
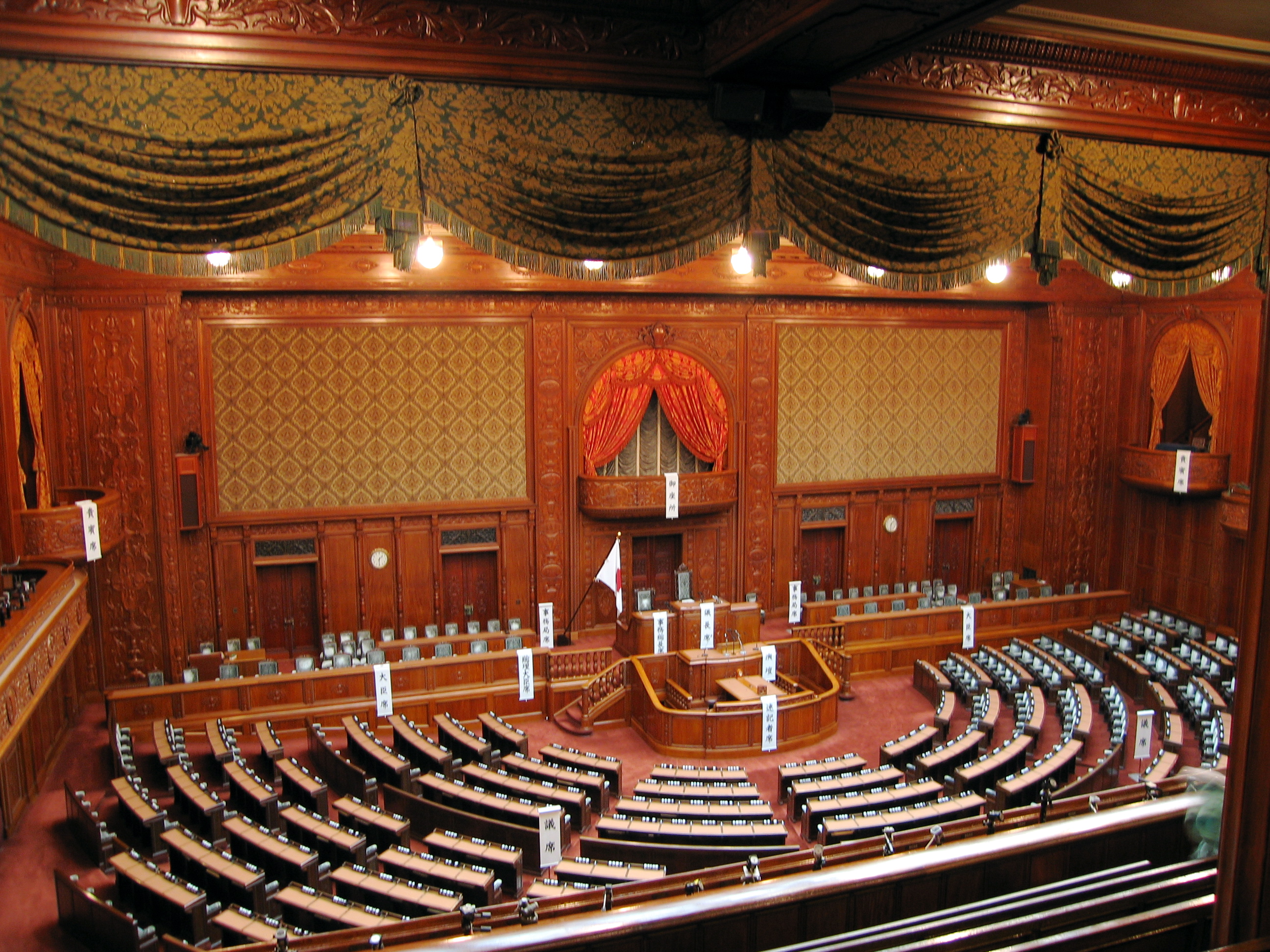

In modern politics and history, a parliament is a
legislative
A legislature (, ) is a deliberative assembly with the legal authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country, nation or city on behalf of the people therein. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial powers ...
body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions:
representing the
electorate
Electorate may refer to:
* The people who are eligible to vote in an election, especially their number e.g. the term ''size of (the) electorate''
* The dominion of a prince-elector in the Holy Roman Empire until 1806
* An electoral district
...
, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. The term is similar to the idea of a
senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
,
synod
A synod () is a council of a Christian denomination, usually convened to decide an issue of doctrine, administration or application. The word '' synod'' comes from the Ancient Greek () ; the term is analogous with the Latin word . Originally, ...
or
congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
and is commonly used in countries that are current or former
monarchies
A monarchy is a form of government in which a person, the monarch, reigns as head of state for the rest of their life, or until abdication. The extent of the authority of the monarch may vary from restricted and largely symbolic (constitutio ...
. Some contexts restrict the use of the word ''parliament'' to
parliamentary system
A parliamentary system, or parliamentary democracy, is a form of government where the head of government (chief executive) derives their Election, democratic legitimacy from their ability to command the support ("confidence") of a majority of t ...
s, although it is also used to describe the legislature in some
presidential system
A presidential, strong-president, or single-executive system (sometimes also congressional system) is a form of government in which a head of government (usually titled " president") heads an executive branch that derives its authority and l ...
s (e.g., the
Parliament of Ghana
The Parliament of Ghana is the unicameral legislature of Ghana. It consists of 276 members, who are elected for four-year terms in single-seat Electoral district, constituencies using a first-past-the-post voting system.
History
Legislature, L ...
), even where it is not in the
official name.
Historically, parliaments included various kinds of deliberative, consultative, and judicial assemblies. What is considered to be the first modern parliament, was the
Cortes of León
Cortes, Cortés, Cortês, Corts, or Cortès may refer to:
People
* Cortes (surname), including a list of people with the name
** Hernán Cortés (1485–1547), a Spanish conquistador
Places
* Cortes, Navarre, a village in the South border of ...
, held in the
Kingdom of León
The Kingdom of León was an independent kingdom situated in the northwest region of the Iberian Peninsula. It was founded in 910 when the Christian princes of Kingdom of Asturias, Asturias along the Bay of Biscay, northern coast of the peninsula ...
in 1188. According to the
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
, the Decreta of Leon of 1188 is the oldest documentary manifestation of the European parliamentary system. In addition, UNESCO granted the 1188 Cortes of Alfonso IX the title of "Memory of the World" and the city of
Leon has been recognized as the "Cradle of Parliamentarism".
Etymology
The English term is derived from
Anglo-Norman and dates to the 14th century, coming from the 11th century
Old French
Old French (, , ; ) was the language spoken in most of the northern half of France approximately between the late 8th [2-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ...
word , from , . The meaning evolved over time, originally referring to any discussion, conversation, or negotiation through various kinds of deliberative or judicial groups, often summoned by a monarch. By the 15th century, in Britain, it had come to specifically mean the legislature.
Early parliaments
Since ancient times, when societies were tribal, there were councils or a headman whose decisions were assessed by village elders. This is called tribalism. Some scholars suggest that in ancient Mesopotamia there was a primitive democratic government where the kings were assessed by council. The same has been said about ancient India, where some form of deliberative assemblies existed, and therefore there was some form of
democracy
Democracy (from , ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which political power is vested in the people or the population of a state. Under a minimalist definition of democracy, rulers are elected through competitiv ...
. However, these claims are not accepted by other scholars, who see these forms of government as
oligarchies
Oligarchy (; ) is a form of government in which power rests with a small number of people. Members of this group, called oligarchs, generally hold usually hard, but sometimes soft power through nobility, fame, wealth, or education; or thr ...
.
Ancient Athens
Athens is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest named cities in the world, having been continuously inhabited for perhaps 5,000 years. Situated in southern Europe, Athens became the leading city of ancient Greece in t ...
was the cradle of
democracy
Democracy (from , ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which political power is vested in the people or the population of a state. Under a minimalist definition of democracy, rulers are elected through competitiv ...
. The
Athenian assembly
The ecclesia or ekklesia () was the assembly of the citizens in city-states of ancient Greece.
The ekklesia of Athens
The ekklesia of ancient Athens is particularly well-known. It was the popular assembly, open to all male citizens as soon a ...
(, ''ekklesia'') was the most important institution, and every free male
citizen
Citizenship is a membership and allegiance to a sovereign state.
Though citizenship is often conflated with nationality in today's English-speaking world, international law does not usually use the term ''citizenship'' to refer to nationality ...
could take part in the discussions. Slaves and women could not. However,
Athenian democracy
Athenian democracy developed around the 6th century BC in the Ancient Greece, Greek city-state (known as a polis) of Classical Athens, Athens, comprising the city of Athens and the surrounding territory of Attica, and focusing on supporting lib ...
was not representative, but rather direct, and therefore the ''ekklesia'' was different from the parliamentary system.
The
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
had
legislative assemblies, who had the final say regarding the election of magistrates, the enactment of new
statute
A statute is a law or formal written enactment of a legislature. Statutes typically declare, command or prohibit something. Statutes are distinguished from court law and unwritten law (also known as common law) in that they are the expressed wil ...
s, the carrying out of capital punishment, the declaration of war and peace, and the creation (or dissolution) of alliances. The
Roman Senate
The Roman Senate () was the highest and constituting assembly of ancient Rome and its aristocracy. With different powers throughout its existence it lasted from the first days of the city of Rome (traditionally founded in 753 BC) as the Sena ...
controlled money, administration, and the details of foreign policy.
Some Muslim scholars argue that the Islamic
shura
Shura () is the term for collective decision-making in Islam. It can, for example, take the form of a council or a referendum. The Quran encourages Muslims to decide their affairs in consultation with each other.
Shura is mentioned as a praise ...
(a method of taking decisions in Islamic societies) is analogous to the parliament. However, other scholars (notably from
Hizb ut-Tahrir
Hizb ut-Tahrir (HT; ) is an international pan-Islamist and Islamic fundamentalist political organization whose stated aim is the re-establishment of the Islamic caliphate to unite the Muslim community (called ''ummah'') and implement sharia glo ...
) highlight what they consider fundamental differences between the shura system and the parliamentary system.
England
Early forms of assembly
England has long had a tradition of a body of men who would assist and advise the king on important matters. Under the
Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced t ...
kings, there was an advisory council, the
Witenagemot
The witan () was the king's council in the Anglo-Saxon government of England from before the 7th century until the 11th century. It comprised important noblemen, including ealdormen, thegns, and bishops. Meetings of the witan were sometimes ...
. The name derives from the
Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
ƿitena ȝemōt, or witena gemōt, for "meeting of wise men". The first recorded act of a witenagemot was
the law code issued by King Æthelberht of Kent around 600, the earliest document which survives in sustained Old English prose; however, the Witan was certainly in existence long before then. The Witan, along with the folkmoots (local assemblies), is an important ancestor of the modern English parliament.
As part of the
Norman Conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Normans, Norman, French people, French, Flemish people, Flemish, and Bretons, Breton troops, all led by the Du ...
, the new king,
William I William I may refer to:
Kings
* William the Conqueror (–1087), also known as William I, King of England
* William I of Sicily (died 1166)
* William I of Scotland (died 1214), known as William the Lion
* William I of the Netherlands and Luxembour ...
, did away with the Witenagemot, replacing it with a
Curia Regis ("King's Council"). Membership of the Curia was largely restricted to the
tenants-in-chief
In medieval and early modern Europe, a tenant-in-chief (or vassal-in-chief) was a person who held his lands under various forms of feudal land tenure directly from the king or territorial prince to whom he did homage, as opposed to holding them ...
, the few nobles who "rented" great estates directly from the king, along with
ecclesiastics. William brought to England the
feudal system
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was a combination of legal, economic, military, cultural, and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe from the 9th to 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structuring socie ...
of his native
Normandy
Normandy (; or ) is a geographical and cultural region in northwestern Europe, roughly coextensive with the historical Duchy of Normandy.
Normandy comprises Normandy (administrative region), mainland Normandy (a part of France) and insular N ...
, and sought the advice of the Curia Regis before making laws. This is the original body from which the Parliament, the higher courts of law, and the
Privy Council and Cabinet descend. Of these, the legislature is formally the High Court of Parliament; judges sit in the
Supreme Court of Judicature. Only the executive government is no longer conducted in a royal court.
Most historians date the emergence of a parliament with some degree of power, to which the throne had to defer, no later than the reign of
Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots (Latin: Malleus Scotorum), was King of England from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he was Lord of Ireland, and from 125 ...
. Like previous kings, Edward called leading nobles and church leaders to discuss government matters, especially
finance
Finance refers to monetary resources and to the study and Academic discipline, discipline of money, currency, assets and Liability (financial accounting), liabilities. As a subject of study, is a field of Business administration, Business Admin ...
and
taxation
A tax is a mandatory financial charge or levy imposed on an individual or legal person, legal entity by a governmental organization to support government spending and public expenditures collectively or to Pigouvian tax, regulate and reduce nega ...
. A meeting in 1295 became known as the
Model Parliament
The Model Parliament was the 1295 Parliament of England of Edward I of England, King Edward I. Its composition became the model for later parliaments.
History
The term ''Model Parliament'' was coined by William Stubbs (1825-1901) and later use ...
because it set the pattern for later Parliaments. The significant difference between the Model Parliament and the earlier Curia Regis was the addition of the Commons: that is, the inclusion of elected representatives of rural landowners and of townsmen. In 1307, Edward agreed not to collect certain taxes without the "consent of the realm" through parliament. He also enlarged the court system.
''Magna Carta'' and the model parliament
The tenants-in-chief often struggled for power with the ecclesiastics and the king. In 1215, they secured ''
Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter"), sometimes spelled Magna Charta, is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by the Archbishop of Canterbury, Cardin ...
'' from
King John of England
John (24 December 1166 – 19 October 1216) was King of England from 1199 until his death in 1216. He lost the Duchy of Normandy and most of his other French lands to King Philip II of France, resulting in the collapse of the Angevin Empi ...
. This established that the king may not levy or collect any taxes (except the feudal taxes to which they were hitherto accustomed), save with the consent of a council. It was also established that the most important tenants-in-chief and ecclesiastics be summoned to the council by personal writs from the sovereign, and that all others be summoned to the council by general writs from the
sheriff
A sheriff is a government official, with varying duties, existing in some countries with historical ties to England where the office originated. There is an analogous, although independently developed, office in Iceland, the , which is common ...
s of their counties. Modern government has its origins in the Curia Regis; parliament descends from the Great Council, later known as the ''parliamentum'', established by ''Magna Carta''.
During the reign of
King Henry III (13th century),
English Parliaments included elected representatives from shires and towns. Thus these parliaments are considered forerunners of the modern parliament.
In 1265,
Simon de Montfort, then in rebellion against Henry III, summoned
a parliament of his supporters without royal authorisation. The
archbishop
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdi ...
s,
bishop
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of Episcopal polity, authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of di ...
s,
abbot
Abbot is an ecclesiastical title given to the head of an independent monastery for men in various Western Christian traditions. The name is derived from ''abba'', the Aramaic form of the Hebrew ''ab'', and means "father". The female equivale ...
s,
earl
Earl () is a rank of the nobility in the United Kingdom. In modern Britain, an earl is a member of the Peerages in the United Kingdom, peerage, ranking below a marquess and above a viscount. A feminine form of ''earl'' never developed; instead, ...
s, and
baron
Baron is a rank of nobility or title of honour, often Hereditary title, hereditary, in various European countries, either current or historical. The female equivalent is baroness. Typically, the title denotes an aristocrat who ranks higher than ...
s were summoned, as were two
knight
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of a knighthood by a head of state (including the pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church, or the country, especially in a military capacity.
The concept of a knighthood ...
s from each shire and two
burgesses from each
borough
A borough is an administrative division in various English language, English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
...
. Knights had been summoned to previous councils, but it was unprecedented for the boroughs to be represented. In 1295,
Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots (Latin: Malleus Scotorum), was King of England from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he was Lord of Ireland, and from 125 ...
adopted De Montfort's ideas for representation and election in the so-called "
Model Parliament
The Model Parliament was the 1295 Parliament of England of Edward I of England, King Edward I. Its composition became the model for later parliaments.
History
The term ''Model Parliament'' was coined by William Stubbs (1825-1901) and later use ...
". At first, each
estate debated independently; by the reign of
Edward III
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring royal authority after t ...
, however, Parliament had grown closer to its modern form, with the legislative body having two separate chambers.
Parliament under Henry VIII and Edward VI
The purpose and structure of Parliament in Tudor England underwent a significant transformation under the reign of
Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ...
. Originally its methods were primarily medieval, and the monarch still possessed a form of inarguable dominion over its decisions. According to Elton, it was
Thomas Cromwell
Thomas Cromwell (; – 28 July 1540) was an English statesman and lawyer who served as List of English chief ministers, chief minister to King Henry VIII from 1534 to 1540, when he was beheaded on orders of the king, who later blamed false cha ...
, 1st Earl of Essex, then chief minister to Henry VIII, who initiated still other changes within parliament.
The
Acts of Supremacy
The Acts of Supremacy are two acts passed by the Parliament of England in the 16th century that established the English monarchs as the head of the Church of England; two similar laws were passed by the Parliament of Ireland establishing the En ...
established the monarch as head of the Church of England.
Civil War and beyond
The power of Parliament, in its relationship with the monarch, increased considerably after the
Civil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
, and again at the
Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution, also known as the Revolution of 1688, was the deposition of James II and VII, James II and VII in November 1688. He was replaced by his daughter Mary II, Mary II and her Dutch husband, William III of Orange ...
. It also provided the country with unprecedented stability. More stability, in turn, helped assure more effective management, organisation, and efficiency. Parliament printed statutes and devised a more coherent
parliamentary procedure
Parliamentary procedures are the accepted Procedural law, rules, ethics, and Norm (sociology), customs governing meetings of an deliberative assembly, assembly or organization. Their object is to allow orderly deliberation upon questions of inte ...
.
The rise of Parliament proved especially important in the sense that it limited the repercussions of dynastic complications that had so often plunged England into civil war. Parliament still ran the country even in the absence of suitable heirs to the throne, and its legitimacy as a decision-making body reduced the royal prerogatives of kings like Henry VIII and the importance of their whims. For example, Henry VIII could not simply establish supremacy by proclamation; he required Parliament to enforce statutes and add felonies and treasons. An important liberty for Parliament was its freedom of speech; Henry allowed anything to be spoken openly within Parliament and speakers could not face arrest – a fact which they exploited incessantly. Nevertheless, Parliament in Henry VIII's time offered up very little objection to the monarch's desires. Under his and
Edward
Edward is an English male name. It is derived from the Anglo-Saxon name ''Ēadweard'', composed of the elements '' ēad'' "wealth, fortunate; prosperous" and '' weard'' "guardian, protector”.
History
The name Edward was very popular in Anglo-S ...
's reign, the legislative body complied willingly with the majority of the kings' decisions.
Much of this compliance stemmed from how the English viewed and traditionally understood authority. As Williams described it, "King and parliament were not separate entities, but a single body, of which the monarch was the senior partner and the Lords and the Commons the lesser, but still essential, members."

Although its role in government had expanded significantly in the mid 16th century, the Parliament of England saw some of its most important gains in the 17th century. A
series of conflicts between the Crown and Parliament culminated in the execution of
King Charles I in 1649. For a brief period, England became a
commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the 15th century. Originally a phrase (the common-wealth ...
, with
Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English statesman, politician and soldier, widely regarded as one of the most important figures in British history. He came to prominence during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, initially ...
the de facto ruler, with the title of
Lord Protector
Lord Protector (plural: ''Lords Protector'') is a title that has been used in British constitutional law for the head of state. It was also a particular title for the British heads of state in respect to the established church. It was sometime ...
. Frustrated with its decisions, Cromwell purged and suspended Parliament on several occasions.
A controversial figure notorious for
his actions in Ireland, Cromwell is nonetheless regarded as essential to the growth of democracy in England. The years of the Commonwealth, coupled with the
restoration of the monarchy in 1660 and the subsequent
Glorious Revolution of 1688
The Glorious Revolution, also known as the Revolution of 1688, was the deposition of James II and VII, James II and VII in November 1688. He was replaced by his daughter Mary II, Mary II and her Dutch husband, William III of Orange ...
, helped reinforce and strengthen Parliament as an institution separate from the Crown.
Acts of Union
The Parliament of England met until it merged with the
Parliament of Scotland
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
under the
Acts of Union. This union created the new
Parliament of Great Britain
The Parliament of Great Britain was formed in May 1707 following the ratification of the Acts of Union 1707, Acts of Union by both the Parliament of England and the Parliament of Scotland. The Acts ratified the treaty of Union which created a ...
in 1707. The Parliament of the United Kingdom followed at the union with Ireland.
France
Originally, there was only the
Parlement of Paris
The ''Parlement'' of Paris () was the oldest ''parlement'' in the Kingdom of France, formed in the 14th century. Parlements were judicial, rather than legislative, bodies and were composed of magistrates. Though not representative bodies in the p ...
, born out of the Curia Regis in 1307, and located inside the medieval royal palace, now the
Paris Hall of Justice. The jurisdiction of the ''Parliament'' of Paris covered the entire kingdom. In the thirteenth century, judicial functions were added. In 1443, following the turmoil of the
Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a conflict between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France and a civil war in France during the Late Middle Ages. It emerged from feudal disputes over the Duchy ...
, King
Charles VII of France
Charles VII (22 February 1403 – 22 July 1461), called the Victorious () or the Well-Served (), was King of France from 1422 to his death in 1461. His reign saw the end of the Hundred Years' War and a ''de facto'' end of the English claims to ...
granted
Languedoc
The Province of Languedoc (, , ; ) is a former province of France.
Most of its territory is now contained in the modern-day region of Occitanie in Southern France. Its capital city was Toulouse. It had an area of approximately .
History
...
its own ''parliament'' by establishing the ''Parliament'' of
Toulouse
Toulouse (, ; ; ) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Haute-Garonne department and of the Occitania (administrative region), Occitania region. The city is on the banks of the Garonne, River Garonne, from ...
, the first ''parliament'' outside of Paris, whose jurisdiction extended over the most part of southern France. From 1443 until the
French Revolution several other ''parliaments'' were created in some provinces of France (
Grenoble
Grenoble ( ; ; or ; or ) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of the Isère Departments of France, department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes Regions of France, region ...
,
Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( ; ; Gascon language, Gascon ; ) is a city on the river Garonne in the Gironde Departments of France, department, southwestern France. A port city, it is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the Prefectures in F ...
).
All the ''parliaments'' could issue regulatory decrees for the application of royal edicts or of customary practices; they could also refuse to register laws that they judged contrary to fundamental law or simply as being untimely. Parliamentary power in France was suppressed more so than in England as a result of
absolutism, and parliaments were eventually overshadowed by the larger
Estates General, up until the
French Revolution, when the last Estates General transformed itself into a
National Assembly
In politics, a national assembly is either a unicameral legislature, the lower house of a bicameral legislature, or both houses of a bicameral legislature together. In the English language it generally means "an assembly composed of the repr ...
, a legislative body whose existence is independent of the royal power.
Germanic and Nordic countries
A ''
thing'' or ''ting'' (
Old Norse
Old Norse, also referred to as Old Nordic or Old Scandinavian, was a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants ...
and ; other modern
Scandinavian: ''ting'', ''ding'' in
Dutch) was the governing assembly in
Germanic societies, made up of the free men of the community and presided by
lawspeaker
A lawspeaker or lawman ( Swedish: ''lagman'', Old Swedish: ''laghmaþer'' or ''laghman'', Danish: ''lovsigemand'', Norwegian: ''lagmann'', Icelandic: , Faroese: '' løgmaður'', Finnish: ''laamanni'', ) is a unique Scandinavian legal offic ...
s.
The thing was the assembly of the free men of a country, province or a
hundred
100 or one hundred (Roman numerals, Roman numeral: C) is the natural number following 99 (number), 99 and preceding 101 (number), 101.
In mathematics
100 is the square of 10 (number), 10 (in scientific notation it is written as 102). The standar ...
''(hundare/härad/herred)''. There were consequently, hierarchies of things, so that the local things were represented at the thing for a larger area, for a province or land. At the thing, disputes were solved and political decisions were made. The place for the thing was often also the place for public religious rites and for commerce.
The thing met at regular intervals, legislated, elected
chieftains and
kings, and judged according to the law, which was memorised and recited by the "
law speaker" (the judge).
The Icelandic, Faroese and Manx parliaments trace their origins back to the
Viking expansion
Viking expansion was the historical movement which led Norsemen, Norse explorers, traders and warriors, the latter known in modern scholarship as Vikings, to sail most of the North Atlantic, reaching south as far as North Africa and east as fa ...
originating from the
petty kingdoms of Norway
The petty kingdoms of Norway () were the entities from which the later Kingdom of Norway was founded. Before the unification of Norway in 872 and during the period of fragmentation after King Harald Fairhair's death, Norway was divided in se ...
as well as Denmark, replicating Viking government systems in the conquered territories, such as those represented by the
Gulating
Gulating () was one of the four ancient popular assemblies or things (') of medieval Norway. Historically, it was the site of court and assembly for most of Western Norway, and assembled at Gulen. It functioned as a judicial and legislative bo ...
near Bergen in western Norway:
* The Icelandic
Althing
The (; ), anglicised as Althingi or Althing, is the Parliamentary sovereignty, supreme Parliament, national parliament of Iceland. It is the oldest surviving parliament in the world. The Althing was founded in 930 at ('Thing (assembly), thing ...
, dating from 930.
* The Faroese
Løgting
The Løgting (pronounced ; ) is the unicameral parliament of the Faroe Islands, an autonomous territory within the Danish Realm.
The name literally means "''Law Thing''"—that is, a law assembly—and derives from Old Norse ''lǫgþing ...
, dating from a similar period.
* The Manx
Tynwald
Tynwald (), or more formally, the High Court of Tynwald () or Tynwald Court, is the legislature of the Isle of Man. It consists of two chambers, known as the branches of Tynwald: the directly elected House of Keys and the indirectly chosen Leg ...
, which claims to be over 1,000 years old.

Later national diets with chambers for different estates developed, e.g. in Sweden and in Finland (which was part of Sweden until 1809), each with a
House of Knights for the nobility. In both these countries, the national parliaments are now called
riksdag
The Riksdag ( , ; also or , ) is the parliament and the parliamentary sovereignty, supreme decision-making body of the Kingdom of Sweden. Since 1971, the Riksdag has been a unicameral parliament with 349 members (), elected proportional rep ...
(in Finland also ''eduskunta''), a word used since the Middle Ages and equivalent of the German word
Reichstag.
Today the term lives on in the official names of national legislatures and other institutions in the North Germanic countries. In
Yorkshire
Yorkshire ( ) is an area of Northern England which was History of Yorkshire, historically a county. Despite no longer being used for administration, Yorkshire retains a strong regional identity. The county was named after its county town, the ...
and former
Danelaw
The Danelaw (, ; ; ) was the part of History of Anglo-Saxon England, England between the late ninth century and the Norman Conquest under Anglo-Saxon rule in which Danes (tribe), Danish laws applied. The Danelaw originated in the conquest and oc ...
areas of England, which were subject to Norse invasion and settlement, the
wapentake
A hundred is an administrative division that is geographically part of a larger region. It was formerly used in England, Wales, some parts of the United States, Denmark, Sweden, Finland, Norway, and in Cumberland County in the British Colony of ...
was another name for the same institution.
Italy
The
Sicilian Parliament, dating to 1097, evolved as the legislature of the
Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily (; ; ) was a state that existed in Sicily and the southern Italian peninsula, Italian Peninsula as well as, for a time, in Kingdom of Africa, Northern Africa, from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 until 1816. It was ...
.
Hungary
The Diet of Hungary, or originally Parlamentum Publicum and Parlamentum Generale (), became the supreme legislative institution in the
medieval kingdom of Hungary from the 1290s, and in its successor states,
Royal Hungary and the
Habsburg kingdom of Hungary throughout the
Early Modern period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
. The name of the legislative body was originally "Parlamentum" during the Middle Ages, the "Diet" expression gained mostly in the Early Modern period. It convened at regular intervals with interruptions during the period of 1527 to 1918, and again until 1946.
Some researchers have traced the roots of the Hungarian institution of national assemblies as far back as the 11th century. This based on documentary evidence that, on certain "important occasions" under the reigns of
King Ladislaus I and
King Coloman "the Learned", assemblies were held on a national scale where both ecclesiastic and secular dignitaries made appearances.
The first exact written mention of the word "parlamentum" (Parliament) for the nation-wide assembly originated during the reign of
King Andrew II in the
Golden Bull of 1222
The Golden Bull of 1222 was a golden bull, or edict, issued by Andrew II of Hungary. King Andrew II was forced by his nobles to accept the Golden Bull (Aranybulla), which was one of the first examples of constitutional limits being placed on th ...
, which reaffirmed the rights of the smaller nobles of the old and new classes of royal servants (servientes regis) against both the crown and the magnates, and to defend the rights of the whole nation against the crown by restricting the powers of the latter in certain fields and legalizing refusal to obey its unlawful/unconstitutional commands (the "''ius resistendi''").
The lesser nobles also began to present Andrew with grievances, a practice that evolved into the institution of the Hungarian Diet.
An institutionalized Hungarian parliament emerged during the 14th and 15th centuries. Beginning under
King Charles I, continuing under subsequent kings through into the reign of
King Matthias I, the Diet was essentially convened by the king. However, under the rule of heavy handed kings like Louis the Great and during reign of the early absolutist Matthias Corvinus the parliaments were often convened to announce the royal decisions, and had no significant power of its own. Since the reign of the Jagiellonian dynasty, the parliament has regained most of its former power.
Poland

According to the ''
Chronicle
A chronicle (, from Greek ''chroniká'', from , ''chrónos'' – "time") is a historical account of events arranged in chronological order, as in a timeline. Typically, equal weight is given for historically important events and local events ...
s'' of
Gallus Anonymus, the first legendary Polish ruler,
Siemowit, who began the
Piast dynasty
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented List of Polish monarchs, Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I of Poland, Mieszko I (–992). The Poland during the Piast dynasty, Piasts' royal rule in Pol ...
, was chosen by an ancient ''
wiec'' council. The idea of the ''wiec'' led to the development of the Polish parliament, the ''
Sejm
The Sejm (), officially known as the Sejm of the Republic of Poland (), is the lower house of the bicameralism, bicameral parliament of Poland.
The Sejm has been the highest governing body of the Third Polish Republic since the Polish People' ...
'', in around 1180.

The term "sejm" comes from an old Polish expression denoting a meeting of the populace. The power of early sejms grew between 1146 and 1295, when the power of individual rulers waned and various councils grew stronger. Since the 14th century irregular sejms (described in various
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
sources as ''contentio generalis, conventio magna, conventio solemna, parlamentum, parlamentum generale, dieta'') have been convened by Poland's monarchs. From 1374, the king had to receive permission from that assembly to raise
tax
A tax is a mandatory financial charge or levy imposed on an individual or legal entity by a governmental organization to support government spending and public expenditures collectively or to regulate and reduce negative externalities. Tax co ...
es and the 1454
Nieszawa Statutes granted the
szlachta
The ''szlachta'' (; ; ) were the nobility, noble estate of the realm in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Depending on the definition, they were either a warrior "caste" or a social ...
(nobles) unprecedented concessions and authority. The General Sejm (Polish ''sejm generalny'' or ''sejm walny''), first convoked by the
John I Albert
John I Albert (; 27 December 1459 – 17 June 1501) was King of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of Roy ...
in 1493 near
Piotrków, evolved from earlier regional and provincial meetings called ''
sejmik
A sejmik (, diminutive of ''sejm'', occasionally translated as a ''dietine''; ) was one of various local parliaments in the history of Poland and history of Lithuania. The first sejmiks were regional assemblies in the Kingdom of Poland (before ...
s''. Simultaneously, the
Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
was founded on the earlier ''
curia regis'', convened at the king's discretion. Hence, the year 1493 marked the beginning of a
bicameral legislative body of government. With the subsequent development of Polish
Golden Liberty
Golden Liberty (; , ), sometimes referred to as Golden Freedoms, Nobles' Democracy or Nobles' Commonwealth ( or ''Złota wolność szlachecka'') was a political system in the Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569), Kingdom of Poland and, after the Unio ...
in the next several decades, the Sejm's powers systematically increased. Poland was among the few countries in Europe where the parliament played an especially important role in its national identity as it contributed to the unity of the nation and the state.
The general parliament of the
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
consisted of three estates – the King of Poland, the Senate (consisting of Ministers, Palatines, Castellans and Roman Catholic Bishops) and the Chamber of Envoys comprising 170 nobles acting on behalf of their holdings as well as representatives of major cities, who did not possess any voting privileges. In 1573, a convocation sejm established an
elective monarchy
An elective monarchy is a monarchy ruled by a monarch who is elected, in contrast to a hereditary monarchy in which the office is automatically passed down as a family inheritance. The manner of election, the nature of candidate qualifications, ...
in the Commonwealth.
Portugal
After its self-proclamation as an independent kingdom in 1139 by
Afonso I of Portugal
Dom Afonso IOr also ''Affonso'' (Archaic Portuguese-Galician) or ''Alphonso'' (Portuguese-Galician languages, Portuguese-Galician) or ''Alphonsus'' (Latin version), sometimes rendered in English as ''Alphonzo'' or ''Alphonse'', depending on th ...
(followed by the recognition by the
Kingdom of León
The Kingdom of León was an independent kingdom situated in the northwest region of the Iberian Peninsula. It was founded in 910 when the Christian princes of Kingdom of Asturias, Asturias along the Bay of Biscay, northern coast of the peninsula ...
in the
Treaty of Zamora of 1143), the first historically established Cortes of the
Kingdom of Portugal
The Kingdom of Portugal was a Portuguese monarchy, monarchy in the western Iberian Peninsula and the predecessor of the modern Portuguese Republic. Existing to various extents between 1139 and 1910, it was also known as the Kingdom of Portugal a ...
occurred in 1211 in
Coimbra
Coimbra (, also , , or ), officially the City of Coimbra (), is a city and a concelho, municipality in Portugal. The population of the municipality at the 2021 census was 140,796, in an area of .
The fourth-largest agglomerated urban area in Po ...
by initiative of
Afonso II of Portugal
Afonso II (; 23 April 118525 March 1223), also called Afonso the Fat () and Afonso the Leper (), was List of Portuguese monarchs, King of Portugal from 1211 until 1223. Afonso was the third monarch of Portugal.
Afonso was the second but eldest ...
. These established the first general laws of the kingdom (''Leis Gerais do Reino''): protection of the king's property, stipulation of measures for the administration of justice and the rights of his subjects to be protected from abuses by royal officials, and confirming the clerical donations of the previous king
Sancho I of Portugal
Sancho I (born ; Coimbra, 11 November 115426 March 1211) also referred to as Sancho the Populator (), was King of Portugal from 1185 until his death in 1211. He was the second king of Portugal.
Sancho was the second but only surviving legitimat ...
. These Cortes also affirmed the validity of canon law for the Church in Portugal, while introducing the prohibition of the purchase of lands by churches or monasteries (although they can be acquired by donations and legacies).
After the conquest of
Algarve
The Algarve (, , ) is the southernmost NUTS statistical regions of Portugal, NUTS II region of continental Portugal. It has an area of with 467,495 permanent inhabitants and incorporates 16 municipalities (concelho, ''concelhos'' or ''município ...
in 1249, the
Kingdom of Portugal
The Kingdom of Portugal was a Portuguese monarchy, monarchy in the western Iberian Peninsula and the predecessor of the modern Portuguese Republic. Existing to various extents between 1139 and 1910, it was also known as the Kingdom of Portugal a ...
completed its
Reconquista
The ''Reconquista'' (Spanish language, Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese for ) or the fall of al-Andalus was a series of military and cultural campaigns that European Christian Reconquista#Northern Christian realms, kingdoms waged ag ...
. In 1254 King
Afonso III of Portugal
Afonso IIIrare English alternatives: ''Alphonzo'' or ''Alphonse'', or ''Affonso'' (Archaic Portuguese), ''Alfonso'' or ''Alphonso'' (Portuguese-Galician languages, Portuguese-Galician) or ''Alphonsus'' (Latin). (; 5 May 121016 February 1279), ca ...
summoned
Portuguese Cortes
In the medieval Kingdom of Portugal, the Cortes was an assembly of representatives of the estates of the realm – the nobility, clergy and bourgeoisie. It was called and dismissed by the King of Portugal at will, at a place of his choosing.O' ...
in
Leiria
Leiria () is a city and municipality in the Central Region, Portugal, Central Region of Portugal. It is the 2nd largest city in that same region, after Coimbra, with a municipality population of 128,640 (as of 2021) in an area of . It is the seat o ...
, with the inclusion of
burghers from old and newly incorporated municipalities. This inclusion establishes the Cortes of Leiria of 1254 as the second sample of modern
parliamentarism
A parliamentary system, or parliamentary democracy, is a form of government where the head of government (chief executive) derives their democratic legitimacy from their ability to command the support ("confidence") of a majority of the legisl ...
in the history of Europe (after the
Cortes of León
Cortes, Cortés, Cortês, Corts, or Cortès may refer to:
People
* Cortes (surname), including a list of people with the name
** Hernán Cortés (1485–1547), a Spanish conquistador
Places
* Cortes, Navarre, a village in the South border of ...
in 1188). In these Cortes the
monetagio was introduced: a fixed sum was to be paid by the burghers to the Crown as a substitute for the
septennium (the traditional revision of the face value of coinage by the Crown every seven years). These Cortes also introduced
staple laws on the
Douro River
The Douro (, , , ; ; ) is the largest river of the Iberian Peninsula by discharge. It rises near Duruelo de la Sierra in the Spanish province of Soria, meanders briefly south, then flows generally west through the northern part of the Meseta ...
, favoring the new royal city of
Vila Nova de Gaia
Vila Nova de Gaia (; ), or simply Gaia, is a city and a municipality in Porto District in Norte Region, Portugal, Norte Region, Portugal. It is located south of the city of Porto on the other side of the Douro River. The city proper had a populati ...
at the expense of the old episcopal city of Porto.
The
Portuguese Cortes
In the medieval Kingdom of Portugal, the Cortes was an assembly of representatives of the estates of the realm – the nobility, clergy and bourgeoisie. It was called and dismissed by the King of Portugal at will, at a place of his choosing.O' ...
met again under King
Afonso III of Portugal
Afonso IIIrare English alternatives: ''Alphonzo'' or ''Alphonse'', or ''Affonso'' (Archaic Portuguese), ''Alfonso'' or ''Alphonso'' (Portuguese-Galician languages, Portuguese-Galician) or ''Alphonsus'' (Latin). (; 5 May 121016 February 1279), ca ...
in 1256, 1261 and 1273, always by royal summon. Medieval Kings of Portugal continued to rely on small assemblies of notables, and only summoned the full Cortes on extraordinary occasions. A Cortes would be called if the king wanted to introduce new taxes, change some fundamental laws, announce significant shifts in foreign policy (e.g. ratify treaties), or settle matters of royal succession, issues where the cooperation and assent of the towns was thought necessary. Changing taxation (especially requesting war subsidies), was probably the most frequent reason for convening the Cortes. As the nobles and clergy were largely tax-exempt, setting taxation involved intensive negotiations between the royal council and the
burgher delegates at the Cortes.
Delegates (''procuradores'') not only considered the king's proposals, but, in turn, also used the Cortes to submit petitions of their own to the royal council on a myriad of matters, e.g. extending and confirming town privileges, punishing abuses of officials, introducing new price controls, constraints on
Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
, pledges on coinage, etc. The royal response to these petitions became enshrined as ordinances and statutes, thus giving the Cortes the aspect of a legislature. These petitions were originally referred to as ''aggravamentos'' (grievances) then ''artigos'' (articles) and eventually ''capitulos'' (chapters). In a Cortes-Gerais, petitions were discussed and voted upon separately by each estate and required the approval of at least two of the three estates before being passed up to the royal council. The proposal was then subject to royal veto (either accepted or rejected by the king in its entirety) before becoming law.
Nonetheless, the exact extent of Cortes power was ambiguous. Kings insisted on their ancient prerogative to promulgate laws independently of the Cortes. The compromise, in theory, was that ordinances enacted in Cortes could only be modified or repealed by Cortes. But even that principle was often circumvented or ignored in practice.
The Cortes probably had their heyday in the 14th and 15th centuries, reaching their apex when
John I of Portugal
John I ( WP:IPA for Portuguese, �uˈɐ̃w̃ 11 April 1357 – 14 August 1433), also called John of Aviz, was King of Portugal from 1385 until his death in 1433. He is recognized chiefly for his role in Portugal's victory in 1383–85 crisi ...
relied almost wholly upon the bourgeoisie for his power. For a period after the 1383–1385 Crisis, the Cortes were convened almost annually. But as time went on, they became less important. Portuguese monarchs, tapping into the riches of the
Portuguese empire
The Portuguese Empire was a colonial empire that existed between 1415 and 1999. In conjunction with the Spanish Empire, it ushered in the European Age of Discovery. It achieved a global scale, controlling vast portions of the Americas, Africa ...
overseas, grew less dependent on Cortes subsidies and convened them less frequently.
John II (r.1481-1495) used them to break the high nobility, but dispensed with them otherwise.
Manuel I (r.1495-1521) convened them only four times in his long reign. By the time of
Sebastian (r.1554–1578), the Cortes was practically an irrelevance.
Curiously, the Cortes gained a new importance with the Iberian Union of 1581, finding a role as the representative of Portuguese interests to the new
Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout Europe d ...
monarch. The Cortes played a critical role in the
1640 Restoration, and enjoyed a brief period of resurgence during the reign of
John IV of Portugal
''Dom (honorific), Dom'' John IV (; 19 March 1604 – 6 November 1656), also known by the Portuguese as John the Restorer (), was the List of Portuguese monarchs, King of Portugal from 1640 until his death in 1656. He Portuguese Restoration War, ...
(r.1640-1656). But by the end of the 17th century, it found itself sidelined once again. The last Cortes met in 1698, for the mere formality of confirming the appointment of Infante John (future
John V of Portugal
''Dom (title), Dom'' John V (; 22 October 1689 – 31 July 1750), known as the Magnanimous (''o Magnânimo'') and the Portuguese Sun King (''o Rei-Sol Português''), was King of Portugal from 9 December 1706 until his death in 1750. His reig ...
) as the successor of
Peter II of Portugal
'' Dom'' Pedro II (Peter II; 26 April 1648 – 9 December 1706), nicknamed the Pacific (''Português:'' O Pacífico) was King of Portugal from 1683 until his death, previously serving as regent for his brother Afonso VI from 1668 until his own ...
. Thereafter, Portuguese kings ruled as absolute monarchs and no Cortes were assembled for over a century. This state of affairs came to an end with the
Liberal Revolution of 1820
The Liberal Revolution of 1820 () was a Portuguese political revolution that erupted in 1820. It began with a military insurrection in the city of Porto, in northern Portugal, that quickly and peacefully spread to the rest of the country. The Rev ...
, which set in motion the introduction of a new constitution, and a permanent and proper parliament, that however inherited the name of Cortes Gerais.
Russia
The
zemsky sobor
The ''Zemsky Sobor'' ( rus, зе́мский собо́р, p=ˈzʲemskʲɪj sɐˈbor, t=assembly of the land) was a parliament of the Tsardom of Russia's estates of the realm active during the 16th and 17th centuries.
The assembly represented ...
(Russian: зе́мский собо́р) was the first Russian parliament of the feudal Estates type, in the 16th and 17th centuries. The term roughly means assembly of the land.
It could be summoned either by
tsar
Tsar (; also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar''; ; ; sr-Cyrl-Latn, цар, car) is a title historically used by Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word '' caesar'', which was intended to mean ''emperor'' in the Euro ...
, or
patriarch
The highest-ranking bishops in Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy, the Roman Catholic Church (above major archbishop and primate), the Hussite Church, Church of the East, and some Independent Catholic Churches are termed patriarchs (and ...
, or the
Boyar Duma. Three categories of population, comparable to the Estates-General of France but with the numbering of the first two Estates reversed, participated in the assembly:
* Nobility and high bureaucracy, including the Boyar Duma
* The Holy Sobor of high
Orthodox clergy
* Representatives of merchants and townspeople (third estate)
The name of the parliament of nowadays Russian Federation is the
Federal Assembly of Russia
The Federal Assembly is the bicameral national legislature of Russia. The upper house is the Federation Council (Russia), Federation Council, and the lower house is the State Duma. The assembly was established by the Constitution of the Russian F ...
. The term for its lower house,
State Duma
The State Duma is the lower house of the Federal Assembly (Russia), Federal Assembly of Russia, with the upper house being the Federation Council (Russia), Federation Council. It was established by the Constitution of Russia, Constitution of t ...
(which is better known than the Federal Assembly itself, and is often mistaken for the entirety of the parliament) comes from the Russian word ''думать'' (''dumat''), "to think". The
Boyar Duma was an advisory council to the
grand prince
Grand prince or great prince (feminine: grand princess or great princess) (; ; ; ; ) is a hereditary title, used either by certain monarchs or by members of certain monarchs' families.
Grand duke is the usual and established, though not litera ...
s and
tsars of
Muscovy Muscovy or Moscovia () is an alternative name for the Principality of Moscow (1263–1547) and the Tsardom of Russia (1547–1721).
It may also refer to:
*Muscovy Company, an English trading company chartered in 1555
*Muscovy duck (''Cairina mosch ...
. The Duma was discontinued by
Peter the Great
Peter I (, ;
– ), better known as Peter the Great, was the Sovereign, Tsar and Grand Prince of all Russia, Tsar of all Russia from 1682 and the first Emperor of Russia, Emperor of all Russia from 1721 until his death in 1725. He reigned j ...
, who transferred its functions to the
Governing Senate
From 1711 to 1917, the Governing Senate was the highest legislative, judicial, and executive body subordinate to the Russian emperors. The senate was instituted by Peter the Great to replace the Boyar Duma and lasted until the very end of the R ...
in 1711.
Novgorod and Pskov
The ''
veche
A ''veche'' was a popular assembly during the Middle Ages. The ''veche'' is mentioned during the times of Kievan Rus' and it later became a powerful institution in Russian cities such as Veliky Novgorod, Novgorod and Pskov, where the ''veche'' a ...
'' was the highest legislature and judicial authority in the republic of
Novgorod
Veliky Novgorod ( ; , ; ), also known simply as Novgorod (), is the largest city and administrative centre of Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is one of the oldest cities in Russia, being first mentioned in the 9th century. The city lies along the V ...
until 1478. In its sister state,
Pskov
Pskov ( rus, Псков, a=Ru-Псков.oga, p=psˈkof; see also Names of Pskov in different languages, names in other languages) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in northwestern Russia and the administrative center of Pskov O ...
, a separate veche operated until 1510.
Since the Novgorod revolution of 1137 ousted the ruling
grand prince
Grand prince or great prince (feminine: grand princess or great princess) (; ; ; ; ) is a hereditary title, used either by certain monarchs or by members of certain monarchs' families.
Grand duke is the usual and established, though not litera ...
, the veche became the supreme state authority. After the reforms of 1410, the veche was restructured on a model similar to that of
Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
, becoming the
Commons
The commons is the cultural and natural resources accessible to all members of a society, including natural materials such as air, water, and a habitable Earth. These resources are held in common even when owned privately or publicly. Commons ...
chamber of the parliament. An upper
Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
-like Council of Lords was also created, with title membership for all former city magistrates. Some sources indicate that veche membership may have become full-time, and parliament deputies were now called ''vechniks''. It is recounted that the Novgorod assembly could be summoned by anyone who rung the veche
bell
A bell /ˈbɛl/ () is a directly struck idiophone percussion instrument. Most bells have the shape of a hollow cup that when struck vibrates in a single strong strike tone, with its sides forming an efficient resonator. The strike may be m ...
, although it is more likely that the common procedure was more complex. This bell was a symbol of republican sovereignty and independence. The whole population of the city—boyars, merchants, and common citizens—then gathered at
Yaroslav's Court. Separate assemblies could be held in the districts of Novgorod. In Pskov the veche assembled in the court of the
Trinity cathedral.
Roman Catholic Church
"
Conciliarism
Conciliarism was a movement in the 14th-, 15th- and 16th-century Catholic Church which held that supreme authority in the Church resided with an ecumenical council, apart from, or even against, the pope.
The movement emerged in response to the We ...
" or the "conciliar movement", was a reform movement in the 14th and 15th century
Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
which held that final authority in spiritual matters resided with the Roman Church as corporation of Christians, embodied by a
general church council, not with the
pope
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the Head of the Church#Catholic Church, visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the po ...
. In effect, the movement sought – ultimately, in vain – to create an All-Catholic Parliament. Its struggle with the Papacy had many points in common with the struggle of parliaments in specific countries against the authority of Kings and other secular rulers.
Scotland
From the 10th century the
Kingdom of Alba
The Kingdom of Alba (; ) was the Kingdom of Scotland between the deaths of Donald II in 900 and of Alexander III in 1286. The latter's death led indirectly to an invasion of Scotland by Edward I of England in 1296 and the First War of Scotti ...
was ruled by chiefs (''
toisechs'') and subkings (''
mormaers'') under the
suzerainty
A suzerain (, from Old French "above" + "supreme, chief") is a person, state (polity)">state or polity who has supremacy and dominant influence over the foreign policy">polity.html" ;"title="state (polity)">state or polity">state (polity)">st ...
, real or nominal, of a
High King. Popular assemblies, as in Ireland, were involved in law-making, and sometimes in king-making, although the introduction of
tanistry
Tanistry is a Gaelic system for passing on titles and lands. In this system the Tanist (; ; ) is the office of heir-apparent, or second-in-command, among the (royal) Gaelic patrilineal dynasties of Ireland, Scotland and Mann, to succeed to ...
—naming a successor in the lifetime of a king—made the second less than common. These early assemblies cannot be considered "parliaments" in the later sense of the word, and were entirely separate from the later, Norman-influenced, institution.
The
Parliament of Scotland
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
evolved during the
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
from the King's Council of Bishops and Earls. The unicameral parliament is first found on record, referred to as a ''
colloquium'', in 1235 at
Kirkliston
Kirkliston is a village and parish to the west of Edinburgh, Scotland, historically within the county of West Lothian but now within the City of Edinburgh council area limits. It lies on high ground immediately north of a northward loop of the ...
(a village now in
Edinburgh
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. The city is located in southeast Scotland and is bounded to the north by the Firth of Forth and to the south by the Pentland Hills. Edinburgh ...
).
By the early fourteenth century the attendance of knights and
freeholders had become important, and from 1326
burgh
A burgh ( ) is an Autonomy, autonomous municipal corporation in Scotland, usually a city, town, or toun in Scots language, Scots. This type of administrative division existed from the 12th century, when David I of Scotland, King David I created ...
commissioners attended. Consisting of the Three Estates; of
clerics
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the ter ...
, lay
tenants-in-chief
In medieval and early modern Europe, a tenant-in-chief (or vassal-in-chief) was a person who held his lands under various forms of feudal land tenure directly from the king or territorial prince to whom he did homage, as opposed to holding them ...
and burgh commissioners sitting in a single chamber, the Scottish parliament acquired significant powers over particular issues. Most obviously it was needed for consent for
taxation
A tax is a mandatory financial charge or levy imposed on an individual or legal person, legal entity by a governmental organization to support government spending and public expenditures collectively or to Pigouvian tax, regulate and reduce nega ...
(although taxation was only raised irregularly in Scotland in the
medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
period), but it also had a strong influence over
justice
In its broadest sense, justice is the idea that individuals should be treated fairly. According to the ''Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy'', the most plausible candidate for a core definition comes from the ''Institutes (Justinian), Inst ...
,
foreign policy
Foreign policy, also known as external policy, is the set of strategies and actions a State (polity), state employs in its interactions with other states, unions, and international entities. It encompasses a wide range of objectives, includ ...
, war, and all manner of other legislation, whether political, ecclesiastical, social or economic. Parliamentary business was also carried out by "sister" institutions, before c. 1500 by
General Council and thereafter by the
Convention of Estates
The Convention of Estates of Scotland was a sister institution to the Scottish Parliament
The Scottish Parliament ( ; ) is the Devolution in the United Kingdom, devolved, unicameral legislature of Scotland. It is located in the Holyrood, Edi ...
. These could carry out much business also dealt with by Parliament – taxation, legislation and policy-making – but lacked the ultimate authority of a full parliament.
The parliament, which is also referred to as the Estates of Scotland, the Three Estates, the Scots Parliament or the auld Scots Parliament (
Eng: ''old''), met until the
Acts of Union merged the Parliament of Scotland and the
Parliament of England
The Parliament of England was the legislature of the Kingdom of England from the 13th century until 1707 when it was replaced by the Parliament of Great Britain. Parliament evolved from the Great Council of England, great council of Lords Spi ...
, creating the new
Parliament of Great Britain
The Parliament of Great Britain was formed in May 1707 following the ratification of the Acts of Union 1707, Acts of Union by both the Parliament of England and the Parliament of Scotland. The Acts ratified the treaty of Union which created a ...
in 1707.
Following the
1997 Scottish devolution referendum, and the passing of the
Scotland Act 1998
The Scotland Act 1998 (c. 46) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which legislated for the establishment of the devolved Scottish Parliament with tax varying powers and the Scottish Government (then Scottish Executive). It was o ...
by the
Parliament of the United Kingdom
The Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, and may also legislate for the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace ...
, the
Scottish Parliament
The Scottish Parliament ( ; ) is the Devolution in the United Kingdom, devolved, unicameral legislature of Scotland. It is located in the Holyrood, Edinburgh, Holyrood area of Edinburgh, and is frequently referred to by the metonym 'Holyrood'. ...
was reconvened on 1 July 1999, although with much more limited powers than its 18th-century predecessor. The parliament has sat since 2004 at its newly constructed
Scottish Parliament Building
The Scottish Parliament Building (; ) is the home of the Scottish Parliament at Holyrood, Edinburgh, Holyrood, within the World Heritage Site, UNESCO World Heritage Site in central Edinburgh. Construction of the building commenced in June 1999 ...
in Edinburgh, situated at the foot of the
Royal Mile
The Royal Mile () is the nickname of a series of streets forming the main thoroughfare of the Old Town, Edinburgh, Old Town of Edinburgh, Scotland. The term originated in the early 20th century and has since entered popular usage.
The Royal ...
, next to the royal palace of
Holyroodhouse.
Spain
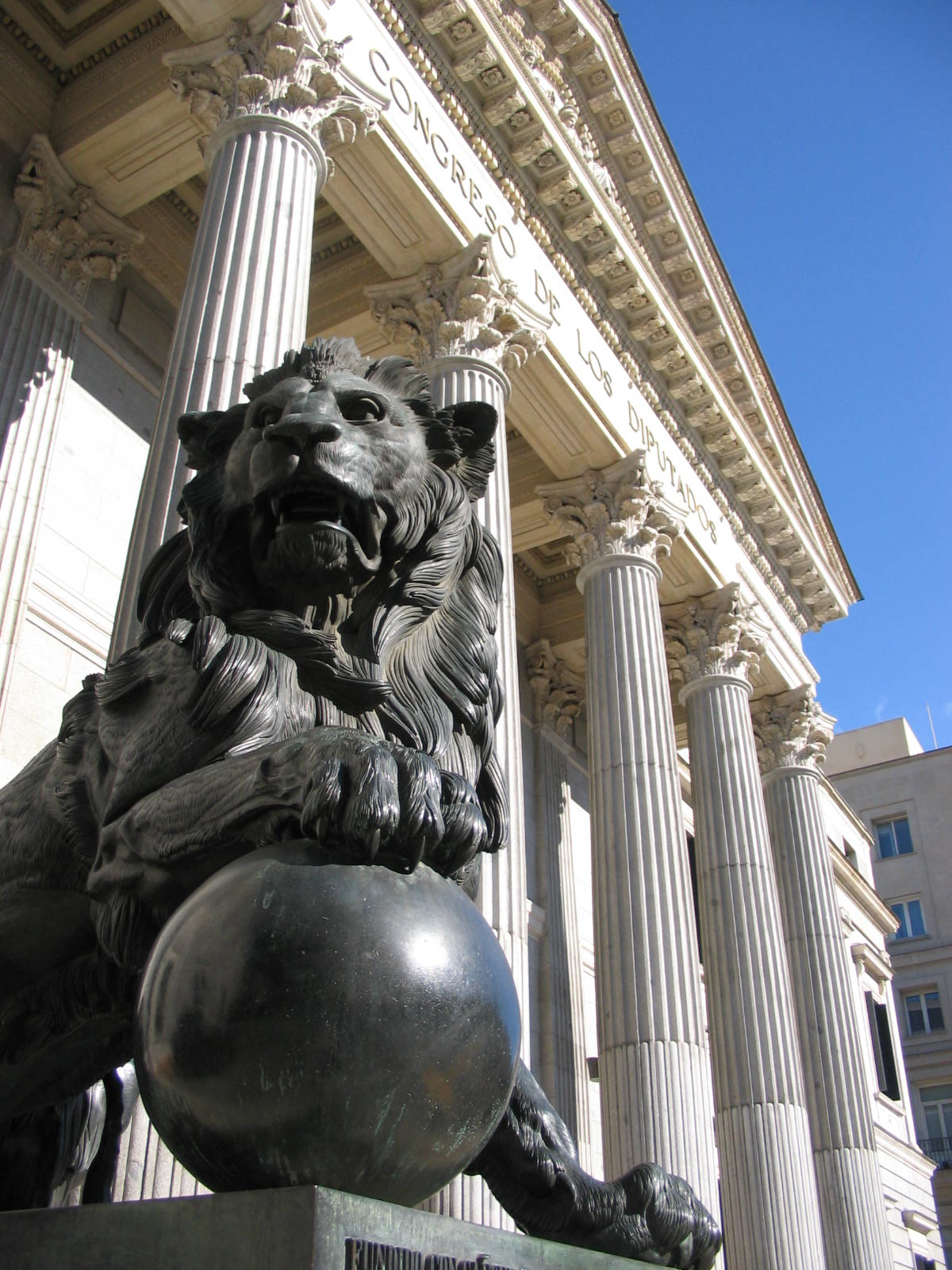

Although there are documented councils held in 873, 1020, 1050 and 1063, there was no representation of commoners. What is considered to be the first parliament, the
Cortes of León
Cortes, Cortés, Cortês, Corts, or Cortès may refer to:
People
* Cortes (surname), including a list of people with the name
** Hernán Cortés (1485–1547), a Spanish conquistador
Places
* Cortes, Navarre, a village in the South border of ...
, was held in the
Kingdom of León
The Kingdom of León was an independent kingdom situated in the northwest region of the Iberian Peninsula. It was founded in 910 when the Christian princes of Kingdom of Asturias, Asturias along the Bay of Biscay, northern coast of the peninsula ...
in 1188. According to the UNESCO, the Decreta of Leon of 1188 is the oldest documentary manifestation of the European parliamentary system. In addition, UNESCO granted the 1188 Cortes of Alfonso IX the title of "Memory of the World" and the city of
Leon has been recognized as the "Cradle of Parliamentarism".
After coming to power, King
Alfonso IX, facing an attack by his two neighbors,
Castile and
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
, decided to summon his
royal council (). This was a medieval organization composed of aristocrats and bishops but because of the seriousness of the situation and the need to maximize political support, Alfonso IX took the decision to also call the representatives of the urban middle class from the most important cities of the kingdom to the assembly. León's Cortes dealt with matters like the right to
private property
Private property is a legal designation for the ownership of property by non-governmental Capacity (law), legal entities. Private property is distinguishable from public property, which is owned by a state entity, and from Collective ownership ...
, the inviolability of domicile, the right to appeal to justice opposite the King and the obligation of the King to consult the Cortes before entering a war. Prelates, nobles, and commoners met separately in the three estates of the Cortes. In this meeting, new laws were approved to protect commoners against the arbitrarities of nobles, prelates, and the king. This important set of laws is known as the .
Following this event, new Cortes would appear in the other different territories that would make up Spain:
Principality of Catalonia
The Principality of Catalonia (; ; ; ) was a Middle Ages, medieval and early modern state (polity), state in the northeastern Iberian Peninsula. During most of its history it was in dynastic union with the Kingdom of Aragon, constituting together ...
in 1192, the
Kingdom of Castile
The Kingdom of Castile (; : ) was a polity in the Iberian Peninsula during the Middle Ages. It traces its origins to the 9th-century County of Castile (, ), as an eastern frontier lordship of the Kingdom of León. During the 10th century, the Ca ...
in 1250,
Kingdom of Aragon
The Kingdom of Aragon (; ; ; ) was a medieval and early modern Monarchy, kingdom on the Iberian Peninsula, corresponding to the modern-day Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Aragon, in Spain. It became a part of the larger ...
in 1274,
Kingdom of Valencia
The Kingdom of Valencia (; ; ), located in the eastern shore of the Iberian Peninsula, was one of the component realms of the Crown of Aragon.
The Kingdom of Valencia was formally created in 1238 when the Moorish taifa of Valencia was taken in ...
in 1283 and
Kingdom of Navarre
The Kingdom of Navarre ( ), originally the Kingdom of Pamplona, occupied lands on both sides of the western Pyrenees, with its northernmost areas originally reaching the Atlantic Ocean (Bay of Biscay), between present-day Spain and France.
The me ...
in 1300.
After the union of the Kingdoms of Leon and Castile under the
Crown of Castile
The Crown of Castile was a medieval polity in the Iberian Peninsula that formed in 1230 as a result of the third and definitive union of the crowns and, some decades later, the parliaments of the kingdoms of Kingdom of Castile, Castile and Kingd ...
, their Cortes were united as well in 1258. The Castilian Cortes had representatives from Burgos, Toledo, León, Seville, Córdoba, Murcia, Jaén, Zamora, Segovia, Ávila, Salamanca, Cuenca, Toro, Valladolid, Soria, Madrid, Guadalajara and Granada (after 1492). The Cortes' assent was required to pass new taxes, and could also advise the king on other matters. The
comunero rebels intended a stronger role for the Cortes, but were defeated by the forces of
Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout Europe d ...
Emperor
Charles V Charles V may refer to:
Kings and Emperors
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500–1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661–1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338–1380), called the Wise
Others
* Charles V, Duke ...
in 1521. The Cortes maintained some power, however, though it became more of a consultative entity. However, by the time of
King Philip II, Charles's son, the Castilian Cortes had come under functionally complete royal control, with its delegates dependent on the Crown for their income.
The Cortes of the
Crown of Aragon
The Crown of Aragon (, ) ;, ; ; . was a composite monarchy ruled by one king, originated by the dynastic union of the Kingdom of Aragon and the County of Barcelona (later Principality of Catalonia) and ended as a consequence of the War of the Sp ...
kingdoms retained their power to control the king's spending with regard to the finances of those kingdoms. But after the
War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict fought between 1701 and 1714. The immediate cause was the death of the childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700, which led to a struggle for control of the Spanish E ...
and the victory of another royal house – the
Bourbons
The House of Bourbon (, also ; ) is a dynasty that originated in the Kingdom of France as a branch of the Capetian dynasty, the royal House of France. Bourbon kings first ruled France and Navarre in the 16th century. A branch descended from ...
– and King
Philip V, their Cortes were suppressed (those of
Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and ; ) is an autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces of Spain, ...
and
Valencia
Valencia ( , ), formally València (), is the capital of the Province of Valencia, province and Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Valencian Community, the same name in Spain. It is located on the banks of the Turia (r ...
in 1707, and those of
Catalonia
Catalonia is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a ''nationalities and regions of Spain, nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy of Catalonia of 2006, Statute of Autonomy. Most of its territory (except the Val d'Aran) is situate ...
and the
Balearic islands
The Balearic Islands are an archipelago in the western Mediterranean Sea, near the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula. The archipelago forms a Provinces of Spain, province and Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Spain, ...
in 1714).
The first Cortes representing the whole of Spain (and the Spanish empire of the day) assembled in 1812, in
Cadiz, where it operated as a government in exile as at that time most of the rest of Spain was in the hands of
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
's army.
Switzerland
The
Federal Diet of Switzerland was one of the longest-lived representative bodies in history, continuing from the 13th century to 1848.
Ukraine
Stemming from the tribal assemblies of the ancient Slavs, the ''viche'' (from Proto-Slavonic *větje, meaning 'council', 'counsel' or 'talk') functioned not only as a form of self-organization in cities of medieval
Kievan Rusʹ but also as a form of protect against policies of the Princes. The tradition of viche contributed to the culture of peaceful assemblies in contemporary Ukraine.
The
Sich Rada (council) was an institution of
Cossack administration from the 16th to the 18th century. With the establishment of the
Cossack Hetmanate
The Cossack Hetmanate (; Cossack Hetmanate#Name, see other names), officially the Zaporozhian Host (; ), was a Ukrainian Cossacks, Cossack state. Its territory was located mostly in central Ukraine, as well as in parts of Belarus and southwest ...
in 1648, it was officially known as the General Military Council, or
Cossack Rada, until 1750.
The
Central Council of Ukraine, or the Central Rada, founded on March 4, 1917, was the All-Ukrainian council of the
Ukrainian People's Republic
The Ukrainian People's Republic (UPR) was a short-lived state in Eastern Europe. Prior to its proclamation, the Central Council of Ukraine was elected in March 1917 Ukraine after the Russian Revolution, as a result of the February Revolution, ...
, which declared its full state independence in the
Fourth Universal of the Ukrainian Central Council in 1918. The contemporary Ukrainian parliament is called the
Verkhovna Rada
The Verkhovna Rada ( ; VR), officially the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine, is the unicameralism, unicameral parliament of Ukraine. It consists of 450 Deputy (legislator), deputies presided over by a speaker. The Verkhovna Rada meets in the Verkhovn ...
of Ukraine.
Development of modern parliaments
The development of the modern concept of parliamentary government dates back to the
Kingdom of Great Britain
Great Britain, also known as the Kingdom of Great Britain, was a sovereign state in Western Europe from 1707 to the end of 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the Kingd ...
(1707–1800).
United Kingdom
The
Parliament of Great Britain
The Parliament of Great Britain was formed in May 1707 following the ratification of the Acts of Union 1707, Acts of Union by both the Parliament of England and the Parliament of Scotland. The Acts ratified the treaty of Union which created a ...
was formed in 1707 by the
Acts of Union that replaced the former parliaments of England and
Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
. A
further union in 1801 united the Parliament of Great Britain and the
Parliament of Ireland
The Parliament of Ireland () was the legislature of the Lordship of Ireland, and later the Kingdom of Ireland, from 1297 until the end of 1800. It was modelled on the Parliament of England and from 1537 comprised two chambers: the Irish Hou ...
into a
Parliament of the United Kingdom
The Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, and may also legislate for the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace ...
.
The British Parliament is often referred to as the ''
Mother of Parliaments'' (in fact a misquotation of
John Bright, who remarked in 1865 that "England is the Mother of Parliaments") because the
British Parliament
The Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, and may also legislate for the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of ...
has been the model for most other parliamentary systems, and its
Acts have created many other parliaments. Many nations with parliaments have to some degree emulated the British "three-tier" model known as the
Westminster system
The Westminster system, or Westminster model, is a type of parliamentary system, parliamentary government that incorporates a series of Parliamentary procedure, procedures for operating a legislature, first developed in England. Key aspects of ...
. Most countries in Europe and the
Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the 15th century. Originally a phrase (the common-wealth ...
have similarly organised parliaments with a largely ceremonial
head of state
A head of state is the public persona of a sovereign state.#Foakes, Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representative of its international persona." The name given to the office of head of sta ...
who formally opens and closes parliament, a large elected lower house and a smaller, upper house. The Parliament of the United Kingdom has been described as characterised by the stability of its governing institutions and its capacity to absorb change.
In the United Kingdom, Parliament consists of the
House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the Bicameralism, bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of ...
, the
House of Lords
The House of Lords is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the lower house, the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminster in London, England. One of the oldest ext ...
, and the
Monarch
A monarch () is a head of stateWebster's II New College Dictionary. "Monarch". Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. Life tenure, for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest ...
. The House of Commons is composed of 650 members who are directly elected by British citizens to represent single-member constituencies. The leader of a party that wins more than half the seats, or less than half but is able to gain the support of smaller parties to achieve a majority in the house, is invited by the Monarch to form a government. The House of Lords is a body of long-serving, unelected members:
Lords Temporal
The Lords Temporal are secular members of the House of Lords, the upper house of the British Parliament. These can be either life peers or hereditary peers, although the hereditary right to sit in the House of Lords was abolished for all but n ...
(92 of whom inherit their titles, of whom 90 are elected internally by members of the House to lifetime seats), 588 of whom have been appointed to lifetime seats, and
Lords Spiritual
The Lords Spiritual are the bishops of the Church of England who sit in the House of Lords of the United Kingdom. Up to 26 of the 42 diocesan bishops and archbishops of the Church of England serve as Lords Spiritual (not including retired bish ...
(26 bishops, who are part of the house while they remain in office).
Legislation can originate from either the Lords or the Commons. It is voted on in several distinct stages, called
readings, in each house. First reading is merely a formality. Second reading is where the bill as a whole is considered. Third reading is detailed consideration of clauses of the bill.
In addition to the three readings a bill also goes through a committee stage where it is considered in great detail. Once the bill has been passed by one house it goes to the other and essentially repeats the process. If after the two sets of readings, there are disagreements between the versions that the two houses passed it is returned to the first house for consideration of the amendments made by the second. If it passes through the amendment stage
Royal Assent
Royal assent is the method by which a monarch formally approves an act of the legislature, either directly or through an official acting on the monarch's behalf. In some jurisdictions, royal assent is equivalent to promulgation, while in othe ...
is granted and the bill becomes law as an
Act of Parliament.
The House of Lords is the less powerful of the two houses as a result of the
Parliament Acts 1911 and 1949
The Parliament Acts 1911 and 1949 are two Acts of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, which form part of the constitution of the United Kingdom. Section 2(2) of the Parliament Act 1949 provides that the two Acts are to be construed as one.
...
. These Acts removed the veto power of the Lords over a great deal of legislation. If a bill is certified by the
Speaker of the House of Commons as a
money bill
In the Westminster system (and, colloquially, in the United States), a money bill or supply bill is a bill that solely concerns taxation or government spending (also known as appropriation of money), as opposed to changes in public law.
Con ...
(i.e. acts raising taxes and similar) then the Lords can only block it for a month. If an ordinary bill originates in the Commons the Lords can only block it for a maximum of one
session of Parliament
A legislative session is the period of time in which a legislature, in both parliamentary and presidential systems, is convened for purpose of lawmaking, usually being one of two or more smaller divisions of the entire time between two elections. ...
. The exceptions to this rule are things like bills to prolong the life of a Parliament beyond five years.
In addition to functioning as the second chamber of Parliament, the House of Lords was also the final court of
appeal
In law, an appeal is the process in which Legal case, cases are reviewed by a higher authority, where parties request a formal change to an official decision. Appeals function both as a process for error correction as well as a process of cla ...
for much of the law of the United Kingdom—a combination of judicial and legislative function that recalls its origin in the Curia Regis. This changed in October 2009 when the
Supreme Court of the United Kingdom
The Supreme Court of the United Kingdom (initialism: UKSC) is the final court of appeal for all civil cases in the United Kingdom and all criminal cases originating in England, Wales and Northern Ireland, as well as some limited criminal cases ...
opened and acquired the former jurisdiction of the House of Lords.
Since 1999, there has been a
Scottish Parliament
The Scottish Parliament ( ; ) is the Devolution in the United Kingdom, devolved, unicameral legislature of Scotland. It is located in the Holyrood, Edinburgh, Holyrood area of Edinburgh, and is frequently referred to by the metonym 'Holyrood'. ...
in
Edinburgh
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. The city is located in southeast Scotland and is bounded to the north by the Firth of Forth and to the south by the Pentland Hills. Edinburgh ...
, and, since 2020, a
Senedd
The Senedd ( ; ), officially known as the Welsh Parliament in English and () in Welsh, is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Wales. A democratically elected body, Its role is to scrutinise the Welsh Government and legislate on devolve ...
—or Welsh Parliament—in
Cardiff
Cardiff (; ) is the capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of Wales. Cardiff had a population of in and forms a Principal areas of Wales, principal area officially known as the City and County of Ca ...
. However, these national, unicameral
legislature
A legislature (, ) is a deliberative assembly with the legal authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country, nation or city on behalf of the people therein. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial power ...
s do not have complete power over their respective
countries of the United Kingdom
Since 1922, the United Kingdom has been made up of four countries: England, Scotland, Wales (which collectively make up Great Britain) and Northern Ireland (#Terminology, variously described as a country, province, jurisdiction or region). The ...
, holding only those powers devolved to them by Westminster from 1997. They cannot legislate on defence issues, currency, or national taxation (e.g. VAT, or Income Tax). Additionally, the bodies can be theoretically dissolved, at any given time, by the British Parliament without the consent of the devolved government.
Sweden
In
Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
, the half-century period of parliamentary government beginning with
Charles XII
Charles XII, sometimes Carl XII () or Carolus Rex (17 June 1682 – 30 November 1718 Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.), was King of Sweden from 1697 to 1718. He belonged to the House of Palatinate-Zweibrücken, a branch line of the House of ...
's death in 1718 and ending with
Gustav III
Gustav III (29 March 1792), also called ''Gustavus III'', was King of Sweden from 1771 until his assassination in 1792. He was the eldest son of King Adolf Frederick and Queen Louisa Ulrika of Sweden.
Gustav was a vocal opponent of what he saw ...
's
self-coup
A self-coup, also called an autocoup () or coup from the top, is a form of coup d'état in which a political leader, having come to power through legal means, stays in power illegally through the actions of themselves or their supporters. The le ...
in 1772 is known as the
Age of Liberty
In Swedish history, the Age of Liberty () was a period that saw parliamentary governance, increasing civil rights, and the decline of the Swedish Empire that began with the adoption of the Instrument of Government in 1719 and ended with Gustav ...
. During this period,
civil rights
Civil and political rights are a class of rights that protect individuals' political freedom, freedom from infringement by governments, social organizations, and private individuals. They ensure one's entitlement to participate in the civil and ...
were expanded and power shifted from the monarch to parliament.
While
suffrage
Suffrage, political franchise, or simply franchise is the right to vote in public, political elections and referendums (although the term is sometimes used for any right to vote). In some languages, and occasionally in English, the right to v ...
did not become universal, the taxed peasantry was represented in Parliament, although with little influence and commoners without taxed property had no suffrage at all.
Poland
Changes in Poland's internal situation in the 1980s led to the Round Table Talks which ended in the signing of the famous Round Table Agreement on 5 April 1989. The Agreement spearheaded the evolutionary transformation of the country's political system; independence was regained once again. The document Position on Political Reforms provided grounds for amending the Constitution. The amended Constitution restored the office of the President of the Polish People's Republic and the Senate – both to be elected in free and democratic elections. In the Sejm, the opposition was allocated 35% of the mandates. Thus the so called "contract" elections could not be fully democratic. The Sejm (first chamber) became superior to the Senate (second chamber). In addition, the institution of National Assembly was established, consisting of the Sejm and the Senate sitting jointly to elect the President of the Polish People's Republic. A declaration of the Solidarity Citizens' Committee heralded the prompt enactment of a new, democratic constitution and electoral law. As a result of Solidarity's success in elections to the Sejm and the Senate, profound reforms of the political system were undertaken by adopting an amendment to the Constitution on 29 December 1989. In the Constitution, the Republic of Poland was defined as a democratic state ruled by law. As the provisional constitution lasted too long, it was decided to adopt a provisional regulation in the form of the so called Small Constitution. The President signed it on 17 October 1992. The Small Constitution regulated above all the relationship between the executive and legislative powers, on the basis of the doctrine of separation of powers. A bicameral parliament was maintained.
After long years of legislative work, on 2 April 1997, the National Assembly adopted The Constitution of the Republic of Poland. It entered into force on 17 October 1997. The new Constitution introduced a "rationalised" parliamentary-cabinet system in Poland. It is the first Constitution of the Third Republic. That was the first Constitution of the Third Republic. The act defined the position of the Sejm and the Senate within the system without using the term "parliament". It adopted the doctrine of separation of powers, which provided for a balance between the legislative and executive powers. In practice the binding provisions of the Constitution ensure the supremacy of the legislative power. Both chambers are autonomous bodies, independent of each other, with their own powers. The Constitution retained the principle of bicameralism of the legislature. The Sejm and the Senate sitting jointly constitute the National Assembly. Characteristically, the new Constitution conferred very extensive powers on the Sejm. On the other hand, the powers of the Senate are limited, as in the Constitutions of 1921 and 1992.
Parliamentary system

Many parliaments are part of a
parliamentary system
A parliamentary system, or parliamentary democracy, is a form of government where the head of government (chief executive) derives their Election, democratic legitimacy from their ability to command the support ("confidence") of a majority of t ...
of government, in which the
executive
Executive ( exe., exec., execu.) may refer to:
Role or title
* Executive, a senior management role in an organization
** Chief executive officer (CEO), one of the highest-ranking corporate officers (executives) or administrators
** Executive dir ...
is constitutionally answerable to the parliament from the genetic moment of the birth of Government (
Motion of confidence
A motion or vote of no confidence (or the inverse, a motion or vote of confidence) is a motion and corresponding vote thereon in a deliberative assembly (usually a legislative body) as to whether an officer (typically an executive) is deemed fi ...
), to the final moment of his termination (
Motion of no confidence
A motion or vote of no confidence (or the inverse, a motion or vote of confidence) is a motion and corresponding vote thereon in a deliberative assembly (usually a legislative body) as to whether an officer (typically an executive) is deemed fi ...
), through all the commitments that can be added to the
government contract
Government procurement or public procurement is the purchase of goods, works (construction) or services by the state, such as by a government agency or a state-owned enterprise. In 2019, public procurement accounted for approximately 12% of Gross ...
from time to time through
motions and
resolutions. Some restrict the use of the word ''parliament'' to parliamentary systems, while others use the word for any elected legislative body. Parliaments usually consist of ''
chambers'' or ''houses'', and are usually either
bicameral
Bicameralism is a type of legislature that is divided into two separate Deliberative assembly, assemblies, chambers, or houses, known as a bicameral legislature. Bicameralism is distinguished from unicameralism, in which all members deliberate ...
or unicameralism, unicameral although more complex models exist, or have existed (''see Tricameralism'').
In some parliamentary systems, the prime minister is a member of the parliament (e.g. Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, in the United Kingdom), whereas in others they are not (e.g. Prime Minister of the Netherlands, in the Netherlands). They are commonly the leader of the majority party in the lower house of parliament, but only hold the office as long as the "confidence of the house" is maintained. If members of the lower house lose faith in the leader for whatever reason, they can call a vote of no confidence and force the prime minister to resign.
This can be particularly dangerous to a government when the distribution of seats among different parties is relatively even, in which case a new election is often called shortly thereafter. However, in case of general discontent with the head of government, their replacement can be made very smoothly without all the complications that it represents in the case of a presidential system.
The parliamentary system can be contrasted with a
presidential system
A presidential, strong-president, or single-executive system (sometimes also congressional system) is a form of government in which a head of government (usually titled " president") heads an executive branch that derives its authority and l ...
, such as the United States Congress, American congressional system, which operates under a stricter separation of powers, whereby the executive does not form part of, nor is it appointed by, the parliamentary or legislative body. In such a system, congresses do not select or dismiss head of government, heads of governments, and governments cannot request an early dissolution as may be the case for parliaments. Some states, such as France, have a semi-presidential system which falls between parliamentary and congressional systems, combining a powerful head of state (president) with a head of government, the prime minister, who is responsible to parliament.
Women in parliament
File:10% Share of women in parliament, OWID.svg, Greater than 10%
File:20% Share of women in parliament, OWID.svg, Greater than 20%
File:30% Share of women in parliament, OWID.svg, Greater than 30%
List of national parliaments





Parliaments of the European Union
* European Parliament
* Parliament of Austria (consisting of the National Council (Austria), National Council and the Federal Council (Austria), Federal Council)
* Belgian Federal Parliament (consisting of the Chamber of Representatives of Belgium, Chamber of Representatives and the Senate of Belgium, Senate)
* National Assembly of Bulgaria
* Croatian Parliament
* House of Representatives of Cyprus, House of Representatives (Cyprus)
* Parliament of the Czech Republic (consisting of the Chamber of Deputies of the Czech Republic, Chamber of Deputies and the Senate of the Czech Republic, Senate)
* Folketing (Denmark)
* Riigikogu (Estonia)
* Parliament of Finland (Eduskunta)
* Parliament of France (consisting of the French National Assembly, National Assembly and the Senate of France, Senate)
* Bundestag and Bundesrat of Germany, Bundesrat (Germany)
* Hellenic Parliament (Greece)
* National Assembly of Hungary, National Assembly (Hungary)
* Oireachtas (Ireland) (consisting of the President of the Republic of Ireland, President of Ireland, Dáil Éireann (Lower House) and Seanad Éireann (Senate))
* Parliament of Italy (consisting of the Chamber of Deputies (Italy), Chamber of Deputies and the Senate of the Republic (Italy), Senate)
* Saeima (Latvia)
* Seimas (Lithuania)
* Chamber of Deputies of Luxembourg, Chamber of Deputies (Luxembourg)
* House of Representatives of Malta, House of Representatives (Malta)
* States General of the Netherlands (consisting of the House of Representatives (Netherlands), Chamber of Representatives and the Senate (Netherlands), Senate)
* Storting (Norway)
* National Assembly of the Republic of Poland (consisting of the Sejm of the Republic of Poland, Sejm and the Senate of the Republic of Poland, Senate)
* Assembly of the Republic of Portugal, Assembly of the Republic (
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
)
* Parliament of Romania (consisting of the Chamber of Deputies of Romania, Chamber of Deputies and the Senate of Romania, Senate)
* National Council of the Slovak Republic, National Council (Slovakia)
* Parliament of Slovenia (consisting of the National Assembly (Slovenia), National Assembly and the National Council (Slovenia), National Council)
* Cortes Generales (Spain) (consisting of the Congress of Deputies of Spain, Congress of Deputies and the Senate of Spain, Senate)
* Riksdag (
Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
)
Others
* Parliament of Albania
* General Council of Andorra
* Parliament of Australia (consisting of the Monarchy of Australia, King, the Australian House of Representatives, House of Representatives, and the Australian Senate, Senate)
** The federal government of the Commonwealth of Australia has a bicameral parliament and each of States and territories of Australia, Australia's six states has a bicameral parliament except for Queensland, which has a unicameral parliament.
* Parliament of The Bahamas
* Jatiya Sangsad (Bangladesh)
* Parliament of Barbados
* Parliament of Canada (consisting of the Monarchy of Canada, King, an Upper House styled the Senate of Canada, Senate, and the House of Commons of Canada, House of Commons)
** The federal government of Canada has a bicameral parliament, and each of Provinces of Canada, Canada's 10 provinces has a unicameral parliament.
* National People's Congress, National People's Congress of the People's Republic of China
* Løgtingið (Faroe Islands)
* Parliament of Fiji
*
Parliament of Ghana
The Parliament of Ghana is the unicameral legislature of Ghana. It consists of 276 members, who are elected for four-year terms in single-seat Electoral district, constituencies using a first-past-the-post voting system.
History
Legislature, L ...
* States of Deliberation of Guernsey
* Althing, Althing (Parliament of Iceland) - Oldest surviving parliament
* Parliament of India (consisting of the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha)
* People's Consultative Assembly of Indonesia (consisting of the People's Representative Council and the Regional Representative Council)
* Council of Representatives of Iraq
* Knesset of Israel
* National Diet of Japan (consisting of the House of Representatives (Japan), House of Representatives and the House of Councillors (Japan), House of Councillors)
* States Assembly of Jersey
* Parliament of Kazakhstan (consisting of the Mäjilis and the Senate of Kazakhstan, Senate)
* Parliament of Lebanon
*
Tynwald
Tynwald (), or more formally, the High Court of Tynwald () or Tynwald Court, is the legislature of the Isle of Man. It consists of two chambers, known as the branches of Tynwald: the directly elected House of Keys and the indirectly chosen Leg ...
, the parliament of the Isle of Man
* Parliament of Malaysia
* Parliament of Moldova
* Parliament of Montenegro
* Parliament of Morocco
* Parliament of Nauru
* Parliament of Nepal (recently reorganised)
* Parliament of New Zealand (consisting of the King of New Zealand, King and NZ House of Representatives, House of Representatives)
* Assembly of the Republic of North Macedonia
* Majlis-e-Shoora, Pakistan
* National Assembly of Serbia
* Parliament of Singapore
* Parliament of South Africa
* National Assembly of South Korea
* Parliament of Sri Lanka
* Legislative Yuan of Taiwan
* National Assembly of Thailand
* Parliament of the Central Tibetan Administration
* Parliament of Trinidad and Tobago
* Grand National Assembly of Turkey
*
Verkhovna Rada
The Verkhovna Rada ( ; VR), officially the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine, is the unicameralism, unicameral parliament of Ukraine. It consists of 450 Deputy (legislator), deputies presided over by a speaker. The Verkhovna Rada meets in the Verkhovn ...
of Ukraine
*
Parliament of the United Kingdom
The Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, and may also legislate for the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace ...
(consisting of the House of Lords of the United Kingdom, House of Lords and the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons
* Parliament of Zimbabwe
List of subnational parliaments
Australia
Australia's States and territories:
*Parliament of New South Wales
*Parliament of Victoria
*Parliament of Queensland
*Parliament of Western Australia
*Parliament of South Australia
*Parliament of Tasmania
*Australian Capital Territory Legislative Assembly
*Parliament of the Northern Territory
Belgium
In the federal (bicameral) kingdom of Belgium, there is a curious asymmetrical constellation serving as directly elected legislatures for three "territorial" ''regions''—Flanders (
Dutch), Brussels (bilingual, certain peculiarities of competence, also the only region not comprising any of the 10 provinces) and Wallonia (French)—and three cultural ''communities''—Flemish (Dutch, competent in Flanders and for the Dutch-speaking inhabitants of Brussels), Francophone (French, for Wallonia and for Francophones in Brussels) and German (for speakers of that language in a few designated municipalities in the east of the Walloon Region, living alongside Francophones but under two different regimes):
* Flemish Parliament serves both the Flemish Community and the region of Flanders (in all matters of regional competence, its decisions have no effect in Brussels-Capital Region)
* Parliament of the French Community
* Parliament of the German-speaking Community
* Parliament of Wallonia
* Parliament of the Brussels-Capital Region (within the capital's regional assembly, however, there also exist two ''Community Commissions'', a Flemish Community Commission, Dutch-speaking one and a French Community Commission, Francophone one, for various matters split up by linguistic community but under Brussels' regional competence, and even "joint community commissions" consisting of both for certain institutions that could be split up but are not.
Brazil
Canada

Canada's provinces and territories:
*Legislature of Ontario, Parliament of Ontario
*Quebec Legislature
*General Assembly of Nova Scotia
*New Brunswick Legislature
*Manitoba Legislature
*Parliament of British Columbia
*General Assembly of Prince Edward Island
*Saskatchewan Legislature
*Alberta Legislature
*General Assembly of Newfoundland and Labrador
*Legislative Assembly of the Northwest Territories
*Yukon Legislative Assembly
*Legislative Assembly of Nunavut
China
* Legislative Council of Hong Kong
* Legislative Assembly of Macau
Denmark
* Inatsisartut
*
Løgting
The Løgting (pronounced ; ) is the unicameral parliament of the Faroe Islands, an autonomous territory within the Danish Realm.
The name literally means "''Law Thing''"—that is, a law assembly—and derives from Old Norse ''lǫgþing ...
Finland

* Åland
Germany
* Landtag#German Legislatures, State legislatures of Germany
Except for the city-states of Berlin, Bremen and Hamburg, where the city council is also the State Parliament (Germany), state parliament, all state parliaments are called ''Landtag'':
*Abgeordnetenhaus of Berlin
*Bürgerschaft of Bremen, Bremische Bürgerschaft
*Hamburg Parliament, Bürgerschaft der Freien und Hansestadt Hamburg
*Landtag of Baden-Württemberg
*Landtag of Bavaria
*Landtag of Brandenburg
*Landtag of Hesse
*Landtag of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
*Landtag of Lower Saxony
*Landtag of North Rhine-Westphalia
*Landtag of Rhineland-Palatinate
*Landtag of Saarland
*Landtag of Saxony
*Landtag of Saxony-Anhalt
*Landtag of Schleswig-Holstein
*Landtag of Thuringia
India
Indian states and territorial legislative assemblies
Indian states legislative councils
* Andhra Pradesh Legislative Council
* Bihar Legislative Council
* Karnataka Legislative Council
* Maharashtra Legislative Council
* Telangana Legislative Council
* Uttar Pradesh Legislative Council
Malaysia
Netherlands
* Provincial council (Netherlands)
* States General of the Netherlands
Norway
Philippines
* Bangsamoro Parliament, Parliament of the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region
Portugal
* Legislative Assembly of the Azores
* Legislative Assembly of Madeira
Spain
Sri Lanka
* Provincial Councils (Sri Lanka)
Switzerland
Trinidad and Tobago
* Tobago House of Assembly
United Kingdom
* Northern Ireland Assembly
*
Scottish Parliament
The Scottish Parliament ( ; ) is the Devolution in the United Kingdom, devolved, unicameral legislature of Scotland. It is located in the Holyrood, Edinburgh, Holyrood area of Edinburgh, and is frequently referred to by the metonym 'Holyrood'. ...
* Senedd (Welsh Parliament)
Other parliaments
Contemporary supranational parliaments
:''List is not exhaustive''
* Pan-African Parliament
* Central American Parliament
* Latin American Parliament
* European Parliament
Equivalent national legislatures
* Majlis, e.g. in Iran
* in Indonesia: People's Consultative Assembly, consists of People's Representative Council (elected, legislative lower house) and Regional Representative Council (elected, legislative upper house with limited powers)
Defunct
* Parliament of Southern Ireland (1921–1922)
* People's Parliament (1940s)
* Silesian Parliament (1922–1945)
* Parliament of Northern Ireland (1921–1973)
* Batasang Pambansa, Batasang Pambansâ (1978–1986)
* National Assembly of the Republic of China (1913–2005)
See also
* Congress
* Delegated legislation
* Democratic mundialization
* Government
* History of democracy
* Inter-Parliamentary Union
* Legislation
* Non-human electoral candidate
* Parliamentary procedure
* Parliamentary records
* Parliament of the World's Religions
* List of current presidents of assembly
References
External links
Comparative Legislators Database A dataset on over 67,000 legislators from 16 countries.
*
United Kingdom Parliament
{{Authority control
Legislatures
Westminster system
Parliamentary procedure


 In modern politics and history, a parliament is a
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a  Although its role in government had expanded significantly in the mid 16th century, the Parliament of England saw some of its most important gains in the 17th century. A series of conflicts between the Crown and Parliament culminated in the execution of King Charles I in 1649. For a brief period, England became a
Although its role in government had expanded significantly in the mid 16th century, the Parliament of England saw some of its most important gains in the 17th century. A series of conflicts between the Crown and Parliament culminated in the execution of King Charles I in 1649. For a brief period, England became a  Later national diets with chambers for different estates developed, e.g. in Sweden and in Finland (which was part of Sweden until 1809), each with a House of Knights for the nobility. In both these countries, the national parliaments are now called
Later national diets with chambers for different estates developed, e.g. in Sweden and in Finland (which was part of Sweden until 1809), each with a House of Knights for the nobility. In both these countries, the national parliaments are now called  According to the ''
According to the '' The term "sejm" comes from an old Polish expression denoting a meeting of the populace. The power of early sejms grew between 1146 and 1295, when the power of individual rulers waned and various councils grew stronger. Since the 14th century irregular sejms (described in various
The term "sejm" comes from an old Polish expression denoting a meeting of the populace. The power of early sejms grew between 1146 and 1295, when the power of individual rulers waned and various councils grew stronger. Since the 14th century irregular sejms (described in various  Although there are documented councils held in 873, 1020, 1050 and 1063, there was no representation of commoners. What is considered to be the first parliament, the
Although there are documented councils held in 873, 1020, 1050 and 1063, there was no representation of commoners. What is considered to be the first parliament, the 



 Canada's provinces and territories:
*Legislature of Ontario, Parliament of Ontario
*Quebec Legislature
*General Assembly of Nova Scotia
*New Brunswick Legislature
*Manitoba Legislature
*Parliament of British Columbia
*General Assembly of Prince Edward Island
*Saskatchewan Legislature
*Alberta Legislature
*General Assembly of Newfoundland and Labrador
*Legislative Assembly of the Northwest Territories
*Yukon Legislative Assembly
*Legislative Assembly of Nunavut
Canada's provinces and territories:
*Legislature of Ontario, Parliament of Ontario
*Quebec Legislature
*General Assembly of Nova Scotia
*New Brunswick Legislature
*Manitoba Legislature
*Parliament of British Columbia
*General Assembly of Prince Edward Island
*Saskatchewan Legislature
*Alberta Legislature
*General Assembly of Newfoundland and Labrador
*Legislative Assembly of the Northwest Territories
*Yukon Legislative Assembly
*Legislative Assembly of Nunavut
 * Åland
* Åland