the user's manual with which they were accompanied. Released in 1979, the Seventh Edition was preceded by Sixth Edition, which was the first version licensed to commercial users. Development of the Research Unix line continued with the Eighth Edition, which incorporated development from 4.1BSD, through the Tenth Edition, after which the Bell Labs researchers concentrated on developing Plan 9. V7 was the first readily portable version of Unix. As this was the era of minicomputers, wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |