Pulse-width Modulator on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pulse-width modulation (PWM), also known as pulse-duration modulation (PDM) or pulse-length modulation (PLM), is any method of representing a signal as a rectangular wave with a varying
published
in 1946) for variable area film
 The intersective method is a simple way to generate a PWM output signal (magenta in above figure) with fixed period and varying duty cycle is by using a
The intersective method is a simple way to generate a PWM output signal (magenta in above figure) with fixed period and varying duty cycle is by using a  * Leading
* Leading
 Delta modulation produces a PWM signal (magenta in above figure) which changes state whenever its integral (blue) hits the limits (green) surrounding the input (red).
Delta modulation produces a PWM signal (magenta in above figure) which changes state whenever its integral (blue) hits the limits (green) surrounding the input (red).

An Introduction to Delta Sigma ConvertersPulse Width Modulation in PID control loop - free simulator
Signal processing
duty cycle
A duty cycle or power cycle is the fraction of one period in which a signal or system is active. Duty cycle is commonly expressed as a percentage or a ratio. A period is the time it takes for a signal to complete an on-and-off cycle. As a for ...
(and for some methods also a varying period
Period may refer to:
Common uses
* Period (punctuation)
* Era, a length or span of time
*Menstruation, commonly referred to as a "period"
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Period (music), a concept in musical composition
* Periodic sentence (o ...
).
PWM is useful for controlling the average power
Power may refer to:
Common meanings
* Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work"
** Engine power, the power put out by an engine
** Electric power, a type of energy
* Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events
Math ...
or amplitude
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of am ...
delivered by an electrical signal. The average value of volt
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, Voltage#Galvani potential vs. electrochemical potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units, International System of Uni ...
age (and current
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (hydr ...
) fed to the load is controlled by switching the supply between 0 and 100% at a rate faster than it takes the load to change significantly. The longer the switch is on, the higher the total power supplied to the load. Along with maximum power point tracking
Maximum power point tracking (MPPT), or sometimes just power point tracking (PPT), is a technique used with variable power sources to maximize energy extraction as conditions vary. The technique is most commonly used with photovoltaic (PV) solar s ...
(MPPT), it is one of the primary methods of controlling the output of solar panels to that which can be utilized by a battery. PWM is particularly suited for running inertial loads such as motors, which are not as easily affected by this discrete switching. The goal of PWM is to control a load; however, the PWM switching frequency must be selected carefully in order to smoothly do so.
The PWM switching frequency can vary greatly depending on load and application. For example, switching only has to be done several times a minute in an electric stove; 100 or 120 Hz (double of the utility frequency
The utility frequency, (power) line frequency (American English) or mains frequency (British English) is the nominal frequency of the oscillations of alternating current (AC) in a wide area synchronous grid transmitted from a power station to t ...
) in a lamp dimmer; between a few kilohertz (kHz) and tens of kHz for a motor drive; and well into the tens or hundreds of kHz in audio amplifiers and computer power supplies. Choosing a switching frequency that is too high for the application may cause premature failure of mechanical control components despite getting smooth control of the load. Selecting a switching frequency that is too low for the application causes oscillations in the load. The main advantage of PWM is that power loss in the switching devices is very low. When a switch is off there is practically no current, and when it is on and power is being transferred to the load, there is almost no voltage drop across the switch. Power loss, being the product of voltage and current, is thus in both cases close to zero. PWM also works well with digital controls, which, because of their on/off nature, can easily set the needed duty cycle. PWM has also been used in certain communication systems where its duty cycle has been used to convey information over a communications channel.
In electronics, many modern microcontroller
A microcontroller (MC, uC, or μC) or microcontroller unit (MCU) is a small computer on a single integrated circuit. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Pro ...
s (MCUs) integrate PWM controllers exposed to external pins as peripheral devices under firmware
In computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computer, computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both computer hardware, h ...
control. These are commonly used for direct current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional electric current, flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor (material), conductor such as a wire, but can also flow throug ...
(DC) motor control
Motor control is the regulation of movements in organisms that possess a nervous system. Motor control includes conscious voluntary movements, subconscious muscle memory and involuntary reflexes, as well as instinctual taxes.
To control ...
in robotics
Robotics is the interdisciplinary study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of robots.
Within mechanical engineering, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in computer s ...
, switched-mode power supply
A switched-mode power supply (SMPS), also called switching-mode power supply, switch-mode power supply, switched power supply, or simply switcher, is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator to electric power conversio ...
regulation, and other applications.
Duty cycle
The term ''duty cycle
A duty cycle or power cycle is the fraction of one period in which a signal or system is active. Duty cycle is commonly expressed as a percentage or a ratio. A period is the time it takes for a signal to complete an on-and-off cycle. As a for ...
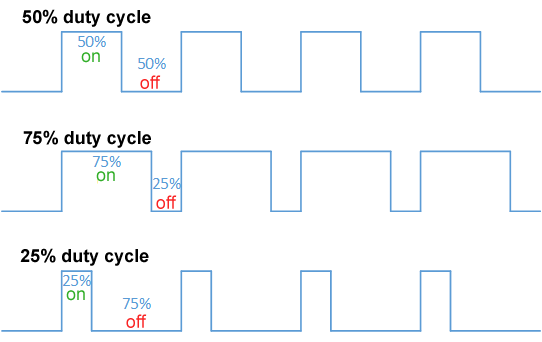
'' describes the proportion of 'on' time to the regular interval or 'period' of time; a low duty cycle corresponds to low power, because the power is off for most of the time. Duty cycle is expressed in percent, 100% being fully on. When a digital signal is on half of the time and off the other half of the time, the digital signal has a duty cycle of 50% and resembles a "square" wave. When a digital signal spends more time in the on state than the off state, it has a duty cycle of >50%. When a digital signal spends more time in the off state than the on state, it has a duty cycle of <50%. Here is a pictorial that illustrates these three scenarios:

History
TheCorliss steam engine
A Corliss steam engine (or Corliss engine) is a steam engine, fitted with rotary valves and with variable valve timing patented in 1849, invented by and named after the US engineer George Henry Corliss of Providence, Rhode Island. Corliss assumed ...
was patented in 1849. It used pulse-width modulation to control the intake valve of a steam engine cylinder. A centrifugal governor
A centrifugal governor is a specific type of governor with a feedback system that controls the speed of an engine by regulating the flow of fuel or working fluid, so as to maintain a near-constant speed. It uses the principle of proportional con ...
was used to provide automatic feedback.
Some machines (such as a sewing machine
Diagram of a modern sewing machine
Animation of a modern sewing machine as it stitches
A sewing machine is a machine used to sew fabric and materials together with thread. Sewing machines were invented during the first Industrial Revolutio ...
motor) require partial or variable power. In the past, control (such as in a sewing machine's foot pedal) was implemented by use of a rheostat
A potentiometer is a three-terminal (electronics), terminal resistor with a sliding or rotating contact that forms an adjustable voltage divider. If only two terminals are used, one end and the wiper, it acts as a variable resistor or rheostat.
...
connected in series with the motor to adjust the amount of current flowing through the motor. It was an inefficient scheme, as this also wasted power as heat in the resistor element of the rheostat, but tolerable because the total power was low. While the rheostat was one of several methods of controlling power (see autotransformer
In electrical engineering, an autotransformer is an electrical transformer with only one winding. The " auto" (Greek for "self") prefix refers to the single coil acting alone. In an autotransformer, portions of the same winding act as both the p ...
s and Variac
In electrical engineering, an autotransformer is an electrical transformer with only one winding. The "auto" (Greek for "self") prefix refers to the single coil acting alone. In an autotransformer, portions of the same winding act as both the pri ...
for more info), a low cost and efficient power switching/adjustment method was yet to be found. This mechanism also needed to be able to drive motors for fans, pumps and robotic
Robotics is the interdisciplinary study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of robots.
Within mechanical engineering, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in computer s ...
servomechanism
In mechanical and control engineering, a servomechanism (also called servo system, or simply servo) is a control system for the position and its time derivatives, such as velocity, of a mechanical system. It often includes a servomotor, and ...
s, and needed to be compact enough to interface with lamp dimmers. PWM emerged as a solution for this complex problem.
PWM telecommunications systems were invented just prior to the start of World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, but at that time time-division multiplexing was already in use and there were only experimental PWM systems. This changed with the introduction of the cavity magnetron
The cavity magnetron is a high-power vacuum tube used in early radar systems and subsequently in microwave ovens and in linear particle accelerators. A cavity magnetron generates microwaves using the interaction of a stream of electrons wit ...
in 1940, which could produce pulses of microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than other radio waves but longer than infrared waves. Its wavelength ranges from about one meter to one millimeter, corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300&n ...
frequency energy but could not vary its frequency or precisely control its amplitude. A PWM encoder was used to trigger a magnetron in the British Army
The British Army is the principal Army, land warfare force of the United Kingdom. the British Army comprises 73,847 regular full-time personnel, 4,127 Brigade of Gurkhas, Gurkhas, 25,742 Army Reserve (United Kingdom), volunteer reserve perso ...
's Wireless Set Number 10, which provided long-distance telephone relay, up to .
The Philips, N. V. company designed an optical scanning systempublished
in 1946) for variable area film
soundtrack
A soundtrack is a recorded audio signal accompanying and synchronised to the images of a book, drama, motion picture, radio program, television show, television program, or video game; colloquially, a commercially released soundtrack album of m ...
which produced the PWM. It was intended to reduce noise when playing back a film soundtrack. The proposed system had a threshold between "white" and "black" parts of soundtrack.
One early application of PWM was in the Sinclair
Sinclair may refer to:
Places
* Lake Sinclair, near Milledgeville, Georgia
* Mount Sinclair, Canada
* Sinclair, Iowa
* Sinclair, West Virginia
* Sinclair, Wyoming
* Sinclair Mills, British Columbia
* Sinclair Township, Minnesota
* Sincl ...
X10, a 10 W audio amplifier available in kit form in the 1960s. At around the same time, PWM started to be used in AC motor control.
Of note, for about a century, some variable-speed electric motors have had decent efficiency, but they were somewhat more complex than constant-speed motors, and sometimes required bulky external electrical apparatus, such as a bank of variable power resistors or rotating converters such as the Ward Leonard drive.
Principle
Periodic pulse wave
If we consider a periodicpulse wave
A pulse wave or pulse train or rectangular wave is a non-sinusoidal waveform that is the periodic version of the rectangular function. It is held high a percent each cycle ( period) called the duty cycle and for the remainder of each cycle is ...
with period , low value , a high value and a constant duty cycle D (Figure 1), the average value of the waveform is given by:
As is a pulse wave, its value is for and for . The above expression then becomes:
This latter expression can be fairly simplified in many cases where as . From this, the average value of the signal () is directly dependent on the duty cycle D.
However, by varying (i.e. modulating) the duty cycle (and possibly also the period), the following more advanced pulse-width modulated waves allow variation of the average
In colloquial, ordinary language, an average is a single number or value that best represents a set of data. The type of average taken as most typically representative of a list of numbers is the arithmetic mean the sum of the numbers divided by ...
value of the waveform.
Intersective method PWM
comparator
In electronics, a comparator is a device that compares two voltages or currents and outputs a digital signal indicating which is larger. It has two analog input terminals V_+ and V_- and one binary digital output V_\text. The output is ideally
...
to switch the PWM output state when the input waveform (red) intersects with a sawtooth or a triangle
A triangle is a polygon with three corners and three sides, one of the basic shapes in geometry. The corners, also called ''vertices'', are zero-dimensional points while the sides connecting them, also called ''edges'', are one-dimension ...
waveform (blue).
Depending on the type of sawtooth or triangle waveform (green in below figure), intersective PWM signals (blue in the below figure) can be aligned in three manners:
edge
Edge or EDGE may refer to:
Technology Computing
* Edge computing, a network load-balancing system
* Edge device, an entry point to a computer network
* Adobe Edge, a graphical development application
* Microsoft Edge, a web browser developed by ...
modulation (top plot) uses a reverse sawtooth wave to generate the PWM. The PWM's leading edge is held at the leading edge of the window and the trailing edge is modulated.
* Trailing edge modulation (middle plot) uses a normal sawtooth wave to generate the PWM. The PWM's trailing edge is fixed and the leading edge is modulated.
* Centered pulses (bottom) uses a triangle waveform to generate the PWM. The pulse center is fixed in the center of the time window and both edges of the pulse are moved to compress or expand the width.
Time proportioning
Many digital circuits can generate PWM signals (e.g., manymicrocontrollers
A microcontroller (MC, uC, or μC) or microcontroller unit (MCU) is a small computer on a single integrated circuit. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Pro ...
have PWM outputs). They normally use a counter that increments periodically (it is connected directly or indirectly to the clock
A clock or chronometer is a device that measures and displays time. The clock is one of the oldest Invention, human inventions, meeting the need to measure intervals of time shorter than the natural units such as the day, the lunar month, a ...
of the circuit) and is reset at the end of every period of the PWM. When the counter value is more than the reference value, the PWM output changes state from high to low (or low to high). This technique is referred to as time proportioning, particularly as time-proportioning control – which ''proportion'' of a fixed cycle time is spent in the high state.
The incremented and periodically reset counter is the discrete version of the intersecting method's sawtooth. The analog comparator of the intersecting method becomes a simple integer comparison between the current counter value and the digital (possibly digitized) reference value. The duty cycle can only be varied in discrete steps, as a function of the counter resolution. However, a high-resolution counter can provide quite satisfactory performance.
Spectrum
The resulting spectra (of the three alignments) are similar. Each contains aDC component
In signal processing, when describing a periodic function in the time domain, the DC bias, DC component, DC offset, or DC coefficient is the mean value of the waveform. A waveform with zero mean or no DC bias is known as a ''DC balanced'' or ''DC ...
, a base sideband containing the modulating signal, and phase modulated carriers at each harmonic
In physics, acoustics, and telecommunications, a harmonic is a sinusoidal wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'' of a periodic signal. The fundamental frequency is also called the ''1st har ...
of the frequency of the pulse. The amplitudes of the harmonic groups are restricted by a envelope (sinc function
In mathematics, physics and engineering, the sinc function ( ), denoted by , has two forms, normalized and unnormalized..
In mathematics, the historical unnormalized sinc function is defined for by
\operatorname(x) = \frac.
Alternatively, ...
) and extend to infinity. The infinite bandwidth is caused by the nonlinear operation of the pulse-width modulator. In consequence, a digital PWM suffers from aliasing
In signal processing and related disciplines, aliasing is a phenomenon that a reconstructed signal from samples of the original signal contains low frequency components that are not present in the original one. This is caused when, in the ori ...
distortion that significantly reduce its applicability for modern communication system
A communications system is a collection of individual telecommunications networks systems, relay stations, tributary stations, and terminal equipment usually capable of interconnection and interoperation to form an integrated whole. Communic ...
s. By limiting the bandwidth of the PWM kernel, aliasing effects can be avoided.
On the contrary, delta modulation
Delta modulation (DM, ΔM, or Δ-modulation) is an analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog signal conversion technique used for transmission of voice information where quality is not of primary importance. DM is the simplest form of differential ...
and delta-sigma modulation
Delta-sigma (ΔΣ; or sigma-delta, ΣΔ) modulation is an oversampling method for encoding signals into low bit depth digital signals at a very high sample-frequency as part of the process of delta-sigma analog-to-digital converters (A ...
are random processes that produces a continuous spectrum without distinct harmonics. While intersective PWM uses a fixed period but a varying duty cycle, the period of delta and delta-sigma modulated PWMs varies in addition to their duty cycle.
Delta modulation
Asynchronous delta-sigma PWM
Asynchronous
Asynchrony is any dynamic far from synchronization. If and as parts of an asynchronous system become more synchronized, those parts or even the whole system can be said to be in sync.
Asynchrony or asynchronous may refer to:
Electronics and com ...
(i.e. unclocked) delta-sigma modulation produces a PWM output (blue in bottom plot) which is subtracted from the input signal (green in top plot) to form an error signal (blue in top plot). This error is integrated (magenta in middle plot). When the integral of the error exceeds the limits (the upper and lower grey lines in middle plot), the PWM output changes state. By integrating the difference of the error with the input signal, delta-sigma modulation shapes noise of the resulting spectrum to be more in higher frequencies above the input signal's band.
Space vector modulation
Space vector modulation is a PWM control algorithm for multi-phase AC generation, in which the reference signal is sampled regularly; after each sample, non-zero active switching vectors adjacent to the reference vector and one or more of the zero switching vectors are selected for the appropriate fraction of the sampling period in order to synthesize the reference signal as the average of the used vectors.Direct torque control (DTC)
Direct torque control is a method used to control AC motors. It is closely related with the delta modulation (see above). Motor torque and magnetic flux are estimated and these are controlled to stay within their hysteresis bands by turning on a new combination of the device's semiconductor switches each time either signal tries to deviate out of its band.PWM sampling theorem
The process of PWM conversion is non-linear and it is generally supposed that low pass filter signal recovery is imperfect for PWM. The PWM sampling theorem shows that PWM conversion can be perfect:AnyFor comparison, thebandlimited Bandlimiting is the process of reducing a signal’s energy outside a specific frequency range, keeping only the desired part of the signal’s spectrum. This technique is crucial in signal processing and communications to ensure signals stay cl ...baseband In telecommunications and signal processing, baseband is the range of frequencies occupied by a signal that has not been modulated to higher frequencies. Baseband signals typically originate from transducers, converting some other variable into ...signal whose amplitude is within ±0.637 can be represented by a PWM waveform of unit amplitude (±1). The number of pulses in the waveform is equal to the number of Nyquist samples and the peak constraint is independent of whether the waveform is two-level or three-level.
Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem
The Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem is an essential principle for digital signal processing linking the frequency range of a signal and the sample rate required to avoid a type of distortion called aliasing. The theorem states that the sample r ...
can be summarized as:
If you have a signal that is bandlimited to a bandwidth of f0 then you can collect all the information there is in that signal by sampling it at discrete times, as long as your sample rate is greater than 2f0.
Applications
Servos
PWM is used to control servomechanisms; seeservo control
Servo control is a method of controlling many types of servo (radio control), RC/hobbyist servos by sending the servo a PWM (pulse-width modulation) signal, a series of repeating pulses of variable width where either the width of the pulse (most ...
.
Telecommunications
Intelecommunications
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of ...
, PWM is a form of signal modulation
Signal modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform in electronics and telecommunication for the purpose of transmitting information.
The process encodes information in form of the modulation or message ...
where the widths of the pulses correspond to specific data values encoded at one end and decoded at the other.
Pulses of various lengths (the information itself) will be sent at regular intervals (the carrier frequency of the modulation).
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , ,
Clock , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , ,
__, , ____, , ____, , ____, , ____, , ____, , ____, , ____, , ____
_ __ ____ ____ _
PWM signal , , , , , , , , , ,
, , , , , , , , , ,
_________, , ____, , ___, , ________, , _, , ___________
Data 0 1 2 4 0 4 1 0
The inclusion of a clock signal
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal (historically also known as ''logic beat'') is an electronic logic signal (voltage or current) which oscillates between a high and a low state at a constant frequency and ...
is not necessary, as the leading edge of the data signal can be used as the clock if a small offset is added to each data value in order to avoid a data value with a zero length pulse.
_ __ ___ _____ _ _____ __ _
, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , ,
PWM signal , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , ,
__, , ____, , ___, , __, , _, , ____, , _, , ___, , _____
Data 0 1 2 4 0 4 1 0
Power delivery
PWM can be used to control the amount of power delivered to a load without incurring the losses that would result from linear power delivery by resistive means. Drawbacks to this technique are that the power drawn by the load is not constant but rather discontinuous (seeBuck converter
file:Commutation cell in converters.svg, Comparison of non-isolated switching DC-to-DC converter topologies: buck, Boost converter, boost, Buck–boost converter, buck–boost, Ćuk converter, Ćuk. The input is left side, the output with load is ...
), and energy delivered to the load is not continuous either. However, the load may be inductive, and with a sufficiently high frequency and when necessary using additional passive electronic filter
Electronic filters are a type of signal processing filter in the form of electrical circuits. This article covers those filters consisting of lumped-element model, lumped electronic components, as opposed to distributed-element filters. That ...
s, the pulse train can be smoothed and average analog waveform recovered. Power flow into the load can be continuous. Power flow from the supply is not constant and will require energy storage on the supply side in most cases. (In the case of an electrical circuit, a capacitor to absorb energy stored in (often parasitic) supply side inductance.)
High frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
PWM power control systems are easily realisable with semiconductor switches. As explained above, almost no power is dissipated by the switch in either on or off state. However, during the transitions between on and off states, both voltage and current are nonzero and thus power is dissipated in the switches. By quickly changing the state between fully on and fully off (typically less than 100 nanoseconds), the power dissipation in the switches can be quite low compared to the power being delivered to the load.
Modern semiconductor switches such as MOSFET
upright=1.3, Two power MOSFETs in amperes">A in the ''on'' state, dissipating up to about 100 watt">W and controlling a load of over 2000 W. A matchstick is pictured for scale.
In electronics, the metal–oxide–semiconductor field- ...
s or insulated-gate bipolar transistor
An insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) is a three-terminal power semiconductor device primarily forming an electronic switch. It was developed to combine high efficiency with fast switching. It consists of four alternating layers (NPNP) that ...
s (IGBTs) are well suited components for high-efficiency controllers. Frequency converters used to control AC motors may have efficiencies exceeding 98%. Switching power supplies have lower efficiency due to low output voltage levels (often even less than 2 V for microprocessors are needed) but still more than 70–80% efficiency can be achieved.
Variable-speed computer fan control
Fan control is the management of the rotational speed of an electric fan. In computers, various types of computer fans are used to provide adequate cooling, and different fan control mechanisms balance their cooling capacities and noise they gene ...
lers usually use PWM, as it is far more efficient when compared to a potentiometer
A potentiometer is a three- terminal resistor with a sliding or rotating contact that forms an adjustable voltage divider. If only two terminals are used, one end and the wiper, it acts as a variable resistor or rheostat.
The measuring instrum ...
or rheostat. (Neither of the latter is practical to operate electronically; they would require a small drive motor.)
Light dimmers for home use employ a specific type of PWM control. Home-use light dimmers typically include electronic circuitry that suppresses current flow during defined portions of each cycle of the AC line voltage. Adjusting the brightness of light emitted by a light source is then merely a matter of setting at what voltage (or phase) in the AC half-cycle the dimmer begins to provide electric current to the light source (e.g. by using an electronic switch such as a triac
A TRIAC (triode for alternating current; also bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor) is a three-terminal electronic component that conducts current in either direction when triggered. The term TRIAC is a genericized trad ...
). In this case the PWM duty cycle is the ratio of the conduction time to the duration of the half AC cycle defined by the frequency of the AC line voltage (50 Hz or 60 Hz depending on the country).
These rather simple types of dimmers can be effectively used with inert (or relatively slow reacting) light sources such as incandescent lamps, for example, for which the additional modulation in supplied electrical energy which is caused by the dimmer causes only negligible additional fluctuations in the emitted light. Some other types of light sources such as light-emitting diodes (LEDs), however, turn on and off extremely rapidly and would perceivably flicker if supplied with low-frequency drive voltages. Perceivable flicker effects from such rapid response light sources can be reduced by increasing the PWM frequency. If the light fluctuations are sufficiently rapid (faster than the flicker fusion threshold
The flicker fusion threshold, also known as critical flicker frequency or flicker fusion rate, is the frequency at which a flickering light appears steady to the average human observer. It is a concept studied in vision science, more specificall ...
), the human visual system can no longer resolve them and the eye perceives the time average intensity without flicker.
In electric cookers, continuously variable power is applied to the heating elements such as the hob or the grill using a device known as a simmerstat. This consists of a thermal oscillator running at approximately two cycles per minute and the mechanism varies the duty cycle according to the knob setting. The thermal time constant of the heating elements is several minutes so that the temperature fluctuations are too small to matter in practice.
Voltage regulation
PWM is also used in efficientvoltage regulator
A voltage regulator is a system designed to automatically maintain a constant voltage. It may use a simple feed-forward design or may include negative feedback. It may use an electromechanical mechanism or electronic components. Depending on the ...
s. By switching the voltage to the load with the appropriate duty cycle, the output will approximate a voltage at the desired level. The switching noise is usually filtered with an inductor
An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a Passivity (engineering), passive two-terminal electronic component, electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when an electric current flows through it. An inductor typic ...
and a capacitor
In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term st ...
.
One method measures the output voltage. When it is lower than the desired voltage, it turns on the switch. When the output voltage is above the desired voltage, it turns off the switch.
Audio effects and amplification
Varying the duty cycle of a pulse waveform in a synthesis instrument creates useful timbral variations. Some synthesizers have a duty-cycle trimmer for their square-wave outputs, and that trimmer can be set by ear; the 50% point (true square wave) is distinctive because even-numbered harmonics essentially disappear at 50%. Pulse waves, usually 50%, 25%, and 12.5%, make up the soundtracks of classic video games. The term PWM as used in sound (music) synthesis refers to the ratio between the high and low level being secondarily modulated with alow-frequency oscillator
Low-frequency oscillation (LFO) is an electronic frequency that is usually below 20 Hz and creates a rhythmic pulse or sweep. This is used to modulate musical equipment such as synthesizers to create audio effects such as vibrato, tremolo ...
. This gives a sound effect similar to chorus
Chorus may refer to:
Music
* Chorus (song), the part of a song that is repeated several times, usually after each verse
* Chorus effect, the perception of similar sounds from multiple sources as a single, richer sound
* Chorus form, song in whic ...
or slightly detuned oscillators played together. (In fact, PWM is equivalent to the sum of two sawtooth wave
The sawtooth wave (or saw wave) is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform. It is so named based on its resemblance to the teeth of a plain-toothed saw with a zero rake angle. A single sawtooth, or an intermittently triggered sawtooth, is called a ...
s with one of them inverted.)
Class-D amplifier
A class-D amplifier, or switching amplifier, is an electronic amplifier in which the amplifying devices (transistors, usually MOSFETs) operate as electronic switches, and not as linear gain devices as in other amplifiers. They operate by rapidl ...
s produce a PWM equivalent of a lower frequency input signal that can be sent to a loudspeaker
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or, more fully, a speaker system) is a combination of one or more speaker drivers, an enclosure, and electrical connections (possibly including a crossover network). The speaker driver is an ...
via a suitable filter network to block the carrier and recover the original lower frequency signal. Since they switch power directly from the high supply rail and low supply rail, these amplifiers have efficiency above 90% and can be relatively compact and light, even for large power outputs. For a few decades, industrial and military PWM amplifiers have been in common use, often for driving servomotor
A servomotor (or servo motor or simply servo) is a rotary or linear actuator that allows for precise control of angular or linear position, velocity, and acceleration in a mechanical system. It constitutes part of a servomechanism, and consi ...
s. Field-gradient coils in MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and rad ...
machines are driven by relatively high-power PWM amplifiers.
Historically, a crude form of PWM has been used to play back PCM
Pulse-code modulation (PCM) is a method used to Digital signal (signal processing), digitally represent analog signals. It is the standard form of digital audio in computers, compact discs, digital telephony and other digital audio application ...
digital sound on the PC speaker
A PC speaker is a loudspeaker built into some IBM PC compatible computers. The first IBM Personal Computer, model 5150, employed a standard 2.25 inch magnetic driven (dynamic) speaker. More recent computers use a tiny moving-iron or pie ...
, which is driven by only two voltage levels, typically 0 V and 5 V. By carefully timing the duration of the pulses, and by relying on the speaker's physical filtering properties (limited frequency response, self-inductance, etc.) it was possible to obtain an approximate playback of mono PCM samples, although at a very low quality, and with greatly varying results between implementations. The Sega 32X
The 32X is an add-on for the Sega Genesis video game console. Codenamed "Project Mars", it was designed to expand the power of the Genesis and serve as a transitional console into the 32-bit era until the release of the Sega Saturn. The 32X ...
uses PWM to play sample-based sound in its games.
In more recent times, the Direct Stream Digital
Direct Stream Digital (DSD) is a trademark used by Sony and Philips for their system for digitally encoding audio signals for the Super Audio CD (SACD).
DSD uses delta-sigma modulation, a form of pulse-density modulation encoding, a techniqu ...
sound encoding method was introduced, which uses a generalized form of pulse-width modulation called pulse-density modulation
Pulse-density modulation (PDM) is a form of modulation used to represent an analog signal with a binary signal. In a PDM signal, specific amplitude values are not encoded into codewords of pulses of different weight as they would be in pulse ...
, at a high enough sampling rate (typically in the order of MHz) to cover the whole acoustic frequencies range with sufficient fidelity. This method is used in the SACD format, and reproduction of the encoded audio signal is essentially similar to the method used in class-D amplifiers.
Electrical
SPWM (sine–triangle pulse-width modulation) signals are used insolar inverter
A solar inverter or photovoltaic (PV) inverter is a type of power inverter which converts the variable direct current (DC) output of a photovoltaic solar panel into a utility frequency alternating current (AC) that can be fed into a commercial ...
design. These switching signals are fed to the FET
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the current through a semiconductor. It comes in two types: junction FET (JFET) and metal-oxide-semiconductor FET (MOSFET). FETs have three termi ...
s that are used in the device. The device's efficiency depends on the harmonic content of the PWM signal. There is much research on eliminating unwanted harmonics and improving the fundamental strength, some of which involves using a modified carrier signal instead of a classic sawtooth signalHirak Patangia, Sri Nikhil Gupta Gourisetti, “A Novel Strategy for Selective Harmonic Elimination Based on a Sine-Sine PWM Model”, MWSCAS, U.S.A, Aug 2012. in order to decrease power losses and improve efficiency. Another common application is in robotics where PWM signals are used to control the speed of the robot by controlling the motors.
Soft-blinking LED indicator
PWM techniques would typically be used to make some indicator (like anLED
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corresp ...
) ''soft blink''. The light will slowly go from dark to full intensity, and slowly dimmed to dark again. Then it repeats. The period would be several soft blinks per second up to several seconds for one blink. An indicator of this type would not disturb as much as a ''hard-blinking'' on/off indicator. The indicator lamp on the Apple iBook G4, PowerBook 6,7 (2005) was of this type. This kind of indicator is also called ''pulsing glow'', as opposed to calling it ''flashing''.
See also
* Analog signal to discrete time interval converter *Class-D amplifier
A class-D amplifier, or switching amplifier, is an electronic amplifier in which the amplifying devices (transistors, usually MOSFETs) operate as electronic switches, and not as linear gain devices as in other amplifiers. They operate by rapidl ...
* Computer fan control
Fan control is the management of the rotational speed of an electric fan. In computers, various types of computer fans are used to provide adequate cooling, and different fan control mechanisms balance their cooling capacities and noise they gene ...
* Continuously variable slope delta modulation
Continuously variable slope delta modulation (CVSD or CVSDM) is a voice coding method. It is a delta modulation with variable step size (i.e., special case of adaptive delta modulation), first proposed by Greefkes and Riemens in 1970.
CVSD enco ...
* Delta-sigma modulation
Delta-sigma (ΔΣ; or sigma-delta, ΣΔ) modulation is an oversampling method for encoding signals into low bit depth digital signals at a very high sample-frequency as part of the process of delta-sigma analog-to-digital converters (A ...
* H-bridge
An H-bridge is an electronic circuit that switches the polarity of a voltage applied to a load. These circuits are often used in robotics and other applications to allow DC motors to run forwards or backwards.
The name is derived from its common s ...
* Pulse-amplitude modulation
Pulse-amplitude modulation (PAM) is a form of signal modulation in which the message information is encoded in the amplitude of a pulse train interrupting the carrier frequency. Demodulation is performed by detecting the amplitude level of th ...
* Pulse-code modulation
Pulse-code modulation (PCM) is a method used to digitally represent analog signals. It is the standard form of digital audio in computers, compact discs, digital telephony and other digital audio applications. In a PCM stream, the amplitud ...
* Pulse-density modulation
Pulse-density modulation (PDM) is a form of modulation used to represent an analog signal with a binary signal. In a PDM signal, specific amplitude values are not encoded into codewords of pulses of different weight as they would be in pulse ...
* Pulse-frequency modulation
Pulse-frequency modulation (PFM) is a modulation method for representing an analog signal using only two levels (1 and 0). It is analogous to pulse-width modulation (PWM), in which the magnitude of an analog signal is encoded in the duty cycle of ...
* Pulse-position modulation
Pulse-position modulation (PPM) is a form of signal modulation in which ''M'' message bits are encoded by transmitting a single pulse in one of 2^M possible required time shifts. This is repeated every ''T'' seconds, such that the transmitted b ...
* Radio control
Radio control (often abbreviated to RC) is the use of control signals transmitted by radio to remotely operate a device. Examples of simple radio control systems are garage door openers and keyless entry systems for vehicles, in which a small ha ...
* Random pulse-width modulation
* RC servo
* Sliding mode control
In control systems, sliding mode control (SMC) is a nonlinear control method that alters the dynamic system, dynamics of a nonlinear system by applying a discontinuous control signal (or more rigorously, a set-valued control signal) that forces th ...
- produces smooth behavior by way of discontinuous switching in systems
* Space vector modulation
* Sound chip
A sound chip is an integrated circuit (chip) designed to produce audio signals through digital, analog or mixed-mode electronics. Sound chips are typically fabricated on metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) mixed-signal chips that process a ...
References
External links
{{Commons category, Pulse width modulationAn Introduction to Delta Sigma Converters
Signal processing