Red Rain In Kerala on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
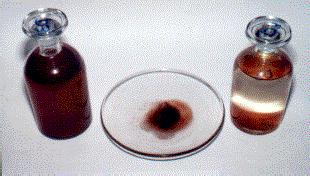 The Kerala red rain phenomenon was a blood rain event that occurred in
The Kerala red rain phenomenon was a blood rain event that occurred in
 The coloured rain of Kerala began falling on 25 July 2001, in the districts of Kottayam and
The coloured rain of Kerala began falling on 25 July 2001, in the districts of Kottayam and
–
–
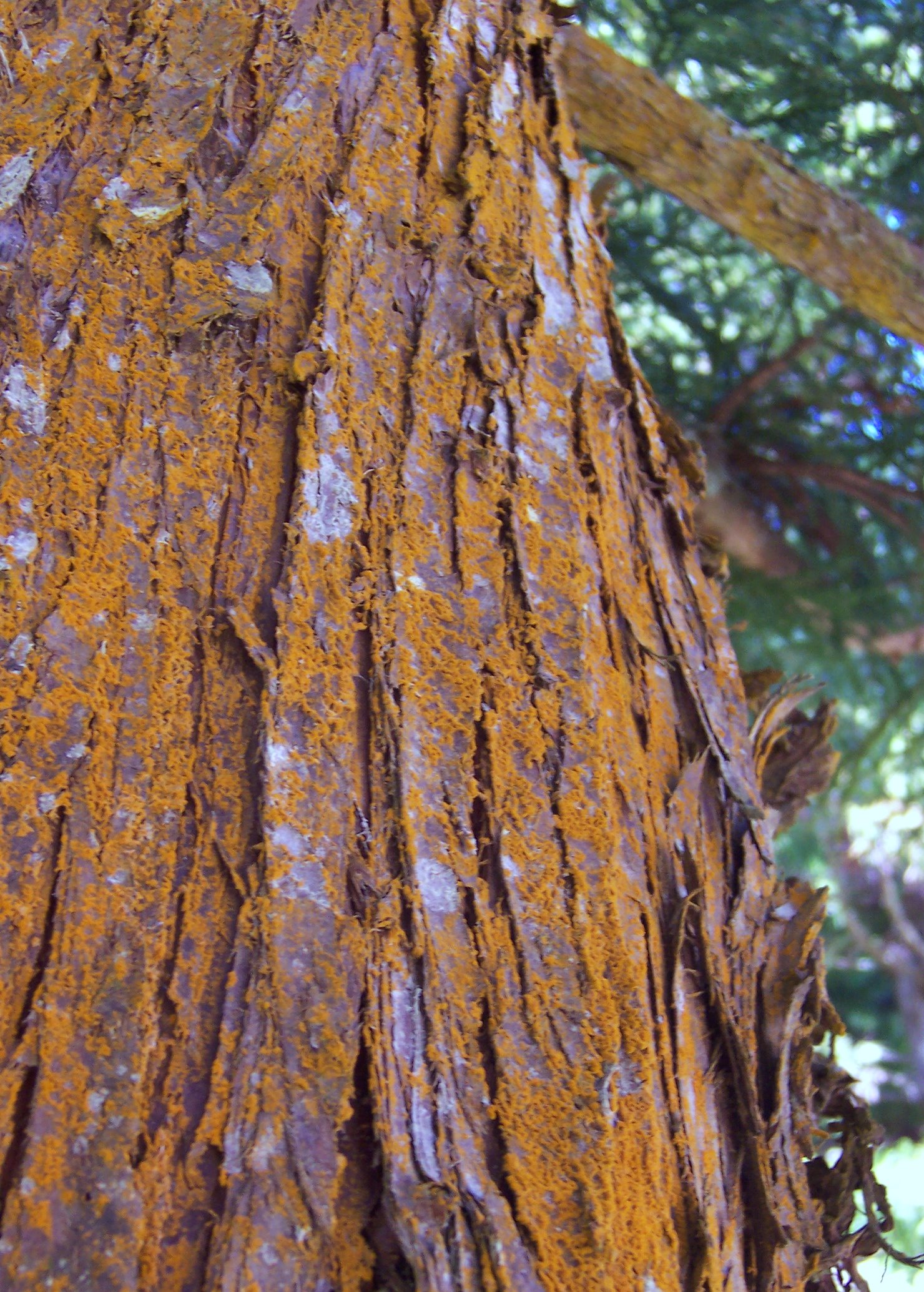 The site was again visited on 16 August 2001 and it was found that almost all the trees, rocks and even lamp posts in the region were covered with ''Trentepohlia'' estimated to be in sufficient amounts to generate the quantity of spores seen in the rainwater. Although red or orange, ''Trentepohlia'' is a
The site was again visited on 16 August 2001 and it was found that almost all the trees, rocks and even lamp posts in the region were covered with ''Trentepohlia'' estimated to be in sufficient amounts to generate the quantity of spores seen in the rainwater. Although red or orange, ''Trentepohlia'' is a
and reported their similarity to algal spores, and found no evidence to suggest that the rain contained dust, sand, fat globules, or blood. In November 2012, Rajkumar Gangappa and Stuart Hogg from the
Sampath, S., Abraham, T. K., Sasi Kumar, V., & Mohanan, C.N. (2001). Colored Rain: A Report on the Phenomenon. CESS-PR-114-2001, Center for Earth Science Studies and Tropical Botanic Garden and Research Institute.
"When aliens rained over India" by Hazel Muir in ''New Scientist''
"Searching for 'our alien origins'" by Andrew Thompson in ''BBC News''
"Fluorescence Mystery in Red Rain Cells of Kerala, India " Linda Moulton Howe ''Earthfiles''
"Home page of Dr A Santhosh Kumar"
{{DEFAULTSORT:Red Rain In Kerala 2001 in India 2001 meteorology Anomalous weather Environment of Kerala Panspermia Weather events in India Rain Changanassery Meteorological hypotheses Trentepohliaceae
 The Kerala red rain phenomenon was a blood rain event that occurred in
The Kerala red rain phenomenon was a blood rain event that occurred in Wayanad district
Wayanad () is a district in the north-east of the Indian state of Kerala, with its administrative headquarters at the municipality of Kalpetta. It is the only plateau in Kerala. The Wayanad Plateau forms a continuation of the Mysore Plateau, ...
of southern Indian state Kerala
Kerala ( , ) is a States and union territories of India, state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile ...
on Monday, 15 July 1957 and the colour subsequently turned yellow and also 25 July to 23 September 2001, when heavy downpours of red-coloured rain fell sporadically in Kerala, staining clothes pink. Yellow, green and black rain was also reported. Coloured rain was also reported in Kerala in 1896 and several times since, most recently in June 2012, and from 15 November 2012 to 27 December 2012 in eastern and north-central provinces of Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
.
Following a light-microscopy examination in 2001, it was initially thought that the rains were coloured by fallout from a hypothetical meteor
A meteor, known colloquially as a shooting star, is a glowing streak of a small body (usually meteoroid) going through Earth's atmosphere, after being heated to incandescence by collisions with air molecules in the upper atmosphere,
creating a ...
burst
Burst may refer to:
*Burst mode (disambiguation), a mode of operation where events occur in rapid succession
**Burst transmission, a term in telecommunications
**Burst switching, a feature of some packet-switched networks
**Bursting, a signaling mo ...
, but a study commissioned by the Government of India
The Government of India (ISO 15919, ISO: Bhārata Sarakāra, legally the Union Government or Union of India or the Central Government) is the national authority of the Republic of India, located in South Asia, consisting of States and union t ...
concluded that the rains had been coloured by airborne spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual reproduction, sexual (in fungi) or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for biological dispersal, dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores fo ...
s from a locally prolific terrestrial green algae from the genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
'' Trentepohlia''.
Occurrence
Idukki
Idukki (ഇടുക്കി; ) is one of the 14 districts in the Indian state of Kerala in the southwest of the country. It is the largest district in Kerala and lies amid the Cardamom Hills of Western Ghats in Kerala. Idukki district co ...
in the southern part of the state. Yellow, green, and black rain was also reported. Many more occurrences of the red rain were reported over the following ten days, and then with diminishing frequency until late September. According to locals, the first coloured rain was preceded by a loud thunder
Thunder is the sound caused by lightning. Depending upon the distance from and nature of the lightning, it can range from a long, low rumble to a sudden, loud crack. The sudden increase in temperature and hence pressure caused by the lightning pr ...
clap and flash of light, and followed by groves of trees shedding shrivelled grey "burnt" leaves. Shriveled leaves and the disappearance and sudden formation of wells were also reported around the same time in the area.Mystery of the scarlet rains and other tales–
Times of India
''The Times of India'' (''TOI'') is an Indian English-language daily newspaper and digital news media owned and managed by the Times Group. It is the List of newspapers in India by circulation, third-largest newspaper in India by circulation an ...
, 6 August 2001Now wells form spontaneously in Kerala–
Times of India
''The Times of India'' (''TOI'') is an Indian English-language daily newspaper and digital news media owned and managed by the Times Group. It is the List of newspapers in India by circulation, third-largest newspaper in India by circulation an ...
, 5 August 2001 (from the Internet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American 501(c)(3) organization, non-profit organization founded in 1996 by Brewster Kahle that runs a digital library website, archive.org. It provides free access to collections of digitized media including web ...
) It typically fell over small areas, no more than a few square kilometres in size, and was sometimes so localised that normal rain could be falling just a few meters away from the red rain. Red rainfalls typically lasted less than 20 minutes. Each millilitre of rain water contained about 9 million red particles. Extrapolating these figures to the total amount of red rain estimated to have fallen, it was estimated that of red particles had fallen on Kerala.
Description of the particles
The brownish-red solid separated from the red rain consisted of about 90% round red particles and the balance consisted of debris. The particles in suspension in the rain water were responsible for the colour of the rain, which at times was strongly coloured red. A small percentage of particles were white or had light yellow, bluish grey and green tints. The particles were typically 4 to 10 μm across and spherical or oval.Electron microscope
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of electrons as a source of illumination. It uses electron optics that are analogous to the glass lenses of an optical light microscope to control the electron beam, for instance focusing it ...
images showed the particles as having a depressed centre. At still higher magnification some particles showed internal structures.
Chemical composition
Some water samples were taken to the Centre for Earth Science Studies (CESS) in India, where they separated the suspended particles by filtration. The pH of the water was found to be around 7 (neutral). Theelectrical conductivity
Electrical resistivity (also called volume resistivity or specific electrical resistance) is a fundamental specific property of a material that measures its electrical resistance or how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity in ...
of the rainwater showed the absence of any dissolved salts
In chemistry, a salt or ionic compound is a chemical compound consisting of an assembly of positively charged ions ( cations) and negatively charged ions (anions), which results in a compound with no net electric charge (electrically neutral). ...
. Sediment (red particles plus debris) was collected and analysed by the CESS using a combination of ion-coupled plasma mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a ''mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used ...
, atomic absorption spectrometry and wet chemical methods. The major elements found are listed below. The CESS analysis also showed significant amounts of heavy metals
upright=1.2, Crystals of lead.html" ;"title="osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead">osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead
Heavy metals is a controversial and ambiguous term for metallic elements with relatively h ...
, including nickel (43 ppm), manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition m ...
(59 ppm), titanium
Titanium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in ...
(321 ppm), chromium
Chromium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6 element, group 6. It is a steely-grey, Luster (mineralogy), lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium ...
(67ppm) and copper (55 ppm).
Physicists Godfrey Louis and Santhosh Kumar of the Mahatma Gandhi University, Kerala, used energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy analysis of the red solid and showed that the particles were composed of mostly carbon and oxygen, with trace amounts of silicon and iron. A CHN analyser showed content of 43.03% carbon, 4.43% hydrogen, and 1.84% nitrogen.
Tom Brenna in the Division of Nutritional Sciences at Cornell University
Cornell University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university based in Ithaca, New York, United States. The university was co-founded by American philanthropist Ezra Cornell and historian and educator Andrew Dickson W ...
conducted carbon and nitrogen isotope analyses using a scanning electron microscope with X-ray micro-analysis, an elemental analyser, and an isotope ratio (IR) mass spectrometer. The red particles collapsed
when dried, which suggested that they were filled with fluid. The amino acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the Proteinogenic amino acid, 22 α-amino acids incorporated into p ...
in the particles were analysed and seven were identified (in order of concentration): phenylalanine
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an essential α-amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituent, substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of ...
, glutamic acid
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α- amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can ...
/glutamine
Glutamine (symbol Gln or Q) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Its side chain is similar to that of glutamic acid, except the carboxylic acid group is replaced by an amide. It is classified as a charge-neutral ...
, serine
Serine
(symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − ...
, aspartic acid
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. The L-isomer of aspartic acid is one of the 22 proteinogenic amino acids, i.e., the building blocks of protei ...
, threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form when dissolved in water), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− ...
, and arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidinium, guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) a ...
. The results were consistent with a marine origin or a terrestrial plant that uses a C4 photosynthetic pathway.
Government report
Initially, the Centre for Earth Science Studies (CESS) stated that the likely cause of the red rain was an exploding meteor, which had dispersed about 1,000 kg (one ton) of material. A few days later, following a basiclight microscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view subjects too small to be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, el ...
evaluation, the CESS retracted this as they noticed the particles resembled spores, and because debris from a meteor would not have continued to fall from the stratosphere onto the same area while unaffected by wind. A sample was, therefore, handed over to the Tropical Botanical Garden and Research Institute (TBGRI) for microbiological
Microbiology () is the scientific study of microorganisms, those being of unicellular (single-celled), multicellular (consisting of complex cells), or acellular (lacking cells). Microbiology encompasses numerous sub-disciplines including virol ...
studies, where the spores were allowed to grow in a medium suitable for growth of algae and fungi. The inoculated petri dishes and conical flasks were incubated for three to seven days and the cultures were observed under a microscope.
In November 2001, commissioned by the Government of India
The Government of India (ISO 15919, ISO: Bhārata Sarakāra, legally the Union Government or Union of India or the Central Government) is the national authority of the Republic of India, located in South Asia, consisting of States and union t ...
's Department of Science & Technology, the Centre for Earth Science Studies (CESS) and the Tropical Botanical Garden and Research Institute (TBGRI) issued a joint report, which concluded:
chlorophyte
Chlorophyta is a division (botany), division of green algae informally called chlorophytes.
Description
Chlorophytes are eukaryotic organisms composed of cells with a variety of coverings or walls, and usually a single green chloroplast in ea ...
green alga which can grow abundantly on tree bark or damp soil and rocks, but is also the photosynthetic symbiont
Symbiosis (Ancient Greek : living with, companionship < : together; and ''bíōsis'': living) is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction, between two organisms of different species. The two organisms, termed symbionts, can fo ...
or photobiont of many lichens, including some of those abundant on the trees in Changanassery area. The strong orange colour of the algae, which masks the green of the chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words (, "pale green") and (, "leaf"). Chlorophyll allows plants to absorb energy ...
, is caused by the presence of large quantities of orange carotenoid
Carotenoids () are yellow, orange, and red organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria, archaea, and fungi. Carotenoids give the characteristic color to pumpkins, carrots, parsnips, corn, tomatoes, cana ...
pigments. A lichen
A lichen ( , ) is a hybrid colony (biology), colony of algae or cyanobacteria living symbiotically among hypha, filaments of multiple fungus species, along with yeasts and bacteria embedded in the cortex or "skin", in a mutualism (biology), m ...
is not a single organism, but the result of a partnership (symbiosis
Symbiosis (Ancient Greek : living with, companionship < : together; and ''bíōsis'': living) is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction, between two organisms of different species. The two organisms, termed symbionts, can fo ...
) between a fungus and an alga or cyanobacterium.
The report also stated that there was no meteoric, volcanic or desert dust origin present in the rainwater and that its colour was not due to any dissolved gases or pollutants. The report concluded that heavy rains in Kerala – in the weeks preceding the red rains – could have caused the widespread growth of lichens, which had given rise to a large quantity of spores into the atmosphere. However, for these lichen to release their spores simultaneously, it is necessary for them to enter their reproductive phase at about the same time. The CESS report noted that while this may be a possibility, it is quite improbable. Also, they could find no satisfactory explanation for the apparently extraordinary dispersal, nor for the apparent uptake of the spores into clouds. CESS scientists noted that "While the cause of the colour in the rainfall has been identified, finding the answers to these questions is a challenge." Attempting to explain the unusual spore proliferation and dispersal, researcher Ian Goddard proposed several local atmospheric models.
Parts of the CESS/TBGRI report were supported by Milton Wainwright
Milton Wainwright (born 23 February 1950) is a British microbiologist who is known for his research into what he claims could be extraterrestrial life found in the stratosphere.
Biography
Wainwright graduated from the University of Nottingham i ...
at the University of Sheffield
The University of Sheffield (informally Sheffield University or TUOS) is a public university, public research university in Sheffield, South Yorkshire, England. Its history traces back to the foundation of Sheffield Medical School in 1828, Fir ...
, who, together with Chandra Wickramasinghe, has studied stratospheric spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual reproduction, sexual (in fungi) or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for biological dispersal, dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores fo ...
s. In March 2006 Wainwright said the particles were similar in appearance to spores of a rust fungus
Rusts are fungal plant pathogens of the order Pucciniales (previously known as Uredinales) causing plant fungal diseases.
An estimated 168 rust genera and approximately 7,000 species, more than half of which belong to the genus ''Puccinia'', are ...
, later saying that he had confirmed the presence of DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
,David Darling's Newsletter #39and reported their similarity to algal spores, and found no evidence to suggest that the rain contained dust, sand, fat globules, or blood. In November 2012, Rajkumar Gangappa and Stuart Hogg from the
University of Glamorgan
The University of Glamorgan () was a public university based in South Wales, that merged with University of Wales, Newport to form the University of South Wales in April 2013. The university was based in Pontypridd, in Rhondda Cynon Taf, with ...
, UK, confirmed that the red rain cells from Kerala contain DNA.
In February 2015, a team of scientists from India and Austria, also supported the identification of the algal spores as '' Trentepohlia annulata'', however, they speculate that the spores from the 2011 incident were carried by winds from Europe to the Indian subcontinent.
Alternative hypotheses
History records many instances of unusual objects falling with the rain – in 2000, in an example of raining animals, a smallwaterspout
A waterspout is a rotating column of air that occurs over a body of water, usually appearing as a funnel-shaped cloud in contact with the water and a cumuliform cloud. There are two types of waterspout, each formed by distinct mechanisms. ...
in the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Se ...
sucked up a school of fish a mile off shore, depositing them shortly afterwards on Great Yarmouth
Great Yarmouth ( ), often called Yarmouth, is a seaside resort, seaside town which gives its name to the wider Borough of Great Yarmouth in Norfolk, England; it straddles the River Yare and is located east of Norwich. Its fishing industry, m ...
in the United Kingdom. Coloured rain is by no means rare, and can often be explained by the airborne transport of rain dust from deserts
A desert is a landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions create unique biomes and ecosystems. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About one-third of the l ...
or other dry regions which have been washed down by rain. "Red Rains" have been frequently described in southern Europe, with increasing reports in recent years.
Bücher, A and Lucas, C, 1984. Sédimentation éolienne intercontinentale, poussières sahariennes et géologie. Bull Centr Rech Explor Prod Elf-Aquitanie 8, pp. 151–65 One such case occurred in England in 1903, when dust was carried from the Sahara
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
and fell with rain in February of that year.Mill H. R., R. K. G. Lempfert, 1904,
''The great dust fall of February 1903 and its origin.'' Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 30:57.
At first, the red rain in Kerala was attributed to the same effect, with dust from the deserts of Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
initially the suspect. LIDAR
Lidar (, also LIDAR, an acronym of "light detection and ranging" or "laser imaging, detection, and ranging") is a method for determining ranging, ranges by targeting an object or a surface with a laser and measuring the time for the reflected li ...
observations had detected a cloud of dust in the atmosphere near Kerala in the days preceding the outbreak of the red rain. However, laboratory tests from all involved teams ruled out the particles were desert sand.
K.K. Sasidharan Pillai, a senior scientific assistant in the Indian Meteorological Department, proposed dust and acidic material from an eruption of Mayon Volcano in the Philippines as an explanation for the coloured rain and the "burnt" leaves. The volcano was erupting in June and July 2001 and Pillai calculated that the Eastern or Equatorial jet stream
Jet streams are fast flowing, narrow thermal wind, air currents in the Earth's Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere.
The main jet streams are located near the altitude of the tropopause and are westerly winds, flowing west to east around the gl ...
could have transported volcanic material to Kerala in 25–36 hours. The Equatorial jet stream is unusual in that it sometimes flows from east to west at about 10° N, approximately the same latitude as Kerala (8° N) and Mayon Volcano (13° N). This hypothesis was also ruled out as the particles were neither acidic nor of volcanic origin, but were spores.
A study has been published showing a correlation between historic reports of coloured rains and of meteors; the author of the paper, Patrick McCafferty, stated that sixty of these colored rain events, or 36%, were linked to meteoritic or cometary activity, though not always strongly. Sometimes the fall of red rain seems to have occurred after an air-burst, as from a meteor exploding in air; other times the odd rainfall is merely recorded in the same year as the appearance of a comet.
Panspermia hypothesis
In 2003 Godfrey Louis and Santhosh Kumar, physicists at the Mahatma Gandhi University inKottayam
Kottayam () is a city in the Kottayam district of Kerala, India. It is the district headquarters of the district and is located about north of the state capital Thiruvananthapuram. As per the 2011 Indian census, Kottayam has a population of ...
, Kerala, posted an article entitled "Cometary panspermia
Panspermia () is the hypothesis that life exists throughout the universe, distributed by space dust, meteoroids, asteroids, comets, and planetoids, as well as by spacecraft carrying unintended contamination by microorganisms,Forward planetary c ...
explains the red rain of Kerala" in the non-peer review
Peer review is the evaluation of work by one or more people with similar competencies as the producers of the work (:wiktionary:peer#Etymology 2, peers). It functions as a form of self-regulation by qualified members of a profession within the ...
ed arXiv
arXiv (pronounced as "archive"—the X represents the Chi (letter), Greek letter chi ⟨χ⟩) is an open-access repository of electronic preprints and postprints (known as e-prints) approved for posting after moderation, but not Scholarly pee ...
web site. While the CESS report said there was no apparent relationship between the loud sound (possibly a sonic boom
A sonic boom is a sound associated with shock waves created when an object travels through the air faster than the speed of sound. Sonic booms generate enormous amounts of sound energy, sounding similar to an explosion or a thunderclap to ...
) and flash of light which preceded the red rain, to Louis and Kumar it was a key piece of evidence. They proposed that a meteor (from a comet containing the red particles) caused the sound and flash and when it disintegrated over Kerala it released the red particles which slowly fell to the ground. However, they omitted an explanation on how debris from a meteor continued to fall in the same area over a period of two months while unaffected by winds.
Their work indicated that the particles were of biological origin (consistent with the CESS report), however, they invoked the panspermia
Panspermia () is the hypothesis that life exists throughout the universe, distributed by space dust, meteoroids, asteroids, comets, and planetoids, as well as by spacecraft carrying unintended contamination by microorganisms,Forward planetary c ...
hypothesis
A hypothesis (: hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. A scientific hypothesis must be based on observations and make a testable and reproducible prediction about reality, in a process beginning with an educated guess o ...
to explain the presence of cells in a supposed fall of meteoric material. Additionally, using ethidium bromide
Ethidium bromide (or homidium bromide, chloride salt homidium chloride) is an intercalating agent commonly used as a fluorescent tag (nucleic acid stain) in molecular biology laboratories for techniques such as agarose gel electrophoresis. It ...
they were unable to detect DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
or RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
in the particles. Two months later they posted another paper on the same web site entitled "New biology of red rain extremophiles prove cometary panspermia" in which they reported that
The microorganism isolated from the red rain of Kerala shows very extraordinary characteristics, like the ability to grow optimally at and the capacity to metabolise a wide range of organic and inorganic materials.These claims and data have yet to be verified and reported in any peer reviewed publication. In 2006 Louis and Kumar published a paper in ''
Astrophysics and Space Science
''Astrophysics and Space Science'' is a bimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering astronomy, astrophysics, and space science and astrophysical aspects of astrobiology. It was established in 1968 and is published by Springer Science+Busin ...
'' entitled "The red rain phenomenon of Kerala and its possible extraterrestrial origin" which reiterated their arguments that the red rain was biological matter from an extraterrestrial source but made no mention of their previous claims to having induced the cells to grow. The team also observed the cells using phase contrast
Phase-contrast imaging is a method of imaging that has a range of different applications. It measures differences in the refractive index of different materials to differentiate between structures under analysis. In conventional light microscopy, ...
fluorescence microscopy, and they concluded that: "The fluorescence behaviour of the red cells is shown to be in remarkable correspondence with the extended red emission observed in the Red Rectangle Nebula and other galactic and extragalactic dust clouds, suggesting, though not proving an extraterrestrial origin." One of their conclusions was that if the red rain particles are biological cells and are of cometary origin, then this phenomenon can be a case of cometary panspermia
Panspermia () is the hypothesis that life exists throughout the universe, distributed by space dust, meteoroids, asteroids, comets, and planetoids, as well as by spacecraft carrying unintended contamination by microorganisms,Forward planetary c ...
.
In August 2008 Louis and Kumar again presented their case in an astrobiology conference. The abstract for their paper states that The red cells found in the red rain in Kerala, India are now considered as a possible case of extraterrestrial life form. These cells can undergo rapid replication even at an extreme high temperature of . They can also be cultured in diverse unconventional chemical substrates. The molecular composition of these cells is yet to be identified.In September 2010 a similar paper was presented at a conference in California, US.
Cosmic ancestry
Researcher Chandra Wickramasinghe used Louis and Kumar's "extraterrestrial origin" claim to further support hispanspermia
Panspermia () is the hypothesis that life exists throughout the universe, distributed by space dust, meteoroids, asteroids, comets, and planetoids, as well as by spacecraft carrying unintended contamination by microorganisms,Forward planetary c ...
hypothesis called cosmic ancestry. This hypothesis postulates that life is neither the product of supernatural creation, nor is it spontaneously generated through abiogenesis
Abiogenesis is the natural process by which life arises from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The prevailing scientific hypothesis is that the transition from non-living to living entities on Earth was not a single even ...
, but that it has always existed in the universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents. It comprises all of existence, any fundamental interaction, physical process and physical constant, and therefore all forms of matter and energy, and the structures they form, from s ...
. Cosmic ancestry speculates that higher life forms, including intelligent life, descend ultimately from pre-existing life which was at least as advanced as the descendants.
Criticism
Louis and Kumar made their first publication of their finding on a web site in 2003, and have presented papers at conferences and in astrophysics magazines a number of times since. The controversial conclusion of Louis et al. is the only hypothesis suggesting that these organisms are of extraterrestrial origin. Such reports have been popular in the media, with major news agencies like CNN repeating the panspermia theory without critique. The hypothesis' authors – G. Louis and Kumar – did not explain how debris from a meteor could have continued to fall on the same area over a period of two months, despite the changes in climatic conditions and wind pattern spanning over two months. Samples of the red particles were also sent for analysis to his collaboratorsMilton Wainwright
Milton Wainwright (born 23 February 1950) is a British microbiologist who is known for his research into what he claims could be extraterrestrial life found in the stratosphere.
Biography
Wainwright graduated from the University of Nottingham i ...
at the University of Sheffield
The University of Sheffield (informally Sheffield University or TUOS) is a public university, public research university in Sheffield, South Yorkshire, England. Its history traces back to the foundation of Sheffield Medical School in 1828, Fir ...
and Chandra Wickramasinghe at Cardiff University
Cardiff University () is a public research university in Cardiff, Wales. It was established in 1883 as the University College of South Wales and Monmouthshire and became a founding college of the University of Wales in 1893. It was renamed Unive ...
. Louis then incorrectly reported on 29 August 2010 in the non-peer reviewed online physics archive "arxiv.org" that they were able to have these cells "reproduce" when incubated at high pressure saturated steam at 121 °C (autoclave
An autoclave is a machine used to carry out industrial and scientific processes requiring elevated temperature and pressure in relation to ambient pressure and/or temperature. Autoclaves are used before surgical procedures to perform steriliza ...
d) for up to two hours. Their conclusion is that these cells reproduced, without DNA, at temperatures higher than any known life form on earth is able to. They claimed that the cells, however, were unable to reproduce at temperatures similar to known organisms.
Regarding the "absence" of DNA, Louis admits he has no training in biology, and has not reported the use of any standard microbiology growth medium
A growth medium or culture medium is a solid, liquid, or semi-solid designed to support the growth of a population of microorganisms or cells via the process of cell proliferation or small plants like the moss ''Physcomitrella patens''. Differe ...
to culture and induce germination
Germination is the process by which an organism grows from a seed or spore. The term is applied to the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an angiosperm or gymnosperm, the growth of a sporeling from a spore, such as the spores of fungi, ...
and growth of the spores, basing his claim of "biological growth" on light absorption measurements following aggregation by supercritical fluids, an inert physical observation. Both his collaborators, Wickramasinghe and Milton Wainwright
Milton Wainwright (born 23 February 1950) is a British microbiologist who is known for his research into what he claims could be extraterrestrial life found in the stratosphere.
Biography
Wainwright graduated from the University of Nottingham i ...
independently extracted and confirmed the presence of DNA from the spores. The absence of DNA was key to Louis and Kumar's hypothesis that the cells were of extraterrestrial origins.
Louis' only reported attempt to stain the spores' DNA was by the use of malachite green
Malachite green is an organic compound that is used as a dyestuff and controversially as an antimicrobial in aquaculture. Malachite green is traditionally used as a dye for materials such as silk, leather, and paper. Despite its name the dye is ...
, which is generally used to stain bacterial endospores, not algal spores, whose primary function of their cell wall and their impermeability is to ensure its own survival through periods of environmental stress. They are therefore resistant to ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
and gamma radiation
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol ), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from high energy interactions like the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei or astronomical events like solar flares. It consists o ...
, desiccation
Desiccation is the state of extreme dryness, or the process of extreme drying. A desiccant is a hygroscopic (attracts and holds water) substance that induces or sustains such a state in its local vicinity in a moderately sealed container. The ...
, lysozyme
Lysozyme (, muramidase, ''N''-acetylmuramide glycanhydrolase; systematic name peptidoglycan ''N''-acetylmuramoylhydrolase) is an antimicrobial enzyme produced by animals that forms part of the innate immune system. It is a glycoside hydrolase ...
, temperature, starvation
Starvation is a severe deficiency in caloric energy intake, below the level needed to maintain an organism's life. It is the most extreme form of malnutrition. In humans, prolonged starvation can cause permanent organ damage and eventually, de ...
and chemical disinfectants
A disinfectant is a chemical substance or compound used to inactivate or destroy microorganisms on inert surfaces. Disinfection does not necessarily kill all microorganisms, especially resistant bacterial spores; it is less effective than ...
. Visualizing algal spore DNA under a light microscope can be difficult due to the impermeability of the highly resistant spore wall to dyes and stains used in normal staining procedures. The spores' DNA is tightly packed, encapsulated and desiccated, therefore, the spores must first be cultured in suitable growth medium
A growth medium or culture medium is a solid, liquid, or semi-solid designed to support the growth of a population of microorganisms or cells via the process of cell proliferation or small plants like the moss ''Physcomitrella patens''. Differe ...
and temperature to first induce germination
Germination is the process by which an organism grows from a seed or spore. The term is applied to the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an angiosperm or gymnosperm, the growth of a sporeling from a spore, such as the spores of fungi, ...
, then cell growth
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
* Cellphone, a phone connected to a cellular network
* Clandestine cell, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization
* Electrochemical cell, a de ...
followed by reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. There are two forms of reproduction: Asexual reproduction, asexual and Sexual ...
before staining the DNA.
Other researchers have noted recurring instances of red rainfalls in 1818, 1846, 1872, 1880, 1896, and 1950 and several times since then. Most recently, coloured rainfall occurred over Kerala during the summers of 2001, 2006, 2007, 2008, and 2012; since 2001, the botanists have found the same ''Trentepohlia'' spores every time. This supports the notion that the red rain is a seasonal local environmental feature caused by algal
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular microalgae, s ...
spores.
In popular culture
* Thescience fiction
Science fiction (often shortened to sci-fi or abbreviated SF) is a genre of speculative fiction that deals with imaginative and futuristic concepts. These concepts may include information technology and robotics, biological manipulations, space ...
film '' Red Rain'' was loosely based on the red rain in Kerala story. It was directed by Rahul Sadasivan and released in India on 6 December 2013.
See also
* * *References
External links
Sampath, S., Abraham, T. K., Sasi Kumar, V., & Mohanan, C.N. (2001). Colored Rain: A Report on the Phenomenon. CESS-PR-114-2001, Center for Earth Science Studies and Tropical Botanic Garden and Research Institute.
"When aliens rained over India" by Hazel Muir in ''New Scientist''
"Searching for 'our alien origins'" by Andrew Thompson in ''BBC News''
"Fluorescence Mystery in Red Rain Cells of Kerala, India " Linda Moulton Howe ''Earthfiles''
"Home page of Dr A Santhosh Kumar"
{{DEFAULTSORT:Red Rain In Kerala 2001 in India 2001 meteorology Anomalous weather Environment of Kerala Panspermia Weather events in India Rain Changanassery Meteorological hypotheses Trentepohliaceae