ping (networking utility) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
ping is a
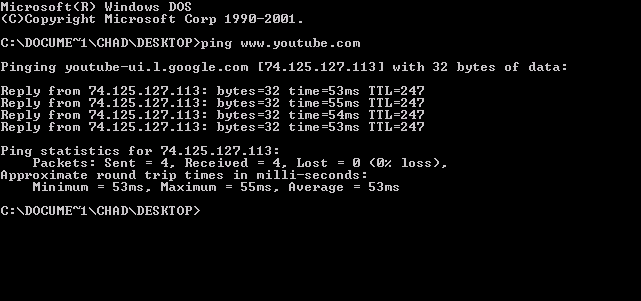 The ping utility was written by
The ping utility was written by
$ ping -c 5 www.example.com
PING www.example.com (93.184.216.34): 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 93.184.216.34: icmp_seq=0 ttl=56 time=11.632 ms
64 bytes from 93.184.216.34: icmp_seq=1 ttl=56 time=11.726 ms
64 bytes from 93.184.216.34: icmp_seq=2 ttl=56 time=10.683 ms
64 bytes from 93.184.216.34: icmp_seq=3 ttl=56 time=9.674 ms
64 bytes from 93.184.216.34: icmp_seq=4 ttl=56 time=11.127 ms
--- www.example.com ping statistics ---
5 packets transmitted, 5 packets received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 9.674/10.968/11.726/0.748 ms
The output lists each probe message and the results obtained. Finally, it lists the statistics of the entire test. In this example, the shortest
16:24:47.966461 IP (tos 0x0, ttl 128, id 15103, offset 0, flags
The payload may include a timestamp indicating the time of transmission and a sequence number, which are not found in this example. This allows ping to compute the round-trip time in a stateless manner without needing to record the time of transmission of each packet.
The payload may also include a ''magic packet'' for the
ping
at
computer network
A computer network is a collection of communicating computers and other devices, such as printers and smart phones. In order to communicate, the computers and devices must be connected by wired media like copper cables, optical fibers, or b ...
administration software utility used to test the reachability of a host
A host is a person responsible for guests at an event or for providing hospitality during it.
Host may also refer to:
Places
* Host, Pennsylvania, a village in Berks County
* Host Island, in the Wilhelm Archipelago, Antarctica
People
* ...
on an Internet Protocol
The Internet Protocol (IP) is the network layer communications protocol in the Internet protocol suite for relaying datagrams across network boundaries. Its routing function enables internetworking, and essentially establishes the Internet.
IP ...
(IP) network. It is available in a wide range of operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
s including most embedded network administration software.
Ping measures the round-trip time
In telecommunications, round-trip delay (RTD) or round-trip time (RTT) is the amount of time it takes for a signal to be sent ''plus'' the amount of time it takes for acknowledgement of that signal having been received. This time delay includes p ...
for messages sent from the originating host to a destination computer that are echoed back to the source. The name comes from active sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect objects on ...
terminology that sends a pulse
In medicine, the pulse refers to the rhythmic pulsations (expansion and contraction) of an artery in response to the cardiac cycle (heartbeat). The pulse may be felt ( palpated) in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surfac ...
of sound and listens for the echo
In audio signal processing and acoustics, an echo is a reflection of sound that arrives at the listener with a delay after the direct sound. The delay is directly proportional to the distance of the reflecting surface from the source and the lis ...
to detect objects under water.
Ping operates by means of Internet Control Message Protocol
The Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is a supporting protocol in the Internet protocol suite. It is used by network devices, including routers, to send error messages and operational information indicating success or failure when com ...
(ICMP) packets. ''Pinging'' involves sending an ICMP echo request to the target host and waiting for an ICMP echo reply. The program reports errors, packet loss
Packet loss occurs when one or more packets of data travelling across a computer network fail to reach their destination. Packet loss is either caused by errors in data transmission, typically across wireless networks, or network congestion.Ku ...
, and a statistical summary of the results, typically including the minimum, maximum, the mean
A mean is a quantity representing the "center" of a collection of numbers and is intermediate to the extreme values of the set of numbers. There are several kinds of means (or "measures of central tendency") in mathematics, especially in statist ...
round-trip times, and standard deviation
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation of the values of a variable about its Expected value, mean. A low standard Deviation (statistics), deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean ( ...
of the mean.
Command-line option
A command-line interface (CLI) is a means of interacting with software via command (computing), commands each formatted as a line of text. Command-line interfaces emerged in the mid-1960s, on computer terminals, as an interactive and more user ...
s and terminal output vary by implementation. Options may include the size of the payload, count of tests, limits for the number of network hops ( TTL) that probes traverse, interval between the requests and time to wait for a response. Many systems provide a companion utility ping6, for testing on Internet Protocol version 6
Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is the most recent version of the Internet Protocol (IP), the communication protocol, communications protocol that provides an identification and location system for computers on networks and routes traffic ...
(IPv6) networks, which implement ICMPv6
Internet Control Message Protocol version 6 (ICMPv6) is the implementation of the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) for Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6). ICMPv6 is an integral part of IPv6 and performs error reporting and diagnostic fu ...
.
History
 The ping utility was written by
The ping utility was written by Mike Muuss
Michael John Muuss (October 16, 1958 – November 20, 2000) was the American author of the freeware network tool Ping (networking utility), ping, as well as the first interactive ray tracing program.
Career
A graduate of Johns Hopkins Universit ...
in December 1983 during his employment at the Ballistic Research Laboratory
The Ballistic Research Laboratory (BRL) was a research facility under the U.S. Army Ordnance Corps and later the U.S. Army Materiel Command that specialized in ballistics as well as vulnerability and lethality analysis. Situated at Aberdeen Pr ...
, now the US Army Research Laboratory
The U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command Army Research Laboratory (DEVCOM ARL) is the foundational research laboratory for the United States Army under the United States Army Futures Command (AFC). DEVCOM ARL conducts intramural an ...
. A remark by David Mills on using ICMP echo packets for IP network diagnosis and measurements prompted Muuss to create the utility to troubleshoot network problems. The author named it after the sound that sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances ( ranging), communicate with or detect objects o ...
makes since its methodology is analogous to sonar's echolocation. The backronym
A backronym is an acronym formed from an already existing word by expanding its letters into the words of a phrase. Backronyms may be invented with either serious or humorous intent, or they may be a type of false etymology or folk etymology. The ...
Packet InterNet Groper for PING has been used for over 30 years. Muuss says that, from his point of view, PING was not intended as an acronym but he has acknowledged Mills' expansion of the name. The first released version was public domain software
Public-domain software is software that has been placed in the public domain, in other words, software for which there is absolutely no ownership such as copyright, trademark, or patent. Software in the public domain can be modified, distributed, ...
; all subsequent versions have been licensed under the BSD license
BSD licenses are a family of permissive free software licenses, imposing minimal restrictions on the use and distribution of covered software. This is in contrast to copyleft licenses, which have share-alike requirements. The original BSD lic ...
. Ping was first included in 4.3BSD. The FreeDOS
FreeDOS (formerly PD-DOS) is a free software operating system for IBM PC compatible computers. It intends to provide a complete MS-DOS-compatible environment for running Legacy system, legacy software and supporting embedded systems. FreeDOS ca ...
version was developed by Erick Engelke and is licensed under the GPL. Tim Crawford developed the ReactOS
ReactOS is a Free and open-source software, free and open-source operating system for i586/amd64 personal computers that is intended to be binary-code compatibility, binary-compatible with computer programs and device drivers developed for Wind ...
version. It is licensed under the MIT License
The MIT License is a permissive software license originating at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in the late 1980s. As a permissive license, it puts very few restrictions on reuse and therefore has high license compatibility.
Unl ...
.
Any host must process ICMP echo requests and issue echo replies in return.
Invocation example
The following is the output of running ping on Linux for sending five probes (1-second interval by default, configurable via -i option) to the target host ''www.example.com'':round-trip time
In telecommunications, round-trip delay (RTD) or round-trip time (RTT) is the amount of time it takes for a signal to be sent ''plus'' the amount of time it takes for acknowledgement of that signal having been received. This time delay includes p ...
was 9.674 ms, the average was 10.968 ms, and the maximum value was 11.726 ms. The measurement had a standard deviation
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation of the values of a variable about its Expected value, mean. A low standard Deviation (statistics), deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean ( ...
of 0.748 ms.
Error indications
In cases of no response from the target host, most implementations display either nothing or periodically print notifications about timing out. Possible ping results indicating a problem include the following: * or host, network or protocol unreachable * source route failed * fragmentation needed * or destination network/host unknown * source host is isolated * communication with destination network administratively prohibited * communication with destination host administratively prohibited * for this ToS the destination network is unreachable * for this ToS the destination host is unreachable * communication administratively prohibited * host precedence violation * precedence cutoff in effect In case of error, the target host or an intermediate router sends back an ICMP error message, for example ''host unreachable'' or ''TTL exceeded in transit''. In addition, these messages include the first eight bytes of the original message (in this case header of the ICMP echo request, including the quench value), so the ping utility can match responses to originating queries.Message format
ICMP packet transported with IPv4
An ICMP packet transported with IPv4 looks like this. ; ; ; ; ; Most Linux systems use a unique ''Identifier'' for every ping process, and ''Sequence number'' is an increasing number within that process. Windows uses a fixed ''Identifier'', which varies between Windows versions, and a ''Sequence number'' that is only reset at boot time. The ''Echo Reply'' is returned as: ; ; ; ;ICMPv6 packet transported with IPv6
An ICMP packet transported with IPv6 looks like this. ; ; ; ; ; Most Linux systems use a unique ''Identifier'' for every ping process, and ''Sequence number'' is an increasing number within that process. Windows uses a fixed ''Identifier'', which varies between Windows versions, and a ''Sequence number'' that is only reset at boot time. The ''Echo Reply'' is returned as: ; ; ; ;Payload
The payload of the packet is generally filled withASCII
ASCII ( ), an acronym for American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for representing a particular set of 95 (English language focused) printable character, printable and 33 control character, control c ...
characters, as the output of the tcpdump
tcpdump is a data-network packet analyzer computer program that runs under a command line interface. It allows the user to display TCP/IP and other packets being transmitted or received over a network to which the computer is attached. Distr ...
utility shows in the last 32 bytes of the following example (after the eight-byte ICMP header starting with ):
one
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sp ...
proto: ICMP (1), length: 60) 192.168.146.22 > 192.168.144.5: ICMP echo request,
id 1, seq 38, length 40
0x0000: 4500 003c 3aff 0000 8001 5c55 c0a8 9216 E..<:.....\U....
0x0010: c0a8 9005 0800 4d35 0001 0026 6162 6364 ......M5...&abcd
0x0020: 6566 6768 696a 6b6c 6d6e 6f70 7172 7374 efghijklmnopqrst
0x0030: 7576 7761 6263 6465 6667 6869 uvwabcdefghi
Wake-on-LAN
Wake-on-LAN (WoL) is an Ethernet or Token Ring computer networking standard that allows a computer to be turned on or awakened from sleep mode by a network message.
The message is usually sent to the target computer by a program executed on a d ...
protocol, but the minimum payload, in that case, is longer than shown. The ''Echo Request'' typically does not receive any reply if the host was sleeping in hibernation state, but the host still wakes up from sleep state if its interface is configured to accept wakeup requests. If the host is already active and configured to allow replies to incoming ICMP ''Echo Request'' packets, the returned reply should include the same payload. This may be used to detect that the remote host was effectively woken up, by repeating a new request after some delay to allow the host to resume its network services. If the host was just sleeping in low power active state, a single request wakes up that host just enough to allow its ''Echo Reply'' service to reply instantly if that service was enabled. The host does not need to wake up all devices completely and may return to low-power mode after a short delay. Such configuration may be used to avoid a host to enter in hibernation state, with much longer wake-up delay, after some time passed in low power active mode.
A packet including IP and ICMP headers must not be greater than the maximum transmission unit
In computer networking, the maximum transmission unit (MTU) is the size of the largest protocol data unit (PDU) that can be communicated in a single network layer transaction. The MTU relates to, but is not identical to the maximum frame size tha ...
of the network, or risk being fragmented.
Security loopholes
To conduct adenial-of-service attack
In computing, a denial-of-service attack (DoS attack) is a cyberattack in which the perpetrator seeks to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users by temporarily or indefinitely disrupting services of a host co ...
, an attacker may send ping requests as fast as possible, possibly overwhelming the victim with ICMP echo requests. This technique is called a ping flood.
Ping requests to multiple addresses, ping sweeps, may be used to obtain a list of all hosts on a network.
See also
* fping *hping
hping is an open-source packet generator and analyzer for the TCP/IP protocol created by Salvatore Sanfilippo (also known as Antirez).
It is one of the common tools used for security auditing and testing of firewalls and networks, and was used ...
* Keepalive
A keepalive (KA) is a message sent by one device to another to check that the link between the two is operating, or to prevent the link from being broken.
Description
Once a TCP connection has been established, that connection is defined to be ...
* nping
* PathPing
The PathPing command is a command-line network utility included in Windows NT operating systems since Windows 2000 that combines the functionality of ping with that of tracert. It is used to locate spots that have network latency and network ...
* Ping of death
A ping of death is a type of attack on a computer system that involves sending a malformed or otherwise malicious ping to a computer. In this attack, a host sends hundreds of ping requests with a packet size that is large or illegal to another ho ...
* Ping-pong scheme
* Smurf attack
A Smurf attack is a distributed denial-of-service attack in which large numbers of Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) packets with the intended victim's spoofed source IP are broadcast to a computer network using an IP broadcast address. ...
* Traceroute
In computing, traceroute and tracert are diagnostic command-line interface commands for displaying possible routes (paths) and transit delays of packets across an Internet Protocol (IP) network.
The command reports the round-trip times of ...
References
Further reading
* * *External links
* * *ping
at
Microsoft Docs
Microsoft Docs was a library of technical documentation for end users, developers, and IT professionals who work with Microsoft products. The Microsoft Docs website provided technical specifications, conceptual articles, tutorials, guides, API ...
{{Windows commands
Free network management software
Internet Protocol based network software
Network analyzers
OS/2 commands
Unix network-related software
Windows administration
Windows communication and services