RF Switch on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
An RF switch or microwave switch is a device to route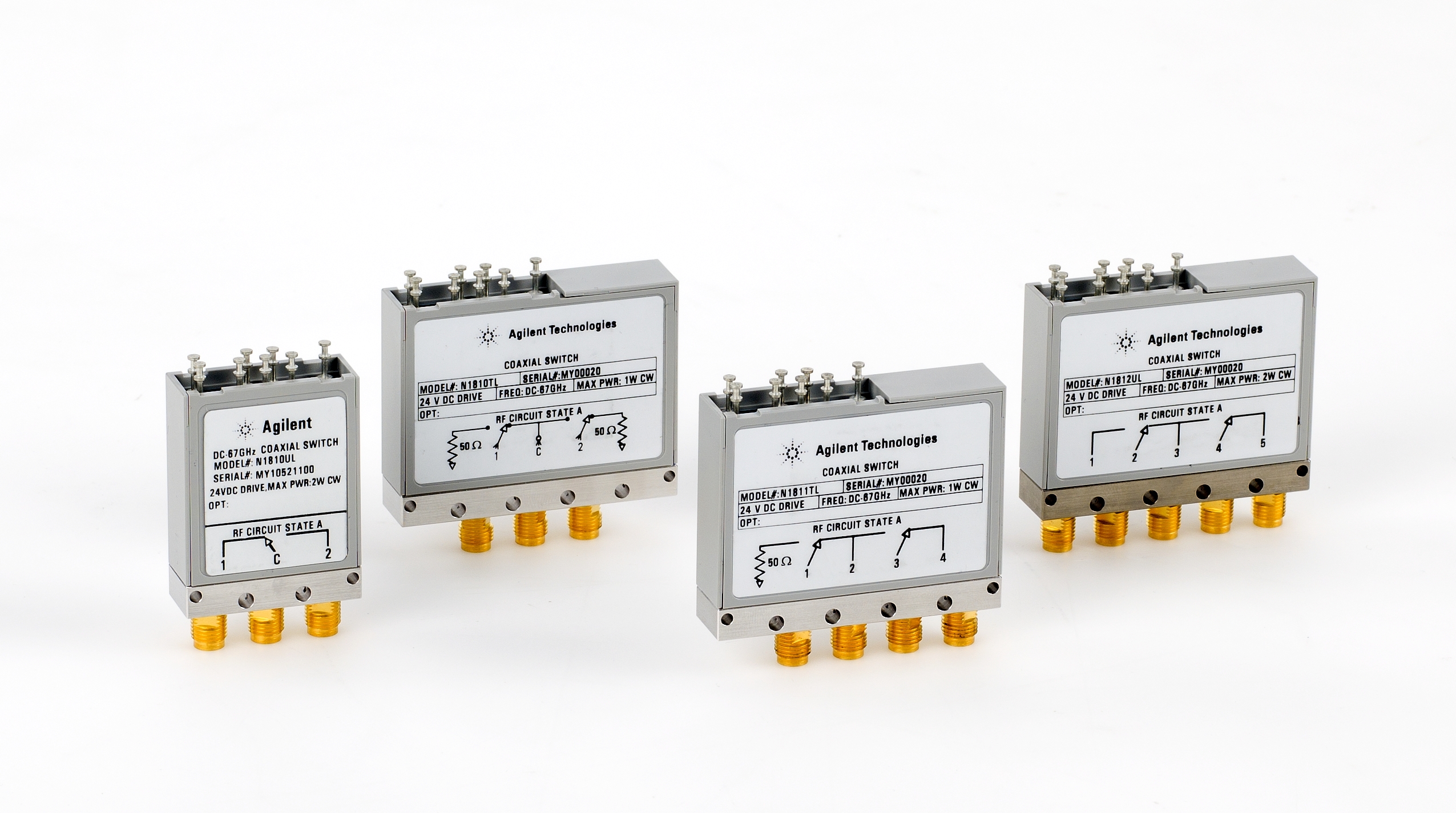  * Multiport switches or single pole, multiple throw (SPnT) switches allow a single input to multiple (three or more) output paths.
* Transfer switches or double pole, double throw (DPDT) switches can serve various purposes.
* Bypass switches insert or remove a test component from a signal path.
RF A/B switches are designed to switch between a cable company CATV signal and an Off-Air antenna signal or other home video products with
* Multiport switches or single pole, multiple throw (SPnT) switches allow a single input to multiple (three or more) output paths.
* Transfer switches or double pole, double throw (DPDT) switches can serve various purposes.
* Bypass switches insert or remove a test component from a signal path.
RF A/B switches are designed to switch between a cable company CATV signal and an Off-Air antenna signal or other home video products with 
 * A solid state switch is an electronic switching device based on semiconductor technology (e.g.
* A solid state switch is an electronic switching device based on semiconductor technology (e.g. 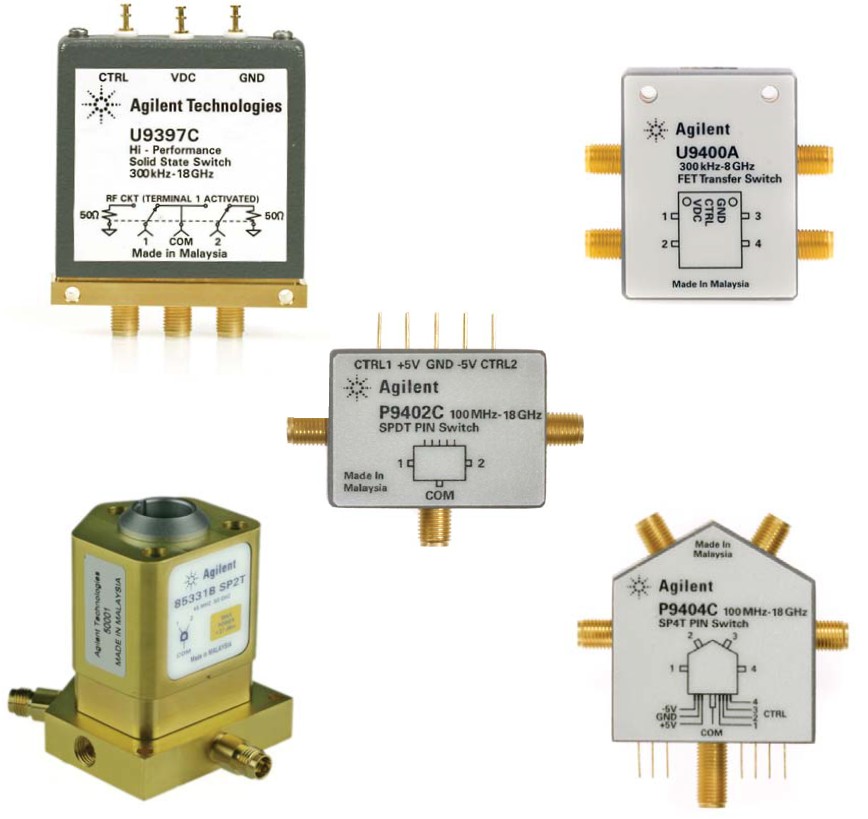 :
:
high frequency
High frequency (HF) is the ITU designation for the band of radio waves with frequency between 3 and 30 megahertz (MHz). It is also known as the decameter band or decameter wave as its wavelengths range from one to ten decameters (ten to one ...
signals through transmission paths. RF (radio frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the u ...
) and microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than other radio waves but longer than infrared waves. Its wavelength ranges from about one meter to one millimeter, corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300&n ...
switches are used extensively in microwave test systems for signal routing between instruments and devices under test (DUT). Incorporating a switch into a switch matrix system enables you to route signals from multiple instruments to single or multiple DUTs. This allows multiple tests to be performed with the same setup, eliminating the need for frequent connects and disconnects. The entire testing process can be automated, increasing the throughput in high-volume production environments.
Like other electrical switches, RF and microwave switches provide different configurations for many different applications. Below is a list of typical switch configurations and usage:
* Single pole, double throw (SPDT or 1:2) switches route signals from one input to two output paths.
 * Multiport switches or single pole, multiple throw (SPnT) switches allow a single input to multiple (three or more) output paths.
* Transfer switches or double pole, double throw (DPDT) switches can serve various purposes.
* Bypass switches insert or remove a test component from a signal path.
RF A/B switches are designed to switch between a cable company CATV signal and an Off-Air antenna signal or other home video products with
* Multiport switches or single pole, multiple throw (SPnT) switches allow a single input to multiple (three or more) output paths.
* Transfer switches or double pole, double throw (DPDT) switches can serve various purposes.
* Bypass switches insert or remove a test component from a signal path.
RF A/B switches are designed to switch between a cable company CATV signal and an Off-Air antenna signal or other home video products with coaxial cable
Coaxial cable, or coax (pronounced ), is a type of electrical cable consisting of an inner Electrical conductor, conductor surrounded by a concentric conducting Electromagnetic shielding, shield, with the two separated by a dielectric (Insulat ...
RF connections.
RF A/B switches come in button or sliding switches.

RF CMOS
RF CMOS is a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit (IC) technology that integrates radio-frequency (RF), analog and digital electronics on a mixed-signal CMOS (complementary MOS) RF circuit chip. It is widely used in modern wir ...
switches are crucial to modern wireless
Wireless communication (or just wireless, when the context allows) is the transfer of information (''telecommunication'') between two or more points without the use of an electrical conductor, optical fiber or other continuous guided transm ...
telecommunication
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of ...
, including wireless networks
A wireless network is a computer network that uses wireless data connections between network nodes. Wireless networking allows homes, telecommunications networks, and business installations to avoid the costly process of introducing cables in ...
and mobile communication devices. Infineon Technologies
Infineon Semiconductor solutions is the largest microcontroller manufacturer in the world, as well as Germany's largest semiconductor manufacturer. It is also the leading automotive semiconductor manufacturer globally. Infineon had roughly 58,0 ...
bulk CMOS RF switches sell over 1billion units annually, reaching a cumulative 5billion units, .
Technologies
The two main kinds of RF and microwave switches have different capabilities: *Electromechanical
Electromechanics combine processes and procedures drawn from electrical engineering and mechanical engineering. Electromechanics focus on the interaction of electrical and mechanical systems as a whole and how the two systems interact with each ...
switches are based on the simple theory of electromagnetic induction
Electromagnetic or magnetic induction is the production of an electromotive force, electromotive force (emf) across an electrical conductor in a changing magnetic field.
Michael Faraday is generally credited with the discovery of induction in 1 ...
. They rely on mechanical contacts as their switching mechanism.
 * A solid state switch is an electronic switching device based on semiconductor technology (e.g.
* A solid state switch is an electronic switching device based on semiconductor technology (e.g. MOSFET
upright=1.3, Two power MOSFETs in amperes">A in the ''on'' state, dissipating up to about 100 watt">W and controlling a load of over 2000 W. A matchstick is pictured for scale.
In electronics, the metal–oxide–semiconductor field- ...
, PIN diode
A PIN diode is a diode with a wide, undoped intrinsic semiconductor region between a p-type semiconductor and an n-type semiconductor region. The p-type and n-type regions are typically heavily doping (semiconductor), doped because they are used ...
). It functions similarly to an electromechanical switch except that it has no moving parts.  :
:
Parameters
Frequency range
RF and microwave applications range in frequency from 100 MHz for semiconductor to 60 GHz for satellite communications. Broadband accessories increase test system flexibility by extending frequency coverage. However, frequency is always application dependent and a broad operating frequency may be sacrificed to meet other critical parameters. For example, a network analyzer may perform a 1 ms sweep for an insertion loss measurement, so for this application settling time or switching speed becomes the critical parameter for ensuring measurement accuracy.Insertion loss
In addition to proper frequency selection,insertion loss
In telecommunications, insertion loss is the loss of signal power resulting from the insertion of a device in a transmission line or optical fiber and is usually expressed in decibels (dB).
If the power transmitted to the load before insertio ...
is critical to testing. Losses greater than 1 or 2 dB will attenuate peak signal levels and increase rising and falling edge times. A low insertion loss system can be achieved by minimizing the number of connectors and through-paths, or by selecting low insertion loss devices for system configuration. As power is expensive at higher frequencies, electromechanical switches provide the lowest possible loss along the transmission path.
Return loss
Return loss is caused by impedance mismatch between circuits. At microwave frequencies, the material properties as well as the dimensions of a network element play a significant role in determining the impedance match or mismatch caused by the distributed effect. Switches with excellent return loss performance ensure optimum power transfer through the switch and the entire network.Repeatability
Low insertion loss repeatability reduces sources of random errors in the measurement path, which improves measurement accuracy. The repeatability and reliability of a switch guarantees measurement accuracy and can cut the cost of ownership by reducing calibration cycles and increasing test system uptime.Isolation
Isolation is the degree of attenuation from an unwanted signal detected at the port of interest. Isolation becomes more important at higher frequencies. High isolation reduces the influence of signals from other channels, sustains the integrity of the measured signal, and reduces system measurement uncertainties. For instance, anRF switch matrix
An RF switch matrix is an array of RF switches arranged to route radio frequency (RF) signals between multiple inputs and multiple outputs. Applications requiring RF matrices include ground systems, test equipment, and communication systems.
An R ...
may need to route a signal to a spectrum analyzer for measurement at –70 dBm and to simultaneously route another signal at +20 dBm. In this case, switches with high isolation, 90 dB or more, will keep the measurement integrity of the low-power signal.
Switching speed
Switching speed is defined as the time needed to change the state of a switch port (arm) from "ON' to "OFF" or from "OFF" to "ON".Settling time
As switching time only specifies an end value of 90% of the settled/final value of the RF signal, settling time is often highlighted in solid state switch performance where the need for accuracy and precision is more critical. Settling time is measured to a level closer to the final value. The widely used margin-to-final value of settling time is 0.01 dB (99.77% of the final value) and 0.05 dB (98.86% of the final value). This specification is commonly used forGaAs
Gallium arsenide (GaAs) is a III-V direct band gap semiconductor with a zinc blende crystal structure.
Gallium arsenide is used in the manufacture of devices such as microwave frequency integrated circuits, monolithic microwave integrated circui ...
FET switches because they have a gate lag effect caused by electrons becoming trapped on the surface of the GaAs.
Power handling
Power handling defines the ability of a switch to handle power and is very dependent on the design and materials used. There are different power handling ratings for switches such as hot switching, cold switching, average power and peak power. Hot switching occurs when RF/microwave power is present at the ports of the switching at the time of the switching. Cold switching occurs when the signal power is removed before switching. Cold switching results in lower contact stress and longer life.Termination
A 50-ohm load termination is critical in many applications, since each open unused transmission line has the possibility to resonate. This is important when designing a system that works up to 26 GHz or higher frequencies where switch isolation drops considerably. When the switch is connected to an active device, the reflected power of an unterminated path could possibly damage the source. :Electromechanical switches are categorized as terminated or unterminated. Terminated switches: when a selected path is closed, all other paths are terminated with 50 ohm loads, and the current to all the solenoids is cut off. Unterminated switches reflect power. :Solid state switches are categorized as absorptive or reflective. Absorptive switches incorporate a 50 ohm termination in each of the output ports to present a lowVSWR
In Radio-frequency engineering, radio engineering and telecommunications, standing wave ratio (SWR) is a measure of impedance matching of Electrical load, loads to the characteristic impedance of a transmission line or waveguide. Impedance misma ...
in both the OFF and ON states. Reflective switches conduct RF power when the diode is reverse biased and reflect RF power when forward biased.
Video leakage
Video leakage refers to the spurious signals present at the RF ports of the switch when it is switched without an RF signal present. These signals arise from the waveforms generated by the switch driver and, in particular, from the leading edge voltage spike required for high-speed switching of PIN diodes. The amplitude of the video leakage depends on the design of the switch and the switch driver.Operating life
A long operating life reduces cost per cycle and budgetary constraints allowing manufacturers to be more competitive.See also
* Butler matrixReferences
External links
* *{{Citation , last= Charter Engineering , title= How to Select an RF Switch , date= August 16, 2021 , publisher= Charter Engineering , series= Application Note , url= https://www.ceiswitches.com/rfswitchselection/ Microwave technology