|
Hindu Architecture
Hindu architecture is the traditional system of Indian architecture for structures such as temples, monasteries, statues, homes, market places, gardens and town planning as described in Hindu texts. The architectural guidelines survive in Sanskrit manuscripts and in some cases also in other regional languages. These texts include the Vastu shastras, Shilpa Shastras, the ''Brihat Samhita'', architectural portions of the Puranas and the Agamas, and regional texts such as the Manasara among others. By far the most important, characteristic and numerous surviving examples of Hindu architecture are Hindu temples, with an Hindu temple architecture, architectural tradition that has left surviving examples in stone, brick, and Indian rock-cut architecture, rock-cut architecture dating back to the Gupta Empire. These architectures had influence of Ancient Persian and Hellenistic influence on Indian art, Hellenistic architecture. Far fewer secular Hindu architecture have survived into th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th Century Nilakantha Mahadeva Hindu Temple, Nagara Architecture, Sunak, Gujarat
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, Numeral (linguistics), numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest Positive number, positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit (measurement), unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In Digital electronics, digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In math ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmajāla Sutta
The ''Brahmajāla Sutta'' is the first of 34 '' sutta'' in the '' Dīgha Nikāya'' (the Long Discourses of the Buddha), the first of the five '' nikāya'', or collections, in the '' Sutta Pitaka'', which is one of the "three baskets" that compose the Pali ''Tipitaka'' of (Theravada) Buddhism. The name means Raft (jāla-made.of inflatable cow or buffalo skins tied to a wooden platform used to convey people from one shore to the other) of Brahmā. The ''sutta'' is also called ''Atthajala'' (Raft of Essence), ''Dhammajala'', (Raft of the Dhamma), ''Ditthijala'' (Raft of Views), ''Anuttarasangama Vijaya'' (Incomparable Victory in Battle). The word "net" is a mistranslation. The words of the Revered Buddha are clear when he describes the Dhamma as teachings that take one to the safe shore (of eternity) The ''sutta'' discusses two main topics: the elaboration of the "Ten Precepts" (''Cula-sila'') and the "Middle Precepts" (''Majjhima-sila''). ''Cula-sila'' deals with the Ten Precepts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matha
A ''matha'' (; , ), also written as ''math'', ''muth'', ''mutth'', ''mutt'', or ''mut'', is a Sanskrit word that means 'institute or college', and it also refers to a monastery in Hinduism.Matha Encyclopædia Britannica Online 2009 An alternative term for such a monastery is ''adheenam''. The earliest epigraphical evidence for ''mathas'' related to Hindu-temples comes from the 7th to 10th century CE. The most famous Advaita Vedanta ''mathas'' or ''peethams'', which came to be affiliated with the Advaita tradition in the 14th century, are Govardhanmaṭha Pīṭhaṃ at |
Southern India
South India, also known as Southern India or Peninsular India, is the southern part of the Deccan Peninsula in India encompassing the states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Telangana as well as the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry, occupying 19.31% of India's area () and 20% of India's population. It is bound by the Bay of Bengal in the east, the Arabian Sea in the west and the Indian Ocean in the south. The geography of the region is diverse, with two mountain ranges, the Western and Eastern Ghats, bordering the plateau heartland. The Godavari, Krishna, Kaveri, Penna, Tungabhadra and Vaigai rivers are important non-perennial sources of water. Chennai, Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Coimbatore and Kochi are the largest urban areas in the region. The majority of the people in South India speak at least one of the four major Dravidian languages: Telugu, Tamil, Kannada and Malayalam. During its history, a number of dynastic kingdoms ruled ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gopuram
A ''gopuram'' or ''gopura'' ( Tamil: கோபுரம், Telugu: గోపురం, Kannada Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a ...: ಗೋಪುರ, Malayalam language, Malayalam: ഗോപുരം) is a monumental entrance tower, usually ornate, at the Entrance Hall, entrance of a Hindu temple, in the Dravidian architecture, South Indian architecture of the southern Indian states of Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, Karnataka, and Telangana, and Sri Lanka. In other areas of India they are much more modest, while in Southern Indian temples they are very often by far the highest part of the temple. Ancient and early medieval temples feature smaller ''gopuram'', while in later temples they are a prominent feature of Hindu temple architecture, Hindu Tamil archi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konark Sun Temple
Konark Sun Temple is a Hindu temple, Hindu Surya, Sun temple at Konark about northeast from Puri, Puri city on the coastline in Puri district, Odisha, India.Konark: India , Encyclopædia Britannica The temple is attributed to king Narasingha Deva I of the Eastern Ganga dynasty about . It is the pinnacle of Hindu Orissan architecture. Dedicated to the Hindu Sun-god Surya, it reflects the pinnacle of kalingan architecture and artistic excellence, what remains of the temple complex has the appearance of a high chariot with immense wheels and horses, all carved from stone. Once over high, much of the temple is now in ruins, in particular the large Vimana (architectural feature), shikara tower over the sanctua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
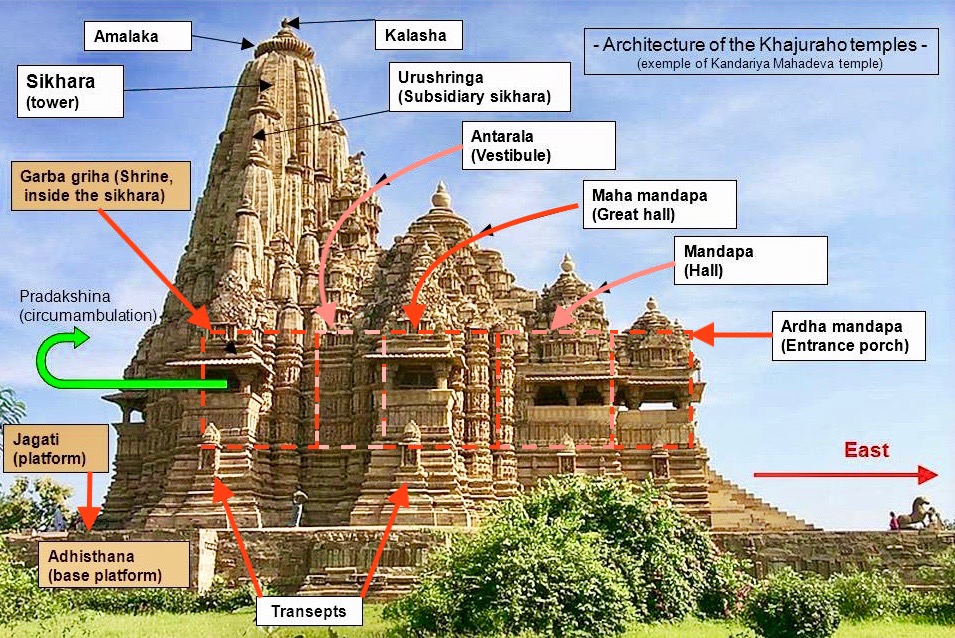
Antarala
''Antarala'' (Sanskrit: अन्तराल; ) is a small antechamber or foyer between the ''garbhagriha A ''garbhagriha'' () is the innermost sanctuary of Hindu and Jain temples, often referred to as the "holy of holies" or " sanctum sanctorum". The term ''garbhagriha'' (literally, "womb chamber") comes from the Sanskrit words ''garbha'' for ...'' (shrine) and the '' mandapa'', more typical of north Indian temples. ''Antarala'' are commonly seen in Chalukyan Style temples, in which the ''vimana'' and the ''mandapa'' are connected through the ''antarala''. References Hindu temple architecture {{India-hindu-temple-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandapa
A ''mandapa'' or ''mantapa'' () is a pillared hall or pavilion for public rituals in Indian architecture, especially featured in Hindu temple architecture and Jain temple architecture. ''Mandapas'' are described as "open" or "closed" depending on whether they have walls. In temples, one or more ''mandapas'' very often lie between the sanctuary and the temple entrance, on the same axis. In a large temple other ''mandapas'' may be placed to the sides, or detached within the temple compound. Temple architecture In the Hindu temple the ''mandapa'' is a porch-like structure through the (''gopuram'') (ornate gateway) and leading to the temple. It is used for religious dancing and music and is part of the basic temple compound. The prayer hall was generally built in front of the temple's '' sanctum sanctorum'' (''garbhagriha''). A large temple would have many ''mandapa''. If a temple has more than one ''mandapa'', each one is allocated for a different function and given a name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vimana (architectural Feature)
''Vimana'' is the structure over the '' garbhagriha'' or inner sanctum in the Hindu temples of South India and Odisha in East India. In typical temples of Odisha using the Kalinga style of architecture, the ''vimana'' is the tallest structure of the temple, as it is in the ''shikhara'' towers of temples in West and North India. By contrast, in large South Indian temples, it is typically smaller than the great gatehouses or '' gopuram'', which are the most immediately striking architectural elements in a temple complex. A ''vimana'' is usually shaped as a pyramid, consisting of several stories or '' tala''. ''Vimana'' are divided in two groups: ''jati vimanas'' that have up to four ''tala'' and ''mukhya vimana'' that have five ''tala'' and more. In North Indian temple architecture texts, the superstructure over the ''garbhagriha'' is called a ''shikhara''. However, in South Indian Hindu architecture texts, the term ''shikhara'' means a dome-shaped crowning cap above the ''vimana' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shikhara
''Shikhara'' (IAST: '), a Sanskrit word translating literally to "mountain peak", refers to the rising tower in the Hindu temple architecture of North India, and also often used in Jain temples. A ''shikhara'' over the ''garbhagriha'' chamber where the presiding deity is enshrined is the most prominent and visible part of a Hindu temple of North India. In South India, the equivalent term is Vimana (architectural feature), ''vimana''; unlike the ''shikhara'', this refers to the whole building, including the sanctum beneath. In the south, ''shikhara'' is a term for the top stage of the vimana only, which is usually a dome capped with a finial; this article is concerned with the northern form. The southern ''vimana'' is not to be confused with the elaborate gateway-towers of south Indian temples, called ''gopuram'', which are often taller and more prominent features in large temples. It is argued that stylistic aspects seen on Buddhist architecture like the ''stupa'' may have bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murti
In the Hinduism, Hindu tradition, a ''murti'' (, ) is a devotional image, such as a statue or icon, of a Hindu deities, deity or Hindu saints, saint used during ''Puja (Hinduism), puja'' and/or in other customary forms of actively expressing devotion or reverence – whether at Hindu temples or shrines. A ''mūrti'' is a symbolic icon representing divinity for the purpose of devotional activities. Thus, not all icons of gods and saints are ''mūrti''; for example, purely decorative depictions of divine figures often adorn Hindu temple architecture in intricately carved doorframes, on colourfully painted walls, and ornately sculpted rooftop domes. A ''mūrti'' itself is not God, but it is merely a representative shape, symbolic embodiment, or iconic manifestation of God. ''Murti'' are also found in some nontheistic Jainism, Jain traditions, where they serve as symbols of revered mortals inside Jain temples, and are worshiped in ''murtipujaka'' rituals. A ''murti'' is typically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garbhagriha
A ''garbhagriha'' () is the innermost sanctuary of Hindu and Jain temples, often referred to as the "holy of holies" or " sanctum sanctorum". The term ''garbhagriha'' (literally, "womb chamber") comes from the Sanskrit words ''garbha'' for womb and ''griha'' for house. Although the term is often associated with Hindu temples, it is also found in Jain and Buddhist temples. The garbhagriha is the location of the ''murti'' (sacred image) of the temple's primary deity. This might be a murti of Shiva, as the lingam, his consort the Goddess in her consecrated image or yoni symbol, Vishnu or his spouse, or some other god in symbol or image. In the Rajarani temple in Bhubaneswar, near Puri, there is no symbol in that lightless garbhagriha. Architecture A garbhagriha started with a circular architecture like at Gudimellam temple (3rd century BCE). Later it evolved as a square (though there are exceptions), sits on a plinth, and is also at least approximately a cube. Compared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |