
was a Japanese ''
daimyō
were powerful Japanese magnates, feudal lords who, from the 10th century to the early Meiji period in the middle 19th century, ruled most of Japan from their vast, hereditary land holdings. They were subordinate to the shogun and nominall ...
'' and one of the leading figures of the
Sengoku period
The was a period in Japanese history of near-constant civil war and social upheaval from 1467 to 1615.
The Sengoku period was initiated by the Ōnin War in 1467 which collapsed the feudal system of Japan under the Ashikaga shogunate. Variou ...
. He is regarded as the first "Great Unifier" of
Japan.
Nobunaga was head of the very powerful
Oda clan
The is a Japanese samurai family who were daimyo and an important political force in the unification of Japan in the mid-16th century. Though they had the climax of their fame under Oda Nobunaga and fell from the spotlight soon after, several ...
, and launched a war against other ''daimyō'' to unify Japan in the 1560s. Nobunaga emerged as the most powerful ''daimyō'', overthrowing the nominally ruling
shogun
, officially , was the title of the military dictators of Japan during most of the period spanning from 1185 to 1868. Nominally appointed by the Emperor, shoguns were usually the de facto rulers of the country, though during part of the Kamakura ...
Ashikaga Yoshiaki
"Ashikaga Yoshiaki" in '' The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 625. was the 15th and final '' shōgun'' of the Ashikaga shogunate in Japan who reigned from 1568 to 1573.Ackroyd, ...
and dissolving the
Ashikaga Shogunate
The , also known as the , was the feudal military government of Japan during the Muromachi period from 1336 to 1573.Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Muromachi-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 669.
The Ashikaga shogunate was establis ...
in 1573. He conquered most of
Honshu
, historically called , is the largest and most populous island of Japan. It is located south of Hokkaidō across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyūshū across the Kanmon Straits. The island ...
island by 1580, and defeated the ''
Ikkō-ikki
were rebellious or autonomous groups of people that were formed in several regions of Japan in the 15th-16th centuries; backed up by the power of the Jōdo Shinshū sect of Buddhism, they opposed the rule of governors or ''daimyō''. Mainly co ...
'' rebels in the 1580s. Nobunaga's rule was noted for innovative military tactics, fostering of free trade, reforms of Japan's civil government, and the start of the
Momoyama historical art period, but also for the brutal suppression of those who refused to cooperate or yield to his demands. Nobunaga was killed in the
Honnō-ji Incident
The was an attempt to assassinate Japanese daimyo Oda Nobunaga at the Honnō-ji temple in Kyoto on 21 June 1582, resulting in the suicide by ''seppuku'' of both Nobunaga and his son Oda Nobutada. The unprotected Nobunaga was ambushed by his ...
in 1582, when his retainer
Akechi Mitsuhide
, first called Jūbei from his clan and later from his title, was a Japanese ''samurai'' general of the Sengoku period best known as the assassin of Oda Nobunaga. Mitsuhide was a bodyguard of Ashikaga Yoshiaki and later a successful general under ...
ambushed him in
Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the ...
and forced him to commit . Nobunaga was succeeded by
Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and '' daimyō'' ( feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: Military Innovations that Changed the C ...
, who along with
Tokugawa Ieyasu
was the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan, which ruled Japan from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was one of the three "Great Unifiers" of Japan, along with his former lord Oda Nobunaga and fel ...
completed his war of unification shortly afterwards.
Nobunaga was an influential figure in Japanese history and is regarded as one of the three great unifiers of Japan, along with his retainers Toyotomi Hideyoshi and Tokugawa Ieyasu. Hideyoshi later united Japan in 1591, and invaded
Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republi ...
a year later. However, he died in 1598, and Ieyasu took power after the
Battle of Sekigahara
The Battle of Sekigahara ( Shinjitai: ; Kyūjitai: , Hepburn romanization: ''Sekigahara no Tatakai'') was a decisive battle on October 21, 1600 ( Keichō 5, 15th day of the 9th month) in what is now Gifu prefecture, Japan, at the end of ...
in 1600, becoming
shogun
, officially , was the title of the military dictators of Japan during most of the period spanning from 1185 to 1868. Nominally appointed by the Emperor, shoguns were usually the de facto rulers of the country, though during part of the Kamakura ...
in 1603, and ending the
Sengoku period
The was a period in Japanese history of near-constant civil war and social upheaval from 1467 to 1615.
The Sengoku period was initiated by the Ōnin War in 1467 which collapsed the feudal system of Japan under the Ashikaga shogunate. Variou ...
.
Early life (1534–1551)
Oda Nobunaga was born on 23 June 1534 in
Nagoya
is the largest city in the Chūbu region, the fourth-most populous city and third most populous urban area in Japan, with a population of 2.3million in 2020. Located on the Pacific coast in central Honshu, it is the capital and the most p ...
,
Owari Province
was a province of Japan in the area that today forms the western half of Aichi Prefecture, including the modern city of Nagoya. The province was created in 646. Owari bordered on Mikawa, Mino, and Ise Provinces. Owari and Mino provinces we ...
, and was the second son of
Oda Nobuhide
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' and magistrate of the Sengoku period known as "Tiger of Owari" and also the father of Oda Nobunaga the first "Great Unifier" of Japan. Nobuhide was a deputy '' shugo'' (Shugodai) of lower Owari Province and head of the ...
, the head of the powerful
Oda clan
The is a Japanese samurai family who were daimyo and an important political force in the unification of Japan in the mid-16th century. Though they had the climax of their fame under Oda Nobunaga and fell from the spotlight soon after, several ...
and a deputy (military governor), and his wife
Dota Gozen.
[Jansen, Marius (2000). ''The Making of Modern Japan, '' p. 11.] Nobunaga is said to have been born in
Nagoya Castle
is a Japanese castle located in Nagoya, Japan.
Nagoya Castle was constructed by the Owari Domain in 1612 during the Edo period on the site of an earlier castle of the Oda clan in the Sengoku period. Nagoya Castle was the heart of one of the ...
, the future seat of the
Owari Domain
The was a feudal domain of Japan in the Edo period. Located in what is now the western part of Aichi Prefecture, it encompassed parts of Owari, Mino, and Shinano provinces. Its headquarters were at Nagoya Castle. At its peak, it was rate ...
, although this is subject to debate. Nobunaga was given the childhood name of , and through his childhood and early teenage years became well-known for his bizarre behavior, receiving the name of .
Nobunaga was a clear speaker with a strong presence about him, and was known to run around with other youths from the area, without any regard to his own rank in society. With the introduction of firearms into Japan he became known for his fondness for guns.
In 1549, Nobuhide made peace with
Saitō Dōsan
, also known as Saitō Toshimasa (斎藤 利政), was a Japanese samurai during the Sengoku period. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"Saitō Dōsan"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 809.
He was also known as the for his ruthless tactics. His hono ...
by arranging a political marriage between his son and heir Nobunaga, and Saitō Dōsan's daughter,
Nōhime
, also known as Kichō (帰蝶), was the legal wife of Oda Nobunaga, a major ''daimyō'' during the Sengoku period of Japanese history. Her proper name was Kichō, but since she came from Mino Province, she is most commonly referred to as Nōhime ...
. Dōsan therefore became Nobunaga's father-in-law.
[
]
Unification of Owari (1551–1560)

Succession crisis
In 1551, Oda Nobuhide
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' and magistrate of the Sengoku period known as "Tiger of Owari" and also the father of Oda Nobunaga the first "Great Unifier" of Japan. Nobuhide was a deputy '' shugo'' (Shugodai) of lower Owari Province and head of the ...
died unexpectedly. It has been said that Nobunaga acted outrageously during his funeral, throwing ceremonial incense
Incense is aromatic biotic material that releases fragrant smoke when burnt. The term is used for either the material or the aroma. Incense is used for aesthetic reasons, religious worship, aromatherapy, meditation, and ceremony. It may also ...
at the altar.Oda clan
The is a Japanese samurai family who were daimyo and an important political force in the unification of Japan in the mid-16th century. Though they had the climax of their fame under Oda Nobunaga and fell from the spotlight soon after, several ...
opposed him. Nobunaga, collecting about 1,000 men, suppressed the hostile members of his family and their allies. However, Imagawa Yoshimoto
was a pre-eminent ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) in the Sengoku period Japan. Based in Suruga Province, he was known as . he was one of the three ''daimyōs'' that dominated the Tōkaidō region.
He died in 1560 while marching to Kyoto to become S ...
sent army under the command of Imagawa Sessai laid siege to Anjō castle, where Oda Nobuhiro
was the eldest son of Oda Nobuhide. After Nobuhiro's father took Anjo Castle in Mikawa Province in 1540, the castle was given to Nobuhiro. During 1551, Nobuhiro was trapped by the Imagawa clan, but was saved when Oda Nobunaga handed over one o ...
, the illegitimate son of Nobuhide and eldest brother of Nobunaga, was living. Nobuhiro was trapped, but was saved when Nobunaga handed over one of his hostages at Honshōji temple, nine-year-old Matsudaira Takechiyo – later known as Tokugawa Ieyasu
was the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan, which ruled Japan from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was one of the three "Great Unifiers" of Japan, along with his former lord Oda Nobunaga and fel ...
– to make up for not lifting the siege of Anjō. Later on, Nobuhiro plotted against Nobunaga with the assistance of Saitō Yoshitatsu
or Toki Yoshitatsu was a Japanese samurai during the Sengoku period. Papinot, Jacques Edmond Joseph. (1906). ''Dictionnaire d’histoire et de géographie du Japon''; Papinot, (2003)">DF 54 of 80">"Saitō," ''Nobiliare du Japon'', p. 50 DF 54 ...
, but Nobunaga forgave Nobuhiro after the plot failed.
In early 1552, barely several months after his father's death, one of Oda's senior retainers, Yamaguchi Noritsugu and his son Yamaguchi Noriyoshi defected to Imagawa clan. In response, Nobunaga attacked Noritsugu, but was repelled by Noriyoshi at Battle of Akatsuka, he retreated and left contested lands in eastern Owari under Imagawa control.
Consolidation of clan leadership
In spring 1552, Nobuhide's younger brother, Oda Nobutomo
was a Japanese warlord during the Sengoku period. He was head of the Kiyosu Oda faction of the Oda clan, and ruled the four southern districts of Owari Province as '' shugodai''.
After Oda Nobuhide died in 1551, Nobuhide's son Nobunaga was ini ...
, attacked Nobunaga domain with the support of Shiba Yoshimune
was the final head of the Shiba clan and lived during the latter half of the Sengoku period of Feudal Japan. Nominally, Yoshimune was the governor of Owari province and resided at Kiyosu castle. Though he was governor the head of the Iwakura Oda ...
, the official governor of Owari province
was a province of Japan in the area that today forms the western half of Aichi Prefecture, including the modern city of Nagoya. The province was created in 646. Owari bordered on Mikawa, Mino, and Ise Provinces. Owari and Mino provinces we ...
. Nobunaga repelled it and burned the outskirts of Kiyosu castle.
In 1553, Hirate Masahide
was a Japanese samurai who served the Oda clan for two generations. His original name was .
Life
Masahide first served Oda Nobuhide. He was a talented samurai as well as skilled in sado and waka. This helped him to act as a skilled diplom ...
, a valuable mentor and retainer to Nobunaga, performed to startle Nobunaga into his obligations.[ In the meantime, ]Shiba Yoshimune
was the final head of the Shiba clan and lived during the latter half of the Sengoku period of Feudal Japan. Nominally, Yoshimune was the governor of Owari province and resided at Kiyosu castle. Though he was governor the head of the Iwakura Oda ...
informed Nobunaga of a plot of Nobutomo to assassinate him, and later, Oda Nobutomo
was a Japanese warlord during the Sengoku period. He was head of the Kiyosu Oda faction of the Oda clan, and ruled the four southern districts of Owari Province as '' shugodai''.
After Oda Nobuhide died in 1551, Nobuhide's son Nobunaga was ini ...
had Yoshimune put to death. Nobunaga mobilized his forces to blockade Kiyosu castle, and waited for the opportunity to attack.
In 1554 Nobunaga defeated the powerful Imagawa clan
was a Japanese samurai clan that claimed descent from the Seiwa Genji by way of the Kawachi Genji. It was a branch of the Minamoto clan by the Ashikaga clan.
Origins
Ashikaga Kuniuji, grandson of Ashikaga Yoshiuji, established himself in ...
, whose army had invaded eastern Owari Province
was a province of Japan in the area that today forms the western half of Aichi Prefecture, including the modern city of Nagoya. The province was created in 646. Owari bordered on Mikawa, Mino, and Ise Provinces. Owari and Mino provinces we ...
, at the Battle of Muraki Castle
The Battle of Muraki Castle (January 24, 1554) was one of the first victories of the young Oda Nobunaga in his struggle to unite the province of Owari against the powerful Imagawa clan, whose army had invaded the eastern parts of Owari.
Backgr ...
.Oda Nobutomo
was a Japanese warlord during the Sengoku period. He was head of the Kiyosu Oda faction of the Oda clan, and ruled the four southern districts of Owari Province as '' shugodai''.
After Oda Nobuhide died in 1551, Nobuhide's son Nobunaga was ini ...
, and forced him to commit suicide.
In 1556, Nobunaga sent an army to Mino Province
was a province of Japan in the area of Japan that is today southern Gifu Prefecture. Mino was bordered by Ōmi to the west, Echizen and Hida to the north, and Shinano to the east, and Ise, Mikawa, and Owari to the south. Its abbrevia ...
to aid his father-in-law, Saitō Dōsan
, also known as Saitō Toshimasa (斎藤 利政), was a Japanese samurai during the Sengoku period. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"Saitō Dōsan"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 809.
He was also known as the for his ruthless tactics. His hono ...
, after Dōsan's son, Saitō Yoshitatsu
or Toki Yoshitatsu was a Japanese samurai during the Sengoku period. Papinot, Jacques Edmond Joseph. (1906). ''Dictionnaire d’histoire et de géographie du Japon''; Papinot, (2003)">DF 54 of 80">"Saitō," ''Nobiliare du Japon'', p. 50 DF 54 ...
, turned against him. The campaign failed, as Dōsan was killed in the Battle of Nagara-gawa, and Yoshitatsu became the new master of Mino.Oda clan
The is a Japanese samurai family who were daimyo and an important political force in the unification of Japan in the mid-16th century. Though they had the climax of their fame under Oda Nobunaga and fell from the spotlight soon after, several ...
, his younger brother Oda Nobuyuki
, also known as , was the son of Oda Nobuhide and younger brother of Oda Nobunaga, who lived during the Sengoku period of Japan.
Nobuyuki conspired against his brother Nobunaga with the Hayashi clan (Owari), which Nobunaga viewed as treason. No ...
, at the Battle of Ino. Nobuyuki survived the battle and began plotting a second rebellion.
Nobuyuki began his second rebellion in 1557, but was defeated and his Suemori Castle was destroyed by Nobunaga's retainer Ikeda Nobuteru.[
In 1558, Nobunaga sent an army to protect Suzuki Shigeteru, lord of Terabe Castle, during the ]Siege of Terabe
The siege of Terabe Castle took place in 1558 in feudal Japan. Terabe Castle was a possession of the Ogasawara clan of Mikawa province. The Siege of Terabe Castle was Matsudaira Motoyasu's first battle, who would later change his name to Tokugaw ...
.[ Shigeteru had defected to Nobunaga's side from ]Imagawa Yoshimoto
was a pre-eminent ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) in the Sengoku period Japan. Based in Suruga Province, he was known as . he was one of the three ''daimyōs'' that dominated the Tōkaidō region.
He died in 1560 while marching to Kyoto to become S ...
, a ''daimyō'' from Suruga Province
was an old province in the area that is today the central part of Shizuoka Prefecture. Suruga bordered on Izu, Kai, Sagami, Shinano, and Tōtōmi provinces; and was bordered by the Pacific Ocean through Suruga Bay to the south. Its abbrev ...
, one of the most powerful men in the Tōkaidō region. In the meantime, Nobunaga defeated Oda Nobukata at the Battle of Ukino
Battle of Ukino (July 12, 1558) was the final victory of Oda Nobunaga in his struggle to unite the province of Owari against his cousin, Oda Nobukata, deputy governor of northern Owari.
Background
After defeating Imigawa clan of Suruga in t ...
. Oda Nobuyuki
, also known as , was the son of Oda Nobuhide and younger brother of Oda Nobunaga, who lived during the Sengoku period of Japan.
Nobuyuki conspired against his brother Nobunaga with the Hayashi clan (Owari), which Nobunaga viewed as treason. No ...
started plotting again, but was denounced by Shibata Katsuie
or was a Japanese samurai and military commander during the Sengoku period.
He served Oda Nobunaga as one of his trusted generals, was severely wounded in the 1571 first siege of Nagashima, but then fought in the 1575 Battle of Nagashino an ...
, one of his retainers, and killed on November 2, 1558.
By 1559, Nobunaga had captured and destroyed Iwakura Castle, eliminated all opposition within the Oda clan
The is a Japanese samurai family who were daimyo and an important political force in the unification of Japan in the mid-16th century. Though they had the climax of their fame under Oda Nobunaga and fell from the spotlight soon after, several ...
, and established his uncontested rule in Owari Province
was a province of Japan in the area that today forms the western half of Aichi Prefecture, including the modern city of Nagoya. The province was created in 646. Owari bordered on Mikawa, Mino, and Ise Provinces. Owari and Mino provinces we ...
.
Rise to power (1560–1568)

Conflict with Imagawa
Imagawa Yoshimoto
was a pre-eminent ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) in the Sengoku period Japan. Based in Suruga Province, he was known as . he was one of the three ''daimyōs'' that dominated the Tōkaidō region.
He died in 1560 while marching to Kyoto to become S ...
was a long-time opponent of Nobunaga's father, and had sought to expand his domain into Oda territory in Owari. In 1560, Imagawa Yoshimoto gathered an army of 25,000 men,[ Takeuchi, Rizō (1985). ''Nihonshi shōjiten'', p. 233.] and marched toward the capital city of Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the ...
, with the pretext of aiding the frail Ashikaga Shogunate
The , also known as the , was the feudal military government of Japan during the Muromachi period from 1336 to 1573.Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Muromachi-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 669.
The Ashikaga shogunate was establis ...
. The Matsudaira clan
The was a Japanese samurai clan that descended from the Minamoto clan. It originated in and took its name from Matsudaira village, in Mikawa Province (modern-day Aichi Prefecture). During the Sengoku period, the chieftain of the main line of t ...
also joined Yoshimoto's forces. The Imagawa forces quickly overran the border fortresses of Washizu, and Matsudaira forces led by Matsudaira Motoyasu took Marune Fortress. Against this, the Oda clan could rally an army of only 2,000 to 3,000 men.Kiyosu Castle
is a Japanese castle located in Kiyosu, eastern Aichi Prefecture, Japan. It is noted for its association with the rise to power of the Sengoku period warlord, Oda Nobunaga. The kanji in the name of the castle was written as 清須城. The curr ...
and wait out a siege by the Imagawa, but Nobunaga refused, stating that "only a strong offensive policy could make up for the superior numbers of the enemy", and calmly ordered a counterattack against Yoshimoto.
Battle of Okehazama
In June 1560, Nobunaga's scouts reported that Yoshimoto was resting at the narrow gorge of Dengaku-hazama, ideal for a surprise attack, and that the Imagawa army was celebrating their victories over the Washizu and Marune fortresses. While Yoshimoto viewed victory ahead, Nobunaga's forces marched to the Atsuta Shrine is a Shinto shrine traditionally believed to have been established during the reign of Emperor Keikō (71-130) located in Atsuta-ku, Nagoya, Aichi Prefecture in Japan. The shrine is familiarly known as ''Atsuta-Sama'' (Venerable Atsuta) or si ...
, a fortified temple overlooking the Imagawa camp. Later, Nobunaga moved to Zensho-ji fort, set up a decoy army there, marched rapidly behind Yoshimoto's camp, and attacked after a terrific thunderstorm. Yoshimoto was killed by two Oda samurai.sandal-bearer
A sandal-bearer is a person who bears the sandals of his superior. The role existed in various cultures and epochs, being first documented in Egypt's Early Dynastic Period (c. 31st century BC).
In Antiquity
In Ancient Egypt the role of sand ...
Kinoshita Tōkichirō, who would eventually become Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and '' daimyō'' ( feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: Military Innovations that Changed the C ...
.
Alliance with Matsudaira (later Tokugawa) and Takeda
Rapidly weakening in the wake of this battle, the Imagawa clan
was a Japanese samurai clan that claimed descent from the Seiwa Genji by way of the Kawachi Genji. It was a branch of the Minamoto clan by the Ashikaga clan.
Origins
Ashikaga Kuniuji, grandson of Ashikaga Yoshiuji, established himself in ...
no longer exerted control over the Matsudaira clan
The was a Japanese samurai clan that descended from the Minamoto clan. It originated in and took its name from Matsudaira village, in Mikawa Province (modern-day Aichi Prefecture). During the Sengoku period, the chieftain of the main line of t ...
. In 1561, an alliance was forged between Oda Nobunaga and Matsudaira Motoyasu (who would become Tokugawa Ieyasu
was the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan, which ruled Japan from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was one of the three "Great Unifiers" of Japan, along with his former lord Oda Nobunaga and fel ...
), despite the decades-old hostility between the two clans. Nobunaga also formed an alliance with Takeda Shingen
, of Kai Province, was a pre-eminent ''daimyō'' in feudal Japan. Known as the "Tiger of Kai", he was one of the most powerful Daimyo, daimyō with exceptional military prestige in the late stage of the Sengoku period.
Shingen was a warlord of ...
through the marriage of his daughter to Shingen's son.
Mino campaign
In 1561, Saitō Yoshitatsu
or Toki Yoshitatsu was a Japanese samurai during the Sengoku period. Papinot, Jacques Edmond Joseph. (1906). ''Dictionnaire d’histoire et de géographie du Japon''; Papinot, (2003)">DF 54 of 80">"Saitō," ''Nobiliare du Japon'', p. 50 [PDF 54 ...
, an enemy of the Oda clan
The is a Japanese samurai family who were daimyo and an important political force in the unification of Japan in the mid-16th century. Though they had the climax of their fame under Oda Nobunaga and fell from the spotlight soon after, several ...
, died suddenly of illness and was succeeded by his son, Saitō Tatsuoki. However, Tatsuoki was young and much less effective as a ruler and military strategist compared to his father and grandfather.[ Taking advantage of this situation, Nobunaga moved his base to Komaki Castle and started his campaign in ]Mino Province
was a province of Japan in the area of Japan that is today southern Gifu Prefecture. Mino was bordered by Ōmi to the west, Echizen and Hida to the north, and Shinano to the east, and Ise, Mikawa, and Owari to the south. Its abbrevia ...
, defeating Tatsuoki in both the Battle of Moribe
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and fo ...
[and the ]Battle of Jushijo
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and fo ...
in June that same year.
By convincing Saitō retainers to abandon their incompetent and foolish master, Nobunaga significantly weakened the Saitō clan
The was a Japanese samurai clan that ruled Mino province in the Sengoku period. The clan appropriated the name of a defunct samurai clan named "Saitō" that had previously hailed from Echizen province and claimed descent from Fujiwara Toshihi ...
. In 1564, Oda Nobunaga dispatched his retainer, Kinoshita Tōkichirō, to bribe many of the warlords in the Mino area to support the Oda clan
The is a Japanese samurai family who were daimyo and an important political force in the unification of Japan in the mid-16th century. Though they had the climax of their fame under Oda Nobunaga and fell from the spotlight soon after, several ...
. In 1566, Nobunaga charged Kinoshita with building Sunomata Castle on the bank of the Sai River opposite Saitō territory, to serve as a staging point for the Oda forces, and to intimidate, surprise, and demoralize the enemy.
In 1567, the Mino Triumvirate (西美濃三人衆, Nishi-Mino Sanninshū) was commanded by three samurai generals serving the Saitō clan
The was a Japanese samurai clan that ruled Mino province in the Sengoku period. The clan appropriated the name of a defunct samurai clan named "Saitō" that had previously hailed from Echizen province and claimed descent from Fujiwara Toshihi ...
: Inaba Ittetsu, Andō Michitari, and Ujiie Bokuzen. The triumvirate agreed to change sides and join the forces of Oda Nobunaga. Their combined forces mounted a victorious final attack at the Siege of Inabayama Castle
The of 1567 was the final battle in Oda Nobunaga's campaign to defeat the Saitō clan in their mountaintop castle and conquer Mino Province, Japan.
It was a short two-week siege, fought between 13 and 27 September 1567, or in the Japanese ...
.[ After taking possession of the castle, Nobunaga changed the name of both Inabayama Castle and the surrounding town to ]Gifu
is a city located in the south-central portion of Gifu Prefecture, Japan, and serves as the prefectural capital. The city has played an important role in Japan's history because of its location in the middle of the country. During the Sengoku ...
. Nobunaga derived the term ''Gifu'' from the legendary Mount Qi (岐山 ''Qi'' in Standard Chinese
Standard Chinese ()—in linguistics Standard Northern Mandarin or Standard Beijing Mandarin, in common speech simply Mandarin, better qualified as Standard Mandarin, Modern Standard Mandarin or Standard Mandarin Chinese—is a modern standa ...
) in China, on which the Zhou dynasty
The Zhou dynasty ( ; Old Chinese ( B&S): *''tiw'') was a royal dynasty of China that followed the Shang dynasty. Having lasted 789 years, the Zhou dynasty was the longest dynastic regime in Chinese history. The military control of China by ...
is fabled to have started. Nobunaga revealed his ambition to conquer the whole of Japan, and also started using a new personal seal
Seal may refer to any of the following:
Common uses
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, or "true seal"
** Fur seal
* Seal (emblem), a device to impr ...
that read Tenka Fubu (天下布武),[Gifu Castle](_blank)
. Oumi-castle.net. Retrieved December 5, 2007. literally "All under heaven
''Tianxia'' (), literally meaning "(all) under Heaven", is a Chinese term for a historical Chinese cultural concept that denoted either the entire geographical world or the metaphysical realm of mortals, and later became associated with poli ...
, spreading military force", or more idiomatically, " All the world by force of arms". Remains of Nobunaga's residence in Gifu can be found today in Gifu Park
is a public park located at the base of Mount Kinka in the city of Gifu, Gifu Prefecture, Japan. Inside the park, there are many attractions, including Gifu Castle, Mount Kinka, the Mt. Kinka Ropeway, the Gifu City Museum of History, the Eizō ...
.
Ise campaign, Omi campaign and march to Kyoto
Following Nobunaga's conquest of Mino Province
was a province of Japan in the area of Japan that is today southern Gifu Prefecture. Mino was bordered by Ōmi to the west, Echizen and Hida to the north, and Shinano to the east, and Ise, Mikawa, and Owari to the south. Its abbrevia ...
in 1567, Nobunaga sent Takigawa Kazumasu
, also known as Sakonshōgen (左近将監), was a samurai retainer and military commander of Oda Nobunaga, and later Toyotomi Hideyoshi, during Japan's Sengoku period. His biological son, Toshimasu, was adopted by Toshihisa and later Kazumasu ...
on a campaign comprising two invasions of Ise Province
was a province of Japan in the area of Japan that is today includes most of modern Mie Prefecture. Ise bordered on Iga, Kii, Mino, Ōmi, Owari, Shima, and Yamato Provinces. Its abbreviated form name was .
History
The name of Ise appears ...
in 1567 and 1568 that defeated numerous families of Ise. Also in an effort to cement an alliance between Nobunaga and rival warlord Azai Nagamasa
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' of the Sengoku period known as the brother-in-law and enemy of Oda Nobunaga. Nagamasa was head of the Azai clan seated at Odani Castle in northern Ōmi Province and married Nobunaga's sister Oichi in 1564, fathering ...
from Omi Province
is a hereditary noble title (''kabane'') of ancient Japan. It was given to the descendants of the Imperial Family before Emperor Kōgen. Along with ''Muraji'', ''Omi'' was reserved for the head of the most powerful clans during the Kofun perio ...
, Nobunaga arranged for Oichi
was a female historical figure in the late Sengoku period. She is known primarily as the mother of three daughters who became prominent figures in their own right – Yodo-dono, Ohatsu Nagamasa had no hope of winning, and chose to commit seppu ...
, his sister, to marry Nagamasa. Nobunaga desired peaceful relations with the Azai clan
The , also rendered as Asai, was a Japanese clan during the Sengoku period.
History
The Azai was a line of ''daimyōs'' (feudal lords) seated at Odani Castle in northeastern Ōmi Province, located within present day Nagahama, Shiga Prefecture ...
because of their strategic position in between the Oda clan's land and the capital, Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the ...
.
In 1568, Ashikaga Yoshiaki
"Ashikaga Yoshiaki" in '' The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 625. was the 15th and final '' shōgun'' of the Ashikaga shogunate in Japan who reigned from 1568 to 1573.Ackroyd, ...
and Akechi Mitsuhide
, first called Jūbei from his clan and later from his title, was a Japanese ''samurai'' general of the Sengoku period best known as the assassin of Oda Nobunaga. Mitsuhide was a bodyguard of Ashikaga Yoshiaki and later a successful general under ...
, as Yoshiaki's bodyguard, went to Gifu
is a city located in the south-central portion of Gifu Prefecture, Japan, and serves as the prefectural capital. The city has played an important role in Japan's history because of its location in the middle of the country. During the Sengoku ...
to ask Nobunaga to start a campaign toward Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the ...
. Yoshiaki was the brother of the murdered 13th shogun of the Ashikaga Shogunate
The , also known as the , was the feudal military government of Japan during the Muromachi period from 1336 to 1573.Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Muromachi-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 669.
The Ashikaga shogunate was establis ...
, Yoshiteru, who had been killed by the Miyoshi ''sanninshu'' (three chiefs of the Miyoshi clan
is a Japanese family descended from Emperor Seiwa (850–880) and the Minamoto clan (Seiwa-Genji). They were a cadet branch of the Ogasawara clan and the Takeda clan.
At the beginning of the 14th century AD, Ogasawara Nagafusa settled in Shik ...
, Miyoshi Nagayuki, Miyoshi Masayasu and Iwanari Tomomichi
was a Japanese samurai of the 16th century. Also known as Ishinari Tomomichi (石成友通), he was a senior retainer of the Miyoshi clan. He was one of the three great samurai of the Miyoshi clan called ''Miyoshi Sanninshu'' along with Miyoshi ...
). Yoshiaki wanted revenge against the killers who had already set up a puppet shogun, Ashikaga Yoshihide. Nobunaga agreed to install Yoshiaki as the new shogun, and grasping the opportunity to enter Kyoto, started his campaign. An obstacle in southern Ōmi Province was the , led by Rokkaku Yoshikata, who refused to recognize Yoshiaki as shogun and was ready to go to war to defend Yoshihide. In response, Nobunaga launched a rapid attack of Chōkō-ji Castle, driving the Rokkaku clan
The was a Japanese samurai clan Papinot, Jacques Edmond Joseph. (1906). ''Dictionnaire d’histoire et de géographie du Japon''; Papinot, (2003)">DF 53 of 80">"Rokkaku" at ''Nobiliare du Japon'', p. 49 [PDF 53 of 80/nowiki> retrieved 2013-4-30. ...
out of their castles.[ Other forces led by Niwa Nagahide defeated the Rokkaku on the battlefield and entered Kannonji Castle, before resuming Nobunaga's march to Kyoto. Later in 1570, the Rokkaku tried to Siege of Chōkō-ji, retake the castle, but they were driven back by Oda forces led by ]Shibata Katsuie
or was a Japanese samurai and military commander during the Sengoku period.
He served Oda Nobunaga as one of his trusted generals, was severely wounded in the 1571 first siege of Nagashima, but then fought in the 1575 Battle of Nagashino an ...
. The approaching Oda army influenced the Matsunaga clan to submit to the future shogun. The ''daimyō'' Matsunaga Hisahide
Matsunaga Danjo Hisahide (松永 弾正 久秀 1508 – November 19, 1577) was a ''daimyō'' and head of the Yamato Matsunaga clan in Japan during the Sengoku period of the 16th century.
Biography
He was a retainer of Miyoshi Nagayoshi fro ...
kept his title by making this decision to ally his clan with the shogun.
On November 9, 1568, Nobunaga entered Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the ...
, drove out the Miyoshi clan
is a Japanese family descended from Emperor Seiwa (850–880) and the Minamoto clan (Seiwa-Genji). They were a cadet branch of the Ogasawara clan and the Takeda clan.
At the beginning of the 14th century AD, Ogasawara Nagafusa settled in Shik ...
, who had supported the 14th shogun and who fled to Settsu
is a city located in Osaka Prefecture, Japan.
As of 2017, the city has an estimated population of 85,290 and a population density of 5,664 people per km². The total area is 14.88 km².
Surrounding municipalities
*Osaka Prefecture
**Hi ...
, and installed Yoshiaki as the 15th shogun of the Ashikaga Shogunate
The , also known as the , was the feudal military government of Japan during the Muromachi period from 1336 to 1573.Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Muromachi-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 669.
The Ashikaga shogunate was establis ...
. However, Nobunaga refused the title of shogun's deputy (Kanrei
or, more rarely, ''kanryō'', was a high political post in feudal Japan; it is usually translated as ''shōguns deputy''. After 1349, there were actually two ''Kanrei'', the ''Kyoto Kanrei'' and the ''Kantō Kanrei''.
Originally, from 1219 until ...
), or any appointment from Yoshiaki, even though Nobunaga had great respect for the Emperor Ōgimachi
was the 106th Emperor of Japan, according to the traditional order of succession. He reigned from November 17, 1557, to his abdication on December 17, 1586, corresponding to the transition between the Sengoku period and the Azuchi–Momoyama per ...
.
Unification of Japan (1568–1582)

Conflict with Asakura, Ashikaga and Azai
After installing Yoshiaki as shogun, Nobunaga had evidently pressed Yoshiaki to request all the local ''daimyō'' to come to Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the ...
and attend a certain banquet. Asakura Yoshikage
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' of the Sengoku period (1467–1603) who ruled a part of Echizen Province in present-day Fukui Prefecture. He was a regent of Ashikaga Shogunate. Yoshikage's conflicts with Oda Nobunaga (1534–1582) resulted in his deat ...
, head of the Asakura clan
The is a Japanese kin group. Papinot, Jacques Edmond Joseph. (1906). ''Dictionnaire d'histoire et de géographie du Japon''; Papinot, (2003)">DF 7 of 80">"Asakura", ''Nobiliare du Japon'', p. 3 Ashikaga Yoshiaki
"Ashikaga Yoshiaki" in '' The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 625. was the 15th and final '' shōgun'' of the Ashikaga shogunate in Japan who reigned from 1568 to 1573.Ackroyd, ...
, refused, an act Nobunaga declared disloyal to both the shogun and the emperor. With this pretext well in hand, Nobunaga raised an army and marched on Echizen.[ In early 1570, Nobunaga launched a campaign into the Asakura clan's domain and besieged Echizen Province">Echizen.][ In early 1570, Nobunaga launched a campaign into the Asakura clan's domain and besieged Kanagasaki Castle. This action made a conflict between Nobunaga and shogun Ashikaga Yoshiaki, as their relationship grew difficult, Yoshiaki secretly started an "anti-Nobunaga alliance", conspiring with other ''daimyō'' to get rid of Nobunaga. ]Azai Nagamasa
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' of the Sengoku period known as the brother-in-law and enemy of Oda Nobunaga. Nagamasa was head of the Azai clan seated at Odani Castle in northern Ōmi Province and married Nobunaga's sister Oichi in 1564, fathering ...
, to whom Nobunaga's sister Oichi
was a female historical figure in the late Sengoku period. She is known primarily as the mother of three daughters who became prominent figures in their own right – Yodo-dono, Ohatsu Nagamasa had no hope of winning, and chose to commit seppu ...
was married, broke the alliance with the Oda clan
The is a Japanese samurai family who were daimyo and an important political force in the unification of Japan in the mid-16th century. Though they had the climax of their fame under Oda Nobunaga and fell from the spotlight soon after, several ...
to honor the Azai-Asakura clan">Asakura alliance, which had lasted for generations. With the help of the Rokkaku clan
The was a Japanese samurai clan Papinot, Jacques Edmond Joseph. (1906). ''Dictionnaire d’histoire et de géographie du Japon''; Papinot, (2003)">DF 53 of 80">"Rokkaku" at ''Nobiliare du Japon'', p. 49 [PDF 53 of 80/nowiki> retrieved 2013-4-30. ...
, Miyoshi clan
is a Japanese family descended from Emperor Seiwa (850–880) and the Minamoto clan (Seiwa-Genji). They were a cadet branch of the Ogasawara clan and the Takeda clan.
At the beginning of the 14th century AD, Ogasawara Nagafusa settled in Shik ...
, and the Ikkō-ikki
were rebellious or autonomous groups of people that were formed in several regions of Japan in the 15th-16th centuries; backed up by the power of the Jōdo Shinshū sect of Buddhism, they opposed the rule of governors or ''daimyō''. Mainly co ...
, the anti-Nobunaga alliance sprang into full force, taking a heavy toll on the Oda clan. After Nobunaga found himself facing both the Asakura and Azai forces and when defeat looked certain, Nobunaga decided to retreat from Kanagasaki, which he did successfully.
Battle of Anegawa
In July 1570, the Oda- Tokugawa allies laid siege to Tokugawa clan">Tokugawa allies laid siege to Yokoyama Castle and Odani Castle">Yokoyama_Castle.html" ;"title="Tokugawa clan">Tokugawa allies laid siege to Tokugawa clan">Tokugawa allies laid siege to Yokoyama Castle and Odani Castle. later, the combined Azai clan">Azai-Asakura clan">Asakura force marched out to confront Nobunaga. Nobunaga advanced to the southern bank of the Anegawa River
The Ane River () is a river that flows through the northern part of Shiga Prefecture, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and i ...
. The following morning, on 30 July 1570, the battle between the Oda and the Azai-Asakura forces began. Tokugawa Ieyasu
was the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan, which ruled Japan from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was one of the three "Great Unifiers" of Japan, along with his former lord Oda Nobunaga and fel ...
joined his forces with Nobunaga, with the Oda and Azai clashing on the right while Tokugawa and Asakura grappled on the left. The battle turned into a melee fought in the middle of the shallow Anegawa River
The Ane River () is a river that flows through the northern part of Shiga Prefecture, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and i ...
. For a time, Nobunaga's forces fought the Azai upstream, while the Tokugawa warriors fought the Asakura downstream. After the Tokugawa forces finished off the Asakura, they turned and hit the Azai right flank. The troops of the Mino Triumvirate, who had been held in reserve, then came forward and hit the Azai left flank. Soon both the Oda and Tokugawa forces defeated the combined forces of the Asakura and Azai clans.[
In 1573, Nobunaga marched leading 30,000 troops which mainly consisted of the troops of Owari, Mino, and Ise Provinces. He launched the Siege of Ichijōdani Castle and Siege of Odani Castle. Nobunaga successfully destroyed the Azai and Asakura clans by driving them both to the point that the clan leaders committed suicide.]
Ikkō-ikki Campaigns
Nobunaga faced a significant threat from the Ikkō-ikki
were rebellious or autonomous groups of people that were formed in several regions of Japan in the 15th-16th centuries; backed up by the power of the Jōdo Shinshū sect of Buddhism, they opposed the rule of governors or ''daimyō''. Mainly co ...
, a resistance movement centered around the Jōdo Shinshū
, also known as Shin Buddhism or True Pure Land Buddhism, is a school of Pure Land Buddhism. It was founded by the former Tendai Japanese monk Shinran.
Shin Buddhism is the most widely practiced branch of Buddhism in Japan.
History
Shinran ...
sect of Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
. The Ikkō-ikki began as a cult association for self-defence, but popular antipathy against the samurai
were the hereditary military nobility and officer caste of History of Japan#Medieval Japan (1185–1573/1600), medieval and Edo period, early-modern Japan from the late 12th century until their abolition in 1876. They were the well-paid retai ...
from the constant violence of the Sengoku period
The was a period in Japanese history of near-constant civil war and social upheaval from 1467 to 1615.
The Sengoku period was initiated by the Ōnin War in 1467 which collapsed the feudal system of Japan under the Ashikaga shogunate. Variou ...
caused their numbers to swell. By the time of Nobunaga's rise to power, the Ikkō-ikki was a major organized armed force opposed to samurai rule in Japan. In August 1570, Nobunaga launched the Ishiyama Hongan-ji War
The , taking place from 1570 to 1580 in Sengoku period Japan, was a ten-year campaign by lord Oda Nobunaga against a network of fortifications, temples, and communities belonging to the Ikkō-ikki, a powerful faction of Jōdo Shinshū Buddhist m ...
against the Ikkō-ikki, while simultaneously fighting against his samurai rivals. In May 1571, Nobunaga besieged Nagashima, a series of Ikkō-ikki fortifications in Owari Province
was a province of Japan in the area that today forms the western half of Aichi Prefecture, including the modern city of Nagoya. The province was created in 646. Owari bordered on Mikawa, Mino, and Ise Provinces. Owari and Mino provinces we ...
, beginning the Sieges of Nagashima The , taking place in 1571, 1573, and 1574, were part of Oda Nobunaga's campaigns against the Ikkō-ikki, arguably among his greatest enemies. Nagashima, in Owari Province along Japan's Pacific coast, was the location of a string of river islan ...
. However, Nobunaga's first siege of Nagashima ended in failure, as his trusted general Shibata Katsuie
or was a Japanese samurai and military commander during the Sengoku period.
He served Oda Nobunaga as one of his trusted generals, was severely wounded in the 1571 first siege of Nagashima, but then fought in the 1575 Battle of Nagashino an ...
was severely wounded and many of his samurai were lost before retreating. Despite this defeat, Nobunaga was inspired to launch another siege, the Siege of Mount Hiei
The siege of Mount Hiei was a battle of the Sengoku period of Japan fought between Oda Nobunaga and the ''sōhei'' ( warrior monks) of the monasteries of Mount Hiei near Kyoto on September 30, 1571. It is said that Oda Nobunaga killed all the m ...
.
Siege of Mount Hiei
The Enryaku-ji
is a Tendai monastery located on Mount Hiei in Ōtsu, overlooking Kyoto. It was first founded in 788 during the early Heian period (794–1185) by Saichō (767–822), also known as Dengyō Daishi, who introduced the Tendai sect of ...
temple on Mount Hiei
is a mountain to the northeast of Kyoto, lying on the border between the Kyoto and Shiga Prefectures, Japan.
The temple of Enryaku-ji, the first outpost of the Japanese Tendai (Chin. Tiantai) sect of Buddhism, was founded atop Mount Hiei ...
was an issue for Nobunaga. The monastery's ( warrior monks) of the Tendai school
, also known as the Tendai Lotus School (天台法華宗 ''Tendai hokke shū,'' sometimes just "''hokke shū''") is a Mahāyāna Buddhist tradition (with significant esoteric elements) officially established in Japan in 806 by the Japanese m ...
were aiding his opponents in the Azai- Asakura alliance and the temple was close to his base of power. In September 1571, Nobunaga preemptively attacked the Enryaku-ji temple, then besieged Mount Hiei and razed it. In the process of making their way to the Enryaku-ji temple, Nobunaga's forces destroyed and burnt all buildings, killing monks, laymen
In religious organizations, the laity () consists of all members who are not part of the clergy, usually including any non-ordained members of religious orders, e.g. a nun or a lay brother.
In both religious and wider secular usage, a layperson ...
, women, children and eliminating anyone who had previously escaped their attack. It is said that "The whole mountainside was a great slaughterhouse and the sight was one of unbearable horror."[ This action gained him renown as the "Demon ''daimyō''" or "Devil King".
]
Siege of Nagashima
After the success of the Siege of Mount Hiei
The siege of Mount Hiei was a battle of the Sengoku period of Japan fought between Oda Nobunaga and the ''sōhei'' ( warrior monks) of the monasteries of Mount Hiei near Kyoto on September 30, 1571. It is said that Oda Nobunaga killed all the m ...
.
In July 1573, Nobunaga besieged Nagashima for a second time, personally leading a sizable force with many arquebusiers
An arquebus ( ) is a form of long gun that appeared in Europe and the Ottoman Empire during the 15th century. An infantryman armed with an arquebus is called an arquebusier.
Although the term ''arquebus'', derived from the Dutch word ''Haakbus ...
. However, a rainstorm rendered his arquebuses inoperable while the Ikkō-ikki
were rebellious or autonomous groups of people that were formed in several regions of Japan in the 15th-16th centuries; backed up by the power of the Jōdo Shinshū sect of Buddhism, they opposed the rule of governors or ''daimyō''. Mainly co ...
's own arquebusiers could fire from covered positions. Nobunaga himself was almost killed and forced to retreat, with the second siege being considered his greatest defeat.
In 1574, Nobunaga launched a third siege of Nagashima as his general Kuki Yoshitaka
(1542 – November 17, 1600) was a naval commander during Japan's Sengoku Period, under Oda Nobunaga, and later, Toyotomi Hideyoshi. He was also the ninth headmaster of the Kuki family's school of martial arts, Kukishin-ryū and thus a very skil ...
began a naval blockade and bombardment of Nagashima, allowing him to capture the outer forts of Nakae and Yanagashima as well as part of the Nagashima complex. The sieges of Nagashima finally ended when Nobunaga's men completely surrounded the complex and set fire to it, killing the remaining tens of thousands of defenders and inflicting tremendous losses to the Ikkō-ikki.
Conflict with Mori
Before death, Mori Motonari had declared himself no friend to Nobunaga, and his successor the young Terumoto openly challenged Nobunaga. It happened that the Môri were to be drawn into the Ishiyama Hongan-ji War
The , taking place from 1570 to 1580 in Sengoku period Japan, was a ten-year campaign by lord Oda Nobunaga against a network of fortifications, temples, and communities belonging to the Ikkō-ikki, a powerful faction of Jōdo Shinshū Buddhist m ...
, Nobunaga's siege of a religious stronghold in Settsu
is a city located in Osaka Prefecture, Japan.
As of 2017, the city has an estimated population of 85,290 and a population density of 5,664 people per km². The total area is 14.88 km².
Surrounding municipalities
*Osaka Prefecture
**Hi ...
, which he had begun in 1570.
Siege of Ishiyama Hongan-ji
Simultaneously, Nobunaga had been besieging the Ikkō-ikki
were rebellious or autonomous groups of people that were formed in several regions of Japan in the 15th-16th centuries; backed up by the power of the Jōdo Shinshū sect of Buddhism, they opposed the rule of governors or ''daimyō''. Mainly co ...
's main stronghold at Ishiyama Hongan-ji
The was the primary fortress of the Ikkō-ikki, leagues of warrior priests and commoners who opposed samurai rule during the Sengoku period. It was established in 1496, at the mouth of the Yodo River, on the coast of the Seto Inland Sea. At the t ...
in present-day Osaka
is a designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the third most populous city in Japan, following Special wards of Tokyo and Yokohama. With a population of ...
. Nobunaga's Siege of Ishiyama Hongan-ji
The , taking place from 1570 to 1580 in Sengoku period Japan, was a ten-year campaign by lord Oda Nobunaga against a network of fortifications, temples, and communities belonging to the Ikkō-ikki, a powerful faction of Jōdo Shinshū Buddhist m ...
began to slowly make some progress, but the Mōri clan
The Mōri clan (毛利氏 ''Mōri-shi'') was a Japanese samurai clan descended from Ōe no Hiromoto. Ōe no Hiromoto was descended from the Fujiwara clan. The family's most illustrious member, Mōri Motonari, greatly expanded the clan's pow ...
of the Chūgoku region
The , also known as the region, is the westernmost region of Honshū, the largest island of Japan. It consists of the prefectures of Hiroshima, Okayama, Shimane, Tottori, and Yamaguchi. In 2010, it had a population of 7,563,428.
History
'' ...
broke his naval blockade and started sending supplies into the strongly fortified complex by sea. As a result, in 1577, Nobunaga ordered Takigawa Kazumasu
, also known as Sakonshōgen (左近将監), was a samurai retainer and military commander of Oda Nobunaga, and later Toyotomi Hideyoshi, during Japan's Sengoku period. His biological son, Toshimasu, was adopted by Toshihisa and later Kazumasu ...
to suppress Ikko-ikki at Kii Province
, or , was a province of Japan in the part of Honshū that is today Wakayama Prefecture, as well as the southern part of Mie Prefecture. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "''Kii''" in . Kii bordered Ise, Izumi, Kawachi, Shima, and Yamato ...
, Hashiba Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and ''daimyō'' ( feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: Military Innovations that Changed the Co ...
to conquer the Chūgoku region
The , also known as the region, is the westernmost region of Honshū, the largest island of Japan. It consists of the prefectures of Hiroshima, Okayama, Shimane, Tottori, and Yamaguchi. In 2010, it had a population of 7,563,428.
History
'' ...
from the Mori clan, before advancing upon the Mori clan in Nagato Province
, often called , was a province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empir ...
,[ ]Akechi Mitsuhide
, first called Jūbei from his clan and later from his title, was a Japanese ''samurai'' general of the Sengoku period best known as the assassin of Oda Nobunaga. Mitsuhide was a bodyguard of Ashikaga Yoshiaki and later a successful general under ...
to pacify Tanba Province
was a province of Japan in the area of central Kyoto and east-central Hyōgo Prefectures. Tanba bordered on Harima, Ōmi, Settsu, Tajima, Wakasa, and Yamashiro Provinces. Its abbreviated form name was . In terms of the Gokishichidō syst ...
, Kuki Yoshitaka
(1542 – November 17, 1600) was a naval commander during Japan's Sengoku Period, under Oda Nobunaga, and later, Toyotomi Hideyoshi. He was also the ninth headmaster of the Kuki family's school of martial arts, Kukishin-ryū and thus a very skil ...
to support attack from the sea, and Nobunaga eventually blocked the Mōri's supply lines.[
In 1580, ten years after the siege of Ishiyama Hongan-ji began, the son of Chief Abbot ]Kōsa
, also known as Hongan-ji Kennyo (本願寺 顕如), was the 11th head of the Hongan-ji in Kyoto, and Chief Abbot of Ishiyama Hongan-ji, cathedral fortress of the Ikkō-ikki (Buddhist warrior priests and peasants who opposed samurai rule), dur ...
surrendered the fortress to Nobunaga after their supplies were exhausted, and they received an official request from the Emperor to do so. Nobunaga spared the lives of Ishiyama Hongan-ji's defenders, but expelled them from Osaka and burnt the fortress to the ground. Although the Ikkō-ikki
were rebellious or autonomous groups of people that were formed in several regions of Japan in the 15th-16th centuries; backed up by the power of the Jōdo Shinshū sect of Buddhism, they opposed the rule of governors or ''daimyō''. Mainly co ...
continued to make a last stand in Kaga Province
was a province of Japan in the area that is today the south and western portion of Ishikawa Prefecture in the Hokuriku region of Japan. Kaga bordered on Echizen, Etchū, Hida, and Noto Provinces. It was part of Hokurikudō Circuit. Its ab ...
, Nobunaga's capture of Ishiyama Hongan-ji crippled them as a major military force.
Conflict with Takeda
One of the strongest rulers in the anti-Nobunaga alliance was Takeda Shingen
, of Kai Province, was a pre-eminent ''daimyō'' in feudal Japan. Known as the "Tiger of Kai", he was one of the most powerful Daimyo, daimyō with exceptional military prestige in the late stage of the Sengoku period.
Shingen was a warlord of ...
, who used to be an ally of the Oda clan
The is a Japanese samurai family who were daimyo and an important political force in the unification of Japan in the mid-16th century. Though they had the climax of their fame under Oda Nobunaga and fell from the spotlight soon after, several ...
. At the apex of the anti-Nobunaga coalition, in 1572, Takeda Shingen
, of Kai Province, was a pre-eminent ''daimyō'' in feudal Japan. Known as the "Tiger of Kai", he was one of the most powerful Daimyo, daimyō with exceptional military prestige in the late stage of the Sengoku period.
Shingen was a warlord of ...
ordered Akiyama Nobutomo
was a samurai during the Sengoku period in Japan. He is known as one of the "Twenty-Four Generals of Takeda Shingen". Nobutomo also served under Shingen's son, Takeda Katsuyori.
Biography
In 1531, Akiyama Nobutomo was born at in Kai provin ...
, one of the " Twenty-Four Generals" of Shingen, to attack Iwamura castle. Nobunaga's aunt, Lady Otsuya
Lady Otsuya (おつやの方 ''Otsuya no Kata'') was a Japanese female samurai (onna-musha) from the Sengoku period. She was the aunt of the famous samurai Oda Nobunaga, the wife of Tōyama Kagetō and foster mother of Oda Katsunaga. She was the ...
, conspired against the Oda clan, surrendered the castle to the Takeda and married Nobutomo. From there, the Takeda-Oda relationship declined and Nobunaga started a war against the Takeda clan
The was a Japanese samurai clan active from the late Heian period until the late 16th century. The clan was historically based in Kai Province in present-day Yamanashi Prefecture. The clan reached its greatest influence under the rule of T ...
.
In the same year, Shingen decided to make a drive for Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the ...
at the urgings of the shogun Ashikaga Yoshiaki
"Ashikaga Yoshiaki" in '' The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 625. was the 15th and final '' shōgun'' of the Ashikaga shogunate in Japan who reigned from 1568 to 1573.Ackroyd, ...
, starting with invading Tokugawa territory. Nobunaga, tied down on the western front, sent lackluster aid to Tokugawa Ieyasu
was the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan, which ruled Japan from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was one of the three "Great Unifiers" of Japan, along with his former lord Oda Nobunaga and fel ...
who suffered defeat at the Battle of Mikatagahara in early 1573. However, after the battle, Tokugawa's forces launched night raids and convinced Takeda of an imminent counter-attack, thus saving the vulnerable Tokugawa with the bluff. This would play a pivotal role in Tokugawa's philosophy of strategic patience in his campaigns with Nobunaga. Shortly thereafter, the Takeda forces were neutralized after Shingen died in April of 1573.
Battle of Nagashino
 In 1575,
In 1575, Takeda Katsuyori
was a Japanese '' daimyō'' of the Sengoku period, who was famed as the head of the Takeda clan and the successor to the legendary warlord Takeda Shingen. He was son in law of Hojo Ujiyasu.
Early life
He was the son of Shingen by the daugh ...
, son of Takeda Shingen
, of Kai Province, was a pre-eminent ''daimyō'' in feudal Japan. Known as the "Tiger of Kai", he was one of the most powerful Daimyo, daimyō with exceptional military prestige in the late stage of the Sengoku period.
Shingen was a warlord of ...
, moved to Tokugawa territory, attacked Yoshida castle and later besieged Nagashino Castle. Katsuyori, angered when Okudaira Sadamasa
called Okudaira Sadamasa (奥平 貞昌), was a Japanese ''daimyō'' of the Sengoku and early Edo periods. Nobumasa's family considered their origins to have been associated with Mikawa Province. The clan was descended through the Akamatsu f ...
rejoined the Tokugawa, had originally conspired with Oga Yashiro
Oga Yashiro is a traitor who offered to let Takeda Katsuyori
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' of the Sengoku period, who was famed as the head of the Takeda clan and the successor to the legendary warlord Takeda Shingen. He was son in law of Hojo U ...
to take the Tokugawa-controlled Okazaki Castle
is a Japanese castle located in Okazaki, Aichi Prefecture, Japan. At the end of the Edo period, Okazaki Castle was home to the Honda clan, ''daimyō'' of Okazaki Domain, but the castle is better known for its association with Tokugawa Ieyasu ...
, the capital of Mikawa Province
was an old province in the area that today forms the eastern half of Aichi Prefecture. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "''Mikawa''" in . Its abbreviated form name was . Mikawa bordered on Owari, Mino, Shinano, and Tōtōmi Provinces.
M ...
. This plot failed.Tokugawa Ieyasu
was the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan, which ruled Japan from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was one of the three "Great Unifiers" of Japan, along with his former lord Oda Nobunaga and fel ...
appealed to Nobunaga for help and Nobunaga personally led an army of about 30,000 men to the relief of Nagashino Castle. The combined force of 38,000 men under Oda Nobunaga and Tokugawa Ieyasu defeated and devastated the Takeda clan
The was a Japanese samurai clan active from the late Heian period until the late 16th century. The clan was historically based in Kai Province in present-day Yamanashi Prefecture. The clan reached its greatest influence under the rule of T ...
with the strategic use of arquebus
An arquebus ( ) is a form of long gun that appeared in Europe and the Ottoman Empire during the 15th century. An infantryman armed with an arquebus is called an arquebusier.
Although the term ''arquebus'', derived from the Dutch word ''Haakbu ...
es at the decisive Battle of Nagashino
The took place in 1575 near Nagashino Castle on the plain of Shitaragahara in the Mikawa Province of Japan. Takeda Katsuyori attacked the castle when Okudaira Sadamasa rejoined the Tokugawa, and when his original plot with Oga Yashiro for t ...
. Nobunaga compensated for the arquebus' slow reloading time by organizing the arquebusiers and archers in three rows, firing in rotation. Takeda Katsuyori also wrongly assumed that rain had ruined the gunpowder of Nobunaga's forces. This battle was the greatest defeat of the Takeda clan.
The end of the Takeda clan
The was a Japanese samurai clan active from the late Heian period until the late 16th century. The clan was historically based in Kai Province in present-day Yamanashi Prefecture. The clan reached its greatest influence under the rule of T ...
came in 1582, when Oda Nobutada
was a samurai and the eldest son of Oda Nobunaga, who fought in many battles during the Sengoku period of Japan. He commanded armies under his father in battles against Matsunaga Hisahide and against the Takeda clan.
Biography
Oda Nobutada ...
and Tokugawa Ieyasu
was the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan, which ruled Japan from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was one of the three "Great Unifiers" of Japan, along with his former lord Oda Nobunaga and fel ...
forces conquered Kai Province. Takeda Katsuyori
was a Japanese '' daimyō'' of the Sengoku period, who was famed as the head of the Takeda clan and the successor to the legendary warlord Takeda Shingen. He was son in law of Hojo Ujiyasu.
Early life
He was the son of Shingen by the daugh ...
was defeated at the Battle of Tenmokuzan
The 1582 in Japan, also known as the Battle of Toriibata, is regarded as the last stand of the Takeda clan. This was the final attempt by Takeda Katsuyori to resist the combined forces of Tokugawa Ieyasu and Oda Nobunaga, who had been campaigni ...
and then committed ''seppuku''.
End of the Ashikaga Shogunate
After the death of Takeda Shingen
, of Kai Province, was a pre-eminent ''daimyō'' in feudal Japan. Known as the "Tiger of Kai", he was one of the most powerful Daimyo, daimyō with exceptional military prestige in the late stage of the Sengoku period.
Shingen was a warlord of ...
in May, 1573, Nobunaga's entry into Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the ...
presented him with a situation very different from that from which he had come. He focused on Ashikaga Yoshiaki
"Ashikaga Yoshiaki" in '' The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 625. was the 15th and final '' shōgun'' of the Ashikaga shogunate in Japan who reigned from 1568 to 1573.Ackroyd, ...
, who had openly declared hostility more than once, despite the Imperial Court's intervention. Nobunaga was able to defeat Yoshiaki's forces, and the power of the Ashikaga was effectively destroyed on 27 August 1573, when Nobunaga drove Yoshiaki out of Kyoto and sent him into exile. Yoshiaki became a Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
monk, shaving his head and taking the name ''Sho-san'', which he later changed to ''Rei-o In'', bringing the Ashikaga Shogunate
The , also known as the , was the feudal military government of Japan during the Muromachi period from 1336 to 1573.Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Muromachi-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 669.
The Ashikaga shogunate was establis ...
to an end.
Imperial Court appointments
After the Ashikaga Shogunate
The , also known as the , was the feudal military government of Japan during the Muromachi period from 1336 to 1573.Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Muromachi-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 669.
The Ashikaga shogunate was establis ...
came to end, the authority of the Imperial Court of Emperor Ōgimachi
was the 106th Emperor of Japan, according to the traditional order of succession. He reigned from November 17, 1557, to his abdication on December 17, 1586, corresponding to the transition between the Sengoku period and the Azuchi–Momoyama per ...
also began to fall. This trend reversed after Oda Nobunaga entered Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the ...
in a show of allegiance that indicated that the Emperor had the Oda clan
The is a Japanese samurai family who were daimyo and an important political force in the unification of Japan in the mid-16th century. Though they had the climax of their fame under Oda Nobunaga and fell from the spotlight soon after, several ...
's support.
In early 1574, Nobunaga was promoted to the Lower Third Rank () of the Imperial Court and made a Court Advisor (). Court appointments would continue to be lavished on a nearly annual basis, possibly in hope of placating him. Nobunaga acquired many official titles, including Major Counselor (), General of the Right of the Imperial Army (), and Minister of the Right () in 1576. In February 1578 the court made him Grand Minister of State (), the highest post that could be given.
Construction of Azuchi Castle

Azuchi Castle
was one of the primary Castles in Japan, castles of Oda Nobunaga located in the Azuchi, Shiga, Azuchi neighborhood of the city of Ōmihachiman, Shiga Prefecture. The site of the castle was designated a Monuments of Japan, National Historic Site ...
was built from 1576 to 1579 on Mount Azuchi on the eastern shore of Lake Biwa
is the largest freshwater lake in Japan, located entirely within Shiga Prefecture (west-central Honshu), northeast of the former capital city of Kyoto. Lake Biwa is an ancient lake, over 4 million years old. It is estimated to be the 13th o ...
in Ōmi Province
was a province of Japan, which today comprises Shiga Prefecture. It was one of the provinces that made up the Tōsandō circuit. Its nickname is . Under the ''Engishiki'' classification system, Ōmi was ranked as one of the 13 "great countri ...
.Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the ...
that he could watch over and guard the approaches to the capital. Azuchi Castle's location was also strategically advantageous in managing the communications and transportation routes between Nobunaga's greatest foes - Uesugi Uesugi (sometimes written ''Uyesugi'') is a Japanese surname. Notable people with the surname include:
People
*Uesugi clan, a Japanese samurai clan
**Uesugi Akisada, (1454–1510), a samurai of the Uesugi clan
**Uesugi Harunori (1751–1822), a Jap ...
to the north, the in the east, and the Mōri to the west.[Ōrui, N. and M. Toba (1935). Castles in Japan. Tokyo: Board of Tourist Industry & Japan Government Railways.]
Conflict with Uesugi
The conflict of Oda and Uesugi precipitated by Uesugi Uesugi (sometimes written ''Uyesugi'') is a Japanese surname. Notable people with the surname include:
People
*Uesugi clan, a Japanese samurai clan
**Uesugi Akisada, (1454–1510), a samurai of the Uesugi clan
**Uesugi Harunori (1751–1822), a Jap ...
intervention in the domain of the Hatakeyama clan
The was a Japanese samurai clan. Originally a branch of the Taira clan and descended from Taira no Takamochi, they fell victim to political intrigue in 1205, when Hatakeyama Shigeyasu, first, and his father Shigetada later were killed in battl ...
in Noto Province
was a province of Japan in the area that is today the northern part of Ishikawa Prefecture in Japan, including the Noto Peninsula (''Noto-hantō'') which is surrounded by the Sea of Japan. Noto bordered on Etchū and Kaga provinces to the s ...
, an Oda client state
A client state, in international relations, is a state that is economically, politically, and/or militarily subordinate to another more powerful state (called the "controlling state"). A client state may variously be described as satellite sta ...
. This event provoked the Uesugi incursion, a ''coup d'état'' led by the pro-Oda general Chō Shigetsura, who killed Hatakeyama Yoshinori Hatakeyama (written: 畠山 or 畑山) is a Japanese surname. Notable people with the surname include:
*, Japanese rhythmic gymnast
*, Japanese electronic musician
*, Japanese baseball player
*, Japanese rugby union player
*, Japanese shogi player
...
, the lord of Noto and replaced him with Hatakeyama Yoshitaka
Hatakeyama Yoshitaka (畠山 義隆 died 1576) was a Japanese ''daimyō'' of the Sengoku period, who was head of the Hatakeyama of Noto Province.
Some sources state that he lived up until 1577, committing suicide after Uesugi Kenshin
, late ...
as a puppet ruler. As a result, Uesugi Kenshin
, later known as was a Japanese ''daimyō''. He was born in Nagao clan, and after adoption into the Uesugi clan, ruled Echigo Province in the Sengoku period of Japan. He was one of the most powerful ''daimyō'' of the Sengoku period. Know ...
, the head of the Uesugi clan, mobilized an army and led it into Noto against Shigetsura. Consequently, Nobunaga sent an army led by Shibata Katsuie
or was a Japanese samurai and military commander during the Sengoku period.
He served Oda Nobunaga as one of his trusted generals, was severely wounded in the 1571 first siege of Nagashima, but then fought in the 1575 Battle of Nagashino an ...
and some of his most experienced generals to attack Kenshin. They clashed at the Battle of Tedorigawa
The took place near the Tedori River in Japan's Kaga Province in 1577, between the forces of Oda Nobunaga against Uesugi Kenshin. Kenshin tricked Nobunaga into launching a frontal attack across the Tedorigawa and defeated him. Having suffere ...
in Kaga Province
was a province of Japan in the area that is today the south and western portion of Ishikawa Prefecture in the Hokuriku region of Japan. Kaga bordered on Echizen, Etchū, Hida, and Noto Provinces. It was part of Hokurikudō Circuit. Its ab ...
in 1577.
Battle of Tedorigawa
In November, 1577, The Battle of Tedorigawa took place near the Tedori River in Japan's Kaga Province
was a province of Japan in the area that is today the south and western portion of Ishikawa Prefecture in the Hokuriku region of Japan. Kaga bordered on Echizen, Etchū, Hida, and Noto Provinces. It was part of Hokurikudō Circuit. Its ab ...
. Kenshin tricked Nobunaga's forces into launching a frontal attack across the Tedorigawa and defeated him. Having suffered the loss of 1,000 men, the Oda withdrew south. The result was a decisive Uesugi victory, and Nobunaga considered ceding the northern provinces to Kenshin, but Kenshin's sudden death in early 1578 caused a succession crisis that ended the Uesugi's movement to the south.[
By 1580, Nobunaga was the most powerful lord in Japan, controlling 20 provinces in central Japan: Owari, ]Mino Mino may refer to:
Places in Japan
* Mino, Gifu, a city in Gifu Prefecture
* Mino, Kagawa, a former town in Kagawa Prefecture
* Mino, Tokushima, a town in Tokushima Prefecture
* Mino, an alternate spelling of Minoh, a city in Osaka Prefecture
* Mi ...
, Omi
is a hereditary noble title (''kabane'') of ancient Japan. It was given to the descendants of the Imperial Family before Emperor Kōgen. Along with ''Muraji'', ''Omi'' was reserved for the head of the most powerful clans during the Kofun period. ...
, Iga Iga may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Ambush at Iga Pass, a 1958 Japanese film
* Iga no Kagemaru, Japanese manga series
* Iga, a set of characters from the Japanese novel ''The Kouga Ninja Scrolls''
Biology
* Iga (beetle), ''Iga'' (be ...
, Ise, Yamato, Yamashiro, Kawachi, Izumi
, meaning "spring" or "fountain", is a Japanese given name and surname. While a unisex name, it is more commonly used by women. It can alternately be written as , , , or . People with the name include:
As given name
* , actress
* , stage name Mi ...
, Settsu
is a city located in Osaka Prefecture, Japan.
As of 2017, the city has an estimated population of 85,290 and a population density of 5,664 people per km². The total area is 14.88 km².
Surrounding municipalities
*Osaka Prefecture
**Hi ...
, Echizen, Hida, Kaga, Shinano, Kai, Tango
Tango is a partner dance and social dance that originated in the 1880s along the Río de la Plata, the natural border between Argentina and Uruguay. The tango was born in the impoverished port areas of these countries as the result of a combina ...
, Harima
or Banshū (播州) was a province of Japan in the part of Honshū that is the southwestern part of present-day Hyōgo Prefecture. Harima bordered on Tajima, Tanba, Settsu, Bizen, and Mimasaka Provinces. Its capital was Himeji.
During th ...
, Inaba
Inaba (written: or ) is a Japanese surname. Notable people with the surname include:
*, Japanese shogi player
*, Japanese singer
*, Japanese baseball player
*, Japanese video game producer and designer
* Carrie Ann Inaba (born 1968), American da ...
, Tanba and Bizen.[
]
Tenshō Iga War
 The was two invasions of
The was two invasions of Iga province
was a province of Japan located in what is today part of western Mie Prefecture. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "Iga" in . Its abbreviated name was . Iga is classified as one of the provinces of the Tōkaidō. Under the '' Engishiki'' ...
by the Oda clan
The is a Japanese samurai family who were daimyo and an important political force in the unification of Japan in the mid-16th century. Though they had the climax of their fame under Oda Nobunaga and fell from the spotlight soon after, several ...
during the Sengoku period
The was a period in Japanese history of near-constant civil war and social upheaval from 1467 to 1615.
The Sengoku period was initiated by the Ōnin War in 1467 which collapsed the feudal system of Japan under the Ashikaga shogunate. Variou ...
. The province was conquered by Oda Nobunaga in 1581 after an unsuccessful attempt in 1579 by his son Oda Nobukatsu
was a Japanese samurai of the Azuchi–Momoyama period. He was the second son of Oda Nobunaga. He survived the decline of the Oda clan from political prominence, becoming a ''daimyō'' in the early Edo period. Though often described as an inco ...
. The name of the war is derived from the Tenshō era name
A regnal year is a year of the reign of a sovereign, from the Latin ''regnum'' meaning kingdom, rule. Regnal years considered the date as an ordinal, not a cardinal number. For example, a monarch could have a first year of rule, a second year o ...
(1573–92) in which it occurred. Other names for the campaign include or . Oda Nobunaga himself toured the conquered province in early November 1581, and then withdrew his troops, placing control in Nobukatsu's hands.
Death
 By 1582, Nobunaga was at the height of his power and, as the most powerful warlord, the ''
By 1582, Nobunaga was at the height of his power and, as the most powerful warlord, the ''de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with '' de jure'' ("by l ...
'' leader of Japan. Oda Nobunaga and Tokugawa Ieyasu
was the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan, which ruled Japan from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was one of the three "Great Unifiers" of Japan, along with his former lord Oda Nobunaga and fel ...
finally defeated the at the Battle of Tenmokuzan
The 1582 in Japan, also known as the Battle of Toriibata, is regarded as the last stand of the Takeda clan. This was the final attempt by Takeda Katsuyori to resist the combined forces of Tokugawa Ieyasu and Oda Nobunaga, who had been campaigni ...
, destroying the clan and resulting in Takeda Katsuyori
was a Japanese '' daimyō'' of the Sengoku period, who was famed as the head of the Takeda clan and the successor to the legendary warlord Takeda Shingen. He was son in law of Hojo Ujiyasu.
Early life
He was the son of Shingen by the daugh ...
fleeing from the battle before committing suicide with his wife while being pursued by Oda forces.[ By this point, Nobunaga was preparing to launch invasions into ]Echigo Province
was an old provinces of Japan, old province in north-central Japan, on the shores of the Sea of Japan. It bordered on Uzen Province, Uzen, Iwashiro Province, Iwashiro, Kōzuke Province, Kōzuke, Shinano Province, Shinano, and Etchū Province, ...
and Shikoku
is the smallest of the four main islands of Japan. It is long and between wide. It has a population of 3.8 million (, 3.1%). It is south of Honshu and northeast of Kyushu. Shikoku's ancient names include ''Iyo-no-futana-shima'' (), ...
. Nobunaga's former sandal-bearer, Hashiba Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and ''daimyō'' ( feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: Military Innovations that Changed the Co ...
, invaded Bitchū Province
was a province of Japan on the Inland Sea side of western Honshū, in what is today western Okayama Prefecture. It was sometimes called , with Bizen and Bingo Provinces; those three provinces were settled in the late 7th Century, dividing former ...
and laid siege to Takamatsu Castle. The castle was vital to the Mori clan, and losing it would have left the Mori's home domain vulnerable. Mori reinforcements led by Mōri Terumoto
Mōri Terumoto (毛利 輝元, January 22, 1553 – June 2, 1625) was a Japanese ''daimyō''. The son of Mōri Takamoto, and grandson and successor of the great warlord Mōri Motonari, he fought against Oda Nobunaga but was eventually overcom ...
arrived to relieve the siege, prompting Hideyoshi to ask in turn for reinforcements from Nobunaga. Nobunaga immediately ordered his leading generals and also Akechi Mitsuhide
, first called Jūbei from his clan and later from his title, was a Japanese ''samurai'' general of the Sengoku period best known as the assassin of Oda Nobunaga. Mitsuhide was a bodyguard of Ashikaga Yoshiaki and later a successful general under ...
to prepare their armies, with the overall expedition to be led by Nobunaga.[ Nobunaga left ]Azuchi Castle
was one of the primary Castles in Japan, castles of Oda Nobunaga located in the Azuchi, Shiga, Azuchi neighborhood of the city of Ōmihachiman, Shiga Prefecture. The site of the castle was designated a Monuments of Japan, National Historic Site ...
for Honnō-ji
is a temple of the Nichiren branch of Buddhism located in Kyoto, Japan.
Honnō-ji incident
Honnō-ji is most famous for the Honnō-ji incident – the assassination of Oda Nobunaga – that occurred there on 21 June 1582. Nobunaga lodged a ...
, a temple in Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the ...
he frequented when visiting the city, where he was to hold a tea ceremony
An East Asian tea ceremony, or ''Chádào'' (), or ''Dado'' ( ko, 다도 (茶道)), is a ceremonially ritualized form of making tea (茶 ''cha'') practiced in East Asia by the Chinese, Japanese, and Koreans. The tea ceremony (), literally transl ...
. Hence, Nobunaga only had 30 pages with him, while his son Oda Nobutada
was a samurai and the eldest son of Oda Nobunaga, who fought in many battles during the Sengoku period of Japan. He commanded armies under his father in battles against Matsunaga Hisahide and against the Takeda clan.
Biography
Oda Nobutada ...
had brought 2,000 of his cavalrymen
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry in ...
.
Honnō-ji incident

Akechi Mitsuhide
, first called Jūbei from his clan and later from his title, was a Japanese ''samurai'' general of the Sengoku period best known as the assassin of Oda Nobunaga. Mitsuhide was a bodyguard of Ashikaga Yoshiaki and later a successful general under ...
, stationed in the Tanba province
was a province of Japan in the area of central Kyoto and east-central Hyōgo Prefectures. Tanba bordered on Harima, Ōmi, Settsu, Tajima, Wakasa, and Yamashiro Provinces. Its abbreviated form name was . In terms of the Gokishichidō syst ...
, led his army toward Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the ...
under the pretense of following the order of Nobunaga, but as they were crossing Katsura River
The is a continuation of two other rivers, the Hozu River, a small, speedy river which begins in the mountains near Kameoka and then slithers through the mountains separating Kameoka and Kyoto; and the Ōi River (大堰川 ''Ōi-gawa''), whi ...
, he decided to assassinate Nobunaga for unknown reasons, and the cause of his betrayal is controversial. Mitsuhide, aware that Nobunaga was nearby and unprotected for his tea ceremony, saw an opportunity to act, Mitsuhide announced to his troops that "''The enemy awaits at Honnō-ji!''" (敵は本能寺にあり, Teki wa Honnō-ji ni ari). On 21 June 1582, before dawn, the Akechi army surrounded the Honnō-ji
is a temple of the Nichiren branch of Buddhism located in Kyoto, Japan.
Honnō-ji incident
Honnō-ji is most famous for the Honnō-ji incident – the assassination of Oda Nobunaga – that occurred there on 21 June 1582. Nobunaga lodged a ...
temple with Nobunaga present, while another unit of Akechi troops were sent to Myōkaku-ji in a coup. Although Nobunaga and his servants resisted the unexpected intrusion, they were soon overwhelmed. As the Akechi troops closed in, Nobunaga decided to commit in one of the inner rooms. Reportedly his last words were, "''Ran, don't let them come in...''" referring to his young page, Mori Ranmaru
, also known as Mori Naritoshi (森 成利), was the son of Mori Yoshinari, and had 5 brothers in total, from the province of Mino. He was a member of the Mori Clan, descendants of the Seiwa Genji.
Biography
From an early age, Ranmaru was an ...
, who set the temple on fire as Nobunaga requested so that no one would be able to get his decapitated head. Ranmaru then followed his lord, with his loyalty and devotion making him a revered figure in Japanese history. Nobunaga's remains were never found, a fact often speculated about by writers and historians. After capturing Honnō-ji, Mitsuhide attacked Nobutada, eldest son and heir of Nobunaga, who also committed suicide.Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and '' daimyō'' ( feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: Military Innovations that Changed the C ...
, subsequently abandoned his campaign against the Mōri clan
The Mōri clan (毛利氏 ''Mōri-shi'') was a Japanese samurai clan descended from Ōe no Hiromoto. Ōe no Hiromoto was descended from the Fujiwara clan. The family's most illustrious member, Mōri Motonari, greatly expanded the clan's pow ...
to pursue Mitsuhide to avenge his beloved lord. Hideyoshi intercepted one of Mitsuhide's messengers trying to deliver a letter to the Mōri requesting to form an alliance against the Oda after informing them of Nobunaga's death. Hideyoshi managed to pacify the Mōri by demanding the suicide of Shimizu Muneharu in exchange for ending his siege of Takamatsu Castle, which the Mōri accepted.
Mitsuhide failed to establish his position after Nobunaga's death and Oda forces under Hideyoshi defeated his army at the Battle of Yamazaki
The was fought in 1582 in Yamazaki, Japan, located in current-day Kyoto Prefecture. This battle is sometimes referred to as the Battle of Mt. Tennō (天王山の戦い ''Tennō-zan no tatakai'').
In the Honnō-ji Incident, Akechi Mitsuhide ...
in July 1582, however, Mitsuhide was murdered by bandit
Banditry is a type of organized crime committed by outlaws typically involving the threat or use of violence. A person who engages in banditry is known as a bandit and primarily commits crimes such as extortion, robbery, and murder, either as an ...
s while fleeing after the battle. Hideyoshi continued and completed Nobunaga's conquest of Japan within the following decade.

Historical context
 The goal of national unification and a return to the comparative political stability of the earlier
The goal of national unification and a return to the comparative political stability of the earlier Muromachi period
The is a division of Japanese history running from approximately 1336 to 1573. The period marks the governance of the Muromachi or Ashikaga shogunate (''Muromachi bakufu'' or ''Ashikaga bakufu''), which was officially established in 1338 by ...
was widely shared by the multitude of autonomous ''daimyō
were powerful Japanese magnates, feudal lords who, from the 10th century to the early Meiji period in the middle 19th century, ruled most of Japan from their vast, hereditary land holdings. They were subordinate to the shogun and nominall ...
'' during the Sengoku period
The was a period in Japanese history of near-constant civil war and social upheaval from 1467 to 1615.
The Sengoku period was initiated by the Ōnin War in 1467 which collapsed the feudal system of Japan under the Ashikaga shogunate. Variou ...
. Oda Nobunaga was the first for whom this goal seemed attainable. Nobunaga had gained control over most of Honshu
, historically called , is the largest and most populous island of Japan. It is located south of Hokkaidō across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyūshū across the Kanmon Straits. The island ...
before his death during the 1582 Honnō-ji incident
The was an attempt to assassinate Japanese daimyo Oda Nobunaga at the Honnō-ji temple in Kyoto on 21 June 1582, resulting in the suicide by ''seppuku'' of both Nobunaga and his son Oda Nobutada. The unprotected Nobunaga was ambushed by his ...
, a coup attempt executed by Nobunaga's vassal, Akechi Mitsuhide
, first called Jūbei from his clan and later from his title, was a Japanese ''samurai'' general of the Sengoku period best known as the assassin of Oda Nobunaga. Mitsuhide was a bodyguard of Ashikaga Yoshiaki and later a successful general under ...
. Nobunaga was betrayed by his own retainers who set the Honno-Ji temple on fire; then, instead of burning in flames, Oda Nobunaga had committed to escape the flames. The motivation behind Mitsuhide's betrayal was never revealed to anyone who survived the incident, and has been a subject of debate and conjecture ever since the incident.
Following the incident, Mitsuhide declared himself master over Nobunaga's domains, but was quickly defeated by Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and '' daimyō'' ( feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: Military Innovations that Changed the C ...
, who regained control of and greatly expanded the Oda holdings. Nobunaga's successful subjugation of much of Honshu
, historically called , is the largest and most populous island of Japan. It is located south of Hokkaidō across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyūshū across the Kanmon Straits. The island ...
enabled the later successes of his allies Hideyoshi and Tokugawa Ieyasu
was the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan, which ruled Japan from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was one of the three "Great Unifiers" of Japan, along with his former lord Oda Nobunaga and fel ...
toward the goal of national unification by subjugating local ''daimyō'' under a hereditary shogunate, which was ultimately accomplished in 1603 when Ieyasu was granted the title of Shogun
, officially , was the title of the military dictators of Japan during most of the period spanning from 1185 to 1868. Nominally appointed by the Emperor, shoguns were usually the de facto rulers of the country, though during part of the Kamakura ...
by Emperor Go-Yōzei
was the 107th Emperor of Japan, according to the traditional order of succession. Go-Yōzei's reign spanned the years 1586 through to his abdication in 1611, corresponding to the transition between the Azuchi–Momoyama period and the Edo period ...
following the successful Sekigahara Campaign
The Sekigahara Campaign was a series of battles in Japan fought between the Eastern Army aligned with Tokugawa Ieyasu and the Western Army loyal to Ishida Mitsunari, culminating in the decisive Battle of Sekigahara. The conflict was sparked ...
of 1600. The nature of the succession of power through the three ''daimyō'' is reflected in a well-known Japanese idiom:
The changing character of power through Nobunaga, Hideyoshi and Ieyasu is reflected in another well-known idiom:
All three were born within eight years of each other (1534 to 1542), started their careers as samurai and finished them as statesmen. Nobunaga inherited his father's domain at the age of 17, and quickly gained control of Owari Province
was a province of Japan in the area that today forms the western half of Aichi Prefecture, including the modern city of Nagoya. The province was created in 646. Owari bordered on Mikawa, Mino, and Ise Provinces. Owari and Mino provinces we ...
through . Hideyoshi started his career in Nobunaga's army as an but quickly rose up through the ranks as a samurai. Ieyasu initially fought against Nobunaga as the heir of a rival ''daimyō'', but later expanded his own inheritance through a profitable alliance with Nobunaga.
Influence
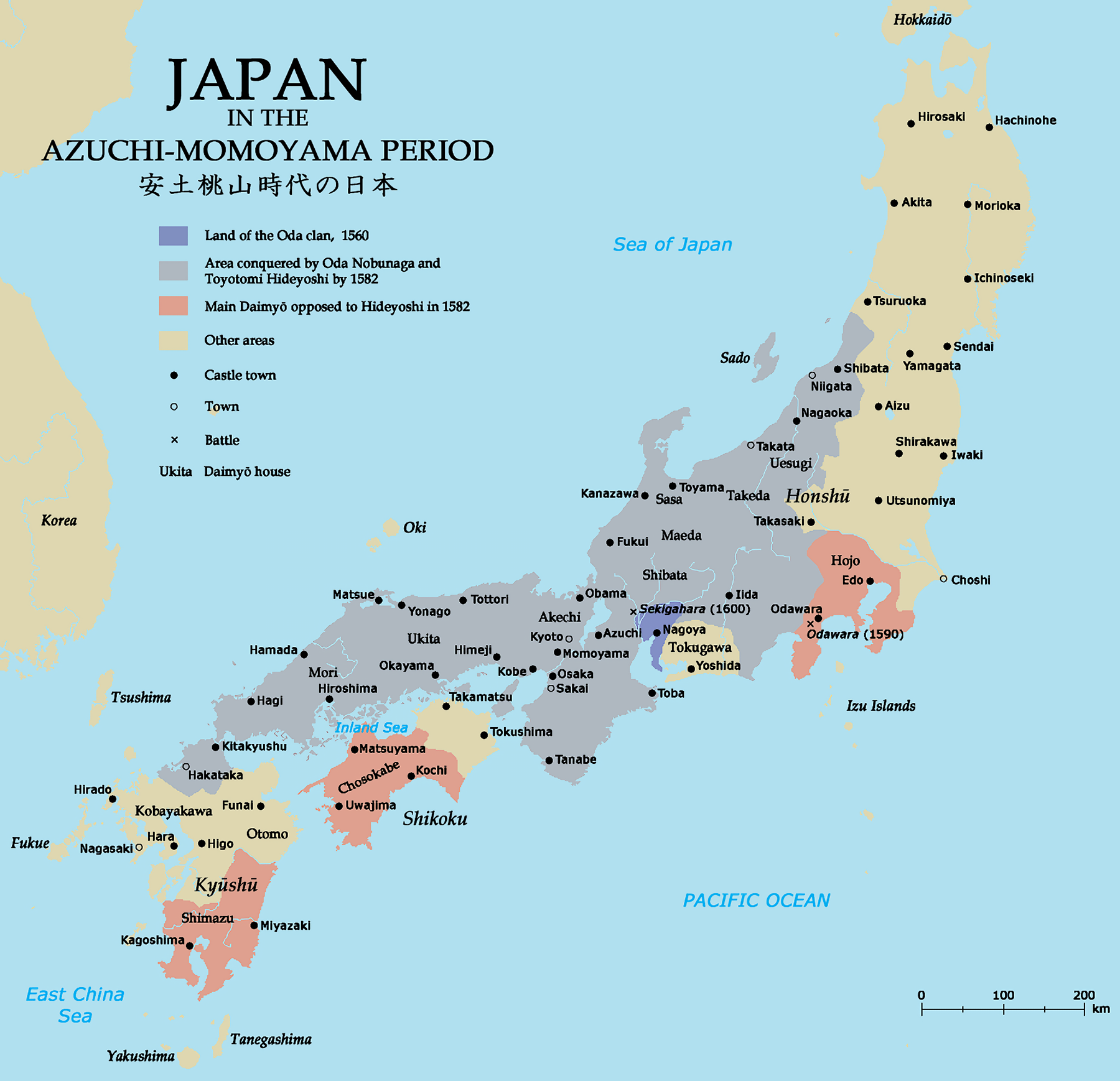
Military
Militarily, Nobunaga changed the way of war was fought in Japan. His gunners and spear-wielding foot soldiers (who used unusually long spears between 18 and 21 feet which Nobunaga had designed himself) displaced mounted soldiers armed with bow and sword. His foot soldiers were trained and disciplined for group and mass movements, which replaced hand-to-hand fighting tactics. They wore distinctive uniforms which fostered esprit de corps, with red troops and black troops.
He was ruthless in battle, pursuing fugitives and killing traitors without compassion. Through his methods, he became the ruler of 20 provinces.[
He built iron-plated warships and imported saltpeter to produce gunpowder, while also promoting the manufacture of artillery and ammunition.
]
Policies
After consolidating military power in provinces he came to dominate, starting with Owari and Mino, Nobunaga implemented a plan for economic development. This included the declaration of free markets (''rakuichi''), the breaking of trade monopolies, and providing for open guilds (''rakuza''). Nobunaga instituted policies as a way to stimulate business and the overall economy through the use of a free market system.monopolies
A monopoly (from Greek el, μόνος, mónos, single, alone, label=none and el, πωλεῖν, pōleîn, to sell, label=none), as described by Irving Fisher, is a market with the "absence of competition", creating a situation where a spec ...
and opened once closed and privileged unions, associations and guild
A guild ( ) is an association of artisans and merchants who oversee the practice of their craft/trade in a particular area. The earliest types of guild formed as organizations of tradesmen belonging to a professional association. They sometimes ...
s, which he saw as impediments to commerce. Even though these policies provided a major boost to the economy, they were still heavily dependent on the support of other ''daimyō''. Copies of his original proclamations can be found in Entoku-ji in the city of Gifu
is a city located in the south-central portion of Gifu Prefecture, Japan, and serves as the prefectural capital. The city has played an important role in Japan's history because of its location in the middle of the country. During the Sengoku ...
.[''Gifu City Walking Map''. Gifu Lively City Public Corporation, 2007.][
Nobunaga initiated policies for civil administration, which included currency regulations, construction of roads and bridges. This included setting standards for the road widths and planting trees along roadsides. This was to ease the transport of soldiers and war material in addition to commerce. In general, Nobunaga thought in terms of "unifying factors", in the words of ]George Sansom
Sir George Bailey Sansom (28 November 1883 – 8 March 1965) was a British diplomat and historian of pre-modern Japan, particularly noted for his historical surveys and his attention to Japanese society and culture.
Early life
Sansom was born ...
.[
]
Culture
Nobunaga initiated a period in Japanese art history known as Fushimi, or the Azuchi-Momoyama period, in reference to the area south of Kyoto. He built extensive gardens and castles which were themselves great works of art. Azuchi Castle
was one of the primary Castles in Japan, castles of Oda Nobunaga located in the Azuchi, Shiga, Azuchi neighborhood of the city of Ōmihachiman, Shiga Prefecture. The site of the castle was designated a Monuments of Japan, National Historic Site ...
included a seven-story Tenshukaku, which included a treasury filled with gold and precious objects. Works of art included paintings on movable screens (''byōbu
are Japanese folding screens made from several joined panels, bearing decorative painting and calligraphy, used to separate interiors and enclose private spaces, among other uses.
History
are thought to have originated in Han dynast ...
''), sliding doors (''fusuma
In Japanese architecture, are vertical rectangular panels which can slide from side to side to redefine spaces within a room, or act as doors. They typically measure about wide by tall, the same size as a ''tatami'' mat, and are thick. The ...
''), and walls by Kanō Eitoku. During this time, Nobunaga's tea master Sen no Rikyū
, also known simply as Rikyū, is considered the historical figure with the most profound influence on ''chanoyu,'' the Japanese "Way of Tea", particularly the tradition of ''wabi-cha''. He was also the first to emphasize several key aspects o ...
established key elements of the Japanese tea ceremony
The Japanese tea ceremony (known as or ) is a Japanese cultural activity involving the ceremonial preparation and presentation of , powdered green tea, the procedure of which is called . While in the West it is known as "tea ceremony", it is se ...
.[
Nobunaga was also famous for his ''meibutsu-gari'' hunt-down and acquisition of famous objects by which he collected tea ceremony objects with famous poetic or historic lineages.
Additionally, Nobunaga was very interested in European culture which was still very new to Japan. He collected pieces of Western art as well as arms and armor, and he is considered to be among the first Japanese people in recorded history to wear European clothes. He also became the patron of the Jesuit missionaries in Japan and supported the establishment of the first Christian church in Kyoto in 1576,][Shunkoin Temple in Kyoto, JAPAN](_blank)
Shunkoin Temple Organization. Retrieved 19 September 2007. although he never converted to Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesu ...
.
Family
 Depending upon the source, Oda Nobunaga and the entire
Depending upon the source, Oda Nobunaga and the entire Oda clan
The is a Japanese samurai family who were daimyo and an important political force in the unification of Japan in the mid-16th century. Though they had the climax of their fame under Oda Nobunaga and fell from the spotlight soon after, several ...
are descendants of either the Fujiwara clan
was a powerful family of imperial regents in Japan, descending from the Nakatomi clan and, as legend held, through them their ancestral god Ame-no-Koyane. The Fujiwara prospered since the ancient times and dominated the imperial court until ...
or the Taira clan
The Taira was one of the four most important clans that dominated Japanese politics during the Heian, Kamakura and Muromachi Periods of Japanese history – the others being the Fujiwara, the Tachibana, and the Minamoto. The clan is divi ...
(specifically, Taira no Shigemori
was the eldest regent of the Taira clan patriarch, Taira no Kiyomori. He supported his father in the Heiji Rebellion. He died two years before his father. His son, Taira no Koremori, became a monk in 1184, and drowned himself. Oda Nobunaga c ...
's branch). His lineage can be directly traced to his great-great-grandfather, Oda Hisanaga, who was followed by Oda Toshisada, Oda Nobusada, Oda Nobuhide
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' and magistrate of the Sengoku period known as "Tiger of Owari" and also the father of Oda Nobunaga the first "Great Unifier" of Japan. Nobuhide was a deputy '' shugo'' (Shugodai) of lower Owari Province and head of the ...
, and Nobunaga himself.
Immediate family
Nobunaga was the eldest legitimate son of Oda Nobuhide
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' and magistrate of the Sengoku period known as "Tiger of Owari" and also the father of Oda Nobunaga the first "Great Unifier" of Japan. Nobuhide was a deputy '' shugo'' (Shugodai) of lower Owari Province and head of the ...
, a minor warlord from Owari Province
was a province of Japan in the area that today forms the western half of Aichi Prefecture, including the modern city of Nagoya. The province was created in 646. Owari bordered on Mikawa, Mino, and Ise Provinces. Owari and Mino provinces we ...
, and Tsuchida Gozen
, also known as Tsuchida Gozen, was a Japanese noblewoman and the mother of Oda Nobunaga, a major ''daimyō'' and politician of the Sengoku period regarded as the first "Great Unifier" of Japan.
Biography
Dota Gozen's origins are unknown, incl ...
, who was also the mother to three of his brothers ( Nobuyuki, Nobukane, and Hidetaka) and two of his sisters (Oinu
Oinu (お犬, died September 24, 1582) was a Japanese historical figure and a member of the prominent Oda clan in the Sengoku period. She was the daughter of Oda Nobuhide and the younger sister of Oda Nogunaga, one of the leading figures of the Se ...
and Oichi
was a female historical figure in the late Sengoku period. She is known primarily as the mother of three daughters who became prominent figures in their own right – Yodo-dono, Ohatsu Nagamasa had no hope of winning, and chose to commit seppu ...
).
* Father: Oda Nobuhide
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' and magistrate of the Sengoku period known as "Tiger of Owari" and also the father of Oda Nobunaga the first "Great Unifier" of Japan. Nobuhide was a deputy '' shugo'' (Shugodai) of lower Owari Province and head of the ...
(1510–1551)
* Mother: Tsuchida Gozen
, also known as Tsuchida Gozen, was a Japanese noblewoman and the mother of Oda Nobunaga, a major ''daimyō'' and politician of the Sengoku period regarded as the first "Great Unifier" of Japan.
Biography
Dota Gozen's origins are unknown, incl ...
(died 1594)
* Brothers
** Oda Nobuhiro
was the eldest son of Oda Nobuhide. After Nobuhiro's father took Anjo Castle in Mikawa Province in 1540, the castle was given to Nobuhiro. During 1551, Nobuhiro was trapped by the Imagawa clan, but was saved when Oda Nobunaga handed over one o ...
(died 1574)
** Oda Nobuyuki
, also known as , was the son of Oda Nobuhide and younger brother of Oda Nobunaga, who lived during the Sengoku period of Japan.
Nobuyuki conspired against his brother Nobunaga with the Hayashi clan (Owari), which Nobunaga viewed as treason. No ...
(1536–1557)
** Oda Nobukane
was a Japanese samurai, the younger brother of the warlord, Oda Nobunaga following the Sengoku period of the 16th century.
Following the year of 1568, Nobukane was destined to be adopted into the Nagano clan. Nobukane afterwards shaved his ...
(1548–1614)
** Oda Nagamasu
was a Japanese daimyō and a brother of Oda Nobunaga who lived from the late Sengoku period through the early Edo period. Also known as or , the Tokyo neighborhood Yūrakuchō is named for him. Nagamasu converted to Christianity in 1588 ...
(1548–1622)
** Oda Nobuharu
was a Japanese samurai of the Sengoku period, who served the Oda clan. Nobuharu was the younger brother of Oda Nobunaga. Nobunaga granted him Nobu Castle and its surroundings as a private fief. While fighting the Asakura and Asai, Nobuharu was ...
(1549–1570)
** Oda Nobutoki
or Hidetoshi was born the sixth son of Oda Nobuhide, a feudal warlord in Owari Province, Japan, during the Sengoku period. He was the half-brother of Oda Nobunaga and the full brother of Oda Nobuhiro, with all three having the same father.' He ...
(died 1556)
** Oda Nobuoki
** Oda Hidetaka
was a Sengoku period
The was a period in Japanese history of near-constant civil war and social upheaval from 1467 to 1615.
The Sengoku period was initiated by the Ōnin War in 1467 which collapsed the feudal system of Japan under the As ...
(died 1555)
** Oda Hidenari
** Oda Nobuteru
** Oda Nagatoshi
* Sisters:
** Oichi
was a female historical figure in the late Sengoku period. She is known primarily as the mother of three daughters who became prominent figures in their own right – Yodo-dono, Ohatsu Nagamasa had no hope of winning, and chose to commit seppu ...
(1547–1583)
** Oinu
Oinu (お犬, died September 24, 1582) was a Japanese historical figure and a member of the prominent Oda clan in the Sengoku period. She was the daughter of Oda Nobuhide and the younger sister of Oda Nogunaga, one of the leading figures of the Se ...
, married Saji Nobukata Saji may refer to:
* Saji, Tottori, a Japanese village
* Saji Observatory, an astronomical observatory in Japan
* 8738 Saji, a main-belt asteroid, named after the Japanese Saji Observatory
People
* Alia Al-Saji, associate professor of philoso ...
later married Hosokawa Nobuyoshi Hosokawa (typically ja, 細川, meaning "narrow river" or "little river") is a Japanese surname.
People with the name include:
*Bill Hosokawa (1915–2007), Japanese American author and journalist
*Chieko Hosokawa (born 1929), a Japanese manga a ...
Descendants
Nobunaga married Nōhime
, also known as Kichō (帰蝶), was the legal wife of Oda Nobunaga, a major ''daimyō'' during the Sengoku period of Japanese history. Her proper name was Kichō, but since she came from Mino Province, she is most commonly referred to as Nōhime ...
, the daughter of Saitō Dōsan
, also known as Saitō Toshimasa (斎藤 利政), was a Japanese samurai during the Sengoku period. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"Saitō Dōsan"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 809.
He was also known as the for his ruthless tactics. His hono ...
, as a matter of political strategy; however, she was unable to give birth to children and was considered to be barren. It was his concubines Kitsuno and Lady Saka who bore his children. Kitsuno gave birth to Nobunaga's eldest son, Nobutada. Nobutada's son Hidenobu became ruler of the Oda clan
The is a Japanese samurai family who were daimyo and an important political force in the unification of Japan in the mid-16th century. Though they had the climax of their fame under Oda Nobunaga and fell from the spotlight soon after, several ...
after the deaths of Nobunaga and Nobutada. His son Oda Nobuhide was a Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ ...
, and took the baptismal name Peter; he was adopted by Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and '' daimyō'' ( feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: Military Innovations that Changed the C ...
and commissioned chamberlain.
*Wife: Lady Nohime, daughter of Saitō Dōsan
*Concubines:
** Lady Kitsuno
**Lady Saka
**Kyōun'in
**Lady Hijikata
**Lady Jitokuin
**
* Sons
** Oda Nobutada
was a samurai and the eldest son of Oda Nobunaga, who fought in many battles during the Sengoku period of Japan. He commanded armies under his father in battles against Matsunaga Hisahide and against the Takeda clan.
Biography
Oda Nobutada ...
(1557–1582) by Kitsuno
** Oda Nobukatsu
was a Japanese samurai of the Azuchi–Momoyama period. He was the second son of Oda Nobunaga. He survived the decline of the Oda clan from political prominence, becoming a ''daimyō'' in the early Edo period. Though often described as an inco ...
(1558–1630) by Kitsuno
** Oda Nobutaka
was a samurai and member of the Oda clan. He was adopted as the head of the Kanbe clan, which ruled the middle region of Ise Province and so he was also called Kanbe Nobutaka (神戸信孝).
Biography
Nobutaka was born as the third son of Od ...
(1558–1583) by Lady Saka
** Hashiba Hidekatsu
Hall, John Whitney ''et al.'' (1991). ''The Cambridge History of Japan'', volume 4, p. 115 was a Japanese samurai, and the fourth son of the famed feudal warlord Oda Nobunaga and was adopted by Toyotomi Hideyoshi at a young age.
At the time of N ...
(1567–1585)
** Oda Katsunaga
was a Japanese samurai of the Sengoku period through early Azuchi-Momoyama Period, who was the fifth son of Oda Nobunaga.
At a very young age, Katsunaga, then known as "Gobomaru", was given in adoption to Toyama Kagetou and his wife, Lady Ots ...
(died 1582)
** Oda Nobuhide (1571–1597)
** Oda Nobutaka by Kyōun'in, later Toyotomi Takajuro (1576–1602) adopted by Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and '' daimyō'' ( feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: Military Innovations that Changed the C ...
** Oda Nobuyoshi by Kyōun'in, later Toyotomi Musashimori (1573–1615) adopted by Toyotomi Hideyoshi
** Oda Nobusada (1574–1624) by Lady Hijikata
** Oda Nobuyoshi (died 1609) adopted by Toyotomi Hideyoshi
** Oda Nagatsugu (died 1600)
** Oda Nobumasa (1554–1647, illegitimate child) by Lady Harada, sister of Narada Naomasa
* Daughters
** Tokuhime Tokuhime may refer to:
* Tokuhime (Oda) (徳姫) (1559–1636), daughter of Oda Nobunaga; also known as Gotokuhime
* Tokuhime (Tokugawa) (督姫) (1565–1615), daughter of Tokugawa Ieyasu
* (登久姫) (1576–1607), daughter of Matsudaira ...
(1559–1636), by Kitsuno and married Matsudaira Nobuyasu
was the eldest son of Matsudaira Ieyasu. His ''tsūshō'' ("common name") was . He was called also , because he had become the lord of in 1570. Because he was a son of Tokugawa Ieyasu, he is often referred to, retroactively, as .
Biography
No ...
** Fuyuhime (1561–1641), married Gamō Ujisato
or Gamō Yasuhide was a Japanese ''daimyō'' of the Sengoku and Azuchi–Momoyama periods. He was heir and son of Gamō Katahide, lord of Hino Castle in Ōmi Province, he later held Matsusaka ( Ise Province) and finally Aizuwakamatsu Castle in ...
** Hideko (died 1632), married Tsutsui Sadatsugu
** Eihime (1574–1623), married Maeda Toshinaga
** Hōonin, married Niwa Nagashige
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' who served the Oda clan. Nagashige was the eldest son of Niwa Nagahide and married the 5th daughter of Oda Nobunaga. He took part in his first campaign in 1583, assisting his father in the Battle of Shizugatake agains ...
** Sannomarudono (died 1603), by Lady Jitokuin, concubine to Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and '' daimyō'' ( feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: Military Innovations that Changed the C ...
, married Nijō Akizane
, son of regent Nijō Haruyoshi, was a Japanese ''kugyō'' (court noble) of the Azuchi–Momoyama period and the early Edo period. He held the regent position of '' kanpaku'' two times: once in 1585, and again from 1615 to 1619. He married a daught ...
** Tsuruhime, married Nakagawa Hidemasa
** Oushin by Kyōun'in, concubine of Saji Kazunari
was a Japanese samurai warrior of the Sengoku period and Edo period. Turnbull, Stephen R. (2000)''The Samurai Tradition,'' Vol. 2, p. 149 excerpt, "Hideyoshi married Oeyo the younger sister of Yodo-Dono his chief concubine to Saji Kazunari, ward ...
** Ofuri, married Mizune Tadatane
** Marikoji Mitsufusa's wife
** Tokudaiji Sanehisa's wife
* Adopted children:
** Toyama Fujin, married Takeda Katsuyori
was a Japanese '' daimyō'' of the Sengoku period, who was famed as the head of the Takeda clan and the successor to the legendary warlord Takeda Shingen. He was son in law of Hojo Ujiyasu.
Early life
He was the son of Shingen by the daugh ...
** Ashikaga Yoshiaki
"Ashikaga Yoshiaki" in '' The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 625. was the 15th and final '' shōgun'' of the Ashikaga shogunate in Japan who reigned from 1568 to 1573.Ackroyd, ...
Other relatives
One of Nobunaga's younger sisters, Oichi, gave birth to three daughters. These three nieces of Nobunaga became involved with important historical figures. Chacha (also known as Lady Yodo), the eldest, became the mistress of Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and '' daimyō'' ( feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: Military Innovations that Changed the C ...
. O-Hatsu married Kyōgoku Takatsugu
was a ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) of Ōmi Province and Wakasa Province during the late Sengoku period of Japan's history. Papinot, Edmond. (2003)''Nobiliare du Japon'', pp. 27–28./ref>
Biography
His childhood name was Koboshi (小法師). Takat ...
. The youngest, O-go
, , or : 1573 – September 15, 1626) was a prominently-placed female figure in the Azuchi–Momoyama period and early Edo period. She was daughter of Oichi and the sister of Yodo-dono and Ohatsu. When she rose to higher political status durin ...
, married the son of Tokugawa Ieyasu
was the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan, which ruled Japan from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was one of the three "Great Unifiers" of Japan, along with his former lord Oda Nobunaga and fel ...
, Tokugawa Hidetada
was the second ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa dynasty, who ruled from 1605 until his abdication in 1623. He was the third son of Tokugawa Ieyasu, the first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa shogunate.
Early life (1579–1593)
Tokugawa Hidetada was bo ...
(the second shogun of the Tokugawa shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate (, Japanese 徳川幕府 ''Tokugawa bakufu''), also known as the , was the military government of Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in ...
). O-go's daughter Senhime
(May 26, 1597 – March 11,February 6 in the old calendar 1666), or Lady Sen, was the eldest daughter of the ''shōgun'' Tokugawa Hidetada and later the wife of Toyotomi Hideyori. She was remarried to Honda Tadatoki after the death of her first ...
married her cousin Toyotomi Hideyori, Lady Yodo's son.
Nobunaga's nephew was Tsuda Nobuzumi
was a Japanese samurai and member of the main Oda clan of Owari Province during the Sengoku and Azuchi–Momoyama periods. Nobuzumi was the son of Oda Nobuyuki, thus making the famed Oda Nobunaga his uncle.
In 1579, Tsuda Nobuzumi led a requis ...
, the son of Nobuyuki. Nobuzumi married Akechi Mitsuhide's daughter and was killed after the Honnō-ji coup by Nobunaga's third son, Nobutaka, who suspected him of being involved in the plot.
Later descendants
Nobunaga's granddaughter Oyu no Kata, by his son Oda Nobuyoshi, married Tokugawa Tadanaga
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' of the early Edo period. The son of the second ''shōgun'' Tokugawa Hidetada, his elder brother was the third ''shōgun'' Tokugawa Iemitsu.
Life
Often called ''Suruga Dainagon'' (the major counsellor of Suruga), ...
.
Nobunari Oda
is a Japanese competitive figure skater. He is the 2006 Four Continents champion, a four-time Grand Prix Final medalist (silver in 2009 and 2010; bronze in 2006 and 2013), the 2005 World Junior champion and the 2008 Japanese national champ ...
, a retired figure skater, claims to be a 17th generation direct descendant of Nobunaga.[Crystal Report Viewer. International Skating Union. Retrieved on 2007-08-19 from ][Smile Wind. Nobunari Oda. Retrieved on 2007-09-15 from ] The ex-monk celebrity Mudō Oda also claims descent from the Sengoku period warlord, but his claims have not been verified.
Honors
* Imperial Court, Senior First Rank
The court ranks of Japan, also known in Japanese language, Japanese as ''ikai'' (位階), are indications of an individual's court rank in Japan based on the system of the Nation, state. ''Ikai'' as a system was originally used in the Ritsuryō, R ...
(November 17, 1917; posthumous)
The Tutors of young Nobunaga
*Hirate Masahide
was a Japanese samurai who served the Oda clan for two generations. His original name was .
Life
Masahide first served Oda Nobuhide. He was a talented samurai as well as skilled in sado and waka. This helped him to act as a skilled diplom ...
(平手 政秀, 1492 – 25 February 1553). Served the Oda clan
The is a Japanese samurai family who were daimyo and an important political force in the unification of Japan in the mid-16th century. Though they had the climax of their fame under Oda Nobunaga and fell from the spotlight soon after, several ...
for two generations. His original name was Hirate Kiyohide (平手 清秀).
*Hayashi Hidesada
was a Japanese samurai and retainer of Oda clan, who lived during the Sengoku period. He was also known as . His court title was Governor of Sado Province (''Sado no Kami'')''.
The Hayashi family, a branch of the Inaba clan, originated from t ...
(林 秀貞, ? – November 21, 1580). He was also known as Michikatsu (通勝). His court title was ''Sado no Kami''.
Sword
Dōjigiri
Dōjigiri (童子切, "Slayer of Shuten-dōji") is a ''tachi''-type Japanese sword that has been identified as a National Treasure of Japan. This sword is one of the "Five Swords Under Heaven" (天下五剣 Tenka-Goken).
Dōjigiri is someti ...
Yasutsuna sword
One of the Five Swords under Heaven The are a group of five Japanese swords. Three are National Treasures of Japan
Some of the National Treasures of Japan
A is the most precious of Japan's Tangible Cultural Properties, as determined and designated by the Agency for Cultu ...
(天下五剣) made by Hōki Yasutsuna, this was the legendary sword with which Minamoto no Yorimitsu
, also known as Minamoto no Raikō, served the regents of the Fujiwara clan along with his brother Yorinobu, taking the violent measures the Fujiwara were themselves unable to take. He is one of the earliest Minamoto of historical note for his mil ...
killed the boy-faced oni Shuten-dōji
Shuten-dōji (, also sometimes called , or ) is a mythical ''oni'' or demon leader of Japan, who according to legend was killed by the hero Minamoto Raikō. Although decapitated, the demon's detached head still took a bite at the hero, who avoi ...
(酒呑童子) living near Mount Oe. It was presented to Oda Nobunaga by the Ashikaga family and was subsequently in the possession of Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and '' daimyō'' ( feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: Military Innovations that Changed the C ...
and Tokugawa Ieyasu
was the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan, which ruled Japan from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was one of the three "Great Unifiers" of Japan, along with his former lord Oda Nobunaga and fel ...
.
Kotegiri Masamune sword
means " cutter". In this case is a contraction of (弓籠手), the arm guard used by a samurai archer. This name comes from an episode in which Asakura Ujikage
was the 8th head of the Asakura clan
The is a Japanese kin group. Papinot, Jacques Edmond Joseph. (1906). ''Dictionnaire d'histoire et de géographie du Japon''; Papinot, (2003)">DF 7 of 80">"Asakura", ''Nobiliare du Japon'', p. 3 retrieved 2 ...
cut an opposing samurai's in the Battle of Toji
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
in Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the ...
. Oda Nobunaga gained possession of this sword and had it shortened to its present length.
In popular culture
Nobunaga appears frequently within fiction and continues to be portrayed in many different anime, manga, video games, and cinematic films. Many depictions show him as villainous or even demonic in nature, though some portray him in a more positive light. The latter type of works include Akira Kurosawa
was a Japanese filmmaker and painter who directed thirty films in a career spanning over five decades. He is widely regarded as one of the most important and influential filmmakers in the history of cinema. Kurosawa displayed a bold, dy ...
's film ''Kagemusha
is a 1980 jidaigeki film directed by Akira Kurosawa. It is set in the Sengoku period of Japanese history and tells the story of a lower-class criminal who is taught to impersonate the dying ''daimyō'' Takeda Shingen to dissuade opposing lords f ...
'', which portrays Nobunaga as energetic, athletic and respectful towards his enemies. The film '' Goemon'' portrays him as a saintly mentor of Ishikawa Goemon
was a legendary Japanese outlaw hero who stole gold and other valuables to give to the poor. He and his son were boiled alive in public after their failed assassination attempt on the Sengoku period warlord Toyotomi Hideyoshi. His legend liv ...
. Nobunaga is a central character in Eiji Yoshikawa
was a Japanese historical novelist. Among his best-known novels are revisions of older classics. He was mainly influenced by classics such as ''The Tale of the Heike'', ''Tale of Genji'', ''Water Margin'' and ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'', m ...
's historical novel ''Taiko Ki'', where he is a firm but benevolent lord. Nobunaga is also portrayed in a heroic light in some video games such as '' Kessen III'', '' Ninja Gaiden II'', and the ''Warriors Orochi
is a hack and slash video game for PlayStation 2 and Xbox 360, developed by Koei and Omega Force. It is a crossover of two of Koei's popular video game series, '' Dynasty Warriors'' and '' Samurai Warriors'' (specifically '' Dynasty Warrior ...
'' series, while in the anime series "Nobunaga no Shinobi" Nobunaga is portrayed as a kind person as well as having a major sweet tooth.
By contrast, in the novel ''The Samurai's Tale'' by Erik Christian Haugaard, he is portrayed as an antagonist "known for his merciless cruelty". He is portrayed as evil or megalomaniacal in some anime and manga series including ''Samurai Deeper Kyo
is a manga series written and illustrated by Akimine Kamijyo. Set during the Edo period of Japan's history, ''Samurai Deeper Kyo'' follows , a feared samurai seeking to regain his body after his soul is sealed inside the body of his rival, ...
'' and ''Flame of Recca
is a Japanese manga series written and illustrated by Nobuyuki Anzai. It was serialized in Shogakukan's '' Weekly Shōnen Sunday'' from April 1995 to February 2002, with its chapters collected in 33 ''tankōbon'' volumes.
The series was ...
''. Nobunaga is portrayed as evil, villainous, bloodthirsty, and/or demonic in many video games, such as the ''Onimusha
is a series of video games developed and published by Capcom. It makes use of the historic figures that shaped Japan's history, retelling their stories with supernatural elements. Most of the games are of the action-adventure genre, a combinati ...
'' series, '' Ninja Master's'', ''Sengoku
The was a period in Japanese history of near-constant civil war and social upheaval from 1467 to 1615.
The Sengoku period was initiated by the Ōnin War in 1467 which collapsed the feudal system of Japan under the Ashikaga shogunate. Variou ...
'', ''Maplestory
''MapleStory'' () is a free-to-play, 2D, side-scrolling massively multiplayer online role-playing game, developed by South Korean company Wizet. Several versions of the game are available for specific countries or regions, published by var ...
'', '' Inindo: Way of the Ninja'', ''Atlantica Online
''Atlantica Online'' is a free-to-play (F2P) 3D tactical massively multiplayer online role-playing game (MMORPG) developed by NDOORS Corporation. The game is currently published bValofe The game's primary setting is a fantasy-themed alternate ...
'', the ''Samurai Warriors
is the first title in the series of hack and slash video games created by Koei's Omega Force team based closely around the Sengoku ("Warring States") period of Japanese history and it is a sister series of the ''Dynasty Warriors'' series, releas ...
'' series, the ''Sengoku BASARA
is a series of video games developed and published by Capcom, and a bigger media franchise based on it, including four anime shows, an anime movie, a live action show, a magazine series, a trading card game, and numerous drama CDs, light n ...
series'' (and its anime adaptation), and the ''Soulcalibur
is a weapon-based fighting video game franchise by Bandai Namco Entertainment.
There are seven main installments of video games and various media spin-offs, including music albums and a series of manga books. The first game in the series, '' ...
'' series.
Nobunaga has been portrayed numerous times in a more neutral or historic framework, especially in the Taiga dramas shown on television in Japan. Oda Nobunaga appears in the manga series '' Tail of the Moon'', ''Kacchū no Senshi Gamu
is a Japanese manga artist. He writes under a pen name in which his first name ''Yoshihiro'' is spelled out in hiragana (よしひろ).
Takahashi was born September 18, 1953, in Higashinaruse, Akita. He was very interested in drawing coming of ...
'', and Tsuji Kunio
was a Japanese author, novelist, and scholar of French literature.
Tsuji was born in Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly k ...
's historical fiction ''The Signore: Shogun of the Warring States''. Historical representations in video games (mostly Western-made strategy or action titles) include '' Shogun: Total War'', '' Total War: Shogun 2'', ''Throne of Darkness
''Throne of Darkness'' is a Japanese-themed action role-playing game released in 2001 by Sierra On-Line, a subsidiary of Vivendi Universal Interactive Publishing. Players control up to four (out of seven) different samurai at a time. The game h ...
'', the eponymous ''Nobunaga's Ambition
is a series of turn-based grand strategy role-playing simulation video games. The original game was one of the first in its genre, being released in March 1983 by the Japanese video game developer Koei. ''Nobunaga's Ambition'' takes place during ...
'' series, as well as ''Civilization V
''Sid Meier's Civilization V'' is a 4X video game in the Civilization (series), ''Civilization'' series developed by Firaxis Games. The game was released on Microsoft Windows on September 21, 2010, on OS X on November 23, 2010, and on Linux on J ...
'', '' Age of Empires II: The Conquerors'', ''Nioh
is an action role-playing video game developed by Team Ninja. It was released for PlayStation 4 in February 2017, and was published by Sony Interactive Entertainment internationally, and by Koei Tecmo in Japan. An edition for PlayStation 4 and ...
'', and '' Nioh 2''. Kamenashi Kazuya
is a Japanese singer, actor, host, producer, magazine model and a member of KAT-TUN. Born and raised in Edogawa, Tokyo, he joined the Japanese talent agency, Johnny & Associates, at the age of 12.
He was drafted as a member and co-lead vocalist o ...
of the Japanese pop group KAT-TUN
is a Japanese boy band formed under Johnny & Associates (Johnny's) in 2001. The group's name was originally an acronym based on the first letter of each member's family name: Kazuya Kamenashi, Jin Akanishi, Junnosuke Taguchi, Koki Tanaka, ...
wrote and performed a song titled "1582" which is written from the perspective of Mori Ranmaru
, also known as Mori Naritoshi (森 成利), was the son of Mori Yoshinari, and had 5 brothers in total, from the province of Mino. He was a member of the Mori Clan, descendants of the Seiwa Genji.
Biography
From an early age, Ranmaru was an ...
during the coup at Honnō temple.James Clavell
James Clavell (born Charles Edmund Dumaresq Clavell; 10 October 1921 – 7 September 1994) was an Australian-born British (later naturalized American) writer, screenwriter, director, and World War II veteran and prisoner of war. Clavell is best ...
's novel ''Shōgun
, officially , was the title of the military dictators of Japan during most of the period spanning from 1185 to 1868. Nominally appointed by the Emperor, shoguns were usually the de facto rulers of the country, though during part of the Kamakur ...
'', the character Goroda is a pastiche
A pastiche is a work of visual art, literature, theatre, music, or architecture that imitates the style or character of the work of one or more other artists. Unlike parody, pastiche pays homage to the work it imitates, rather than mocking it ...
of Nobunaga. In the film '' Sengoku Jieitai 1549'', Nobunaga is killed by time-travellers. The novel and anime series ''Yōtōden
is a 3-episode Japanese original video animation produced by J.C.Staff, the studio's first production. In 1989, ''Yōtōden'' was re-edited into a feature film version titled ''Wrath of the Ninja'' for English-speaking regions, but is curren ...
'', the novel ''The Ouka Ninja Scrolls: Basilisk New Chapter'' and the anime and manga ''Basilisk
In European bestiaries and legends, a basilisk ( or ) is a legendary reptile reputed to be a serpent king, who causes death to those who look into its eyes. According to the ''Naturalis Historia'' of Pliny the Elder, the basilisk of Cyrene ...
'' portray Nobunaga as a literal demon in addition to a power-mad warlord. Nobunaga also appears as a major character in the eroge
An ''eroge'' ( or , ''erogē''; ; a portmanteau of ''erotic game'' , ''erochikku gēmu'') is a Japanese genre of erotic video game. In 1982, Japan's Koei, founded by husband-and-wife team Yoichi and Keiko Erikawa (and later known for stra ...
''Sengoku Rance'' and is a playable character in '' Pokémon Conquest'', with his partner Pokémon
(an abbreviation for in Japan) is a Japanese media franchise managed by The Pokémon Company, founded by Nintendo, Game Freak, and Creatures (company), Creatures, the owners of the trademark and copyright of the franchise.
In terms of ...
being Hydreigon, Rayquaza and Zekrom.
See also
* Azuchi-Momoyama Period
* Sengoku Jidai
The was a period in Japanese history of near-constant civil war and social upheaval from 1467 to 1615.
The Sengoku period was initiated by the Ōnin War in 1467 which collapsed the feudal system of Japan under the Ashikaga shogunate. Various ...
* Nobunari Oda
is a Japanese competitive figure skater. He is the 2006 Four Continents champion, a four-time Grand Prix Final medalist (silver in 2009 and 2010; bronze in 2006 and 2013), the 2005 World Junior champion and the 2008 Japanese national champ ...
References
Bibliography
* Hall, John Whitney, ed. ''The Cambridge History of Japan, Vol. 4: Early Modern Japan'' (1991
table of contents
* Jansen, Marius B. (2000). ''The Making of Modern Japan''. Cambridge: Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the reti ...
. ,
* Perkins, Dorothy ''Encyclopedia of Japan''. New York, Roundtable Press, 1991
* Eisenstadt S. N. ''Japanese Civilization'' London, University of Chicago Press
The University of Chicago Press is the largest and one of the oldest university presses in the United States. It is operated by the University of Chicago and publishes a wide variety of academic titles, including '' The Chicago Manual of Style'' ...
, 1996
* Morton W. Scott & Olenik J. Kenneth, ''Japan, Its History and Culture'' (4th edition). United States, McGraw-Hill company, 1995
External links
OdaNobunaga.com
a history website dedicated to Oda Nobunaga
at the Samurai Archive
The Christian Century in Japan, by Charles Boxer
{{DEFAULTSORT:Oda, Nobunaga
1534 births
1582 deaths
16th-century Japanese people
Daimyo
Forced suicides
Oda clan
People from Nagoya
People of Muromachi-period Japan
People of Azuchi–Momoyama-period Japan
Japanese atheists
Suicides by seppuku
Warlords
Deified Japanese people



 In 1575,
In 1575, 
 By 1582, Nobunaga was at the height of his power and, as the most powerful warlord, the ''
By 1582, Nobunaga was at the height of his power and, as the most powerful warlord, the ''


