pyramidal on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A pyramid () is a
A pyramid () is a
 The
The
 The most famous African pyramids are in Egypt—huge structures built of bricks or stones, primarily limestone, some of which are among the world's largest constructions. They are shaped in reference to the sun's rays. Most had a smoothed white
The most famous African pyramids are in Egypt—huge structures built of bricks or stones, primarily limestone, some of which are among the world's largest constructions. They are shaped in reference to the sun's rays. Most had a smoothed white
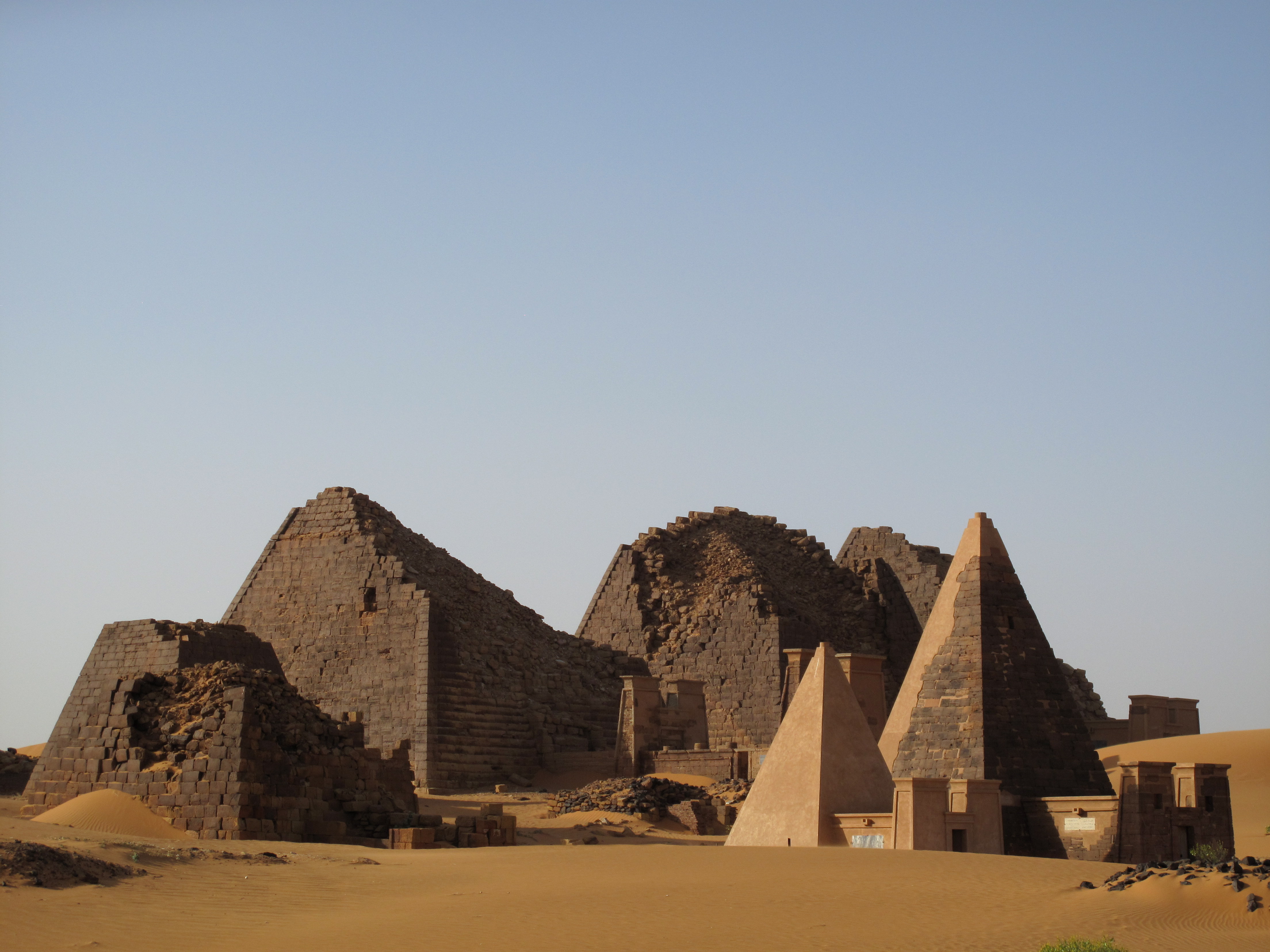
 While African pyramids are commonly associated with Egypt, Sudan has 220 extant pyramids, the most in the world. Nubian pyramids were constructed (roughly 240 of them) at three sites in
While African pyramids are commonly associated with Egypt, Sudan has 220 extant pyramids, the most in the world. Nubian pyramids were constructed (roughly 240 of them) at three sites in
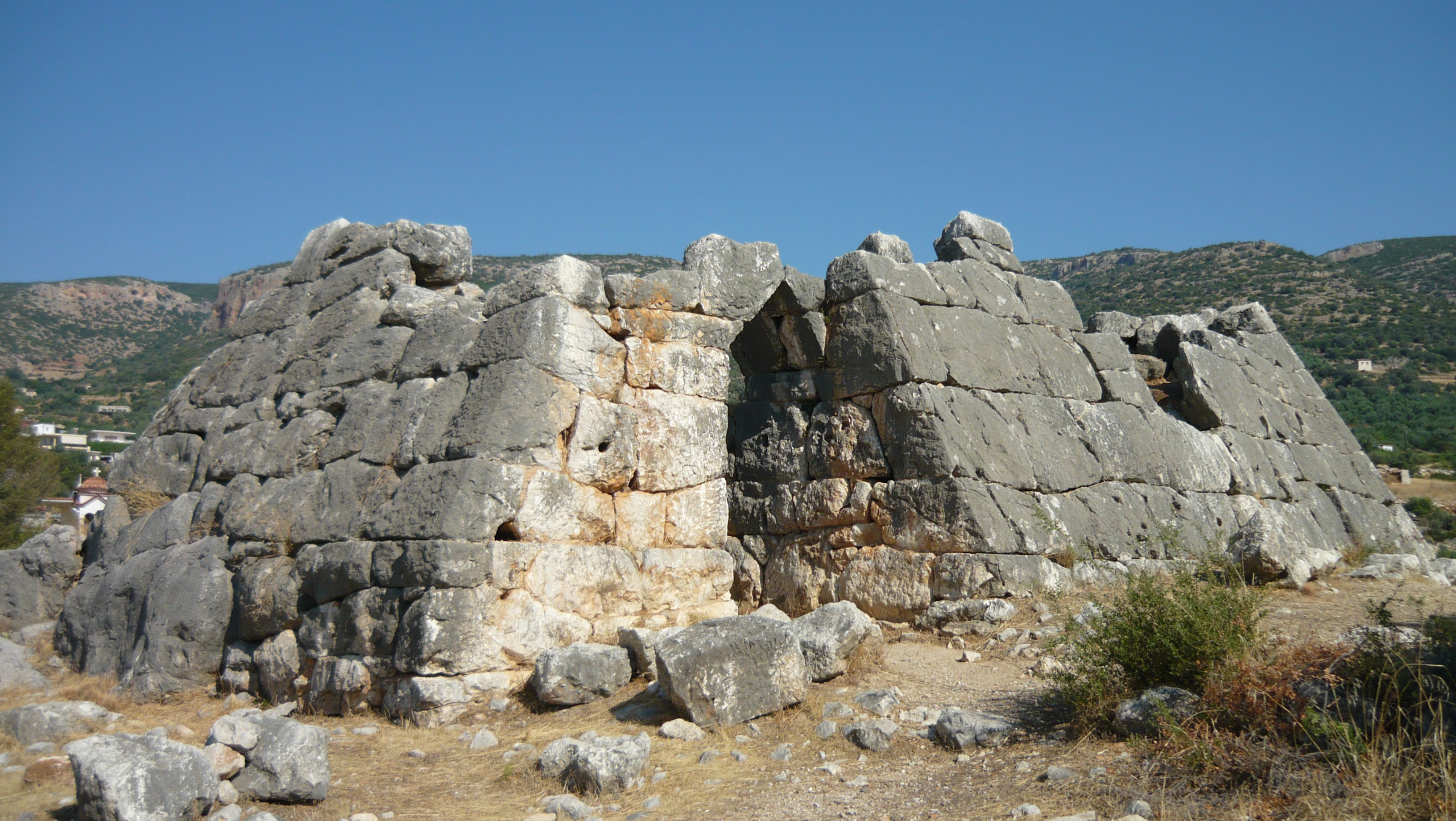 Pausanias (2nd century AD) mentions two buildings resembling pyramids, one, 19 kilometres (12 mi) southwest of a still standing structure at Hellenikon, a common tomb for soldiers who died in a legendary struggle for the throne of Argos and another that he was told was the tomb of Argives killed in a battle around 669/8 BC. Neither survives and no evidence indicates that they resembled Egyptian pyramids.
At least two surviving pyramid-like structures are available to study, one at Hellenikon and the other at Ligourio/Ligurio, a village near the ancient theatre
Pausanias (2nd century AD) mentions two buildings resembling pyramids, one, 19 kilometres (12 mi) southwest of a still standing structure at Hellenikon, a common tomb for soldiers who died in a legendary struggle for the throne of Argos and another that he was told was the tomb of Argives killed in a battle around 669/8 BC. Neither survives and no evidence indicates that they resembled Egyptian pyramids.
At least two surviving pyramid-like structures are available to study, one at Hellenikon and the other at Ligourio/Ligurio, a village near the ancient theatre
 The 27-metre-high
The 27-metre-high
 Several
Several
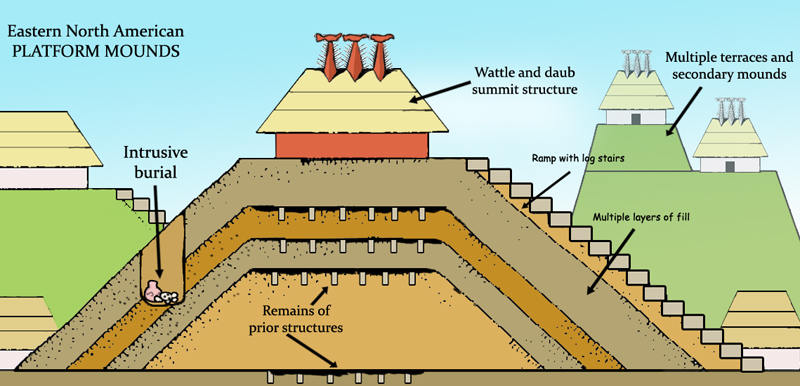
 Many pre-Columbian Native American societies of ancient North America built large pyramidal
Many pre-Columbian Native American societies of ancient North America built large pyramidal
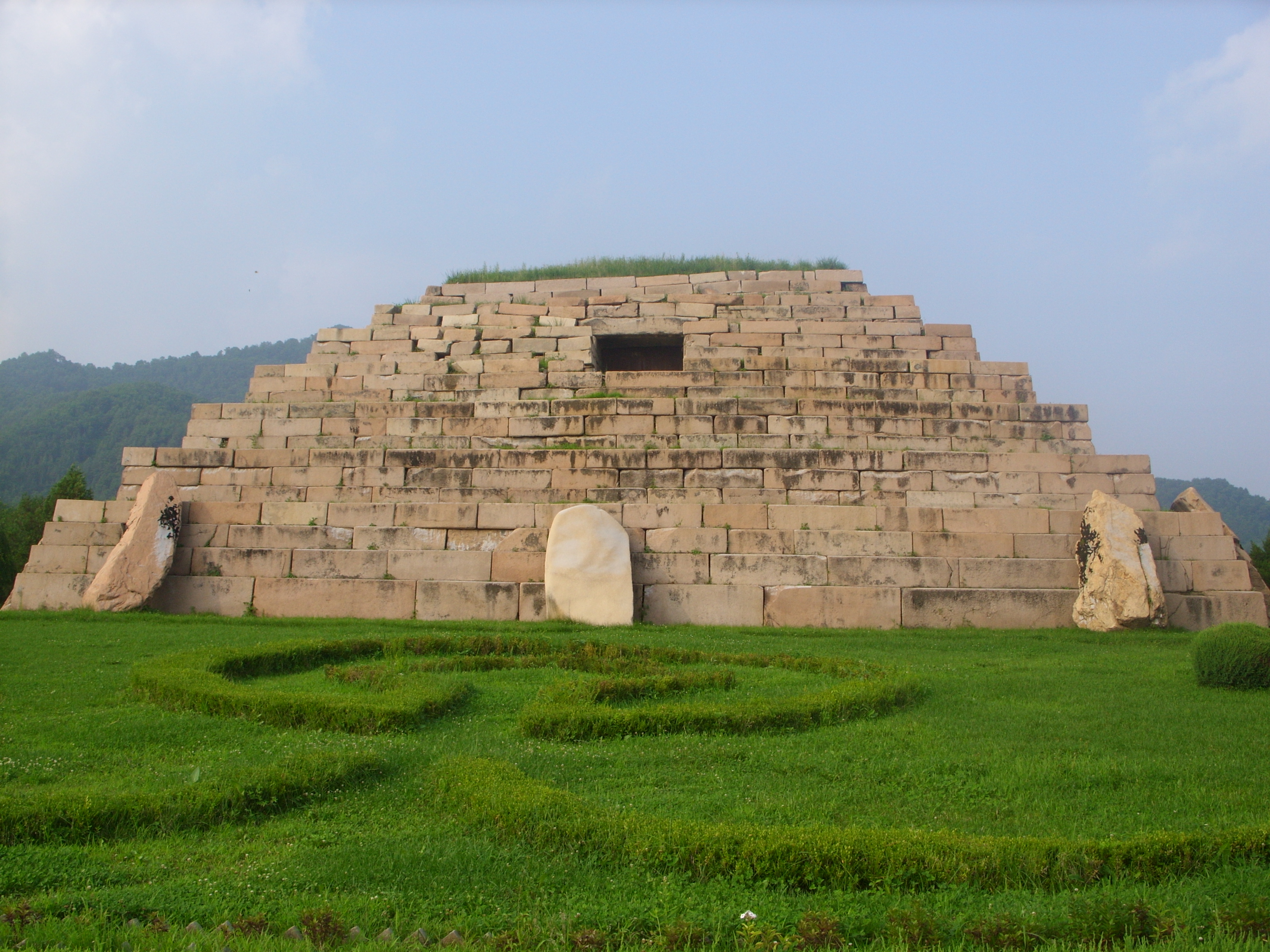

 Many square flat-topped mound tombs in
Many square flat-topped mound tombs in
File:Big Temple-Temple.jpg, The granite gopuram (tower) of Brihadeeswarar Temple, 1010 AD.
File:Back view of Raja gopuram.jpg, The pyramidal structure above the sanctum at
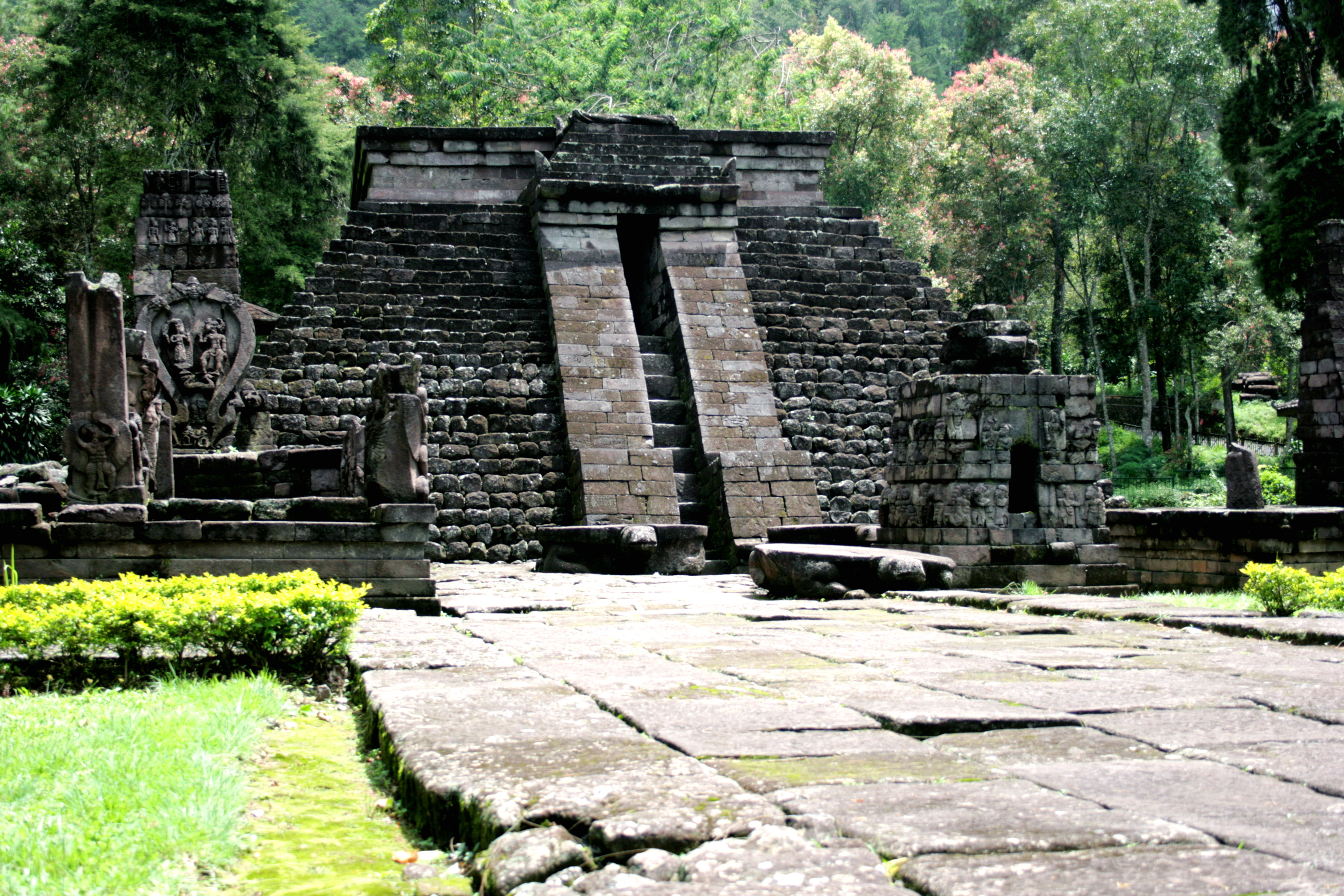
 Austronesian
Austronesian
 The
The  * The 48-story Transamerica Pyramid in San Francisco, California, designed by
* The 48-story Transamerica Pyramid in San Francisco, California, designed by  * Sunway Pyramid shopping mall is in Selangor, Malaysia.
* Hanoi Museum has an overall design of a reversed pyramid.
* The Ha! Ha! Pyramid by artist in La Baie, Quebec is made out of 3,000 give way signs.
* The culture-entertainment complex and is in Kazan, Russia.
* The Time pyramid in Wemding, Germany is a pyramid begun in 1993 and scheduled for completion in the year 3183.Conception
* Sunway Pyramid shopping mall is in Selangor, Malaysia.
* Hanoi Museum has an overall design of a reversed pyramid.
* The Ha! Ha! Pyramid by artist in La Baie, Quebec is made out of 3,000 give way signs.
* The culture-entertainment complex and is in Kazan, Russia.
* The Time pyramid in Wemding, Germany is a pyramid begun in 1993 and scheduled for completion in the year 3183.Conception
Official ''Zeitpyramide'' website, accessed: 14 December 2010 * Triangle (Paris building), Triangle is a proposed skyscraper in Paris. * The Shimizu Mega-City Pyramid is a proposed project for construction of a massive pyramid over Tokyo Bay in Japan. * The Donkin Memorial was erected on a Xhosa people, Xhosa reserve in 1820 by Cape Governor Sir Rufane Shaw Donkin in memory of his late wife Elizabeth, in Port Elizabeth, South Africa. The pyramid is used in many different coats-of-arms associated with Port Elizabeth. *
*
File:Stockport Pyramid.jpg, Stockport Pyramid in
 With the Egyptian Revival movement in the nineteenth and early twentieth century, pyramids became more common in funerary architecture. The tomb of Quintino Sella, outside the monumental cemetery of Oropa, is pyramid-shaped. This style was popular with tycoons in the US. The Schoenhofen Pyramid Mausoleum (1889) in Chicago and Hunt's Tomb (1930) in Phoenix, Arizona are notable examples. Some people build pyramid tombs for themselves. Nicolas Cage bought a pyramid tomb for himself in a famed New Orleans graveyard.
With the Egyptian Revival movement in the nineteenth and early twentieth century, pyramids became more common in funerary architecture. The tomb of Quintino Sella, outside the monumental cemetery of Oropa, is pyramid-shaped. This style was popular with tycoons in the US. The Schoenhofen Pyramid Mausoleum (1889) in Chicago and Hunt's Tomb (1930) in Phoenix, Arizona are notable examples. Some people build pyramid tombs for themselves. Nicolas Cage bought a pyramid tomb for himself in a famed New Orleans graveyard.
 A pyramid () is a
A pyramid () is a structure
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
whose visible surfaces are triangular in broad outline and converge toward the top, making the appearance roughly a pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid can be of any polygon
In geometry, a polygon () is a plane figure made up of line segments connected to form a closed polygonal chain.
The segments of a closed polygonal chain are called its '' edges'' or ''sides''. The points where two edges meet are the polygon ...
shape, such as triangular
A triangle is a polygon with three corners and three sides, one of the basic shapes in geometry. The corners, also called ''vertices'', are zero-dimensional points while the sides connecting them, also called ''edges'', are one-dimensional ...
or quadrilateral
In Euclidean geometry, geometry a quadrilateral is a four-sided polygon, having four Edge (geometry), edges (sides) and four Vertex (geometry), corners (vertices). The word is derived from the Latin words ''quadri'', a variant of four, and ''l ...
, and its surface-lines either filled or stepped.
A pyramid has the majority of its mass closer to the ground with less mass towards the pyramidion
A pyramidion (plural: pyramidia) is the capstone of an Egyptian pyramid or the upper section of an obelisk. Speakers of the Ancient Egyptian language referred to pyramidia as ''benbenet'' and associated the pyramid as a whole with the sacred b ...
at the apex
The apex is the highest point of something. The word may also refer to:
Arts and media Fictional entities
* Apex (comics)
A-Bomb
Abomination
Absorbing Man
Abraxas
Abyss
Abyss is the name of two characters appearing in Ameri ...
. This is due to the gradual decrease in the cross-sectional area along the vertical axis with increasing elevation. This offers a weight distribution that allowed early civilizations to create monumental structures.Ancient civilizations
A civilization (also spelled civilisation in British English) is any complex society characterized by the development of the state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond signed or spoken languag ...
in many parts of the world pioneered the building of pyramids. The largest pyramid by volume is the Mesoamerican Great Pyramid of Cholula
The Great Pyramid of Cholula, also known as (Nahuatl for "constructed mountain"), is a complex located in Cholula, Puebla, Cholula, Puebla, Mexico. It is the largest archaeological site of a pyramid (temple) in the world, as well as the largest ...
, in the Mexican state of Puebla
Puebla, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Puebla, is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 217 municipalities and its capital is Puebla City. Part of east-centr ...
. For millennia, the largest structures on Earth were pyramids—first the Red Pyramid
The Red Pyramid, also called the North Pyramid, is the largest of the pyramids located at the Dahshur necropolis in Cairo, Egypt. Named for the rusty reddish hue of its red limestone stones, it is also the third largest Egyptian pyramid, after ...
in the Dashur Necropolis
DahshurAlso transliterated ''Dahshour'' (in English often called ''Dashur'' ' ) is an ancient Egyptian pyramid complex and necropolis and shares the name of the nearby village of Manshiyyat Dahshur () in markaz Badrashin, Giza.
Dahshur is lis ...
and then the Great Pyramid
The Great Pyramid of Giza is the largest Egyptian pyramid. It served as the tomb of pharaoh Khufu, who ruled during the Fourth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom. Built , over a period of about 26 years, the pyramid is the oldest of the Seven Wond ...
of Khufu
Khufu or Cheops (died 2566 BC) was an ancient Egyptian monarch who was the second pharaoh of the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt, Fourth Dynasty, in the first half of the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom period (26th century BC). Khufu succeeded his ...
, both in Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
—the latter is the only extant example of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World
The Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, also known as the Seven Wonders of the World or simply the Seven Wonders, is a list of seven notable structures present during classical antiquity, first established in the 1572 publication '' Octo Mundi M ...
.
Ancient monuments
West Asia
Mesopotamia
 The
The Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
ns built the earliest pyramidal structures, called ''ziggurat
A ziggurat (; Cuneiform: 𒅆𒂍𒉪, Akkadian: ', D-stem of ' 'to protrude, to build high', cognate with other Semitic languages like Hebrew ''zaqar'' (זָקַר) 'protrude'), ( Persian: Chogha Zanbilچغازنجبیل) is a type of massive ...
s''. In ancient times, these were brightly painted in gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
/bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloid ...
. They were constructed of sun-dried mud-brick, and little remains of them. Ziggurats were built by the Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age, early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. ...
ians, Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-s ...
ians, Elam
Elam () was an ancient civilization centered in the far west and southwest of Iran, stretching from the lowlands of what is now Khuzestan and Ilam Province as well as a small part of modern-day southern Iraq. The modern name ''Elam'' stems fr ...
ites, Akkadians
The Akkadian Empire () was the first known empire, succeeding the long-lived city-states of Sumer. Centered on the city of Akkad ( or ) and its surrounding region, the empire united Akkadian and Sumerian speakers under one rule and exercised ...
, and Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
ns. Each ziggurat was part of a temple complex that included other buildings. The ziggurat's precursors were raised platforms that date from the Ubaid period
The Ubaid period (c. 5500–3700 BC) is a prehistoric period of Mesopotamia. The name derives from Tell al-'Ubaid where the earliest large excavation of Ubaid period material was conducted initially in 1919 by Henry Hall, Leonard Woolley in 19 ...
Crawford, page 73 of the fourth millennium
A millennium () is a period of one thousand years, one hundred decades, or ten centuries, sometimes called a kiloannum (ka), or kiloyear (ky). Normally, the word is used specifically for periods of a thousand years that begin at the starting ...
BC.
The earliest ziggurats began near the end of the Early Dynastic Period. The original pyramidal structure, the anu ziggurat, dates to around 4000 BC. The White Temple was built on top of it circa 3500 BC.
Built in receding tiers upon a rectangular, oval, or square platform, the ziggurat was a pyramidal structure with a flat top. Sun-baked brick
A brick is a type of construction material used to build walls, pavements and other elements in masonry construction. Properly, the term ''brick'' denotes a unit primarily composed of clay. But is now also used informally to denote building un ...
s made up the core of the ziggurat with facings of fired bricks on the outside. The facings were often glazed in different colors and may have had astrological
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that propose that information about human affairs and terrestrial events may be discerned by studying the apparent positions of celesti ...
significance. Kings sometimes had their names engraved on them. The number of tiers ranged from two to seven. It is assumed that they had shrines at the top, but no archaeological evidence supports this and the only textual evidence is from Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
. Access to the shrine would have been by a series of ramps on one side of the ziggurat or by a spiral ramp from base to summit.
Africa
Egypt
limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
surface. Many of the facing stones have fallen or were removed and used for construction in Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, L ...
. The capstone was usually made of limestone, granite or basalt and some were plated with electrum
Electrum is a naturally occurring alloy of gold and silver, with trace amounts of copper and other metals. Its color ranges from pale to bright yellow, depending on the proportions of gold and silver. It has been produced artificially and is ...
.
Ancient Egyptians built pyramids from 2700 BC until around 1700 BC. The first pyramid was erected during the Third Dynasty by the Pharaoh Djoser
Djoser (also read as Djeser and Zoser) was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh of the 3rd Dynasty during the Old Kingdom, and was the founder of that epoch. He is also known by his Hellenized names Tosorthros (from Manetho) and Sesorthos (from Euse ...
and his architect Imhotep
Imhotep (; "(the one who) comes in peace"; ) was an Egyptian chancellor to the King Djoser, possible architect of Djoser's step pyramid, and high priest of the sun god Ra at Heliopolis. Very little is known of Imhotep as a historical figur ...
. This step pyramid
A step pyramid or stepped pyramid is an architectural structure that uses flat platforms, or steps, receding from the ground up, to achieve a completed shape similar to a geometric pyramid. Step pyramids – typically large and made of several la ...
consisted of six stacked mastaba
A mastaba ( , or ), also mastabah or mastabat) is a type of ancient Egyptian tomb in the form of a flat-roofed, rectangular structure with inward sloping sides, constructed out of mudbricks or limestone. These edifices marked the burial sites ...
s. Early kings such as Snefru built pyramids, with subsequent kings adding to the number until the end of the Middle Kingdom. The age of the pyramids reached its zenith at Giza
Giza (; sometimes spelled ''Gizah, Gizeh, Geeza, Jiza''; , , ' ) is the third-largest city in Egypt by area after Cairo and Alexandria; and fourth-largest city in Africa by population after Kinshasa, Lagos, and Cairo. It is the capital of ...
in 2575–2150 BC. The last king to build royal pyramids was Ahmose, with later kings hiding their tomb
A tomb ( ''tumbos'') or sepulchre () is a repository for the remains of the dead. It is generally any structurally enclosed interment space or burial chamber, of varying sizes. Placing a corpse into a tomb can be called '' immurement'', alth ...
s in the hills, such as those in the Valley of the Kings
The Valley of the Kings, also known as the Valley of the Gates of the Kings, is an area in Egypt where, for a period of nearly 500 years from the Eighteenth Dynasty to the Twentieth Dynasty, rock-cut tombs were excavated for pharaohs and power ...
in Luxor's West Bank. In Medinat Habu and Deir el-Medina
Deir el-Medina (), or Dayr al-Madīnah, is an ancient Egyptian workmen's village which was home to the artisans who worked on the tombs in the Valley of the Kings during the 18th to 20th Dynasties of the New Kingdom of Egypt (ca. 1550–1080 BC). ...
, smaller pyramids were built by individuals. Smaller pyramids with steeper sides were built by the Nubians
Nubians () ( Nobiin: ''Nobī,'' ) are a Nilo-Saharan speaking ethnic group indigenous to the region which is now northern Sudan and southern Egypt. They originate from the early inhabitants of the central Nile valley, believed to be one of th ...
who ruled Egypt in the Late Period.
The Great Pyramid of Giza
The Great Pyramid of Giza is the largest Egyptian pyramid. It served as the tomb of pharaoh Khufu, who ruled during the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt, Fourth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom. Built , over a period of about 26 years ...
is the largest in Egypt and one of the largest in the world. At it was the tallest structure in the world until the Lincoln Cathedral
Lincoln Cathedral, also called Lincoln Minster, and formally the Cathedral Church of the Blessed Virgin Mary of Lincoln, is a Church of England cathedral in Lincoln, England, Lincoln, England. It is the seat of the bishop of Lincoln and is the Mo ...
was finished in 1311 AD. Its base covers an area of around . The Great Pyramid is the only extant one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World
The Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, also known as the Seven Wonders of the World or simply the Seven Wonders, is a list of seven notable structures present during classical antiquity, first established in the 1572 publication '' Octo Mundi M ...
.
Ancient Egyptian pyramids were, in most cases, placed west of the river Nile
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the List of river sy ...
because the divine pharaoh's soul was meant to join with the sun during its descent before continuing with the sun in its eternal round. As of 2008, some 135 pyramids had been discovered in Egypt, most located near Cairo.
Sudan

 While African pyramids are commonly associated with Egypt, Sudan has 220 extant pyramids, the most in the world. Nubian pyramids were constructed (roughly 240 of them) at three sites in
While African pyramids are commonly associated with Egypt, Sudan has 220 extant pyramids, the most in the world. Nubian pyramids were constructed (roughly 240 of them) at three sites in Sudan
Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It borders the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Libya to the northwest, Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the east, Eritrea and Ethiopi ...
to serve as tombs for the kings and queens of Napata
Napata
(2020). (Old Egyptian ''Npt'', ''Npy''; Meroitic language, Meroitic ''Napa''; and Ναπάται) was a city of ...
and (2020). (Old Egyptian ''Npt'', ''Npy''; Meroitic language, Meroitic ''Napa''; and Ναπάται) was a city of ...
Meroë
Meroë (; also spelled ''Meroe''; Meroitic: ; and ; ) was an ancient city on the east bank of the Nile about 6 km north-east of the Kabushiya station near Shendi, Sudan, approximately 200 km north-east of Khartoum. Near the site is ...
. The pyramids of Kush, also known as Nubian Pyramids
]
The Nubian pyramids were constructed by the rulers of the ancient Kushite kingdoms in the region of the Nile Valley known as Nubia, located in present-day northern Sudan. This area was the site of three ancient Kushite kingdoms. The capital of ...
, have different characteristics than those of Egypt. The Nubian pyramids had steeper sides than the Egyptian ones. Pyramids were built in Sudan as late as 200 AD.
Sahel
The Tomb of Askia, inGao
Gao (or Gawgaw/Kawkaw) is a city in Mali and the capital of the Gao Region. The city is located on the River Niger, east-southeast of Timbuktu on the left bank at the junction with the Tilemsi valley.
For much of its history Gao was an imp ...
, Mali
Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the List of African countries by area, eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east b ...
, is believed to be the burial place of Askia Mohammad I
Askia Muhammad Ture I (1443–1538), born Muhammad ibn Abi Bakr al-Turi or Muhammad Ture, was the first ruler of the Askia dynasty of the Songhai Empire, reigning from 1493 to 1528. He is also known as Askia the Great, and his name in modern So ...
, one of the Songhai Empire
The Songhai Empire was a state located in the western part of the Sahel during the 15th and 16th centuries. At its peak, it was one of the largest African empires in history. The state is known by its historiographical name, derived from its lar ...
's most prolific emperors
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife ( empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/ grand empress dowager), or a woman who rule ...
. It was built at the end of the fifteenth century and is designated as a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
.
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
describes the tomb as an example of the monumental mud-building traditions of the West African Sahel
The Sahel region (; ), or Sahelian acacia savanna, is a Biogeography, biogeographical region in Africa. It is the Ecotone, transition zone between the more humid Sudanian savannas to its south and the drier Sahara to the north. The Sahel has a ...
. The complex includes the pyramidal tomb, two mosque
A mosque ( ), also called a masjid ( ), is a place of worship for Muslims. The term usually refers to a covered building, but can be any place where Salah, Islamic prayers are performed; such as an outdoor courtyard.
Originally, mosques were si ...
s, a cemetery
A cemetery, burial ground, gravesite, graveyard, or a green space called a memorial park or memorial garden, is a place where the remains of many death, dead people are burial, buried or otherwise entombed. The word ''cemetery'' (from Greek ...
and an assembly ground. At 17 metres (56 ft) in height it is the largest pre- colonial architectural
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and construction, constructi ...
monument in Gao. It is a notable example of the Sudano-Sahelian architectural style that later spread throughout the region.
Nigeria
One of the unique structures of Igbo culture was the Nsude pyramids, in the Nigerian town of Nsude, northernIgboland
Igbo land ( Standard ) is a cultural and common linguistic region in southeastern Nigeria which is the indigenous homeland of the Igbo people. Geographically, it is divided into two sections, eastern (the larger of the two) and western. Its popu ...
. Ten pyramidal structures were built of clay/mud. The first base section was in circumference and in height. The next stack was in circumference. Circular stacks continued to the top. The structures were temples for the god Ala, who was believed to reside there. A stick was placed at the top to represent the god's residence. The structures were laid in groups of five parallel to each other. Because it was built of clay/mud like the Deffufa of Nubia, over time periodic reconstruction has been required.
Europe
Greece
 Pausanias (2nd century AD) mentions two buildings resembling pyramids, one, 19 kilometres (12 mi) southwest of a still standing structure at Hellenikon, a common tomb for soldiers who died in a legendary struggle for the throne of Argos and another that he was told was the tomb of Argives killed in a battle around 669/8 BC. Neither survives and no evidence indicates that they resembled Egyptian pyramids.
At least two surviving pyramid-like structures are available to study, one at Hellenikon and the other at Ligourio/Ligurio, a village near the ancient theatre
Pausanias (2nd century AD) mentions two buildings resembling pyramids, one, 19 kilometres (12 mi) southwest of a still standing structure at Hellenikon, a common tomb for soldiers who died in a legendary struggle for the throne of Argos and another that he was told was the tomb of Argives killed in a battle around 669/8 BC. Neither survives and no evidence indicates that they resembled Egyptian pyramids.
At least two surviving pyramid-like structures are available to study, one at Hellenikon and the other at Ligourio/Ligurio, a village near the ancient theatre Epidaurus
Epidaurus () was a small city (''polis'') in ancient Greece, on the Argolid Peninsula at the Saronic Gulf. Two modern towns bear the name Epidavros: ''Palaia Epidavros'' and ''Nea Epidavros''. Since 2010 they belong to the new municipality of Epi ...
. These buildings have inwardly sloping walls, but bear no other resemblance to Egyptian pyramids. They had large central rooms (unlike Egyptian pyramids) and the Hellenikon structure is rectangular rather than square, which means that the sides could not have met at a point. The stone used to build these structures was limestone quarried locally and was cut to fit, not into freestanding blocks like the Great Pyramid of Giza.
These structures were dated from pot shards excavated from the floor and grounds. The latest estimates are around the 5th and 4th centuries. Normally this technique is used for dating pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other raw materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. The place where such wares are made by a ''potter'' is al ...
, but researchers used it to try to date stone flakes from the structure walls. This launched debate about whether or not these structures are actually older than Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, part of the Black Athena
''Black Athena: The Afroasiatic Roots of Classical Civilization'', published in 1987 (vol. 1), 1991 (vol. 2), and 2006 (vol. 3), is a pseudoarchaeological trilogy by the British Professor of Government and Near Eastern Studies Martin Bernal pr ...
controversy.
Lefkowitz criticised this research, suggesting that some of the research was done not to determine the reliability of the dating method, as was suggested, but to back up a claim and to make points about pyramids and Greek civilization. She claimed that not only were the results imprecise, but that other structures mentioned in the research are not in fact pyramids, e.g. a tomb alleged to be the tomb of Amphion
There are several characters named Amphion in Greek mythology:
* Amphion, son of Zeus and Antiope, and twin brother of Zethus (see Amphion and Zethus). Together, they are famous for building Thebes. Pausanias recounts an Egyptian legend acco ...
and Zethus near Thebes, a structure at Stylidha (Thessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, a ...
) which is a long wall, etc. She pushed the possibility that the stones that were dated might have been recycled from earlier constructions. She claimed that earlier research from the 1930s, confirmed in the 1980s by Fracchia, was ignored.
Liritzis responded that Lefkowitz failed to understand and misinterpreted the methodology.
Spain
The Pyramids of Güímar refer to six rectangular pyramid-shaped, terraced structures, built fromlava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a Natural satellite, moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a Fissure vent, fractu ...
without mortar. They are located in the district of Chacona, part of the town of Güímar on the island of Tenerife
Tenerife ( ; ; formerly spelled ''Teneriffe'') is the largest and most populous island of the Canary Islands, an Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Spain. With a land area of and a population of 965,575 inhabitants as of A ...
in the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; ) or Canaries are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean and the southernmost Autonomous communities of Spain, Autonomous Community of Spain. They are located in the northwest of Africa, with the closest point to the cont ...
. The structures were dated to the 19th century and their function explained as a byproduct of contemporary agricultural
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created f ...
techniques.
Autochthonous
Autochthon, autochthons or autochthonous may refer to:
Nature
* Autochthon (geology), a sediment or rock that can be found at its site of formation or deposition
* Autochthon (nature), or landrace, an indigenous animal or plant
* Autochthonou ...
Guanche Guanche may refer to:
*Guanches, the indigenous people of the Canary Islands
*Guanche language, an extinct language, spoken by the Guanches until the 16th or 17th century
*''Conus guanche
''Conus guanche'' is a species of sea snail, a marine ga ...
traditions as well as surviving images indicate that similar structures (also known as, "Morras", "Majanos", "Molleros", or "Paredones") were built in many locations on the island. However, over time they were dismantled and used as building material. Güímar hostred nine pyramids, only six of which survive.
Roman Empire
 The 27-metre-high
The 27-metre-high Pyramid of Cestius
The pyramid of Cestius (in Italian language, Italian, ''Piramide di Caio Cestio'' or ''Piramide Cestia'') is an ancient Roman pyramid in Rome, Italy, near the Porta San Paolo and the Protestant Cemetery, Rome, Protestant Cemetery. It was built i ...
was built by the end of the 1st century BC and survives close to the Porta San Paolo. Another, named '' Meta Romuli'', stood in the ''Ager Vaticanus'' (today's Borgo), but was destroyed at the end of the 15th century.
Medieval Europe
Pyramids were occasionally used inChristian architecture
Church architecture refers to the architecture of Christian buildings, such as churches, chapels, convents, and seminaries. It has evolved over the two thousand years of the Christian religion, partly by innovation and partly by borrowing oth ...
during the feudal
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was a combination of legal, economic, military, cultural, and political customs that flourished in Middle Ages, medieval Europe from the 9th to 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of struc ...
era, e.g. as the tower of Oviedo
Oviedo () or Uviéu (Asturian language, Asturian: ) is the capital city of the Principality of Asturias in northern Spain and the administrative and commercial centre of the region. It is also the name of the municipality that contains th ...
's Gothic Cathedral of San Salvador.
Americas

Peru
Andean
The Andes ( ), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long and wide (widest between 18°S ...
cultures used pyramids in various architectural structures such as the ones in Caral
The Sacred City of Caral-Supe, or simply Caral, is an archaeological site in Peru where the remains of the main city of the Caral civilization are found. It is located in the Supe valley of Peru, near the current town of Caral, 182 kilometers n ...
, Túcume and Chavín de Huantar, constructed around the same time as early Egyptian pyramids.
Mesoamerica
 Several
Several Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area that begins in the southern part of North America and extends to the Pacific coast of Central America, thus comprising the lands of central and southern Mexico, all of Belize, Guatemala, El S ...
n cultures built pyramid-shaped structures. Mesoamerican pyramids
Mesoamerican pyramids form a prominent part of ancient Mesoamerican architecture. Although similar in some ways to Egyptian pyramids, these New World structures have flat tops (many with temples on the top) and stairs ascending their faces, more ...
were usually stepped, with temples on top, more similar to the Mesopotamian ziggurat than the Egyptian pyramid.
The largest by volume is the Great Pyramid of Cholula
The Great Pyramid of Cholula, also known as (Nahuatl for "constructed mountain"), is a complex located in Cholula, Puebla, Cholula, Puebla, Mexico. It is the largest archaeological site of a pyramid (temple) in the world, as well as the largest ...
, in the Mexican state of Puebla
Puebla, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Puebla, is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 217 municipalities and its capital is Puebla City. Part of east-centr ...
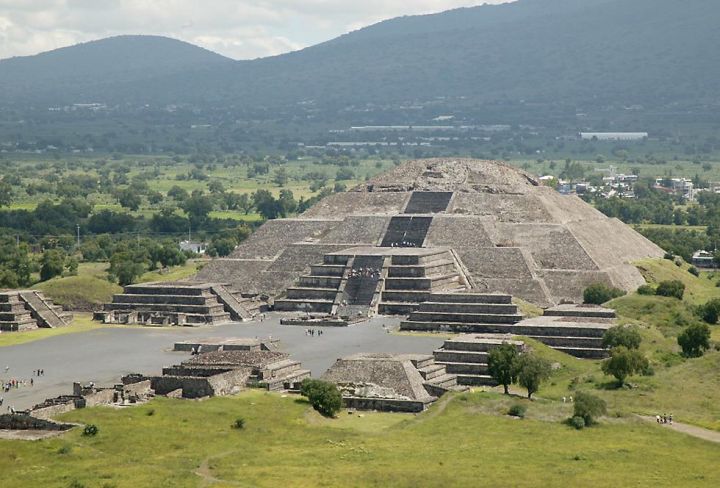
. Constructed from the 3rd century BC to the 9th century AD, this pyramid is the world's largest monument, and is still not fully excavated. The third largest pyramid in the world, the Pyramid of the Sun
The Pyramid of the Sun is the largest building in Teotihuacan, and one of the largest in Mesoamerica. It is believed to have been constructed about 200 AD. Found along the Avenue of the Dead, in between the Pyramid of the Moon and the Ciudadela ...
, at Teotihuacan
Teotihuacan (; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Teotihuacán'', ; ) is an ancient Mesoamerican city located in a sub-valley of the Valley of Mexico, which is located in the State of Mexico, northeast of modern-day Mexico City.
Teotihuacan is ...
, is also located in Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
. An unusual pyramid with a circular plan survives at the site of Cuicuilco
Cuicuilco is an important archaeological site located on the southern shore of Lake Texcoco in the southeastern Valley of Mexico, in what is today the borough of Tlalpan in Mexico City.
Construction of the Cuicuilco pyramid began a few centuri ...
, now inside Mexico City
Mexico City is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Mexico, largest city of Mexico, as well as the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North America. It is one of the most important cultural and finan ...
and mostly covered with lava from an eruption of the Xitle Volcano in the 1st century BC. Several circular stepped pyramids called Guachimontones
Los Guachimontones is the largest Late Formative to Classic period (300 BCE to 450/500 CE) pre-Columbian archaeological site in the state of Jalisco.Christopher S. Beekman (2018). La secuencia cronológica temprana en Los Guachimontones. In Nuevos ...
survive in Teuchitlán, Jalisco
Jalisco, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Jalisco, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is located in western Mexico and is bordered by s ...
.
Pyramids in Mexico were often used for human sacrifice
Human sacrifice is the act of killing one or more humans as part of a ritual, which is usually intended to please or appease deity, gods, a human ruler, public or jurisdictional demands for justice by capital punishment, an authoritative/prie ...
. Harner stated that for the dedication of the Great Pyramid of Tenochtitlan in 1487, "one source states 20,000, another 72,344, and several give 80,400" as the number of humans sacrificed.
United States

 Many pre-Columbian Native American societies of ancient North America built large pyramidal
Many pre-Columbian Native American societies of ancient North America built large pyramidal earth structure
An earth structure is a building or other structure made largely from soil. Since soil is a widely available material, it has been used in construction since prehistory. It may be combined with other materials, compressed and/or baked to add ...
s known as platform mound
A platform mound is any earthwork or mound intended to support a structure or activity. It typically refers to a flat-topped mound, whose sides may be pyramidal.
In Eastern North America
The indigenous peoples of North America built substru ...
s. Among the largest and best-known of these structures is Monks Mound
Monks Mound is the largest Pre-Columbian earthwork in the Americas and the largest pyramid north of Mesoamerica. The beginning of its construction dates from 900 to 955 CE. Located at the Cahokia Mounds UNESCO World Heritage Site near Collins ...
at the site of Cahokia
Cahokia Mounds ( 11 MS 2) is the site of a Native American city (which existed 1050–1350 CE) directly across the Mississippi River from present-day St. Louis. The state archaeology park lies in south-western Illinois between East St. L ...
in what became Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. It borders on Lake Michigan to its northeast, the Mississippi River to its west, and the Wabash River, Wabash and Ohio River, Ohio rivers to its ...
, completed around 1100 AD. It has a base larger than that of the Great Pyramid. Many mounds underwent repeated episodes of expansion. They are believed to have played a central role in the mound-building peoples' religious life. Documented uses include semi-public chief's house platforms, public temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a place of worship, a building used for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. By convention, the specially built places of worship of some religions are commonly called "temples" in Engli ...
platforms, mortuary
A morgue or mortuary (in a hospital or elsewhere) is a place used for the storage of human corpses awaiting identification (ID), removal for autopsy, respectful burial, cremation or other methods of disposal. In modern times, corpses have cus ...
platforms, charnel house
A charnel house is a vault or building where human skeletal remains are stored. They are often built near churches for depositing bones that are unearthed while digging graves. The term can also be used more generally as a description of a plac ...
platforms, earth lodge/town house platforms, residence platforms, square ground and rotunda platforms, and dance platforms. Cultures that built substructure mounds include the Troyville culture, Coles Creek culture
Coles Creek culture is a Late Woodland archaeological culture in the Lower Mississippi valley in the Southeastern Woodlands. It followed the Troyville culture. The period marks a significant change in the cultural history of the area. Population ...
, Plaquemine culture and Mississippian culture
The Mississippian culture was a collection of Native American societies that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 to 1600 CE, varying regionally. It was known for building la ...
s.
Asia

China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
. The first emperor Qin Shi Huang
Qin Shi Huang (, ; February 25912 July 210 BC), born Ying Zheng () or Zhao Zheng (), was the founder of the Qin dynasty and the first emperor of China. He is widely regarded as the first ever supreme leader of a unitary state, unitary d ...
(, who unified the seven pre-imperial kingdoms) was buried under a large mound outside modern-day Xi'an
Xi'an is the list of capitals in China, capital of the Chinese province of Shaanxi. A sub-provincial city on the Guanzhong plain, the city is the third-most populous city in Western China after Chongqing and Chengdu, as well as the most populou ...
. In the following centuries about a dozen more Han dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC ...
royal persons were also buried under flat-topped pyramidal earthworks.
India
Numerous giant,granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly coo ...
, temple pyramids were built in South India
South India, also known as Southern India or Peninsular India, is the southern part of the Deccan Peninsula in India encompassing the states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Telangana as well as the union territories of ...
during the Chola Empire
The Chola Empire, which is often referred to as the Imperial Cholas, was a medieval thalassocratic empire based in southern India that was ruled by the Chola dynasty, and comprised overseas dominions, protectorates and spheres of influence ...
, many of which remain in use. Examples include Brihadisvara Temple
Brihadishvara Temple, called Rajarajesvaram () by its builder, and known locally as ''Thanjai Periya Kovil'' () and ''Peruvudaiyar Kovil'', is a Shaivite Hindu temple built in a Chola architectural style located on the south bank of the Cau ...
at Thanjavur
Thanjavur (), also known as Thanjai, previously known as Tanjore, Pletcher 2010, p. 195 is a city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is the 12th biggest city in Tamil Nadu. Thanjavur is an important center of southern Indian religion, art ...
, Brihadisvara Temple
Brihadishvara Temple, called Rajarajesvaram () by its builder, and known locally as ''Thanjai Periya Kovil'' () and ''Peruvudaiyar Kovil'', is a Shaivite Hindu temple built in a Chola architectural style located on the south bank of the Cau ...
at Gangaikonda Cholapuram
Gaṅgaikoṇḍa Chōḻapuram is a village located near to Jayankondam, Ariyalur district, Tamil Nadu, India. It became the capital of the Chola dynasty in c. 1025 by Chola emperor Rajendra Chola I, Rajendra I, and served as the capital for a ...
, and the Airavatesvara Temple at Darasuram
Darasuram or Dharasuram is a neighbourhood in the city of Kumbakonam, Tamil Nadu, India. The area is known for the Airavateswara temple constructed by the Rajaraja Chola II in the 12th century CE. The temple is a recognised UNESCO World Heritage ...
. However, the largest temple (area) is the Ranganathaswamy Temple in Srirangam, Tamil Nadu. The Thanjavur temple was built by Raja Raja Chola in the 11th century. The Brihadisvara Temple
Brihadishvara Temple, called Rajarajesvaram () by its builder, and known locally as ''Thanjai Periya Kovil'' () and ''Peruvudaiyar Kovil'', is a Shaivite Hindu temple built in a Chola architectural style located on the south bank of the Cau ...
was declared a World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
by UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
in 1987; the Temple of Gangaikondacholapuram and the Airavatesvara Temple at Darasuram were added in 2004.
Brihadisvara Temple
Brihadishvara Temple, called Rajarajesvaram () by its builder, and known locally as ''Thanjai Periya Kovil'' () and ''Peruvudaiyar Kovil'', is a Shaivite Hindu temple built in a Chola architectural style located on the south bank of the Cau ...
.
File:"Architecture of World Heritage Monument Airavatesvara Temple".JPG, Pyramid-structure inside Airavatesvara Temple.
File:Sri Ranganathaswamy Temple, dedicated to Vishnu, in Srirangam, near Tiruchirappali (24) (37254366620).jpg, Ranganathaswamy Temple gopurams at Srirangam dedicated to Ranganatha
Ranganatha, also known as Ranganathar, Rangan, Aranganathar, Sri Ranga, and Thenarangathan, is a Hindu deity with his origin in South India, southern India, serving as the chief deity of the Sri Ranganathaswamy Temple, Srirangam. The deity is a re ...
, a reclining form of the Hindu deity
Hindu deities are the gods and goddesses in Hinduism. Deities in Hinduism are as diverse as its traditions, and a Hindu can choose to be polytheistic, pantheistic, monotheistic, monistic, even agnostic, atheistic, or humanist.Julius J. Lipne ...
Maha Vishnu
Vishnu (; , , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism, and the god of preservation ( ...
.
Indonesia

megalithic
A megalith is a large Rock (geology), stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. More than 35,000 megalithic structures have been identified across Europe, ranging ...
culture in Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
featured earth and stone step pyramid
A step pyramid or stepped pyramid is an architectural structure that uses flat platforms, or steps, receding from the ground up, to achieve a completed shape similar to a geometric pyramid. Step pyramids – typically large and made of several la ...
structures called ''punden berundak.'' These were discovered in Pangguyangan near Cisolok and in Cipari near Kuningan. The stone pyramids were based on beliefs that mountains and high places were the abode for the spirit of the ancestors
An ancestor, also known as a forefather, fore-elder, or a forebear, is a parent or ( recursively) the parent of an antecedent (i.e., a grandparent, great-grandparent, great-great-grandparent and so forth). ''Ancestor'' is "any person from w ...
.
The step pyramid is the basic design of the 8th century Borobudur
Borobudur, also transcribed Barabudur (, ), is a 9th-century Mahayana Buddhist temple in Magelang Regency, near the city of Magelang and the town of Muntilan, in Central Java, Indonesia.
Constructed of gray andesite-like stone, the temple consi ...
Buddhist monument in Central Java
Central Java (, ) is a Provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia, located in the middle of the island of Java. Its administrative capital is Semarang. It is bordered by West Java in the west, the Indian Ocean and the Special Region of Yogya ...
. However later Java temples were influenced by Indian Hindu architecture
Hindu architecture is the traditional system of Indian architecture for structures such as temples, monasteries, statues, homes, market places, gardens and town planning as described in Hindu texts. The architectural guidelines survive in Sans ...
, as exemplified by the spires of Prambanan
Prambanan (, , Javanese script, Hanacaraka: ꦫꦫꦗꦺꦴꦁꦒꦿꦁ) is a 9th-century Hindu temple, Hindu Candi of Indonesia, temple compound in the Special Region of Yogyakarta, in southern Java, Indonesia, dedicated to the Trimurti, Trimūr ...
temple. In the 15th century, during late Majapahit
Majapahit (; (eastern and central dialect) or (western dialect)), also known as Wilwatikta (; ), was a Javanese people, Javanese Hinduism, Hindu-Buddhism, Buddhist thalassocracy, thalassocratic empire in Southeast Asia based on the island o ...
period, Java saw the revival of indigenous Austronesian elements as displayed by Sukuh temple that somewhat resemble Mesoamerican pyramids, and also stepped pyramids of Mount Penanggungan.
East Asia, Southeast Asia and Central Asia
In east Asia, Buddhist stupas were usually represented as tallpagodas
A pagoda is a tiered tower with multiple eaves common to Thailand, Cambodia, Nepal, India, China, Japan, Korea, Myanmar, Vietnam, and other parts of Asia. Most pagodas were built to have a religious function, most often Buddhist, but sometime ...
. However, some pyramidal stupas survive. One theory is that these pyramids were inspired by the Borobudur
Borobudur, also transcribed Barabudur (, ), is a 9th-century Mahayana Buddhist temple in Magelang Regency, near the city of Magelang and the town of Muntilan, in Central Java, Indonesia.
Constructed of gray andesite-like stone, the temple consi ...
monument through Sumatra
Sumatra () is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the list of islands by area, sixth-largest island in the world at 482,286.55 km2 (182,812 mi. ...
n and Javanese monks. A similar Buddhist monument survives in Vrang, Tajikistan
Tajikistan, officially the Republic of Tajikistan, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Dushanbe is the capital city, capital and most populous city. Tajikistan borders Afghanistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, south, Uzbekistan to ...
. At least nine Buddhist step pyramids survive, 4 from former Gyeongsang Province
Gyeongsang Province (; ) was one of the Eight Provinces of Joseon Korea. Gyeongsang was located in southeastern Korea.
The provincial capital of Gyeongsang was Daegu. The region was the birthplace of the kingdom of Silla, which unified Korea i ...
of Korea, 3 from Japan, 1 from Indonesia (Borobudur) and 1 from Tajikistan
Tajikistan, officially the Republic of Tajikistan, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Dushanbe is the capital city, capital and most populous city. Tajikistan borders Afghanistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, south, Uzbekistan to ...
.
Oceania
Several pyramids were erected throughout the Pacific islands, such as Puʻukoholā Heiau inHawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
, the Pulemelei Mound in Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa and known until 1997 as Western Samoa, is an island country in Polynesia, part of Oceania, in the South Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main islands (Savai'i and Upolu), two smaller, inhabited ...
, and Nan Madol
Nan Madol is an archaeological site adjacent to the eastern shore of the island of Pohnpei, now part of the Madolenihmw district of Pohnpei state in the Federated States of Micronesia in the western Pacific Ocean. Nan Madol was the capital o ...
in Pohnpei
Pohnpei (formerly known as Ponape or Ascension, from Pohnpeian: "upon (''pohn'') a stone altar (''pei'')") is an island of the Senyavin Islands which are part of the larger Caroline Islands group. It belongs to Pohnpei State, one of the fou ...
.
Modern pyramids
* Two pyramid-shaped tombs were erected in Maudlin's Cemetery, Ireland, c. 1840, belonging to theDe Burgh
de Burgh ( , ; ; ) is an Anglo-Norman surname deriving from the ancient Anglo-Norman and Hiberno-Norman noble dynasty, the House of Burgh. In Ireland, the descendants of William de Burgh (c.1160–1206) had the surname ''de Burgh'' which was gae ...
family.
* Louvre Pyramid
The Louvre Pyramid () is a large glass-and-metal entrance way and skylight designed by the Chinese-American architect I. M. Pei. The pyramid is in the main courtyard (Cour Napoléon) of the Louvre Palace in Paris, surrounded by three smaller pyr ...
in Paris, France, in the court of the Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is a national art museum in Paris, France, and one of the most famous museums in the world. It is located on the Rive Droite, Right Bank of the Seine in the city's 1st arrondissement of Paris, 1st arron ...
Museum, is a 20.6 metre (about 70 foot) glass structure that acts as a museum entrance. It was designed by American architect I. M. Pei and completed in 1989. The Pyramide Inversée (Inverted Pyramid) is displayed in the underground Louvre shopping mall.
* The Tama-Re village was an Egyptian-themed set of buildings and monuments built near Eatonton, Georgia
Eatonton is a city in and the county seat of Putnam County, Georgia, United States. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 6,307. It was named after William Eaton, an officer and diplomat involved in the First Barbary War. The n ...
by Nuwaubians in 1993 that was mostly demolished after it was sold in 2005.
* The Luxor Hotel in Las Vegas
Las Vegas, colloquially referred to as Vegas, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Nevada and the county seat of Clark County. The Las Vegas Valley metropolitan area is the largest within the greater Mojave Desert, and second-l ...
, United States, is a 30-story pyramid.
* The 32-story Memphis Pyramid
The Memphis Pyramid, formerly known as the Great American Pyramid and the Pyramid Arena, and colloquially known as the Bass Pro Shops Pyramid, is a pyramid-shaped building located in downtown Memphis, Tennessee, Memphis, Tennessee, United State ...
( Memphis was named after the Egyptian capital whose name was derived from the name of one of its pyramids). Built in 1991, it was the home court for the University of Memphis
The University of Memphis (Memphis) is a public university, public research university in Memphis, Tennessee, United States. Founded in 1912, the university has an enrollment of more than 20,000 students.
The university maintains the Herff Col ...
men's basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular Basketball court, court, compete with the primary objective of #Shooting, shooting a basketball (ball), basketball (appro ...
program, and the National Basketball Association
The National Basketball Association (NBA) is a professional basketball league in North America composed of 30 teams (29 in the United States and 1 in Canada). The NBA is one of the major professional sports leagues in the United States and Ca ...
's Memphis Grizzlies
The Memphis Grizzlies (referred to locally as the Grizz) are an American professional basketball team based in Memphis, Tennessee. The Grizzlies compete in the National Basketball Association (NBA) as a member of the Southwest Division of the ...
until 2004. It was not regularly used as a sports or entertainment venue after 2007, and in 2015 was re-purposed as a Bass Pro Shops
BPS Direct, LLC, trade name, doing business as Bass Pro Shops, is an American privately held sporting goods retailer that offers hunting, fishing, camping, and other related outdoor recreation equipment, marine manufacturing and sales, and outd ...
megastore.
* The Walter Pyramid, home of the basketball and volleyball
Volleyball is a team sport in which two teams of six players are separated by a net. Each team tries to score points by grounding a ball on the other team's court under organized rules. It has been a part of the official program of the Summ ...
teams of the California State University, Long Beach
California State University, Long Beach (CSULB), also known in athletics as Long Beach State University (LBSU), is a public teaching-focused institution in Long Beach, California, United States. The 322-acre campus is the second largest in the ...
, campus in California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
, United States, is an 18-story-tall blue true pyramid.
 * The 48-story Transamerica Pyramid in San Francisco, California, designed by
* The 48-story Transamerica Pyramid in San Francisco, California, designed by William Pereira
William Leonard Pereira (April 25, 1909 – November 13, 1985) was an American architect from Chicago, Illinois, who was noted for his Futurist architecture#Post-modern futurism, futuristic designs of landmark buildings such as the Transamer ...
, is a city symbol.
* The 105-story Ryugyong Hotel
The Ryugyong Hotel (; sometimes spelled as Ryu-Gyong Hotel), or Yu-Kyung Hotel, is a tall unfinished pyramid-shaped skyscraper in Pyongyang, North Korea. Its name ( "capital of willows") is also one of the historical names for Pyongyang. The ...
is in Pyongyang
Pyongyang () is the Capital city, capital and largest city of North Korea, where it is sometimes labeled as the "Capital of the Revolution" (). Pyongyang is located on the Taedong River about upstream from its mouth on the Yellow Sea. Accordi ...
, North Korea.
* A former museum/monument in Tirana, Albania is commonly known as the " Pyramid of Tirana". It differs from typical pyramids in having a radial rather than square or rectangular shape, and gently sloped sides that make it short in comparison to the size of its base.
* The Slovak Radio Building in Bratislava
Bratislava (German: ''Pressburg'', Hungarian: ''Pozsony'') is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the Slovakia, Slovak Republic and the fourth largest of all List of cities and towns on the river Danube, cities on the river Danube. ...
, Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
is an inverted pyramid.
* The Palace of Peace and Reconciliation
The Palace of Peace and Reconciliation (, ''Beibıtşılık pen kelısım saraiy''), also translated as the ''Pyramid of Peace and Accord'', is a pyramid in Astana, the capital of Kazakhstan, since 2019, that serves as a non-denominational natio ...
is in Astana
Astana is the capital city of Kazakhstan. With a population of 1,423,726 within the city limits, it is the second-largest in the country after Almaty, which had been the capital until 1997. The city lies on the banks of the Ishim (river), Ishim ...
, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
.
* The three pyramids of Moody Gardens are in Galveston
Galveston ( ) is a Gulf Coast of the United States, coastal resort town, resort city and port off the Southeast Texas coast on Galveston Island and Pelican Island (Texas), Pelican Island in the U.S. state of Texas. The community of , with a pop ...
, Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
.
* The Co-Op Bank Pyramid or Stockport Pyramid in Stockport
Stockport is a town in Greater Manchester, England, south-east of Manchester, south-west of Ashton-under-Lyne and north of Macclesfield. The River Goyt, Rivers Goyt and River Tame, Greater Manchester, Tame merge to create the River Mersey he ...
, England is a large pyramid-shaped office block. (The surrounding part of the valley of the upper Mersey has sometimes been called the "Kings Valley" after the Egypt's Valley of the Kings
The Valley of the Kings, also known as the Valley of the Gates of the Kings, is an area in Egypt where, for a period of nearly 500 years from the Eighteenth Dynasty to the Twentieth Dynasty, rock-cut tombs were excavated for pharaohs and power ...
.)
* The Ames Monument in southeastern Wyoming honors the brothers who financed the Union Pacific Railroad.
* The Trylon and Perisphere, Trylon, a triangular pyramid was erected for the 1939 World's Fair in Flushing, Queens and demolished after the Fair closed.
* The Ballandean Pyramid, at Ballandean in rural Queensland is a 15-metre folly pyramid made from blocks of local granite.
* The Karlsruhe Pyramid is a pyramid made of red sandstone, located in the centre of the market square of Karlsruhe, Germany. It was erected in 1823–1825 over the vault of the city's founder, Margrave Charles III William (1679–1738).
* Muttart Conservatory greenhouses are in Edmonton, Alberta.
 * Sunway Pyramid shopping mall is in Selangor, Malaysia.
* Hanoi Museum has an overall design of a reversed pyramid.
* The Ha! Ha! Pyramid by artist in La Baie, Quebec is made out of 3,000 give way signs.
* The culture-entertainment complex and is in Kazan, Russia.
* The Time pyramid in Wemding, Germany is a pyramid begun in 1993 and scheduled for completion in the year 3183.Conception
* Sunway Pyramid shopping mall is in Selangor, Malaysia.
* Hanoi Museum has an overall design of a reversed pyramid.
* The Ha! Ha! Pyramid by artist in La Baie, Quebec is made out of 3,000 give way signs.
* The culture-entertainment complex and is in Kazan, Russia.
* The Time pyramid in Wemding, Germany is a pyramid begun in 1993 and scheduled for completion in the year 3183.ConceptionOfficial ''Zeitpyramide'' website, accessed: 14 December 2010 * Triangle (Paris building), Triangle is a proposed skyscraper in Paris. * The Shimizu Mega-City Pyramid is a proposed project for construction of a massive pyramid over Tokyo Bay in Japan. * The Donkin Memorial was erected on a Xhosa people, Xhosa reserve in 1820 by Cape Governor Sir Rufane Shaw Donkin in memory of his late wife Elizabeth, in Port Elizabeth, South Africa. The pyramid is used in many different coats-of-arms associated with Port Elizabeth.
 *
*
Stockport
Stockport is a town in Greater Manchester, England, south-east of Manchester, south-west of Ashton-under-Lyne and north of Macclesfield. The River Goyt, Rivers Goyt and River Tame, Greater Manchester, Tame merge to create the River Mersey he ...
, United Kingdom
File:Karlsruhe Pyramide Winter Nacht 01.JPG, Karlsruhe Pyramid, Germany
File:Hanoi Museum 01a.JPG, Hanoi Museum in Vietnam features an inverted pyramid shape.
File:Upside down Pyramid, Bratislava 02.jpg, Slovak Radio Building, Bratislava
Bratislava (German: ''Pressburg'', Hungarian: ''Pozsony'') is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the Slovakia, Slovak Republic and the fourth largest of all List of cities and towns on the river Danube, cities on the river Danube. ...
, Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
.
File:Architektura kazan.JPG, "Pyramid" culture-entertainment complex in Kazan, Russia.
File:Luxor Hotel.jpg, Luxor Hotel in Las Vegas Strip, Las Vegas, Nevada
File:Pyramid Arena.jpg, Pyramid Arena in Memphis, Tennessee
File:Walter Pyramid.jpg, Walter Pyramid in Long Beach, California
Modern mausoleums
 With the Egyptian Revival movement in the nineteenth and early twentieth century, pyramids became more common in funerary architecture. The tomb of Quintino Sella, outside the monumental cemetery of Oropa, is pyramid-shaped. This style was popular with tycoons in the US. The Schoenhofen Pyramid Mausoleum (1889) in Chicago and Hunt's Tomb (1930) in Phoenix, Arizona are notable examples. Some people build pyramid tombs for themselves. Nicolas Cage bought a pyramid tomb for himself in a famed New Orleans graveyard.
With the Egyptian Revival movement in the nineteenth and early twentieth century, pyramids became more common in funerary architecture. The tomb of Quintino Sella, outside the monumental cemetery of Oropa, is pyramid-shaped. This style was popular with tycoons in the US. The Schoenhofen Pyramid Mausoleum (1889) in Chicago and Hunt's Tomb (1930) in Phoenix, Arizona are notable examples. Some people build pyramid tombs for themselves. Nicolas Cage bought a pyramid tomb for himself in a famed New Orleans graveyard.
See also
* List of largest monoliths * Lists of pyramids * List of pyramid mausoleums in North America * Mound * Pyramid power * Stupa * Triadic pyramid * Tumulus (burial mound)References
External links
* * {{Authority control Pyramids, Types of monuments and memorials sn:Dumba